Functional Properties of an Oat-Based Postbiotic Aimed at a Potential Cosmetic Formulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain and Feedstock
2.2. Experimental Apparatus
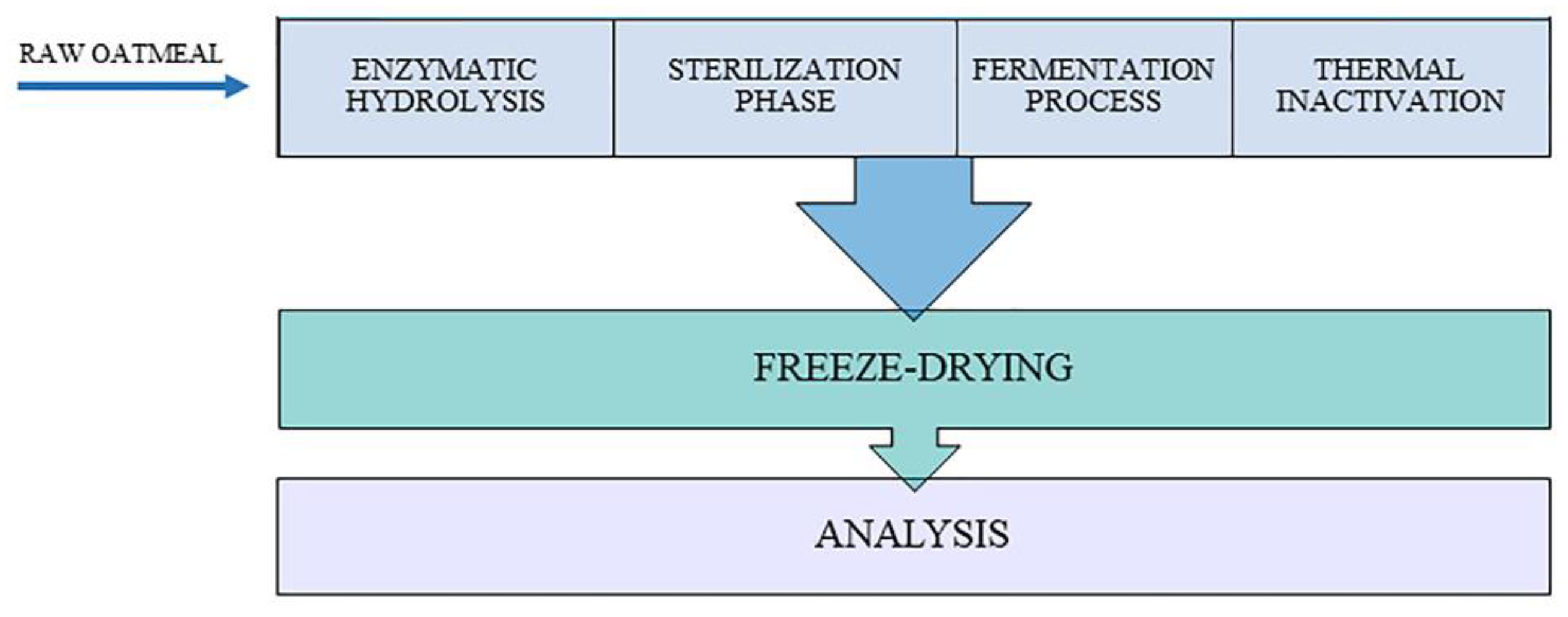
2.3. Fermentation Protocol
2.4. Analytical Methods
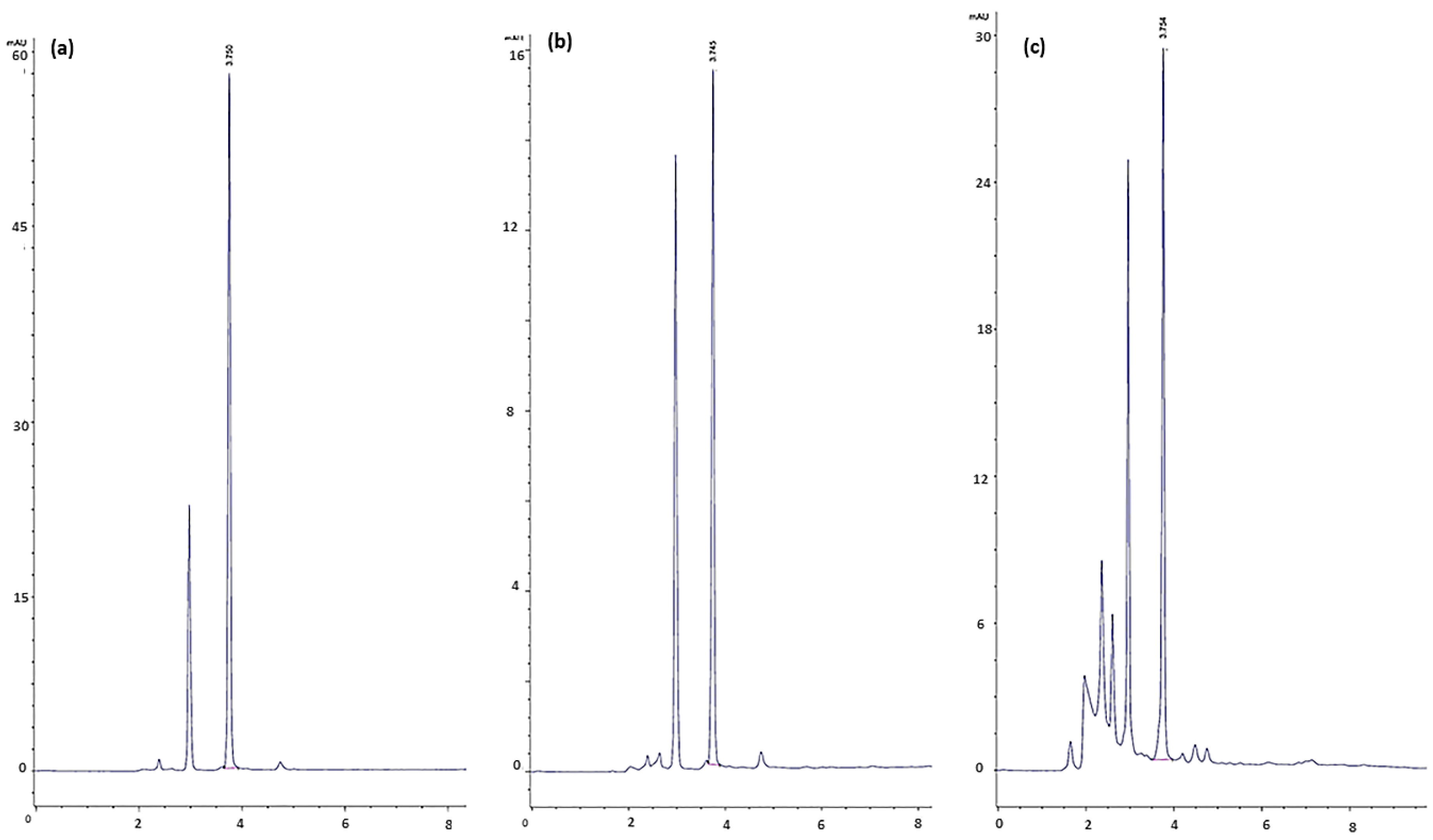
2.4.1. Bacterial Count, Lactic Acid, and Secondary Metabolite Determination
2.4.2. Total Polyphenol Content (TPC) and Antioxidant Activity (AA) Determinations
Extract Preparation
Measurement of Total Polyphenol Content (TPC)
Evaluation of the Antioxidant Activity (AA)
2.4.3. Evaluation of the Tyrosinase Inhibitory Activity (TIA)
2.4.4. Determination of the Sun Protection Factor (SPF)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
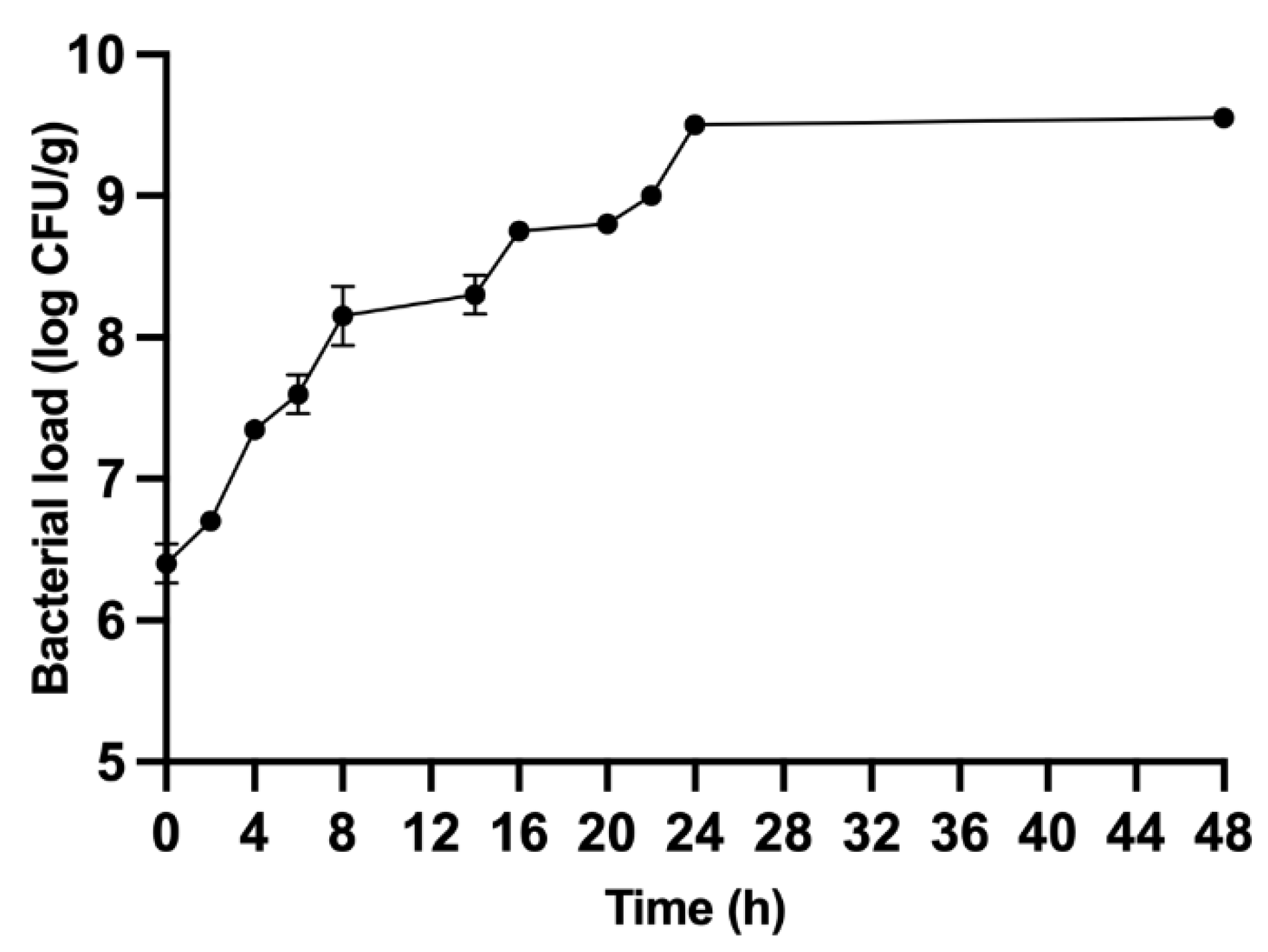
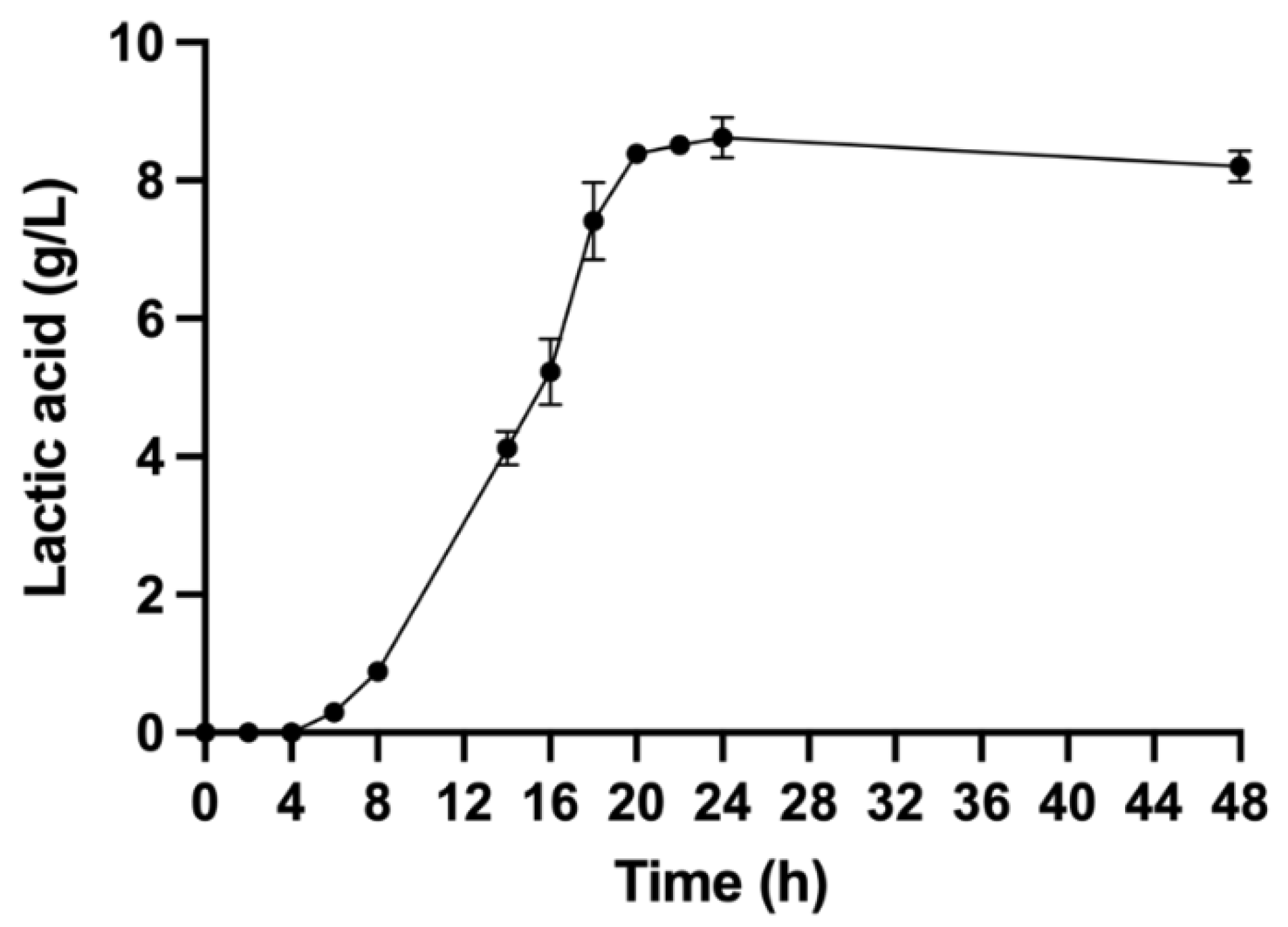
3.1. Fermentation Results
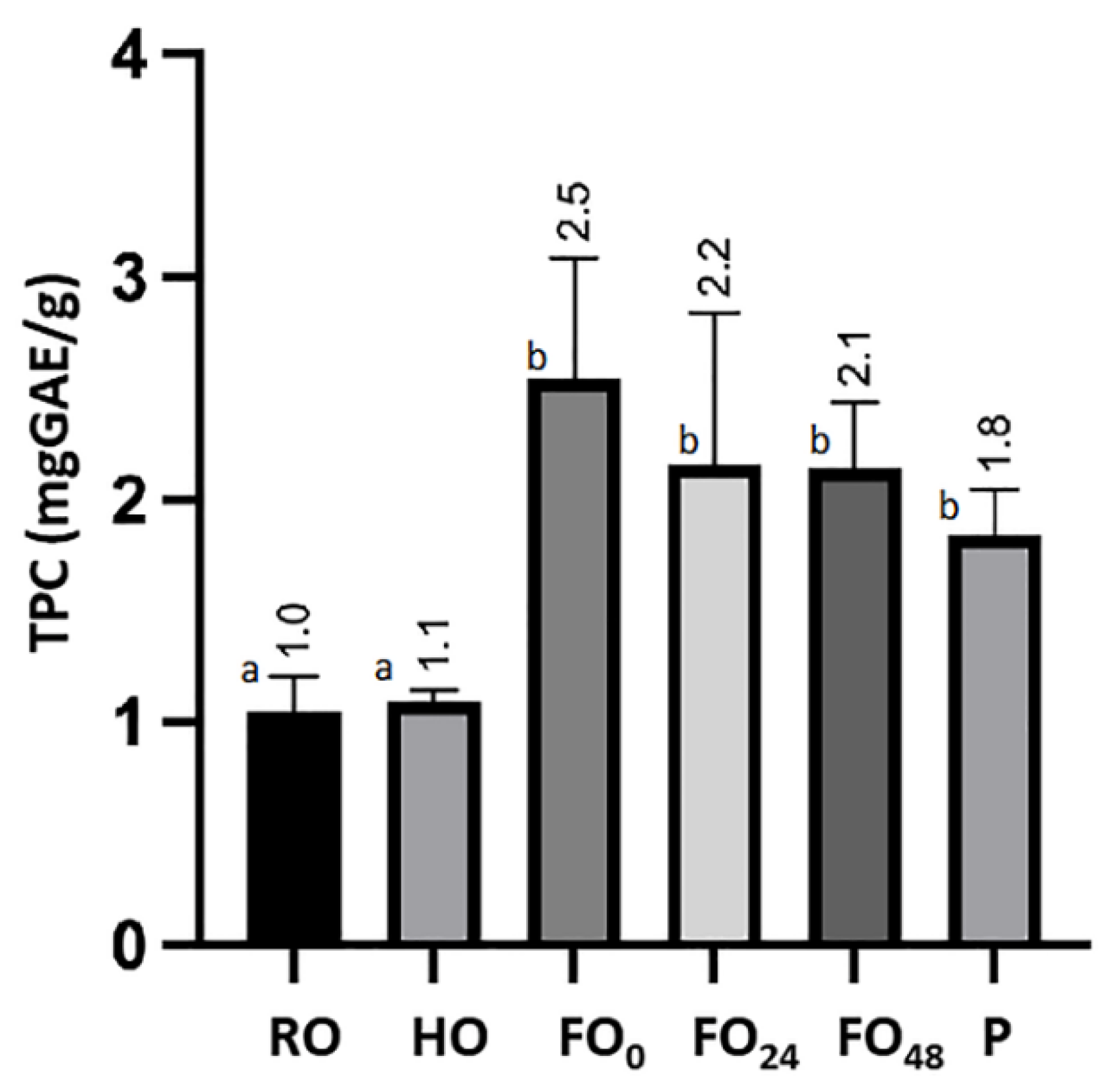
3.2. Total Polyphenolic Content
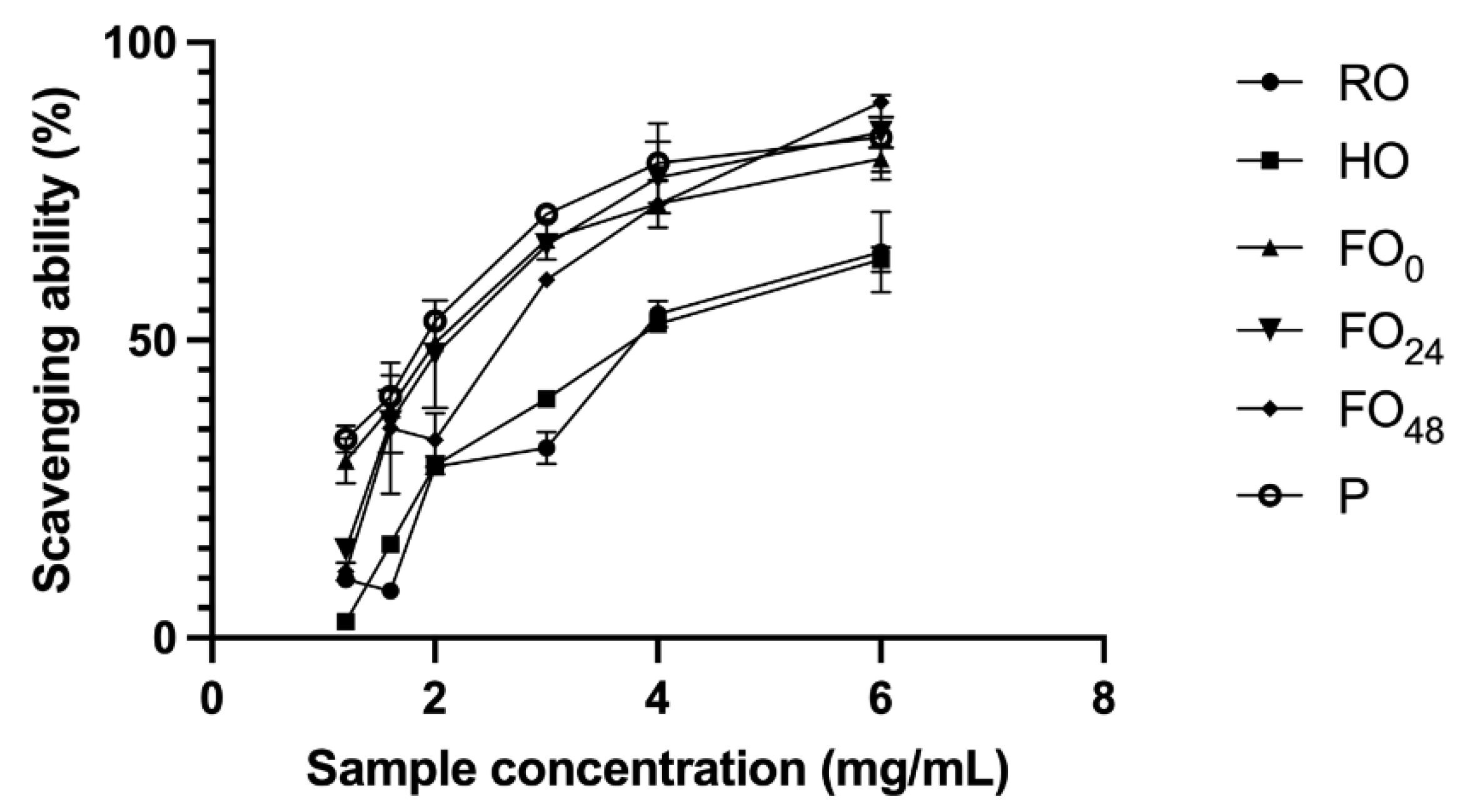
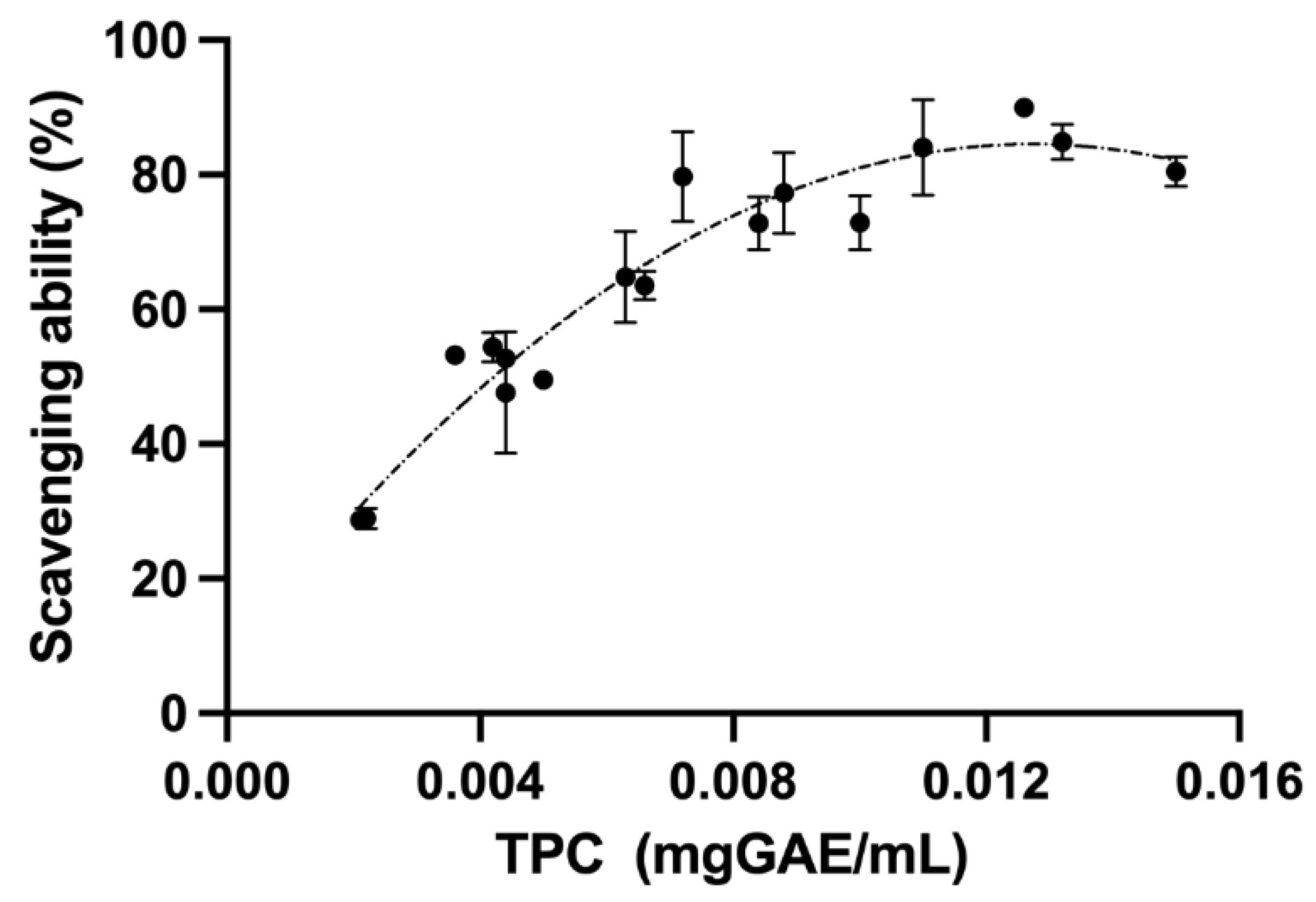
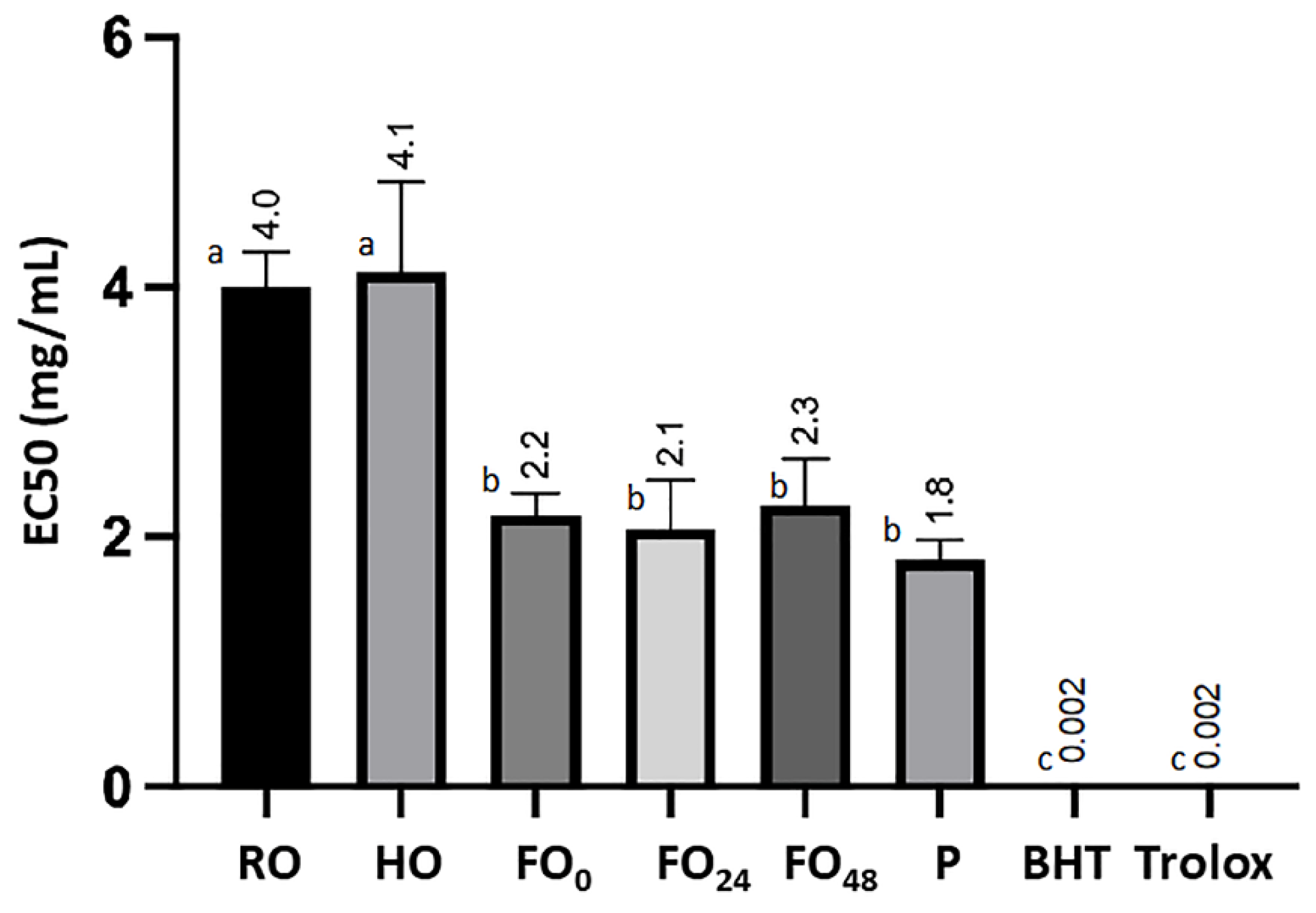
3.3. Antioxidant Activity
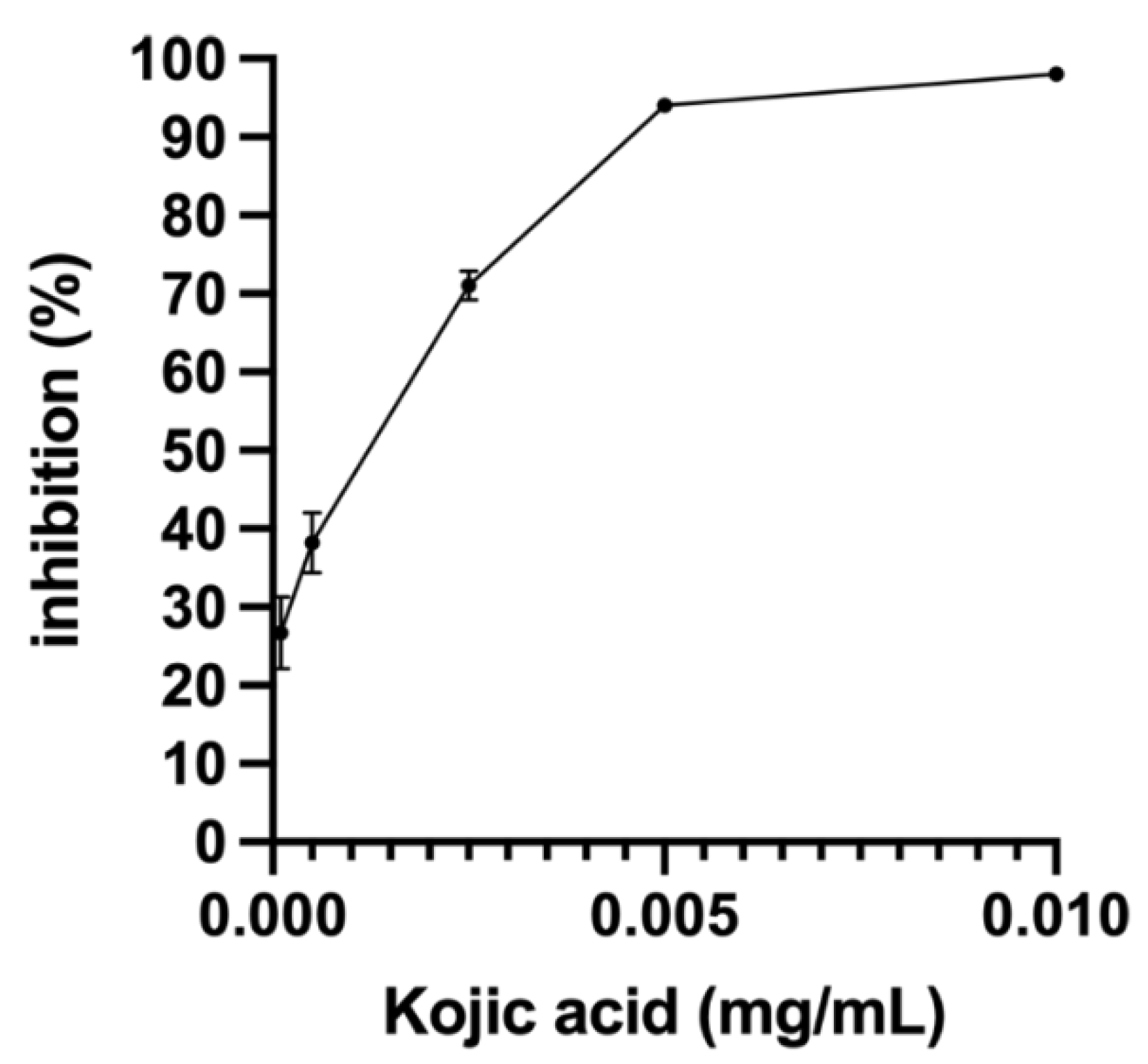
3.4. Determination of Tyrosinase Inhibition
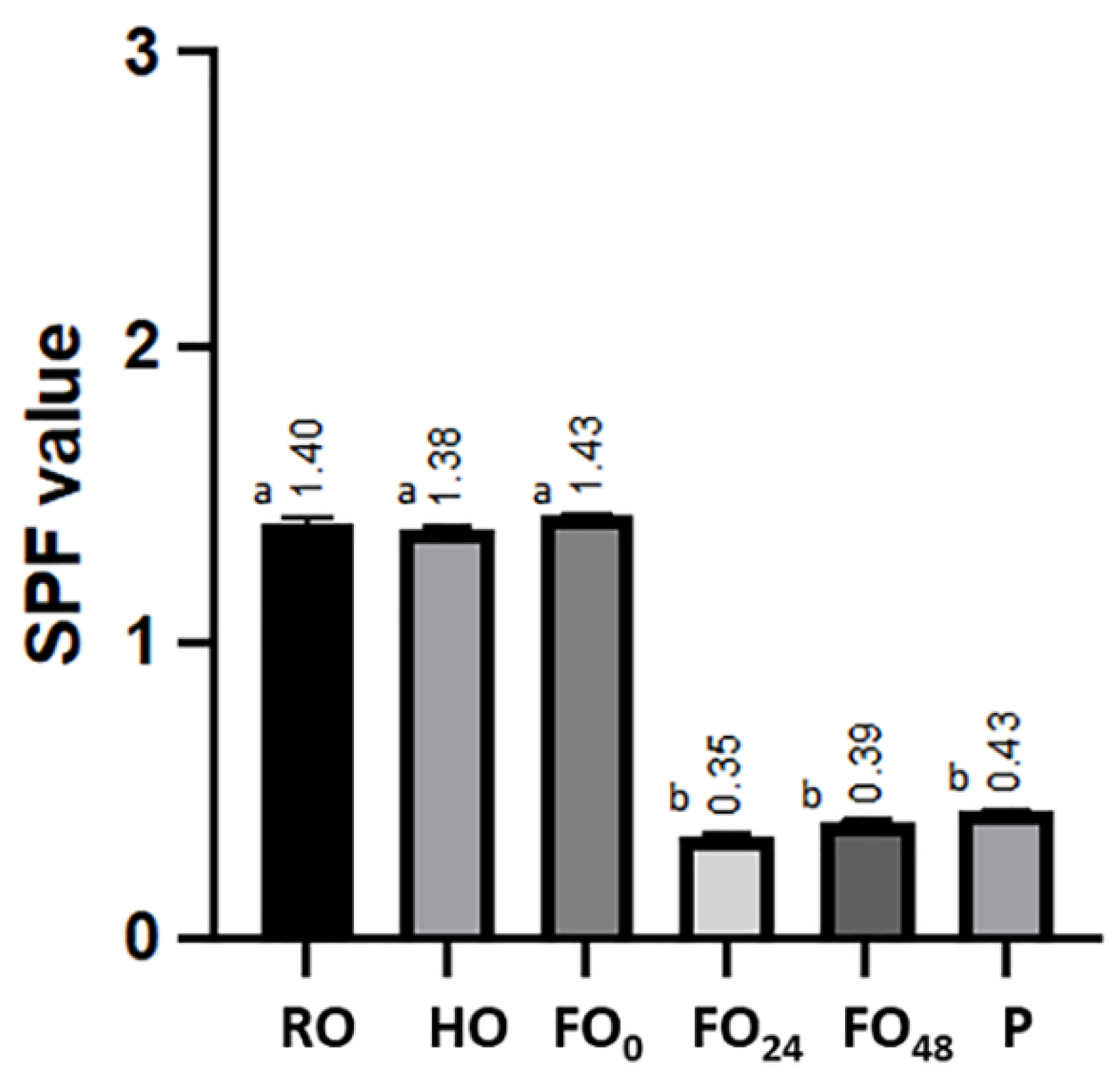
3.5. Sun Protection Factor (SPF) Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hernandez, D.F.; Cervantes, E.L.; Luna-Vital, D.A.; Mojica, L. Food-derived bioactive compounds with anti-aging potential for nutricosmetic and cosmeceutical products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 3740–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, G.; Paramithiotis, S.; Sundaram Sivamaruthi, B.; Wijaya, C.H.; Suharta, S.; Sanlier, N.; Shin, H.S.; Patra, J.K. Traditional fermented foods with anti-aging effect: A concentric review. Food Res. Int. 2020, 134, 109269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.; Lee, Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Lim, H.W.; Jang, K.; Kim, D.D.; Lim, C.J. Probiotic fermentation augments the skin anti-photoaging properties of Agastache rugosa through up-regulating antioxidant components in UV-B-irradiated HaCaT keratinocytes. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, K.F.; Voo, A.Y.H.; Chen, W.N. Bioactive peptides from food fermentation: A comprehensive review of their sources, bioactivities, applications, and future development. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 3825–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schagen, S.K. Topical Peptide Treatments with Effective Anti-Aging Results. Cosmetics 2017, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghazzewi, F.H.; Tester, R.F. Impact of prebiotics and probiotics on skin health. Benef. Microbes 2014, 5, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, S.; Bouladoux, N.; Wilhelm, C.; Molloy, M.J.; Salcedo, R.; Kastenmuller, W.; Deming, C.; Quinones, M.; Koo, L.; Conlan, S.; et al. Compartmentalized control of skin immunity by resident commensals. Science 2012, 337, 1115–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, S.; Collado, M.C.; Endo, A.; Hill, C.; Lebeer, S.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Sanders, M.E. Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Toalá, J.; Garcia-Varela, R.; Garcia, H.; Mata-Haro, V.; González-Córdova, A.; Vallejo-Cordoba, B.; Hernández-Mendoza, A. Postbiotics: An evolving term within the functional foods field. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 75, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirhadi, M.; Alikord, M.; Mohammadi, M.A.; Shariatifar, N. Beneficial effects of postbiotics on food products and its effect on human health: A Critical Review. Plant Biotechnol. Persa 2021, 3, 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande, G.; Athalye-Jape, G.; Patole, S. Para-probiotics for Preterm Neonates-The Next Frontier. Nutrients 2018, 10, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegh, C.; Geerlings, S.Y.; Knol, J.; Roeselers, G.; Belzer, C. Postbiotics and Their Potential Applications in Early Life Nutrition and Beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, M.; Nigro, F.; Porpora, M.; Bellomo, C.; Furone, F.; Budelli, A.L.; Nigro, R.; Barone, M.V.; Nanayakkara, M. Gliadin Peptide P31-43 Induces mTOR/NFkβ Activation and Reduces Autophagy: The Role of Lactobacillus paracasei CBA L74 Postbiotc. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ácsová, A.; Hojerová, J.; Martiniaková, S. Efficacy of postbiotics against free radicals and UV radiation. Chem. Pap. 2022, 76, 2357–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izuddin, W.I.; Humam, A.M.; Loh, T.C.; Foo, H.L.; Samsudin, A.A. Dietary Postbiotic Lactobacillus plantarum Improves Serum and Ruminal Antioxidant Activity and Upregulates Hepatic Antioxidant Enzymes and Ruminal Barrier Function in Post-Weaning Lambs. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Thukral Kaur, S.; Kaur, P.; Samota, M.K. Perturbations associated with hungry gut microbiome and postbiotic perspectives to strengthen the microbiome health. Future Foods 2021, 4, 100043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlomagno, F.; Zanzottera, S. Biotechnological Active Ingredient, Protecting Skin Microbiota. SÖFW-J. 2019, 145, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaoyu, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Yi, K.; Ye, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, S.; Hu, H.; Zou, L.; Wang, Z. Dynamic changes in antioxidant activity and biochemical composition of tartary buckwheat leaves during Aspergillus niger fermentation. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 32, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, Q.; Wu, Z.; Chen, G. Dynamic changes in the phenolic composition and antioxidant activity of oats during simultaneous hydrolysis and fermentation. Food Chem. 2020, 305, 125269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Li, S.; Yan, J.; Peng, Y.; Weng, W.; Yao, X.; Gao, A.; Cheng, J.; Ruan, J.; Xu, B. Bioactive Components and Health Functions of Oat. Food Rev. Int. 2022, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccio, G. Plant Complexity and Cosmetic Innovation. iScience 2020, 23, 101358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.C.; Lee, I.J.; Huang, C.; Chang, T.M. Lactic Acid Bacteria and Lactic Acid for Skin Health and Melanogenesis Inhibition. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2020, 21, 566–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagato, E.; Mileti, E.; Massimiliano, L.; Fasano, F.; Budelli, A.; Penna, G.; Rescigno, M. Lactobacillus paracasei CBA L74 metabolic products and fermented milk for infant formula have anti-inflammatory activity on dendritic cells in vitro and protective effects against colitis and an enteric pathogen In Vivo. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colucci Cante, R.; Gallo, M.; Nigro, F.; Passannanti, F.; Salameh, D.; Budelli, A.; Nigro, R. Lactic fermentation of cooked navy beans by Lactobacillus paracasei CBA L74 aimed at a potential production of functional legume-based foods. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 98, 1955–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salameh, D.; Nigro, F.; Colucci Cante, R.; Passannanti, F.; Gallo, M.; Budelli, A.; Marzocchella, A.; Nigro, R. Fermentation of Rice Flour Supernatant Using Lactobacillus Paracasei Cba L74. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2019, 75, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, M.; Passannanti, P.; Colucci Cante, R.; Nigro, F.; Schiattarella, P.; Zappulla, S.; Budelli, A.; Nigro, R. Lactic fermentation of cereals aqueous mixture of oat and rice flours with and without glucose addition. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, M.; Passannanti, F.; Colucci Cante, R.; Nigro, F.; Salameh, D.; Schiattarella, P.; Schioppa, C.; Budelli, A.; Nigro, R. Effect of the glucose addition during lactic fermentation of rice, oat, and wheat flours. Appl. Food Biotechnol. 2020, 7, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, M.; Passannanti, F.; Schiattarella, P.; Esposito, A.; Colucci Cante, R.; Nigro, F.; Budelli, A.; Nigro, R. Banana Puree Lactic Fermentation: The Role of Ripeness, Heat Treatment, and Ascorbic Acid. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, M.; Passannanti, F.; Schioppa, C.; Montella, S.; Colucci Cante, R.; Nigro, F.; Budelli, A.; Nigro, R. Enzymatic pre-treatment and lactic fermentation of wheat flour suspension at a high solid content. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, M.; Nigro, F.; Passannanti, F.; Salameh, D.; Schiattarella, P.; Budelli, A.L.; Nigro, R. Lactic Fermentation of Cereal Flour: Feasibility Tests on Rice, Oat and Wheat. Appl. Food Biotechnol. 2019, 6, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarno, M.; Lania, G.; Cuomo, M.; Nigro, F.; Passannanti, F.; Budelli, A.; Fasano, F.; Troncone, R.; Auricchio, S.; Barone, M.V.; et al. Lactobacillus paracasei CBA L74 interferes with gliadin peptides entrance in Caco-2 cells. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 65, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labruna, G.; Nanayakkara, M.; Pagliuca, C.; Nunziato, M.; Iaffaldano, L.; D’Argenio, V.; Colicchio, R.; Budelli, A.L.; Nigro, R.; Salvatore, P.; et al. Celiac disease-associated Neisseria flavescens decreases mitochondrial respiration in CaCo-2 epithelial cells: Impact of Lactobacillus paracasei CBA L74 on bacterial-induced cellular imbalance. Cell Microbiol. 2019, 21, e13035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colucci Cante, R.; Gallo, M.; Nigro, F.; Passannanti, F.; Budelli, A.; Nigro, R. Mathematical modelling of Lactobacillus paracasei CBA L74 growth during rice flour fermentation performed with and without pH control. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, M.; Nigro, F.; Passannanti, F.; Nanayakkara, M.; Lania, G.; Parisi, F.; Salameh, D.; Budelli, A.; Barone, M.V.; Nigro, R. Effect of pH control during rice fermentation in preventing a gliadin P31-43 entrance in epithelial cells. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 70, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, E.R. Aseptic laboratory techniques: Plating methods. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 63, e3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordis-Krapez, M.; Abram, V.; Kac, M.H.; Ferjan, S. Determination of organic acids in white wines by RP-HPLC. Food Tech. Biotechnol. 2001, 39, 93–99. [Google Scholar]
- Aikpokpodion, P.E.; Dongo, L.N. Effects of fermentation intensity on polyphenols and antioxidant capacity of cocoa beans. Int. J. Sustain. Crop Prod. 2010, 5, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Colucci Cante, R.; Gallo, M.; Nigro, F.; Vitelli, C.; Passannanti, F.; Budelli, A.L.; Nigro, R. Optimization of Mixing Conditions for Improving Lactobacillus Paracasei Cba L74’ S Growth During Lactic Fermentation of Cooked Navy Beans and Functional Characterization of the Fermented Products. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2022, 93, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.; Devaki, M. The ferric reducing/antioxidant power (FRAP) assay for non-enzymatic antioxidant capacity: Concepts, procedures, limitations and applications. In Measurement of Antioxidant Activity & Capacity; Apak, R., Capanoglu, E., Shahidi, F., Eds.; Wiley Online Library: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 77–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.P.; Tan, H.Y.; Wang, M. Tyrosinase inhibition constituents from the roots of Morus australis. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 1008–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Jang, D.H.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, K.D.; Shah, A.B.; Zhumanova, K.; Park, K.H. Tyrosinase Inhibition and Kinetic Details of Puerola Having But-2-Enolide Structure from Amorpha fruticosa. Molecules 2020, 25, 2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansur, J.S.; Breder, M.N.R.; Mansur, M.C.A.; Azulay, R.D. Determinação do fator de proteção solar por espectrofotometria. An. Bras. Dermatol. 1986, 61, 121–124. [Google Scholar]
- Mbanga, L.; Mulenga, M.; Mpiana, P.T.; Bokolo, K.; Mumbwa, M.; Mvingu, K. Determination of Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of Some Body Creams and Lotions Marketed in Kinshasa by Ultraviolet Spectrophotometry. Int. J. Adv. Res. Chem. Sci. 2014, 1, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Igual, M.; García-Martínez, E.; Camacho, M.M.; Martínez-Navarrete, N. Effect of thermal treatment and storage on the stability of organic acids and the functional value of grapefruit juice. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, X.; Deng, J.; Ouyang, D.; Wang, D.; Liang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y. Effect of thermal processing on free and bound phenolic compounds and antioxidant activities of hawthorn. Food Chem. 2020, 332, 127429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randhir, R.; Kwon, Y.; Shetty, K. Effect of thermal processing on phenolics, antioxidant activity and health-relevant functionality of select grain sprouts and seedlings. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2008, 9, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Călinoiu, L.F.; Vodnar, D.C. Thermal Processing for the Release of Phenolic Compounds from Wheat and Oat Bran. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico, D.; Villaverde, A.; Martinez-Villaluenga, C.; Gutierrez, A.L.; Caballero, P.A.; Ronda, F.; Peñas, E.; Frias, J.; Martin Diana, A.B. Application of Autoclave Treatment for Development of a Natural Wheat Bran Antioxidant Ingredient. Foods 2020, 9, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, A.; Shabbir, U.; Chelliah, R.; Daliri, E.B.M.; Chen, X.; Oh, D.H. Limosilactobacillus reuteri Fermented Brown Rice: A Product with Enhanced Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Potential. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, M.Y.; Chou, C.C. Enhancement of antioxidant activity, total phenolic and flavonoid content of black soybeans by solid state fermentation with Bacillus subtilis BCRC 14715. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Chen, I.C.; Chen, P.Y.; Huang, P.H. Efficacy of rice bran fermentation in cosmetics and skin care products. Biosci. J. 2018, 34, 1102–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummun, N.; Somanah, J.; Ramsaha, S.; Bahorun, T.; Neergheen-Bhujun, V.S. Bioactivity of Nonedible Parts of Punica granatum L.: A Potential Source of Functional Ingredients. Int. J. Food Sci. 2013, 2013, 602312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denga, G.X.; Xub, X.R.; Guoa, Y.J.; Xiaa, E.Q.; Lia, S.; Wua, S.; Chenc, F.; Linga, W.H.; Li, H.-B. Determination of antioxidant property and their lipophilic and hydrophilic phenolic contents in cereal grains. J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Jubete, L.; Wijngaard, H.; Arendt, E.K.; Gallagher, E. Polyphenol composition and in vitro antioxidant activity of amaranth, quinoa buckwheat and wheat as affected by sprouting and baking. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.Y.; Yang, H.J.; Moon, H.I.; Cho, Y.S. Inhibitory effect and mechanism on melanogenesis from fermented herbal composition for medical or food uses. Int. Food Res. J. 2012, 45, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.M.; Shih, T.W.; Chiu, C.P.; Pan, T.M.; Tsai, T.Y. Effects of lactic acid bacteria-fermented soy milk on melanogenesis in B16F0 melanocytes. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manosroi, A.; Ruksiriwanich, W.; Kietthanakorn, B.; Manosroi, W.; Manosroi, J. Relationship between biological activities and bioactive compounds in the fermented rice sap. Int. Food Res. J. 2011, 44, 2757–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizioł-Łukaszewska, Z.; Ziemlewska, A.; Bujak, T.; Zagórska-Dziok, M.; Zarebska, M.; Hordyjewicz-Baran, Z.; Wasilewski, T. Effect of Fermentation Time on Antioxidant and Anti-Ageing Properties of Green Coffee Kombucha Ferments. Molecules 2020, 25, 5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagemaker, T.A.L.; Carvalho, C.R.L.; Maia, N.B.; Baggio, S.R.; Filho, O.G. Sun protection factor, content, and composition of lipid fraction of green coffee beans. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2011, 33, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejeki, S.; Fahrun, N.; Siwi, H. The SPF value determination of sunscreen lotio of lime rind spectrometry UV-VIS method. In Proceeding of the International Conference on Medical and Healthcare, Tsukuba, Japan, 8–10 June 2018; Volume 1, pp. 16–19. [Google Scholar]

| Oat Samples | Description |
|---|---|
| RO | Raw oatmeal |
| HO | Hydrolyzed oatmeal |
| FO0 | Fermented oatmeal at time 0 |
| FO24 | Fermented oatmeal after 24 h of fermentation |
| FO48 | Fermented oatmeal after 48 h of fermentation |
| P | Postbiotic, after 48 h of fermentation and deactivation. |
| Sample | mmol Fe2+/g | mmol TE/g |
|---|---|---|
| RO | 7.14 × 10−3 ± 3.03 × 10−3 a | 4.13 × 10−3 ± 1.63 × 10−3 b |
| HO | 7.50 × 10−3 ± 1.98 × 10−3 a | 4.40 × 10−3 ± 2.55 × 10−3 b |
| FO0 | 1.38 × 10−2 ± 2.60 × 10−3 a | 7.30 × 10−3 ± 2.27 × 10−3 b |
| FO24 | 1.30 × 10−2 ± 2.83 × 10−3 a | 7.70 × 10−3 ± 1.13 × 10−3 b |
| FO48 | 1.40 × 10−2 ± 2.05 × 10−3 a | 8.10 × 10−3 ± 1.27 × 10−3 b |
| P | 1.42 × 10−2 ± 3.18 × 10−3 a | 7.94 × 10−3 ± 1.72 × 10−3 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lentini, G.; Nigro, F.; Colucci Cante, R.; Passannanti, F.; Gallo, M.; Budelli, A.L.; Nigro, R. Functional Properties of an Oat-Based Postbiotic Aimed at a Potential Cosmetic Formulation. Fermentation 2022, 8, 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110632
Lentini G, Nigro F, Colucci Cante R, Passannanti F, Gallo M, Budelli AL, Nigro R. Functional Properties of an Oat-Based Postbiotic Aimed at a Potential Cosmetic Formulation. Fermentation. 2022; 8(11):632. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110632
Chicago/Turabian StyleLentini, Giulia, Federica Nigro, Rosa Colucci Cante, Francesca Passannanti, Marianna Gallo, Andrea Luigi Budelli, and Roberto Nigro. 2022. "Functional Properties of an Oat-Based Postbiotic Aimed at a Potential Cosmetic Formulation" Fermentation 8, no. 11: 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110632
APA StyleLentini, G., Nigro, F., Colucci Cante, R., Passannanti, F., Gallo, M., Budelli, A. L., & Nigro, R. (2022). Functional Properties of an Oat-Based Postbiotic Aimed at a Potential Cosmetic Formulation. Fermentation, 8(11), 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110632








