Assessment of Effects of Storage Time on Fermentation Profile, Chemical Composition, Bacterial Community Structure, Co-Occurrence Network, and Pathogenic Risk in Corn Stover Silage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. CS Silage (CSTS) Sample Preparation
2.2. Chemical Composition, Fermentation Quality, and Microbial Population
2.3. Measurement of Bacterial Community Structure by SMRT
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Biochemical Composition of CS
4.2. Fermentation Quality of Silage
4.3. Microbial Alpha Diversity and Community Dynamics
4.4. Correlation Analysis Between Microbial Network and Fermentation Product
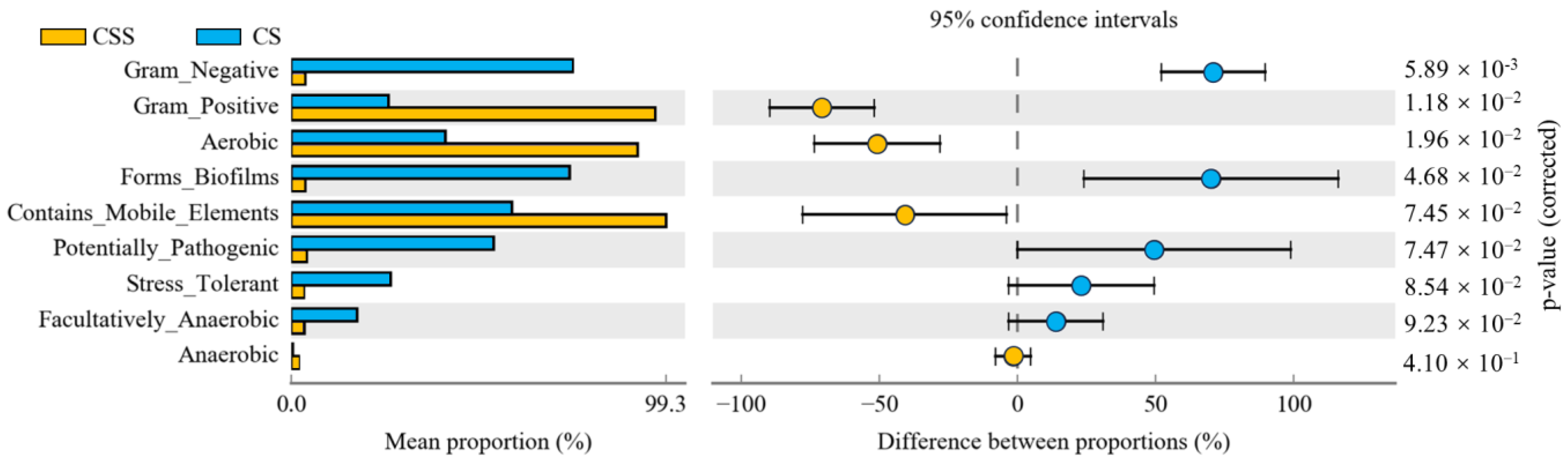
4.5. Bugbase Phenotypes Predicted in the Bacterial Community
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boval, M.; Dixon, R.M. The importance of grasslands for animal production and other functions: A review on management and methodological progress in the tropics. Animal 2012, 6, 748–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, R.E.; Shapero, M.W.K.; Striby, K.; Althouse, L.D.; Meade, D.E.; Brown, K.; Horney, M.R.; Rao, D.R.; Davy, J.S.; Rigby, C.W.; et al. Forage quantity and quality dynamics due to weathering over the dry season on California annual rangelands. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 76, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, J.P.; Phillips, C.J.C. Starvation of ruminant livestock. In Nutrition and the Welfare of Farm Animals. Animal Welfare; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dunière, L.; Sindou, J.; Chaucheyras-Durand, F.; Chevallier, I.; Thévenot-Sergentet, D. Silage processing and strategies to prevent persistence of undesirable microorganisms. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2013, 182, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranum, P.; Peña-Rosas, J.P.; Garcia-Casal, M.N. Global maize production, utilization, and consumption. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1312, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Stokes, M.R.; Wallace, C.R. Effects of enzyme-inoculant systems on preservation and nutritive value of hay crop and corn silages. J. Dairy Sci. 1994, 77, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.L.; Wang, P.; Zhou, C.H.; Li, P.; Tang, H.Y.; Zhang, J.B.; Cai, Y. Chemical composition and in vitro digestibility of corn stover during field exposure and their fermentation characteristics of silage prepared with microbial additives. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 1854–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosher, J.J.; Bowman, B.; Bernberg, E.L.; Shevchenko, O.; Kan, J.; Korlach, J.; Kaplan, L.A. Improved performance of the PacBio SMRT technology for 16S rDNA sequencing. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2014, 104, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 17th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Arlington, VA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y. Analysis method for silage. In Field and Laboratory Methods for Grassland Science; Tosho Printing Co., Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Benno, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Kumai, S. Effect of applying lactic acid bacteria isolated from forage crops on fermentation characteristics and aerobic deterioration of silage. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.H.; Li, X.M.; Guan, H.; Huang, L.K.; Ma, X.; Peng, Y.; Li, Z.; Nie, G.; Zhou, J.Q.; Yang, W.Y. Microbial community and fermentation characteristic of Italian ryegrass silage prepared with corn stover and lactic acid bacteria. Bioresource Technol. 2019, 279, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Q.; Xu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Xi, X.; Kwok, L.Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W. Evaluation of bacterial contamination in raw milk, ultra-high temperature milk and infant formula using single molecule, real-time sequencing technology. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 8464–8472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shade, A.; Handselman, J. Beyond the Venn diagram: The hunt for a core microbiome. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree: Computing large minimum evolution trees with profiles instead of a distance matrix. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, R.; Shimodaira, H. Pvclust: An R package for assessing the uncertainty in hierarchical clustering. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1540–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennang Ouamba, A.J.; Gagnon, M.; Varin, T.; Chouinard, P.Y.; LaPointe, G.; Roy, D. Metataxonomic insights into the microbial ecology of farm-scale hay, grass or legume, and corn silage produced with and without inoculants. Front. Syst. Biol. 2022, 2, 955611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, R.G.; Torrie, J.H. Principles and Procedures of Statistics: A Biometrical Approach, 1st ed.; McGraw Hill Company: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Ginni, G.; Kavitha, S.; Yukesh Kannah, R.; Shashi Kant, B.; Adish Kumar, S.; Rajkumar, M.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Arivalagan, P.; Nguyen Thuy Lan, C.; Rajesh Banu, J. Valorization of agricultural residues: Different biorefinery routes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filonchyk, M.; Peterson, M.P.; Zhang, L.; Hurynovich, V.; He, Y. Greenhouse gases emissions and global climate change: Examining the influence of CO2, CH4, and N2O. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 935, 173359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarbrough, D.A.; Coblentz, W.K.; Coffey, K.P.; Turner, J.E.; Davis, G.V.; Kellogg, D.W.; Hellwig, D.H. Effects of summer management and fall harvest date on ruminal in situ degradation of crude protein in stockpiled bermudagrass. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2002, 96, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, L., Jr.; Shaver, R.D.; Grant, R.J.; Schmidt, R.J. Silage review: Interpretation of chemical, microbial, and organoleptic components of silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4020–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okoye, C.O.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, J.; Jiang, J. The performance of lactic acid bacteria in silage production: A review of modern biotechnology for silage improvement. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 266, 127212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, F.; He, R.; Zhou, X.; Gu, Q.; Xia, Z.; Liang, M.; Zhou, J.; Lin, B.; Zou, C. Dynamic changes in fermentation profiles and bacterial community composition during sugarcane top silage fermentation: A preliminary study. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 285, 121315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAllister, T.A.; Dunière, L.; Drouin, P.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Munns, K.; Zaheer, R. Silage review: Using molecular approaches to define the microbial ecology of silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4060–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Wang, X.; Lin, Y.; Yang, X.; Ni, K.; Yang, F. Microorganisms that are critical for the fermentation quality of paper mulberry silage. Food Energy Secur. 2021, 10, e304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wang, N.; Rinne, M.; Ke, W.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Da, M.; Bai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Guo, X. The bacterial community and metabolome dynamics and their interactions modulate fermentation process of whole crop corn silage prepared with or without inoculants. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zivkovic Zaric, R.; Zaric, M.; Sekulic, M.; Zornic, N.; Nesic, J.; Rosic, V.; Vulovic, T.; Spasic, M.; Vuleta, M.; Jovanovic, J.; et al. Antimicrobial treatment of Serratia marcescens invasive infections: Systematic review. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, A.; Khanna, M.; Aggarwal, A. Serratia marcescens-a rare opportunistic nosocomial pathogen and measures to limit its spread in hospitalized patients. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2013, 7, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rocchetti, M.T.; Russo, P.; Capozzi, V.; Drider, D.; Spano, G.; Fiocco, D. Bioprospecting antimicrobials from Lactiplantibacillus plantarum: Key factors underlying its probiotic action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Shi, W.; Sun, J.; Xia, T.; Huang, F.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Teng, K.; Zhong, J. Dynamic changes in fermentation quality and structure and function of the microbiome during mixed silage of Sesbania cannabina and sweet sorghum grown on saline-alkaline land. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0248322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ianniello, R.G.; Zheng, J.; Zotta, T.; Ricciardi, A.; Gänzle, M.G. Biochemical analysis of respiratory metabolism in the heterofermentative Lactobacillus spicheri and Lactobacillus reuteri. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valcheva, R.; Korakli, M.; Onno, B.; Prévost, H.; Ivanova, I.; Ehrmann, M.A.; Dousset, X.; Gänzle, M.G.; Vogel, R.F. Lactobacillus hammesii sp. nov. isolated from French sourdough. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55 Pt 2, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carasi, P.; Malamud, M.; Serradell, M.A. Potentiality of food-isolated Lentilactobacillus kefiri strains as probiotics: State-of-art and perspectives. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mermejo, B.C.; Bortolucci, J.; de Andrade, A.R.; Reginatto, V. The non-solventogenic Clostridium beijerinckii Br 21 produces 1,3-propanediol from glycerol with butyrate as the main by-product. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6, 848022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Usman, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Su, R.; Chen, H.; Li, Q.; Jia, M.; Amole, T.A.; Guo, X. Effects of bacteriocin-producing Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on bacterial community and fermentation profile of whole-plant corn silage and its in vitro ruminal fermentation, microbiota, and CH4 emissions. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 15, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Benno, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Ohmomo, S.; Kumai, S.; Nakase, T. Influence of Lactobacillus spp. from an inoculant and of Weissella and Leuconostoc spp. from forage crops on silage fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2982–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Shang, L.; Li, J.; Chou, S.; Lyu, Y.; Shan, A. pH-responsive antimicrobial peptide with selective killing activity for bacterial abscess therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 5355–5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Xu, D.; Li, F.; Bai, J.; Su, R. Current approaches on the roles of lactic acid bacteria in crop silage. Microb. Biotechnol. 2023, 16, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
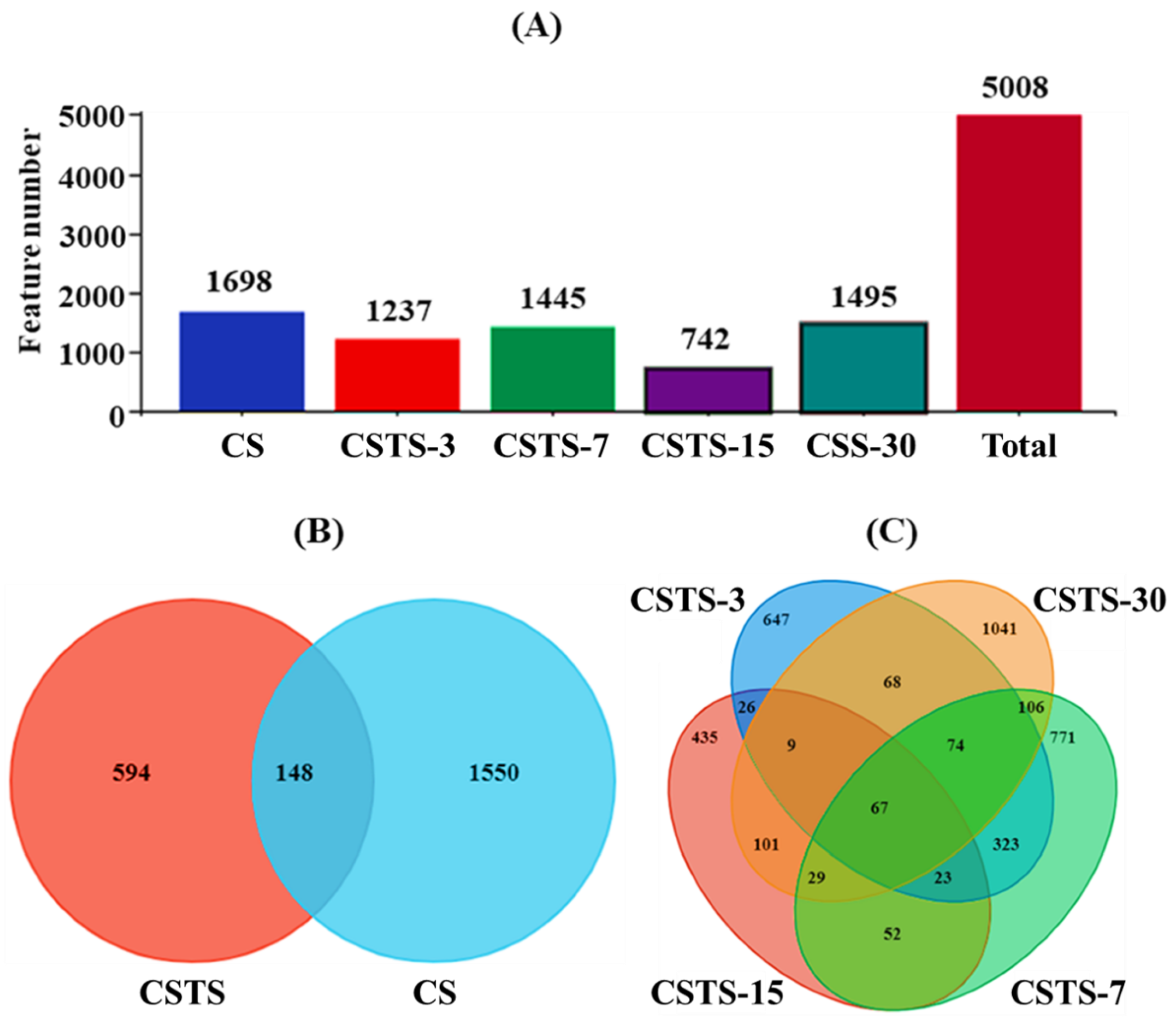
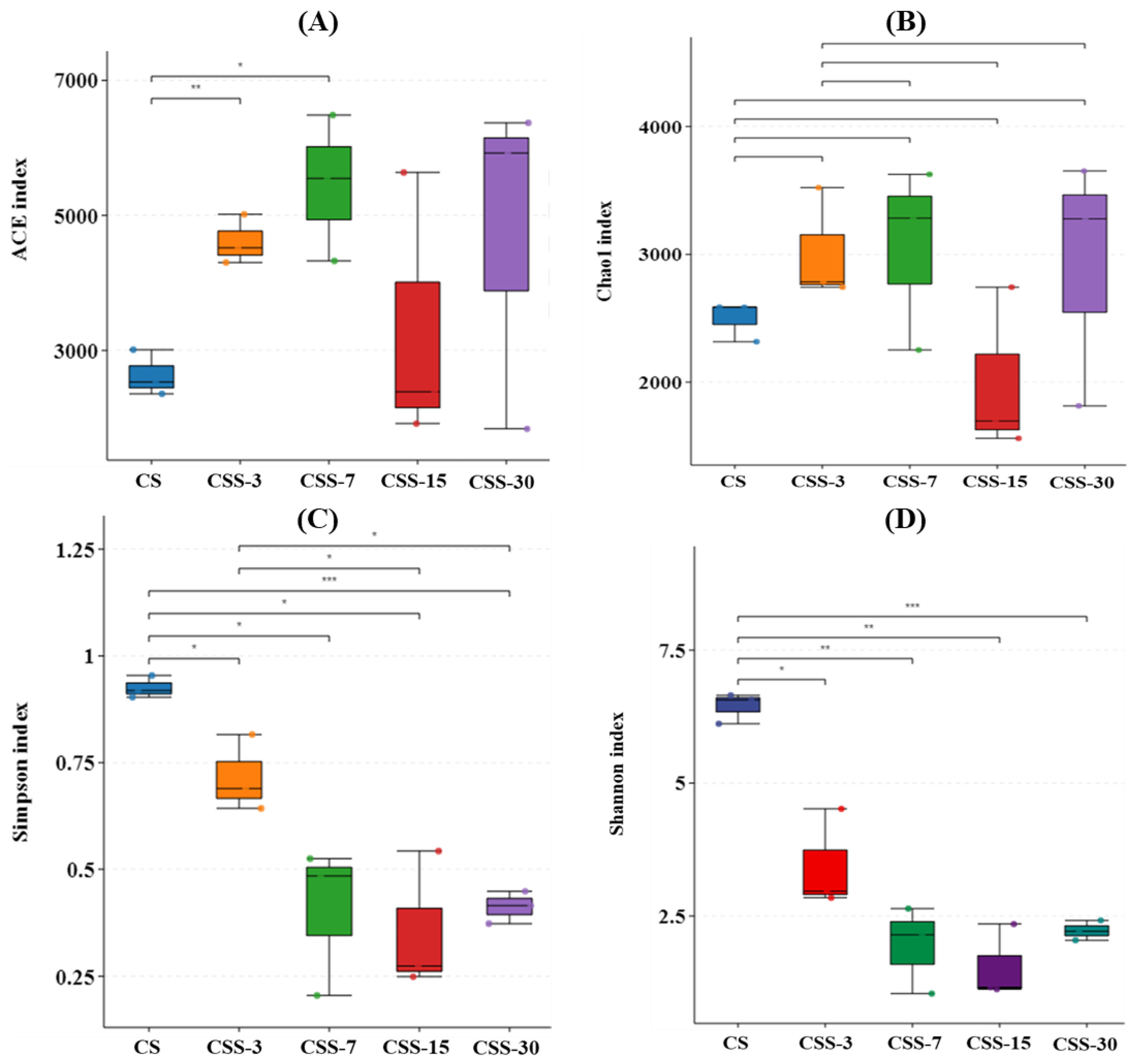
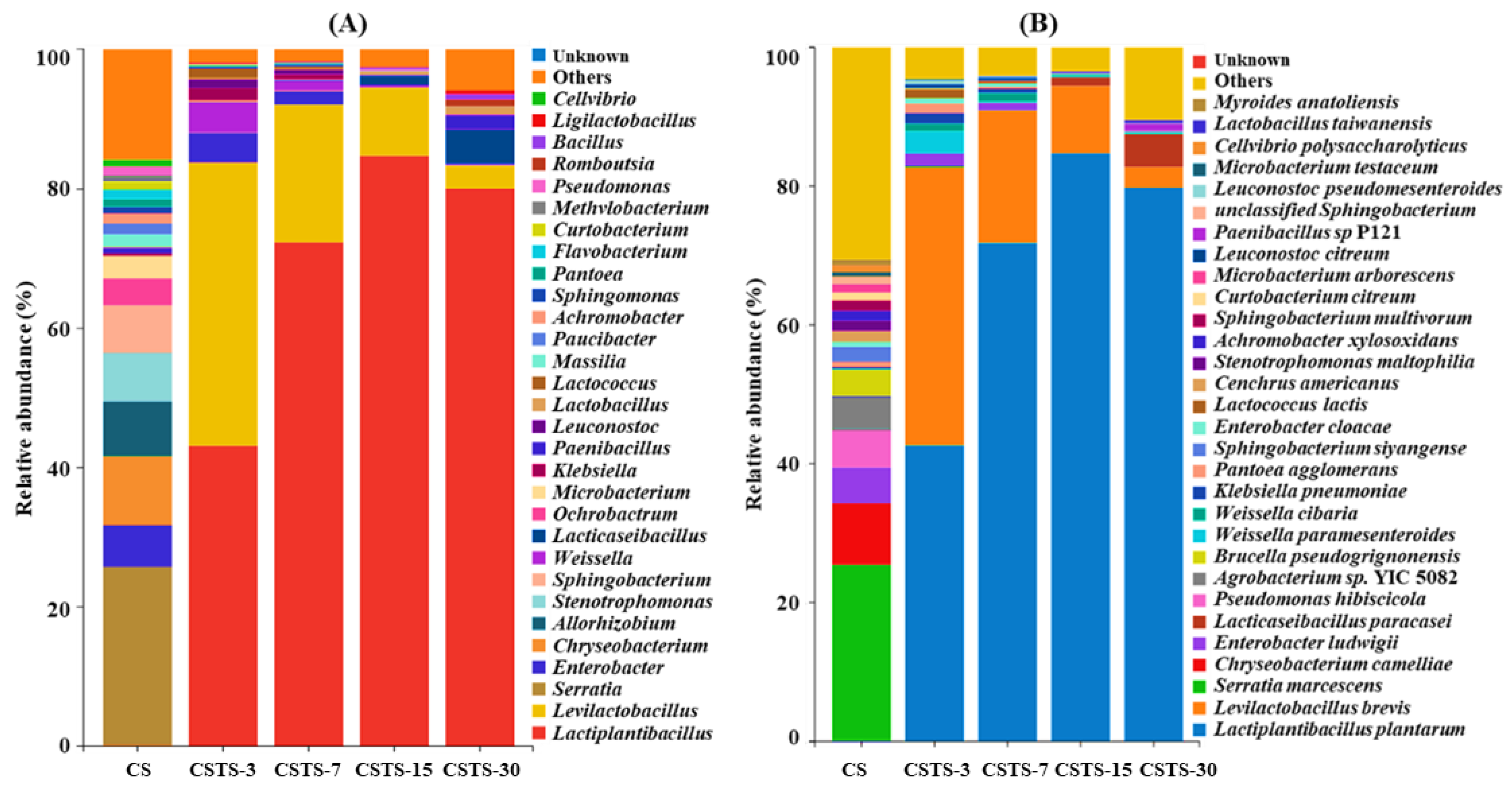
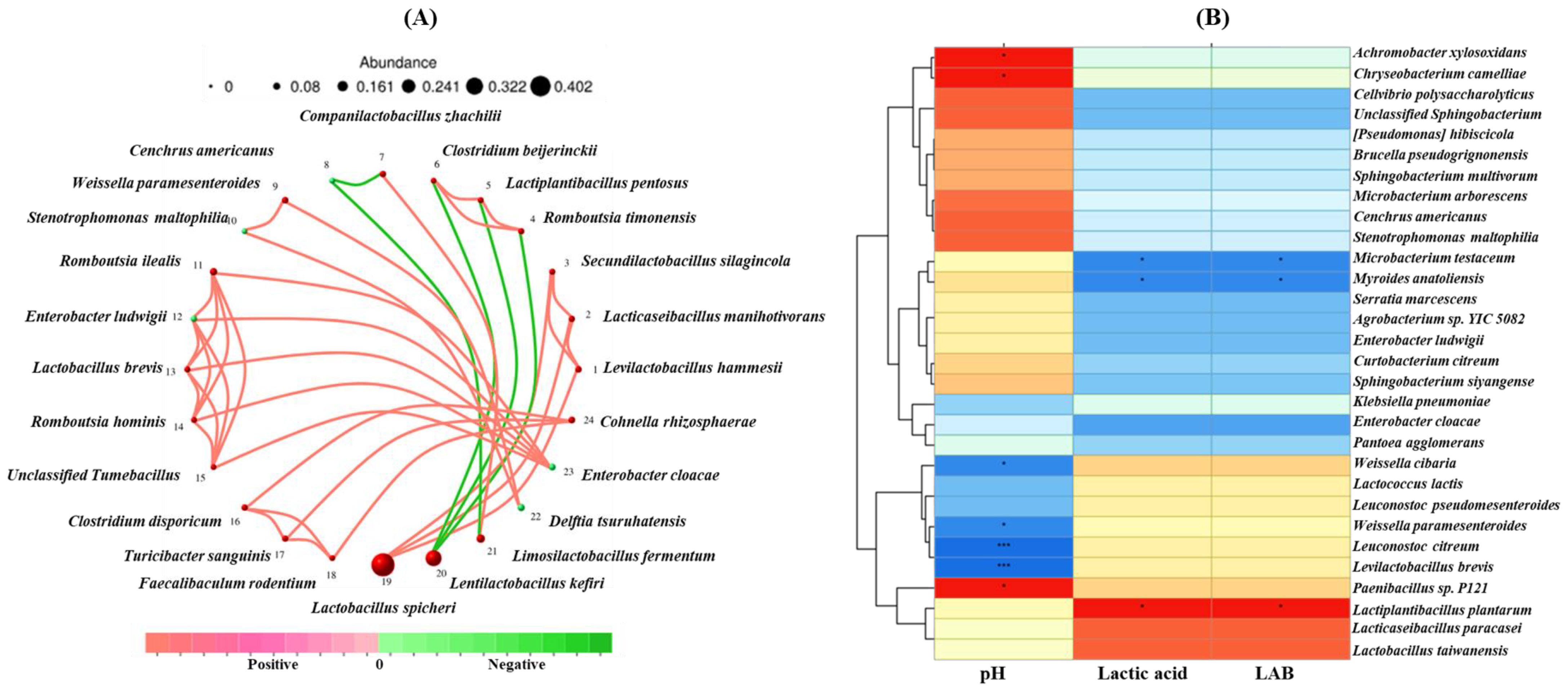
| Items | CS |
|---|---|
| Chemical composition | |
| DM (%) | 31.21 ± 0.22 |
| OM (% DM) | 91.38 ± 1.14 |
| CP (% DM) | 7.01 ± 0.04 |
| EE (% DM) | 2.08 ± 0.03 |
| NDF (% DM) | 54.95 ± 1.23 |
| ADF (% DM) | 28.74 ± 0.67 |
| WSC (% DM) | 6.65 ± 0.30 |
| Microbial population (lg cfu/g FM) | |
| Lactic acid bacteria | 5.84 ± 0.10 |
| Aerobic bacteria | 7.54 ± 0.12 |
| Coliform bacteria | 5.31 ± 0.19 |
| Yeast | 5.05 ± 0.06 |
| Mold | 4.22 ± 0.11 |
| Items | Treatments | SEM | p Value for Contrasts | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSTS-3 | CSTS-7 | CSTS-15 | CSTS-30 | P-L | P-Q | ||
| Chemical composition | |||||||
| DM (%) | 31.82 | 31.22 | 31.97 | 31.49 | 0.31 | 0.86 | 0.86 |
| OM (% DM) | 91.05 | 90.93 | 90.89 | 91.00 | 0.23 | 0.86 | 0.63 |
| CP (% DM) | 6.17 a | 5.76 ab | 5.66 ab | 5.28 b | 0.18 | <0.01 | 0.96 |
| EE (% DM) | 2.02 a | 1.94 ab | 1.78 bc | 1.65 c | 0.05 | <0.01 | 0.69 |
| NDF (% DM) | 53.54 a | 52.76 ab | 52.27 b | 52.10 b | 0.24 | <0.01 | 0.24 |
| ADF (% DM) | 28.26 a | 27.94 ab | 27.63 bc | 27.31 c | 0.12 | <0.01 | 0.99 |
| Fermentation quality | |||||||
| pH | 3.88 a | 3.80 a | 3.53 c | 3.64 b | 0.02 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Lactic acid (% DM) | 0.62 b | 1.84 a | 2.03 a | 1.90 a | 0.07 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Acetic acid (% DM) | 0.32 b | 0.57 a | 0.56 a | 0.59 a | 0.05 | <0.01 | 0.41 |
| Propionic acid (% DM) | ND | ND | ND | ND | -- | -- | -- |
| Butyric acid (% DM) | ND | ND | ND | ND | -- | -- | -- |
| NH3-N (% DM) | 0.83 a | 0.77 ab | 0.66 c | 0.72 bc | 0.02 | <0.01 | 0.02 |
| Microbial population (lg cfu/g FM) | |||||||
| Lactic acid bacteria | 5.35 c | 6.16 b | 6.51 a | 6.45 a | 0.05 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Aerobic bacteria | 6.19 a | 5.68 b | 5.10 c | 5.13 c | 0.05 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Coliform bacteria | ND | ND | ND | ND | -- | -- | -- |
| Yeast | 5.52 | 5.30 | 5.24 | 5.36 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.04 |
| Mold | ND | ND | ND | ND | -- | -- | -- |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, Z.; Meng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cui, S.; Wang, S.; Yan, X. Assessment of Effects of Storage Time on Fermentation Profile, Chemical Composition, Bacterial Community Structure, Co-Occurrence Network, and Pathogenic Risk in Corn Stover Silage. Fermentation 2025, 11, 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080425
Du Z, Meng Y, Chen Y, Cui S, Wang S, Yan X. Assessment of Effects of Storage Time on Fermentation Profile, Chemical Composition, Bacterial Community Structure, Co-Occurrence Network, and Pathogenic Risk in Corn Stover Silage. Fermentation. 2025; 11(8):425. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080425
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Zhumei, Ying Meng, Yifan Chen, Shaojuan Cui, Siran Wang, and Xuebing Yan. 2025. "Assessment of Effects of Storage Time on Fermentation Profile, Chemical Composition, Bacterial Community Structure, Co-Occurrence Network, and Pathogenic Risk in Corn Stover Silage" Fermentation 11, no. 8: 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080425
APA StyleDu, Z., Meng, Y., Chen, Y., Cui, S., Wang, S., & Yan, X. (2025). Assessment of Effects of Storage Time on Fermentation Profile, Chemical Composition, Bacterial Community Structure, Co-Occurrence Network, and Pathogenic Risk in Corn Stover Silage. Fermentation, 11(8), 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11080425







