A Comparative Proteomic Analysis of the Acetification Process of Komagataeibacter europaeus Using Different Substrates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Starter Inoculum
2.3. Fermentation Conditions
2.4. Sampling
2.5. Analytical Methods
2.6. Proteomics
2.6.1. Cellular Collection and Protein Extraction
2.6.2. LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.6.3. Data Analysis
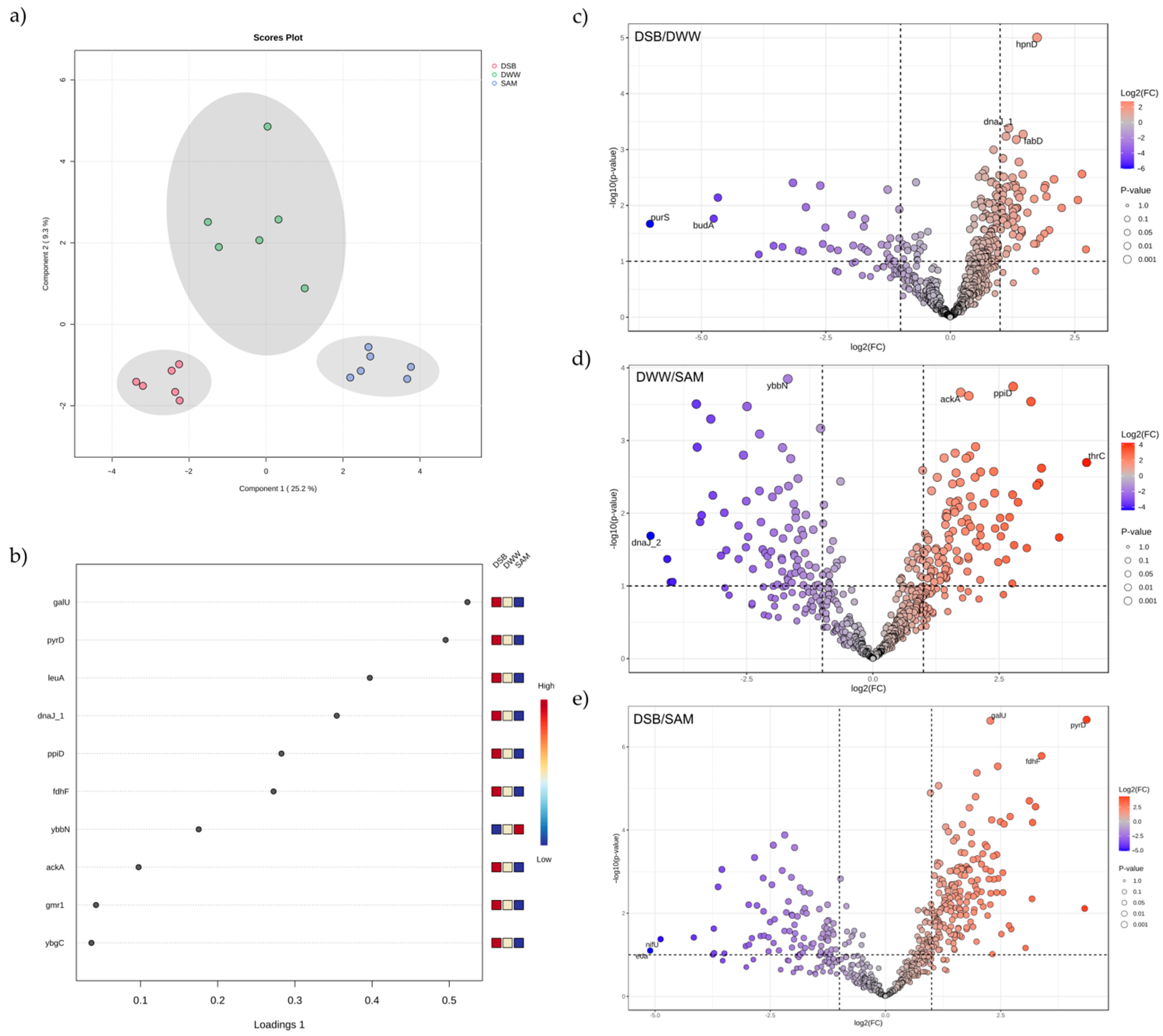
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Description of Acetification Profiles
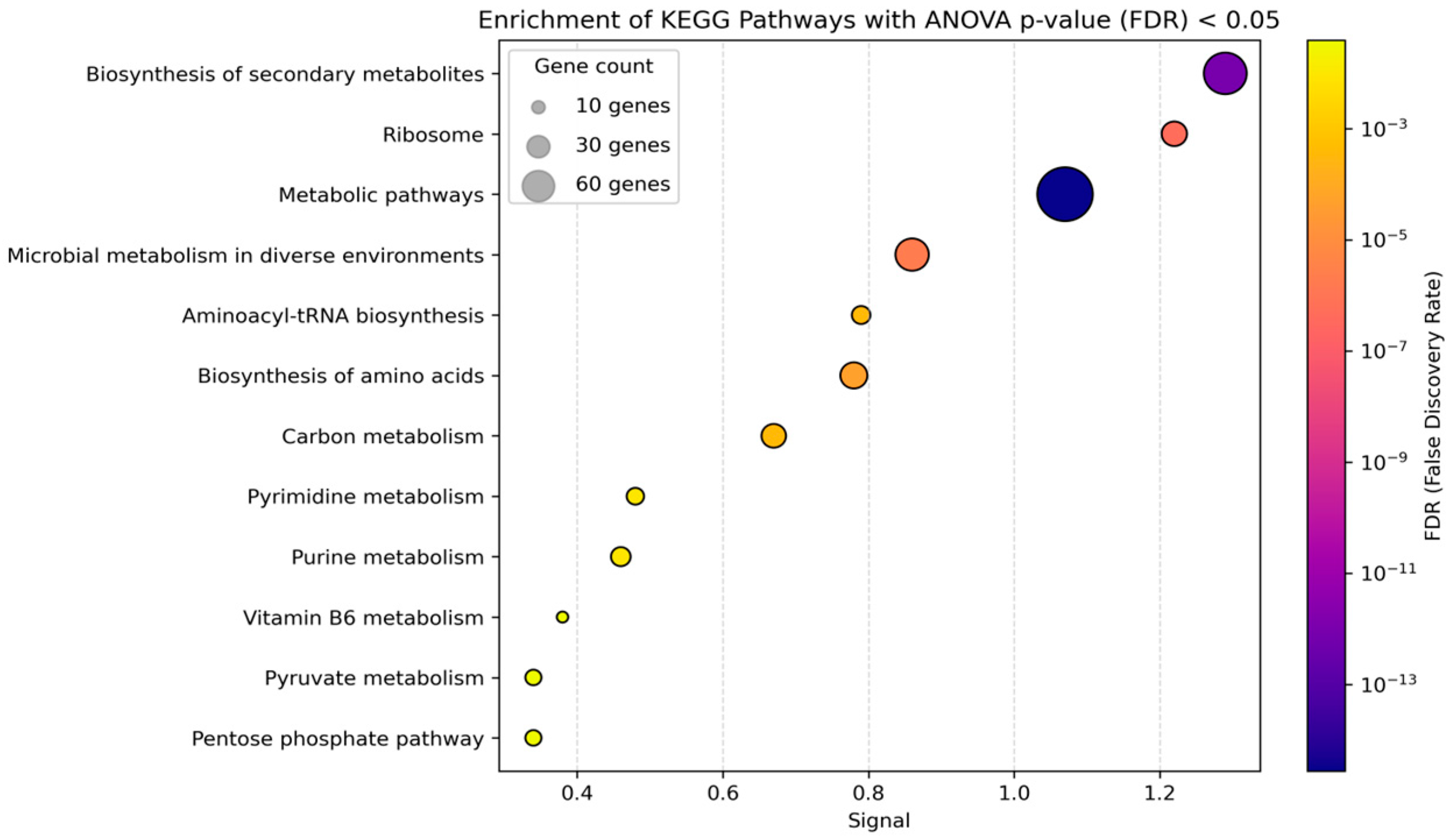
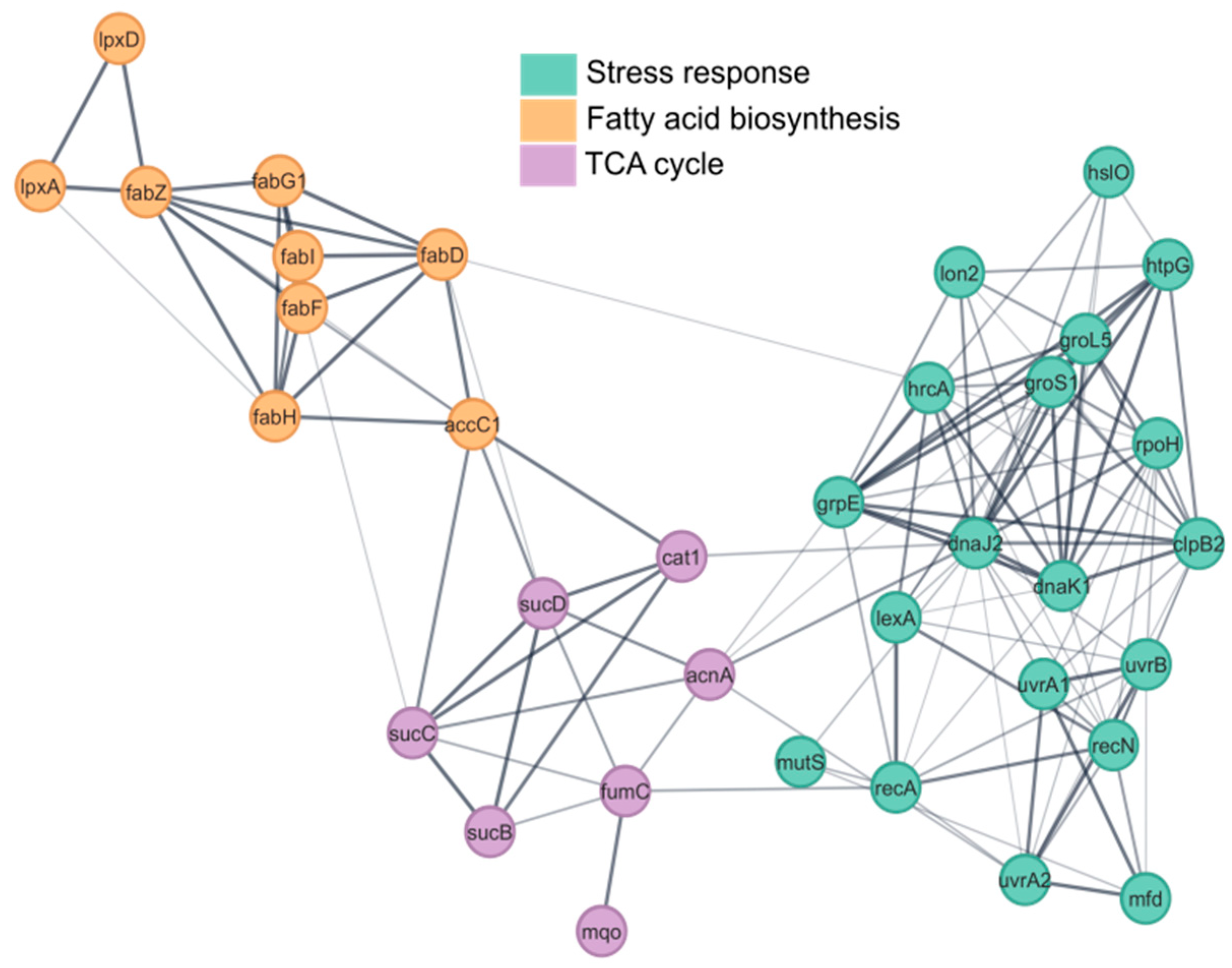
3.2. Functional Enrichment Analysis
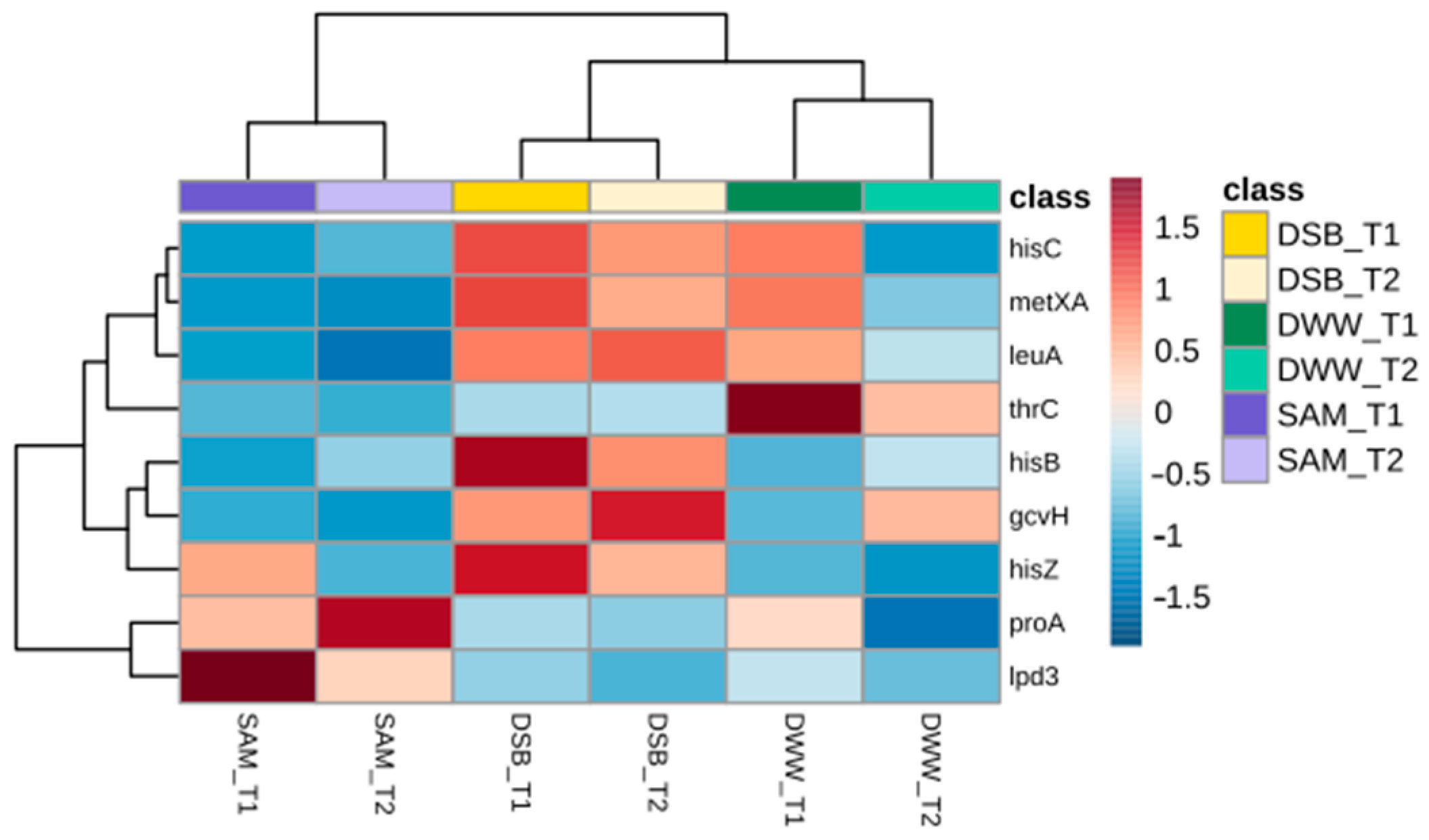
3.3. Proteomic Profile Involved in Amino Acid Biosynthesis
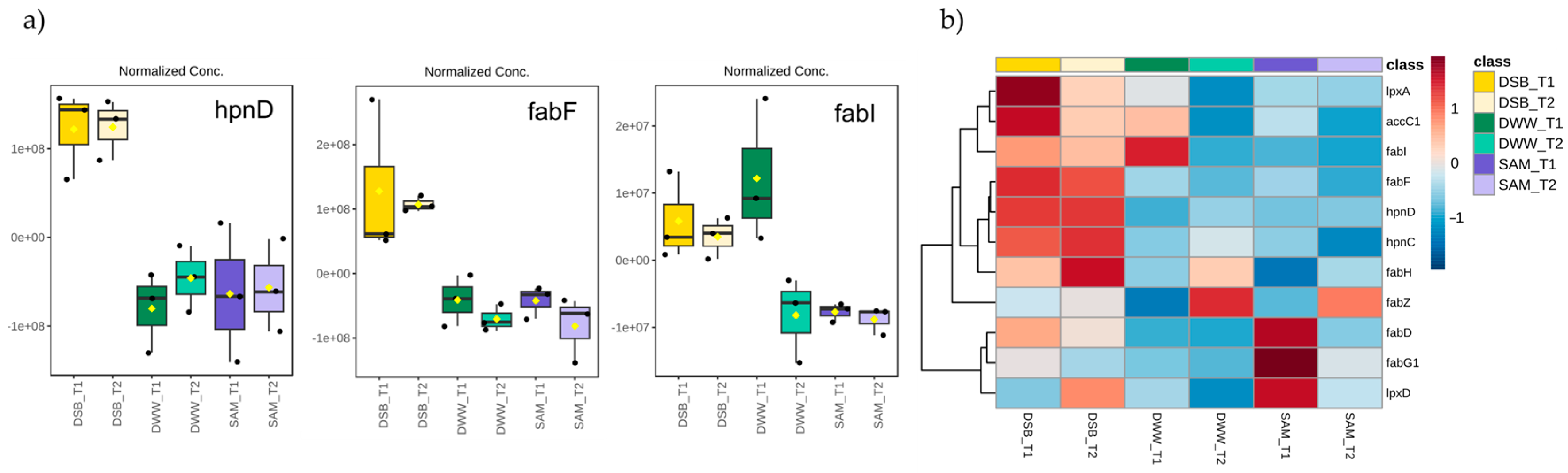
3.4. Proteomic Profile Related to Lipid and Fatty Acid Biosynthesis
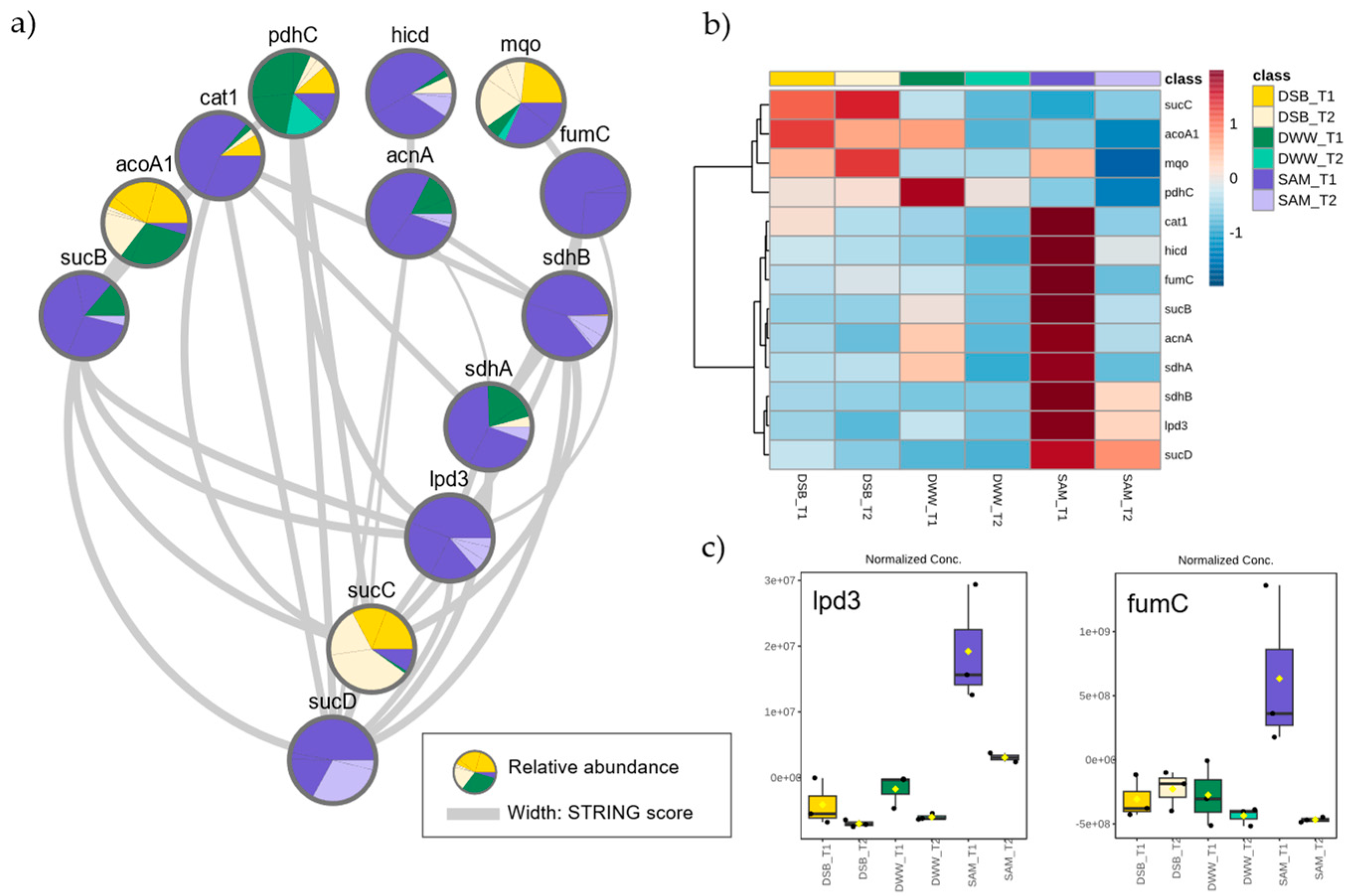
3.5. Proteins Related to Acetic Acid Metabolism
3.6. Stress-Related Proteins
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAB | Acetic Acid Bacteria |
| PDO | Protected Designation of Origin |
| VBNC | Viable But Non-Culturable |
| PQQ-ADH | Pyrroloquinoline Quinone-Dependent Alcohol Dehydrogenase |
| PQQ-ALDH | Pyrroloquinoline Quinone-Dependent Aldehyde Dehydrogenase |
| NAD-ADH | Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide-Dependent Alcohol Dehydrogenase |
| NAD(P)-ALDH | NAD or NADP-Dependent Aldehyde Dehydrogenase |
| TCA | Tricarboxylic Acid (Cycle) |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| SAM | Synthetic Alcohol Medium |
| DWW | Dry White Wine |
| DSB | Dark Sugary Beer |
| UHPLC | Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| MS/MS | Tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| PSM | Peptide Spectral Match |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| TSN | Total Sum Normalization |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| MDA | Mean Decrease Accuracy |
| sPLS-DA | Sparse Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis |
| PPI | Protein–Protein Interaction |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
References
- Ali, Z.; Wang, Z.; Amir, R.M.; Younas, S.; Wali, A.; Adowa, N.; Ayim, I. Potential Uses of Vinegar as a Medicine and Related in Vivo Mechanisms. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2016, 86, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengun, I.Y.; Kilic, G.; Charoenyingcharoen, P.; Yukphan, P.; Yamada, Y. Investigation of the Microbiota Associated with Traditionally Produced Fruit Vinegars with Focus on Acetic Acid Bacteria and Lactic Acid Bacteria. Food Biosci. 2022, 47, 101636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvanathan, Y.; Masngut, N. Optimization of Process Factor and Characterization of Vinegar-like Beverage Production via Spontaneous Fermentation from Pineapple Peel Waste. LWT 2023, 182, 114818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, A.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liang, K.; Román-Camacho, J.-J.; Zhou, J.; Song, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, M. Identification of Aroma Active Compounds in Shanxi Aged Vinegar and Tracing the Source in the Entire Production Process. Food Chem. X 2024, 24, 101918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Reina, R.; Segura-Borrego, M.P.; Morales, M.L.; Callejón, R.M. Characterization of the Aroma Profile and Key Odorants of the Spanish PDO Wine Vinegars. Food Chem. 2020, 311, 126012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cejudo-Bastante, C.; Durán-Guerrero, E.; García-Barroso, C.; Castro-Mejías, R. Comparative Study of Submerged and Surface Culture Acetification Process for Orange Vinegar. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzón-Quintana, L.M.; Castro, R.; Durán-Guerrero, E. Biotechnological Processes in Fruit Vinegar Production. Foods 2021, 10, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullo, M.; Verzelloni, E.; Canonico, M. Aerobic Submerged Fermentation by Acetic Acid Bacteria for Vinegar Production: Process and Biotechnological Aspects. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román-Camacho, J.J.; Santos-Dueñas, I.M.; García-García, I.; Moreno-García, J.; García-Martínez, T.; Mauricio, J.C. Metaproteomics of Microbiota Involved in Submerged Culture Production of Alcohol Wine Vinegar: A First Approach. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 333, 108797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Yang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Chen, K.; Dai, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Wang, K.; Liu, P.; et al. Metagenomics Profiling of the Microbial Community and Functional Differences in Solid-State Fermentation Vinegar Starter (Seed Pei) from Different Chinese Regions. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1389737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, W.; Liu, J.; Li, P.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, A.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J. Dynamics of Microbial Communities, Flavor, and Physicochemical Properties during Ziziphus jujube Vinegar Fermentation: Correlation between Microorganisms and Metabolites. Foods 2022, 11, 3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, H. Classification of Acetic Acid Bacteria and Their Acid Resistant Mechanism. AMB Express 2021, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.-Y.; Zhang, X.-J.; Huang, T.; Zhong, X.-Z.; Chai, L.-J.; Lu, Z.-M.; Shi, J.-S.; Xu, Z.-H. Komagataeibacter europaeus Improves Community Stability and Function in Solid-State Cereal Vinegar Fermentation Ecosystem: Non-Abundant Species Plays Important Role. Food Res. Int. 2021, 150, 110815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hong, H.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Z.; Guo, H. Transcriptome Analysis of Komagataeibacter europaeus CGMCC 20445 Responses to Different Acidity Levels During Acetic Acid Fermentation. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2021, 70, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román-Camacho, J.J.; Mauricio, J.C.; Santos-Dueñas, I.M.; García-Martínez, T.; García-García, I. Unraveling the Role of Acetic Acid Bacteria Comparing Two Acetification Profiles from Natural Raw Materials: A Quantitative Approach in Komagataeibacter europaeus. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 840119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés-Barrao, C.; Saad, M.M.; Cabello Ferrete, E.; Bravo, D.; Chappuis, M.-L.; Ortega Pérez, R.; Junier, P.; Perret, X.; Barja, F. Metaproteomics and Ultrastructure Characterization of Komagataeibacter spp. Involved in High-Acid Spirit Vinegar Production. Food Microbiol. 2016, 55, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liebl, W.; Toyama, H.; Chen, F. Oxidative Fermentation of Acetic Acid Bacteria and Its Products. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 879246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, C.; Dong, L.; Huan, Y.; Yoshimoto, M.; Zhu, Y.; Tada, I.; Wang, X.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, F.; et al. Comprehensive Metabolomic Comparison of Five Cereal Vinegars Using Non-Targeted and Chemical Isotope Labeling LC-MS Analysis. Metabolites 2022, 12, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Gu, C.; Guo, X.; Guo, R.; Zhu, L.; Qiu, X.; Chai, J.; Liu, F.; Feng, Z. Dynamic Changes of Microbiota and Metabolite of Traditional Hainan Dregs Vinegar during Fermentation Based on Metagenomics and Metabolomics. Food Chem. 2024, 444, 138641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Tang, J.; Yang, Q.; Su, Z.; Zhu, L.; Li, Q.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S. Microbial Succession and Its Effect on Key Aroma Components during Light-Aroma-Type Xiaoqu Baijiu Brewing Process. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, P.; Frey, L.J.; Berger, A.; Bolten, C.J.; Hansen, C.E.; Wittmann, C. The Key to Acetate: Metabolic Fluxes of Acetic Acid Bacteria under Cocoa Pulp Fermentation-Simulating Conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 4702–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Román-Camacho, J.; Mauricio, J.; Sánchez-León, I.; Santos-Dueñas, I.; Fuentes-Almagro, C.; Amil-Ruiz, F.; García-Martínez, T.; García-García, I. Implementation of a Novel Method for Processing Proteins from Acetic Acid Bacteria via Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2024, 29, 2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Vinagre de Vino; Llaguno Marchena, C., Polo, M.C., Eds.; Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas: Madrid, Spain, 1991; ISBN 978-84-00-07205-6. [Google Scholar]
- Román-Camacho, J.J.; Santos-Dueñas, I.M.; García-García, I.; García-Martínez, T.; Peinado, R.A.; Mauricio, J.C. Correlating Microbial Dynamics with Key Metabolomic Profiles in Three Submerged Culture-Produced Vinegars. Foods 2025, 14, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román-Camacho, J.J.; Mauricio, J.C.; Santos-Dueñas, I.M.; García-Martínez, T.; García-García, I. Recent Advances in Applying Omic Technologies for Studying Acetic Acid Bacteria in Industrial Vinegar Production: A Comprehensive Review. Biotechnol. J. 2024, 19, 2300566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devanthéry, T.; Nakamura, K.; Hashiguchi, S.; Hashimoto, M. Structure of a Heptose-Containing Polysaccharide Derived from Komagataeibacter Europaeus NBRC 3261. Carbohydr. Res. 2020, 492, 107989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trček, J.; Mira, N.P.; Jarboe, L.R. Adaptation and Tolerance of Bacteria against Acetic Acid. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 6215–6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, S.; Ebisuya, H. Physiology of Acetobacter and Komagataeibacter spp.: Acetic Acid Resistance Mechanism in Acetic Acid Fermentation. In Acetic Acid Bacteria; Matsushita, K., Toyama, H., Tonouchi, N., Okamoto-Kainuma, A., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2016; pp. 223–234. ISBN 978-4-431-55931-3. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto-Kainuma, A.; Ishikawa, M. Physiology of Acetobacter spp.: Involvement of Molecular Chaperones During Acetic Acid Fermentation. In Acetic Acid Bacteria; Matsushita, K., Toyama, H., Tonouchi, N., Okamoto-Kainuma, A., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2016; pp. 179–199. ISBN 978-4-431-55931-3. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Guo, L.; Zhao, N.; Meng, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Wei, X.; Fan, M. Response Mechanisms to Acid Stress of Acid-Resistant Bacteria and Biotechnological Applications in the Food Industry. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2023, 43, 258–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Zhang, R.; Xia, M.; Bai, X.; Mou, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, M. Effect of Aspartic Acid and Glutamate on Metabolism and Acid Stress Resistance of Acetobacter pasteurianus. Microb. Cell Fact. 2017, 16, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankuan, X.; Cuimei, Z.; Bingqian, F.; Yu, Z.; Menglei, X.; Linna, T.; Jia, S.; Xinyi, Z.; Min, W. Metabolic Network of Ammonium in Cereal Vinegar Solid-State Fermentation and Its Response to Acid Stress. Food Microbiol. 2021, 95, 103684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Han, C.; Xu, J.; Liang, X. Transcriptome Response of Acetobacter pasteurianus Ab3 to High Acetic Acid Stress during Vinegar Production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 10585–10599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yan, P.; Lei, Q.; Li, B.; Sun, Y.; Li, S.; Lei, H.; Xie, N. Metabolic Adaptability Shifts of Cell Membrane Fatty Acids of Komagataeibacter hansenii HDM1-3 Improve Acid Stress Resistance and Survival in Acidic Environments. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 46, 1491–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriherfyna, F.H.; Matsutani, M.; Hirano, K.; Koike, H.; Kataoka, N.; Yamashita, T.; Nakamaru-Ogiso, E.; Matsushita, K.; Yakushi, T. The Auxiliary NADH Dehydrogenase Plays a Crucial Role in Redox Homeostasis of Nicotinamide Cofactors in the Absence of the Periplasmic Oxidation System in Gluconobacter oxydans NBRC3293. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e02155-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, H.; Hu, T.; Feng, Z.; Lei, Z.; Li, W.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, M. Improving the Acetic Acid Fermentation of Acetobacter pasteurianus by Enhancing the Energy Metabolism. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 815614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yassunaka Hata, N.N.; Surek, M.; Sartori, D.; Vassoler Serrato, R.; Aparecida Spinosa, W. Role of Acetic Acid Bacteria in Food and Beverages. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2023, 61, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Yin, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, M. Expression of Gene uvrA from Acetobacter pasteurianus and Its Tolerance to Acetic Acid in Escherichia coli. In Advanced Applications in Biotechnolog; Zhang, T.-C., Nakajima, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2015; pp. 163–169. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Rutherfurd-Markwick, K.; Zhang, X.-X.; Mutukumira, A.N. Isolation and Characterisation of Dominant Acetic Acid Bacteria and Yeast Isolated from Kombucha Samples at Point of Sale in New Zealand. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-González, J.J.; Amil-Ruiz, F.; Zazzu, S.; Sánchez-Lucas, R.; Fuentes-Almagro, C.A.; Rodríguez-Ortega, M.J. Proteomic Analysis of Goat Milk Kefir: Profiling the Fermentation-Time Dependent Protein Digestion and Identification of Potential Peptides with Biological Activity. Food Chem. 2019, 295, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, N.; Petersen, K.; Vollstedt, C.; Garcia, P.P.; Chow, J.; Ferrer, M.; Fernandez-Lopez, L.; Falke, S.; Perbandt, M.; Hinrichs, W.; et al. The Komagataeibacter europaeus GqqA Is the Prototype of a Novel Bifunctional N-Acyl-Homoserine Lactone Acylase with Prephenate Dehydratase Activity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
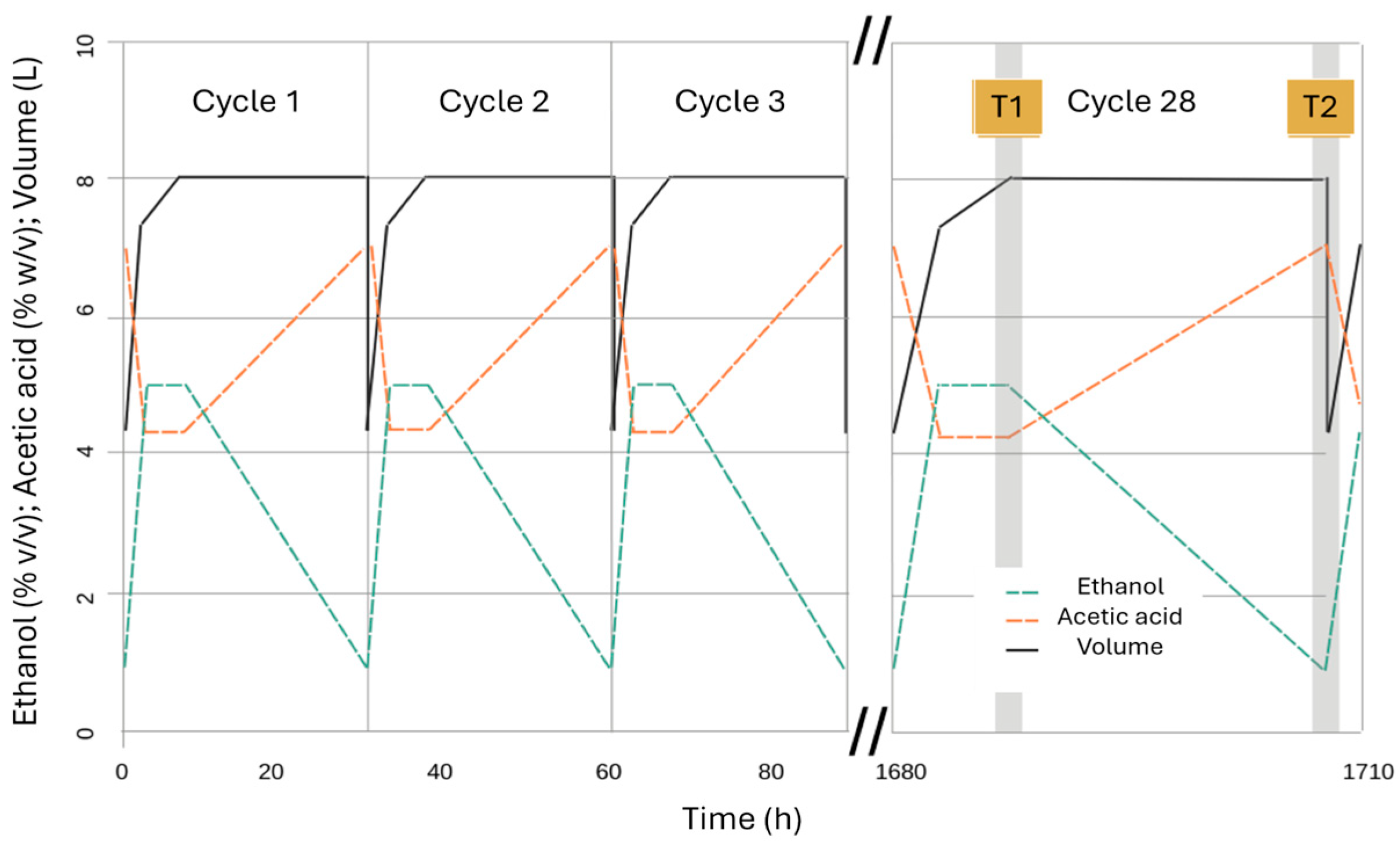


| Variable (Mean ± SD) | SAM_T0 | SAM_T1 | SAM_T2 | DSB_T0 | DSB_T1 | DSB_T2 | DWW_T0 | DWW_T1 | DWW_T2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cycle time (h) | − | 8.8 ± 2.8 | 28.9 ± 2.6 | − | 2.8 ± 0.4 | 24.3 ± 1.1 | − | 3.0 ± 0.1 | 21.4 ± 0.1 |
| Volume (L) | − | 8.0 ± 0.1 | 8.0 ± 0.1 | − | 7.0 ± 0.2 | 7.0 ± 0.2 | − | 8.0 ± 0.1 | 8.0 ± 0.1 |
| Ethanol (% v/v) | 10.0 ± 0.3 | 5.0 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 9.5 ± 0.3 | 4.7 ± 0.2 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 9.8 ± 0.3 | 4.9 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.3 |
| Total acidity (% w/v) | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 4.5 ± 0.2 | 7.2 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 4.2 ± 0.4 | 6.8 ± 0.7 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 4.3 ± 0.1 | 7.9 ± 0.2 |
| Viable cell (108 cell/mL) | − | 1.69 ± 0.34 | 2.30 ± 0.29 | − | 0.84 ± 0.70 | 1.05 ± 0.70 | − | 1.43 ± 0.33 | 1.47 ± 0.28 |
| SAM | DSB | DWW | |||||||
| Mean acetification rate (rA) [g acetic acid/(L h)] | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 1.6 ± 0.1 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | ||||||
| Global acidity production (pA) (g acetic acid/h) | 10.2 ± 1.0 | 11.3 ± 0.5 | 15.2 ± 0.5 |
| Gene | Protein | Amino Acid |
|---|---|---|
| Lpd3 | Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase | Glycine |
| LeuA | 2-isopropyl-malate synthase | L-leucine |
| MetxA | Homoserine o-acetyltransferase | L-methionine |
| ProA | Gamma-glutamyl phosphate reductase | L-proline |
| HisC | Histidinol-phosphate aminotransferase | L-histidine |
| GcvH | H-protein glycine cleavage system | Glycine |
| HisB | Imidazole glycerol-phosphate dehydratase | L-histidine |
| ThrC | Threonine synthase | L-threonine |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herrera-Rosero, D.; Román-Camacho, J.J.; García-García, J.C.; Santos-Dueñas, I.M.; García-Martínez, T.; García-García, I.; Mauricio, J.C. A Comparative Proteomic Analysis of the Acetification Process of Komagataeibacter europaeus Using Different Substrates. Fermentation 2025, 11, 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080484
Herrera-Rosero D, Román-Camacho JJ, García-García JC, Santos-Dueñas IM, García-Martínez T, García-García I, Mauricio JC. A Comparative Proteomic Analysis of the Acetification Process of Komagataeibacter europaeus Using Different Substrates. Fermentation. 2025; 11(8):484. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080484
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerrera-Rosero, Daniela, Juan J. Román-Camacho, Juan Carlos García-García, Inés M. Santos-Dueñas, Teresa García-Martínez, Isidoro García-García, and Juan Carlos Mauricio. 2025. "A Comparative Proteomic Analysis of the Acetification Process of Komagataeibacter europaeus Using Different Substrates" Fermentation 11, no. 8: 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080484
APA StyleHerrera-Rosero, D., Román-Camacho, J. J., García-García, J. C., Santos-Dueñas, I. M., García-Martínez, T., García-García, I., & Mauricio, J. C. (2025). A Comparative Proteomic Analysis of the Acetification Process of Komagataeibacter europaeus Using Different Substrates. Fermentation, 11(8), 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080484








