Abstract
Koumiss, a traditional fermented beverage made from mare’s milk, is typically consumed by nomads. Industrialized production of koumiss has been increasingly applied recently due to the increased demand for the beverage and awareness of its potential health benefits. However, it is unknown whether industrial koumiss is comparable to the traditional koumiss in terms of quality. In this study, we compared the microbiological and physicochemical properties in the industrial and traditional koumiss fermentation processes synchronously using culture-dependent and culture-independent approaches. Although Lactobacillus and Kazachstania species were similarly dominant in the bacterial and fungal communities, respectively, in both processes, the microbial counts and diversity in the traditional koumiss were significantly higher than those in the industrial koumiss. Furthermore, the traditional koumiss fermentation consumed more lactose, produced more flavor substances including acetic acid, lactic acid, ethanol, and free amino acids, and reached a lower pH value at the final stage. The physicochemical characters of traditional koumiss were mainly associated with Lactobacillus and Kazachstania species, which, in turn, were positively correlated with each other but negatively correlated with other non-dominant microbes. The starter was the major source of the microbial community of industrial koumiss, whereas both the starter and environment were the major sources of traditional koumiss. Random forest analysis recognized 11 significantly important genera as microbial indicators to distinguish industrial from traditional koumiss. Overall, this study shows that the microbial and physicochemical dynamics during the traditional and industrial fermentation of koumiss differ significantly, and the results obtained are valuable for improving the quality of industrial koumiss.
1. Introduction
Koumiss, also referred to as kumys, kumiss, or airag, is a fermented acidic–alcoholic beverage traditionally made via back-slopping fermentation, a technique in which a small quantity of koumiss from the previous batch is added to raw mare’s milk as the starter for the next batch of fermentation. It is primarily consumed by nomads in China, Kazakhstan, Mongolia, and Russia and has recently gained popularity in western Europe, particularly in France, Italy, Hungary, and the Netherlands [1]. Koumiss is rich in vitamins and essential amino acids and has β-galactosidase activity as well as therapeutic potential including anticarcinogenic, hypocholesterolemia, antioxidative, and antibacterial properties [2]. Due to its lower lactose content compared to raw mare’s milk, koumiss is favorable for individuals suffering from lactose intolerance, which cause symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting [3]. Additionally, previous studies have shown that koumiss can alleviate the symptoms of hyperlipidemia and chronic atrophic gastritis [4,5]. The lactic acid bacteria (LAB) isolated from koumiss are considered a good potential source of probiotics as they have a higher tolerance to bile and effectively inhibit pathogenic bacteria [6,7].
The fermentation of koumiss mainly relies on two types of microbes: LAB and yeasts [8]. The microbes and taste of traditional koumiss vary in different regions [9]. With a global increasing demand for koumiss, there is a demand for industrialization of its production. This can be achieved through fermenting milk with pure cultures or back-slopping on a larger scale [10]. However, it is unclear whether the industrial koumiss is comparable to the traditional koumiss in terms of quality, despite its ability to produce stable products.
Previous studies have focused on various aspects of koumiss fermentation, including microbial composition [9,11], metabolites [12], core microbiota for main flavor compounds [13,14], bacterial function during fermentation [15], and differences between different sites [16] or before and after fermentation [17]. However, it is unknown whether there are significant differences in the quality of koumiss produced through industrial versus traditional fermentation. The purpose of this study is to test the quality of koumiss by comparing the microbiota (yeasts and bacteria) and physicochemical characters of koumiss under industrial and traditional fermentation. Specifically, we identified the microbes involved in koumiss fermentation and tracked their dynamics using culture-dependent and culture-independent methods. Changes in the physicochemical profile during fermentation were also monitored to further analyze the correlation between them and microbes. Finally, we analyzed the contributions of the starter and mare’s milk to koumiss using the source tracker model and identified important genera to distinguish between fermentation modes using the random forest model.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Koumiss Fermentation and Sampling
Koumiss products were prepared using the industrial and traditional fermentation modes in August 2020 in Xilingol League, Inner Mongolia. The back-slopping technique was employed in both modes, in which a small quantity of koumiss from the previous batch was used as the starter for the next fermentation step. For the traditional fermentation, 2.5 L of back-slop starter was added to 25 L of raw mare’s milk and fermented at room temperature (27 ± 3 °C). For the industrial fermentation, 60 L of back-slop starter was added to 600 L of pasteurized mare’s milk and fermented at a lower temperature (20 ± 3 °C). Five batches of koumiss were fermented using their own unique starter and tracked from the beginning to the end. Two of the batches were fermented in industrial mode and three in traditional mode. A total of 150 samples from the 5 batches were collected at 10 sampling points (starter, raw mare’s milk, 0 h, 5 h, 11 h, 22 h, 27 h, 30 h, 33 h, and 46 h) and triplicate samples were collected from each point of each batch. A part of one sample was immediately subjected to pH measurement and microbial strain isolation. The other part was transferred to the laboratory using dry ice boxes and stored at −80 °C until being subjected to DNA extractions and other physicochemical analyses.
2.2. Microbial Isolation, Counts, and Identification
Culturable microbial populations during fermentation were monitored via colony counting. A series of 10-fold dilutions were prepared for each sample and aliquots of 100 μL of appropriate dilutions (10−2 to 10−4) were spread on different agar plates. YPD (w/v, 1% yeast extract, 2% peptone, and 2% D-glucose) agar plates with 200 μg/mL chloramphenicol and de Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe (MRS) agar plates with 2 μg/mL Amphotericin B were used for yeast and bacterium isolation and enumeration, respectively. The automated colony counter (Interscience Scan 1200, St. Nom, France) was used to enumerate the number of colony-forming units (CFUs).
Representative colonies were isolated and identified from the plates showing the highest morphological diversity. Species-level molecular identification of fungi was performed by amplifying and sequencing the D1/D2 domains of the 26S rDNA using NL1/NL4 primers [18] and the ITS region using ITS1/ITS4 [19]. Bacteria were identified via 16S rDNA sequencing after amplification with the 27F/1492R primer pair [20].
2.3. Culture-Independent Analyses
2.3.1. Total DNA Extraction
Samples (4 mL) were centrifuged at 15,000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C. The obtained pellets were used to extract DNA using the FastDNA® Spin Kit for Soil (MP Biomedicals, Santa Ana, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The quality of DNA was assessed using a Nanodrop 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.3.2. Amplification and Sequencing Parameters
To study the diversity of bacteria and fungi, amplification was performed using universal primers. For bacteria, the V3-V4 region of the 16S rDNA was targeted using 338F 5′-ACT CCT ACG GGA GGC AGC AG-3′ and 806R 5′-GGA CTA CHV GGG TWT CTA AT-3′ primers [21]. For fungi, fITS7 5′-GTG ART CAT CGA ATC TTT G-3′ and ITS4ngs 5′-TTC CTS CGC TTA TTG ATA TGC-3′ primers [22,23] targeting the ITS2 region were used. The amplicons from sample triplicates were mixed and sequenced using Illumina Miseq PE300 (Majorbio, Shanghai, China). A total of 4.4 and 6.3 Gb of data for bacterial and fungal amplicons were generated, respectively.
2.3.3. Bioinformatics
FastQC [24] was employed to evaluate the initial quality of the raw Illumina paired-end reads and Trimmomatic (v0.36) [25] was utilized to remove low-quality and ambiguous reads. The downstream analysis was performed using QIIME 2 (v2020.8) [26]. The paired-end sequences were subjected to denoising and clustering into amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) using DADA2 (v2020.8) [27]. Sequences with less than 10 reads in 1 sample or present in only 1 sample were removed. The determination of taxonomy for bacteria was based on the Silva database, while the UNITE database was utilized for fungi. Normalized ASVs tables generated by usearch11 [28] and the following analyses were performed in R (version 4.1.2) [29]. Alpha diversity analysis was performed using indexes including the Shannon index, Pielou evenness, observed features, and Faith’s phylogenetic diversity (Faith’s pd). The Shannon index considers both richness and evenness, while Pielou evenness only focuses on evenness. The observed features refer to richness based on observed ASVs, and Faith’s PD is a phylogenetically weighted measure of richness [30]. For beta diversity analysis, we employed principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) with unweighted and weighted Unifrac metrics, which assess the differences in phylogenetic lineages among samples. The unweighted Unifrac calculates distances based only on branch length proportions, while the weighted Unifrac calculates distances by weighting sequence abundance against the branch lengths [31].
2.4. Physicochemical Analyses
The pH value was determined using a portable pH meter (ASONE, AS700, C1-2815-01). Salinity, which was expressed by the concentration of dissolved salts in a koumiss sample, was determined using the CDC401 probe and HQ40d instrument (HACH, Loveland, CO, USA). For sugar, alcohol, and organic acid quantification, samples were centrifuged at 15,000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C and the supernatants were filtered through a 0.22 μm nylon membrane (Jin Teng Corp., Tianjin, China) before determination. The identification and quantification of sugars, alcohols, and organic acids were carried out using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with the same column but two different detectors (Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan). Specifically, sugars and alcohols were detected using the RID detector, while organic acids were detected using the UV detector. Ten μL injections of the samples were performed on column Bio-Rad HPX-87H (300 mm × 7.8 mm, Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). The column and detector temperatures were 60 °C and 40 °C, respectively. The mobile phase was 5 mM H2SO4 flowing at a rate of 0.6 mL/min, and the total run time was 35 min. The retention time of the standards was utilized for identification, and the peak area of the standards was used for quantification.
Free amino acids were determined using HPLC with a UV detector after precolumn derivatization with phenyl isothiocyanate (PITC), as previously described with modifications [32]. The derivatized samples were filtered through a 0.22 μm nylon membrane before determination. Then, 10 μL injections of samples were performed on column ZORBAX Eclipse XDB-C18 (4.6 mm × 250 mm, 5 μm, Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) using gradient elution with a binary system of acetonitrile and 0.1 M sodium acetate at a flow rate of 1 mL/min and the run time of 45 min. The column and detector temperatures were both 40 °C. Six concentration levels were prepared to plot the standard curve using an amino acid standard solution (GBW(E)100062) containing a mixture of alanine, arginine, aspartic acid, cystine, glutamic acid, glycine, histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, proline, serine, threonine, tyrosine, and valine. Separate standards were prepared to determine the peak position of each amino acid in the mixture. The contribution of an individual amino acid to the taste (umami, sweetness, or bitterness) was inferred according to Schiffman et al. [33]. Umami, sweetness, and bitterness were then expressed by the sum of the concentrations of the amino acids contributing to each taste.
2.5. Statistical Analyses
The data’s normality was evaluated using the Shapiro–Wilk test, and the Wilcoxon test was used to assess the significance of the differences between groups when normality was rejected. Hypotheses were rejected at p < 0.05. Unless otherwise indicated, the data were represented as means ± standard error (SE).
3. Results
3.1. Changes and Composition of Culturable Microbes during Koumiss Fermentation
The microbial changes at different stages in both the industrial and traditional fermentation modes were monitored simultaneously. In the industrial fermentation mode, the bacterial count in the pasteurized mare’s milk was 2.4 log10 CFUs, but fungi were not detected. In the traditional fermentation mode, the bacterial and fungal counts in the raw mare’s milk were 7.7 and 2.3 log10 CFUs, respectively (Figure 1A). From the beginning to the end of fermentation, the bacterial counts ranged from 5.9 to 7.1 log10 CFUs and 7.2 to 7.9 log10 CFUs in the industrial and traditional fermentation modes, respectively; the fungal counts ranged from 5.9 to 7.0 and 6.5 to 7.3 log10 CFUs in the industrial and traditional modes, respectively (Figure 1A). Overall, when considering all samples from both fermentation modes, the microbial counts were significantly higher in the traditional fermentation than that in the industrial fermentation (p < 0.05), and the bacterial counts were significantly higher than that of fungi (p < 0.05) (Figure 1B).
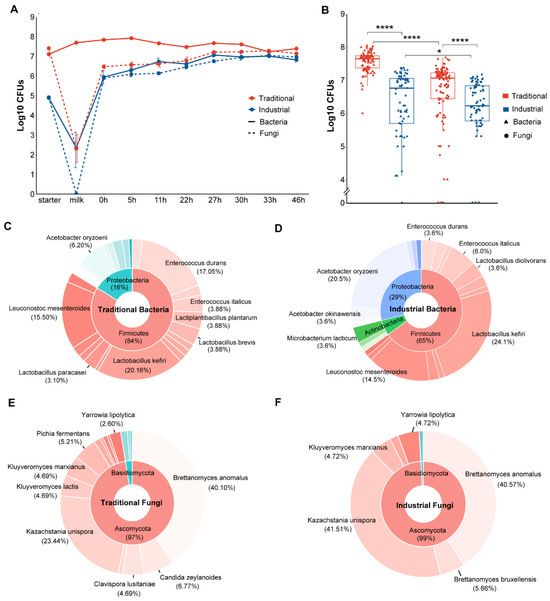
Figure 1.
Culture-dependent microbial changes and composition during koumiss fermentation: (A) CFUs of bacteria and fungi per milliliter of samples in traditional and industrial modes. Each point represents the average of triplicates ± SE. (B) Paired comparison of CFUs between bacteria and fungi in traditional and industrial mode according to the Wilcoxon test. ns means p > 0.05, * p ≤ 0.05, and **** p ≤ 0.0001. Global composition based on isolate identification of bacteria in traditional (C) and industrial mode (D) and fungi in traditional (E) and industrial (F) mode.
A total of 510 strains were isolated and identified from all 150 samples collected from both the industrial and traditional fermentation processes, including 212 bacterial strains belonging to 36 species and 298 fungal strains belonging to 18 species. The traditional fermentation process contained 24 bacterial and 17 fungal species and the industrial fermentation process contained 22 bacterial and 7 fungal species. In the traditional fermentation, the bacterial species mainly included Lactobacillus kefiri (20.2%), Enterococcus durans (17.1%), Leuconostoc mesenteroides (15.5%), and Acetobacter oryzoeni (6.2%) (Figure 1C), while the fungal species mainly included Brettanomyces anomalus (40.1%), Kazachstania unispora (23.4%), Candida zeylanoides (6.8%), Kluyveromyces marxianus (4.7%), and Kluyveromyces lactis (4.7%) (Figure 1E). In the industrial fermentation, the bacterial species primarily included L. kefiri (24.1%), A. oryzoeni (20.5%), Leu. Mesenteroides (14.5%), and Enterococcus italicus (6.0%) (Figure 1D), while the fungal species mainly included K. unispora (41.5%), B. anomalus (40.6%), Brettanomyces bruxellensis (5.7%), Klu. marxianus (4.7%), and Yarrowia lipolytica (4.7%) (Figure 1F). The bacteria obtained through culture-dependent methods primarily belonged to Firmicutes (76%) and Proteobacteria (21%) at the phylum level and L. kefiri (21.7%), Leu. mesenteroides (15.1%), E. durans (11.8%), and A. oryzoeni (11.8%) at the species level (Figure S1A). The majority of the fungal isolates belonged to the phylum Ascomycota (98%) and B. anomalus (40.3%) and K. unispora (29.9%) at the species level (Figure S1B).
3.2. Microbial Community Dynamics during Koumiss Fermentation Revealed by Culture-Independent Analyses
3.2.1. Fungal Dynamics
Through ITS2 Illumina sequencing, a total of 4,153,102 filtered reads were obtained and clustered into 165 ASVs. The rarefaction curves had reached a plateau, indicating enough sequences for bioinformatic analysis (Figure S2). Most of the ASVs (88%) belonged to Ascomycota and the remaining 12% belonged to Basidiomycota; Kazachstania (80.8%) and Trichosporon (10.8%) were present at the genus level (Figure S1D).
A total of 49 fungal genera were observed, and 11 abundant genera were retained for further analyses. Kazachstania was the dominant genus in both the industrial and traditional starters, followed by Brettanomyces and Trichosporon in the industrial starter and Trichosporon and Candida in the traditional starter. Trichosporon and Candida also dominated in the raw mare’s milk, and Kazachstania dominated in both the traditional and industrial fermentation processes. During the traditional fermentation (0 h to 46 h), the relative abundance of Kazachstania increased, while the abundance of other fungi such as Trichosporon and Candida decreased. Notably, no fungi were found in pasteurized mare’s milk, which was consistent with the culture-dependent observations. During industrial fermentation, the relative abundance of Kazachstania remained consistently high (Figure 2A). The UpSet plot of all fungi at the genus level indicated that 29 genera were unique to the traditional fermentation, 1 genus was unique to the industrial fermentation, and 19 genera were shared between the two fermentation modes (Figure 2B).
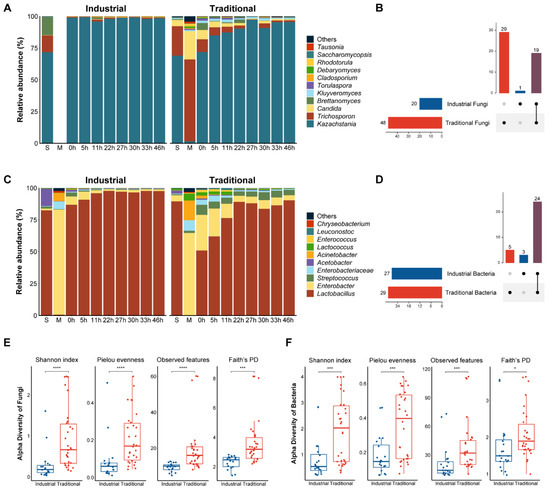
Figure 2.
Culture-independent microbial community dynamics during koumiss fermentation. Relative abundance of fungi (A) and bacteria (C) at the genus level during fermentation in industrial and traditional modes. Genera with a relative abundance less than 0.1% were combined and recorded as “Others”. The letters “S” and “M” in (A,C) represent starter and milk, respectively. UpSet plots for fungi (B) and bacteria (D) at the genus level in industrial and traditional modes. Horizontal bars represent the total number of genera in each mode. Vertical bars represent the number of genera in each intersection indicated by the connected dots. The color purple represents the number of genera shared between industrial and traditional modes. Comparisons between industrial and traditional modes based on fungal (E) and bacterial (F) alpha diversity. ns means p > 0.05, * p ≤ 0.05, *** p ≤ 0.001, and **** p ≤ 0.0001.
After normalization, 41,943 reads per sample (corresponding to the sample with the lowest reads) were used for diversity analyses. Alpha diversity indexes showed significant differences between the two fermentation modes, with traditional fermentation exhibiting significantly higher fungal diversity compared to the industrial fermentation (p < 0.001) (Figure 2E). The changes in the alpha diversity of the fungal communities during the industrial and traditional fermentation were analyzed separately (Figure S3). The Shannon and Pielou indexes which indicate the richness and evenness, respectively, of the fungal communities in different stages during the traditional fermentation process differed significantly (p < 0.05) (Figure S3).
Beta diversity analyses were performed based on unweighted and weighted Unifrac distances to estimate the difference among fungal communities from different fermentation modes. Although a difference between the fungal communities associated with different fermentation modes was shown in the PCoA plots, the difference was not statistically significant (p > 0.05) (Figure S5). The beta diversities of the fungal communities associated with different fermentation stages were significantly different regardless of fermentation modes (p < 0.05) (Figure S6).
3.2.2. Bacterial Dynamics
Illumina sequencing of the16S rDNA V3–V4 region resulted in 2,873,214 filtered reads with an average length of 427 bp. These reads were clustered into 203 ASVs, mainly belonging to Firmicutes (77.9%) and Proteobacteria (21.8%) at the phylum level and Lactobacillus (72.9%) and Enterobacter (16.3%) at the genus level (Figure S1C). A total of 32 bacterial genera were identified from the ASVs, of which 10 abundant genera were visualized on the bacterial composition plots (Figure 2C). Lactobacillus was the dominant genus in both the industrial and traditional starters, followed by Acetobacter in the industrial starter and Enterobacter in the traditional starter. Enterobacter and Acinetobacter were the dominant genera in mare’s milk whether pasteurized or not, while Lactobacillus was the dominant genus in both the traditional and industrial fermentation processes. During the fermentation process from 0 h to 46 h, the relative abundance of Lactobacillus increased, while other non-dominant bacteria such as Enterobacter and Acinetobacter decreased in both fermentation modes. The UpSet plot indicated that five genera were unique to the traditional fermentation, three genera were unique to the industrial fermentation, and twenty-four genera were shared by both fermentation modes (Figure 2D).
To conduct alpha and beta diversity analyses, all samples were normalized to 25,635 reads per sample according to the sample with the lowest reads. The alpha diversity indexes of the total bacteria were significantly higher in the traditional than in the industrial fermentation (p < 0.05) (Figure 2F). For fermentation stages, the observed features and Faith’s PD indexes of samples from the traditional fermentation were significantly different (p < 0.05) (Figure S4). The bacterial communities from different fermentation modes exhibited a difference in the PCoA plots, but the difference was not statistically significant (p > 0.05) (Figure S5). However, significant differences were observed in the beta diversities of bacterial communities associated with different fermentation stages (p < 0.05) (Figure S6).
3.3. Physicochemical Dynamics during Fermentation
A similar trend of pH change was observed in the industrial and traditional fermentation processes. At the beginning, the pH of the mare’s milk in the traditional mode was 6.8, higher than that (6.6) in the industrial mode (p < 0.05), probably due to the pasteurization of the raw milk in the latter. However, at the end of fermentation, the pH of the traditional fermentation (pH 3.3) was lower than that (pH 3.5) of the industrial fermentation (p < 0.05) (Figure 3A and Figure S7). The salinity increased slowly during fermentation, ranging from approximately 1‰ to 2.5‰, with no significant differences observed between the fermentation modes. Initially, the lactose content in the mare’s milk was around 74.4 g/L, then it gradually decreased to 55.3 g/L and 28.3 g/L at the end of the industrial and traditional fermentation modes, respectively (p < 0.05) (Figure 3A and Figure S7). Consequently, the lactose utilization rate was 25.7% in the industrial mode and 62.0% in the traditional mode. Acetic acid, lactic acid, ethanol, and amino acids were monitored and quantified as major flavor substances of koumiss. While these substances were almost absent or present in very low concentrations in the mare’s milk, they showed a progressive increase during the fermentation process. Significant differences in their concentrations were observed between the traditional and industrial fermentation modes (p < 0.05) (Figure 3 and Figure S7). Acetic acid showed a low concentration at the end of fermentation, reaching 0.4 g/L and 0.8 g/L in the industrial and traditional modes, respectively, while lactic acid showed a higher concentration at the end of fermentation, reaching 14.8 g/L in the industrial mode and 24.6 g/L in the traditional mode. Ethanol gradually increased to 4.5 g/L and 12.1 g/L in the industrial and the traditional modes, respectively.
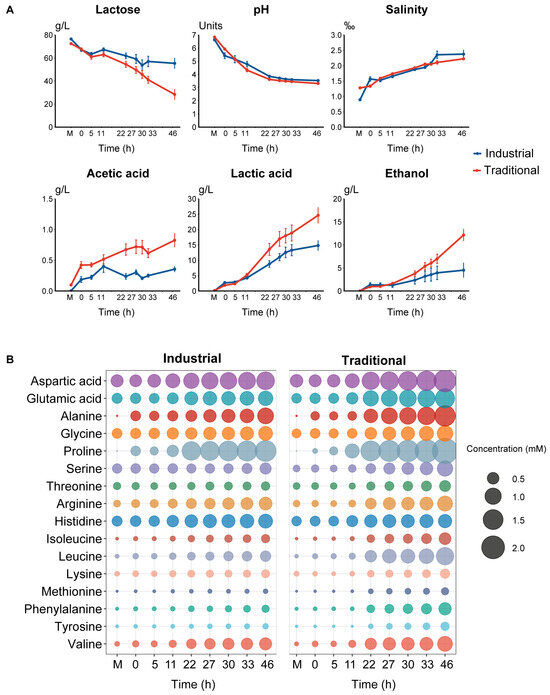
Figure 3.
Physicochemical dynamics during fermentation. Dynamics during fermentation in different modes: (A) Lactose, pH, salinity, acetic acid, lactic acid, and ethanol; (B) Free amino acids. The letter “M” represents the raw milk.
The contents of amino acids contributing to umami (aspartic acids and glutamic acid), sweetness (alanine, glycine, proline, serine, and threonine), and bitterness (arginine, histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, tyrosine, and valine) inferred based on [33] all increased in both the industrial and traditional fermentation processes (Figure 3B). Proline was the most abundant amino acid at the end (46 h), followed by aspartic acid, alanine, and glutamic acid, which contributed to umami and sweetness (Figure 3B). The combined concentrations of the amino acids responsible for umami (3.2 vs. 2.0 mM), sweetness (6.4 vs. 4.1 mM), and bitterness (5.3 vs. 3.1 mM) were all significantly higher in the traditional mode than in the industrial mode at the end of fermentation (p < 0.05) (Figure S7).
3.4. Correlation between Microbes and Physicochemical Profile during Fermentation
In the traditional fermentation, Spearman’s correlation analysis revealed that 14 genera exhibited significant correlations with physicochemical characters (p < 0.05) (Figure 4B). The dominant bacterial genus Lactobacillus and the dominant fugal genus Kazachstania showed significant positive correlations with lactic acid, ethanol, and salinity and umami, sweetness, and bitterness, and negative correlations with lactose and pH, while the non-dominant genera usually exhibited an opposite pattern with the physicochemical characters (Figure 4B). In the industrial fermentation, however, a general clear correlation between the microbes and physicochemical characters was not observed. Among the 21 genera analyzed, only Enterococcus exhibited a significant positive correlation with pH and negative correlations with lactic acid, salinity, and sweetness (p < 0.05) (Figure 4A).
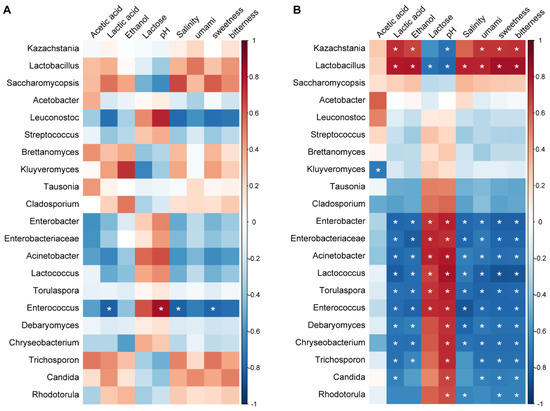
Figure 4.
Spearman correlations between microbes and physicochemical characters: (A) Industrial fermentation; (B) Traditional fermentation. The color of the scale indicates the type of correlation: “1” represents a perfect positive correlation (dark red) and “−1” represents a perfect negative correlation (dark blue). * p < 0.05. Umami, sweetness, and bitterness are expressed by the sum of the concentrations of the amino acids contributing to each taste.
3.5. Microbial Co-Occurrence during Fermentation
The patterns of microbial co-occurrence differed between the industrial and traditional fermentation modes. In the industrial fermentation, only a few bacterial genera showed significant correlations. Streptococcus with Lactococcus; unclassified Enterobacteriaceae with Enterobacter; and Enterococcus with Leuconostoc and Acinetobacter showed significant positive correlations, respectively (p < 0.05) (Figure 5A). In contrast, more significant correlations were found in the traditional fermentation (Figure 5B). The fungal genus Kazachstania and the bacterial genus Lactobacillus, which were the two most dominant genera in koumiss, showed a significant positive correlation with each other but negative correlations with almost all other genera (p < 0.05). Specifically, Kazachstania negatively correlated with bacterial genera Lactococcus, Enterobacter, and Chryseobacterium and fungal genera Trichosporon, Rhodotorula, Debaryomyces, Candida, Torulaspora, and Tausonia. Lactobacillus showed negative correlations with bacterial genera Lactococcus, Enterobacter, Chryseobacterium, Enterococcus, and unclassified Enterobacteriaceae and fungal genera Trichosporon, Rhodotorula, and Debaryomyces (p < 0.05). Significant positive correlations were found among most non-dominant microbes including bacterial genera Lactococcus, Enterobacter, Chryseobacterium, and Enterococcus and fungal genera Trichosporon, Rhodotorula, Debaryomyces, Torulaspora, and Candida (p < 0.05) (Figure 5B).
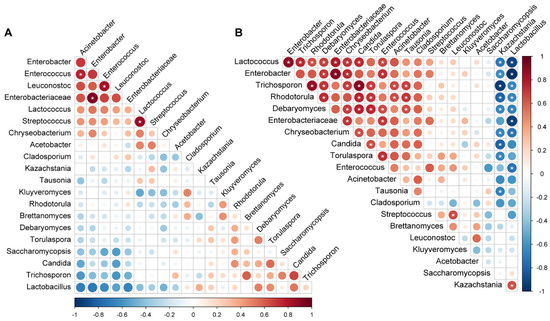
Figure 5.
Microbial co-occurrence during fermentation: (A) Industrial fermentation; (B) Traditional fermentation. The color of the scale indicates the type of correlation: “1” represents a perfect positive correlation (dark red) and “−1” represents a perfect negative correlation (dark blue). * p < 0.05.
3.6. Source Tracking of Koumiss Microbial Community
To further understand the microbial transmission during koumiss fermentation, source tracking analysis was performed using bacterial ASVs as the input data. The starter and the mare’s milk were set as “sources” and the koumiss from 0h to 46 h was set as “sinks”. The analysis identified the proportion of source contributions to a sink and attributed 96.4% of the bacteria in the industrial koumiss to the starter, followed by the mare’s milk (2.7%) and environment source (0.9%). For the traditional koumiss, 59.6% of the bacteria depended on the starter, followed by the environment source (34.5%) and the mare’s milk (5.9%). Overall, the koumiss bacterial community was primarily dependent on the starter rather than the mare’s milk (Figure 6A). Notably, the environment source which generally involved processing tools also contributed heavily to the bacteria in the traditional koumiss. Although the contribution of the mare’s milk to the koumiss bacteria was higher in traditional than in industrial fermentation, the bacteria in the mare’s milk usually diminished over time regardless of the fermentation mode (Figure 6B).
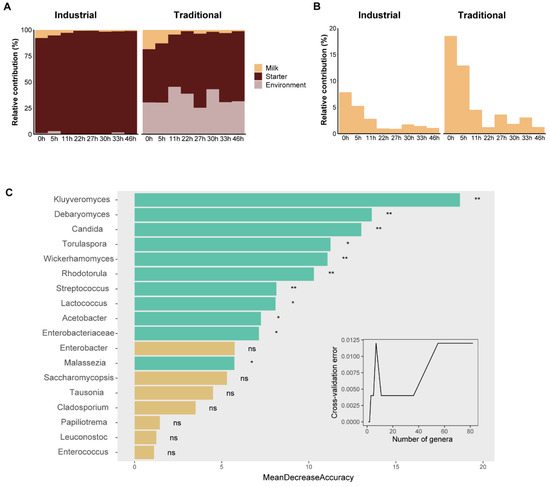
Figure 6.
Source tracking and random forest analyses of microbial communities. The relative contributions of various (mare’s milk, starter, and environment) sources (A) and mare’s milk (B) to the bacterial communities in different fermentation stages. (C) The importance of genera to distinguish fermentation modes and the significantly important genera are indicated by green bars with asterisks. ns, p > 0.05; *, p ≤ 0.05; and **, p ≤ 0.01.
3.7. Microbial Genera Distinguishing Fermentation Modes
To distinguish between the industrial and traditional fermentation modes in terms of microbiology, 49 fungal genera and 32 bacterial genera were ranked based on their relative contribution to model prediction accuracy. After cross-validation error testing, the 18 most important genera were chosen for verification. Among them, 11 genera were significantly important, including fungal genera Kluyveromyces, Debaryomyces, Candida, Torulaspora, Wickerhamomyces, Rhodotorula, and Malassezia and bacterial genera Streptococcus, Lactococcus, Acetobacter, and unclassified Enterobacteriaceae (Figure 6C). We observed that these predicting genera were primarily non-dominant genera in koumiss fermentation, and many had a higher relative abundance in the traditional mode (Figure S8).
4. Discussion
In this study, we comparatively analyzed the microbial and physicochemical dynamics in the entire fermentation processes of traditionally and industrially fermented koumiss products. Our results showed that the traditional fermentation exhibited significantly higher microbial counts and diversity compared to the industrial fermentation, though the dominant genera involved in the two fermentation modes were similar. We observed notable differences in the physicochemical dynamics and microbial correlations and sources between the two fermentation modes. Furthermore, we identified 11 key genera as microbial indicators distinguishing the two fermentation modes.
Unlike previous studies that solely relied on either culture-dependent [9] or culture-independent approaches [13], we employed a combination of both approaches to investigate the dynamics of microbial communities during koumiss fermentation. The culture-dependent approach can provide information about viable micro-organisms, thus confirming the trends observed through the culture-independent approach [34]. Culture-independent analysis can reveal uncultivable and late-growing microbes, as well as sub-dominant populations [35]. During koumiss fermentation, the bacterial genus Chryseobacterium and fungal genera Cladosporium, Saccharomycopsis, and Tausonia were revealed via culture-independent analysis. Chryseobacterium is associated with food or dairy products spoilage, while Cladosporium is commonly found in raw milk [36]. Saccharomycopsis fibuligera is important in food fermentation due to its enzymatic capabilities [37], and Tausonia can inhibit pathogen growth in co-culture by producing auxin-like compounds [38].
Kazachstania and Lactobacillus were identified as dominant genera via both culture-dependent and culture-independent methods. The dominant microbes in koumiss fermentation were not consistent across studies. Some studies found Brettanomyces and Lactobacillus to be dominant [14,16,39], while another study identified Kazachstania and Lactobacillus as dominant groups [13]. Lactobacillus, a dominant genus in dairy fermentation, opens a niche for its followers by converting lactose into galactose and glucose [40]. On the other hand, K. unispora can ferment galactose and glucose but not lactose, allowing it to avoid competition with lactose-fermenting microbes and occupy its niche [8]. K. unisporus, which was recognized as the primary fungal species responsible for the alcoholic fermentation of traditional koumiss [8], possesses the ability to withstand high osmolarity, acidity, ethanol, and salt [41]. B. anomalus, a lactose-fermenting yeast, converts lactose into galactose and glucose and subsequently produces ethanol under anaerobic conditions or acetic acid under aerobic conditions. Both are valuable metabolites in the fermented beverage industry [42].
Microbiome data allows us to quantify microbial differences in both alpha and beta diversity. Alpha diversity measures the richness (number of taxa) and evenness (distribution of abundances of the taxa) within a group, while beta diversity assesses the dissimilarity between groups based on the abundance or the presence of certain sequences [31]. Traditional fermentation showed significantly higher alpha diversity of fungi and bacteria, indicating a greater variety and balance of genera. Although beta diversity did not significantly differ between the traditional and industrial fermentation modes, it varied significantly across stages, suggesting that variations in beta diversity are more dependent on the stage of the fermentation process. The entire process of traditional fermentation involves a higher count of micro-organisms, with bacteria outnumbering fungi. Pasteurization is likely a major driver of differences in microbial diversity and counts, primarily due to the heat susceptibility of certain microbes, such as yeasts and molds, leading to their elimination following pasteurization [43].
Quality evaluation of fermented beverages typically involves parameters such as the contents of residual sugars, alcohol, organic acids, and amino acids [44]. The overall physicochemical dynamics observed during koumiss fermentation in our study correspond with those reported in previous studies [14,45]. Specifically, the pH value and residual lactose levels decreased, while the concentrations of acetic acid, lactic acid, ethanol, and free amino acids increased during the fermentation process. Notably, significant differences exist between the traditional and industrial fermentation modes. Koumiss can be categorized into three main flavors (mild, medium, and strong) based on the final acidity and ethanol content [1]. Our results indicate that the industrial koumiss attained a mild flavor, whereas the traditional koumiss achieved a medium flavor at the end of fermentation. Moreover, the traditional koumiss had a lower pH, which can better prevent spoilage and improve preservation [46]. Traditional koumiss, due to its lower residual lactose content, is more suitable for adults with lactose intolerance. The composition of free amino acids plays a significant role in shaping the unique flavor profiles of fermented products [47]. The concentrations of free amino acids responsible for sweetness, umami, and bitterness in the traditional mode were higher than those in the industrial mode, which implies the unique flavor of the traditional koumiss. The adoption of low temperatures in industrial fermentation processes diminishes microbial activity and metabolic rates, consequently prolonging the completion of fermentation. This factor provides partial elucidation for the observed incomplete fermentation in industrial settings [48].
Correlation analysis revealed that the abundance of dominant genera Lactobacillus and Kazachstania was significantly positively correlated with the consumption of residual lactose, the decrease in pH, and the production of main flavors compounds. Previous studies found that four bacterial genera (Lactobacillus, Acetobacter, Lactococcus, and Pseudomonas) and two fungal genera (Kazachstania and Candida) played key roles in creating the main volatile flavor compounds of koumiss [13]. Another study found that Lactobacillus and Brettanomyces were particularly important for koumiss flavor [14]. The correlations between the non-dominant genera and physicochemical characteristics basically showed a pattern opposite to that of the dominant genera. Specifically, the non-dominant genera exhibited a positive correlation with pH, which implies that the abundance of these non-dominant genera decreases as pH decreases. Micro-organisms tend to co-occur out of co-operative interactions or a similar niche preference. In our study, we observed a significant positive correlation between the dominant genera Lactobacillus and Kazachstania. Considering their minimal competition for carbon sources in the dairy environment, we infer that there might be a cooperative relationship between them. Further studies are required to verify this hypothesis.
Source tracking analysis revealed that the microbial community in both industrial and traditional koumiss primarily originates from the starter. However, in the traditional koumiss, there were also contributions from environment source. This observation aligns with previous research, which demonstrated a strong association between the micro-organisms present in the final milk product and those found in both the product tank and raw milk [49]. Our results suggest potential contamination in the processing environment, underscoring the need for further investigation. Future research should aim to identify the environment source in traditional koumiss and develop strategies to mitigate potential contamination during the production process.
Random forest models suggested that several non-dominant microbes can effectively distinguish between the traditional and industrial fermentation modes, with most of them being more abundant in the traditional mode. Among them, Kluyveromyces contributes to the production of low-lactose fermented milk due to its ability to utilize lactose [50]. Debaryomyces is commonly found in high-osmolarity foods that are salted, sugared, or fermented [51]. Streptococcus, a potential cause of opportunistic udder infections in mares, is prevalent in raw mare’s milk [52] and traditional koumiss [13,39]. Lactococcus, as thermolabile LAB, significantly decreases after pasteurization [53]. Enterobacteriaceae, opportunistic pathogens often used as indicators of microbial quality, survive pasteurization primarily due to inadequate plant design, improper operation of the pasteurizer, and cross-contamination from persistent bacteria in dairy processing environments [54].
5. Conclusions
Koumiss is traditionally a homemade acidic–alcoholic beverage. With the increased demand for the beverage due to its potential health benefits, industrialized production of koumiss has been increasingly applied recently in China. In this study, we found significant differences in microbial communities and physicochemical dynamics between traditional and industrial koumiss products which were fermented in the same time and place using the same raw mare’s milk. Compared to the industrial koumiss, the traditional product consumed more lactose, produced more flavor compounds, and reached a lower pH value at the end of fermentation and, thus, was judged to be of higher quality. The higher quality of the traditional koumiss probably resulted from the higher microbial counts and diversity involved in the traditional fermentation approach. The differences in the pasteurization of the raw milk, starters, fermentation facilities, and temperature were probably the main causes of the microbial differences between the traditional and industrial fermentation processes. The utilization of pure microbial cultures as a starter or supplementary source of the functional microbes involved in koumiss fermentation is probably helpful for improving the quality of industrially produced koumiss. This underscores the value of the microbes isolated in this study, the correlation of the microbes with the physicochemical dynamics, the co-occurrence of them in the fermentation process, and the identification of the 11 critical microbial markers distinguishing the traditional and industrial fermentation modes. Collectively, these findings provide a roadmap for improving the quality and consistency of industrial koumiss production.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fermentation10010066/s1, Figure S1: Global composition of bacteria and fungi based on (A, B) culture-dependent and (C, D) culture-independent methods; Figure S2: Rarefaction curves of samples from different fermentation modes. (A) Fungal rarefaction curves. (B) Bacterial rarefaction curves; Figure S3: Dynamics in alpha diversity of fungal communities during (A) the industrial and (B) the traditional fermentation process; Figure S4: Dynamics in alpha diversity of bacterial communities during fermentation in (A) industrial and (B) traditional mode; Figure S5: Principal Coordinate analysis (PCoA) based on unweighted and weighted Unifrac distances of (A, B) fungal and (C, D) bacterial communities; Figure S6: Principal Coordinate analysis (PCoA) based on unweighted and weighted Unifrac distances of the fungal and bacterial communities in different fermentation stages of the industrial (A, B, C, D) and traditional (E, F, G, H) modes; Figure S7: Comparison of the dynamics of pH, salinity, lactose, ethanol, acetic acid, lactic acid, and free amino acids with different tastes between industrial and traditional modes during fermentation; Figure S8: Comparison of the relative abundance of the top 18 fungal and bacterial genera between industrial and traditional fermentation modes; Table S1: Taxonomy of bacterial ASVs and corresponding reads; Table S2: Taxonomy of fungal ASVs and corresponding reads; Table S3: Kruskal-Wallis test of category effects based on alpha diversity indexes; Table S4: Permutational multivariate analysis of variance (PERMANOVA) of category effects based on unweighted and weighted Unifrac distances.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.B. and X.Z.; Methodology, X.Z. and L.S.; Formal Analysis, X.Z.; Investigation, X.Z.; Resources, X.Z. and P.H.; Data Curation, X.Z. and D.H.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, X.Z.; Writing—Review and Editing, F.B. and X.Z.; Visualization, X.Z.; Funding Acquisition, F.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by grant 32170006 from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw sequence data reported in this paper have been deposited in the Genome Sequence Archive in the National Genomics Data Center, China National Center for Bioinformation/Beijing Institute of Genomics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (GSA: CRA013665) and are publicly accessible at https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/gsa (accessed on 17 January 2024).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Uniacke-Lowe, T. Koumiss. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences, 3rd ed.; McSweeney, P.L.H., McNamara, J.P., Eds.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 3, pp. 446–452. [Google Scholar]
- Afzaal, M.; Saeed, F.; Anjum, F.; Waris, N.; Husaain, M.; Ikram, A.; Ateeq, H.; Muhammad Anjum, F.; Suleria, H. Nutritional and ethnomedicinal scenario of koumiss: A concurrent review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 6421–6428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomer, M.C.; Parkes, G.; Sanderson, J. Review article: Lactose intolerance in clinical practice—Myths and realities. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 27, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Q.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Siqinbateer; Bao, Y.; Saqila, W.; Zhang, H.; Menghe, B. Koumiss consumption modulates gut microbiota, increases plasma high density cholesterol, decreases immunoglobulin G and albumin. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 52, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Fan, H.; Mi, Z.; Kwok, L.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Menghe, B.; Sun, Z.; Chen, Y. Koumiss consumption induced changes in the fecal metabolomes of chronic atrophic gastritis patients. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 62, 103522. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.-F.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, Y.-H.; Yue, T.-L.; Li, J.-Y. Comparison of lactobacilli isolated from Chinese suan-tsai and koumiss for their probiotic and functional properties. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 12, 294–302. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.-Z.; Song, Q.-J.; Guo, H.; Liu, C.-Y.; Yang, C.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.-X.; Ma, Z.-P.; Wang, F.-X.; Wen, Y.-J. Characterization of a Potential Probiotic Strain in Koumiss. Fermentation 2023, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanari, G.; Zambonelli, C.; Grazia, L.; Kamesheva, G.K.; Shigaeva, M.K. Saccharomyces unisporus as the principal alcoholic fermentation microorganism of traditional koumiss. J. Dairy Res. 1996, 63, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Z.; Yang, X.; Yuan, H. Detection and identification of wild yeast in Koumiss. Food Microbiol. 2012, 31, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biçer, Y.; Telli, A.E.; Sönmez, G.; Turkal, G.; Telli, N.; Uçar, G. Comparison of commercial and traditional kefir microbiota using metagenomic analysis. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2021, 74, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Ya, M.; Guo, Y.S.; Xu, W.L.; Li, C.D.; Sun, J.P.; Zhu, J.J.; Qian, J.P. Study of bacterial and fungal community structures in traditional koumiss from Inner Mongolia. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 1972–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Yu, J.; Miao, W.; Shuang, Q. A UPLC-Q-TOF-MS-based metabolomics approach for the evaluation of fermented mare’s milk to koumiss. Food Chem. 2020, 320, 126619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Chen, X.; Sun, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, D.; Fang, S.; Chen, J. Exploring core microbiota responsible for the production of volatile flavor compounds during the traditional fermentation of Koumiss. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 135, 110049. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Yu, J.; Liu, H.; Feng, C.; Shuang, Q. Novel insight into physicochemical and flavor formation in koumiss based on microbial metabolic network. Food Res. Int. 2021, 149, 110659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Gesudu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Z.; Halatu, H.; Menghe, B.; Liu, W. Bacterial composition and function during fermentation of Mongolia koumiss. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 4146–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Ma, H.; Hou, Q.; Li, W.; Xu, H.; Liu, W.; Sun, Z.; Haobisi, H.; Menghe, B. Profiling of koumiss microbiota and organic acids and their effects on koumiss taste. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Siqin, B.; Xilin, T.; Zhang, N.; Li, M. Changes in Microbial Diversity and Nutritional Components of Mare Milk Before and After Traditional Fermentation. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6, 913763. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzman, C.; Robnett, C. Identification of clinically important ascomycetous yeasts based on nucleotide divergence in the 5’end of the large-subunit (26S) ribosomal DNA gene. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar]
- Gardes, M.; Bruns, T.D. ITS primers with enhanced specificity for basidiomycetes-application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Mol. Ecol. 1993, 2, 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- DeLong, E.F. Archaea in coastal marine environments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 5685–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Hoffman, N.G.; Morgan, M.T.; Matsen, F.A.; Fiedler, T.L.; Hall, R.W.; Ross, F.J.; McCoy, C.O.; Bumgarner, R.; Marrazzo, J.M. Bacterial communities in women with bacterial vaginosis: High resolution phylogenetic analyses reveal relationships of microbiota to clinical criteria. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihrmark, K.; Bodeker, I.T.; Cruz-Martinez, K.; Friberg, H.; Kubartova, A.; Schenck, J.; Strid, Y.; Stenlid, J.; Brandstrom-Durling, M.; Clemmensen, K.E.; et al. New primers to amplify the fungal ITS2 region–evaluation by 454-sequencing of artificial and natural communities. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 82, 666–677. [Google Scholar]
- Tedersoo, L.; Bahram, M.; Põlme, S.; Kõljalg, U.; Yorou, N.S.; Wijesundera, R.; Ruiz, L.V.; Vasco-Palacios, A.M.; Thu, P.Q.; Suija, A. Global diversity and geography of soil fungi. Science 2014, 346, 1256688. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.; Pirrung, M.; McCue, L.A. FQC Dashboard: Integrates FastQC results into a web-based, interactive, and extensible FASTQ quality control tool. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3137–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. 2023. R: Alanguage and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 8 December 2023).
- Olszewski, T.D. A unified mathematical framework for the measurement of richness and evenness within and among multiple communities. Oikos 2004, 104, 377–387. [Google Scholar]
- Kers, J.G.; Saccenti, E. The Power of Microbiome Studies: Some Considerations on Which Alpha and Beta Metrics to Use and How to Report Results. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 796025. [Google Scholar]
- Heinrikson, R.L.; Meredith, S.C. Amino acid analysis by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography: Precolumn derivatization with phenylisothiocyanate. Anal. Biochem. 1984, 136, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffman, S.S.; Sennewald, K.; Gagnon, J. Comparison of taste qualities and thresholds of D-and L-amino acids. Physiol. Behav. 1981, 27, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Penland, M.; Deutsch, S.M.; Falentin, H.; Pawtowski, A.; Poirier, E.; Visenti, G.; Le Meur, C.; Maillard, M.B.; Thierry, A.; Mounier, J.; et al. Deciphering Microbial Community Dynamics and Biochemical Changes During Nyons Black Olive Natural Fermentations. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 586614. [Google Scholar]
- de Melo Pereira, G.V.; de Carvalho Neto, D.P.; Maske, B.L.; De Dea Lindner, J.; Vale, A.S.; Favero, G.R.; Viesser, J.; de Carvalho, J.C.; Goes-Neto, A.; Soccol, C.R. An updated review on bacterial community composition of traditional fermented milk products: What next-generation sequencing has revealed so far? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1870–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quigley, L.; O’Sullivan, O.; Stanton, C.; Beresford, T.P.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Cotter, P.D. The complex microbiota of raw milk. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 664–698. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.-B.; Zhang, K.-Z.; Kang, Z.-H.; Yang, J.-G. Saccharomycopsis fibuligera in liquor production: A review. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 1569–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogundeji, A.O.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Meng, L.; Sang, P.; Mu, Y.; Wu, H.; Ma, Z.; Hou, J.; Li, S. Eggplant by grafting enhanced with biochar recruits specific microbes for disease suppression of Verticillium wilt. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 163, 103912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Oyunsuren, E.; Yang, Y.; Shuang, Q. Comparative metabolomics and microbial communities associated network analysis of black and white horse-sourced koumiss. Food Chem. 2021, 370, 130996. [Google Scholar]
- de Vos, W.M.; Vaughan, E.E. Genetics of lactose utilization in lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1994, 15, 217–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korcari, D.; Ricci, G.; Capusoni, C.; Fortina, M.G. Physiological performance of Kazachstania unispora in sourdough environments. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 88. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.T.; Yamazaki, M.; Poot, G.J.Y. Dekkera, Brettanomyces and Eeniella: Electrophoretic comparison of enzymes and DNA–DNA homology. Yeast 1990, 6, 299–310. [Google Scholar]
- Hayaloglu, A.A. Microbiology of Cheese. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences, 3rd ed.; McSweeney, P.L.H., McNamara, J.P., Eds.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 3, pp. 225–237. [Google Scholar]
- Blasche, S.; Kim, Y.; Mars, R.A.; Machado, D.; Maansson, M.; Kafkia, E.; Milanese, A.; Zeller, G.; Teusink, B.; Nielsen, J. Metabolic cooperation and spatiotemporal niche partitioning in a kefir microbial community. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wurihan; Bao, L.; Hasigaowa; Bao, X.; Dai, Y.; Jia, S. Bacterial community succession and metabolite changes during the fermentation of koumiss, a traditional Mongolian fermented beverage. Int. Dairy J. 2019, 98, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gram, L.; Ravn, L.; Rasch, M.; Bruhn, J.B.; Christensen, A.B.; Givskov, M. Food spoilage—Interactions between food spoilage bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 78, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Li, T.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, F.; Wang, H.; Suo, H.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y. Microbial composition and correlation between microbiota and quality-related physiochemical characteristics in chongqing radish paocai. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Liu, L.-X.; Liu, J.; Aihaiti, A.; Tang, X.-J.; Liu, Y.-G. New Insights on Low-Temperature Fermentation for Food. Fermentation 2023, 9, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Meng, L.; Wu, H.; Yang, H.; Liu, H.; Zheng, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J. Source Tracker Modeling Based on 16S rDNA Sequencing and Analysis of Microbial Contamination Sources for Pasteurized Milk. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 845150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounier, J.; Coton, M. Kluyveromyces spp. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences, 3rd ed.; McSweeney, P.L.H., McNamara, J.P., Eds.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 4, pp. 569–574. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, E.A.; Echavarri-Erasun, C. Yeast Biotechnology. In The Yeasts, 5th ed.; Kurtzman, C.P., Fell, J.W., Boekhout, T., Eds.; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 21–44. [Google Scholar]
- Salimei, E.; Park, Y.W. Mare milk. In Handbook of Milk of Non-Bovine Mammals, 2nd ed.; Park, Y.W., Haenlein, G.F.W., Wendorff, W.L., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 369–408. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Renye, J.A., Jr.; Feng, L.; Zeng, Q.; Tang, Y.; Huang, L.; Ren, D.; Yang, P. Characterization of the indigenous microflora in raw and pasteurized buffalo milk during storage at refrigeration temperature by high-throughput sequencing. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 7016–7024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Anand, S. Enterobacteriaceae. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences, 3rd ed.; McSweeney, P.L.H., McNamara, J.P., Eds.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 4, pp. 482–489. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).