Microbial Dynamics and Volatile Compound Profiles in Artisanal Kefir During Storage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
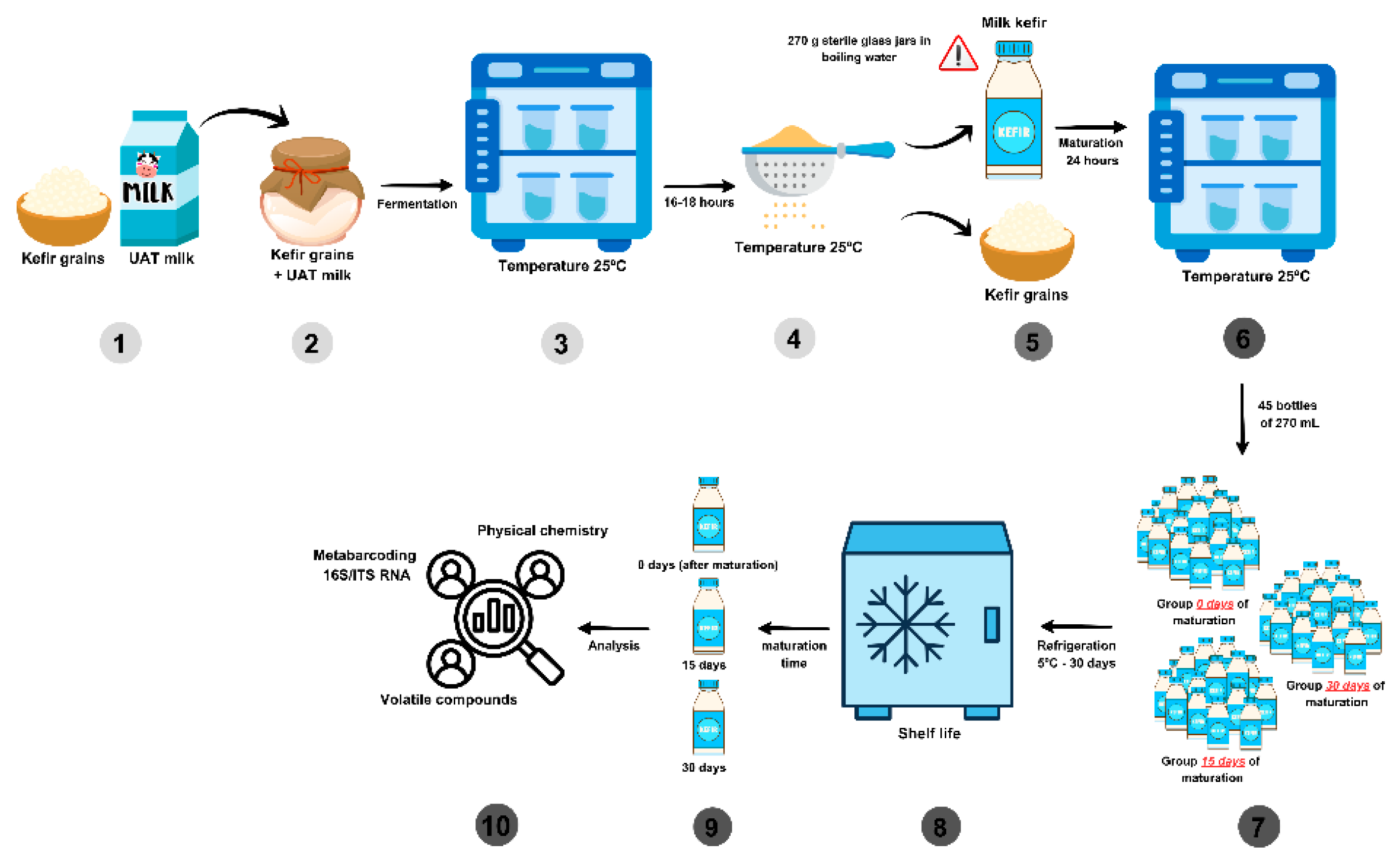
2.1. Raw Material and Kefir Production
2.2. Metabarcoding Analysis
2.3. Analysis of Volatile Compounds
2.4. Physico-Chemical Analysis of Kefir
2.4.1. pH Analysis
2.4.2. Lactic Acidity Analysis
2.4.3. Lactose Analysis
2.4.4. Ethanol Analysis
2.4.5. Fat Analysis
2.4.6. Ash Analysis
2.4.7. Protein Analysis
2.4.8. Moisture Analysis
2.4.9. Color Analysis
2.4.10. Total Solids Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
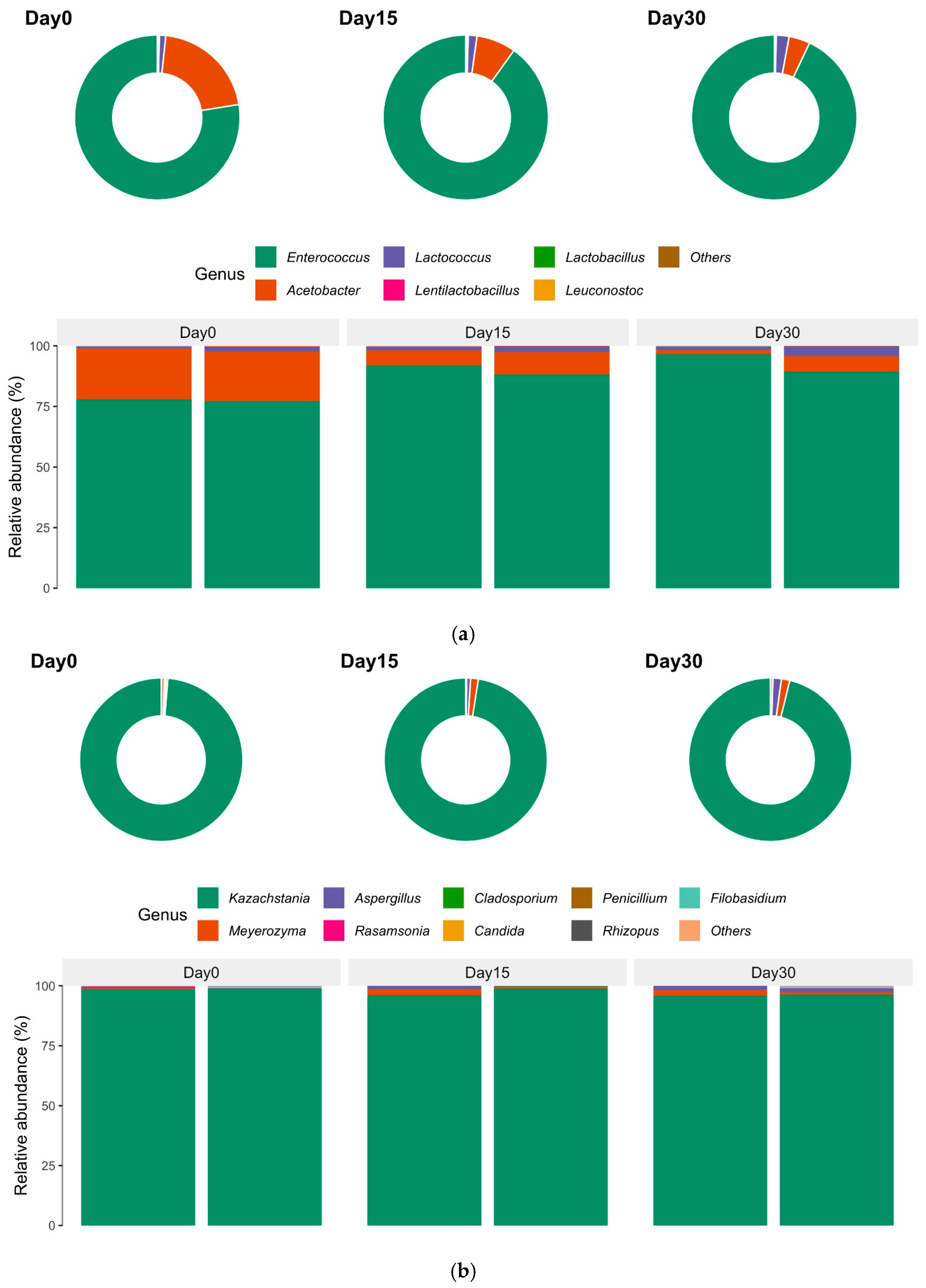
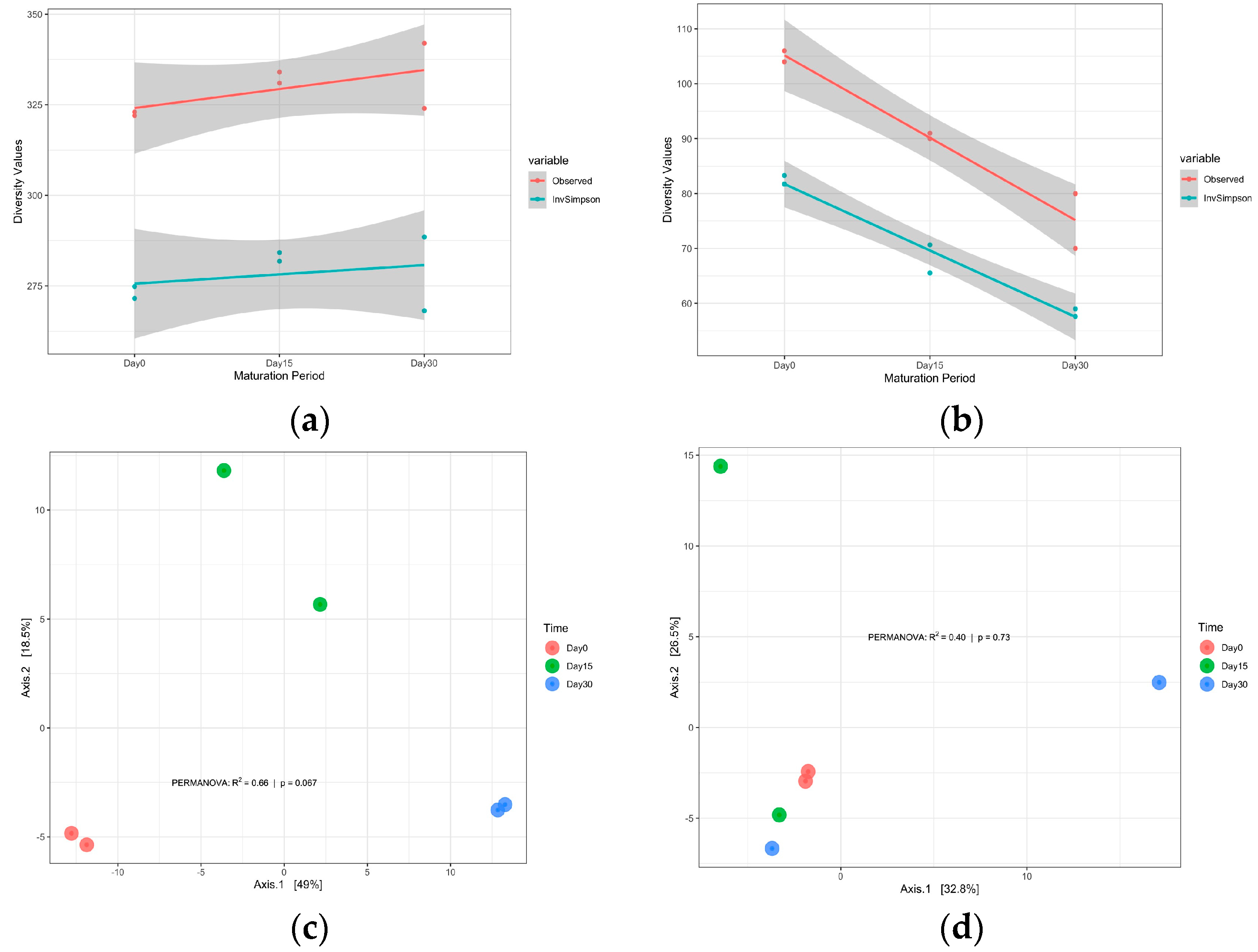
3.1. Microbial Distribution of Kefir Throughout Its Shelf Life
Alpha and Beta Diversity
3.2. Analysis of Kefir Volatiles
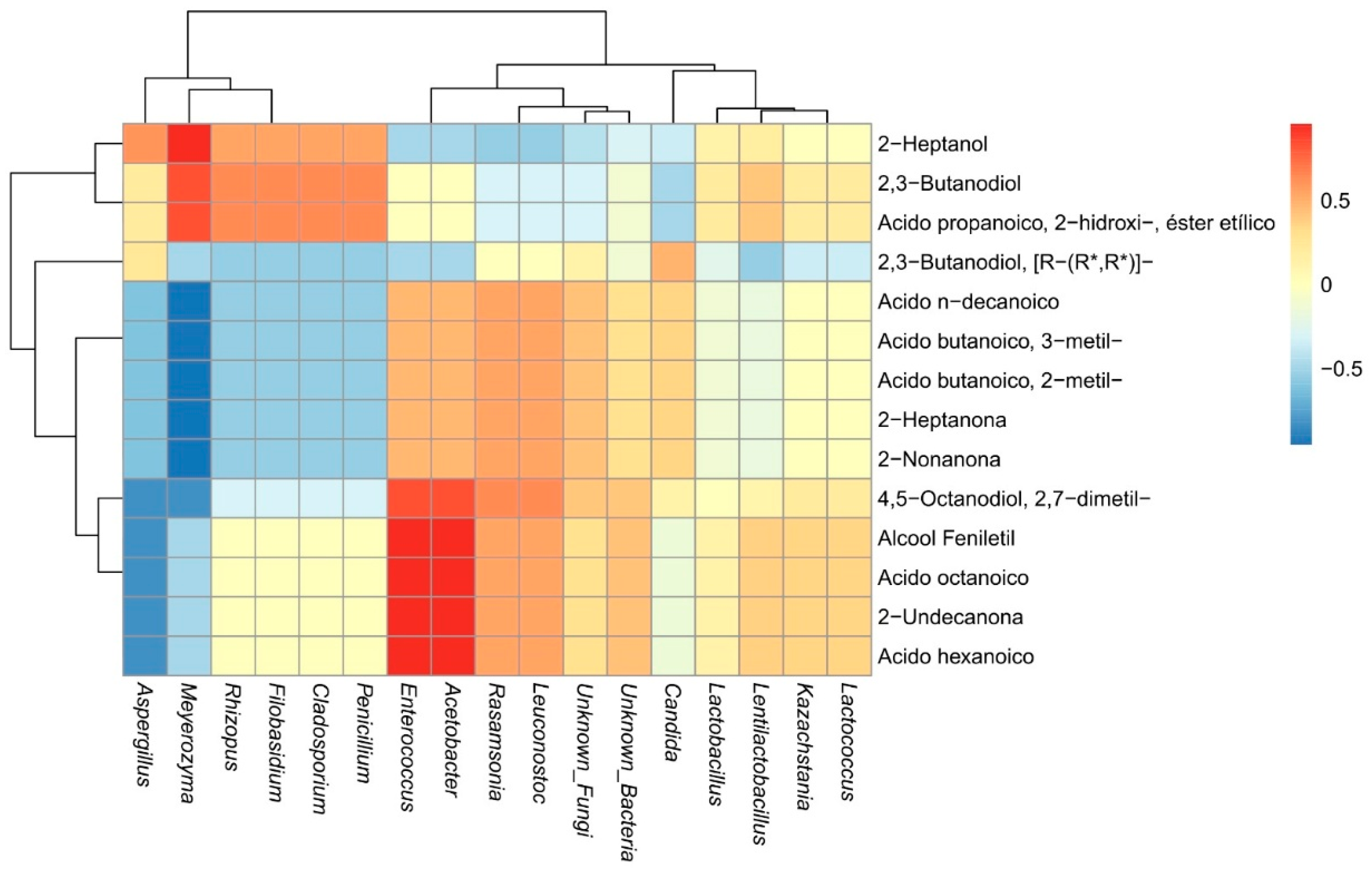
3.3. Correlation Between the Abundance of Microorganisms and Volatiles
3.4. Physical and Chemical Analysis of Kefir Throughout Its Shelf Life
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosa, D.D.; Dias, M.M.S.; Grześkowiak, L.M.; Reis, S.A.; Conceição, L.L.; Peluzio, M.D.C.G. Milk kefir: Nutritional, microbiological and health benefits. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2017, 30, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanirati, D.F.; Abatemarco, M.J.; Sandes, S.H.C.; Nicoli, J.R.; Nunes, Á.C.; Neumann, E. Selection of lactic acid bacteria from Brazilian kefir grains for potential use as starter or probiotic cultures. Anaerobe 2015, 32, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, B.I. Nutritional management of metabolic endotoxemia: A clinical review. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2017, 23, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira Leite, A.M.; Miguel, M.A.; Peixoto, R.S.; Rosado, A.S.; Silva, J.T.; Paschoalin, V.M. Microbiological, technological and therapeutic properties of kefir: A natural probiotic beverage. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2013, 44, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourrie, B.C.; Willing, B.P.; Cotter, P.D. The microbiota and health promoting characteristics of the fermented beverage kefir. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 196946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopitz-Otsoa, F.; Rementeria, A.; Elguezabal, N.; Garaizar, J. Kefir: Una comunidad simbiótica de bacterias y levaduras con propiedades saludables. Iberoam. De Micol. 2006, 23, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengoa, A.A.; Iraporda, C.; Garrote, G.L.; Abraham, A.G. Kefir micro-organisms: Their role in grain assembly and health properties of fermented milk. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 686–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, L.; Yaoming, C.; Xiangzhen, L.; Minjie, Y. Microeco: An R package for data mining in microbial community ecology. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2021, 97, fiaa255. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Li, B. Chemical and microbiological characteristics of kefir grains and their fermented dairy products: A review. Cogent Food Agric. 2016, 2, 1272152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, C.; Osimani, A.; Milanović, V.; Aquilanti, L.; De Filippis, F.; Stellato, G.; Di Mauro, S.; Turchetti, B.; Buzzini, P.; Ercolini, D.; et al. Bacteria and yeast microbiota in milk kefir grains from different Italian regions. Food Microbiol. 2015, 49, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farnworth, E.R.; Mainville, I. Kefir: A fermented milk product. Handb. Fermented Funct. Foods 2003, 2, 89–127. [Google Scholar]
- Santini, G.; Bonazza, F.; Pucciarelli, S.; Polidori, P.; Ricciutelli, M.; Klimanova, Y.; Silvi, S.; Polzonetti, V.; Vincenzetti, S. Proteomic characterization of kefir milk by two-dimensional electrophoresis followed by mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 55, e4635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghedini, T.G.M.; Bento, L.V.; Mioto, L.S.; de Oliveira, L.C.; Ambrosio, M.A.L.V.; Martins, C.H.G.; Magrin, T.F. Qualidade microbiológica do kefir. Braz. J. Dev. 2020, 6, 4336–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, C.M.; Haubert, L.; Macagnan, F.T.; Vieira, M.A. Estudo das Propriedades e da Viabilidade Comercial de um Alimento Probiótico Funcional: Kefir; Instituto Federal de Santa Catarina: Florianópolis, Brazil, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Diário das Leis—Regulamento Técnico—Leites Fermentados. Adota o Regulamento Técnico de Identidade e Qualidade de Leites Fermentados. Available online: https://www.cidasc.sc.gov.br/inspecao/files/2019/09/INSTRU%C3%87%C3%83O-NORMATIVA-N-46-de-23-de-outubro-de-2007-Leites-Fermentados.pdf (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Ströher, J.A.; da Silva, L.D.F.F.; Lehn, D.N.; Bresciani, L.; Rama, G.R.; de Souza, E.M.; Wilsmann, L.M.; Salazar, M.M. A influência das boas práticas de fabricação nos atributos físico-químicos do kefir artesanal durante sua vida útil. Obs. De La Econ. Latinoam. 2024, 22, e8459. [Google Scholar]
- Araujo, J.; Ribeiro, N.; Bezerra, K.; Landim, L. Desenvolvimento de kefir em leite de coco babaçu. Res. Soc. Dev. 2020, 9, e3559119891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, F.D.O.; Silva, M.; Sousa, P.B.; Freitas, T.K.T.; Silva, D.J.S.; Araújo, R. Avaliação físico-química de uma bebida à base de kefir saborizada com pequi. Braz. J. Dev. 2020, 6, 10755–10762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenorio-Salgado, S.; Castelán-Sánchez, H.G.; Dávila-Ramos, S.; Huerta-Saquero, A.; Rodríguez-Morales, S.; Merino-Pérez, E.; Roa de la Fuente, L.F.; Solis-Pereira, S.E.; Pérez-Rueda, E.; Lizama-Uc, G. Metagenomic analysis and antimicrobial activity of two fermented milk kefir samples. Microbiol. Open 2021, 10, e1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Yang, C.; Jin, H.; Kwok, L.-Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, H. Metagenomic features of traditional fermented milk products. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 155, 112945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejati, F.; Junne, S.; Kurreck, J.; Neubauer, P. Quantification of Major Bacteria and Yeast Species in Kefir Consortia by Multiplex TaqMan qPCR. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellanos-Rozo, J.; Pérez Pulido, R.; Grande, M.J.; Lucas, R.; Gálvez, A. Analysis of the Bacterial Diversity of Paipa Cheese (a Traditional Raw Cow’s Milk Cheese from Colombia) by High-Throughput Sequencing. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamilari, E.; Anagnostopoulos, D.A.; Papademas, P.; Kamilaris, A.; Tsaltas, D. Characterizing Halloumi cheese’s bacterial communities through metagenomic analysis. LWT 2020, 126, 109298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresciani, L.; Ströher, J.A.; da Silva, L.D.F.F.; Lehn, D.N.; Rama, G.R.; de Souza, E.M.; Salazar, M.M. Kefir artesanal: Análise dos atributos de qualidade em relação aos requisitos da legislação brasileira. Obs. De La Econ. Latinoam. 2024, 22, e8101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, S.; Chen, M. Microbiological study of lactic acid bacteria in kefir grains by culture-dependent and culture-independent methods. Food Microbiol. 2008, 25, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarbati, A.; Ciani, M.; Canonico, L.; Galli, E.; Comitini, F. Exploitation of yeasts with probiotic traits for kefir production: Effectiveness of the microbial consortium. Fermentation 2021, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Huntley, J.; Fierer, N.; Owens, S.M.; Betley, J.; Fraser, L.; Bauer, M.; et al. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J. 2012, 6, 621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.D.; Lee, S.B.; Taylor, J.W. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Gardes, M.; Bruns, T.D. ITS primers with enhanced specificity for basidiomycetes—Application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Mol. Ecol. 1993, 2, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, W.; Hyde, E.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Ackermann, G.; Humphrey, G.; Alma, E.; Jack, G.; Jansson, J.; Caporaso, J.; Fuhrman, J.; et al. Improved bacterial 16S rRNA gene (V4 and V4-5) and fungal internal transcribed spacer marker gene primers for microbial community surveys. mSystems 2016, 1, e00009-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2023, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardi, G.; Vendruscolo, R.G.; dos Santos Ferrão, T.; Barin, J.S.; Cichoski, A.J.; Wagner, R. Vinho de Geléia de Palmeira (Butia odorata): Caracterização de Compostos Voláteis Responsáveis pelo Aroma. Métodos Analíticos De Aliment. 2014, 71982–71991. Available online: https://repositorio.ufsm.br/handle/1/22890 (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento. Instrução Normativa n.° 68 de 12 de dezembro de 2006 do Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento. Diário Oficial da União. Estabelece os Métodos Analíticos Oficiais Físico-Químicos para Controle de Leite e Produtos Lácteos. Available online: https://wp.ufpel.edu.br/inspleite/files/2016/03/Instru%C3%A7%C3%A3o-normativa-n%C2%B0-68-de-12-dezembro-de-2006.pdf (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Miller, G.L. Use of Dinitrosalicylic Acid Reagent for Determination of Reducing Sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanin, G.M.; Moraes, F.F. Tecnologia de Imobilização de Células e Enzimas Aplicada à Produção de Álcool de biomassas. Relatório 1987, 2, 315–321. [Google Scholar]
- Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e do Abastecimento. Instrução Normativa n.° 24, de 8 de Setembro de 2005. Padrões Oficiais para Análise Físico-Química de Bebidas e Vinagre. Diário Oficial da União, Brasília, 20 set. 2005. Available online: https://www.gov.br/agricultura/pt-br/assuntos/riscos-seguro/seguro-rural/documentos-seguro-rural/bev-lanagro-rs.pdf (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Granjeiro, J.M.; Oliveira, R.C.; Bustos-Valenzuela, J.C.; Sogayar, M.C.; Taga, R. Bone morphogenetic proteins: From structure to clinical use. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2005, 38, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castanheira, A.C.G. Controle de Qualidade de leite e derivados. In Manual Básico Comentado, 2nd ed.; Cap-Lab Indústria e Comércio Ltda: São Paulo, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Valero-Mora, P.M. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 35, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinno, A. Nonparametric pairwise multiple comparisons in independent groups using dunns test. Stata J. 2015, 15, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, P. Vegan, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, C.M.A.P.; Huch, M.; Abriouel, H.; Holzapfel, W.; Gálvez, A. Enterococci as probiotics and their implications in food safety. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 151, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraffa, G. Functionality of enterococci in dairy products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 88, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, M.R.; Blandón, L.M.; Vandenberghe, L.P.; Rodrigues, C.; Castro, G.R.; Thomaz-Soccol, V.; Soccol, C.R. Milk kefir: Composition, microbial cultures, biological activities, and related products. Front. Microbiol. 2005, 6, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsigkrimani, M.; Panagiotarea, K.; Paramithiotis, S.; Bosnea, L.; Pappa, E.; Drosinos, E.H.; Mataragas, M. Microbial ecology of sheep milk, artisanal feta, and kefalograviera cheeses. Part II: Technological, safety, and probiotic attributes of lactic acid bacteria isolates. Foods 2022, 11, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Askri, T.; Yatim, M.; Sehli, Y.; Rahou, A.; Belhaj, A.; Castro, R.; Zouhair, R. Triagem e caracterização de novas cepas de Acetobacter fabarum e Acetobacter pasteurianus com alta tolerância ao etanol-termo e otimização da produção de ácido acético. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alraddadi, F.A.J.; Ross, T.; Powell, S.M. Evaluation of the microbial communities in kefir grains and kefir over time. Int. Dairy J. 2023, 136, 105490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindi, A.; Badsha, M.B.; Ünlü, G. Bacterial populations in international artisanal kefirs. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diosma, G.; Romanin, D.E.; Rey-Burusco, M.F.; Londero, A.; Garrote, G.L. Yeasts from kefir grains: Isolation, identification, and probiotic characterization. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardjan, T.; Mohar Lorbeg, P.; Rogelj, I.; Čanžek Majhenič, A. Characterization and stability of lactobacilli and yeast microbiota in kefir grains. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 2729–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulitz, A.; Stadie, J.; Wenning, M.; Ehrmann, M.A.; Vogel, R.F. The microbial diversity of water kefir. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 151, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, R.; Lee, S.; Bennett, J.W. Fungal volatile organic compounds and their role in ecosystems. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 3395–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pablo, A.G.; Balmori, V. Water Kefir Beverages and Probiotic Properties. In Natural Products in Beverages: Botany, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology and Processing; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Brasiel, P.G.A.; Medeiros, J.D.; Machado, A.B.F.; Ferreira, M.S.; Peluzio, M.C.G.; Luquetti, S.C.P.D. Microbial community dynamics of fermented kefir beverages changes over time. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2021, 74, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumarmono, J.; Kusuma, R.J.; Rahayu, N.; Sukarno, A.S.; Wulansari, P.D. Metagenomic analysis of the microbial community in kefir grains from different milk sources. Biodiversitas J. Biol. Divers. 2023, 24, 5302–5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamang, J.P.; Shin, D.-H.; Jung, S.-J.; Chae, S.-W. Functional properties of microorganisms in fermented foods. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamang, J.P.; Watanabe, K.; Holzapfel, W.H. Diversity of microorganisms in global fermented foods and beverages. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva Salas, M.; Mounier, J.; Valence, F.; Coton, M.; Thierry, A.; Coton, E. Antifungal Microbial Agents for Food Biopreservation—A Review. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savastano, M.L.; Pati, S.; Bevilacqua, A.; Corbo, M.R.; Rizzuti, A.; Pischetsrieder, M.; Losito, I. Influence of the production technology on kefir characteristics: Evaluation of microbiological aspects and profiling of phosphopeptides by LC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS. Food Res. Int. 2020, 129, 108853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarhir, S.T.; Amanpour, A.; Bouseta, A.; Selli, S. Fingerprint of aroma-active compounds and odor activity values in a traditional Moroccan fermented butter “Smen” using GC–MS–Olfactometry. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 96, 103761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helinck, S.; Le Bars, D.; Moreau, D.; Yvom, M. Ability of thermophilic lactic acid bacteria to produce aroma compounds from amino acids. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 3855–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randazzo, W.; Corona, O.; Guarcello, R. Development of new non-dairy beverages from Mediterranean fruit juices fermented with water kefir microorganisms. Food Microbiol. 2016, 54, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carunchia-Whetstine, M.E.; Karagul-Yuceer, Y.; Avsar, Y.K.; Drake, M.A. Identification and quantifcation of character aroma components in fresh Chevre-style goat cheese. J. Food Sci. 2004, 68, 2441–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Teng, K.; Cao, Y.; Shi, W.; Xuan, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, J. Effects of Lactobacillus hilgardii 60TS-2, with or without homofermentative Lactobacillus plantarum B90, on the aerobic stability, fermentation quality and microbial community dynamics in sugarcane top silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 312, 123600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Dong, N.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, B.; Wang, B.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, S. Metabolic profiling of wort fermented with water kefir grains and its effect on wort quality. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, A.M.; Crispie, F.; Kilcawley, K.; O’Sullivan, O.; O’Sullivan, M.G.; Claesson, M.J.; Cotter, P.D. Microbial succession and flavor production in the fermented dairy beverage kefir. Msystems 2016, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraud, S.; Rees, E.L.; Mahenthiralingam, E.; Russell, A.D.; Maillard, J.Y. Aromatic alcohols and their effect on Gram-negative bacteria, cocci and mycobacteria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 51, 1435–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guangsen, T.; Xiang, L.; Jiahu, G. Microbial diversity and volatile metabolites of kefir prepared by different milk types. CyTA-J. Food 2021, 19, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H. Volatile flavor compounds in yogurt: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2010, 50, 938–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duran, F.E.; Özdemir, N.; Güneşer, O.; Kök-Taş, T. Prominent strains of kefir grains in the formation of volatile compound profile in milk medium; the role of Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens subsp. kefiranofaciens, Lentilactobacillus kefiri and Lentilactobacillus parakefiri. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2022, 248, 975–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamini, C.V.; Wolf, I.V.; Perotti, M.C.; Zalazar, C.A. Characterisation of biochemical changes during ripening in Argentinean sheep cheeses. Small Rumin. Res. 2010, 94, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majcher, M.A.; Myszka, K.; Gracka, A.; Grygier, A.; Jeleń, H.H. Key odorants of lazur, a polish mold-ripened cheese. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 66, 2443–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, Y. The efect of soluble saccharides on the activity of key enzymes linked to methyl ketone synthesis in Lactococcus lactis. CyTA-J. Food 2018, 16, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cagno, R.; Filannino, P.; Gobbetti, M. Lactic acid fermentation drives the optimal volatile favor-aroma profle of pomegranate juice. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 248, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, S.; Hao, G.; Yu, H.; Tian, H.; Zhao, G. Role of lactic acid bacteria on the yogurt favour: A review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, S316–S330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dertli, E.; Çon, A.H. Microbial diversity of traditional kefir grains and their role on kefir aroma. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 85, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, M. Microbiological profiles, physiochemical properties and volatile compounds of goat milk kefir fermented by reconstituted kefir grains. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 183, 114943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.D.; Wu, Z.; Peng, T.; Zeng, X.Q.; Li, H. Volatile organic compounds profile during milk fermentation by Lactobacillus pentosus and correlations between volatiles flavor and carbohydrate metabolism. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán-Guerrero, E.; Castro, R.; García-Moreno, M.V.; Rodríguez-Dodero, M.D.C.; Schwarz, M.; Guillén-Sánchez, D. Aroma of sherry products: A review. Foods 2021, 10, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO/WHO. Codex Alimentarius International Food Standards. In Codex Standard for Fermented Milks (Codex Stan CXS 243-2003) Codex Alimentarius; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2003; ISBN 5856420187. [Google Scholar]
- Barukčić Jurina, I.; Gracin, L.; Režek Jambrak, A.; Božanić, R. Comparison of chemical, rheological and sensory properties of kefir produced by kefir grains and commercial kefir starter. Mljekarstvo Časopis Za Unaprjeđenje Proizv. I Prerade Mlijeka 2017, 67, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, O.; Atalar, I.; Mortaş, M.; Dervisoglu, M. Rheological, textural, color and sensorial properties of kefir produced with buffalo milk using kefir grains and starter culture: A comparison with cows’ milk kefir. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2018, 71, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windayani, N.; Kurniati, T.; Listiawati, M. Psychochemical and organoleptic characteristics of colostrum kefir as antibacterial. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. IOP Publ. 2019, 1175, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilac, C.; Rodrigues, L.; Araújo, M.; Gomes, K.; De Souza Silva, C.; Silva, I.; Orsi, D. Physicochemical characterization and antibacterial activity of Brazilian artisanal milk kefir. Sci. Plena 2023, 19, 091501. [Google Scholar]
- Sainz, I.; Redondo-Solano, M.; Solano, G.; Ramírez, L. Effect of different kefir grains on the attributes of kefir produced with milk from Costa Rica. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, A.T.S. Análise Sensorial: Uma Ferramenta Analítica para Desenvolvimento de Produtos Alimentícios. Bachelor’s Thesis, Trabalho de Conclusão de Curso, Curso de Graduação em Nutrição do Centro Acadêmico de Vitória da Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Recife, Brazil, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, W.C.; De Oliveira Martins, A.D.; Júnior, S.M. Kefir: Características e benefícios. Aliment. Ciência Tecnol. E Meio Ambiente 2020, 1, 22–42. [Google Scholar]
- Vujičić, I.F.; Vulić, M.; Könyves, T. Assimilation of cholesterol in milk by kefir cultures. Biotechnol. Lett. 1992, 14, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, C.P.; Álvares, T.S.; Gomes, L.S.; Torres, A.G.; Paschoalin, V.M.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Kefir grains change fatty acid profile of milk during fermentation and storage. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, C.; Ferrocino, I.; Reale, A.; Sabbatini, R.; Milanović, V.; Alkić-Subašić, M.; Boscaino, F.; Aquilanti, L.; Pasquini, M.; Trombetta, M.F.; et al. Study of kefir drinks produced by backslopping method using kefir grains from Bosnia and Herzegovina: Microbial dynamics and volatilome profile. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter | 0 Days | 15 Days | 30 Days | Legal Parameter ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 4.40 a ± 0.01 | 4.32 a ± 0.01 | 4.25 a ± 0.02 | - |
| Titratable acidity (g lactic acid) | 0.87 a ± 0.02 | 0.92 a ± 0.05 | 0.95 a ± 0.05 | <1.0 |
| Lactose (g/100 g) | 4.01 a ± 0.01 | 4.05 a ± 0.01 | 4.03 a ± 0.01 | - |
| Ethanol (%) | <0.1 a ± 0.00 | <0.1 a ± 0.00 | <0.1 a ± 0.00 | 0.5 to 1.5 |
| Fat (g/100 g) | 2.65 a ± 0.05 | 2.65 a ± 0.00 | 2.60 a ± 0.00 | 0.5 to 5.9 |
| Ash (%) | 0.831 a ± 0.02 | 0.834 a ± 0.01 | 0.827 a ± 0.01 | - |
| Proteins (g/100 g) | 5.27 a ± 0.05 | 5.22 a ± 0.11 | 5.25 a ± 0.08 | Min. 2.9 |
| Humidity | 90.11a ± 0.38 | 89.30 a ± 0.47 | 89.22 a ± 0.63 | - |
| Color | Total Solids | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | L* | a* | b* | |
| Milk | 74.11 a ± 0.64 | −2.41 a ± 0.05 | 20.93 ± 0.33 | 12.24 a ± 0.11 |
| Grain | 77.19 a ± 0.22 | −0.85 a ± 2.28 | 21.76 a ± 0.07 | - |
| 0 days | 88.03 a ± 0.84 | −3.42 a ± 0.15 | 10.09 a ± 0.19 | 5.95 b ± 0.23 |
| 15 days | 86.45 a ± 0.86 | −3.40 a ± 0.17 | 9.57 a ± 0.60 | 5.65 b ± 0.18 |
| 30 days | 85.52 a ± 0.90 | −1.09 a ± 2.94 | 8.69 a ± 0.27 | 6.15 b ± 0.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ströher, J.A.; Oliveira, W.d.C.; Freitas, A.S.d.; Salazar, M.M.; Flôres, S.H.; Malheiros, P.d.S. Microbial Dynamics and Volatile Compound Profiles in Artisanal Kefir During Storage. Fermentation 2025, 11, 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11020105
Ströher JA, Oliveira WdC, Freitas ASd, Salazar MM, Flôres SH, Malheiros PdS. Microbial Dynamics and Volatile Compound Profiles in Artisanal Kefir During Storage. Fermentation. 2025; 11(2):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11020105
Chicago/Turabian StyleStröher, Jeferson Aloísio, Wemerson de Castro Oliveira, Anderson Santos de Freitas, Marcela Mendes Salazar, Simone Hickmann Flôres, and Patrícia da Silva Malheiros. 2025. "Microbial Dynamics and Volatile Compound Profiles in Artisanal Kefir During Storage" Fermentation 11, no. 2: 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11020105
APA StyleStröher, J. A., Oliveira, W. d. C., Freitas, A. S. d., Salazar, M. M., Flôres, S. H., & Malheiros, P. d. S. (2025). Microbial Dynamics and Volatile Compound Profiles in Artisanal Kefir During Storage. Fermentation, 11(2), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11020105







