Combination Strategy of Bioenzymes and Sophorolipid Pretreatments Enhance Volatile Fatty Acid Production Based on Co-Fermentation of Waste Activated Sludge and Rubberwood Hydrolysates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sludge Source and Rubber Wood Characteristics
2.2. Rubberwood Feedstock Hydrolysis-Enzymatic Hydrolysis
2.3. Anaerobic Fermentation
2.4. Detection Methods
2.5. Analysis of the Sludge Organic Composition
2.6. Microbial Community Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
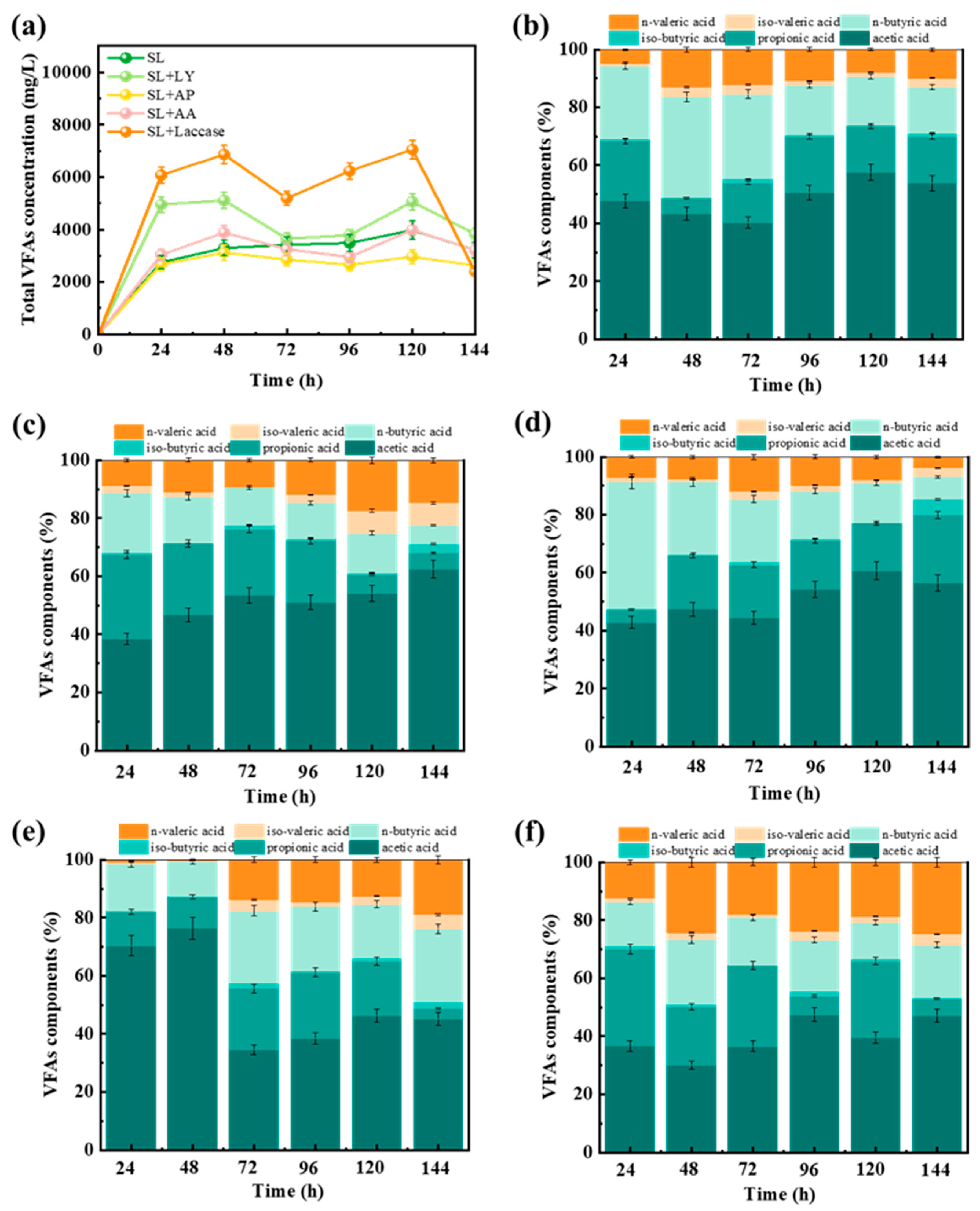
3.1. Impact of Pretreatment Methods on VFA Generation
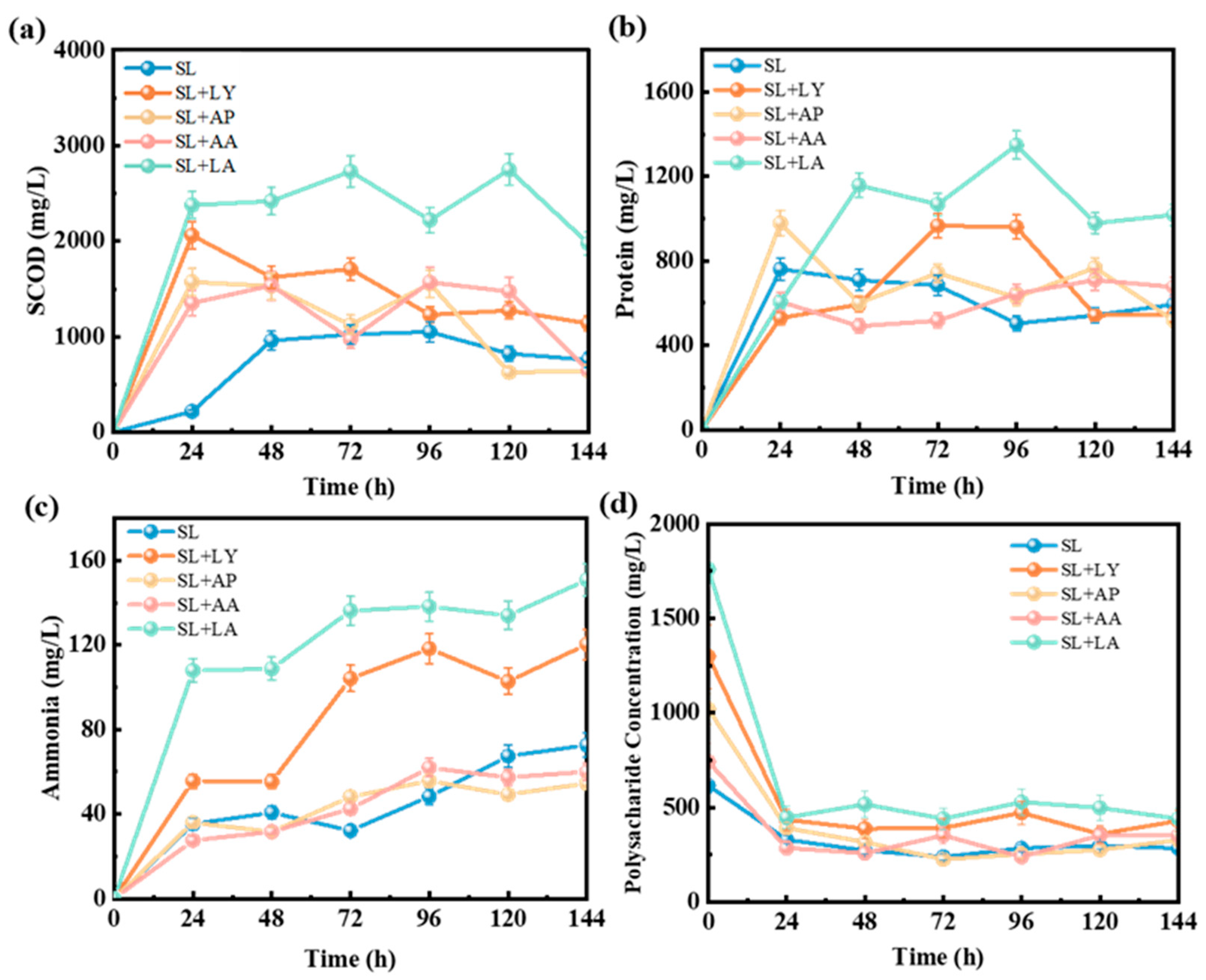
3.2. Enhancement of Bioavailable Substrates Facilitated by Various Pretreatment Methods
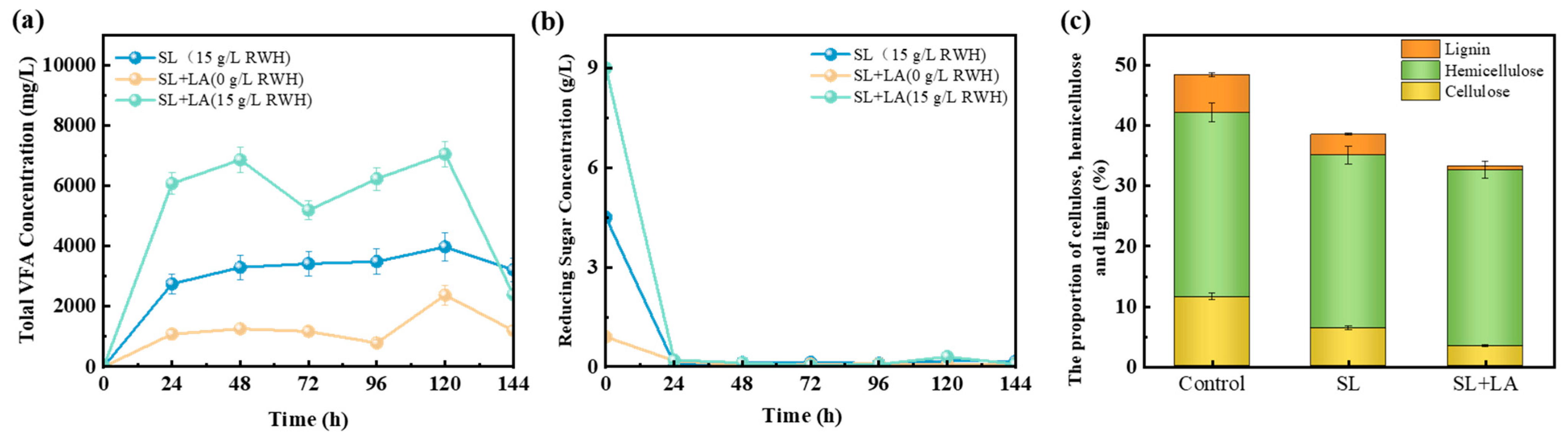
3.3. The Conversion of Rubberwood Hydrolysates into VFAs
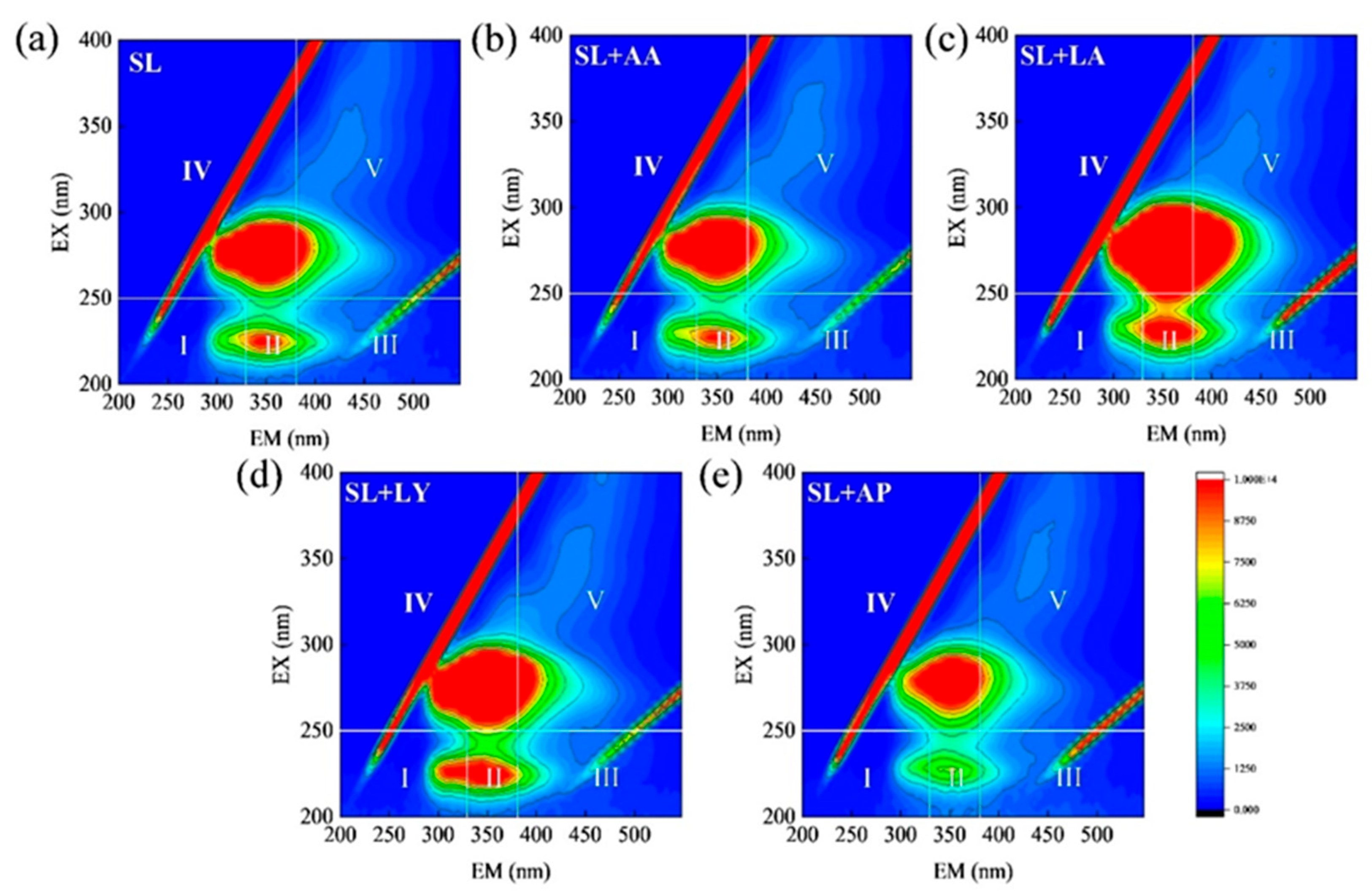
3.4. Organic Matter Compositions in Fermented Liquids Across Various Pretreatment Groups
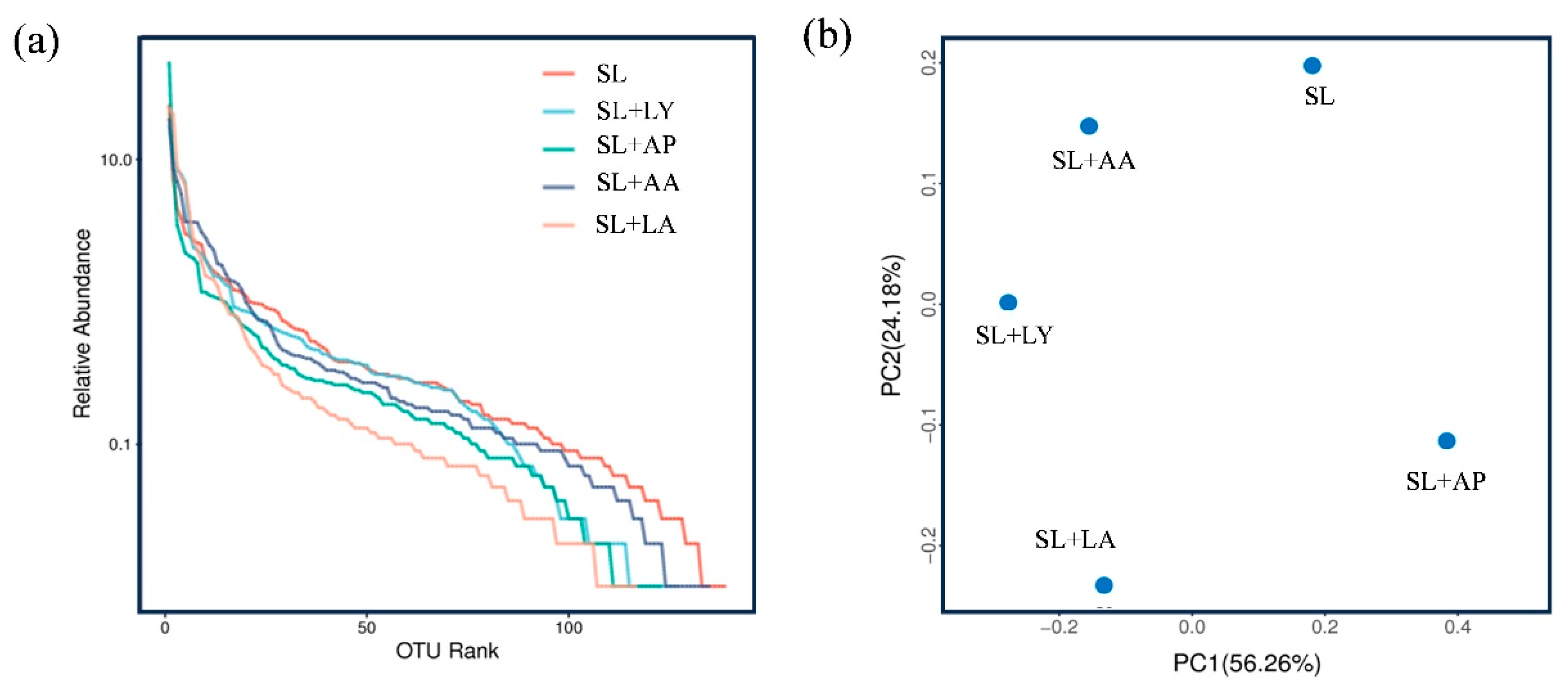
3.5. Impact of Pretreatment Techniques on Microbial Communities During Anaerobic Fermentation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Yang, G.; Yuan, X.; Xu, Q.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ni, B.-J.; Tang, W.; et al. Enhanced Dewaterability of Anaerobically Digested Sludge by In-Situ Free Nitrous Acid Treatment. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, X.; Li, S.; Lv, Q.; Liang, C. Removal of Heavy Metals from Sewage Sludge by Chemical Leaching with Biodegradable Chelator Methyl Glycine Diacetic Acid. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ma, X.; Li, J.; Sun, B. Insights into Enhanced Polyhydroxyalkanoate Production by the Synergistic Use of Waste Wood Hydrolysate and Volatile Fatty Acids by Mixed Microbial Cultures. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 337, 125488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.-W.; Zou, Z.-S.; Sun, Q.; Jin, H.-Y.; Yao, X.-Y.; Yang, W.-J.; Tang, C.-C.; Zhou, A.-J.; Liu, W.; Ren, Y.-X.; et al. Freezing-Low Temperature Treatment Facilitates Short-Chain Fatty Acids Production from Waste Activated Sludge with Short-Term Fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, X.; Li, X. A Membrane Bioreactor with Iron Dosing and Acidogenic Co-Fermentation for Enhanced Phosphorus Removal and Recovery in Wastewater Treatment. Water Res. 2018, 129, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Ren, N.; Ho, S.-H. Optimizing the Production of Short and Medium Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs and MCFAs) from Waste Activated Sludge Using Different Alkyl Polyglucose Surfactants, through Bacterial Metabolic Analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.; Zhang, L.; Jia, B.; Yang, B.; Luo, Z.; Yang, J.; Boguta, P.; Su, X. Effects of Enzymes on Organic Matter Conversion in Anaerobic Fermentation of Sludge to Produce Volatile Fatty Acids. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 366, 128227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wei, W.; Chen, X.; Mannina, G.; Ni, B.-J. A Novel Strategy for Efficiently Transforming Waste Activated Sludge into Medium-Chain Fatty Acid Using Free Nitrous Acid. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 862, 160826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-X.; Zhao, S.; Guo, Z.-C.; Liu, W.-Z.; Wang, L.; Yu, S.-P.; Liu, B.-L.; Cong, X. Alkaline Aided Thermophiles Pretreatment of Waste Activated Sludge to Increase Short Chain Fatty Acids Production: Microbial Community Evolution by Alkaline on Hydrolysis and Fermentation. Environ. Res. 2020, 186, 109503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.-Y.; Park, B.-S.; Lee, J.; Oh, M.-K. Engineered Enterobacter Aerogenes for Efficient Utilization of Sugarcane Molasses in 2,3-butanediol Production. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 139, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Cheng, J.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Li, K.; Wei, L. Adaptive Evolution-Assisted Riboflavin Production of Ashbya Gossypii from Cane Molasses. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 5132198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, T.; Chaiprapat, S.; Charnnok, B. Enhanced Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Methane Production from Rubber Wood Waste Using Steam Explosion. J. Environ. Manage. 2019, 235, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inkrod, C.; Raita, M.; Champreda, V.; Laosiripojana, N. Characteristics of Lignin Extracted from Different Lignocellulosic Materials via Organosolv Fractionation. Bioenergy Res. 2018, 11, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Wu, B.; Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Wu, W.; Zhuang, J.; Li, H.; Huang, T. Enhanced VFAs Production from Microalgal Hydrolytic Acidification with Ultrasonic-Alkali Pretreatment. Algal Res. 2023, 71, 103056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, C.; Liu, H.; Gao, R.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Bi, X.; Pang, H. Synergistic Enhancement of Volatile Fatty Acid Production from Waste Activated Sludge by Citric Acid Assisted Potassium Ferrate Co-Pretreatment: Crucial Role of Citric Acid. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 516, 164205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, P. Enhanced Volatile Fatty Acid Production from Anaerobic Fermentation of Waste Activated Sludge by Combined Sodium Citrate and Heat Pretreatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, P.; Jia, Y. Optimization of Dissolution and Fermentation Acid Production of Rhamnolipid-Alkali-Heat Synergistic Pretreatment of Sludge. Chemosphere 2022, 306, 135607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Dou, C. Enhancing Organic Matter Dissolution and Microbial Community Structure in Waste Activated Sludge Using Thermal-Alkali-Rhamnolipid Pretreatment: Focus on Thermal Optimization. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 320, 100848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Fang, S.; Huang, W.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Fang, F.; Cao, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, D. New Insights into Different Surfactants’ Impacts on Sludge Fermentation: Focusing on the Particular Metabolic Processes and Microbial Genetic Traits. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2021, 16, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ni, B.-J.; Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Li, H. Enhanced Short-Chain Fatty Acids Production from Waste Activated Sludge by Sophorolipid: Performance, Mechanism, and Implication. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 284, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, K.; Li, X.; Ma, L.; Ma, X.; Chen, H. Enhancement of Excess Sludge Hydrolysis and Decomposition with Different Lysozyme Dosage. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlin Christy, P.; Gopinath, L.R.; Divya, D. A Review on Anaerobic Decomposition and Enhancement of Biogas Production through Enzymes and Microorganisms. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 34, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federation, W.E.; Association, A. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2005; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for Dietary Fiber, Neutral Detergent Fiber, and Nonstarch Polysaccharides in Relation to Animal Nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, W.; Yin, F.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Zheng, Y. Strategy for sophorolipid pretreatment to enhance the production of volatile fatty acids from rubberwood hydrolysates during anaerobic fermentation of sludge. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2025, 229, 121029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wu, Q.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, A.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Xue, G.; Chen, H.; Gao, P. Activation of Peroxymonosulfate by Sewage Sludge-Derived Biochar to Promote Short-Chain Fatty Acid Production during Sludge Anaerobic Fermentation. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 148041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xie, H.; Liu, G.; Zhang, R.; Ma, X.; Chen, H. Optimizing Temperature for Enhancing Waste Activated Sludge Decomposition in Lysozyme and Rhamnolipid Pretreatment System. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 341, 125868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.-Q.; Zheng, X.-J.; Hu, Z.-H.; Gu, G.-W. High-Rate Anaerobic Hydrolysis and Acidogenesis of Sewage Sludge in a Modified Upflow Reactor. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.S.; Xu, Y.F. Review of Enzymatic Sludge Hydrolysis. J. Biorem. Biodegrad. 2010, 2, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chang, S. Impact of Temperatures on Microbial Community Structures of Sewage Sludge Biological Hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Dai, X.; Chai, X. Critical Review on Dewatering of Sewage Sludge: Influential Mechanism, Conditioning Technologies and Implications to Sludge Re-Utilizations. Water Res. 2020, 180, 115912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, W.; Chen, Y.; Lv, D.; Yan, Y.; Zheng, X.; Shi, X.; Xu, Z.; Guan, W.; Wu, J.; Guan, Y. Metal-Organic Framework Based Nanozyme Hybrid for Synergistic Bacterial Eradication by Lysozyme and Light-Triggered Carvacrol Release. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 134003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, X.; Ma, X.; Ma, L.; Chen, H. Hydrolysis and Decomposition of Waste Activated Sludge with Combined Lysozyme and Rhamnolipid Treatment: Effect of pH. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 293, 122074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Abbt-Braun, G.; Horn, H. Changes in the Characteristics of Dissolved Organic Matter during Sludge Treatment: A Critical Review. Water Res. 2020, 187, 116441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, T.; Elmaadawy, K.; Liu, B.; Hu, J.; Hou, H.; Yang, J. Anaerobic Fermentation of Waste Activated Sludge for Volatile Fatty Acid Production: Recent Updates of Pretreatment Methods and the Potential Effect of Humic and Nutrients Substances. Process Saf. Environ. 2021, 145, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lu, Q.; Du, M.; Xu, Q.; Wang, D. Hormesis-Like Effects of Tetrabromobisphenol A on Anaerobic Digestion: Responses of Metabolic Activity and Microbial Community. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 11277–11287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Pretreatment Methods | Pretreatment Conditions | VFA Yield | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ultrasonic-alkali | 6 W/mL, 120 min | 392.5 mg COD/g VSS | [14] |
| Citric acid-potassium ferrate | 35 °C, 60 min | 4751.6 mg COD/L | [15] |
| Sodium citrate-heat | 120 °C, 30 min | 354.5 mg COD/g VS | [16] |
| Rhamnolipid-alkali | 70 °C, 60 min | 1584.89 mg/L | [17] |
| Rhamnolipid-alkali | 90 °C, 60 min | 1500 mg/L | [18] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, F.; Bie, W.; Ma, X.; Li, J.; Zheng, Y.; Li, D. Combination Strategy of Bioenzymes and Sophorolipid Pretreatments Enhance Volatile Fatty Acid Production Based on Co-Fermentation of Waste Activated Sludge and Rubberwood Hydrolysates. Fermentation 2025, 11, 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080486
Yin F, Bie W, Ma X, Li J, Zheng Y, Li D. Combination Strategy of Bioenzymes and Sophorolipid Pretreatments Enhance Volatile Fatty Acid Production Based on Co-Fermentation of Waste Activated Sludge and Rubberwood Hydrolysates. Fermentation. 2025; 11(8):486. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080486
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Fen, Wenxuan Bie, Xiaojun Ma, Jianing Li, Yingying Zheng, and Dongna Li. 2025. "Combination Strategy of Bioenzymes and Sophorolipid Pretreatments Enhance Volatile Fatty Acid Production Based on Co-Fermentation of Waste Activated Sludge and Rubberwood Hydrolysates" Fermentation 11, no. 8: 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080486
APA StyleYin, F., Bie, W., Ma, X., Li, J., Zheng, Y., & Li, D. (2025). Combination Strategy of Bioenzymes and Sophorolipid Pretreatments Enhance Volatile Fatty Acid Production Based on Co-Fermentation of Waste Activated Sludge and Rubberwood Hydrolysates. Fermentation, 11(8), 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080486







