Overexpression of a Thermostable α-Amylase through Genome Integration in Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids, and Chemicals
2.2. Construction of the Recombinant Plasmids and Strains
2.3. Construction of the Single Gene Knockout Strain Library of Macromolecular Transporters
2.4. Fermentation of the Engineered Strains to Produce Thermostable α-Amylase
2.5. Production Stability of the Engineered Strains
2.6. Determination of the Extracellular Amylase Activity and Protein Expression
2.7. Data Analytic Methods
3. Results
3.1. Fusing CBM68 to the N-Terminal of BLA702, Enhancing Its Secretory Expression in B. subtilis SCK6
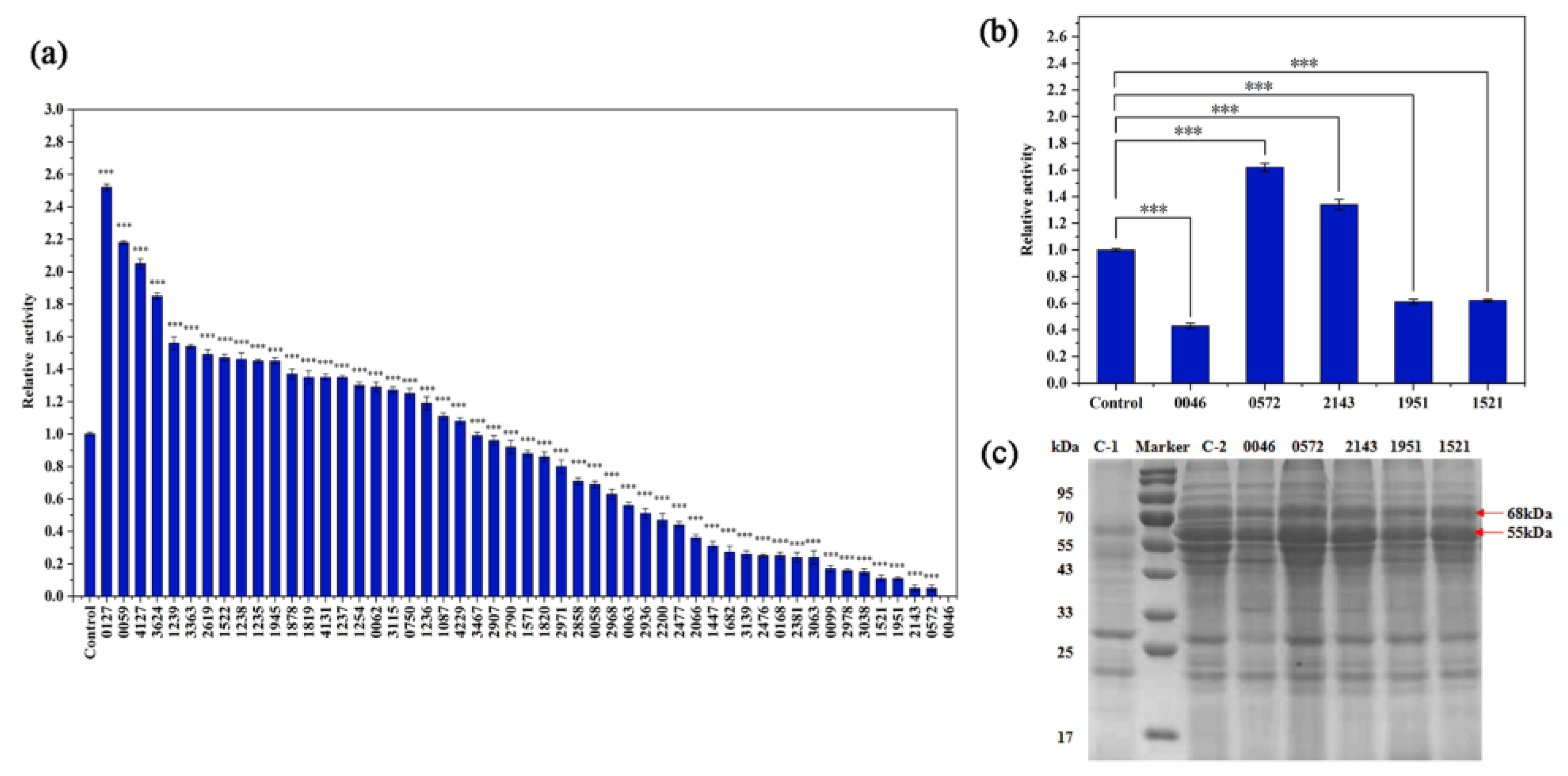
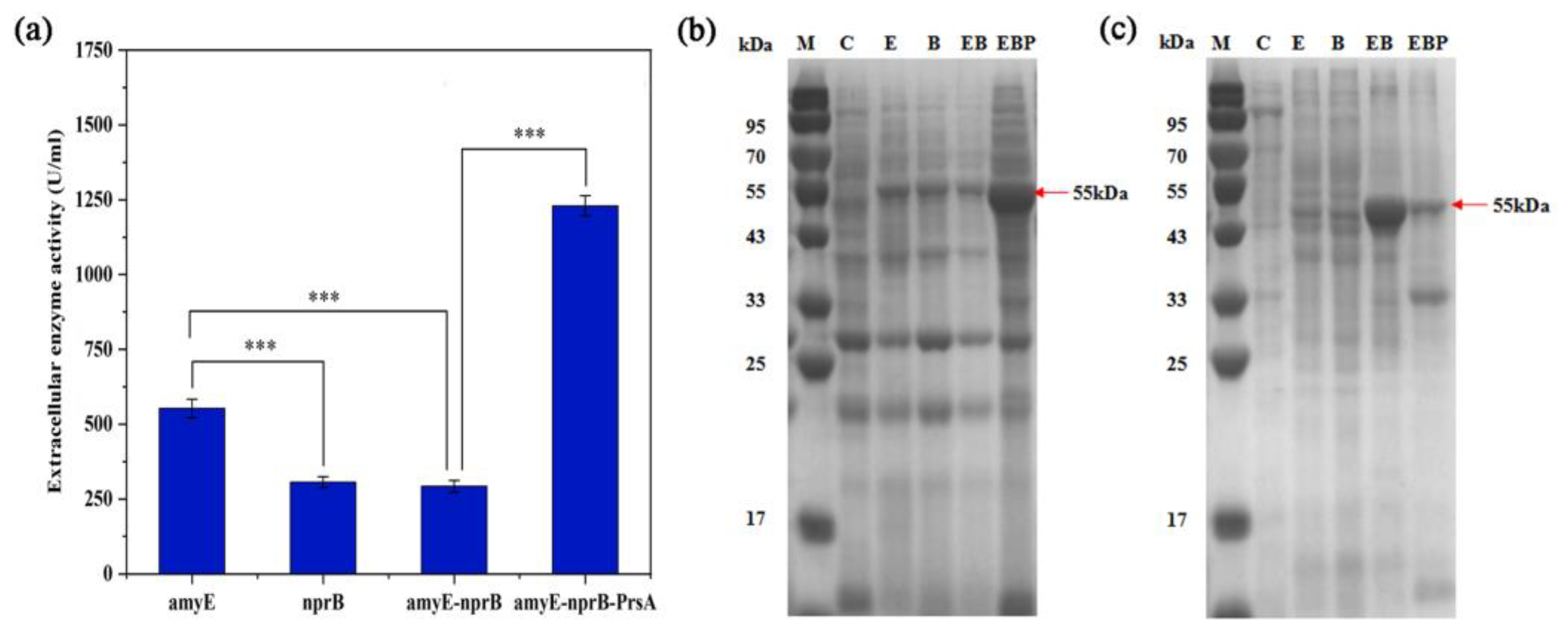
3.2. Macromolecular Protein Transporters Effecting the Secretory Expression of BLA702 in B. subtilis SCK6
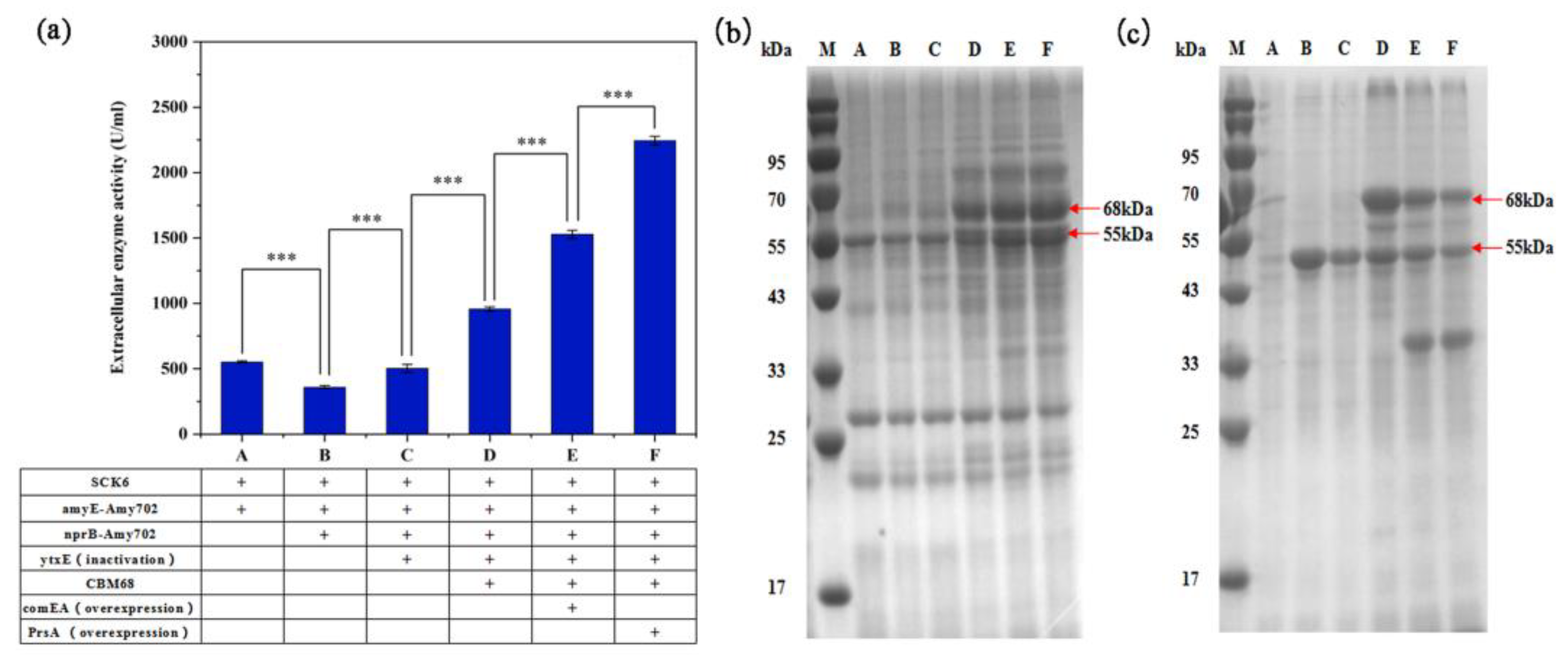
3.3. Genome Integration Expression of BLA702 in B. subtilis SCK6
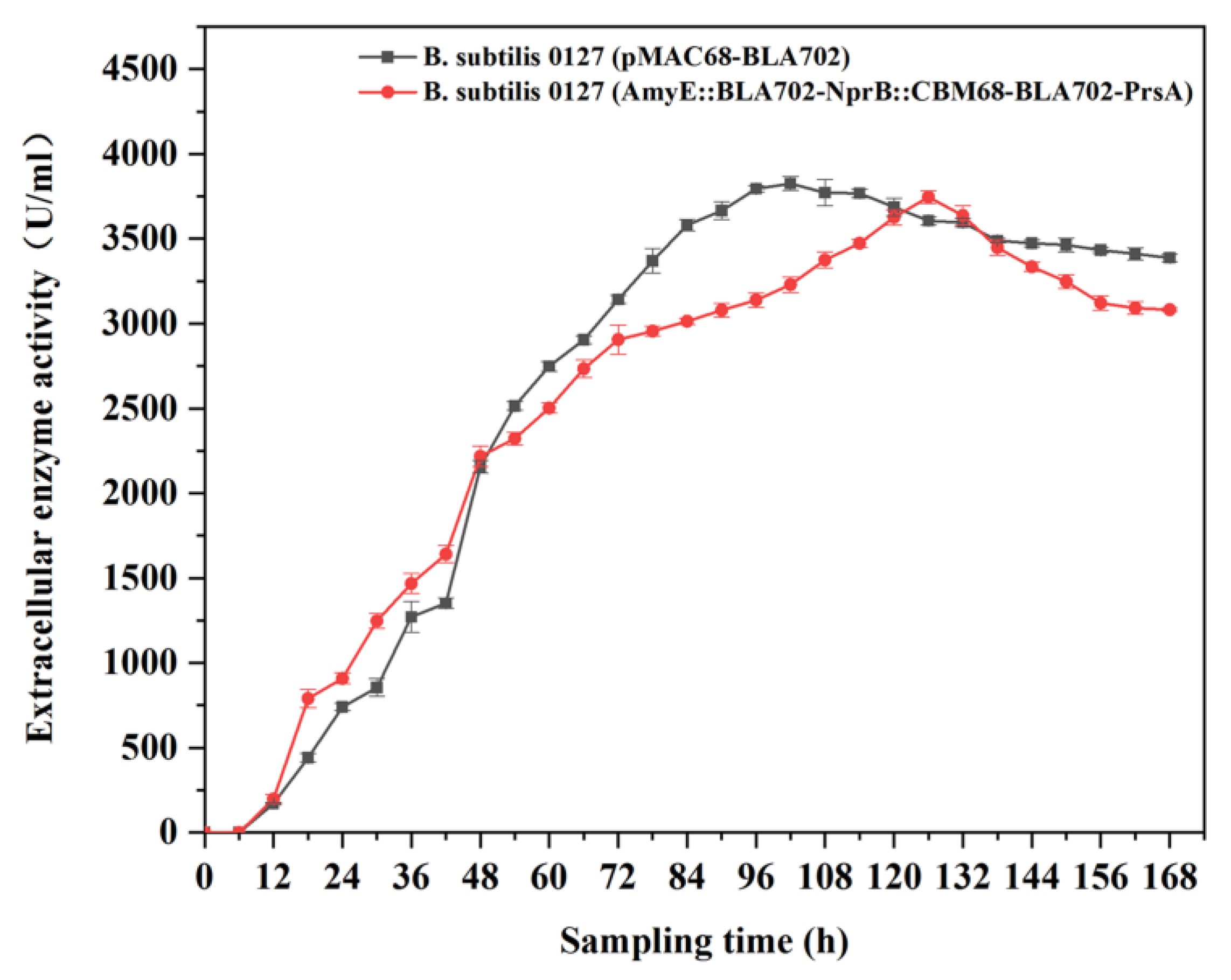
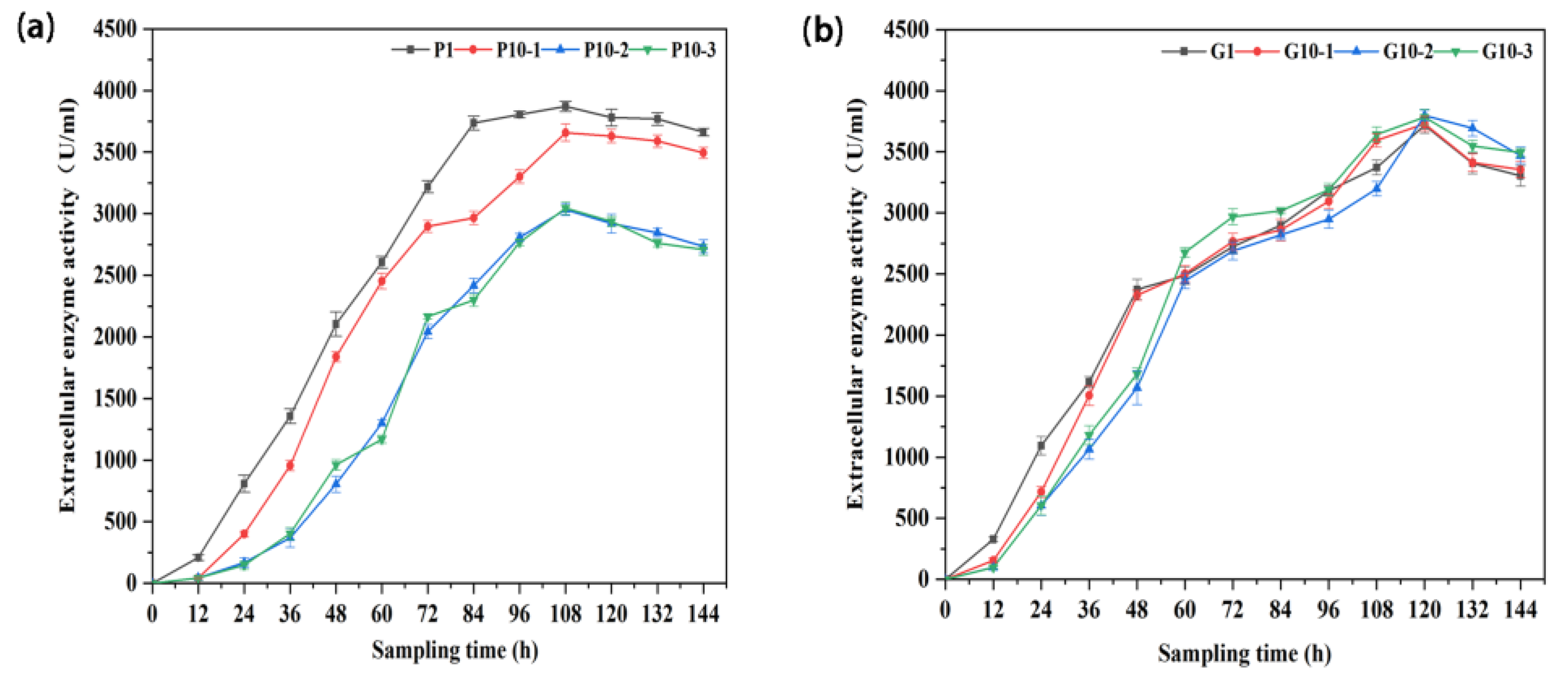
3.4. BLA702 Production and Strain Stability of the Engineered Strains
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, Z.; Yang, S.; Yuan, X.; Shi, Y.; Ouyang, L.; Jiang, S.; Yi, L.; Zhang, G. CRISPR-assisted multi-dimensional regulation for fine-tuning gene expression in Bacillus subtilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Du, G.; Chen, J.; Liu, L. Metabolic engineering of Bacillus subtilis fueled by systems biology: Recent advances and future directions. Biotechnol. Adv. 2017, 35, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, X.M.; Cai, X.; Huang, Z.H.; Liu, Z.Q.; Zheng, Y.G. Construction of a highly active secretory expression system in Bacillus subtilis of a recombinant amidase by promoter and signal peptide engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 143, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jin, K.; Zhang, L.; Ding, Z.; Gu, Z.; Shi, G. Development of an Inducible Secretory Expression System in Bacillus licheniformis Based on an Engineered Xylose Operon. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9456–9464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Zhou, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, F. Reducing the cell lysis to enhance yield of acid-stable alpha amylase by deletion of multiple peptidoglycan hydrolase-related genes in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, H.; Lu, F. Optimization of alkaline protease production by rational deletion of sporulation related genes in Bacillus licheniformis. Microb. Cell Fact. 2019, 18, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Ye, B.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, D.; Zhou, C.; Cheng, S.; Yan, X. Construction of second generation protease-deficient hosts of Bacillus subtilis for secretion of foreign proteins. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2019, 116, 2052–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldeck, J.; Meyer-Rammes, H.; Wieland, S.; Feesche, J.; Maurer, K.H.; Meinhardt, F. Targeted deletion of genes encoding extracellular enzymes in Bacillus licheniformis and the impact on the secretion capability. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 130, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, J.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, X.; Fu, X.; Yang, S.; Xu, J.; Song, H.; Ma, Y. Regulate the hydrophobic motif to enhance the non-classical secretory expression of Pullulanase PulA in Bacillus subtilis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling Lin, F.; Zi Rong, X.; Wei Fen, L.; Jiang Bing, S.; Ping, L.; Chun Xia, H. Protein secretion pathways in Bacillus subtilis: Implication for optimization of heterologous protein secretion. Biotechnol. Adv. 2007, 25, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, J.; Sun, J.; Zhang, D. Multimer recognition and secretion by the non-classical secretion pathway in Bacillus subtilis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quesada-Ganuza, A.; Antelo-Varela, M.; Mouritzen, J.C.; Bartel, J.; Becher, D.; Gjermansen, M.; Hallin, P.F.; Appel, K.F.; Kilstrup, M.; Rasmussen, M.D.; et al. Identification and optimization of PrsA in Bacillus subtilis for improved yield of amylase. Microb. Cell Fact. 2019, 18, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Qin, G.; Zhao, X.; Shen, Y. Enhanced extracellular beta-mannanase production by overexpressing PrsA lipoprotein in Bacillus subtilis and optimizing culture conditions. J. Basic. Microbiol. 2022, 62, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geissler, A.S.; Poulsen, L.D.; Doncheva, N.T.; Anthon, C.; Seemann, S.E.; Gonzalez-Tortuero, E.; Breuner, A.; Jensen, L.J.; Hjort, C.; Vinther, J.; et al. The impact of PrsA over-expression on the Bacillus subtilis transcriptome during fed-batch fermentation of alpha-amylase production. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 909493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, C.; Syvertsson, S.; Bohorquez, L.C.; Cruz, R.; Harwood, C.R.; van Rij, T.; Hamoen, L.W. Effect of Genome Position on Heterologous Gene Expression in Bacillus subtilis: An Unbiased Analysis. ACS Synth. Biol. 2016, 5, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niaudet, B.; Janniere, L.; Ehrlich, S.D. Integration of Linear, Heterologous DNA Molecules into the Bacillus subtilis Chromosome: Mechanism and Use in Induction of Predictable Rearrangements. J. Bacteriol. 1985, 163, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couturier, E.; Rocha, E.P. Replication-associated gene dosage effects shape the genomes of fast-growing bacteria but only for transcription and translation genes. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 59, 1506–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, P.; Mader, U.; Dervyn, E.; Rochat, T.; Leduc, A.; Pigeonneau, N.; Bidnenko, E.; Marchadier, E.; Hoebeke, M.; Aymerich, S.; et al. Condition-dependent transcriptome reveals high-level regulatory architecture in Bacillus subtilis. Science 2012, 335, 1103–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez Carrillo, V.H.; Rose-Sperling, D.; Tran, M.A.; Wiedemann, C.; Hellmich, U.A. Backbone NMR assignment of the nucleotide binding domain of the Bacillus subtilis ABC multidrug transporter BmrA in the post-hydrolysis state. Biomol. NMR Assign. 2022, 16, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quentin, Y.; Fichant, G.; Denizot, F. Inventory, assembly and analysis of Bacillus subtilis ABC transport systems. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 287, 467–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Z.; You, C.; Zhang, Y.H. Transformation of Bacillus subtilis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1151, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Xin, X.; Hu, M.; Price, M.A.; Rosser, S.J.; Bi, C.; Zhang, X. New base editors change C to A in bacteria and C to G in mammalian cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Price, M.A.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ni, X.; Rosser, S.J.; Bi, C.; Wang, M. CRISPR-dCas9 Mediated Cytosine Deaminase Base Editing in Bacillus subtilis. ACS Synth. Biol. 2020, 9, 1781–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Lu, F.P.; Li, Y.; Yin, X.B.; Wang, Y.; Gao, C. Characterisation of mutagenised acid-resistant alpha-amylase expressed in Bacillus subtilis WB600. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 78, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Lu, F. A highly active alpha amylase from Bacillus licheniformis: Directed evolution, enzyme characterization and structural analysis. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 24, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Plasmids | Properties | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| pMA0911-SP-BLA702 | E.coli/B. subtilis shuttle plasmid, Ampr (E. coli), Kanr (B. subtilis), SP signal peptide, highly thermostable amylase gene | In this work |
| pMA0911-LipA-BLA702 | E.coli/B. subtilis shuttle plasmid, Ampr (E. coli), Kanr (B. subtilis), LipA signal peptide, highly thermostable amylase gene | In this work |
| pMA0911-LipA-BLA702codon | E.coli/B. subtilis shuttle plasmid, Ampr (E. coli), Kanr (B. subtilis), LipA signal peptide, Codon optimized gene sequence of BLA702 | In this work |
| pMA0911-YncM-BLA702 | E.coli/B. subtilis shuttle plasmid, Ampr (E. coli), Kanr (B. subtilis), YncM signal peptide, High thermostable amylase gene | In this work |
| pMA0911-CBM68-BLA702 | E.coli/B. subtilis shuttle plasmid, Ampr (E. coli), Kanr (B. subtilis), CBM68 domain, highly thermostable amylase gene | In this work |
| pMAC68-BLA702-0046 | E.coli/B. subtilis shuttle plasmid, Ampr (E. coli), Kanr (B. subtilis), CBM68-BLA702, ytnA gene | In this work |
| pMAC68-BLA702-0572 | E.coli/B. subtilis shuttle plasmid, Ampr (E. coli), Kanr (B. subtilis), CBM68-BLA702, comEA gene | In this work |
| pMAC68-BLA702-1521 | E.coli/B. subtilis shuttle plasmid, Ampr (E. coli), Kanr (B. subtilis), CBM68-BLA702, motA gene | In this work |
| pMAC68-BLA702-1951 | E.coli/B. subtilis shuttle plasmid, Ampr (E. coli), Kanr (B. subtilis), CBM68-BLA702, crh gene | In this work |
| pMAC68-BLA702-2143 | E.coli/B. subtilis shuttle plasmid, Ampr (E. coli), Kanr (B. subtilis), CBM68-BLA702, SpoIIQ gene | In this work |
| pDG1730-BLA702 | B. subtilis integrative plasmid, Ampr (E. coli), Spcr (B. subtilis), upstream and downstream sequences of homologous gene amyE, sandwiched between them is the BLA702 gene | In this work |
| pDG1730-nprB-BLA702/CBM68-BLA702 | B. subtilis integrative plasmid, Ampr (E. coli), Spcr (B. subtilis), upstream and downstream sequences of homologous gene nprB, sandwiched between them is the BLA702 or CBM68-BLA702 gene | In this work |
| pDG1730-aprE-PrsA | B. subtilis integrative plasmid, Ampr (E. coli), Spcr (B. subtilis), upstream and downstream sequences of homologous gene aprE, sandwiched between them is the chaperonin PrsA gene | In this work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Fu, X.; Zhao, X.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Bai, W.; Song, H. Overexpression of a Thermostable α-Amylase through Genome Integration in Bacillus subtilis. Fermentation 2023, 9, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020139
Yang Y, Fu X, Zhao X, Xu J, Liu Y, Zheng H, Bai W, Song H. Overexpression of a Thermostable α-Amylase through Genome Integration in Bacillus subtilis. Fermentation. 2023; 9(2):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020139
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yifan, Xiaoping Fu, Xingya Zhao, Jianyong Xu, Yihan Liu, Hongchen Zheng, Wenqin Bai, and Hui Song. 2023. "Overexpression of a Thermostable α-Amylase through Genome Integration in Bacillus subtilis" Fermentation 9, no. 2: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020139
APA StyleYang, Y., Fu, X., Zhao, X., Xu, J., Liu, Y., Zheng, H., Bai, W., & Song, H. (2023). Overexpression of a Thermostable α-Amylase through Genome Integration in Bacillus subtilis. Fermentation, 9(2), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020139







