Free Amino Nitrogen in Brewing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Sources of Nitrogen
1.2. Wort Nitrogen
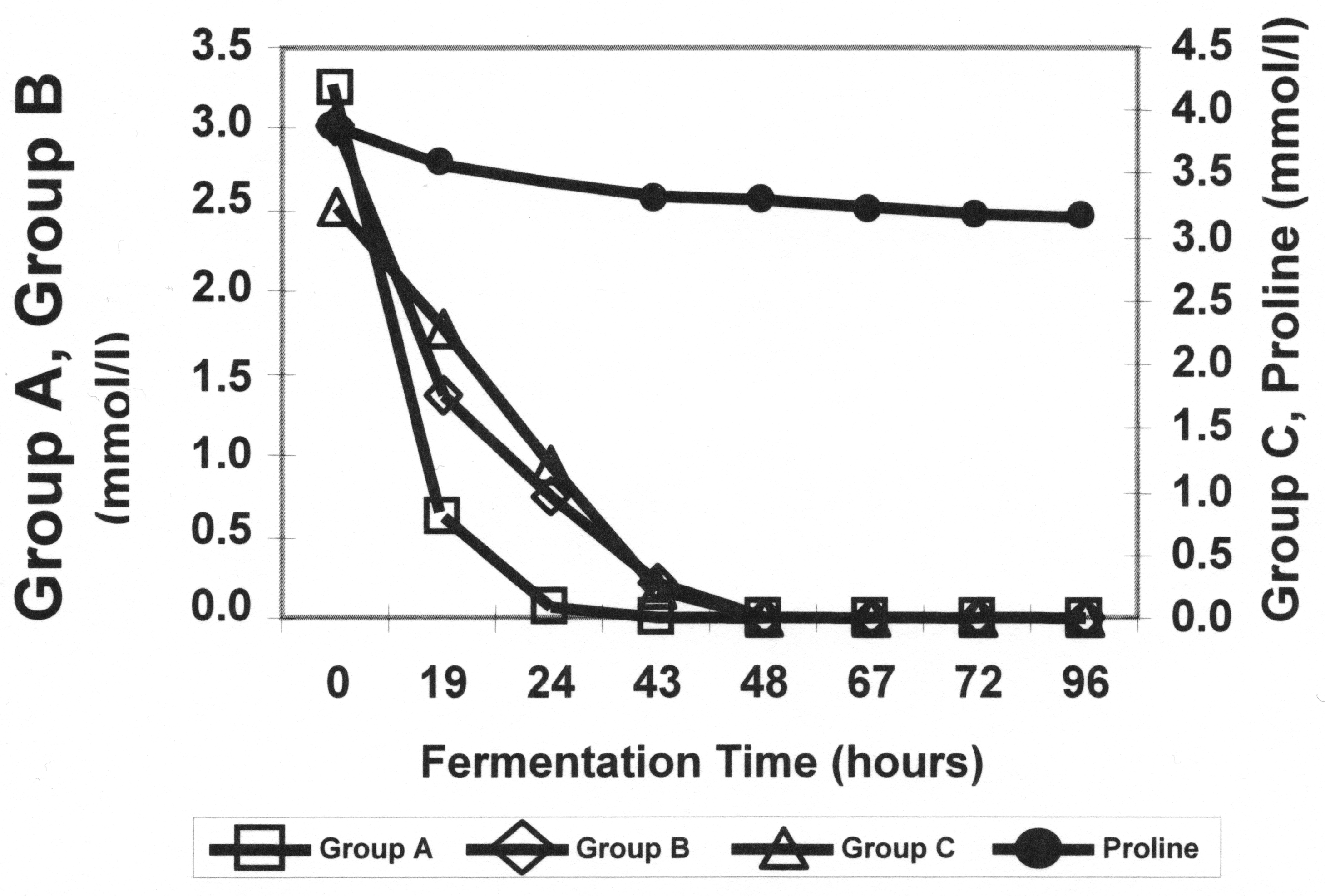
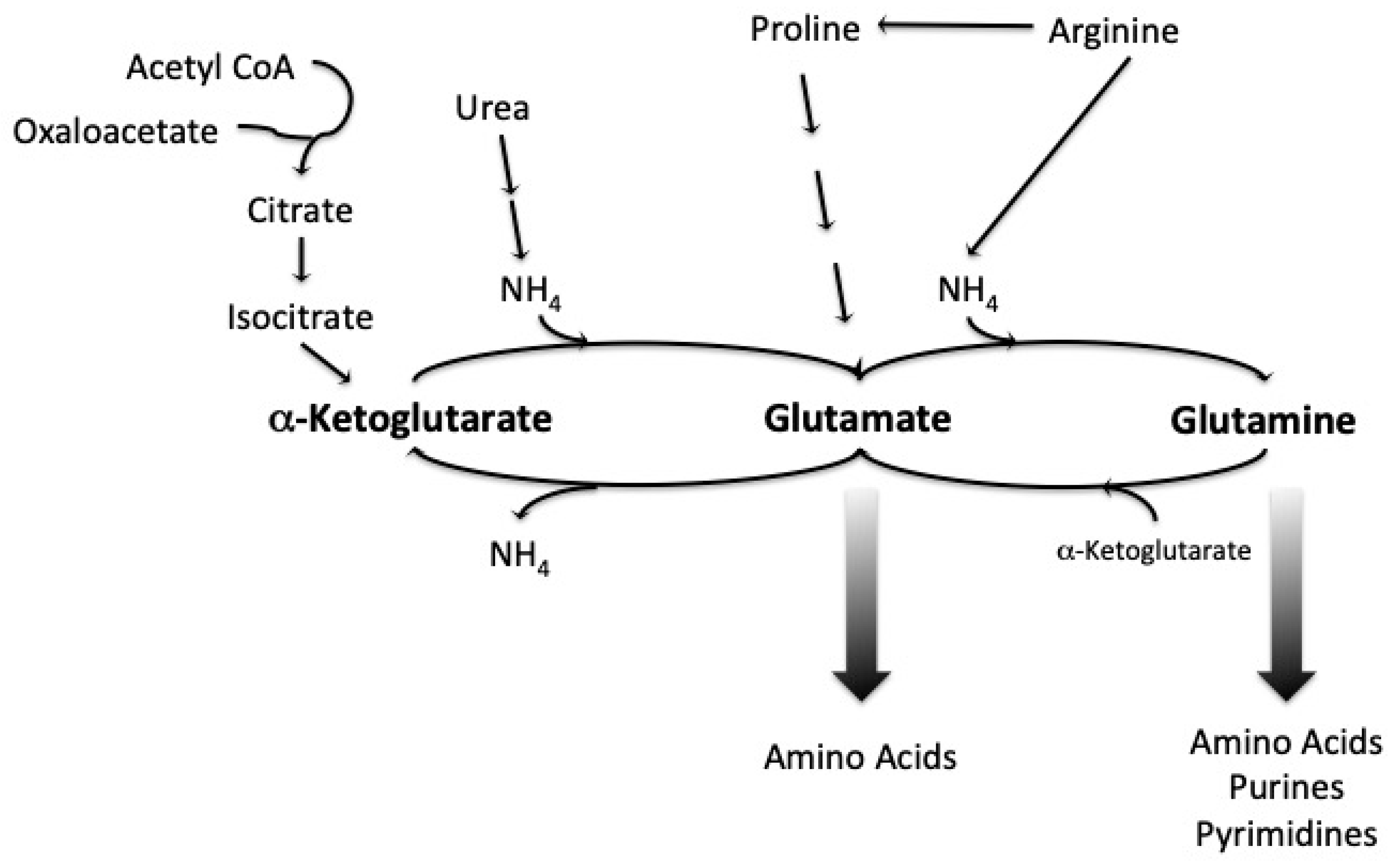
1.3. Amino Acid Uptake and Metabolism during Wort Fermentation
- The total wort concentration of assimilable nitrogen;
- The concentration of individual nitrogenous compounds and their ratio;
- The competitive inhibition of the uptake of these components (mainly amino acids) [28].
- The enzymes responsible for the synthesis and interconversion of nitrogenous compounds;
- The permeases for the uptake of nitrogenous compounds;
- The transcription factors and membrane trafficking proteins that regulate the activity of the enzymes and permeases [33].
1.4. Peptide Uptake
1.5. Impact of Wort Nitrogen
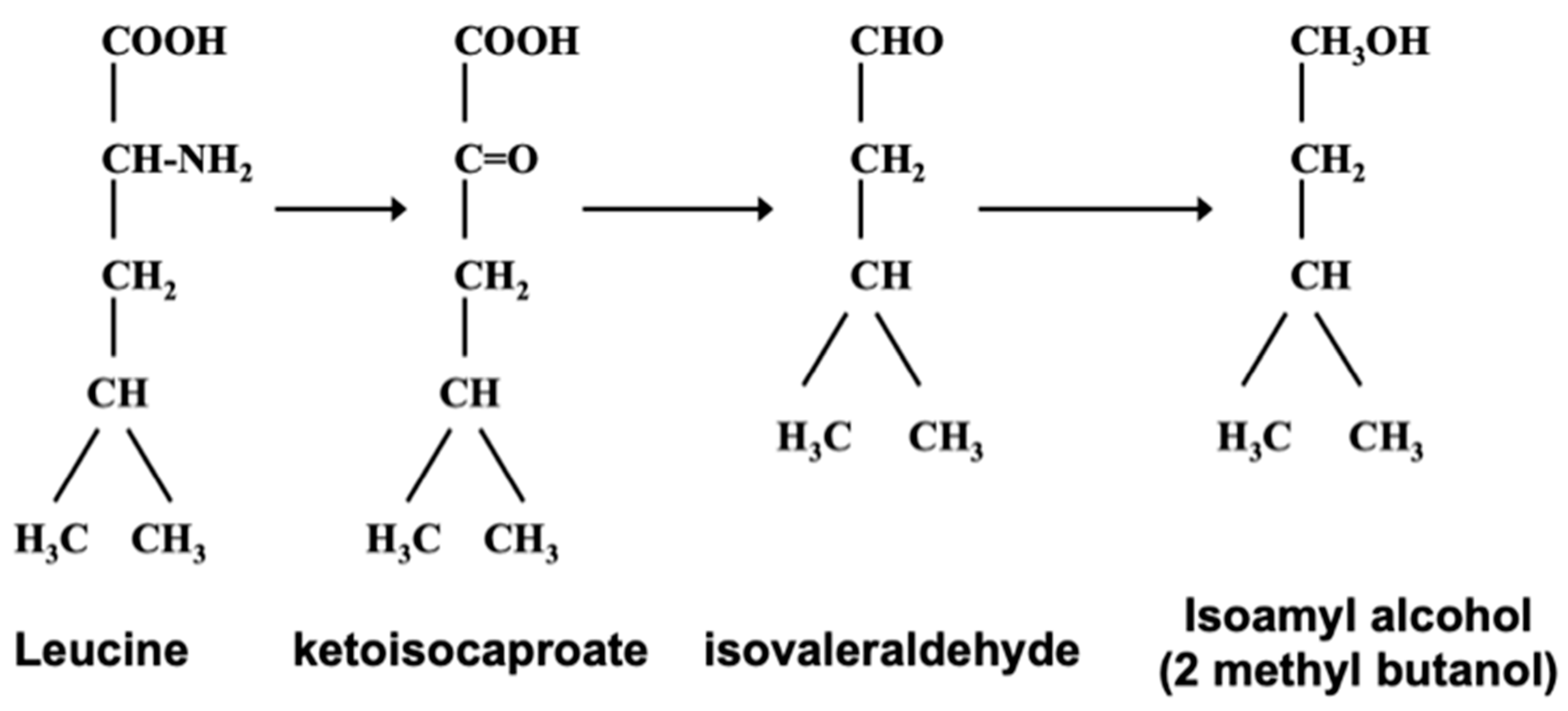
1.6. Erlich Pathway
2. Measuring Wort Nitrogen
3. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hornsey, I.S. A History of Beer and Brewing; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Barnett, J.A.; Lichtenthaler, F.W. A history of research on yeast 3: Emil Fischer, Eduard Buchner and their contemporaries, 1880–1900. Yeast 2001, 18, 363–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, J.A. A history of research on yeast 1: Work by chemists and biologists, 1789–1850. Yeast 1998, 14, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, J.A. A history of research on yeast 2: Louis Pasteur and his contemporaries, 1850–1880. Yeast 2000, 16, 755–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, G.G.; Hill, A.E.; Russell, I. 125th anniversary review: Developments in brewing and distilling yeast strains. J. Inst. Brew. 2013, 119, 202–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikola, J.; Kolehmainen, L. Localization and activity of various peptidases in germinating barley. Planta 1972, 104, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shewry, P.R.; Halford, N.G. Cereal seed storage proteins: Structures, properties and role in grain utilization. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkes, B.F.; Yemm, E.W. The amino acid content of the proteins of barley grains. Biochem. J. 1956, 62, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agu, R.C. Some relationships between malted barleys of different nitrogen levels and the wort properties. J. Inst. Brew. 2003, 109, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.L.; Budde, A.D. How various malt endoproteinase classes affect wort soluble protein levels. J. Cereal Sci. 2005, 41, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, W.C.; Schroeder, R.L. Factors contributing to wort nitrogen. I. Contributions of malting and mashing, and effect of malting time. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 1976, 34, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agu, R.C.; Palmer, G.H. A reassessment of sorghum for lager-beer brewing. Bioresour. Technol. 1998, 66, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agu, R.C.; Palmer, G.H. The effect of temperature on the modification of sorghum and barley during malting. Process Biochem. 1997, 32, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajomo, M.F.; Young, T.W. Development of a mashing profile for the use of microbial enzymes in brewing with raw sorghum (80%) and malted barley or sorghum malt (20%). J. Inst. Brew. 1992, 98, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmaki, H.B.; Babiker, E.E.; El Tinay, A.H. Changes in chemical composition, grain malting, starch and tannin contents and protein digestibility during the germination of sorghum cultivars. Food Chem. 1999, 64, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owuama, C.I. Sorghum: A cereal with lager beer brewing potential. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1997, 13, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, G.H.; Etokakpan, O.U.; Igyor, M.A. Sorghum as brewing material. MIRCEN J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1989, 5, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkes, B.F.; Yemm, E.W. The respiration of barley plants. New Phytol. 1958, 57, 106–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.R. Effect of malting on the protein and free amino nitrogen composition of sorghum. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1983, 34, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.M.; Ingledew, W.M. Fuel alcohol production: Appraisal of nitrogenous yeast foods for very high gravity wheat mash fermentation. Process Biochem. 1994, 29, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J.; Kirsop, B.H. The relative contributions to wort nitrogen of nitrogenous substances solubilized during malting and mashing. J. Inst. Brew. 1971, 77, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.M.; Coverdale, S.M.; Cole, N.; Hamilton, S.E.; De Jersey, J.; Inkerman, P.A. Characterisation and assessment of the role of barley malt endoproteases during malting and mashing 1. J. Inst. Brew. 2002, 108, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekkas, C.; Hill, A.E.; Stewart, G.G. Extraction of FAN from malting barley during malting and mashing. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2014, 72, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Enari, T.M.; Mikola, J.; Linko, M. Restriction of proteolysis in mashing by using a mixture of barley and malt. J. Inst. Brew. 1964, 70, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamforth, C.W. Wort composition and beer quality. In Brewing Yeast Fermentation Performance, 2nd ed.; Smart, K., Ed.; Blackwell Scientific: Oxford, UK, 2001; pp. 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, I.M.; Guido, L.F. Impact of wort amino acids on beer flavour: A review. Fermentation 2018, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macwilliam, J.C.; Clapperton, J.F. Dynamic aspects of nitrogen metabolism in yeast. In Proceedings of the European Brewers Convention Congress, Interlaken; Elsevier: London, UK, 1969; pp. 271–279. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, M.; Pierce, J.S. Absorption of amino acids from wort by yeasts. J. Inst. Brew. 1964, 70, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, J.S. Horace Brown memorial lecture the role of nitrogen in brewing. J. Inst. Brew. 1987, 93, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekkas, C.; Stewart, G.G.; Hill, A.E.; Taidi, B.; Hodgson, J. Elucidation of the role of nitrogenous wort components in yeast fermentation. J. Inst. Brew. 2007, 113, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, G.G.; Hill, A.E.; Lekkas, C. Wort FAN—Its characteristics and importance during fermentation. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2013, 71, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regenberg, B.; During-Olsen, L.; Kielland-Brandt, M.C.; Holmberg, S. Substrate specificity and gene expression of the amino-acid permeases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr. Genet. 1999, 36, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magasanik, B.; Kaiser, C.A. Nitrogen regulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene 2002, 290, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, N.; Stahl, U. Amino acid permeases and their influence on flavour compounds in beer. Brew. Sci. 2014, 67, 120–127. [Google Scholar]
- Dharmadhikari, M. Nitrogen metabolism during fermentation. Vineyard Vintage View 2001, 17, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Garrett, J.M. Amino acid transport through the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Gap1 permease is controlled by the Ras/cAMP pathway. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, G.G.; Lekkas, C.; Hill, A.E.; Taidi, B.; Hodgson, J. Wort oligopeptides: Their formation and utilisation during fermentation. Proc. Inst. Brew. Dist. Con. (Afr. Sect.) 2005, 10, 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Boulton, C.A. Developments in brewery fermentation. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 1991, 9, 127–181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nisbet, T.M.; Payne, J.W. Peptide uptake in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Characteristics of transport system. Microbiology 1979, 115, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Lekkas, C.; Hill, A.E.; Taidi, B.; Hodgson, J.; Stewart, G.G. The role of small wort peptides in brewing fermentations. J. Inst. Brew. 2009, 115, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, G.G.; Russell, I.; Anstruther, A. Handbook of Brewing, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 591–602. [Google Scholar]
- Butzke, C.E. Survey of yeast assimilable nitrogen status in musts from California, Oregon, and Washington. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1998, 49, 220–224. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, G.G.; Russell, I. An Introduction to Brewing Science & Technology: Brewer’s Yeast, 2nd ed.; Institute of Brewing: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pickerall, A.T.W. The influence of free alpha-amino nitrogen in sorghum beer fermentations. J. Inst. Brew. 1986, 92, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bely, M.; Rinaldi, A.; Dubourdieu, D. Influence of assimilable nitrogen on volatile acidity production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae during high sugar fermentation. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2003, 96, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrau, F.M.; Medina, K.; Farina, L.; Boido, E.; Henschke, P.A.; Dellacassa, E. Production of fermentation aroma compounds by Saccharomyces cerevisiae wine yeasts: Effects of yeast assimilable nitrogen on two model strains. FEMS Yeast Res. 2008, 8, 1196–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrau, F.; Medina, K.; Fariña, L.; Boido, E.; Dellacassa, E. Effect of Saccharomyces cerevisiae inoculum size on wine fermentation aroma compounds and its relation with assimilable nitrogen content. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 143, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilanova, M.; Ugliano, M.; Varela, C.; Siebert, T.; Pretorius, I.S.; Henschke, P.A. Assimilable nitrogen utilisation and production of volatile and non-volatile compounds in chemically defined medium by Saccharomyces cerevisiae wine yeasts. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 77, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazelwood, L.A.; Daran, J.M.; van Maris, A.J.; Pronk, J.T.; Dickinson, J.R. The Ehrlich pathway for fusel alcohol production: A century of research on Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2259–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, P.L. Kjeldahl method for total nitrogen. Anal. Chem. 1950, 22, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebeling, M.E. The Dumas method for nitrogen in feeds. J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. 1968, 51, 766–770. [Google Scholar]
- Analytica-EBC, Method Collection from European Brewery Convention, Free Amino Nitrogen in Beer by Spectrophotometry. Verlag Hans Carl Getranke-Fachverlag: Nürnberg, Germany (IM) 9.10, 2000.
- ASBC Methods of Analysis, American Society of Brewing Chemists, Free Amino Nitrogen Wort-12, 2009.
- ASBC Methods of Analysis, American Society of Brewing Chemists, Free Amino Nitrogen Beer-31, 2009.
- Lie, S. The EBC-ninhydrin method for determination of free alpha amino nitrogen. J. Inst. Brew. 1973, 79, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, H. A modified ninhydrin colorimetric analysis for amino acids. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1957, 67, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abernathy, D.; Spedding, G.; Starcher, B. Analysis of protein and total usable nitrogen in beer and wine using a Microwell Ninhydrin Assay. J. Inst. Brew. 2009, 115, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, M.R.; Budde, A.D. Wort free amino nitrogen analysis adapted to a microplate format. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2012, 70, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A new way to test the free amino nitrogen content in alcoholic beverages with the SPECTROstar® Nano. Available online: https://www.bmglabtech.com/fileadmin/06_Support/Download_Documents/Application_Notes/AN226.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2018).
- Mackey, L.N.; Beck, T.A. Quantitative high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of sulfur amino acids in protein hydrolysates. J. Chromatogr. 1982, 240, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, M. Fluorescence reaction for amino acids. Anal. Chem. 1971, 43, 880–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedmeier, V.T.; Porterfield, S.P.; Hendrich, C.E. Quantitation of DNS-amino acids from body tissues and fluids using high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. 1982, 231, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correlation of the Free Amino Nitrogen and Nitrogen by O-Phthaldialdehyde Methods in the Assay of Beer. Available online: https://tools.thermofisher.com/content/sfs/brochures/AN-71798-DA-FAN-Nitrogen-Beer-AN71798-EN.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2018).
| Group A | Group B | Group C | Group D |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fast absorption | Intermediate absorption | Slow absorption | Little or no absorption |
| Glutamate | |||
| Aspartate | Glycine | ||
| Asparagine | Valine | Phenylalanine | |
| Glutamine | Methionine | Tyrosine | |
| Serine | Leucine | Tryptophan | Proline |
| Threonine | Isoleucine | Alanine | |
| Lysine | Histidine | Ammonia | |
| Arginine |
| Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Glutamate | ||
| Aspartate | Valine | |
| Asparagine | Isoleucine | Leucine |
| Serine | Phenylalanine | Histidine |
| Threonine | Glycine | Lysine |
| Methionine | Tyrosine | Arginine |
| Proline |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hill, A.E.; Stewart, G.G. Free Amino Nitrogen in Brewing. Fermentation 2019, 5, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation5010022
Hill AE, Stewart GG. Free Amino Nitrogen in Brewing. Fermentation. 2019; 5(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation5010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleHill, Annie E., and Graham G. Stewart. 2019. "Free Amino Nitrogen in Brewing" Fermentation 5, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation5010022
APA StyleHill, A. E., & Stewart, G. G. (2019). Free Amino Nitrogen in Brewing. Fermentation, 5(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation5010022






