The Xylose Metabolizing Yeast Spathaspora passalidarum is a Promising Genetic Treasure for Improving Bioethanol Production
Abstract
1. Fermentation Technology and Challenges
2. Spathaspora passalidarum a Promising Genetic Source
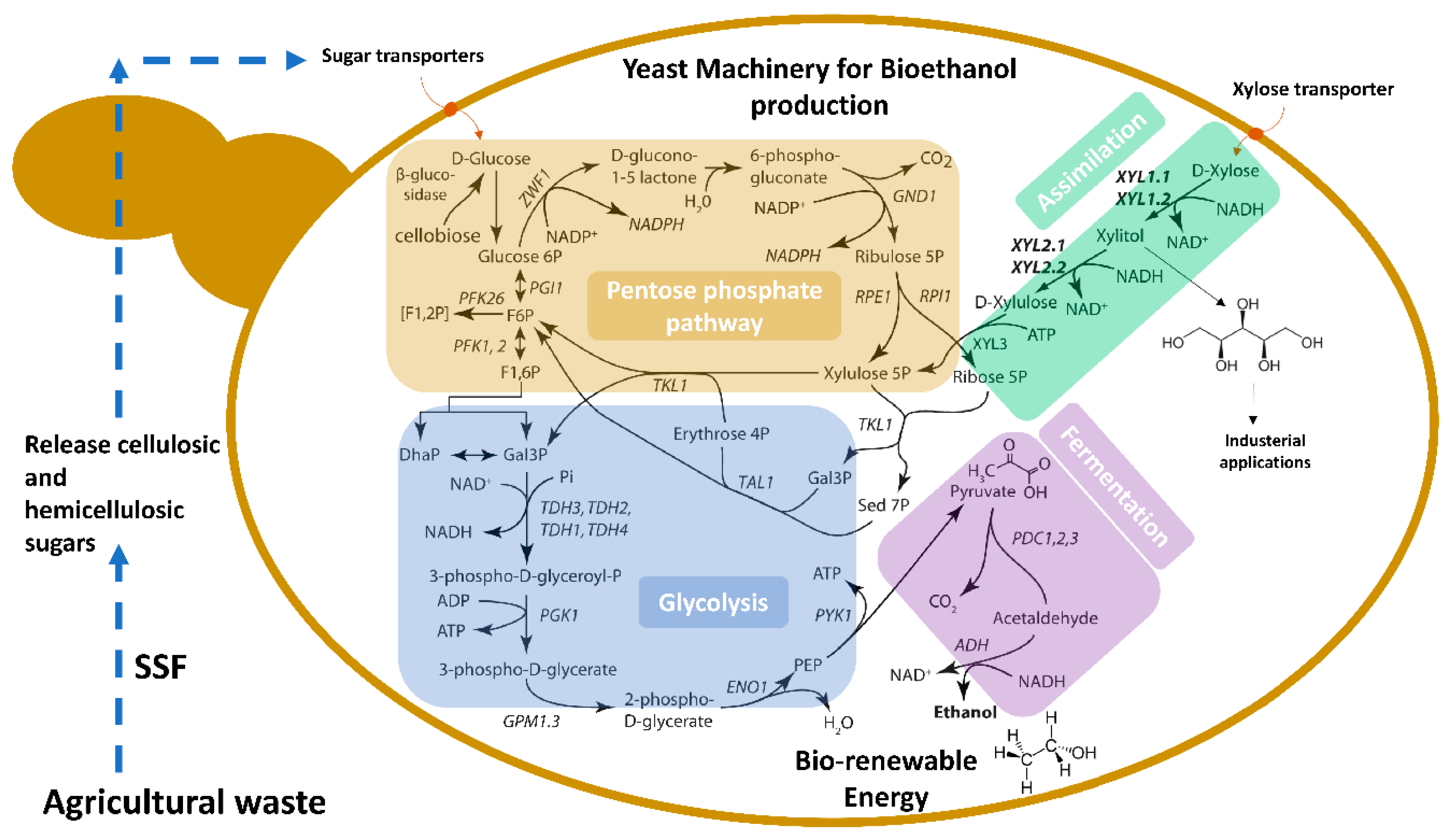
3. Fermentation Capability of Spathaspora passalidarum
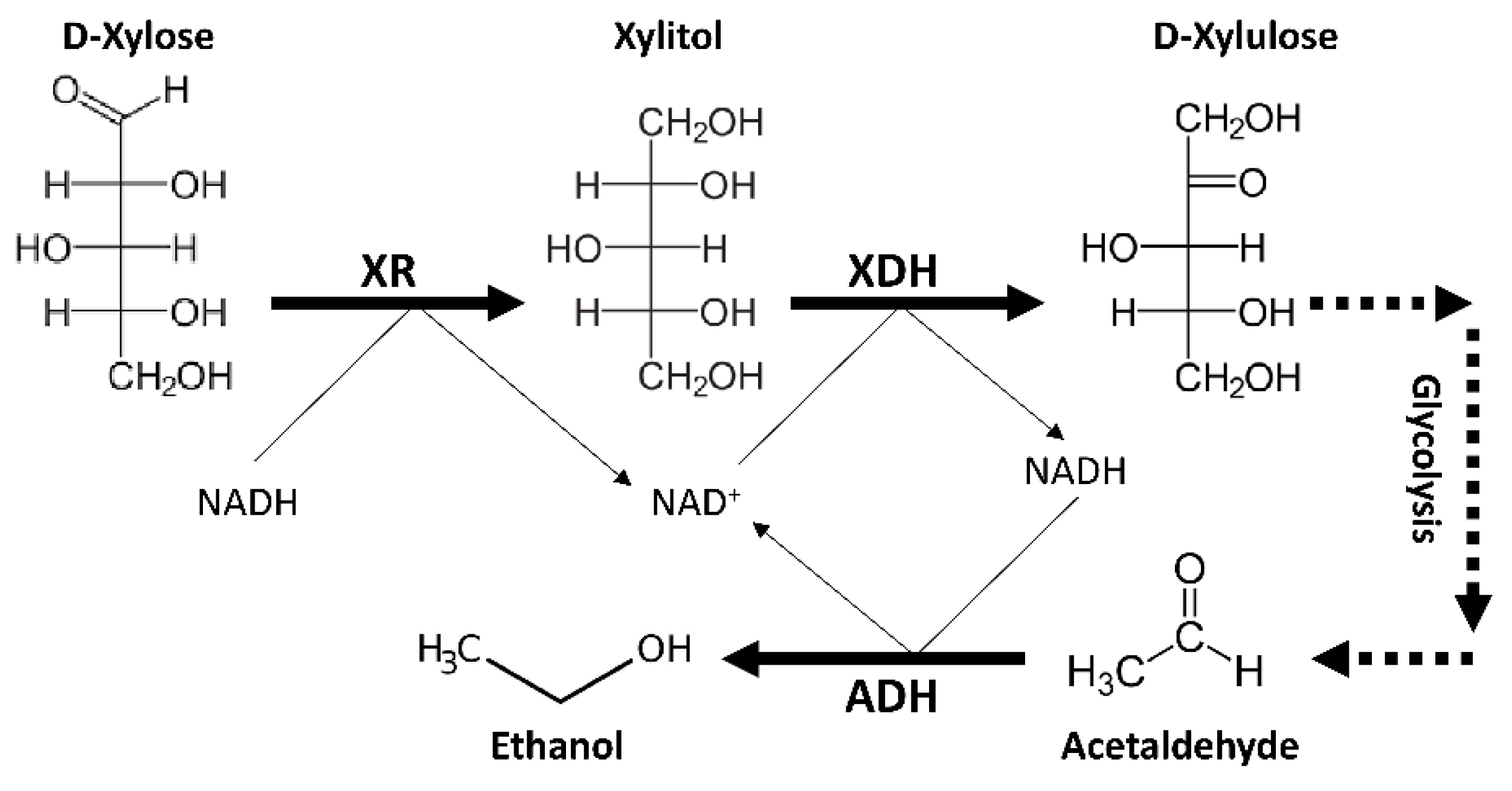
4. Genetic and Physiological Features of Spathaspora passalidarum Emphasis Special Roles for Xylose Reductase and Xylitol Dehydrogenase
5. New Adaptive Strains of Spathaspora passalidarum for Potential Industrial Applications
6. Future Perspective for Engineering New Strains for Better Bioethanol Production
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeffries, T.W. Engineering yeasts for xylose metabolism. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2006, 17, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balat, M.; Balat, H. Recent trends in global production and utilization of bio-ethanol fuel. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 2273–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarboe, L.R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Moore, J.C.; Shanmugam, K.T.; Ingram, L.O. Metabolic Engineering for Production of Biorenewable Fuels and Chemicals: Contributions of Synthetic Biology. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 761042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selim, K.A.; El-Ghwas, D.E.; Easa, S.M.; Hassan, M.I.A. Bioethanol a Microbial Biofuel Metabolite; New Insights of Yeasts Metabolic Engineering. Fermentation 2018, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffries, T.W.; Shi, N.Q. Genetic engineering for improved xylose fermentation by yeasts. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 1999, 65, 117–161. [Google Scholar]
- Ruchala, J.; Kurylenko, O.O.; Dmytruk, K.V.; Sibirny, A.A. Construction of advanced producers of first- and second-generation ethanol in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and selected species of non-conventional yeasts (Scheffersomyces stipitis, Ogataea polymorpha). J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 47, 109–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinmann, N.D.; Wright, J.D.; Hoagland, W.; Wyman, C.E. Xylose fermentation—An economic analysis. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1989, 20, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.C.; Dien, B.S.; Bothast, R.J. Fuel ethanol production from corn fiber—Current status and technical prospects. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1998, 70, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadete, R.M.; Rosa, C.A. The yeasts of the genus Spathaspora: Potential candidates for second-generation biofuel production. Yeast 2018, 35, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X. Anaerobic xylose fermentation by Spathaspora passalidarum. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 94, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtzman, C.P. Candida shehatae—Genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationships with other xylose-fermenting yeasts. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 1990, 57, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melake, T.; Passoth, V.V.; Klinner, D. Characterization of the genetic system of the xylose-fermenting yeast Pichia stipitis. Curr. Microbial. 1996, 33, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffries, T.W.; Van Vleet, J.R.H. Pichia stipitis genomics, transcriptomics, and gene clusters. FEMS Yeast Res. 2009, 9, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vleet, J.H.; Jeffries, T.W. Yeast metabolic engineering for hemicellulosic ethanol production. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2009, 20, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtzman, C.P.; Suzuki, M. Phylogenetic analysis of the ascomycete yeasts that form coezyme Q-9 and the proposal of the new genera Babjeviella, Meyerozyma, Millerozyma, Priceomyces and Scheffersomyces. Mycoscience 2010, 51, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijken, J.P.; van den Bosch, E.; Hermans, J.J.; de Miranda, L.R.; Scheffers, W.A. Alcoholic fermentation by ‘nonfermentative’ yeasts. Yeast 1986, 2, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffries, T.W.; Grigoriev, I.V.; Grimwood, J.; Laplaza, J.M.; Aerts, A.; Salamov, A.; Schmutz, J.; Lindquist, E.; Dehal, P.; Shapiro, H.; et al. Genome sequence of the lignocellulose-bioconverting and xylose fermenting yeast Pichia stipitis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplaza, J.M.; Torres, B.R.; Jin, Y.S.; Jeffries, T.W. Sh ble and Cre adapted for functional genomics and metabolic engineering of Pichia stipitis. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2006, 38, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, T.M.; Su, Y.K.; Headman, J.; Higbee, A.; Willis, L.B.; Jeffries, T.W. Cofermentation of glucose, xylose, and cellobiose by the beetle-associated yeast, Spathaspora passalidarum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 5492–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.K.; Willis, L.B.; Jeffries, T.W. Effects of aeration on growth, ethanol and polyol accumulation by Spathaspora passalidarum NRRL Y-27907 and Scheffersomyces stipitis NRRL Y-7124. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2015, 112, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.H.; Suh, S.O.; Marshall, C.J.; Blackwell, M. Morphological and ecological similarities: Wood-boring beetles associated with novel xylose-fermenting yeasts, Spathaspora passalidarum gen. sp. nov. and Candida jeffriesii sp. nov. Mycol. Res. 2006, 110, 1232–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadete, R.M.; Santos, R.O.; Melo, M.A.; Mouro, A.; Gonc¸alves, D.L.; Stambuk, B.U.; Gomes, F.C.O.; Lachance, M.A.; Rosa, C.A. Spathaspora arborariae sp. nov., a D-xylose-fermenting yeast species isolated from rotting wood in Brazil. FEMS Yeast Res. 2009, 9, 1338–1342. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cadete, R.M.; Melo, M.A.; Dussán, K.J.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Silva, S.S.; Zilli, J.E.; Vital, M.J.; Gomes, F.C.; Lachance, M.A.; Rosa, C.A. Diversity and physiological characterization of D-xylose-fermenting yeasts isolated from the Brazilian Amazonian Forest. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadete, R.M.; Melo, M.A.; Zilli, J.E.; Vital, M.J.; Mouro, A.; Prompt, A.H.; Gomes, F.C.; Stambuk, B.U.; Lachance, M.A.; Rosa, C.A. Spathaspora brasiliensis sp. nov., Spathaspora suhii sp. nov., Spathaspora roraimanensis sp. nov. and Spathaspora xylofermentans sp. nov., four novel (D)-xylose-fermenting yeast species from Brazilian Amazonian forest. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2013, 103, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, G.F.L.; Valentim, L.T.C.N.; Nogueira, S.R.P.; Abegg, M.A. Efficient production of second generation ethanol and xylitol by yeasts from Amazonian beetles (Coleoptera) and their galleries. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 11, 814–824. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Chen, L.; Niu, Q.; Hui, F. Description of Scheffersomyces henanensis sp. nov., a new D-xylose-fermenting yeast species isolated from rotten wood. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrussamee, N.; Sattayawat, P.; Yamada, M. Highly efficient conversion of xylose to ethanol without glucose repression by newly isolated thermotolerant Spathaspora passalidarum CMUWF1-2. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadete, R.M.; de las Heras, A.M.; Sandström, A.G.; Ferreira, C.; Gírio, F.; Gorwa-Grauslund, M.-F.; Rosa, C.A.; Fonseca, C. Exploring xylose metabolism in Spathaspora species: XYL1.2 from Spathaspora passalidarum as the key for efficient anaerobic xylose fermentation in metabolic engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 167. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, S.; Jin, Y.S. Production of fuels and chemicals from xylose by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae: A review and perspective. Microb. Cell Fact. 2017, 16, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veras, H.C.T.; Parachin, N.S.; Almeida, J.R.M. Comparative assessment of fermentative capacity of different xylose-consuming yeasts. Microb. Cell Fact. 2017, 16, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veras, H.C.T.; Campos, C.G.; Nascimento, I.F.; Abdelnur, P.V.; Almeida, J.R.M.; Parachin, N.S. Metabolic flux analysis for metabolome data validation of naturally xylose-fermenting yeasts. BMC Biotechnol. 2019, 19, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, S.C.; Soares, L.B.; Biazi, L.E.; Nascimento, V.M.; Costa, A.C.; Rocha, G.J.M.; Ienczak, J.L. Fermentation strategy for second generation ethanol production from sugarcane bagasse hydrolyzate by Spathaspora passalidarum and Scheffersomyces stipitis. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 114, 2211–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, R.D.F.R.; Dutra, E.D.; Leite, F.C.B.; Cadete, R.M.; Rosa, C.A.; Stambuk, B.U.; Stamford, T.L.M.; de Morais, M.A., Jr. Production of ethanol fuel from enzyme-treated sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate using d-xylose-fermenting wild yeast isolated from Brazilian biomes. 3 Biotech. 2018, 8, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlbach, D.J.; Kuo, A.; Sato, T.K.; Potts, K.M.; Salamov, A.A.; Labutti, K.M.; Sun, H.; Clum, A.; Pangilinan, J.L.; Lindquist, E.A.; et al. Comparative genomics of xylose-fermenting fungi for enhanced biofuel production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13212–13217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppsson, M.; Bengtsson, O.; Franke, K.; Lee, H.; Hahn-Hagerdal, B.; Gorwa-Grauslund, M.F. The expression of a Pichia stipitis xylose reductase mutant with higher K(m) for NADPH increases ethanol production from xylose in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2006, 93, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petschacher, B.; Nidetzky, B. Altering the coenzyme preference of xylose reductase to favor utilization of NADH enhances ethanol yield from xylose in a metabolically engineered strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb. Cell 2008, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, O.; Hahn-Hagerdal, B.; Gorwa-Grauslund, M.F. Xylose reductase from Pichia stipitis with altered coenzyme preference improves ethanolic xylose fermentation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2009, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Huang, S.; Chen, Y.; Guo, X.; Xiao, D. Heterologous expression of Spathaspora passalidarum xylose reductase and xylitol dehydrogenase genes improved xylose fermentation ability of Aureobasidium pullulans. Microb. Cell Fact. 2018, 17, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fan, H.; Li, Y.; Shi, G.Y.; Ding, Z.Y.; Gu, Z.H.; Zhang, L. Construction and application of multi-host integrative vector system for xylose-fermenting yeast. FEMS Yeast Res. 2017, 17, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hou, X.; Yao, S. Improved inhibitor tolerance in xylosefermenting yeast Spathaspora passalidarum by mutagenesis and protoplast fusion. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 2591–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, P.; Gentina, J.C.; Aroca, G.; Mussatto, S.I. Development of an acetic acid tolerant Spathaspora passalidarum strain through evolutionary engineering with resistance to inhibitors compounds of autohydrolysate of Eucalyptus globulus. Ind. Crop Prod. 2017, 106, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Guo, J.; Chen, Y.; Fu, G.; Li, B.; Guo, X.; Xiao, D. Efficient utilization of hemicellulose and cellulose in alkali liquor-pretreated corncob for bioethanol production at high solid loading by Spathaspora passalidarum U1–58. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 232, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.K.; Willis, L.B.; Rehmann, L.; Smith, D.R.; Jeffries, T.W. Spathaspora passalidarum selected for resistance to AFEX hydrolysate shows decreased cell yield. FEMS Yeast Res. 2018, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.Y.; Jeffries, T.W. Pichia stipitis genes for alcohol dehydrogenase with fermentative and respiratory functions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; He, P.; Wang, Q.; Lu, D.; Li, Z.; Wu, C.; Jiang, N. The alcohol dehydrogenase system in the xylose-fermenting yeast Candida maltosa. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.Y.; Jeffries, T.W. Transcriptional control of ADH genes in the xylose fermenting yeast Pichia stipitis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 2363–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passoth, V.; Schafer, B.; Liebel, B.; Weierstall, T.; Klinner, U. Molecular cloning of alcohol dehydrogenase genes of the yeast Pichia stipitis and identification of the fermentative ADH. Yeast 1998, 14, 1311–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passoth, V.; Cohn, M.; Schafer, B.; Hahn-Hagerdal, B.; Klinner, U. Molecular analysis of the hypoxia induced ADH2-promoter in the respiratory yeast Pichia stipitis. Yeast 2003, 20, S199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passoth, V.; Cohn, M.; Schafer, B.; Hahn-Hagerdal, B.; Klinner, U. Analysis of the hypoxia-induced ADH2 promoter of the respiratory yeast Pichia stipitis reveals a new mechanism for sensing of oxygen limitation in yeast. Yeast 2003, 20, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Chapter, V. In Elucidating Physiological Roles of Pichia stipitis Alcohol Dehydrogenases in Xylose Fermentation and Shuffling Promoters for Multiple Genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae to Improve Xylose Fermentation. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Selim, K.A.; Easa, S.M.; El-Diwany, A.I. The Xylose Metabolizing Yeast Spathaspora passalidarum is a Promising Genetic Treasure for Improving Bioethanol Production. Fermentation 2020, 6, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation6010033
Selim KA, Easa SM, El-Diwany AI. The Xylose Metabolizing Yeast Spathaspora passalidarum is a Promising Genetic Treasure for Improving Bioethanol Production. Fermentation. 2020; 6(1):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation6010033
Chicago/Turabian StyleSelim, Khaled A., Saadia M. Easa, and Ahmed I. El-Diwany. 2020. "The Xylose Metabolizing Yeast Spathaspora passalidarum is a Promising Genetic Treasure for Improving Bioethanol Production" Fermentation 6, no. 1: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation6010033
APA StyleSelim, K. A., Easa, S. M., & El-Diwany, A. I. (2020). The Xylose Metabolizing Yeast Spathaspora passalidarum is a Promising Genetic Treasure for Improving Bioethanol Production. Fermentation, 6(1), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation6010033



