The Role of Quorum Sensing in Enhancing Lovastatin and Pigment Production in Monascus purpureus C322
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganism and Culture Maintenance
2.2. Fermentation Setup and Culture Conditions
2.3. Preparation and Supplementation of Quorum-Sensing Molecules
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
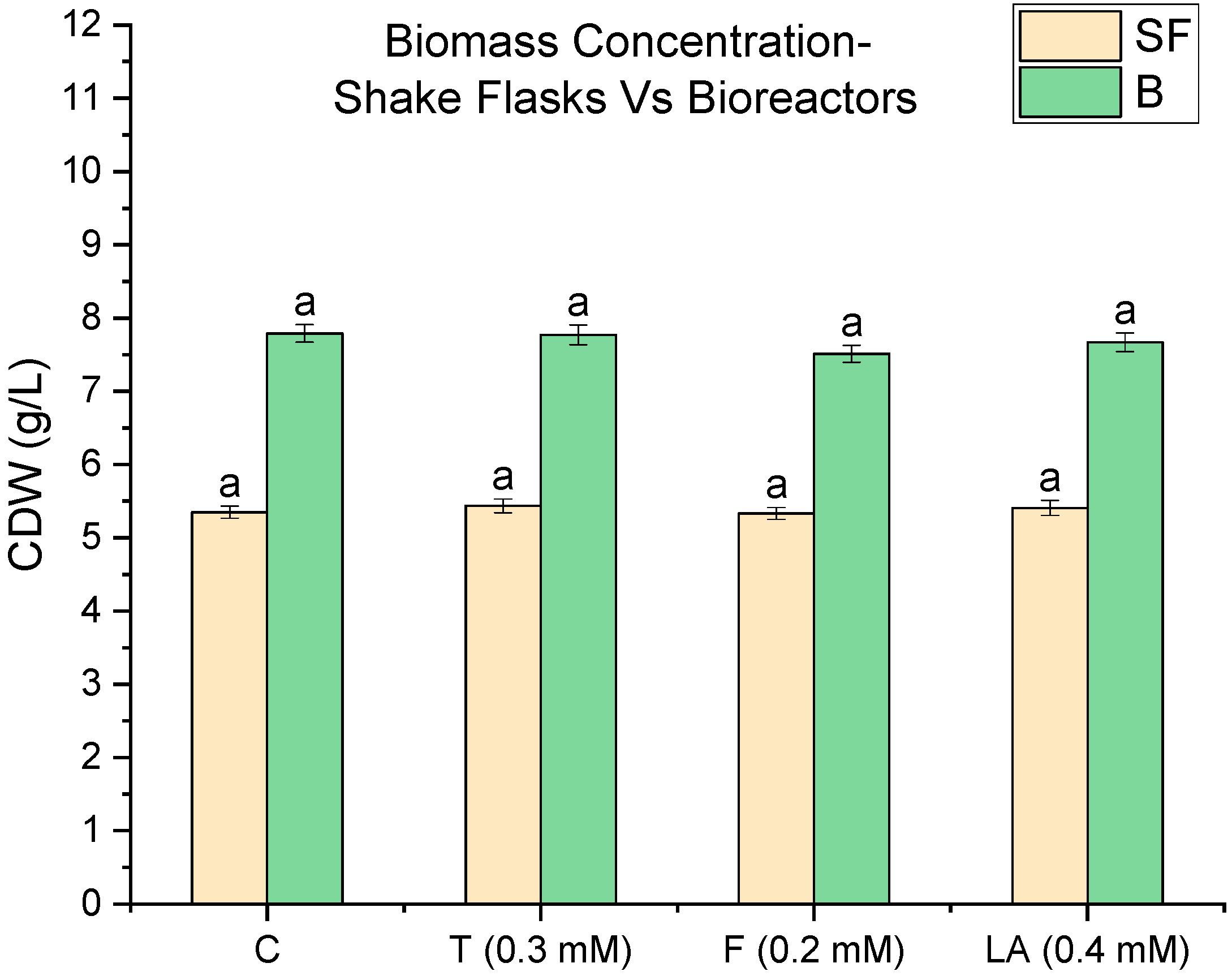
3.1. Impact of Quorum-Sensing Molecules on Biomass Concentration in Shake Flasks and Bioreactors
3.2. Quorum-Sensing-Mediated Modulation of Monascus Pigment Biosynthesis in Shake Flask and Bioreactor Systems
3.3. Enhancement of Lovastatin Biosynthesis by Quorum-Sensing Molecules
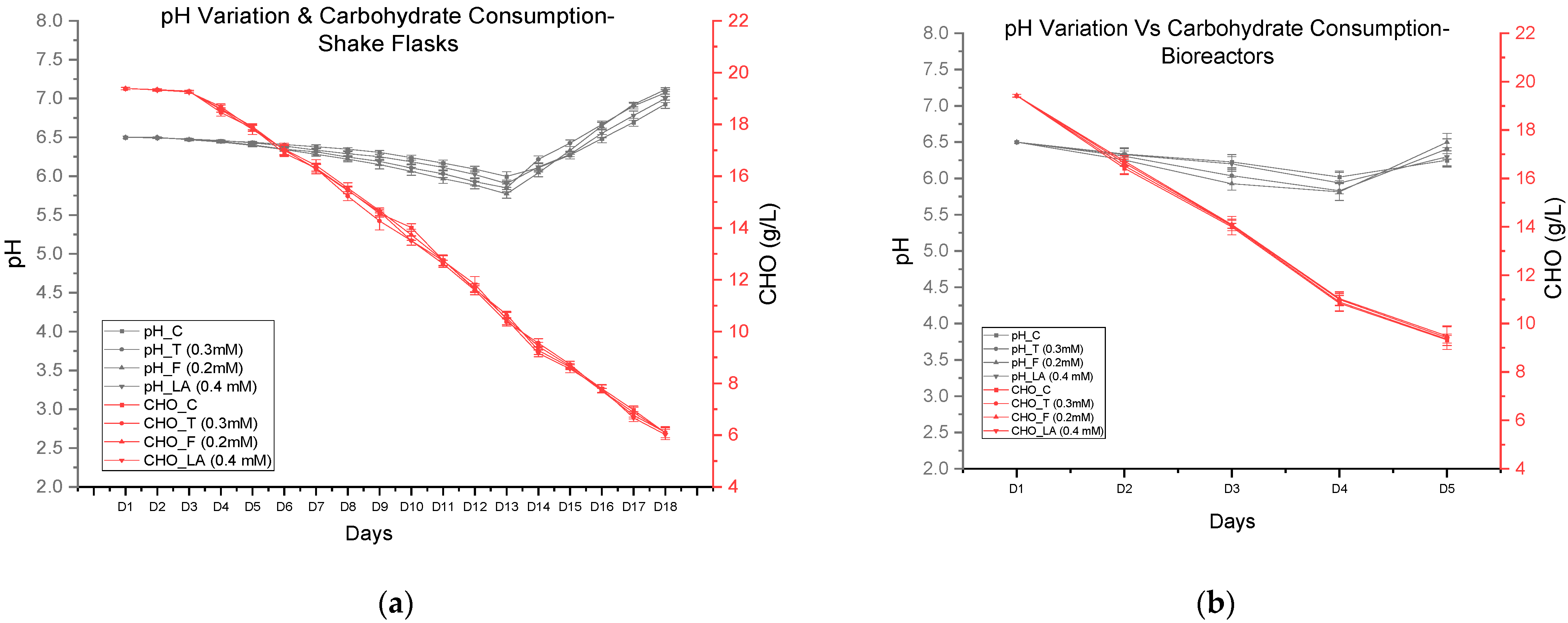
3.4. pH Variation and Carbohydrate Consumption in Shake Flask and Bioreactor Cultures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| QS | Quorum Sensing |
| QSM | Quorum-Sensing Molecule |
| F | Farnesol |
| T | Tyrosol |
| LA | Linoleic Acid |
| CHO | Carbohydrate |
| CDW | Cell Dry Weight |
| SF | Shake Flasks |
| B | Bioreactor |
| OD | Optical Density |
| AU | Absorbance Units |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| HPLC | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
References
- Reshi, Z.A.; Ahmad, W.; Lukatkin, A.S.; Javed, S. Bin From Nature to Lab: A Review of Secondary Metabolite Biosynthetic Pathways, Environmental Influences, and In Vitro Approaches. Metabolites 2023, 13, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Du, Y.; Ma, H.; Pei, X.; Li, M. Enhancement of Monascus Yellow Pigments Production by Activating the CAMP Signalling Pathway in Monascus purpureus HJ11. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 19, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, P.A.; Andhare, P.; Upadhyay, D.; Kumari, S. Microbial secondary metabolites. Int. J. Biol. Pharm. Allied Sci. 2021, 10, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Qin, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, X.; Yu, X.; Feng, Y. Strategies to Enhance the Production Efficiency of Monascus Pigments and Control Citrinin Contamination. Process Biochem. 2022, 117, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.B.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum Sensing in Bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2001, 55, 165–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albuquerque, P.; Casadevall, A. Quorum Sensing in Fungi—A Review. Med. Mycol. 2012, 50, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriuso, J.; Hogan, D.A.; Keshavarz, T.; Martínez, M.J. Role of Quorum Sensing and Chemical Communication in Fungal Biotechnology and Pathogenesis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrocal, A.; Navarrete, J.; Oviedo, C.; Nickerson, K.W. Quorum Sensing Activity in Ophiostoma ulmi: Effects of Fusel Oils and Branched Chain Amino Acids on Yeast-Mycelial Dimorphism. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amache, R.; Yerramalli, S.; Giovanni, S.; Keshavarz, T. Quorum Sensing Involvement in Response Surface Methodology for Optimisation of Sclerotiorin Production by Penicillium sclerotiorum in Shaken Flasks and Bioreactors. Ann. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Ding, H.; Ke, W.; Wang, L. Quorum Sensing in Fungal Species. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 75, 449–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrocal, A.; Oviedo, C.; Nickerson, K.W.; Navarrete, J. Quorum Sensing Activity and Control of Yeast-Mycelium Dimorphism in Ophiostoma floccosum. Biotechnol. Lett. 2014, 36, 1503–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agboyibor, C.; Kong, W.B.; Chen, D.; Zhang, A.M.; Niu, S.Q. Monascus Pigments Production, Composition, Bioactivity and Its Application: A Review. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Shi, R.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Q.; Wang, C.; Chen, W. Recent Advances in Monascus Pigments Produced by Monascus purpureus: Biosynthesis, Fermentation, Function, and Application. LWT 2023, 185, 115162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, S.; De Vizio, D.; Palonen, E.K.; Odell, M.; Brandt, A.M.; Soini, J.T.; Keshavarz, T. Is Quorum Sensing Involved in Lovastatin Production in the Filamentous Fungus Aspergillus terreus? Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.; Katyal, P.; Poonia, A.K.; Kaur, J.; Puniya, A.K.; Panwar, H. Natural Pigment from Monascus: The Production and Therapeutic Significance. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 18–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberts, A.W.; Chen, J.; Kuron, G.; Hunt, V.; Huff, J.; Hoffman, C.; Rothrock, J.; Lopez, M.; Joshua, H.; Harris, E.; et al. Mevinolin: A Highly Potent Competitive Inhibitor of Hydroxymethylglutaryl-Coenzyme A Reductase and a Cholesterol-Lowering Agent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 3957–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentovic, M. Lovastatin. In xPharm: The Comprehensive Pharmacology Reference; Enna, S.J., Bylund, D.B., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 1–5. ISBN 9780080552323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Luo, Q.; Liu, Y.; Meng, G.; Chen, W.; Wang, C. Effect of γ-Butyrolactone, a Quorum Sensing Molecule, on Morphology and Secondary Metabolism in Monascus. LWT 2022, 172, 114225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, S.; Odell, M.; Keshavarz, T. Quorum Sensing as a Method for Improving Sclerotiorin Production in Penicillium sclerotiorum. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 148, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajdari, Z.; Ebrahimpour, A.; Abdul Manan, M.; Hamid, M.; Mohamad, R.; Ariff, A.B. Nutritional Requirements for the Improvement of Growth and Sporulation of Several Strains of Monascus purpureus on Solid State Cultivation. Biomed. Res. Int. 2011, 2011, 487329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Maity, S.; Chattopadhyay, P.; Sarkar, A.; Laskar, S.; Sen, S.K. Characterization of Red Pigment from Monascus in Submerged Culture Red Pigment from Monascus purpureus. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2009, 5, 2102–2108. [Google Scholar]
- Amache, R. Quorum Sensing for Improved Production of Industrially Useful Products from Filamentous Fungi. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Westminster, London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tamimi, R. Effects of Quorum Quenchers on Aspergillus Fumigatus Conidia Aggregation, Adhesion to Surfaces, and Biofilm Formation. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Westminster, London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Merchant, M. Investigating Physical and Chemical Interaction of Aspergillus terreus Spores for Changes in Morphology and Physiology. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Westminster, London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Raina, S.; Vizio, D.D.; Odell, M.; Clements, M.; Vanhulle, S.; Keshavarz, T. Microbial Quorum Sensing: A Tool or a Target for Antimicrobial Therapy? Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2009, 54, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, F.; Roy, I.; Keshavarz, T. Impact of Linoleic Acid Supplementation on Lovastatin Production in Aspergillus terreus Cultures. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 88, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bühler, R.M.M.; Dutra, A.C.; Vendruscolo, F.; Moritz, D.E.; Ninow, J.L. Monascus Pigment Production in Bioreactor Using a Co-Product of Biodiesel as Substrate. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 33, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin, M.F.; Kennedy, J.F. Carbohydrate Analysis: A Practical Approach; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1987; p. 228. [Google Scholar]
- Nichols, L. 4.6: Step-by-Step Procedures For Extractions—Chemistry LibreTexts 2025. Available online: https://www.citethisforme.com/citation-generator/multidisciplinary-digital-publishing-institute (accessed on 25 December 2024).
- Esmaeilishirazifard, E. Investigation of a quorum sensing peptide in bacillus licheniformis and its novel antifungal property. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Westminster, London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, C.F.; Černáková, L. Farnesol and Tyrosol: Secondary Metabolites with a Crucial Quorum-Sensing Role in Candida Biofilm Development. Genes 2020, 11, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, A.M.; Wilson, R.A.; Bok, J.W.; Keller, N.P. Relationship between Secondary Metabolism and Fungal Development. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2002, 66, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiziler, M.E.; Orak, T.; Doymus, M.; Arslan, N.P.; Adiguzel, A.; Taskin, M. Farnesol and Tyrosol: Novel Inducers for Microbial Production of Carotenoids and Prodigiosin. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Qi, F.; Wu, J.; Yin, G.; Hua, J.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, L. Red Yeast Rice: A Systematic Review of the Traditional Uses, Chemistry, Pharmacology, and Quality Control of an Important Chinese Folk Medicine. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Liang, J.; Zhang, A.; Hao, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, B.; Wang, C. Overexpression of Monacolin K Biosynthesis Genes in the Monascus purpureus Azaphilone Polyketide Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2563–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, B.; Lim, Y.J.; Hwang, S.H.; Lee, D.W.; Park, S.H.; Kwon, H.J. Selective Production of Red Azaphilone Pigments in a Monascus purpureus MppDEG Deletion Mutant. J. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2017, 60, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdaguer, I.B.; Crispim, M.; Hernández, A.; Katzin, A.M. The Biomedical Importance of the Missing Pathway for Farnesol and Geranylgeraniol Salvage. Molecules 2022, 27, 8691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruppa, M. Quorum Sensing and Candida Albicans. Mycoses 2009, 52, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.L.; Cannon, R.D.; Villas-Bôas, S.G. The Metabolic Basis of Candida Albicans Morphogenesis and Quorum Sensing. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2011, 48, 747–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsigiannis, D.I.; Keller, N.P. Oxylipins as Developmental and Host–Fungal Communication Signals. Trends Microbiol. 2007, 15, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsigiannis, D.I.; Kowieski, T.M.; Zarnowski, R.; Keller, N.P. Endogenous Lipogenic Regulators of Spore Balance in Aspergillus nidulans. Eukaryot. Cell 2004, 3, 1398–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsigiannis, D.I.; Zarnowski, R.; Keller, N.P. The Lipid Body Protein, PpoA, Coordinates Sexual and Asexual Sporulation in Aspergillus nidulans. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 11344–11353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, O.Y.; Song, J. Important Roles of Linoleic Acid and α-Linolenic Acid in Regulating Cognitive Impairment and Neuropsychiatric Issues in Metabolic-Related Dementia. Life Sci. 2024, 337, 122356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beccaccioli, M.; Pucci, N.; Salustri, M.; Scortichini, M.; Zaccaria, M.; Momeni, B.; Loreti, S.; Reverberi, M.; Scala, V. Fungal and bacterial oxylipins are signals for intra- and inter-cellular communication within plant disease. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 823233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Luo, J.; Ma, Z.; Sun, Q.; Wu, C.; Li, X. Quality and Authenticity Control of Functional Red Yeast Rice—A Review. Molecules 2019, 24, 1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palonen, E.K.; Neffling, M.R.; Raina, S.; Brandt, A.; Keshavarz, T.; Meriluoto, J.; Soini, J. Butyrolactone I Quantification from Lovastatin Producing Aspergillus terreus Using Tandem Mass Spectrometry—Evidence of Signalling Functions. Microorganisms 2014, 2, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Wu, H.; Chen, M. Effect of Temperature-Shift and Temperature-Constant Cultivation on the Monacolin K Biosynthetic Gene Cluster Expression in Monascus sp. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 55, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lind, A.L.; Smith, T.D.; Saterlee, T.; Calvo, A.M.; Rokas, A. Regulation of Secondary Metabolism by the Velvet Complex Is Temperature-Responsive in Aspergillus. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2016, 6, 4023–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Félix, C.; Meneses, R.; Gonçalves, M.F.M.; Duarte, A.S.; Jorrín-Novo, J.V.; van de Peer, Y.; Deforce, D.; Van Nieuwerburgh, F.; Alves, A.; Esteves, A.C. How Temperature Modulates the Expression of Pathogenesis-Related Molecules of the Cross-Kingdom Pathogen Lasiodiplodia hormozganensis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 927, 171917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hua, X.; Gao, C.; Liu, J. Morphological Engineering of Filamentous Fungi: Research Progress and Perspectives. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 34, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Guo, D.; Li, Z.; Lei, S.; Shi, J.; Shaoa, D. Clinostat Rotation Affects Metabolite Transportation and Increases Organic Acid Production by Aspergillus carbonarius, as Revealed by Differential Metabolomic Analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01023-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, D.; Weloosamy, H.; Lim, S.-H. Effect of Agitation Speed on the Morphology of Aspergillus niger HFD5A-1 Hyphae and Its Pectinase Production in Submerged Fermentation. World J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 6, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peñalva, M.A.; Arst Jr, H.N. Regulation of Gene Expression by Ambient PH in Filamentous Fungi and Yeasts. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2002, 66, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banti, D.C.; Tsali, A.; Mitrakas, M.; Samaras, P. The Dissolved Oxygen Effect on the Controlled Growth of Filamentous Microorganisms in Membrane Bioreactors. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2020, 2, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Soto, M.; Botello-Alvarez, E.; Jiménez-Islas, H.; Navarrete-Bolaños, J.L.; Barajas-Conde, E.; Rico-Martínez, R.; Guevara-González, R.; Torres-Pacheco, I. Growth Morphology and Hydrodynamics of Filamentous Fungi in Submerged Cultures. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2000, 20, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Ghosh, A.K.; Dhurandhar, R.; Chakrabortty, S. Downstream Process: Toward Cost/Energy Effectiveness. In Handbook of Biofuels; Sahay, S., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 249–260. ISBN 9780128228104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makepa, D.C.; Chihobo, C.H. Sustainable Pathways for Biomass Production and Utilization in Carbon Capture and Storage—A Review. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2024, 15, 11397–11419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punia Bangar, S.; Suri, S.; Trif, M.; Ozogul, F. Organic Acids Production from Lactic Acid Bacteria: A Preservation Approach. Food Biosci. 2022, 46, 101615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubicek, C.P.; Punt, P.; Visser, J. Production of Organic Acids by Filamentous Fungi. Ind. Appl. 2011, 10, 215–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaud, N.; Giniés, C.; Navarro, D.; Fabre, N.; Crapart, S.; Gimbert, I.H.; Levasseur, A.; Raouche, S.; Sigoillot, J.-C. Exploring Fungal Biodiversity: Organic Acid Production by 66 Strains of Filamentous Fungi. Fungal Biol. Biotechnol. 2014, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, M.; Li, K.; Li, Z. β-Alanine Metabolism Leads to Increased Extracellular PH during the Heterotrophic Ammonia Oxidation of Pseudomonas putida Y-9. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, H.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Koehler, P.E. Regulation of Growth and Pigmentation of Monascus purpureus by Carbon and Nitrogen Concentrations. Mycologia 1981, 73, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, F.; Valenzuela, P.L.; Gimenez, J.; Tur, C.; Ferreria, D.; Domínguez, R.; Sanchez-Oliver, A.J.; Sanz, J.M.M. Carbohydrate Availability and Physical Performance: Physiological Overview and Practical Recommendations. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
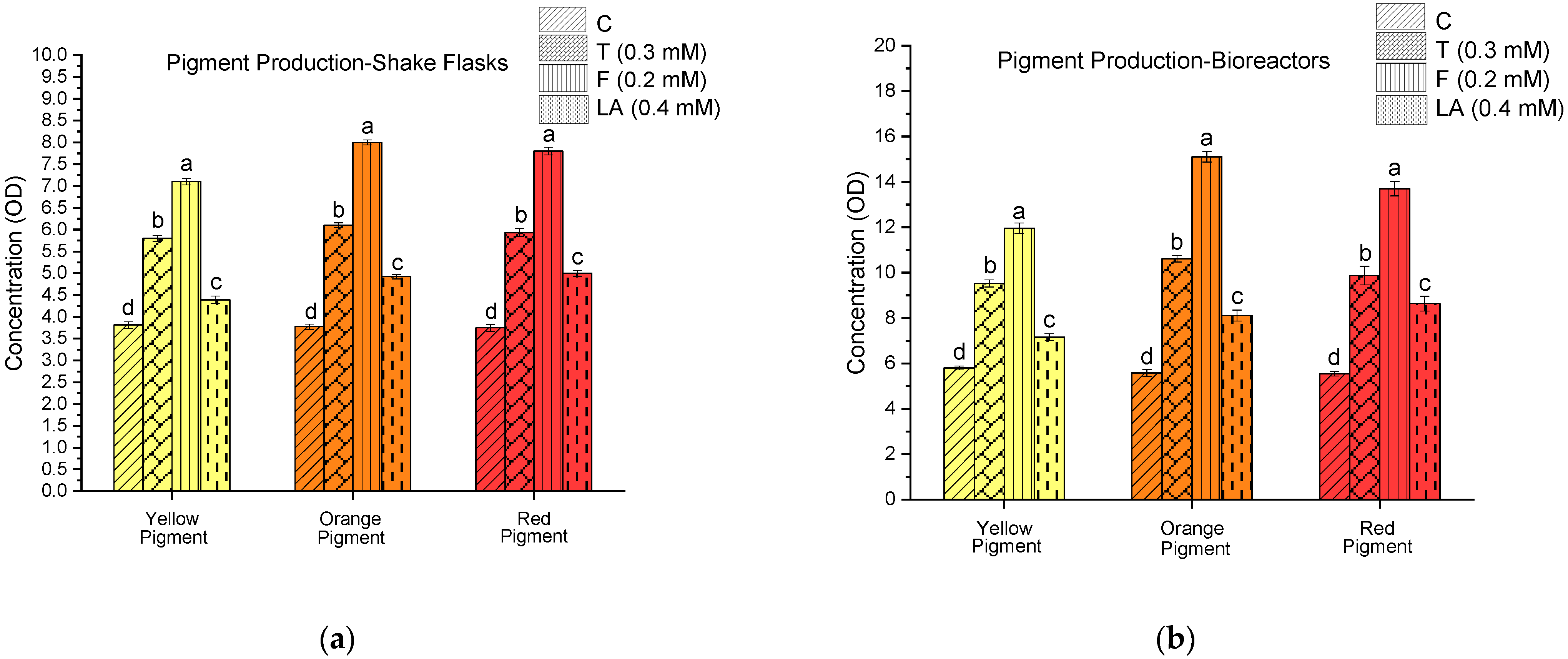


| QSM | Yellow Pigment | Orange Pigment | Red Pigment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control (C) | 1.52 | 1.48 | 1.48 |
| Tyrosol (T) | 1.64 | 1.74 | 1.66 |
| Farnesol (F) | 1.68 | 1.89 | 1.76 |
| Linoleic Acid (LA) | 1.63 | 1.65 | 1.73 |
| QSM | Fold Increase (Bioreactor/Flask) |
|---|---|
| Control (C) | 1.08 |
| Tyrosol (T) | 1.15 |
| Farnesol (F) | 1.30 |
| Linoleic acid (LA) | 1.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yerramalli, S.; Getting, S.J.; Kyazze, G.; Keshavarz, T. The Role of Quorum Sensing in Enhancing Lovastatin and Pigment Production in Monascus purpureus C322. Fermentation 2025, 11, 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080461
Yerramalli S, Getting SJ, Kyazze G, Keshavarz T. The Role of Quorum Sensing in Enhancing Lovastatin and Pigment Production in Monascus purpureus C322. Fermentation. 2025; 11(8):461. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080461
Chicago/Turabian StyleYerramalli, Sirisha, Stephen J. Getting, Godfrey Kyazze, and Tajalli Keshavarz. 2025. "The Role of Quorum Sensing in Enhancing Lovastatin and Pigment Production in Monascus purpureus C322" Fermentation 11, no. 8: 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080461
APA StyleYerramalli, S., Getting, S. J., Kyazze, G., & Keshavarz, T. (2025). The Role of Quorum Sensing in Enhancing Lovastatin and Pigment Production in Monascus purpureus C322. Fermentation, 11(8), 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080461







