Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Cattle Manure and Sewage Sludge Using Different Inoculum Proportions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
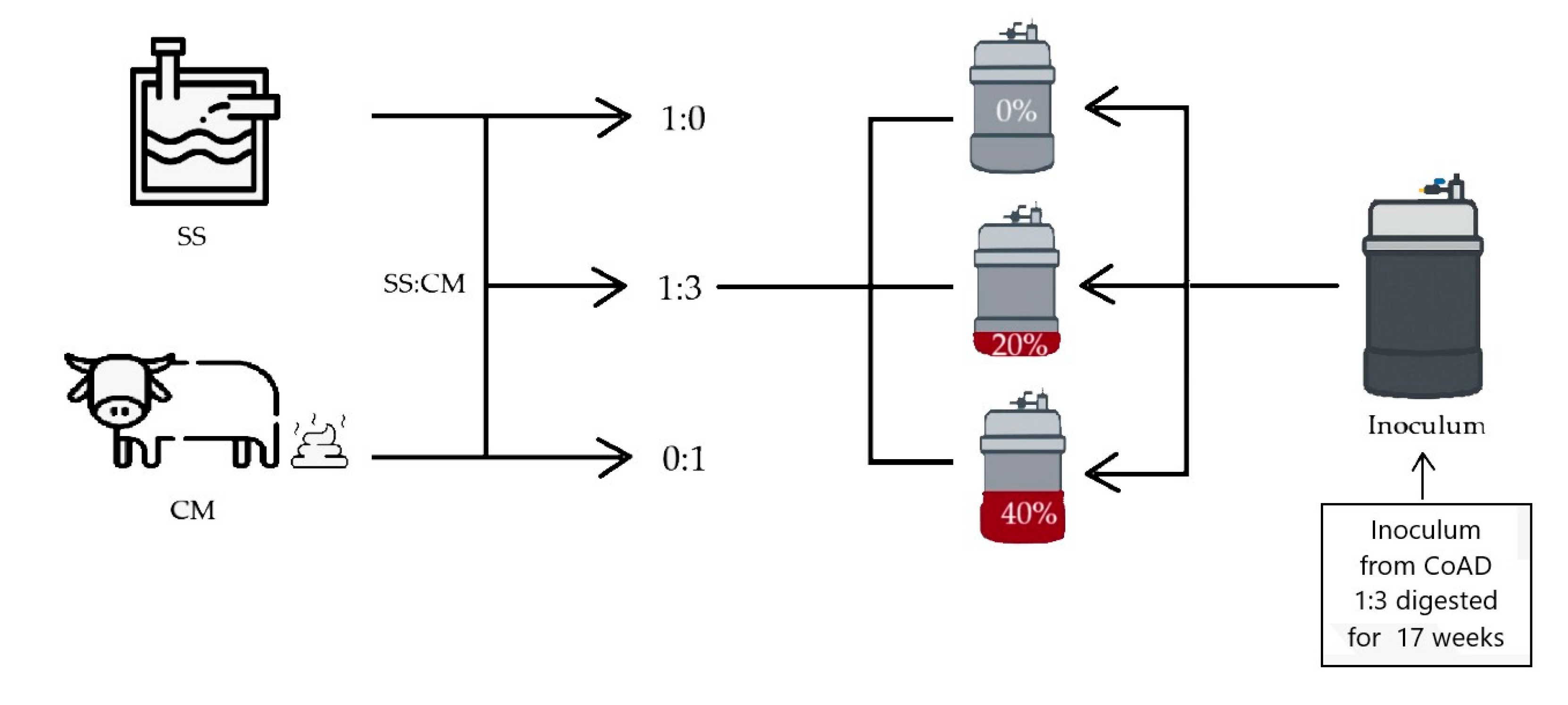
2.1. Experimental Site and Raw Materials
2.2. Anaerobic Biodigester Configuration
2.3. Analysis of Physicochemical Characteristics
2.4. Biogas Analysis
2.4.1. Flame Test
2.4.2. Biogas Temperature
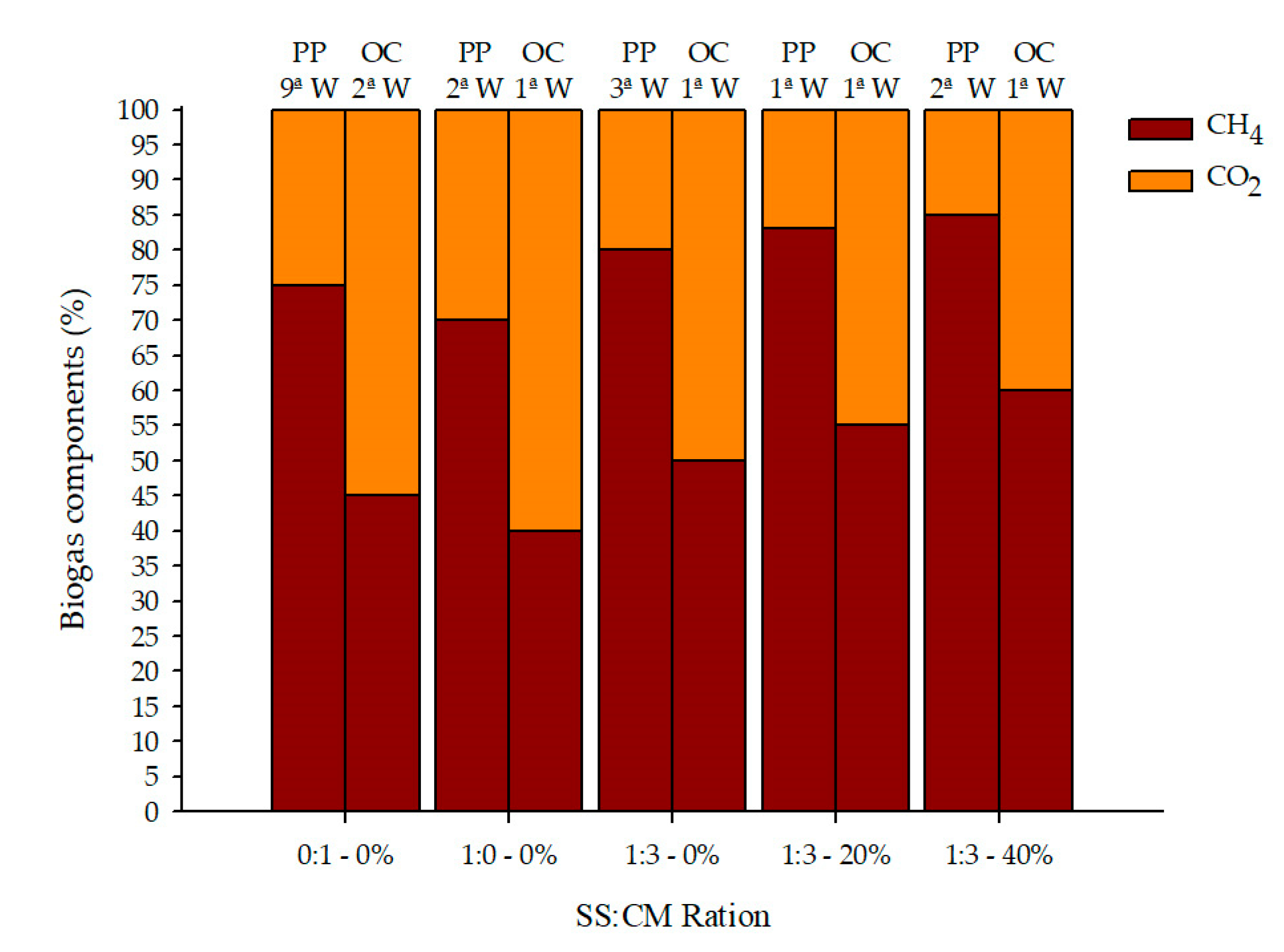
2.4.3. Biogas Composition
2.4.4. Kinetics Modeling
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Biomass Characterization
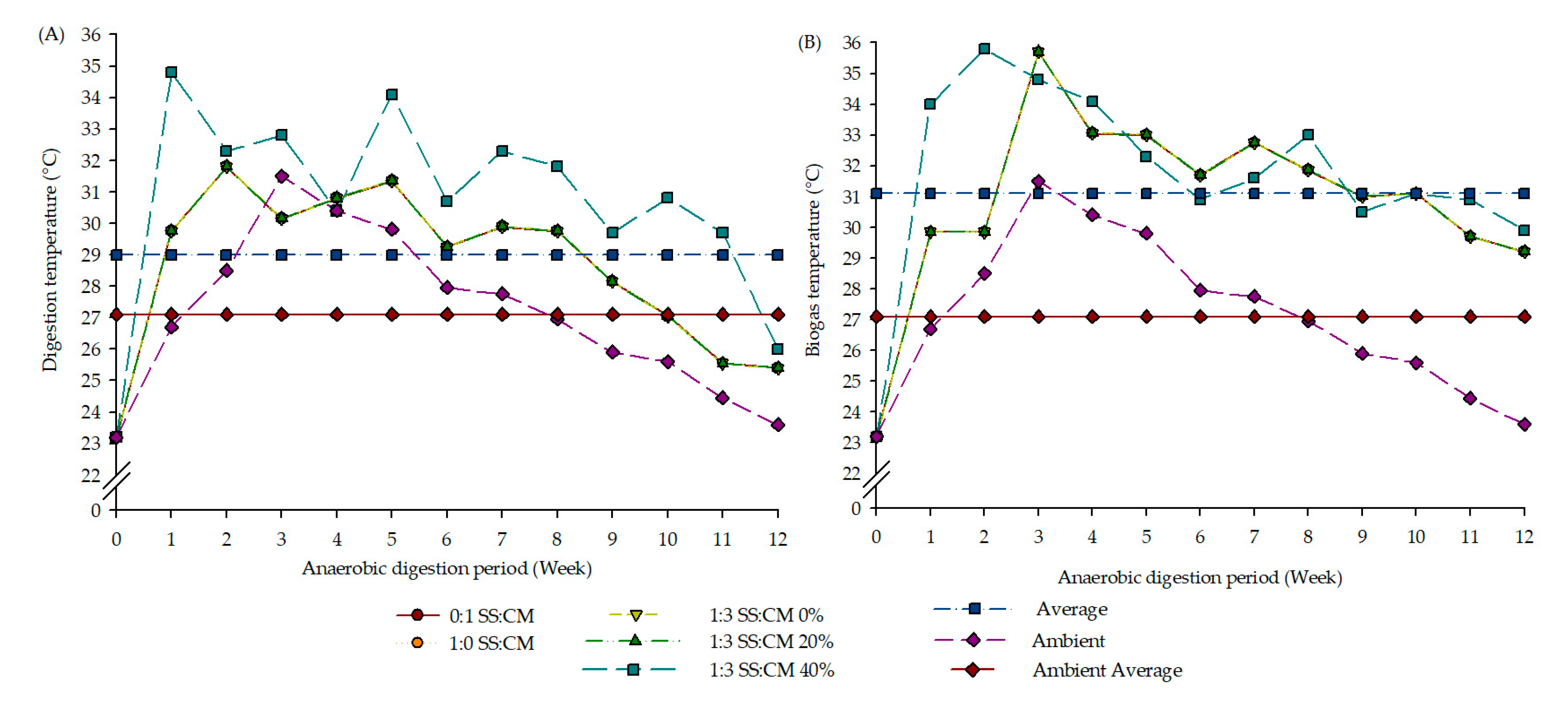
3.2. Digestion, Biogas, and Ambient Environment Temperature Profile
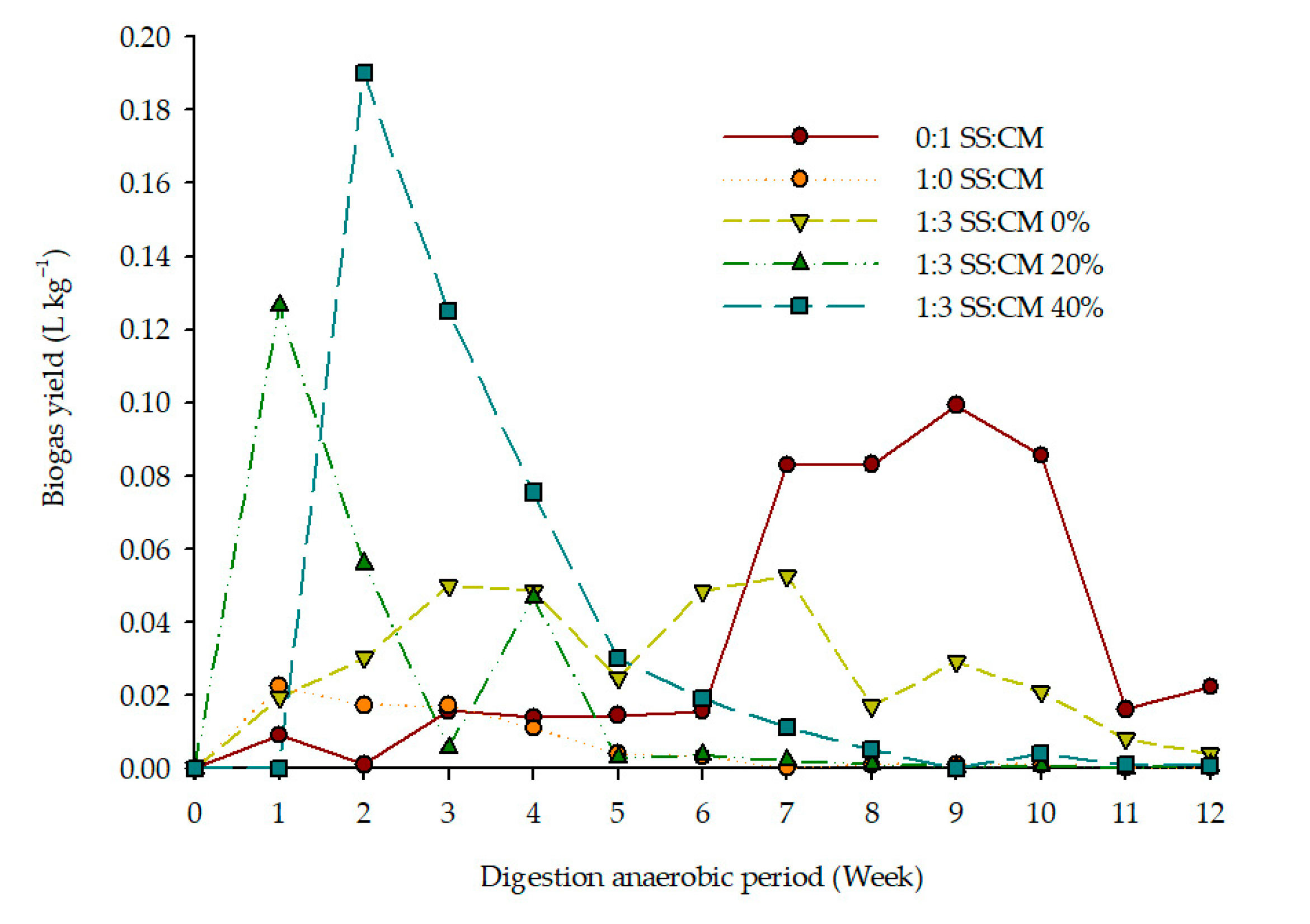
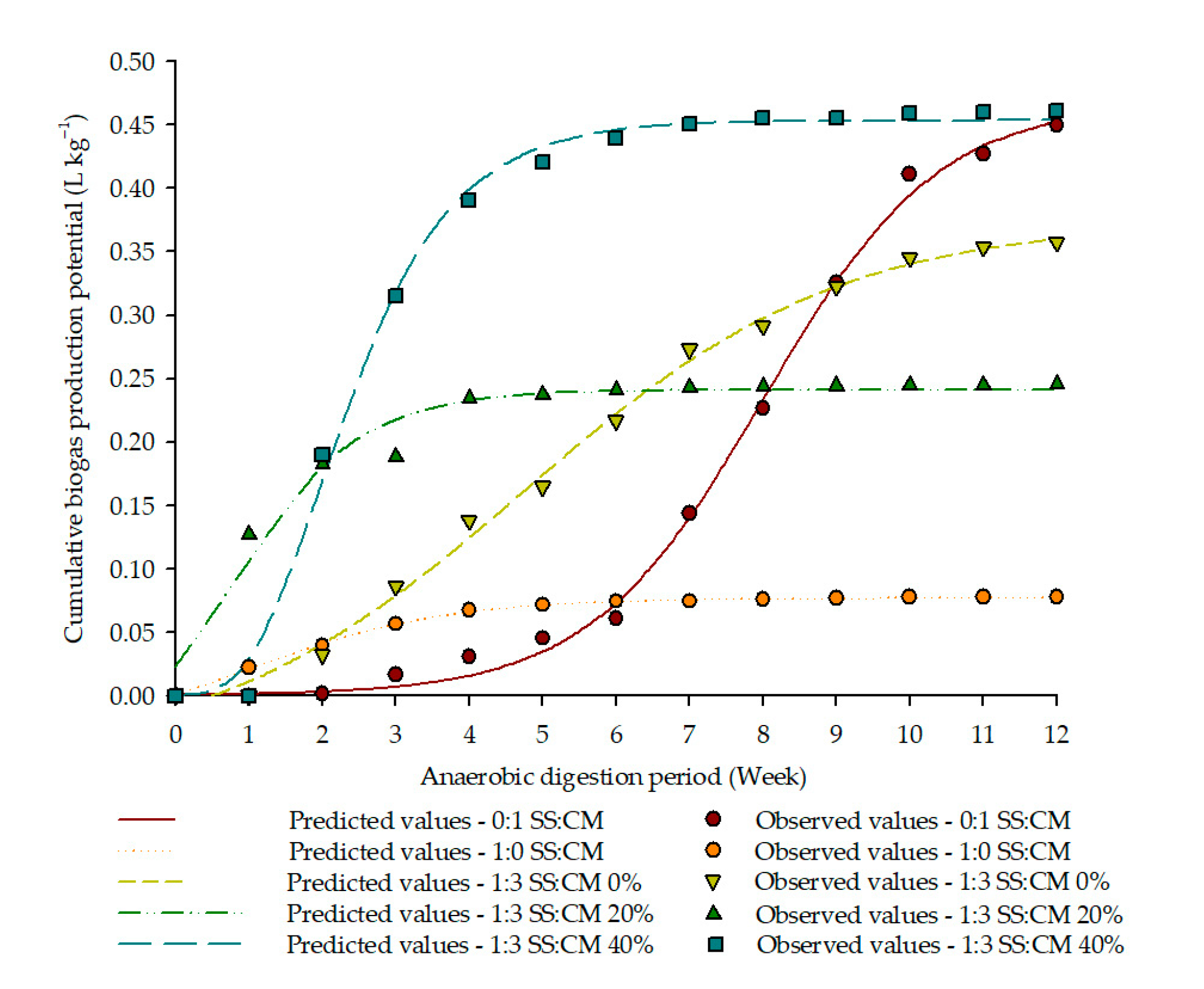
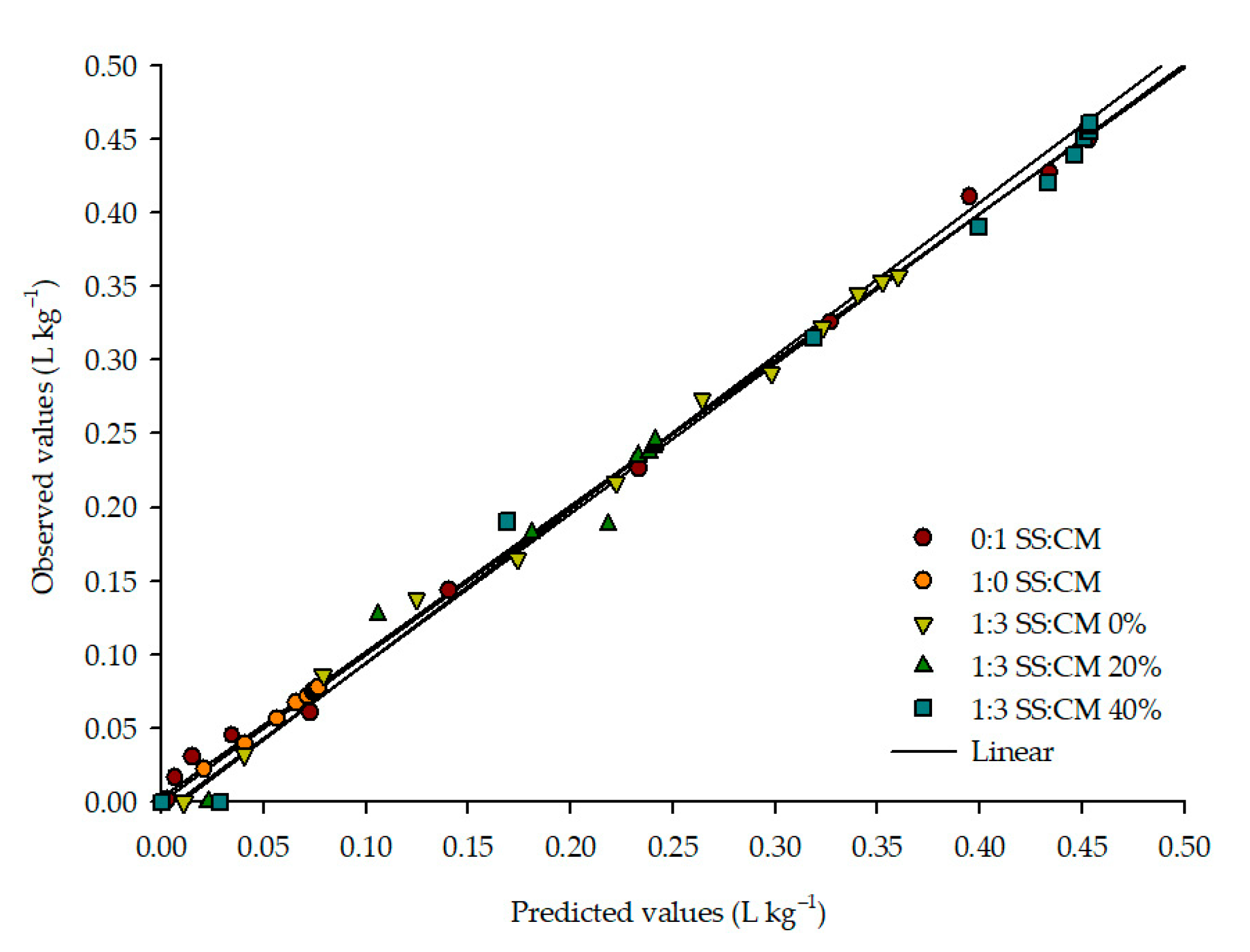
3.3. Biogas Yield
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Anaerobic digestion |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| APHA | American Public Health Association |
| CH4 | Methane |
| CM | Cattle manure |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide |
| CoAD | Anaerobic mono-digestion |
| COD | Chemical oxygen demand |
| CONAMA | National Environmental Council |
| D | Digestate |
| GHG | Greenhouse gas |
| H2S | Hydrogen sulfide |
| L | Liters |
| L kg−1 | Liters per kilogram |
| LabGERAR | Laboratory of the Renewable and Alternative Rural Energy Group |
| MoAD | Anaerobic mono-digestion |
| NH3 | Ammonia |
| N-NO3 | Total nitrogen–nitrate |
| OC | Onset of combustion |
| P | Mean relative error |
| PP | Peak production |
| R2 | Adjusted coefficient of determination |
| RMSD | Root mean square deviation |
| S | Substrate |
| SDGs | Sustainable Development Goals |
| SE | Standard error of the estimate |
| SS | Sewage sludge |
| STP | Sewage treatment plant |
| TA | Total alkalinity |
| TS | Total solids |
| UFRRJ | Federal Rural University of Rio de Janeiro |
| VFA | Volatile fatty acids |
| VTS | Volatile total solids |
References
- Silveira, A.R.R.; Nadaleti, W.C.; Przybyla, G.; Filho, P.B. Potential Use of Methane and Syngas from Residues Generated in Rice Industries of Pelotas, Rio Grande Do Sul: Thermal and Electrical Energy. Renew. Energy 2019, 134, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, B.C.; Santos, N.D.S.A.; Hanriot, V.M.; Sandoval, O.R.; Huebner, R. Energy Conversion of Biogas from Livestock Manure to Electricity Energy Using a Stirling Engine. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2022, 15, 100224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fang, J.; Tong, X.; Huan, C.; Ji, G.; Zeng, Y.; Xu, L.; Yan, Z. Change to Biogas Production in Solid-State Anaerobic Digestion Using Rice Straw as Substrates at Different Temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 293, 122066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xing, Z.; Zeng, L.; Peng, C.; Shi, H.; Cheng, J.J.; Zhang, Q. Anaerobic Codigestion of Excess Sludge with Chicken Manure with a Focus on Methane Yield and Digestate Dewaterability. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 19, 101127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Pradhan, N. Anaerobic Mono-Digestion and Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Mixed Sewage Sludge: A Comparative Analysis of Metabolic Patterns and Taxonomic Profiles. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 489, 151397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Wu, M.; Bao, W.; Wang, H. Performance of a Mixed Inoculum of Sludge and Pit Mud for Short and Medium-Chain Fatty Acids Production: Insight into Key Microbiome and Functional Potential in Anaerobic Fermentation Inoculum. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 466, 143142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niya, B.; Yaakoubi, K.; Azaroual, S.; Beraich, F.; Arouch, M.; Meftah Kadmiri, I. Anaerobic Digestion of Agricultural Waste Using Microbial Inocula: Performance and Characterization of Bacterial Communities Using 16S rRNA Sequencing Approach. Energies 2023, 16, 3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quelal, O.M.; Pilamunga Hurtado, D. Anaerobic Fermentation of Slaughterhouse Waste—Codigestion with Wheat Straw to Determine Methane Biochemical Potential and Kinetic Analysis. Fermentation 2023, 9, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usevičiūtė, L.; Januševičius, T.; Danila, V.; Mažeikienė, A.; Zagorskis, A.; Pranskevičius, M.; Marčiulaitienė, E. Performance and Kinetics of Anaerobic Digestion of Sewage Sludge Amended with Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles, Analyzed Using Sigmoidal Models. Energies 2025, 18, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Barros, R.; Lora, E.; Santos, I.; Ribeiro, E.; de Freitas, J.V.; Crispim, A. Study on Preliminary Economic Availability of Electric Energy Use from Drying Bed Sludge by Biogas from Anaerobic Digestion and Incineration in Brazil. Clean. Waste Syst. 2023, 6, 100117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, M.; Chandel, M.K. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Sewage Sludge and Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste: Focus on Mix Ratio Optimization and Synergistic Effects. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nindhia, T.S.; Bidura, I.G.N.G.; Sampurna, I.P.; Nindhia, T.G.T. Utilization of Continuous Anaerobic Digesters for Processing Cattle Dung and Cabbage (Brassica Oleracea) Waste. Fermentation 2025, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giwa, A.S.; Maurice, N.J.; Zelong, W.; Claire, M.J.; Vakili, M.; Mabi, A.; Liu, B.; Lv, F.; Memon, A.G. Advancing Resource Recovery from Sewage Sludge with IoT-Based Bioleaching and Anaerobic Digestion Techniques. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paes, J.L.; Guimarães, C.G.; Gomes, A.D.S.; Valadão, R.C.; Cecchin, D.; Menino, R. Circularity Between Aquaponics and Anaerobic Digestion for Energy Generation. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paes, J.L.; Alves, T.B.S.; Silva, L.D.B.D.; Marques, A.D.S.; Dias, V.R.S. Use of inoculum in biodigesters with cattle manure under conventional and organic production systems. Eng. Agríc. 2020, 40, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, B.C.; Paes, J.L.; Antunes, B.M.S.; Cunha, J.P.B.; Dos Santos, P.T.; Bergossi, A.S. Thermal energy from biogas generated from cattle manure and sewage sludge. Theor. Appl. Eng. 2020, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freepik Company S.L.—Flaticon. Available online: https://www.flaticon.com (accessed on 24 January 2025).
- BRASIL. Ministério do Meio Ambiente. Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente. Resolução CONAMA nº 375. Define critérios e procedimentos para o uso agrícola de lodos de esgoto gerados em estações de tratamento de esgoto sanitário e seus produtos derivados. Diário Oficial da República Federativa do Brasil: Brasília, DF, ano 2006, n. 167, p. 141–146, 30 ago. 2006. Available online: https://conama.mma.gov.br/index.php?option=com_sisconama&task=documento.download&id=22347 (accessed on 24 January 2025).
- American Public Health Association (APHA); American Water Works Association (AWWA); Water Environment Federation (WEF). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 24th ed.; APHA Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- AlfaKit LTDA. Available online: https://alfakit.com.br/ (accessed on 4 May 2025).
- Ferreira, D.F. SISVAR: A computer analysis system to fixed effects split plot type designs. Rev. Bras. Biom. 2019, 37, 529–535. Available online: https://doi.org/10.28951/rbb.v37i4.450 (accessed on 24 January 2025). [CrossRef]
- Grafiti LLC. Available online: https://grafiti.com/sigmaplot-v16/ (accessed on 4 May 2025).
- Mofatto, P.M.B.; Cosenza, A.; Trapani, D.; Mannina, G. Investigation of intermittent aeration and oxic settling anaerobic process combination for nitrogen removal and sewage sludge reduction. Chemosphere 2024, 363, 142877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacca, L.A.M.; Teleken, J.G.; Oliveira, E.C.L. Co-digestão anaeróbia de substratos suínos e bovinos em diferentes condições operacionais. In Open Science Research VIII; Científica Digital, E., Ed.; Editora Científica Digital, 2022; pp. 1096–1109. Available online: https://www.editoracientifica.com.br/books/chapter/221111099 (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Beschkov, V.N.; Angelov, I.K. Volatile Fatty Acid Production vs. Methane and Hydrogen in Anaerobic Digestion. Fermentation 2025, 11, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, B.P.; Lag-Brotons, A.J.; Ezemonye, L.I.; Semple, K.T.; Martin, A.D. Development of Mass-Conserving Atomistic Mathematical Model for Batch Anaerobic Digestion: Framework and Limitations. Fermentation 2024, 10, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Guo, X.; Zuo, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M. A comparative study of thermophilic and mesophilic anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and wheat straw: Process stability and microbial community structure shifts. Waste Manag. 2018, 75, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayoud, S.; Derbal, K.; Panico, A.; Pontoni, L.; Fabbricino, M.; Pirozzi, F.; Benalia, A. The Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide on Biogas and Methane Produced from Batch Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Spent Coffee Grounds. Fermentation 2025, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo García, P.; Fernández-Rodríguez, M.J.; Borja, R.; Mancilla-Leytón, J.M.; de la Lama-Calvente, D. Research Trends in the Recovery of By-Products from Organic Waste Treated by Anaerobic Digestion: A 30-Year Bibliometric Analysis. Fermentation 2024, 10, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuliarti, R.; Khambali, K.; Rusmiati, R. Risk analysis of exposure to NH3 And H2S gas to workers in the small industrial environment of magetan regency in 2021. Int. J. Adv. Health Sci. Technol. 2022, 2, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.C.; Balbino, M.V.; Viana, L.S.; Farias, N.D.S.N.; XAVIER, M.; Ramos, W.Q.; Antonio, J.O.S.É. Estudo comparativo de biógas produzido com dois tipos de resíduos animais. Rev. Bras. De Energ. Renov. 2018, 7, 406–422. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, A.P.M.D.; Guimarães, M.D.O. A utilização de biogás como estratégia sustentável para a produção de energia: Um estudo bibliográfico. Rease 2022, 8, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonatto, I.D.C.; Moreira, A.J.G.; Restrepo, J.J.B.; Franco, D.; Castilhos Junior, A.B.D. Influência de diferentes tipos de nanopartículas de prata na biodegradação da fração orgânica de resíduos sólidos urbanos. Eng. Sanit. Ambient. 2021, 26, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latinwo, G.K.; Agarry, S.E. Modelling the kinetics of biogas production from mesophilic anaerobic co-digestion of cow dung with plantain peels. Int. J. Renew. Energy Dev. 2015, 4, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franqueto, R.; Silva, J.D.; Starick, E.K.; Jacinto, C.F.S. Anaerobic codigestion of bovine manure and banana tree leaf: The effect of temperature variability on biogas yield in different proportions of waste. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2020, 22, 1444–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumardiono, S.; Jos, B.; Dewanti, A.A.E.; Mahendra, I.; Cahyono, H. Biogas production from coffee pulp and chicken feathers using liquid- and solid-state anaerobic digestions. Energies 2021, 14, 4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Model | Equation | |
|---|---|---|
| Boltzmann Sigmoidal | (1) | |
| Gompertz | (2) | |
| Logistic | (3) |
| Ratio | TS (%) | Removal Efficiency (%) | VTS (%) | Removal Efficiency (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | D | S | D | |||
| 0:1 SS:CM | 13.0 Aa | 10.6 Ba | 18.5 | 11.0 Aa | 7.9 Ba | 28.2 |
| 1:0 SS:CM | 4.6 Ac | 3.3 Bc | 28.3 | 2.6 Ac | 2.4 Bd | 7.7 |
| 1:3 SS:CM—0% | 9.4 Ab | 6.0 Bb | 36.2 | 7.9 Ab | 4.8 Bbc | 39.2 |
| 1:3 SS:CM—20% | 10.7 Ab | 7.5 Bb | 29.9 | 8.6 Ab | 5.7 Bb | 33.7 |
| 1:3 SS:CM—40% | 10.9 Ab | 6.5 Bb | 40.4 | 7.7 Ab | 4.3 Bc | 44.2 |
| Ratio | COD (mg L−1) | Removal Efficiency (%) | N-NO3 (mg L−1) | Removal Efficiency (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | D | S | D | |||
| 0:1 SS:CM | 14,296 Aa | 13,200 Ba | 7.7 | 17.4 Ab | 2.7 Ba | 84.5 |
| 1:0 SS:CM | 7321 Ac | 3146 Be | 57.0 | 30.0 Aa | 2.5 Ba | 91.7 |
| 1:3 SS:CM—0% | 12,746 Ab | 11,679 Bb | 8.4 | 2.5 Ae | 0.9 Bb | 64.0 |
| 1:3 SS:CM—20% | 13,059 Ab | 8900 Bd | 31.8 | 5.8 Ad | 1.1 Bb | 81.0 |
| 1:3 SS:CM—40% | 11,600 Ab | 9921 Bc | 14.5 | 10.0 Ac | 1.5 Bab | 85.0 |
| Ratio | pH | TA (gCaCO3 L−1) | VFA (g eq HAc L−1) | VFA/TA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | D | S | D | S | D | S | D | |
| 0:1 SS:CM | 8.0 Ab | 7.6 Bb | 5.20Aa | 4.73 Bb | 4.56 Bc | 4.88 Aa | 0.88 Ac | 1.03 Ba |
| 1:0 SS:CM | 6.7 Bd | 8.2 Aa | 2.00 Bc | 3.00 Ac | 8.16 Aa | 2.08 Bc | 4.08 Aa | 0.69 Bb |
| 1:3 SS:CM—0% | 8.4 Aa | 7.7 Bb | 3.33 Bb | 7.00 Aa | 5.76 Ab | 3.52 Bb | 1.73 Ab | 0.50 Bc |
| 1:3 SS:CM—20% | 7.4 Ac | 7.6 Ab | 4.00 Bb | 5.33 Ab | 5.28 Ab | 4.96 Ba | 1.32 Ab | 0.93 Ba |
| 1:3 SS:CM—40% | 7.4 Ac | 7.6 Ab | 3.00 Bb | 5.60 Ab | 5.56 Ab | 5.24 Ba | 1.85 Ab | 0.94 Ba |
| Ratio | Model | R2 (%) | P (%) | SE (Decimal) | RMSD (Decimal) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0:1 SS:CM | Boltzmann Sigmoidal | 0.9971 | 10.59 | 0.01035 | 0.00845 |
| Gompertz | 0.9913 | 23.43 | 0.01875 | 0.01531 | |
| Logistic | 0.9970 | 8.74 | 0.01100 | 0.00898 | |
| 1:0 SS:CM | Boltzmann Sigmoidal | 0.9983 | 0.64 | 0.00111 | 0.00090 |
| Gompertz | 0.9952 | 0.71 | 0.00194 | 0.00158 | |
| Logistic | 0.9867 | 1.19 | 0.00323 | 0.00264 | |
| 1:3 SS:CM—0% | Boltzmann Sigmoidal | 0.9952 | 2.85 | 0.01005 | 0.00820 |
| Gompertz | 0.9955 | 3.40 | 0.01022 | 0.00834 | |
| Logistic | 0.9897 | 2.64 | 0.01553 | 0.01268 | |
| 1:3 SS:CM—20% | Boltzmann Sigmoidal | Did not converge | - | - | - |
| Gompertz | 0.9622 | 2.10 | 0.01555 | 0.01270 | |
| Logistic | 0.9369 | 1.04 | 0.02013 | 0.01643 | |
| 1:3 SS:CM—40% | Boltzmann Sigmoidal | 0.9877 | 1.33 | 0.02023 | 0.01652 |
| Gompertz | 0.9941 | 1.15 | 0.01475 | 0.01204 | |
| Logistic | 0.9835 | 1.80 | 0.02467 | 0.02015 |
| Ratio | Model | Ymax (L kg−1) | µmax (L (kg Week)−1) | Λ (Week) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0:1 SS:CM | Logistic | 0.4691 | 0.8418 | 8.0114 |
| 1:0 SS:CM | Boltzmann Sigmoidal | 0.0770 | 1.3675 | 0.8959 |
| 1:3 SS:CM—0% | Boltzmann Sigmoidal | 0.3738 | 2.1343 | 4.7371 |
| 1:3 SS:CM—20% | Gompertz | 0.2413 | 1.0514 | 0.8168 |
| 1:3 SS:CM—40% | Gompertz | 0.4538 | 1.0263 | 1.9866 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinto, C.C.; Paes, J.L.; Gomes, A.d.S.; Cecchin, D.; Oliva, I.F.; Valadão, R.C.; Sant’Anna, V.R.d.S. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Cattle Manure and Sewage Sludge Using Different Inoculum Proportions. Fermentation 2025, 11, 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11070373
Pinto CC, Paes JL, Gomes AdS, Cecchin D, Oliva IF, Valadão RC, Sant’Anna VRdS. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Cattle Manure and Sewage Sludge Using Different Inoculum Proportions. Fermentation. 2025; 11(7):373. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11070373
Chicago/Turabian StylePinto, Caroline Carvalho, Juliana Lobo Paes, Alexia de Sousa Gomes, Daiane Cecchin, Igor Ferreira Oliva, Romulo Cardoso Valadão, and Vânia Reis de Souza Sant’Anna. 2025. "Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Cattle Manure and Sewage Sludge Using Different Inoculum Proportions" Fermentation 11, no. 7: 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11070373
APA StylePinto, C. C., Paes, J. L., Gomes, A. d. S., Cecchin, D., Oliva, I. F., Valadão, R. C., & Sant’Anna, V. R. d. S. (2025). Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Cattle Manure and Sewage Sludge Using Different Inoculum Proportions. Fermentation, 11(7), 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11070373








