Abstract
The aim of this study is to provide an overview of the specificities (milk characteristics, production process, ripening biochemistry, composition, and sensory properties) and novelties of the world-famous traditional cheeses of the Eastern Mediterranean (EM). The EM area is remarkably heterogeneous (11 countries—Egypt, Israel, Lebanon, Syria, Türkiye, Cyprus, Greece, Albania, Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Croatia) in terms of cheese production, but there are some common features that can be associated with EM which are connected to the difficult geoclimaticconditions (hilly terrain and hot summers). Cheesemakers resort to some preservation methods, such as high salt content (in white-brined cheeses), high total solids content (in hard cheeses), the use of hot water in the treatment of the curd (in pasta filata cheeses), the addition of some local herbs with antimicrobial properties, and the use of animal skin sacks for cheese ripening. Due to the high proportion of whey as a by-product, whey is traditionally used in EM for the production of whey cheeses. Preserving the production of traditional EM cheeses is critical to maintaining their cultural significance and meeting the demand of consumers interested in the provenance, craftsmanship, and nutritional value of these unique products.
1. Introduction
The Eastern Mediterranean (EM) area is characterised by hilly terrain and hot summers with irregular/small rainfall [1], which determines the habits of cheese-makers and the characteristics of the cheeses produced in this region. The EM borders three continents, including Africa, Asia, and Europe, and includes 11 countries (Egypt, Israel, Lebanon, Syria, Türkiye, Cyprus, Greece, Albania, Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Croatia; Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Eastern Mediterranean countries.
In general, the origins of traditional cheeses are linked to dietary and consumption habits, climate, relief, geographical location, botanical composition of natural meadows and pastures, breed, type of farming and the transfer of knowledge and experience in cheese production between generations [2]. The traditional cheeses in EM are made from milk from local breeds, as the specific pedoclimatic conditions of this region determine the type of animals kept for milk production. EM is suitable for keeping sheep and goats, which are usually kept in a nomadic or semi-nomadic system based on pastures and crop residues. Therefore, most cheeses in EM countries are made from sheep and goat milk, but due to the seasonality of milk production and the high demand for cheese, some cheeses are also made from cow milk [1]. In many cases, local cheese producers rely on the milk of local breeds that are particularly well adapted to the specific environment. In addition to the technology of cheese production, in many cases, the milk of local breeds determines the special characteristics of the cheeses produced along the EM. For example, the milk of many local sheep breeds is characterised by a unique quality suitable for cheese production, with a remarkably high total solids content and a high fat and protein content [3,4,5]. In addition, the pedoclimatic conditions also determine the botanical composition of the grass [1]. The Croatian indigenous Dalmatian Pramenka breed, for example, is kept on the natural pastures of the sub-Mediterranean karst area, where the main grazing community is Festuco-Koelerietum splendentis and Stipo-Salvetium officinalis. As a natural pasture, Festuco-Koelerietum splendentis is the most important pasture community within the sub-Mediterranean vegetation zone of the Dalmatian hinterland, as it consists of a whole range of high-quality pasture species [6]. Considering that in the EM region, dairy cattle are mainly kept under extensive or semi-extensive management on artificial, natural or semi-natural pastures [7], the effects of herd, year and season on the quality of milk of an indigenous breed in the EM area are remarkable [8,9]. The botanical composition of the pasture affects the organoleptic properties of the cheeses produced, particularly their flavour, especially when they are made from raw milk [10].
The area of EM is remarkably heterogeneous in terms of cheese production, but there are some common features that could be associated with EM. In general, cheeses produced in this area must withstand such unfavourable conditions previously mentioned. Therefore, cheesemakers resort to some strong preservation methods in cheese production, such as the use of high salt content (e.g., in white-brined cheeses [11,12]), the production of cheese with high total solids content (in hard cheeses) that can withstand higher ripening temperatures, e.g., up to 19 °C [5], the use of hot water in the treatment of the curd (in pasta filata cheeses [13]), the addition of some local herbs with probable antimicrobial properties [14], and the use of animal skin sacks for cheese ripening [2]. Due to the high proportion of whey produced during the manufacture of the above-mentioned cheeses, whey is traditionally used in EM for the production of whey cheeses [15].
Many EM cheeses are produced in quantities that meet local demand and needs, and some have become increasingly popular in other regions. For example, the Centre for Dairy Research, University of Wisconsin, USA, organized two short courses on EM cheeses entitled “Cheese and Fermented Milks from the Eastern Mediterranean” (2010) and “Sheep, Goat, and Mixed Milk Cheeses” (2018) to introduce EM cheeses and other dairy products to cheesemakers in Wisconsin and show them what differentiates EM cheeses from similar cheeses. The production of traditional cheeses can preserve the tradition of a country or region by preventing the extinction of traditional dairy products. This study aims to provide an overview of the specificities and novelties of the cheeses of the Eastern Mediterranean. This includes the existing knowledge of the milk characteristics, production process, ripening biochemistry, chemical composition, and sensory properties of the best-known traditional cheeses produced in the Eastern Mediterranean.
2. The Eastern Mediterranean as the Homeland of Cheese
Considering that EM has been the cradle of various civilizations for thousands of years, it is not surprising that the consumption of milk and the knowledge of cheese-making appeared in this area shortly after humans made the first cheese in an agriculturally fertile area known as the “Fertile Crescent”, located between the Euphrates and Tigris rivers, 6000–7000 years before Christ [16]. Through residue analyses of pottery sherds from two Neolithic villages (Pokrovnik and Danilo Bitinj in Mediterranean part of Croatia), lipids demonstrate the presence of milk, meat, and fish during the Early Neolithic (c. 6000–5400 BC) and the processing of milk into fermented products, including cheese, using distinctive pottery wares in the Middle Neolithic (from c. 5200 BC) [17]. Some pottery was probably used for the storage of milk and dairy products as well as for the processing of milk. Further investigations based on the faunal data revealed a large number of bones, teeth, and horn fragments, with the female population clearly dominating in all cultural layers. It is assumed that they were most likely used for reproduction and milk production [18]. The consumption of milk and dairy products gave humans a clear survival advantage at this time, as milk and dairy products are rich in valuable nutrients. In addition, the early centres of cattle domestication were located in the Eastern Mediterranean and North Africa [18].
3. Milk as a Raw Material and Its Characteristics
Raw milk is used widely in the manufacture of Eastern Mediterranean cheeses by small dairies, but in some parts where hot climatic conditions prevail, the product is made from heat-treated milk (e.g., 65–68 °C/5–30 min). In industrial-scale cheese-making, raw milk has largely been replaced by pasteurised milk (72 °C/15 s). Standardization of the casein-to-fat ratio is not common in classical production but is widely employed in industrial production. For instance, for a high-quality Beyaz peynir, a ratio of 0.8:0.9 was reported to be optimum [12].
Cheese that ripens in an animal skin sack is produced from sheep, cow, goat, and buffalo milk but also from mixtures of these types of milk. Croatian Sir iz mišine is made from whole milk. Although the autochthonous Sir iz mišine is made from the milk of the local Dalmatian Pramenka sheep breed, it is also produced in small quantities from cow and goat milk or a mixture of different types of milk [2,19]. Lebanese Darfiyeh cheese is made from full-fat raw goat milk [20]. In contrast, Sir iz mijeha from Bosnia and Herzegovina can be made from skimmed or semi-skimmed milk in addition to whole milk, which is obtained after the production of traditional cream (kajmak) [21,22,23]. As there are different types of Tulum cheese, it can be made from sheep, goat, cow, and buffalo milk or from a mixture of these types. Tulum cheese is usually made from semi-skimmed milk but can also be made from skimmed milk left over from butter production [24,25,26].
Otlu cheese is traditionally made from raw sheep milk, but goat or cow milk can also be added to sheep milk, while Carra cheese is traditionally made from raw, unpasteurised goat’s milk [14]. Less commonly, Carra cheese is made from raw cow milk in small dairies or in private homes [27]. In Lebanon, Shanklish cheese is usually made from sheep milk. However, local dairies also produce it from goat and cow milk to adapt to the changing availability of milk throughout the seasons [28]. “Surk”, which means skimmed milk cheese in Arabic, is made from cow milk by souring yoghurt for 1–2 days, turning it into buttermilk, removing the fat, boiling the fat-free buttermilk, and straining it to obtain skimmed milk cheese [29,30].
Stretched curd cheese (pasta filata) is usually made from sheep milk; however, as this milk has been difficult to obtain in recent years, cow milk has been used for its production. In the production of Kasseri in Greece, up to 20% of sheep milk could be replaced by goat milk [31]. According to Üçüncü (2008) [32], 100 kg of sheep milk can yield 16–18 kg of cheese, while 100 kg of cow milk yields 9–11 kg of cheese.
4. White-Brined Cheeses
Traditionally, white-brined cheeses are mainly made from sheep and goat milk. As the milk fat from these species contains no carotenoids, the cheeses made from them are white in colour, which gave this group of cheeses its name. The best-known white-brined cheeses from EM are feta PDO (Greece), Beyaz peynir (Türkiye), Domiati (Egypt), Teleme (Greece, Türkiye), Halloumi PDO cheese from Cyprus, and Vlašićki sir and Travnički sir (Bosnia and Herzegovina). Their main characteristic is their salty and slightly acidic flavour, which is due to storage in a dense brine (12 to 18% NaCl) and the effect of lactic acid bacteria during the ripening process. Salt and acidity are the decisive parameters for the preservation of these cheeses. However, these cheeses were originally made from sheep or goat milk; more recently, cow milk or mixtures of these types of milk have also been used.
4.1. Manufacturing Procedure
Lactic acid bacteria, which are characterised by a strong acidifying activity, predominate. The most important isolates are Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis, Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris, Lactobacillus casei subsp. casei, Enterococcus faecalis var. liquefaciens and Leuconostoc paramesenteroides. As maturation progresses, the number of lactococci decreases, and lactobacilli species (e.g., L. casei subsp. casei) become dominant [12].
Commercially available calf rennet (enzyme extract) and other suitable coagulants, including proteinases from microorganisms, are used. The sheep milk for Vlašićki sir is rennetted immediately after milking (body temperature ≈ 30 °C; [33]). The cutting of the coagulum takes place after 50–60 min or more and is cut into 1–3 cm cubes. The cut coagulum must rest for 10–15 min, while in the production of Vlašićki cheese, the curd is cut into 10–12 cm cubes and turned over to equalise the temperature of the curd and fat distribution. The cut curd must rest until the whey is separated.
The draining and moulding of the curd is done by self-pressing or light pressing to shape the curd. Cutting the cheese into slices (in Greek, slice = feta) or cubes (Beyaz peynir cheese). Draining in (tied) cheese cloths to form a spherical cheese dough, lasting 6–8 h (Vlašićki sir). The formed cheese ball must be carefully removed from the cloth. Cutting the ball is quite unique. The ball must be cut in half, and then each half cut into three slices (Bosnian = kriška; [33]). The Turkish Beyaz peinir cheese is characterised by a cube shape of ≈10 cm × 10 cm × 10 cm (Figure 2).
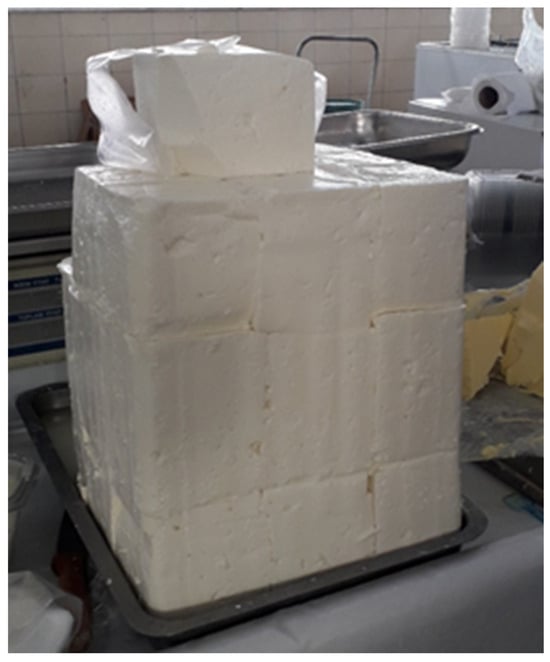

Figure 2.
Local Turkish Beyaz peynir cheese from Burdur city.
The barrel for filling with cheese slices can be made of wood, plastic, or metal. It must be filled gently without pressing, and spaces between the slices should be avoided. This type of cheese can be salted in various ways. Beyaz cheese is salted by immersing the cheese in a dense brine (12 to 18 NaCl g/100 g water at 7 °C) for 9 weeks. More salt in the cheese results in less proteolysis. Greek feta is dry salted, while Egyptian Domiati cheese is salted by adding salt directly to the cheese milk [34,35]. Dry salting involves applying a layer of salt, a layer of cheese slices and a layer of salt. For 100 kg of cheese, 5–7 kg of salt is used. Pressing is not desirable for the first two days to allow the salt to penetrate, and then the cheese must be pressed. The barrel must be filled with cheese slices of the same age. When cheese is not ripened, it should only be placed in the cold room (4–5 °C) when its pH value has reached a value of ~4.6 or less.
A sufficient amount of brine must be added to the containers to ensure that all blocks of cheese are fully submerged. The salt content of the brine must be at least 2% higher than the salt–moisture ratio of the cheese [12].
In the production of Halloumi cheese, the raw milk is curdled with animal rennet at 33–34 °C. The curd is then cut into 1 cm cubes, which are left to rest for around 10 min and scalded within 15 min at approximately 40 °C with constant stirring and passed into transferred to the hoops to drain, usually under pressure. The pressed curd is cut into pieces of 10 cm × 15 cm × 3 cm, placed in its own hot, deproteinised whey and heated to 90–95 °C for 30 min with stirring. The cooked curd is not stretched, as with typical pasta filata cheeses, but drained, cooled on a table, and sprinkled with salt or alternatively with crushed dry mint leaves (Mentha viridis) before being folded in half. Cheese is put into a container and the next day poured with salted whey and kept there for approximately 3 h. It can be packed in plastic bags and marketed immediately or preserved in brine till consumption [16,36]. This cheese is usually fried before consumption (Figure 3).
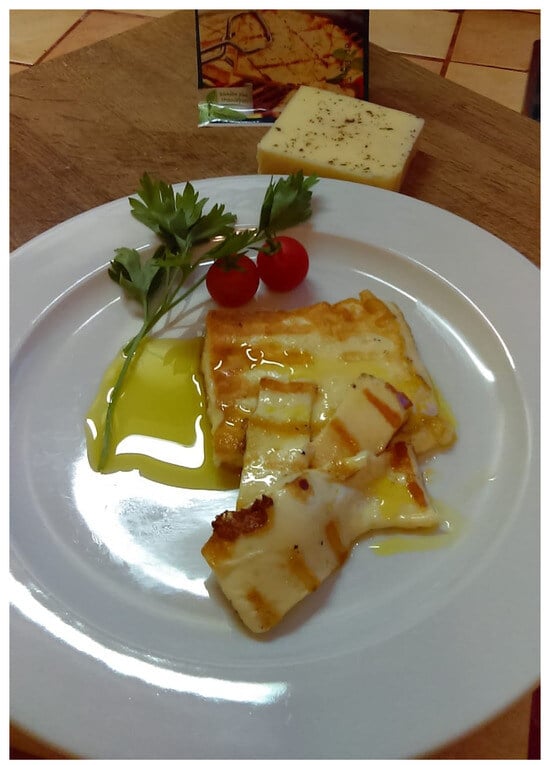

Figure 3.
Halloumi PDO cheese after frying.
4.2. Ripening
Pre-ripening takes place at 16–18 °C for 5–15 d (until the pH value reaches 4.6 or less). Vlašić cheese (Travnik) ripened at a temperature of 13–15 °C/60 days [33]. In the early ripening stages, lactic acid accounted for 95% of the total organic acids, but after 9–12 months of ripening, butyric acid accounted for 20–27% of the total organic acids in the same cheeses [12]. Yaman et al. (2023) [37] used water, methanol and ethanol extractions and collected spectra with a portable Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) device to monitor the ripening of white cheese and predict the content of key compounds that play an important role in the biochemical metabolism of Turkish white cheese. Individual free fatty acids were better predicted in ethanol extracts, while organic acids and total free amino acids were better predicted when water-based extracts were used.
Considering the tank size, the maturation and preservation tanks (large capacity stainless steel tanks of 500 kg versus tin tanks of 17 kg) had no effect on the content of fat in dry matter, total protein, moisture, minerals (Ca, Mg, K, and Na) and texture characteristics. In addition, proteolysis, microbiological (presence of yeasts and moulds), textural and sensory properties and the profile of volatile components were comparable [38].
4.3. Composition and Expected Sensory Characteristics
In general, white-brined cheeses contain 50% dry matter, more than 45% fat in dry matter (FDM), between 3–5% salt and 10% salt and salt in dry matter. The composition of white-brined cheeses can vary considerably (Table 1).

Table 1.
Average physicochemical composition of white-brined cheeses.
White-brined cheeses have special sensory and textural characteristics. Their flavour is slightly sour and salty and sometimes rancid and piquant. The cheese paste is pure white when made from sheep and goat milk, rindless, without gas holes or other openings, except small mechanical ones, and its consistency is smooth and rather soft but always sliceable. They are consumed after a maturation period of more than 2 months in brine [40,41]. The production of Domiati cheese from ultra-filtered goat milk results in a higher pH, moisture, and ash content, while the protein and fat contents are lower compared to cheeses produced using the traditional method [34].
4.4. Novelties
Greek feta is approved as PDO cheese, which means it has strict product specifications regarding the specific composition and the specific traditional production method within clearly limited production regions. Therefore, recent research has focused on the geographical differentiation of feta cheese [42] and the investigation of authenticity [43]. MALDI-TOF-MS proved to be a reliable and rapid method to detect feta cheese adulteration down to 1% cow milk and to differentiate feta cheese from similar white cheese ripened in brine [43]. Compared to physicochemical and volatile compounds, fatty acids are the most effective parameters for differentiating feta cheese from different regions [42].
The low-sodium white-brined cheese production approach showed that the use of a commercially available combination of Na/K salts (COMB) at different concentrations has no effect on the ash content, pH, or aw of the cheese produced. Although white-brined cheese made with COMB alone has a lower Na content, this cheese differs in overall acceptability from cheese made with NaCl. Reducing the amount of NaCl confirmed the possibility of producing white-brined cheeses with low Na content when optimal amounts of a suitable mineral salt are used as a substitute for NaCl, thus reducing the risk of high Na absorption in the human body by consuming this type of cheese [44], which belong to the category of cheeses with the highest salt content.
Plessas et al. (2021) [45] investigated a novel, potentially probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei SP5 as a starter culture for the production of white-brined cheese, free or immobilised on a prebiotic milk–cereal matrix (Greek traditional cereal-milk fermented food Trahanas) to protect the starter culture and achieve a prebiotic effect. The use of Lactobacillus paracasei SP5, either free or immobilised, led to a reduction (approximately 50%) in the number of coliforms, yeasts and fungi compared to cheese produced without starter culture and also improved the aromatic profile of the cheese. It should be emphasised that the use of the new strain resulted in white-brined cheese with improved overall quality and better sensory properties. The potential industrial use of freeze-dried L. paracasei SP5 as a starter culture for the production of high-quality functional white-brined cheeses is promising. Dabevska-Kostoska et al. (2015) [39] focused on traditional white-brined cheese as a carrier for the probiotic bacterium Lactobacillus casei and reported that probiotic counts at the end of ripening ranged from 174 × 108 to 372 × 108 cfu/g, depending on the initial level of concentration of the probiotic bacterium used. For most quality parameters, there were no differences depending on the concentration of probiotic bacteria used. The nitrogen fractions and fat content were the most important components influencing the overall quality of the cheese samples. The sensory characteristics showed that flavour contributed most to the overall acceptability of the cheeses. In addition, a total of 54 volatile compounds were found in probiotic Beyaz peynir produced with two different adjunct probiotic bacteria (Lactobacillus acidophilus DSMZ 20079 and Bifidobacterium bifidum DSMZ 20456), the content of which differed greatly from cheese to cheese depending on adjunct culture used, ripening time and vacuum packaging or brine [46]. In terms of safety, high hydrostatic pressure treatment at 600 MPa for 6 min is effective in eliminating more than 3 logs of Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli in low-salt white cheese [47].
The study conducted by Neofytou et al. [48] aimed to evaluate the effects of the inclusion of ensiled olive cake in the diets of Friesian cows on the fatty acid profile of their milk and, consequently, Halloumi cheese made. The concentration of saturated fatty acids and the atherogenic index are lower in milk and cheese after dietary supplementation with ensiled olive cake, while the concentration of long-chain and monounsaturated fatty acids was increased in both milk and cheese, with no adverse effects on milk yield and composition or the expression of genes involved in lipid metabolism of mammary and adipose tissue in cows. Naziri et al. [49] isolated and identified 11 lactic acid bacteria from Halloumi’s second cheese whey obtained during the production of Anari cheese, a by-product of Halloumi cheese production. The results of this study show the potential of Halloumi second cheese whey for the production of lactic acid cultures in dry form for further use in other fermented dairy products, as production of Halloumi in Cyprus has increased rapidly over the last decade, resulting in large quantities of whey streams that pose serious environmental problems and are difficult to handle. The investigation of goat milk-based Halloumi-type cheeses with different fat contents using the ultrafiltration technique has shown that ultrafiltration can be used to produce higher-yield Halloumi cheeses, as the proteins are better retained, but the meltability and stretchability must be further improved. The addition of fat significantly improves the sensory properties of Halloumi-type cheese, with the greatest impact on overall acceptability and the least on body and texture [50]. Kamilari et al. [51] conducted a study to characterise the bacterial communities of Cyprus Halloumi cheese to describe its specificity and protect it from fraudulent products. The microbiome of Halloumi consists mainly of lactic acid bacteria, including Lactobacillus, Leuconostoc and Pediococcus, as well as halophilic bacteria, such as Marinilactibacillus and Halomonas. Halloumi produced using the “traditional” method showed significantly greater bacterial diversity compared to Halloumi produced using the “industrial” method.
5. Hard Cheeses
Hard cheeses comprise a large group of different cheeses characterised by the fact that the curd is acidified before salting and pressing and has a lower moisture content (35–40%), which is the result of a ripening process that takes 3–12 months [52,53]. It is precisely because of the longer ripening period, during which the flavour compounds unique to each type of cheese are formed, that hard cheeses represent the crown of cheese production. In addition to ripening, the sensory properties of the finished hard cheese are also influenced by other technological production processes, the type of milk and the production area. For example, Graviera cheese is produced in different areas, which is why we distinguish Graviera Kritis, Naxou, Mytilinis and others [54]. The hard cheeses of the Eastern Mediterranean are made from cow, buffalo, sheep, and goat milk in their own combinations, which is why certain production steps may differ. Some of the hard cheeses of the Eastern Mediterranean are Paški sir, Krčki sir, Lečevaćki sir, Istarski sir (Croatia), Livanjski sir (Bosnia and Herzegovina), Njeguški sir (Monte Negro), Graviera, Xinotyri, Kefalotyri, Manura (Greece), and Ras (Egypt).
5.1. Manufacturing Procedure
In the production of certain hard cheeses, a milk culture containing selected lactic acid bacteria (mesophilic—Graviera, Krčki sir, thermophilic—Kefalotyri, mesophilic and termophilic—Istarski sir), lysozyme and calcium chloride (Paški sir, Livanjski sir, Graviera) can be used [3,55,56,57,58,59]. In traditional production, ripening is the result of the action of the autochthonous microbial population, usually LAB, in cooperation with microclimatic factors, as no dairy cultures are used. Furthermore, in the production of Xinotyri, for example, the whey from the previous day is added instead of the microbial dairy cultures [60].
Coagulation in the production of hard cheese is the result of the action of enzymes (animal, vegetable and microbial) in the milk, which usually takes place at temperatures between 32 °C and 36 °C for 25–60 min. An exception is Xinotyri cheese, where milk coagulation takes place at room temperature (20–25 °C) and lasts 24 h [60]. Once coagulation is complete, the coagulum is cut to the appropriate size depending on the type of cheese: the size of a hazelnut and after 5 min to the size of a corn grain—Njeguški sir [61]; cubes of 0.5 cm × 0.5 cm—Kefalotyri cheese, size of a hazelnut—Manura cheese [56]; size of a grain of rice—Paški and Lečevaćki sir [4]; size of peas [58], cubes of 2 cm × 2 cm—Ras cheese [62]. Cutting the curd into smaller pieces increases the surface area of the resulting cheese grain and leads to shrinkage, i.e., an increase in firmness, which reduces the ability to retain moisture in the cheese grain [53]. In contrast, in the production of Xinotyri cheese, the coagulum is not cut, and the cheese grain is not dried but placed in moulds with a cloth for squeezing [60]. Similarly, in the production of Manura cheese, the curd is left in the whey after cutting and then placed in baskets for straining without heating [56]. In general, the purpose of heating cheese grain is to squeeze out the whey remaining after cutting the curd, and in hard cheese production, it is usually carried out at temperatures of ~40 to over 50 °C with constant stirring. The heating of the cheese grains in the production of Njeguški sir is carried out at 40–45 °C [61], Paški sir at 38–45 °C/10–30 min [59], Kefalotyri at 45 °C/20 min [55], Livanjski sir at 46–48 °C [57], Graviera at 48–50 °C [41], Istarski sir at 42–45 °C [58].
After removing the whey, the curd grain can be placed in moulds without previous heating, where it is additionally pressed for 2–3 h in Xinotyri cheese-making [41], in Manura cheese-making [56] in baskets (tyrovolia). When the cheese grain is heated, it is pressed in moulds. In general, the aim of pressing, in addition to moulding and shaping the cheese rind, is to remove the remaining whey and bind the cheese grain [63]. A mechanical or pneumatic press is usually used to press the cheese, but there are also other methods, such as squeezing the whey by hand and then pressing it with materials such as stone (Njeguški sir) [61]. In this sense, pressing can take from 4 h in the production of Ras cheese to 24 h in the production of Graviera cheese [41,62]. Xynotyri and Manura cheeses are not pressed but left to drain and then salted [56,60]. Salting has a preservative effect, contributes to flavour development, and influences the texture of the cheese so that cheeses without added salt have a soft, doughy, and sticky texture, while cheeses with a larger amount of salt have a crumbly, dry, and hard texture [64]. Hard cheeses are most commonly salted by immersion in a prepared brine and by adding salt to the curd (Xinotyri), by rubbing salt on the surface (Graviera), or by combinations of these. In the production of Kefalotyri cheese, the cheese is first salted in brine and then dry salted for 4 months [55].
5.2. Ripening
Ripening takes place under controlled conditions, usually at temperatures of 10–25 °C (10–12 °C cold, 13–17 °C medium-warm, 18–25 °C warm ripening) and a relative humidity of 85–95% [63] with possible deviations. Paški cheese matures at temperatures of 10–20 °C and a relative humidity of 60–90% [59], while Xinotyri ripens at higher temperatures of 22–28 °C and a relative humidity of 60–70% [60]. In addition, Krčki cheese is usually coated with vegetable oil after 20 days of ripening and then continues to ripen, or it can be immersed in oil in a stone container and stored for up to a year [3]. Similarly, Istarski sir is coated with olive or vegetable oil after 20–40 days [58]. A specialty is the ripening of Manura cheese, which includes the following: drying on a bed of straw (3–4 months), immersing the cheeses in a barrel of red wine (5–10 days), placing the cheeses in barrels and covering with wine lees (1 day), storing the cheeses in the empty barrel until it is sold [56].
Cheese ripening involves microbiological, biochemical, and metabolic processes caused by the activity of milk enzymes, rennet, added starter and non-starter bacteria [65]. The result of these processes is the formation of flavour and texture that are characteristic of the respective cheese type. During the ripening of Xinotyri cheese, a total of 114 aromatic components were determined, of which alcohols, acids, esters, and ketones are the most abundant [60]. The ripening index at the end of the three-month ripening process was 22.95% WSN/TN for Istrian cheese, 10.15% WSN/TN for Krčki cheese, and 11.95% WSN/TN for Ras cheese, which was significantly higher compared to the value of 6.10% WSN/TN for Graviera cheese [3,5,66,67]. The variability of the microbial population is present due to different ripening conditions, which contributes to the specific sensory characteristics of the individual cheeses. For example, in the production of Kefalotyri cheese, the predominant microbial population at the beginning of ripening consists of mesophilic LAB, but their number decreases to the level of thermophilic LAB as ripening progresses without changing the number of enterococci and yeasts present [68]. In Ras cheese, an increase in the number of lactobacilli and streptococci was observed at the beginning of ripening, but this gradually decreased after 120 days of ripening [62].
5.3. Composition and Expected Sensory Characteristics
The average physicochemical composition of hard cheeses is presented in Table 2. Sensory characteristics of hard cheeses are influenced by numerous factors that become apparent during a longer ripening period. It generally depends on whether the cheese is made from raw or pasteurized milk, the type of milk, the cheese shape, and the area of production. Thus, Ralli and Spyros (2023) [69] determined in their research that the content of γ-aminobutyric acid, conjugated linoleic acids and linoleic acid differs in Graviera cheese in different areas of the island of Crete and that the total amino acid content was higher in cheeses produced in eastern Crete. Hard cheeses from the eastern Mediterranean generally have a piquant flavour with some special features, e.g., the flavour of Manura cheese is determined by wine and lees [56] or the botanical composition of pasture plants (Livanjski sir) together with sea salt (Paški sir) [57,59]. The internal colour of the cheese varies from white (Xintoyri) to slightly reddish-brown (Paški sir, Figure 4), while the texture can be less elastic (Livanjski sir), thick (Istarski sir), or crumbly (Xinotyri) [5,41,57,59].

Table 2.
Average physicochemical composition of hard cheeses.
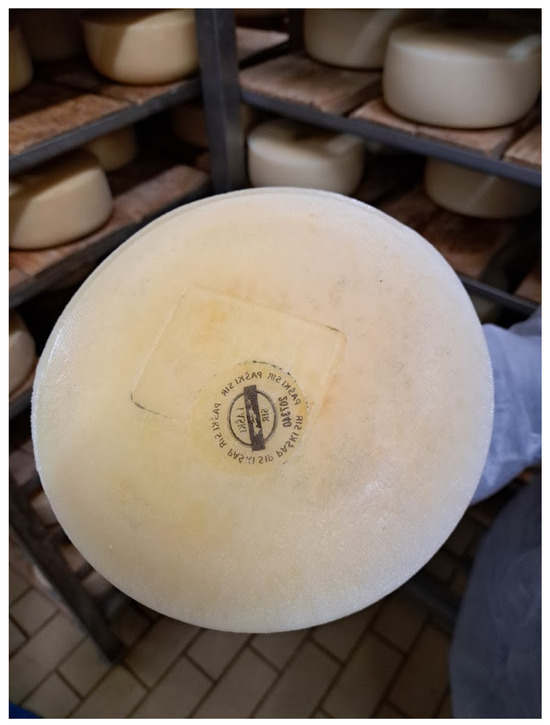

Figure 4.
Paški sir.
5.4. Novelties
The production of hard cheeses in the traditional way, i.e., from raw milk and without the addition of commercial cultures, still has an advantage over industrially produced cheeses in the eyes of consumers. The reason for this is the better sensory properties, especially flavour and texture. In addition, Behera et al. (2018) [71] state that cheeses made from raw milk are a rich source of beneficial microbes such as lactic acid bacteria (LAB) with probiotic properties. In this sense, the process of microencapsulation of the indigenous milk population, together with the addition of other ingredients (simultaneous encapsulation), has great potential for cheese production [72,73]. Kiš et al. (2023) [74] implement a microencapsulated form of selected autochthonous lactic-acid bacteria (LAB) isolated from the cheese-production chain and natural rennet obtained from suckling lambs in the traditional production of Paški sir. Such an approach in producing Paški cheese represents an important segment for biodiversity conservation and could contribute to innovation in cheese production by maintaining authenticity [74,75]. Studies of the same type of cheeses produced in different locations are of increasing interest to researchers in order to determine their detailed composition. For example, in their study, Ralli et al. (2023) [69] use 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy in combination with chemometrics to determine the metabolite profile of 40 compounds of Graviera cheese produced in different geographical locations. Ioannidou et al. (2022) [67] determined the fatty acid profile and lipid oxidation in Graviera cheese by gas chromatography and based on the formation of malondialdehyde. In addition, the use of modern tools such as machine learning and computer vision techniques to automatically detect the ripeness of cheese has potential not only in cheese production but also in the food industry [76].
6. Cheeses That Ripen in Animal Skin Bags
The cheeses that mature in an animal skin bag are specific cheeses that are uniquely linked to the history and culture of the Eastern Mediterranean region. They are traditionally produced in the mountainous regions of Croatia (Sir iz mišine), Bosnia and Herzegovina (Sir iz mijeha), Montenegro (Sir iz mijeha), Lebanon (Darfiyeh), and Türkiye (Tulum). According to historical data, nomadic sheep breeders probably started using a lambskin to store and transport the cheese from the mountains to the valleys, as there was a lack of wood for making storage and transport equipment. In Croatia, it is produced in the Dinara mountain area, Türkiye in the mountainous regions of Eastern and Central Anatolia, Lebanon in the Mount Lebanon range, and Bosnia and Herzegovina in several mountainous regions [19,77]. There are a few differences in the production process, but the main specificity is the ripening in a bag or sack made from the skin of the whole lamb or goat body skin, which has different names: mišina (Croatia), mjeh (Bosnia and Herzegovina), mješina (Montenegro), tulum (Türkiye) and dariff (Lebanon). These cheeses have a distinctive and spicy taste, odour, and aroma, which is due to the special ripening conditions in the skin bag and the naturally present yeast and mould population on the skin, which leads to intensive proteolysis and lipolysis [78,79,80,81].
6.1. Manufacturing Procedure
As the ripening process takes place in a bag made of animal skin, the skin must first be prepared for cheese ripening and particular attention must be paid to this. Cracks/holes in the skin can lead to spoilage of the cheese as air enters the skin bag during the ripening process [77]. Processing the skin involves removing the wool and meat, then washing and drying it in the sun and wind, and sometimes also smoking it. To soften the skin before filling it with cheese, it is soaked in warm water or whey [77] or in salted (5%) water [24], and all skin openings are disinfected with vinegar or a traditional alcoholic drink [77]. When preparing the skin for the ripening of Darfiyeh cheese, the skin is salted from the inside for one week after wind and sun drying [20]. The ripening of Turkish Tulum cheese is usually done in goat skin without hair, although there are some Turkish regions where unprocessed skin is used [82].
The production process of cheeses matured in animal skin is not unified; it differs in some stages. The milk is coagulated by adding homemade goat rennet or commercial rennet to the previously heated milk (temperatures between 32 and 37 °C). The coagulation time in the production of cheese from Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina is 30–50 min [21,83], which is much shorter than in the production of Tulum (90–180 min; [24,84]) or Darfiyeh cheese (60–90 min; [20]). In the production of traditional Sir iz mišine and Sir iz mijeha, the curd is cut into irregularly sized cubes of about 3 cm × 3 cm, heated at 35–40 °C for 20–30 min and then harvested by hand and placed in a cotton cloth. Sir iz mijeha is pressed under pressure for 2–4 h, while Sir iz mišine is obtained for self-pressing. After pressing, Sir iz mišine is cut into approximately 10 cm × 10 cm × 5 cm pieces, salted with coarse sea salt and then placed in a skin bag. After pressing, Sir iz mijeha is salted and stored in a wooden vat for 1–2 days. Before it is filled into the skin bag, it is broken by hand into small, irregularly shaped pieces and salted again.
The curd of the Tulum cheese is cut into 1–3 cm3 cubes, and the cheese grains are heated at 30–35 °C/10–30 min or 50 °C/12–15 min and then harvested by hand. The cheese is wrapped in a cloth in which it is pressed, first by self-pressing and then twice under pressure. The Tulum cheese is also salted twice: I) dry in a cloth after the second pressing, II) after being broken by hand into small, irregularly shaped pieces after the third pressing [24]. The production process of Darfiyeh cheese is slightly different. After cutting the curd into medium-sized cubes, the curd grain is heated at 30–35 °C/20 min, compacted for the first drainage of the whey, pressed by hand into the 12 cm × 9 cm × 9 cm shape and then formed into cheese balls (400–500 g). It is not salted while it matures together with whey cheese Arichi, which is salted [20].
6.2. Ripening
The cheeses produced are inserted into the skin sack through the opening of the neck, and the legs of the skin are tied together with a string. They are usually matured for 1–6 months in a ripening chamber at a temperature of 10–20 °C and a relative humidity of 65–95% [20,83,85]. An exception is Tulum cheese, which ripens at 6–10 °C [24], and the Divle Cave Tulum cheese, which ripens for 4 months in the cave at 5–10 °C [84]. Due to the special conditions inside the skin sack and the natural microflora of the skin sack (moulds and yeasts), these cheeses undergo more intensive proteolysis and lipolysis [83]. Ozturkoglu-Budak et al. (2018) [25] reported that Divle Cave cheese is characterised by very pronounced lipolysis (1200 mg of free fatty acids (FFAs)/100 g of cheese on the 120th day of ripening) due to the lipase activity of the yeasts and moulds originating from the cave. The higher content of yeasts and moulds in the cheese layer close to the skin compared to the cheese from the inside of the skin bag is a consequence of the growth of yeasts and moulds on the skin during the ripening of the cheese in the cave. In addition, the skin bags can be replaced by plastic vats, which influence the rate of the biochemical processes. The proteolysis and lipolysis rates of Tulum cheese matured in skin bags are higher than those of cheese matured in plastic barrels [86]. Tulum cheese made from sheep milk contains 308 mg FFAs/100 g cheese 90 days after ripening in goat skin, while the cheese ripened in plastic barrels has a significantly lower lipolysis rate (188.60 mg FFAs/100 g cheese) [87].
6.3. Composition and Expected Sensory Characteristics
The average physicochemical composition of the cheeses ripen in animal skin is shown in Table 3, and it depends on the type of milk and ripening duration. Specific ripening conditions inside the sack, naturally present population of lactic acid bacteria and other non-starter bacteria, as well as secondary microflora (yeasts and moulds), are responsible for the sensory properties of cheeses ripened in the animal skin [77,78,79], which includes pungent flavour, buttery taste and pronounced odour and a specific (Figure 5a) semi-hard granulated, crumbly texture [21,81,86] with the exception of Croatian Sir iz mišine having hard compact (Figure 5b) texture [83] and Darfiyeh cheese which comes in the shape of balls of semi-hard texture [20]. Due to the intense biochemical processes during ripening in the animal skin, it is necessary to pay attention to the quality of milk when heat treatment of milk is not applied, as it can deteriorate cheese sensory properties [88] and a specific granulated or spreadable and smooth texture.

Figure 5.
(a) Turkish cheese that ripens in an animal skin sack (Tulum cheese); (b) Croatian cheese that ripens in an animal skin sack (Sir iz mišine).
Çakır et al. (2016) [89] found that the addition of black cumin has a positive effect on the proteolysis of cheese, thereby improving the sensory scores by increasing the volatiles in the cheese both qualitatively and quantitatively, such as the total content of alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, sulphur compounds, esters, and terpenes. Similar volatiles are found in raw goat milk Tulum, with acetic acid, 2,3-butanediol, ethyl acetate and a-pinene being the dominant volatiles [90]. Serhan et al. (2015) [91] followed the transfer of three model aroma compounds (2-butanone, 2,3-butanedione and 2-butanol) in an experimental aqueous system of model solution and goat skin after 20, 40 and 60 days of exposure by permeability and sorption tests. Up to 40 days, the transfer of the model molecules depends on their physicochemical properties and the exposure time. After 60 days, the molecules tend to migrate from the goat skin back into the aqueous diluted model solution, which could be evidence of the diffusion of flavour model molecules in a cyclic manner.


Table 3.
Average physicochemical composition of the cheeses that ripen in animal skins.
Table 3.
Average physicochemical composition of the cheeses that ripen in animal skins.
| Type of Cheese | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sir iz Mišine (Croatia) | Tulum (Türkiye) | Tulum (Türkiye) | Tulum (Türkiye) | Tulum (Türkiye) | Divle Cave (Türkiye) | Darfiyeh (Lebanon) | |
| Milk type | sheep | cow | goat | sheep | mixed | sheep | goat |
| Ripening (days) | 60 | 270 | 180 | 90 | 180 | 120 | 60 |
| Component (%) | |||||||
| Total solids | 64.97 | 70.19 | 66.78 | 69.36 | 60.16 | 53.61 | - |
| Fat | 34.53 | 38.75 | 29.08 | 33.85 | 28.42 | 18.67 | - |
| Fat in total solids | 52.96 | 55.20 | - | - | - | 34.55 | 43.46 |
| Protein | 23.93 | 26.99 | 30.76 | 28.10 | 27.58 | 29.54 | 36.72 |
| Minerals | - | - | - | 7.12 | - | - | - |
| NaCl | 2.46 | 8.92 * | - | 5.34 | 2.27 | 3.80 | |
| pH | 5.15 | - | 5.02 | - | 5.08 | 5.06 | 4.99 |
| Literature source | [83] | [87] | [90] | [92] | [81] | [84] | [85] |
* Salt-in moisture.
6.4. Novelties
Recent research on cheese ripened in animal skin has focused on the characterisation and dynamics of bioactive peptides produced by proteolysis during ripening. Various functional properties of bioactive peptides have been identified in Tulum cheese, e.g., angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, antimicrobial, antihypertensive, antibacterial, antioxidant, anticarcinogenic, metal chelating, skin regenerating, antihypercholesterolaemic, immunomodulatory, brain function improving, antidiabetic and cathepsin B inhibitory peptides, with ACE inhibitory peptides dominating [81,93]. The number of bioactive peptides increases with increasing number of days of maturation, as the newly formed peptides are dependent on proteolysis. This indicates the higher nutritional value of long-ripened Tulum cheese and categorises it as a functional food [93,94]. Also, the addition of autochthonous probiotic bacteria Lactobacillus plantarum B and Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis S1 isolated from Croatian Sir iz mišine can not only increase the functional value of the cheese but also improve the ripening properties of the cheese by accelerating proteolysis, which could solve the problem of scarcity of this cheese due to the high demand for this cheese by local consumers and tourists in Croatia [95]. Saber et al. (2015) [96] conducted a randomised prospective case-control study to evaluate the health benefits of Darfiyeh cheese. Subjects were divided into two groups, with the test group receiving 20 g of cheese every two days over a 24-day period. The results suggest that the ratio of the two probiotic strains contained in the cheese (Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis and Lactobacillus plantarum) could cause a change in the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract. Özkan et al. (2021) [97] investigated in vitro probiotic properties and safety characteristics of nine Enterococcus faecium isolates from goat sack Tulum cheese during different ripening periods. One isolate proved to be a potential candidate for further in vivo studies as a probiotic culture, and five of them showed antibacterial activity against both Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 7644 and Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923. Kiliç et al. (2023) [98] isolated ten strains of Lactobacillaceae spp. from Tulum cheese made from cow milk, of which L. plantarum SM27, L. plantarum S74 and L. paracasei RU39-7 show the best probiotic properties. In addition, they show high antimicrobial and antioxidant activity and the ability to remove cholesterol. These results indicate that Tulum cheese can be used as a rich source of probiotic bacteria for the screening and isolation of probiotic strains and starter cultures.
With the aim of improving the flavour of Tulum cheese and producing a new, safe type of mould cheese, Çakır et al. (2022) [86] added a mould strain, P. roqueforti 41, which is commonly found in Tulum cheese. They studied the ripening process of Tulum cheese made from Erzincan sheep milk with added mould, which was made from raw and pasteurised milk and matured in a skin bag and plastic barrels. Proteolysis and lipolysis are more intense in the cheeses matured in the skin than in those matured in plastic barrels, as well as in the cheeses made from raw milk compared to those made from pasteurised milk. The values of phosphotungstic acid soluble nitrogen (PTA-SN), trichloroacetic acid soluble nitrogen (TCA-SN) and pH 4.6 soluble nitrogen (pH 4.6-SN) of the samples inoculated with the P. roqueforti 41 strain and the non-inoculated samples are similar during the entire 90 days of ripening. However, in the last two ripening stages (90th and 120th day), after drilling the cheese mass, the values of PTA-SN, TCA-SN and pH 4.6-SN increased more in the samples inoculated with the P. roqueforti 41 strain. They concluded that it is very important to pierce the cheese mass to provide oxygen for mould growth inside the skin sack.
7. Stretched Curd Cheeses (Pasta Filata Cheeses)
This category of cheese is thought to have originated in the Balkan countries and Italy. Traditional production methods include “acid development”, “curd rolling”, and “curd stretching” pasta filata cheeses from the EM region include Kashar from Türkiye, Kasseri from Greece, Roumi from Egypt, and Kachkavaly from Croatia [99,100,101]. After white cheese, these cheeses are the most commonly produced and consumed cheeses in Türkiye, the Balkan Peninsula, and the Mediterranean region. There are different opinions about the origin of the Turkish word kashar. According to various sources, it is of Latin origin and derives from the Latin word “coerceo”, which means “squeezing out” the whey under pressure. According to reports, the cheese was first made by a Jewish girl in Thessaloniki. Kashar cheese has a very large market share in Türkiye after Beyaz peynir [102].
7.1. Manufacturing Procedure
The main process for making this type of cheese consists of fermenting the curd, boiling it in hot water and then kneading it. In the traditional production of Turkish Kashar cheese, the ability of acid development determined the processes of “leaf opening” and “string pulling”. When the mass has a smooth, creeping, and unbroken structure at the end of this process, it has reached the consistency to be cooked. When the desired degree of acidity is reached, the curd is cut into thin slices and processed into dough in boiling water at 75–80 °C with 3–5% salt. The dough is kneaded, bound into a core, and filled into moulds [103].
The production methods of Kashar cheese, the main representative of this cheese group, vary depending on the region and the experience of the master cheesemaker. Kashar cheese used to be produced in high mountain pastures. Today, numerous large and small farms throughout Türkiye produce Kashar cheese, with Thrace being a particularly active producer. The best-known Kashar cheeses are produced in Edirne, Kars, Kirklareli, Kocaeli, Muş, Trabzon Kadirga, Bayburt, and Tonya. The fat content of the milk is standardised at 2.5% for full-fat and 0.6% for low-fat cheese production. The milk is pasteurised at 65 °C/30 min and then cooled to 34°C. β-carotene (0.7 mg/kg), starter culture (9 mL/kg) and CaCl2 (2 mg kg/) are added. The rennet diluted with pure water is added when the pH of the milk reaches 6.2 to 6.3. After 50 min, the curd is cut into 1 cm3 cubes. The cut curd must settle for 10 min. Cooking is done by raising the temperature from 34 °C to 40 °C within 30 min while stirring. At the end of cooking, the whey is drained off. The curd is fermented until it reaches a pH value of 5.2–5.25. The remaining whey is then drained off. The traditional process of Kashar includes pasteurization or termization of milk, inoculating with lactic cultures up to pH 6.40, coagulation of milk using rennet, cutting and pressing the curd, and scalding and stretching at 75–85 °C. The stretched curd is filled into cylindrical plastic moulds and turned after 30 min to obtain a flat surface. The cheeses are cooled to room temperature, and the moulds are removed. The cheeses are then allowed to take on their yellow colour for 24 h at 18–20 °C. The blocks of cheese are vacuum-packed, shrink-wrapped, and stored at 4–6 °C for 90 days [103].
7.2. Ripening
Stretched curd is either sold fresh or usually stored in a cool place for 3–6 months to allow a rind to form and ripen. The cheese can be stored at a suitable temperature for 2–3 years, but not cheese made from cow milk [104]. According to traditional methods, Kashar cheese is made from raw sheep or cow milk or a mixture of the two, whereby the natural flora of the milk supports the ripening process. The relevant standards [105] dictate that Kashar must be matured within 90 days in order to obtain aged Kashar. Greek Kasseri cheese must be matured for at least two months before it is released onto the market. However, it achieves its best flavour when it has been matured for ten months or more [31].
7.3. Composition and Expected Sensory Characteristics
Kashar cheese is a popular dairy product that is eaten for breakfast all over the world. The same applies to Kasseri in Greece and Roumi in Egypt. This type of cheese is ideal for slicing, melting or grating. For breakfast, this cheese is often combined with white cheese. It is also often used for pizzas, sandwiches, and salads [106]. Kashar cheeses typically have the shape of a millstone and fall into the hard or medium-hard cheese category. Fresh Kashar cheeses weigh 250 g to 2–3 kg, while mature Kashar cheeses weigh 5–25 kg. The round Kashar cheeses produced in the eastern provinces, such as Kars, Erzurum, and Muş, weigh around 5–7 kg and have more mould on the outside, while the western Anatolian Kashar cheeses from places such as Tekirdağ, Kirklareli, Edirne, and Kocaeli weigh 10–12 kg. The Kashar cheeses produced in Eastern Anatolia are higher (10–11 cm) and amber in colour, while the Western Anatolian Kashar cheeses are paler yellow in colour and flatter, with a thinner rind and no mould. In general, Kashar cheeses can be characterised as follows: They are salty, full-fat cheeses with a unique, slightly tangy, pungent flavour and aroma. They have a grainy but not coarse texture and, depending on the ripening period, are hard or soft, plastic consistency, which does not crumble when cut, with a smooth, flat, homogeneous appearance in cross-section. Their colour ranges from white to ivory, pale cream, pale yellow and darker shades of these colours. When mature, they have an outer rind [32,82]. Greek Kasseri develops a rich, complex flavour, a buttery texture and a floral aroma. While the texture of cheese made exclusively from sheep milk is firm, the addition of goat milk results in a harder cheese [31].
7.4. Novelties
Recent studies on Kashar cheese have mainly focussed on the methods used to reduce microbial growth. Demirbaş et al. (2022) [107] reported the efficacy of a mixture of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis as a biocontrol agent for Clostridium spp. in traditional Kashar cheese causing the late blowing defect. In Kashar, samples were prepared with a co-inoculum of L. plantarum and L. lactis subsp. lactis and stored at 4 °C for 40 days, a decrease in the number of C. sporogenes by almost 1 log cfu/g was observed, which is not the case in Kashar samples stored at 25 °C. Coating Kashar cheese with grape seed oil-loaded electrospun nanofibres retarded the rapid total yeast and mould growth and proved to be very effective against rapid oxidation during storage at 4 ± 1 °C [108]. The addition of lysozyme and lactoferrin from donkey milk to Kashar production results in lower microbial load and better physicochemical, textural and sensory properties throughout ripening, demonstrating the potential of using natural antimicrobial agents to extend cheese shelf life and achieve better quality characteristics, as well as to ensure consumer safety [109].
8. Cheeses with Herbs and Spices
The incorporation of herbs into cheese products is a new field in the dairy industry that aims to improve flavour, extend shelf life, and provide health benefits. This approach not only varies the flavour profile of cheese but also helps to extend shelf life by inhibiting the growth of microflora. Furthermore, the addition of herbs can help to reduce physical defects in the cheese by lowering the necessary salt concentration [110]. The variety of cheeses produced is influenced by several factors, including the type of milk used, the specific cheesemaking protocol, the ripening time and the addition of herbs and/or spices. Together, these factors influence the texture and flavour development of the cheese. Cheeses with herbs and spices is a common and valued tradition in the culinary heritage of the countries of the Eastern Mediterranean, especially in Türkiye (Otlu, Surk, and Carra), Lebanon (Shanklish), Israel, Greece, Cyprus, Syria (Shanklish), and Albania. These countries have a rich history of cheese-making, and the use of spices in cheese-making gives the final products a unique flavour and aroma. The most common herbs used in the production of Otlu cheese, whether individually or as part of a mixture, are wild garlic (Allium sp.) and Ferula sp., Prangos sp., Thymus sp., Mentha sp., Chaerophyllum macropodum, and Silene vulgaris [111]. Surk or Shanklish is a traditional cheese for the eastern Mediterranean region of Türkiye, Syria, Lebanon, and the Middle East. The characteristic flavour comes from the use of a spice mixture containing certain proportions of thyme, allspice, cloves, mahaleb, nutmeg, cumin, cinnamon, ginger, basil, fennel, black cumin, chilli pepper, and coriander [29]. The speciality of Carra cheese (Türkiye) is the presence of an aromatic active ingredient (para-cymene) extracted from various aromatic plants, mainly mountain thyme and black cumin [27].
8.1. Manufacturing Procedure
Cheese production begins with the selection of high-quality and hygienically correct milk, regardless of whether the pasteurisation process is carried out or not. While the traditional production method does not involve heat treatment of the milk or the addition of starter cultures so that the naturally present bacterial population in the milk influences the formation of the characteristic flavour, the modern industrial process for the production of Otlu cheese uses pasteurised milk acidified with the addition of mesophilic cultures such as Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis and L. lactis subsp. cremoris [14]. A commercial culture is also traditionally added to milk heated to 30–32 °C in the production of Carra cheese [27]. Surk and Shanklish are produced by heating defatted yoghurt (“ayran”) or buttermilk at boiling temperature for about 30 min to precipitate milk proteins [112,113]. Traditionally, calf rennet is used as a coagulant for Otlu and Carra cheeses for a certain period of time (usually 60–120 min at 30–35 °C) [12], while no rennet is used in the production of Surk and Shanklish cheeses, as curd formation is the result of lactic acid fermentation by a yoghurt starter culture [114]. In the production of Otlu cheese, the curd is cut after coagulation and filled into muslin bags. The herbs are added to the curd and mixed well without draining the whey, with the optimum proportion being 1% [14]. In the production of Surk cheese, the curd is also pressed for 5–6 h to remove excess whey. Then 0.1–0.3% of each of the spices (peppermint, thyme, spearmint, cumin, black pepper, cinnamon and ginger), 2–3% chilli pepper and about 5% salt are added [112]. The mixture is then formed into a conical shape resembling a pear or strawberry, weighing 150–200 g and measuring 5–7 cm in diameter. In the production of Shanklish cheese, after the precipitate is collected and drained through cheesecloth, salt is added, and the curd is moulded into balls. These balls are then air-dried in the sun and finally seasoned with spices such as cumin, ground thyme or dried chilli powder [113]. For Carra cheese, the curd block is cut into approximately 4–5 cm pieces after being pressed for 30 min and coarse salt is sprinkled between the slices and stored for 2–3 days. When making Otlu cheese, the curd is then pressed for 3–4 h so that the whey can drain off. The curd is then cut into blocks measuring 7 cm × 7 cm × 2 cm. The curd blocks are then either salted for 6–10 h in a 14–16% NaCl solution or dry salted. In dry salting, heated whey or defatted yoghurt (known as ‘lor’ or ‘cacik’) is filled into the spaces between the cheese blocks in plastic or earthenware containers. Cheese can also be salted by immersing it in brine (14–16% NaCl solution) for 6–10 h. They are then packed in tins where they are left to mature for a month [14]. After salting, the Otlu cheese is ripened for at least 1 month. In traditional production, the cheese is placed in a container and matures underground, usually 50 cm below the surface, for 2–3 months. In the unique method of making Carrara cheese, the cheese is pressed and salted to remove excess moisture and buried underground in jars to control microbiological activity and biochemical reactions. The jar is filled with a homogeneous mixture of curd and spices (a 5% mixture of black cumin and wild thyme) and sealed with a mixture of wood ash, salt, olive oil, and water [112]. This process ensures that the cheese is stored at low temperatures and, therefore, does not spoil, which is extremely important for this region, which is characterised by an extremely hot climate. Surk cheese is usually consumed fresh and unripened after being air-dried for 3–4 days or wrapped in parchment paper [115]. Shanklish balls are matured for a few weeks at room temperature in clay pots, and the finished product is stored in olive oil for 1–2 years [113].
8.2. Ripening
Studies have shown that lipolysis and proteolysis are more pronounced in maturing herbal cheese samples compared to fresh cheeses [116]. In general, it can be said that both proteolysis and lipolysis increase with the proportion of herbs in the cheese [117]. On the other hand, the addition of herbs increases the accumulation of histamine in cheeses with spices [118]. The method of grinding cheese in pots accelerated the ripening process more efficiently than other methods. In addition, the degradation of the casein fraction in the containers was more pronounced, which significantly influenced the proteolysis of the cheese samples. This method led to visible ripening and clearly visible casein degradation products in the cheese. Significant changes were observed in the casein fractions [119].
Cheese made from raw milk generally has a higher soluble nitrogen content than cheese made from pasteurised milk [120]. In addition, the degree of proteolysis also depends on the method of curing Otlu cheese [121]. This is because the proteolysis indices in Otlu cheese are higher in dry-salted cheeses than in those immersed in brine, which is probably due to the transfer of nitrogen compounds into the brine. The ripening of Otlu cheese increases the content of water-soluble nitrogen in the brine, as peptides and amino acids are washed out in the brine [120]. Therefore, it is important to analyse the nitrogen fractions in cheese and brine during ripening to effectively measure and understand the changes in these fractions in brine-ripened cheeses. In addition, Ekici et al. (2006) [118] found that herbs can introduce histamine-producing microorganisms into cheese, the content of which increases during ripening. In general, the pasteurisation process reduces the formation of histamine, while the addition of herbs increases it [118].
8.3. Composition and Expected Sensory Characteristics
As there is no standardised production protocol for Surk and Carra cheese, its chemical composition varies considerably [27,30]. Tarakci et al. (2011) [111] make similar observations for Otlu cheese and point out that the differences in chemical composition depend on the degree of ripeness and the filling methods (block and ground cheese mixed with 30% whey curd or lor) in different types of containers. Table 4 shows an average physicochemical composition of cheeses with spices that are important for the Eastern Mediterranean region.

Table 4.
Average physicochemical composition of some varieties of cheeses with herbs and spices.
The reason for the lower pH value of Otlu and Surk cheeses and the higher concentration of lactic acid could be due to the addition of herbs that may stimulate the growth of lactic acid bacteria present in the raw milk [117]. The reason for the many different values of lactic acid concentration and pH value may be that these cheeses ripen differently or not at all. Another possible reason is that raw milk is used in the production of certain cheeses, which, if not microbiologically correct, can cause an increase in acidity [30]. In addition, the remarkably high iron (Fe) and vitamin C content in Otlu cheese probably comes from the herbs (such as garlic and thyme) added to the curd during production [122]. These herbs are valued not only for their flavour-enhancing properties but also for their nutritional benefits. The oxidation of vitamin C can occur during cheese ripening, leading to a possible loss of this nutrient in the finished cheese. Historical records show that people in this region had to contend with numerous health problems. As a preventative measure, doctors recommended adding herbs to the cheese to solve these problems [123].
The quality of cheese is significantly influenced by the presence of peptides, amino acids and free fatty acids (FFAs), which are produced by proteolysis and lipolysis. In particular, proteolysis is crucial for the flavour and texture of cheese and is influenced by enzymes from starter and non-starter bacteria. The texture, composition, appearance, and flavour of cheese with herbs vary depending on the geographical region, traditional processing methods, ripening time and the type and composition of milk used [113]. The addition of Ferula sp. to cheese has a negative effect on the appearance and colour of the cheese and improves its texture, taste, and aroma [124]. Fresh Shanklish has a mild flavour and soft texture, but when dried and matured for a longer period of time, it becomes darker with a distinctive, piquant taste and aroma [113].
8.4. Novelties
Cheeses with herbs in the Eastern Mediterranean are mostly produced in the traditional way, which often requires improvements in terms of hygiene and sanitary conditions. The authors state that it is necessary to carry out in-depth studies in order to improve existing technologies and achieve a uniform quality of cheeses while preserving their original characteristics. They even point out that it is necessary to replace traditional, primitive processing methods with modern technologies and facilities for cheese production [112]. Recently, studies have been conducted with the aim of improving the quality of cheese with herbs characteristic of the region of Türkiye. The diverse microbial composition of Surk cheese indicates its potential as a natural functional food. The study conducted by Esen and Cetin (2021) [29] is the first study which analysed the spectrum of bacteria and yeasts present in ripened Surk cheese. From the group of lactic acid bacteria, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum, Companilactobacillus alimentarius, and Ligilactobacillus acidipiscis were found in ripened Surk cheese. In addition, non-LAB species such as Staphylococcus sciuri, Bacillus sp., Staphylococcus lentus, Bacillus pumilus, and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, as well as yeasts such as Debaryomyces hansenii, Candida zeylanoides, Yarrowia lipolytica, and Kluyveromyces lactis, were isolated from the samples. Esen and Turgay (2022) [30] investigated the chemical composition and microbiological quality of Surk cheese and found that only strictly controlled production leads to microbiologically acceptable products. In fact, it was found that Surk cheese may contain mycotoxins due to the presence of various mould species, which is why they suggest that further investigations be carried out to determine the mycotoxin profile. Furthermore, they state that it is necessary to investigate the possibilities of faster and controlled production using isolated bacterial, yeast or mould species as starter cultures. Furthermore, they state that 20 out of 36 cheeses did not fulfil the salt content criteria set out in the Turkish Food Codex.
The Eastern Mediterranean is known for its rich biodiversity, where indigenous plant species are often used in cheese production. For this very reason, the use of herbs in cheese production is an area full of innovation. In the future, research should focus on the potential of the plant species used, which can be summarised in:
- (i)
- Functional benefits of using certain plants such as basil, sage or turmeric, which are known for their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties [14,112,123];
- (ii)
- Extension of shelf life, as herbs with antimicrobial properties (e.g., thyme and rosemary) are used as natural preservatives [125];
- (iii)
- Reducing the salt content in cheese, as the addition of herbs can reduce the salt content without affecting the flavour of the product [126];
- (iv)
- Using organically grown plants to appeal to environmentally conscious consumers and support sustainable agriculture.
9. Whey Cheeses
Whey is a greenish-yellow liquid that remains after the casein curd has been removed during cheese production. It is considered a by-product in the dairy industry, while in traditional small-scale cheese production, it is a valuable raw material for the production of whey cheese or for animal feed [127]. Whey cheeses in the Mediterranean region are mainly made from the whey left over from the production of traditional sheep cheeses [128], such as Croatian Skuta, Urda from Bosnia and Herzegovina, Greek Myzithra, Anthotyros and Manouri, Lor from Türkiye and Arishi from Lebanon. Croatian whey cheeses are mainly produced on the islands of Pag (Paška skuta cheese), Krk (Krčka skuta cheese) and Brač (Bračka skuta cheese) and to a lesser extent in the coastal areas of Istria (Istarska skuta cheese). They are made from sweet whey left over from the production of casein cheeses, such as sheep milk hard cheese after the curd has been removed: Brački sir, Paški sir and Istarski sir [2]. The whey cheese produced in the mountainous regions of Bosnia and Herzegovina is known as Urda [129]. The best-known traditional Greek whey cheeses are Myzithra, Anthotyros and Manouri. They are made from sheep and goat whey or their mixtures with the addition of milk or cream [127,130]. Lor cheese is a soft cheese that is produced in all regions of Türkiye. It is usually consumed without ripening, but in some areas, it is also ripened [82].
9.1. Manufacturing Procedure
The production of whey cheese is based on the thermal denaturation and precipitation of whey proteins. Goat and bovine whey have a lower protein content than sheep whey, which leads to a lower yield of corresponding whey cheese compared to sheep whey. This could be improved by acidifying the whey before heating and adding small amounts of milk to facilitate the co-precipitation of caseins and whey proteins [128]. Croatian whey cheeses are obtained by heating sheep whey until the proteins are coagulated and come to the surface. The process is stopped just before the whey boils (95–97 °C). The coagulum is left at this temperature for 20 min to complete protein aggregation. After aggregation, the coagulum is placed in cheesecloth or cylindrical moulds, allowed to drain at room temperature for 2–3 h, and then stored at 4 °C in the refrigerator. Bračka skuta is not salted, but Paška and Istarska skuta can be salted by adding salt to the whey before heating or by salting the curd before filling it into moulds [15,131]. The Montenegrin whey cheese Urda is made by gradually heating the whey to 85 °C for 1 h with occasional stirring. Salt is added at the end of the heating process. The curd must cool down. After cooling and pressing in linen bags for 10–14 h, the cheese is packaged and stored at refrigerator temperature [132]. Greek Myzithra is made by gradually heating the whey to a temperature of 65–75 °C while stirring constantly and adding whole milk in varying proportions. Salt can also be added during the heating process (1–1.5%). Heating is continued until 85 °C, and when small fragments of whey proteins appear, stirring is reduced. Finally, the process is stopped when a very thin layer of coagulum has formed on the surface of the whey. The temperature is raised to 90 °C, and the curd is left at this temperature for 30 min to complete protein aggregation. The curd is gradually poured into cheesecloth moulds using a perforated ladle and hung on a rack in a well-ventilated room at 20 °C for three hours to drain. The cheese is then stored at 4 °C [127,130]. The production process of Anthotyros is almost similar to that of Myzithra but uses less salt (0.5%), and whole milk (10%) is added to the whey intended for the production of Anthotyros. Compared to Myzithra, up to 25 whole milk or cream is added in the production of Manouri to ensure that the final product contains at least 70% fat in the dry matter [133]. Lor is produced by heating whey or buttermilk to boiling point. It is stirred gently and continuously so that it does not boil too quickly. Coagulation takes place gradually, after which the coagulum is collected and poured into fine cloth bags, which are hung up to drain. The draining process is continued by placing the cheese under the press. After draining (approximately 4 h), the cheese is lightly salted with fine salt. The cheeses are pressed into containers and stored in the refrigerator [82]. To make Libanons Arishi, the whey is usually heated to around 85 °C for 5–10 min with constant stirring. At this point, citric or acetic acid is added. As soon as the curd has formed, it is collected with cheesecloth. Traditionally produced Arishi has a shelf life of only 1–2 days due to its high moisture content and poor handling practises, which limits its marketability and availability [134].
9.2. Composition and Expected Sensory Characteristics
Based on the content of dry matter and fat in the dry matter, whey cheese generally belongs to the group of soft, full-fat cheeses. The physicochemical composition of whey cheeses produced in the Eastern Mediterranean region is shown in Table 5. Whey cheeses are characterised by a milky-sweet taste and a white colour. Croatian cheeses have a smooth and creamy texture with the typical flavour of sheep milk [2], while Urda is a fine-grained soft cheese with a lubricating consistency and pleasant specific smell and taste [132]. Local consumers of the island of Brač had to make a preorder for whey cheese a week in advance from small-scale producers, which indicated not only a significantly higher demand than supply of this dairy product but also showed its excellent quality. Brač whey cheese was also evaluated by non-local consumers. The total sensory score that was achieved indicated a good non-local consumer’s acceptance of Brač whey cheese [135]. Lor cheese is soft and grainy and is therefore used for the preparation of some milk-based desserts [136]. Manouri’s flavour is rich, milky, slightly tangy and citrusy, while its texture is smooth, dense, and buttery [137].

Table 5.
Average physicochemical composition of whey cheeses.
9.3. Novelties
Whey cheeses belong to functional food as a good source of valuable amino acids, some fatty acids and potassium, and a lesser amount of sodium. Considering that Brač whey cheese contains an average of 654 mg of essential amino acids per g of protein, 100 g of this cheese covers 78.14% of an adult’s daily requirement of essential amino acids [15]. Due to the physicochemical properties of fresh whey cheese (high pH, high moisture content and low salt content), these dairy products are highly susceptible to microbial spoilage, which is why research has recently focussed on sustainable preservation methods for whey cheese. Modified atmosphere packaging inhibits the growth of mesophilic bacteria and extends the shelf life of fresh Anthotyros cheese by 20 days while maintaining its good sensory properties [139]. The same authors also reported that the use of modified atmosphere packaging inhibits the growth of microorganisms and consequently extends the shelf life of fresh Lor and Myzithra cheeses without altering their sensory properties. In recent years, many authors have investigated the effect of adding various herbs and plant extracts to extend the shelf life of whey cheese and improve its sensory and antioxidant properties. Akpinar et al. (2022) [140] investigated the addition of black cumin, rosemary and thyme to Lor whey cheese stored in different packaging materials (goat skin bags and artificial casings). After 30 days of storage, the cheeses with added black cumin and thyme packaged in goat skin bags had the highest levels of Lactobacillus spp. while the cheeses with added black cumin and thyme packaged in an artificial casing had the lowest levels. According to these authors, the samples with black cumin were generally favoured, while cheese with rosemary had the lowest sensory values. Christaki et al. (2022) [141] investigated the selection of a suitable system for the delivery of bioactive compounds from oregano essential oil and oregano extracts and their incorporation into Mizithra and Anthotyros whey cheeses. They found that oregano oil-in-water nanoemulsions exhibited antifungal activity against Penicillium expansum, which prolonged the shelf life and improved the organoleptic profile of Mizithra and Anthotyros whey cheeses. On the other hand, by changing the traditional production of whey cheese, a safer product with a longer shelf life can be produced. Hassan et al. (2022) [134] suggested changing the traditional process of making Arishi by adding an extra pasteurisation step or lowering the pH to 4.3. This modification resulted in a safer product with a longer shelf life and no sensory differences between the traditionally produced cheese and the Arishi made from pasteurised whey. With the aim to extend the shelf life of Manouri cheese, Govari and Vareltzis (2024) [142] examined the argon-based modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) effect on quality characteristics of cheese during refrigeration storage. The argon-based MAP of Manouri cheese, as compared with nitrogen-based MAP, provided the same microbiological changes in Manouri cheese during storage under fluorescent light at 4 °C for 4 months. However, the argon-based MAP proved better in keeping the colour (lightness L*), in decreasing lipid oxidation and in sensory attribute properties of Manouri cheese as compared with nitrogen-based MAP during storage under fluorescent light at 4 °C for 4 months.
10. Conclusions
EM is known for its world-famous cheeses, which have a rich tradition of cheese-making that has been adapted to difficult conditions (hilly terrain and hot summers). While traditional cheese-making focuses on producing what consumers like EM’s modern processes respond to changing consumer preferences. Innovations in EM cheese-making include advanced methods of geographical identification and authenticity testing, as well as the use of technologies such as machine learning to assess the ripeness of cheese. To address concerns about salt content, some EM cheeses now use alternative mineral salts or local herbs to reduce sodium content. High-pressure treatment has proven effective in ensuring the safety of low-salt EM white cheese by killing harmful bacteria. In addition, EM cheeses made from raw milk contain beneficial probiotic microbes that can be further enhanced by microencapsulation techniques. The use of probiotics, prebiotics and protective starters has shown promise in combating harmful bacteria, improving flavour and enhancing the quality of EM cheeses. Research on unique EM cheeses matured in animal skin has revealed the accumulation of bioactive peptides with potential health benefits. Natural antimicrobial agents such as lysozyme and lactoferrin from donkey milk are used to extend the shelf life of stretched curd cheese. The inclusion of local herbs and modified atmospheres in cheese production increases functionality, extends shelf life and improves sensory properties. On the other hand, there has been no recent research on the residual lactose content of EM cheeses to meet the needs of people with lactose intolerance, which has increased in recent years due to growing awareness of this condition. Preserving the production of traditional EM cheeses is critical to maintaining their cultural significance and meeting the demand of consumers interested in the provenance, craftsmanship and nutritional value of these unique products. Traditional cheeses appeal to those seeking authentic, labour-intensive products with distinct flavours and aromas that reflect their heritage and quality.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.K.; methodology, S.K. and M.T.K.; data curation, S.K., A.R., S.S.K., I.D.Š., D.B.L. and M.T.K.; resources, S.K., A.R., S.S.K., I.D.Š., D.B.L. and M.T.K.; writing—original draft preparation, S.K., A.R., S.S.K., I.D.Š., D.B.L. and M.T.K.; writing—review and editing, S.K. and M.T.K.; visualization, D.B.L. and I.D.Š.; supervision, M.T.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Alichanidis, E.; Polychroniadou, A. Characteristics of Major Traditional Regional Cheese Varieties of East-Mediterranean Countries: A Review. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2008, 88, 495–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barukčić, I.; Tudor Kalit, M. Origin, Production and Specificities of Croatian Traditional Cheeses. In Cheeses around the World–Types, Production, Properties and Cultural and Nutritional Relevance; Guine, P.F.R., Correia, P.M.R., Ferrao, A.C., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 153–182. [Google Scholar]
- Prpić, Z.; Kalit, S.; Havranek, J.L.; Štimac, M.; Jerković, S. Krčki Sir. Mljekarstvo 2003, 53, 175–194. [Google Scholar]
- Matutinović, S.; Rako, A.; Kalit, S.; Havranek, J. Značaj Tradicijskih Sireva s Posebnim Osvrtom Na Lećevački Sir. Mljekarstvo 2007, 57, 49–65. [Google Scholar]
- Magdić, V.; Kalit, S.; Fuka, M.M.; Skelin, A.; Samaržija, D.; Redžepović, S.; Havranek, J. Hygienic and Physicochemical Properties of Istrian Cheese. Mljekarstvo 2013, 63, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Rogošić, J. Pregled Biljnog Pokrova Mediteranskog Područja Hrvatske. In Gospodarenje Mediteranskim Prirodnim Resursima; Školska naklada: Mostar, Bosna i Hercegovina, 2000; pp. 1–141. [Google Scholar]
- Molle, G.; Decandia, M.; Cabiddu, A.; Landau, S.Y.; Cannas, A. An Update on the Nutrition of Dairy Sheep Grazing Mediterranean Pastures. Small Rumin. Res. 2008, 77, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matutinović, S.; Kalit, S.; Salajpal, K.; Vrdoljak, J. Effects of Flock, Year and Season on the Quality of Milk from an Indigenous Breed in the Sub-Mediterranean Area. Small Rumin. Res. 2011, 100, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matutinović, S.; Salajpal, K.; Kalit, S. Nitrogen Components of Sheep Milk. Mljekarstvo 2014, 64, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Coulon, J.B.; Delacroix-Buchet, A.; Martin, B.; Pirisi, A. Relationships between Ruminant Management and Sensory Characteristics of Cheeses: A Review. Lait 2004, 84, 221–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.K.; Tamime, A.Y. (Eds.) Feta and Related Cheeses; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Hayaloglu, A.A.; Ozer, B.H.; Fox, P.F. Cheeses of Turkey: 2. Varieties Ripened under Brine. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2008, 88, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badem, A.; Uçar, G. The Properties of Kashar Cheese Produced with Added Rennet Casein. Eurasian J. Vet. Sci. 2018, 34, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayaloglu, A.A.; Fox, P.F. Cheeses of Turkey: 3. Varieties Containing Herbs or Spices. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2008, 88, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rako, A.; Tudor Kalit, M.; Kalit, S.; Soldo, B.; Ljubenkov, I. Nutritional Characteristics of Croatian Whey Cheese (Bračka Skuta) Produced in Different Stages of Lactation. LWT 2018, 96, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, R.; Robinson, R.K.; Wilbey, R.A. Cheesemaking Practice; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- McClure, S.B.; Magill, C.; Podrug, E.; Moore, A.M.T.; Harper, T.K.; Culleton, B.J.; Kennett, D.J.; Freeman, K.H. Fatty Acid Specific Δ13C Values Reveal Earliest Mediterranean Cheese Production 7200 Years Ago. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trbojević-Vukičević, T.; Marenj, T.S.; Kužir, S.; Čataj, L. Arheological and Archaeozoological Evidence of Milk as a Food in the Territory of Croatia. Mljekarstvo 2011, 61, 319–325. [Google Scholar]
- Tudor Kalit, M.; Lojbl, T.; Rako, A.; Gün, I.; Kalit, S. Biochemical Changes during Ripening of Cheeses in an Animal Skin. Mljekarstvo 2020, 70, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, M.; Mattar, J. The Goat Dairy Sector in Lebanon. In Goat Science; InTech: London, UK, 2018; pp. 381–396. [Google Scholar]
- Bijeljac, S. Sir Iz Mijeha; Udruga “Pramenka”: Mostar, Bosna i Hercegovina, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Jovanović, S.; Maćej, O.; Kovačević, Z.; Vučić, T.; Marinković, S. Kvalitet Ljubinjskog Autohtonog Sira Iz Mijeha. In Proceedings of the 4. Simpozijum Mleko i Proizvodi od Mleka, Kladovo, Serbia, 9–13 May 2007; Maćej, O., Jovanović, S., Eds.; Ministarstvo Nauke i Zaštite Životne Sredine: Kladovo, Serbia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sarić, Z.; Bijeljac, S.; Dizdarević, T. Autohtono Sirarstvo u Bosni i Hercegovini–Istorijski Aspekt. Biotehnol. Stoč. 2008, 24, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Sert, D.; Akin, N.; Aktumsek, A. Lipolysis in Tulum Cheese Produced from Raw and Pasteurized Goats’ Milk during Ripening. Small Rumin. Res. 2014, 121, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturkoglu-Budak, S.; Aykas, D.P.; Kocak, C.; Dönmez, S.; Gursoy, A.; De Vries, R.P.; Bron, P.A. Temporal Microbiota and Biochemical Profiles during Production and Ripening of Divle Cave Cheese. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2018, 71, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, T.; Akin, N.; Sözeri Atik, D.; Rabia Özkan, E.; Dertli, E.; Akyol, İ. Lactic Acid Bacteria Diversity and Dynamics during Ripening of Traditional Turkish Goatskin Tulum Cheese Produced in Mut Region Assessed by Culturing and PCR-DGGE. LWT 2021, 138, 110701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aygun, O.; Aslantas, O.; Oner, S. A Survey on the Microbiological Quality of Carra, a Traditional Turkish Cheese. J. Food Eng. 2005, 66, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toufeili, I.; Shadarevian, S.; Artinian, T.; Tannous, R. Ripening Changes and Sensory Properties of Bovine, Caprine and Ovine Shankleesh. Int. Dairy J. 1995, 5, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esen, Y.; Çetin, B. Bacterial and Yeast Microbial Diversity of the Ripened Traditional Middle East Surk Cheese. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 117, 105004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esen, Y.; Turgay, O. The Relationship between Physicochemical and Microbiological Characteristics of Surk Cheese. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 4822–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, A.M. Kasseri. In The Oxford Companion to Cheese; Donnelly, C., Kehler, M., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016; p. 398. ISBN 9780199330911. [Google Scholar]
- Üçüncü, M. From A to Z Cheese Technology; Ege University Press: Izmir, Turkey, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bijeljac, S.; Ivanković, S.; Mihaljević, P. Travnički Cheese; Rototisak: Prozor-Rama, Bosna i Hercegovina, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mehaia, M.A. Manufacture of Fresh Soft White Cheese (Domiati-Type) from Ultrafiltered Goats’ Milk. Food Chem. 2002, 79, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Khetra, Y. Buffalo Milk Cheese. In Cheese: Chemistry, Physics and Microbiology; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 1093–1101. ISBN 9780122636530. [Google Scholar]
- Papademas, P.; Robinson, R.K. Halloumi Cheese: The Product and Its Characteristics. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 1998, 51, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaman, H.; Aykas, D.P.; Rodriguez-Saona, L.E. Monitoring Turkish White Cheese Ripening by Portable FT-IR Spectroscopy. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1107491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massouras, T.; Zoidou, E.; Baradaki, Z.; Karela, M. Physicochemical, Microbiological and Sensory Characteristics of White Brined Cheese Ripened and Preserved in Large-Capacity Stainless Steel Tanks. Foods 2023, 12, 2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabevska-Kostoska, M.; Velickova, E.; Kuzmanova, S.; Winkelhausen, E. Traditional White Brined Cheese as a Delivery Vehicle for Probiotic Bacterium Lactobacillus Casei. Maced. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2015, 34, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Moatsou, G.; Govaris, A. White Brined Cheeses: A Diachronic Exploitation of Small Ruminants Milk in Greece. Small Rumin. Res. 2011, 101, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitreli, G.; Exarhopoulos, S.; Goulas, A.; Antoniou, K.D. Traditional Greek Cheeses. In Cheeses around the World; Guine, P.F.R., Correia, P.M.R., Ferrao, C., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 329–378. [Google Scholar]
- Gatzias, I.S.; Karabagias, I.K.; Kontominas, M.G.; Badeka, A.V. Geographical Differentiation of Feta Cheese from Northern Greece Based on Physicochemical Parameters, Volatile Compounds and Fatty Acids. LWT 2020, 131, 109615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritikou, A.S.; Aalizadeh, R.; Damalas, D.E.; Barla, I.V.; Baessmann, C.; Thomaidis, N.S. MALDI-TOF-MS Integrated Workflow for Food Authenticity Investigations: An Untargeted Protein-Based Approach for Rapid Detection of PDO Feta Cheese Adulteration. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 131057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurćubić, V.S.; Lević, S.; Pavlović, V.; Mihailović, R.; Nikolić, A.; Lukić, M.; Jovanović, J.; Danilović, B.; Milinković, M.; Oz, F.; et al. Manufacture of Low-Na White Soft Brined Cheese: Effect of NaCl Substitution with a Combination of Na-K Salts on Proximate Composition, Mineral Content, Microstructure, and Sensory Acceptance. Foods 2024, 13, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plessas, S.; Ganatsios, V.; Mantzourani, I.; Bosnea, L. White Brined Cheese Production by Incorporation of a Traditional Milk-Cereal Prebiotic Matrix with a Candidate Probiotic Bacterial Strain. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkaya-Kotan, T.; Hayaloglu, A.A. Volatilome Profile (HS-SPME/GC–MS) and Proteolysis in Beyaz Peynir (White-Brined Cheese) Made Using Different Probiotic Adjunct Cultures and Ripening under Brine or Vacuum Package Systems, and Chemometric Analysis. Int. Dairy J. 2024, 152, 105894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahein, M.H.; Amr, A.S.; Sadder, M.; Al-Qadiri, H.M.; Albawarshi, Y.; Al-khamaiseh, A.M.; Kanaan, O. Lethality of High Hydrostatic Pressure Processing on Listeria Monocytogenes, Staphylococcus Aureus and Escherichia Coli in Low Salt White Brined Cheese: D-Value. Int. Dairy J. 2023, 143, 105675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neofytou, M.C.; Miltiadou, D.; Sfakianaki, E.; Constantinou, C.; Symeou, S.; Sparaggis, D.; Hager-Theodorides, A.L.; Tzamaloukas, O. The Use of Ensiled Olive Cake in the Diets of Friesian Cows Increases Beneficial Fatty Acids in Milk and Halloumi Cheese and Alters the Expression of SREBF1 in Adipose Tissue. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 8998–9011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naziri, E.; Papadaki, E.; Savvidis, I.; Botsaris, G.; Gkatzionis, K.; Mugampoza, E.; Mantzouridou, F.T. Exploring the Potential of Halloumi Second Cheese Whey for the Production of Lactic Acid Cultures for the Dairy Industry. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshwal, G.K.; Ameta, R.; Sharma, H.; Singh, A.K.; Panjagari, N.R.; Baria, B. Effect of Ultrafiltration and Fat Content on Chemical, Functional, Textural and Sensory Characteristics of Goat Milk-Based Halloumi Type Cheese. LWT 2020, 126, 109341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamilari, E.; Anagnostopoulos, D.A.; Papademas, P.; Kamilaris, A.; Tsaltas, D. Characterizing Halloumi Cheese’s Bacterial Communities through Metagenomic Analysis. LWT 2020, 126, 109298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.F.; McSweeney, P.L.H. Cheeses–Manufacture of Hard and Semi-Hard Varieties of Cheese. In Encyclopedia of Food Sciences and Nutrition; Caballero, B., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 1073–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Shi, X.; Wang, B. A Review on the General Cheese Processing Technology, Flavor Biochemical Pathways and the Influence of Yeasts in Cheese. Front Microbiol. 2021, 12, 703284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozoudi, D.; Pavlidou, S.; Kotzamanidis, C.; Georgakopoulos, P.; Torriani, S.; Kondyli, E.; Claps, S.; Belibasaki, S.; Litopoulou-Tzanetaki, E. Graviera Naxou and Graviera Kritis Greek PDO Cheeses: Discrimination Based on Microbiological and Physicochemical Criteria and Volatile Organic Compounds Profile. Small Rumin. Res. 2016, 136, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litopoulou-Tzanetaki, E. Changes in Numbers and Kinds of Lactic Acid Bacteria During Ripening of Kefalotyri Cheese. J. Food Sci. 1990, 55, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasi, E.; Litopoulou-Tzanetaki, E.; Tzanetakis, N. Microbiological Study of Manura, a Hard Cheese Made from Raw Ovine Milk in the Greek Island Sifnos. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2003, 56, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Product Specification Livanjski Sir, Indication of Geographical Origin; Association for the Protection of the Origin of Livanjski Cheese: Livno, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 2019.
- Istarski Ovčji Sir/Istrski Ovčji Sir, Zaštićena Oznaka Izvornosti, Specifikacija Proizvoda; Association of Istrian Goat and Sheep Breeders: Vodnjan, Croatia, 2023.
- Paški Sir, Zaštićena Oznaka Izvornosti, Specifikacija Proizvoda; Association of Pag Cheese Producers of the Island of Pag: Pag, Croatia, 2018.
- Bontinis, T.G.; Mallatou, H.; Alichanidis, E.; Kakouri, A.; Samelis, J. Physicochemical, Microbiological and Sensory Changes during Ripening and Storage of Xinotyri, a Traditional Greek Cheese from Raw Goat’s Milk. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2008, 61, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirecki, S.; Popović, N.; Antunac, N.; Mikulec, N.; Plavljanić, D. Production Technology and Some Quality Parameters of Njeguši Cheese. Mljekarstvo 2015, 65, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, M.N.-E.F.; El-Kadi, S.M.; Al Esawy Ibrahim, S. Development a Method for Making Ras Cheese from Pasteurized Milk. DJAS 2023, 2, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Havranek, J.; Kalit, S.; Antunac, N.; Samaržija, D. Sirarstvo; Volarić, V., Bašić, Z., Eds.; Hrvatska Mljekarska Udruga: Zagreb, Croatia, 2014; ISBN 978-953-7472-08-5. [Google Scholar]
- Guinee, T.P.; Fox, P.F. Salt in Cheese: Physical, Chemical and Biological Aspects. In Cheese: Chemistry, Physics and Microbiology: Fourth Edition; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 317–375. ISBN 9780122636530. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, P.F.; Guinee, T.P.; Cogan, T.M.; Mcsweeney, P.L.H. Biochemistry of Cheese Ripening; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1-4899-7681-9. [Google Scholar]
- El-Kholy, A.M. Ras Cheese Making with Vegetable Coagulant-a Comparison with Calf Rennet. WJDFS 2015, 10, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidou, M.D.; Maggira, M.; Samouris, G. Physicochemical Characteristics, Fatty Acids Profile and Lipid Oxidation during Ripening of Graviera Cheese Produced with Raw and Pasteurized Milk. Foods 2022, 11, 2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappa, E.C.; Kondyli, E.; Vlachou, A.M.; Kakouri, A.; Malamou, E. Evolution of the Biochemical and Microbiological Characteristics of Mountainous Kefalotyri Cheese during Ripening and Storage. Food Res. 2021, 5, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralli, E.; Spyros, A. A Study of Greek Graviera Cheese by NMR-Based Metabolomics. Molecules 2023, 28, 5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirin, S.; Marijan, Ž.; Mihaljević, D. Livanjski Sir. Mljekarstvo 2003, 53, 281–291. [Google Scholar]
- Behera, S.S.; Ray, R.C.; Zdolec, N. Lactobacillus Plantarum with Functional Properties: An Approach to Increase Safety and Shelf-Life of Fermented Foods. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9361614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurić, S. Bioencapsulation as a Sustainable Delivery of Active Agents for Plant Nutrition/Protection and Production of Functional Foods. Doctoral Dissertation, Faculty of Food Technology and Biotechnology University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mrkonjić Fuka, M.; Zgomba Maksimović, A.; Hulak, N.; Kos, I.; Marušić Radovčić, N.; Jurić, S.; Tanuwidjaja, I.; Karolyi, D.; Vinceković, M. The Survival Rate and Efficiency of Non-Encapsulated and Encapsulated Native Starter Cultures to Improve the Quality of Artisanal Game Meat Sausages. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiš, M.; Zdolec, N.; Kazazić, S.; Vinceković, M.; Jurić, S.; Dobranić, V.; Oštarić, F.; Marić, I.; Mikulec, N. Implementation of Novel Autochthonous Microencapsulated Strains of Lactiplantibacillus Plantarum, Lactococcus Lactis, and Lamb’s Rennet in the Production of Traditional “Paški Sir” Cheese. Fermentation 2023, 9, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oštarić, F.; Antunac, N.; Cubric-Curik, V.; Curik, I.; Jurić, S.; Kazazić, S.; Kiš, M.; Vinceković, M.; Zdolec, N.; Špoljarić, J.; et al. Challenging Sustainable and Innovative Technologies in Cheese Production: A Review. Processes 2022, 10, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedda, L.; Perniciano, A.; Loddo, A.; Di Ruberto, C. Understanding Cheese Ripeness: An Artificial Intelligence-Based Approach for Hierarchical Classification. Knowl. Based Syst. 2024, 295, 111833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudor Kalit, M.; Kalit, S.; Havranek, J. An Overview of Researches on Cheeses Ripening in Animal Skin. Mljekarstvo 2010, 60, 149–155. [Google Scholar]
- Hayaloglu, A.A.; Cakmakci, S.; Brechany, E.Y.; Deegan, K.C.; McSweeney, P.L.H. Microbiology, Biochemistry, and Volatile Composition of Tulum Cheese Ripened in Goat’s Skin or Plastic Bags. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 1102–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lešić, T.; Pleadin, J.; Krešić, G.; Vahčić, N.; Markov, K.; Vrdoljak, M.; Frece, J. Chemical and Fatty Acid Composition of Cow and Sheep Milk Cheeses in a Lamb Skin Sack. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2016, 46, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rako, A.; Kalit, M.T.; Rako, Z.; Petrović, D.; Kalit, S. Effect of Composition and Proteolysis on Textural Characteristics of Croatian Cheese Ripen in a Lamb Skin Sack (Sir Iz Mišine). Mljekarstvo 2019, 69, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, H.İ.; Konak Göktepe, Ç.; Akın, N. Proteolysis Pattern and Functional Peptides in Artisanal Tulum Cheeses Produced from Mut Province in Turkey. LWT 2021, 149, 111642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamber, U. The Traditional Cheeses of Turkey: Cheeses Common to All Regions. Food Rev. Int. 2008, 24, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudor Kalit, M.; Kalit, S.; Delaš, I.; Kelava, N.; Karolyi, D.; Kaić, D.; Vrdoljak, M.; Havranek, J. Changes in the Composition and Sensory Properties of Croatian Cheese in a Lamb Skin Sack (Sir Iz Mišine) during Ripening. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2014, 67, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturkoglu-Budak, S.; Gursoy, A.; Aykas, D.P.; Koçak, C.; Dönmez, S.; de Vries, R.P.; Bron, P.A. Volatile Compound Profiling of Turkish Divle Cave Cheese during Production and Ripening. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 5120–5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhan, M.; Linder, M.; Hosri, C.; Fanni, J. Changes in Proteolysis and Volatile Fraction during Ripening of Darfiyeh, a Lebanese Artisanal Raw Goat’s Milk Cheese. Small Rumin. Res. 2010, 90, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakır, Y.; Çakmakçı, S.; Hayaloğlu, A.A. Proteolysis and Lipolysis in Tulum Cheeses Ripened in Plastic Barrels and Goat Skin Bags Made Using Penicillium Roqueforti 41 Strain. Small Rumin. Res. 2022, 216, 106810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, A.; Güler, Z. Glycolysis, Lipolysis and Proteolysis in Raw Sheep Milk Tulum Cheese during Production and Ripening: Effect of Ripening Materials. Food Chem. 2019, 286, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frece, J.; Vrdoljak, M.; Filipčić, M.; Jelić, M.; Čanak, I.; Jakopović, Ž.; Pleadin, J.; Gobin, I.; Landeka Dragičević, T.; Markov, K. Microbiological Quality and Variability of Natural Microbiota in Croatian Cheese Maturin in Lambskin Sacks. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 54, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakir, Y.; Cakmakci, S.; Hayaloglu, A.A. The Effect of Addition of Black Cumin (Nigella sativa L.) and Ripening Period on Proteolysis, Sensory Properties and Volatile Profiles of Erzincan Tulum (Şavak) Cheese Made from Raw Akkaraman Sheep’s Milk. Small Rumin. Res. 2016, 134, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atik, D.S.; Akın, N.; Akal, C.; Koçak, C. The Determination of Volatile Profile during the Ripening Period of Traditional Tulum Cheese from Turkey, Produced in Anamur in the Central Taurus Region and Ripened in Goatskin. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 117, 104991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, M.; Arab-Tehrany, E.; Linder, M.; Hosri, C.; Fanni, J. Transfer across Goatskin Barrier of 2-Butanone, 2,3-Butanedione and 2-Butanol during Maturation of Traditional Lebanese Cheese, Darfiyeh: Comparison between Experimental Aqueous Model Solution and Goatskin System. Small Rumin. Res. 2015, 133, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, Z.G.; Çaglar, A.; Çakmakçi, S. Some Physicochemical, Microbiological, and Sensory Properties of Tulum Cheese Produced from Ewe’s Milk via a Modified Method. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2007, 60, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, H.; Akın, N. Effect of Ripening Time on Peptide Dynamics and Bioactive Peptide Composition in Tulum Cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 3832–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öztürk, H.İ.; Oraç, A.; Akın, N. Characterization of Bioactive Peptides Derived from Goatskin Tulum Cheese of the Ereğli Region at Different Stages of Ripening. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 112124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrdoljak, M.; Tudor Kalit, M.; Dolenčić Špehar, I.; Radeljević, B.; Jelić, M.; Mandinić, S.; Frece, J.; Kalit, S. Effects of the Autochthonous Probiotic Bacteria Lactobacillus plantarum B and Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis S1 on the Proteolysis of Croatian Cheese Ripened in a Lambskin Sack (Sir Iz Mišine). Fermentation 2022, 8, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, T.; Irani, J.; Afif, C.; Bassil, N.; Estephan, E.; Serhan, M.; Bassil, M. Probiotic Effect of Lebanese Darfiyeh Cheese: A Randomized Case Control Prospective Study in the Elderly. Food Nutr. Sci. 2015, 6, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Özkan, E.R.; Demirci, T.; Akın, N. In Vitro Assessment of Probiotic and Virulence Potential of Enterococcus Faecium Strains Derived from Artisanal Goatskin Casing Tulum Cheeses Produced in Central Taurus Mountains of Turkey. LWT 2021, 141, 110908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiliç Kanak, E.; Öztürk Yilmaz, S. Investigation of Some Probiotic Properties of Lactobacillaceae Strains Isolated from Traditional Tulum Cheese in Turkey. Mljekarstvo 2023, 73, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, M.; Gobbetti, M. Pasta-Filata Cheeses: Traditional Pasta-Filata Cheese. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences; Fuquay, J.W., Fox, P.F., McSweeney, P.L.H., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2011; pp. 745–752. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, F.; Dagdemir, E. The Effects of Beeswax Coating on Quality of Kashar Cheese during Ripening. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 2582–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaşen, A.; Macit, E.; Dertli, E. Microbial Species Playing Roles for the Production of Traditional Kasar Cheese during Pre-Maturation Period. LWT 2018, 91, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aran, N.A. Microbial Study of Kashar Cheese. Milchwissenschaft 1998, 53, 565–568. [Google Scholar]
- Durlu-Özkaya, F.; Gün, İ. Anadolu’da Peynir Kültürü. Anadolu’da Peynir Kültürü 2007, 10, 485–505. [Google Scholar]
- Sert, D.; Ayar, A.; Akın, N. The Effects of Starter Culture on Chemical Composition, Microbiological and Sensory Characteristics of Turkish Kasar Cheese during Ripening. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2007, 60, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TS 3272; Turkish Standards: Kashar Cheese (TS 3272). Turkish Standards Institution: Ankara, Türkiye, 1999.
- Shojaei, M.; Eshaghi, M.; Nateghi, L. Investigation of Nano-Biocomposite for Kashar Cheese and Ground Meat Packaging. J. Nutr. Food Secur. 2021, 6, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbaş, F.; Dertli, E.; Arıcı, M. Prevalence of Clostridium spp., in Kashar Cheese and Efficiency of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis Mix as a Biocontrol Agents for Clostridium spp. Food Biosci. 2022, 46, 101581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, Z.; Kutlu, N.; Meral, R.; Ekin, M.M.; Kose, Y.E. Protective Effect of Grape Seed Oil-Loaded Nanofibers: Limitation of Microbial Growth and Lipid Oxidation in Kashar Cheese and Fish Meat Samples. Food Biosci. 2021, 42, 101076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturkoglu-Budak, S.; Akal, H.C.; Bereli, N.; Cimen, D.; Akgonullu, S. Use of Antimicrobial Proteins of Donkey Milk as Preservative Agents in Kashar Cheese Production. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 120, 105090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulejmani, E.; Sahingil, D.; Hayaloglu, A.A. A Comparative Study of Compositional, Antioxidant Capacity, ACE-Inhibition Activity, RP-HPLC Peptide Profile and Volatile Compounds of Herbal Artisanal Cheeses. Int. Dairy J. 2020, 111, 104837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarakci, Z.; Temiz, H.; Aykut, U.; Turhan, S. Influence of Wild Garlic on Color, Free Fatty Acids, and Chemical and Sensory Properties of Herby Pickled Cheese. Int. J. Food Prop. 2011, 14, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, O.B.; Kırdar, S.S. Traditional Dairy Producs in Hatay Province. J. Int. Sci. Publ. 2016, 4, 339–347. [Google Scholar]
- Nehme, L.; Salameh, C.; Tabet, E.; Nehme, M.; Hosri, C. Innovative Improvement of Shanklish Cheese Production in Lebanon. Int. Dairy J. 2019, 90, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, B.M.d.; Vieira, L.G.d.F.; Beltrami, J.M.; Serenini, G.D.F.; Santos, N.S.d.; Soares, A.A.; Alves, G. Physical-Chemical Characterization of Fresh Shanklish Cheese with Kefir and Turmeric Extract (Curcuma longa L.). Arq. Ciênc. Vet. Zool. 2020, 23, e2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayaloglu, A.A.; Farkye, N. Cheese with Added Herbs, Spices and Condiments. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tarakçi, Z.; Cos¸kun, H.C.; Tunçtürk, Y. Some Properties of Fresh and Ripened Herby Cheese, a Traditional Variety Produced in Turkey. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2004, 42, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Tarakci, Z.; Sagun, E.; Durmaz, H. The Effect of Mendi (Chaerophyllum sp.) on Ripening of Vacuum-Packed Herby Cheese. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2006, 59, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekici, K.; Coskun, H.; Tarakci, Z.; Ondul, E.; Sekeroglu, R. The Contribution of Herbs to the Accumulation of Histamine in Otlu Cheese. J Food Biochem. 2006, 30, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarakci, Z.; Akyuz, N. Effects of Packaging Materials and Filling Methods on Selected Characteristics of Otlu (Herby) Cheese. Int. J. Food Prop. 2009, 12, 496–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncturk, Y.; Cookun, H.; Ghosh, B.C. Nitrogen Fractions in Brine during Ripening of Herby Cheese (Otlu Peynir). Indian J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 56, 208–212. [Google Scholar]
- Tunçtürk, Y.; Coşkun, H. The Effects of Production and Ripening Methods on Some Properties of the Herby Cheese Otlu Peynir. Milchwissenschaft 2002, 57, 638–640. [Google Scholar]
- Mendil, D. Mineral and Trace Metal Levels in Some Cheese Collected from Turkey. Food Chem. 2006, 96, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, S.M.; Youssef, A.M. Potential Application of Herbs and Spices and Their Effects in Functional Dairy Products. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarakci, Z.; Durmaz, H.; Sagun, E.; Sancak, H. Influence of Brine Concentration on Chemical, Microbiological and Sensory Characteristics of Herby Cheese. Indian Vet. J. 2005, 82, 279–282. [Google Scholar]
- Tajkarimi, M.M.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Cliver, D.O. Antimicrobial Herb and Spice Compounds in Food. Food Control 2010, 21, 1199–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayar, A.; Akyüz, N. Effect of Some Herbs Extract Added at during the Ripening of Lipolysis of White Cheese. GTD J. 2003, 28, 295–303. [Google Scholar]
- Kaminarides, S.; Ilias-Dimopoulos, E.; Zoidou, E.; Moatsou, G. The Effect of Addition of Skimmed Milk on the Characteristics of Myzithra Cheeses. Food Chem. 2015, 180, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pintado, M.E.; Macedo, A.C.; Malcata, F.X. Review: Technology, Chemistry and Microbiology of Whey Cheeses. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2001, 7, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozet, N.; Maćej, O.; Jovanović, S. Autohtoni Mliječni Proizvodi Osnova Za Razvoj Specifičnih Originalnih Mliječnih Prerađevina u Savremenim Uslovima. Biotechnol Anim. Husb. 2004, 20, 329–348. [Google Scholar]
- Kalantzopoulos, G.C. Cheeses from Ewes’ and Goats’ Milk. In Cheese: Chemistry, Physics and Microbiology: Volume 2 Major Cheese Groups; Fox, P.F., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1993; pp. 507–553. ISBN 978-1-4615-2648-3. [Google Scholar]
- Antunac, N.; Hudik, S.; Mikulec, N.; Maletić, M.; Horvat, I.; Radeljević, B.; Havranek, J. Proizvodnja i Kemijski Sastav Istarske i Paške Skute. Mljekarstvo 2011, 61, 326–335. [Google Scholar]
- Bojanic Rasovic, M.; Nikolić, N.; Rasovic, R. Quality of “Urda” Obtained after Production of Montenegrin Semi-Hard Cheese. Food Res. 2017, 1, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papademas, P.; Bintsis, T.; Alichanidis, E.; Ardö, Y. Whey Cheeses (Heat Coagulated). In Global Cheesemaking Technology; Papademas, P., Bintsis, T., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: West Sussex, UK, 2018; pp. 446–452. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, H.F.; Tabarani, P.; Abiad, M.G. Microbiological, Chemical, and Sensory Characteristics of Arishi Cheese. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rako, A.; Kalit, S.; Tudor Kalit, M. Nutritive Value and Consumers’ Acceptance of Brački Albumin Cheese. In Proceedings of the 51st Croatian and 11th International Symposium on Agriculture, Opatija, Croatia, 15–18 February 2016; pp. 360–363. [Google Scholar]
- Ozer, C. The Usability of Lor Cheese in Some Dairy-Based Desserts of Turkish and International Cuisines. J. Culin. 2019, 18, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, A.M. Manouri. In The Oxford Companion to Cheese; Donnely, C., Kehler, M., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016; p. 457. ISBN 9780199330911. [Google Scholar]
- Hudik, S. Proizvodnja, Kemijski Sastav i Kvaliteta Albuminskog Sira. Master’s Thesis, Faculty of Agriculture University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bintsis, T.; Papademas, P. Sustainable Approaches in Whey Cheese Production: A Review. Dairy 2023, 4, 249–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpinar, A.; Yerlikaya, O.; Akan, E.; Karagozlu, C.; Kinik, O.; Uysal, H.R. The Effect of Packaging Materials on Physicochemical, Microbiological, and Sensorial Properties of Turkish Whey (Lor) Cheese with Some Plants. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e17060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christaki, S.; Moschakis, T.; Hatzikamari, M.; Mourtzinos, I. Nanoemulsions of Oregano Essential Oil and Green Extracts: Characterization and Application in Whey Cheese. Food Control 2022, 141, 109190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govari, M.; Vareltzis, P. Effect of Argon-Based Modified Atmosphere Packaging Storage on Manouri Cheese. Int. Dairy J. 2024, 150, 105846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).