Online Identification of Beer Fermentation Phases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
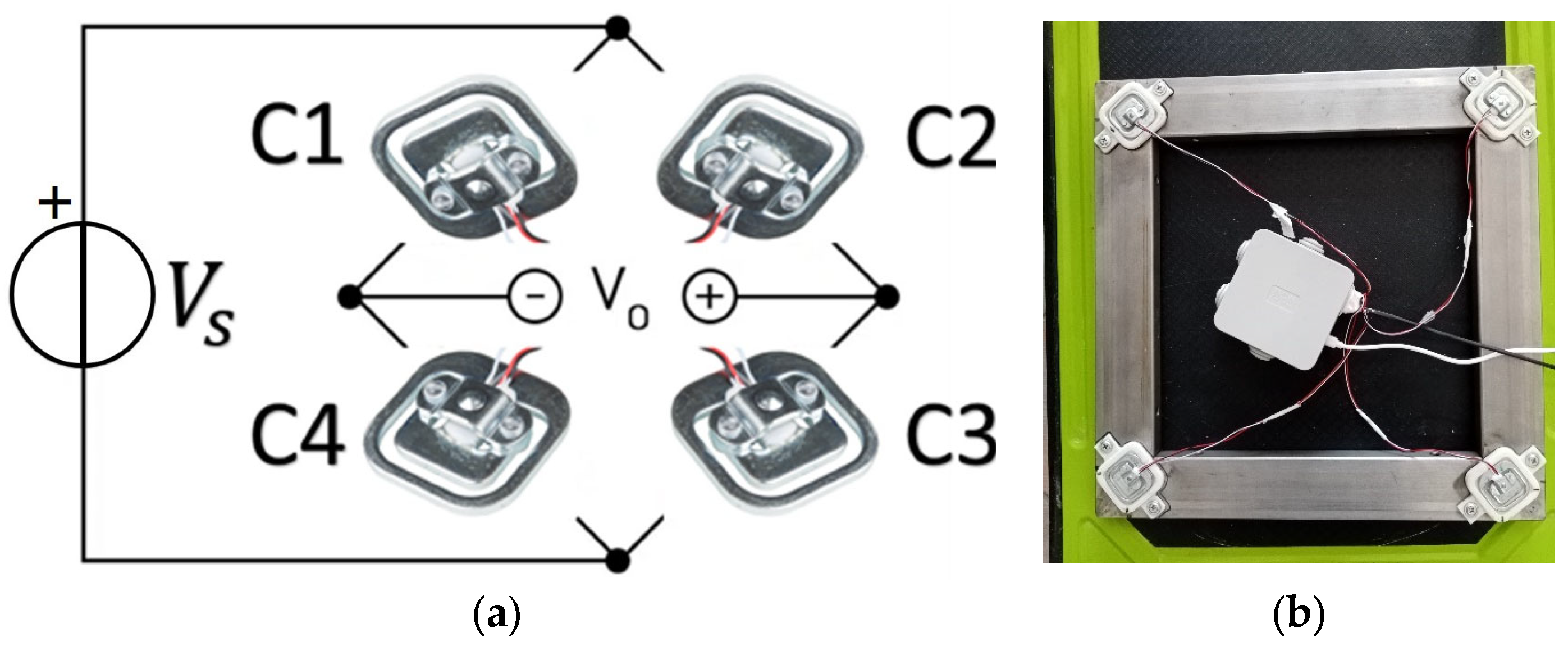
2.1. Proposed Measurement Method
2.2. Proposed Experiments
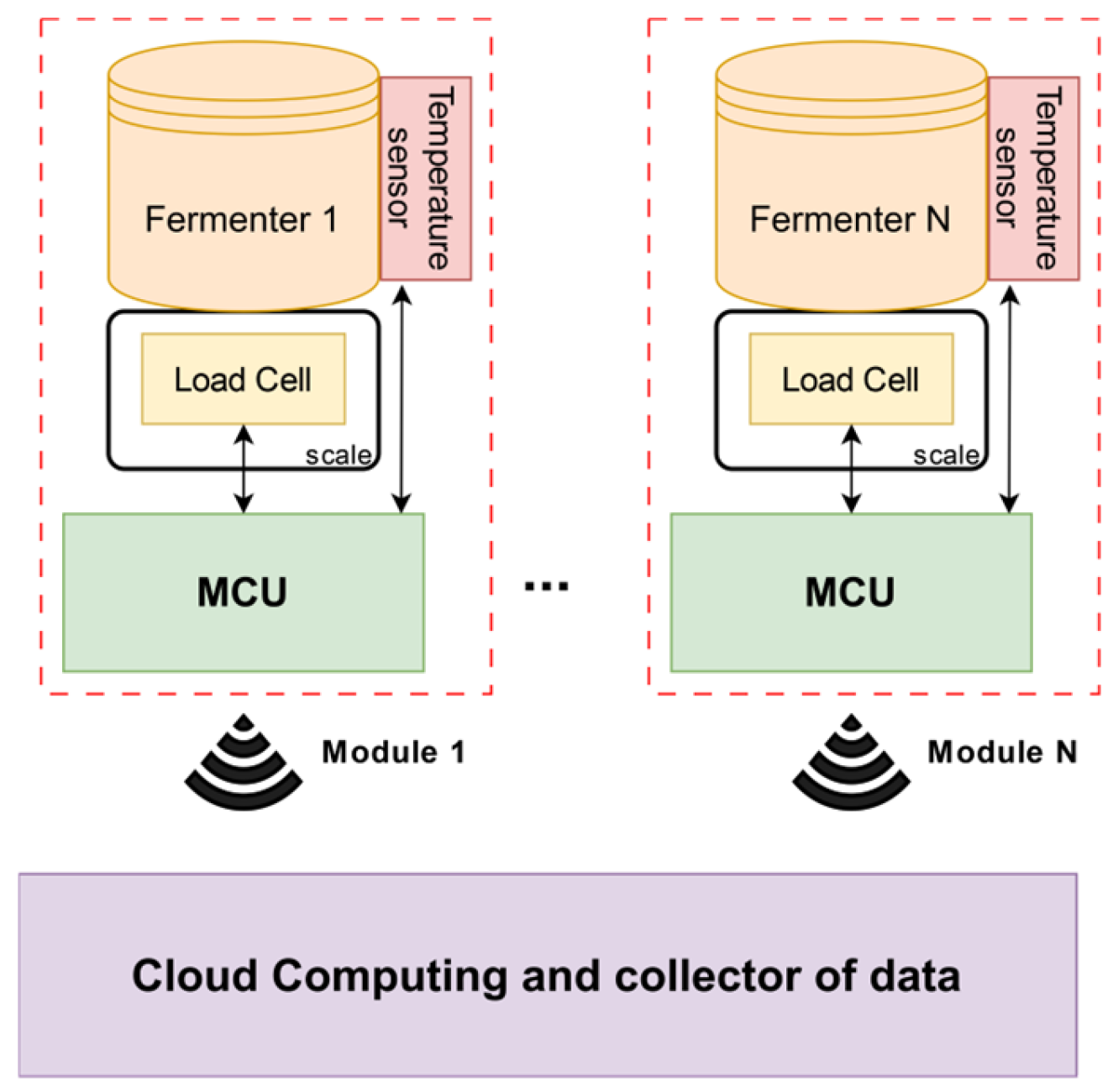
2.3. Monitor Module
- •
- ESP8266 microcontroller with an integrated Wi-Fi module; used as an acquiring and control module, capable of communicating with the server.
- •
- MCP9808 digital temperature sensor placed on the lateral surface of the fermenter. The sensor leads are designed to be long enough to reach the microcontroller without affecting the measure. The metrological specifications are listed here:
- ○
- Accuracy:
- ±0.25 (typical) from −40 °C to +125 °C;
- ±0.5 °C (maximum) from −20 °C to 100 °C;
- ±1 °C (maximum) from −40 °C to +125 °C.
- ○
- User-Selectable Measurement Resolution:
- +0.5 °C, +0.25 °C, +0.125 °C, +0.0625 °C.
- ○
- Communication protocol:
- I2C.
- •
- HX711 24-bit analog to digital converter (ADC) for the weigh scales
- •
- Load cell (Qt. 4):
- ○
- Full scale: 50 kg;
- ○
- Sensibility: 1.0 ± 0.15 mV/V;
- ○
- Linearity: 0.2% F. S.;
- ○
- Hysteresis: 0.2% F. S.;
- ○
- Creep: 0.1% F. S. (3 min).
3. Results
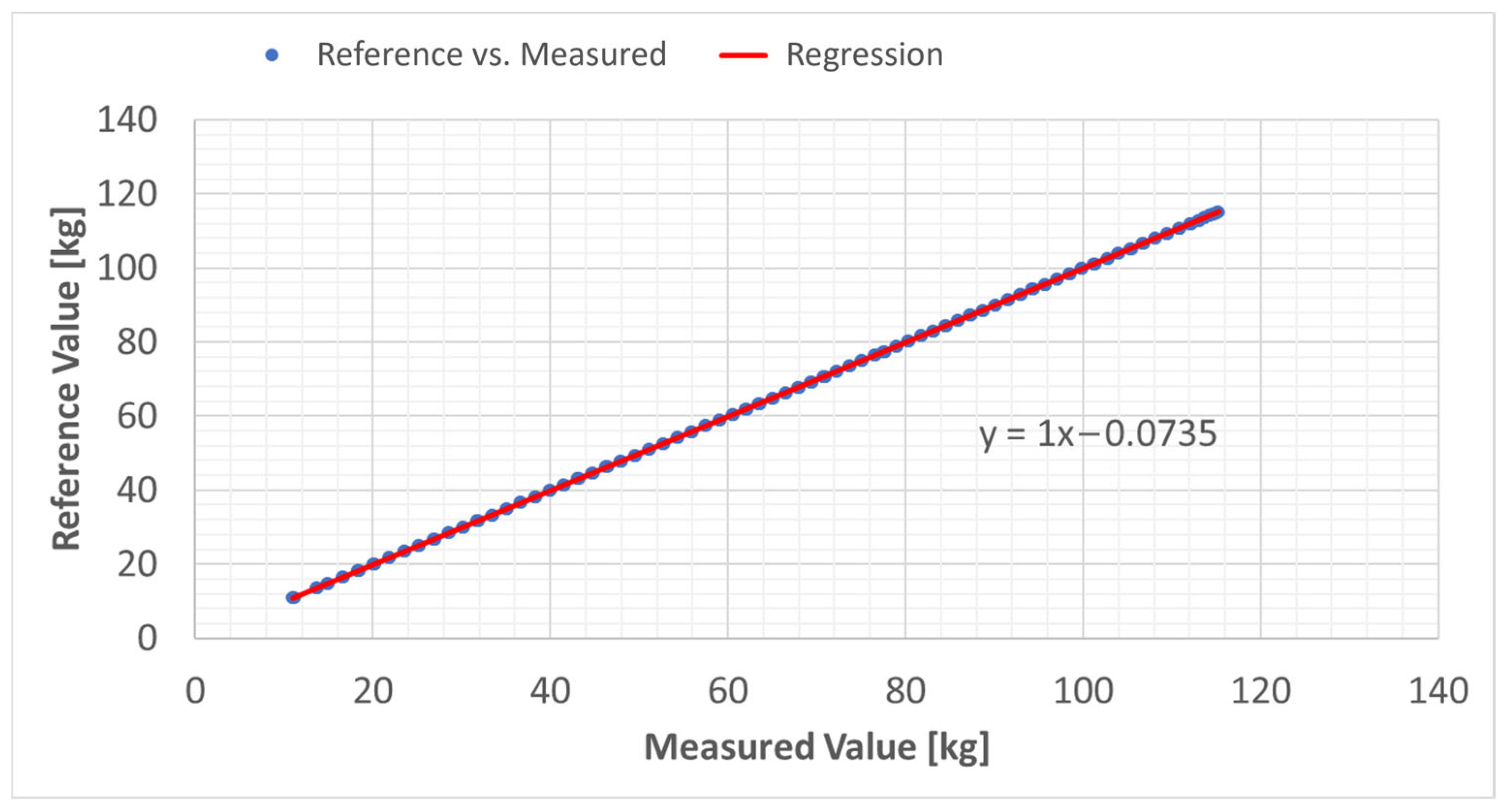
3.1. Calibration Procedures and Parasitic Effect Analysis
- The mean weight recorded was 20.128 kg;
- The minimum was 20.035 kg;
- The maximum was 20.176 kg;
- The standard deviation was 0.028 kg.
3.2. Experimental Setup
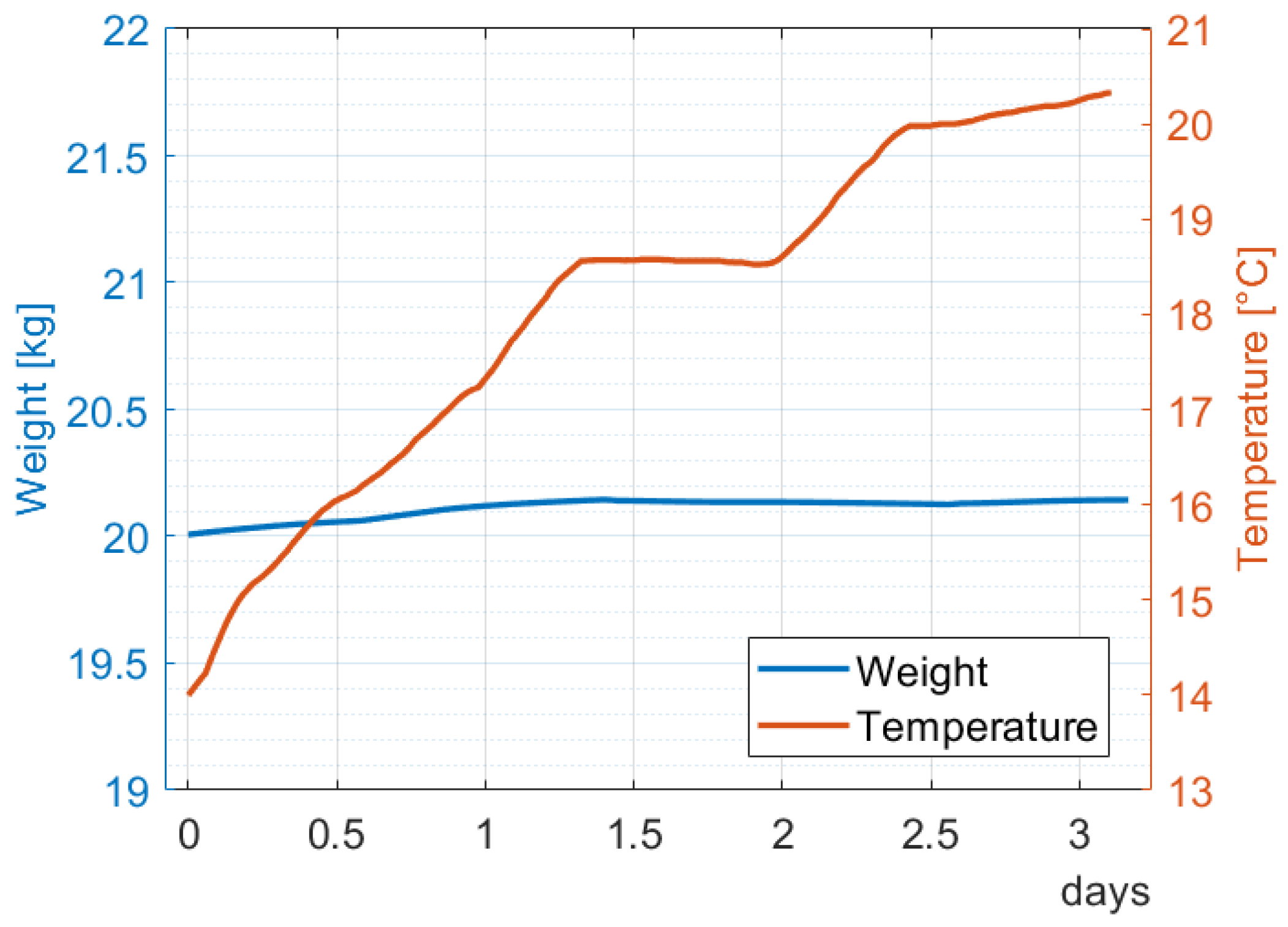
3.2.1. First Test—Weight Monitoring
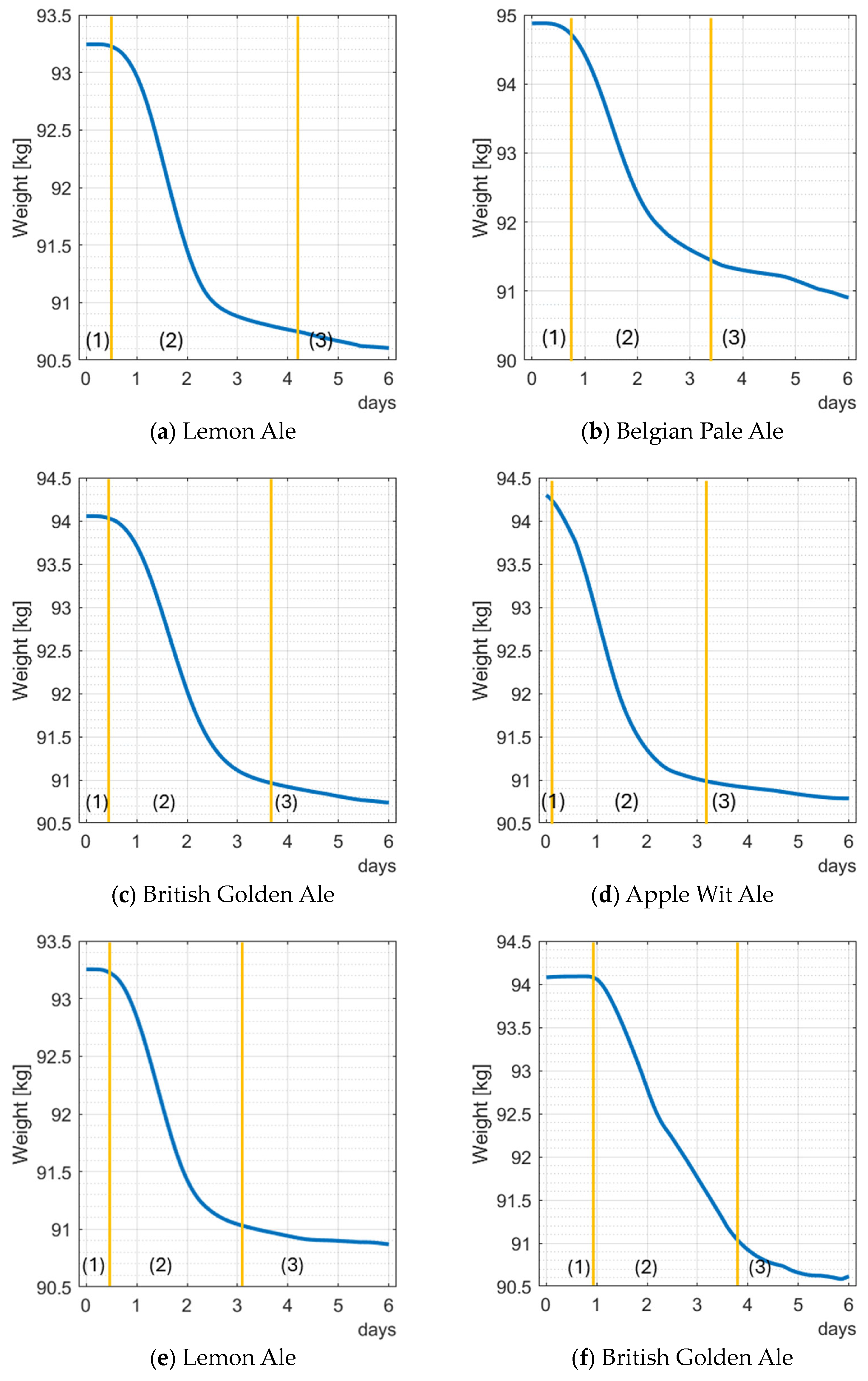
- Lag phase (1): During this phase, yeast acclimates to the environment, absorbs nutrients, and prepares for cellular division with minimal to no fermentation. Depending on the recipe (type and quantity of yeast used), this phase can range from 5–6 h up to 24 h.
- Exponential phase (2) corresponds to rapid yeast growth, doubling cells at a defined rate. At this stage, we have the maximum gradient in weight loss.
- The stationary phase (3) is a halt in yeast reproduction due to a lack of nutrients, which defines the end of fermentation. A negligible weight loss characterizes this phase.
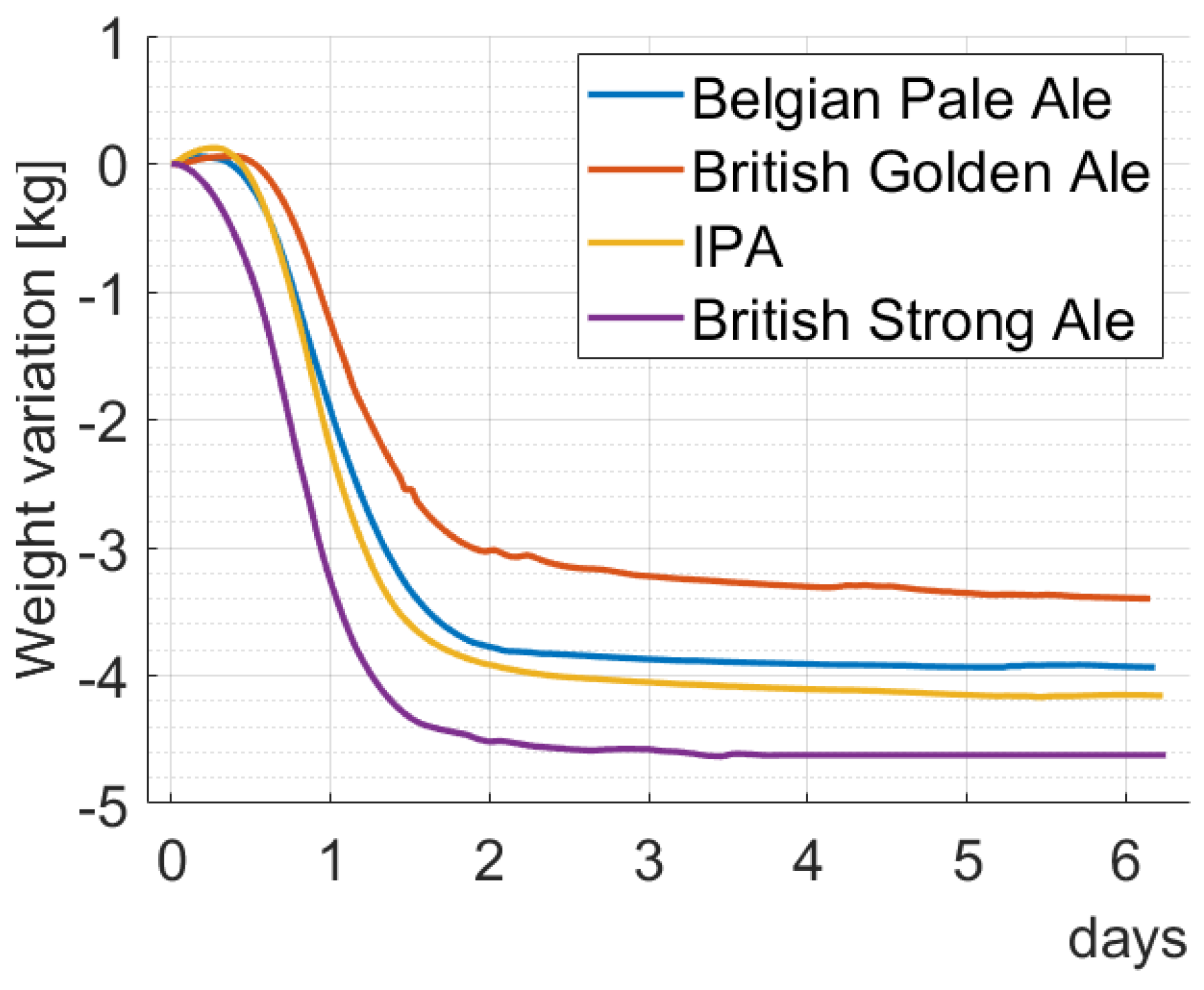
3.2.2. Fermentation Rate
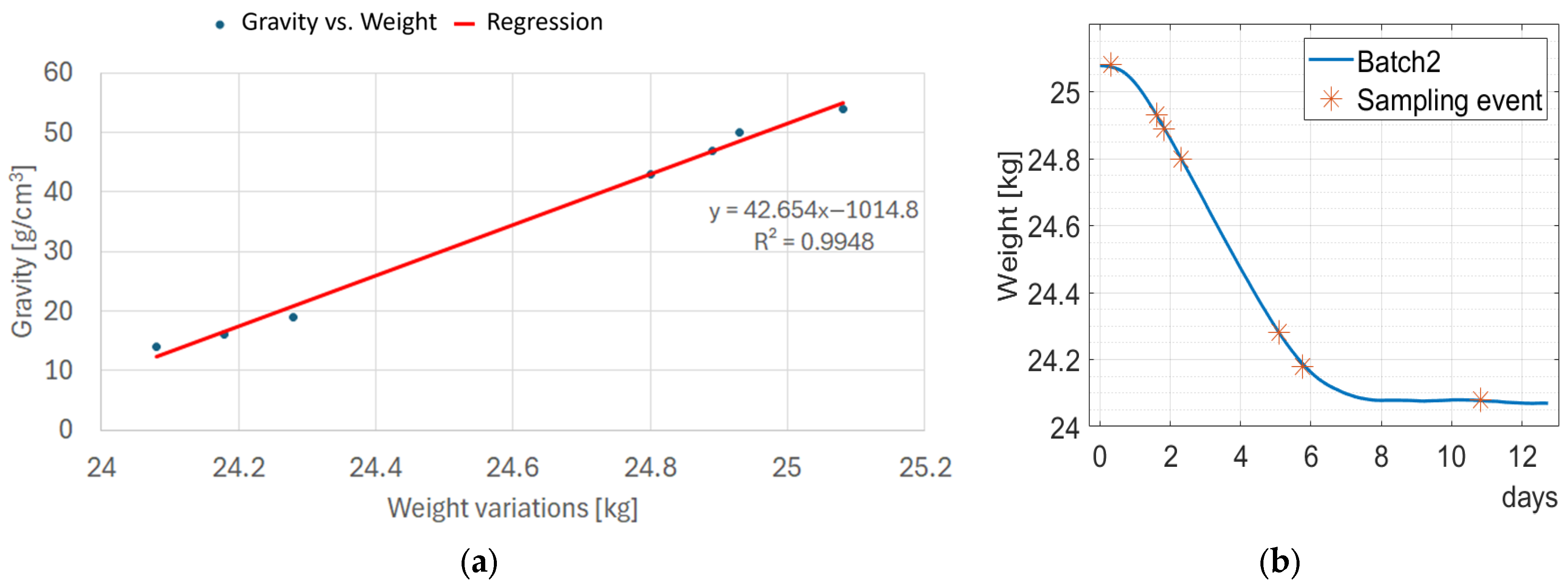
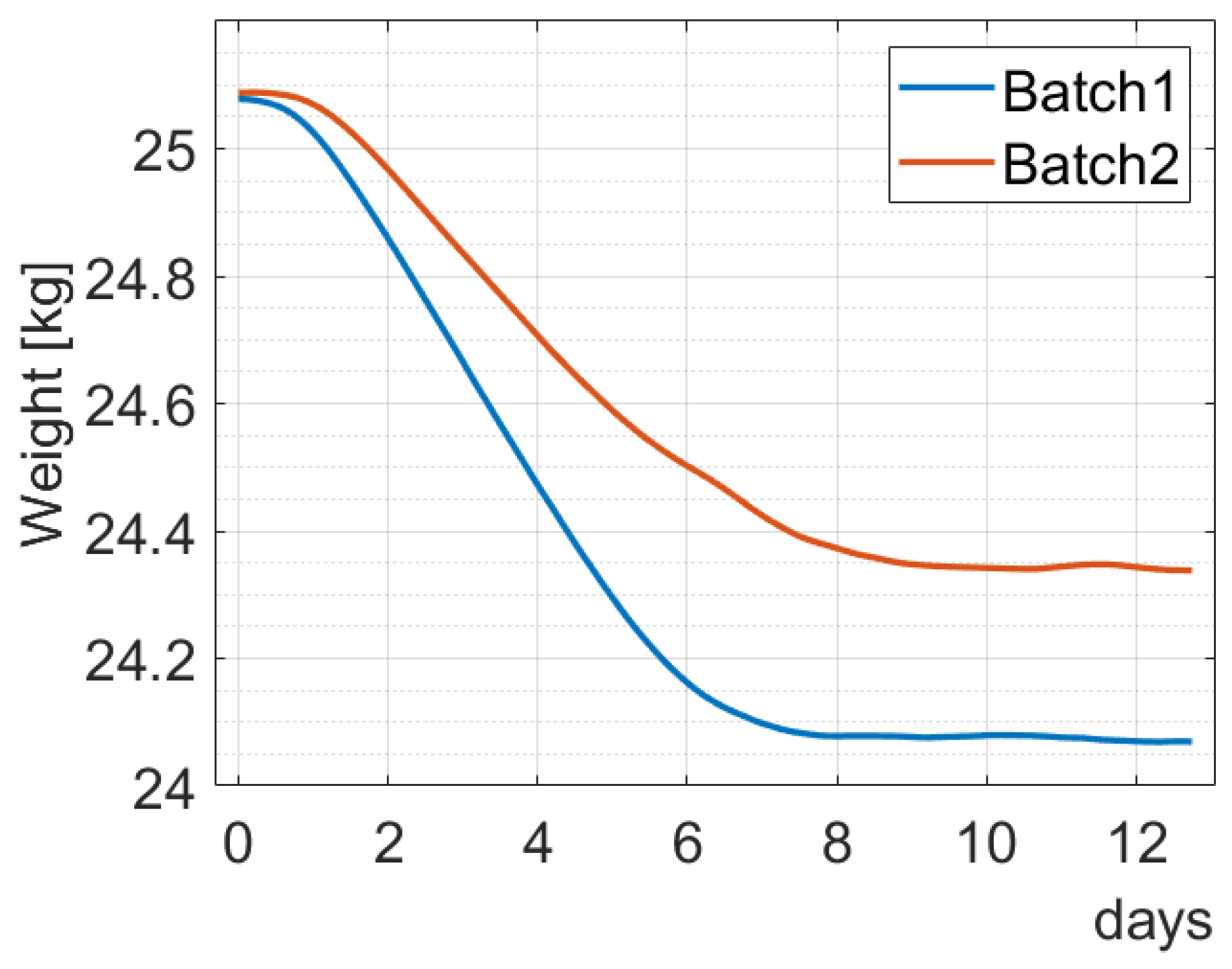
3.2.3. Second Test—Relation between Density and Weights
- Maximum capacity: 50 L;
- Quantity of malt: 4 kg;
- Quantity of water: 20 L;
- OG: 1.054 g/cm3;
- FG: 1.014 g/cm3;
- Yeast: SafAle™ S-04;
- Batch yeast quantity: 22 g.
- ABV range: 0–20%;
- Specific gravity range: 0.99–1.17 [g/cm3];
- BRIX: 0–35 [°Br].
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baiano, A. Craft beer: An overview. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 1829–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nave, E.; Duarte, P.; Rodrigues, R.G.; Paço, A.; Alves, H.; Oliveira, T. Craft beer–a systematic literature review and research agenda. Int. J. Wine Bus. Res. 2022, 34, 278–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violino, S.; Figorilli, S.; Costa, C.; Pallottino, F. Internet of beer: A review on smart technologies from mash to pint. Foods 2020, 9, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez Viejo, C.; Fuentes, S. Low-cost methods to assess beer quality using artificial intelligence involving robotics, an electronic nose, and machine learning. Fermentation 2020, 6, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez Viejo, C.; Fuentes, S.; Hernandez-Brenes, C. Smart detection of faults in beers using near-infrared spectroscopy, a low-cost electronic nose and artificial intelligence. Fermentation 2021, 7, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habschied, K.; Ćosić, I.; Šarić, G.; Krstanović, V.; Mastanjević, K. Sensory Analysis Coupled with Gas Chromatography/Mass spectrometry Analysis in Craft Beer Evaluation. Fermentation 2023, 9, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polshin, E.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Kirsanov, D.; Legin, A.; Saison, D.; Delvaux, F.; Delvaux, F.R.; Nicolaï, B.M.; Lammertyn, J. Electronic tongue as a screening tool for rapid analysis of beer. Talanta 2010, 81, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukinac, J.; Mastanjević, K.; Mastanjević, K.; Nakov, G.; Jukić, M. Computer vision method in beer quality evaluation—A review. Beverages 2019, 5, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeks, M. Arduino controlled brewing. In Proceedings of the SoutheastCon 2015, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 9–12 April 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Caro, D.; Liguori, C.; Pietrosanto, A.; Sommella, P. A low-cost device for beer color measurement. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Agriculture and Forestry (MetroAgriFor), Portici, Italy, 24–26 October 2019; pp. 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacono, S.D.; Erra, A.; Pietrosanto, A.; Di Caro, D.; Liguori, C. pH strip reader for beer samples based on image analysis. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Agriculture and Forestry (MetroAgriFor), Trento, Italy, 4–6 November 2020; pp. 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonocore, D.; Ciavolino, G.; Caro, D.D.; Liguori, C. An IoT-based beer fermentation monitoring system. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Agriculture and Forestry (MetroAgriFor), Trento-Bolzano, Italy, 3–5 November 2021; pp. 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vann, L.; Layfield, J.B.; Sheppard, J.D. The application of near-infrared spectroscopy in beer fermentation for online monitoring of critical process parameters and their integration into a novel feedforward control strategy. J. Inst. Brew. 2017, 123, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutyła-Olesiuk, A.; Zaborowski, M.; Prokaryn, P.; Ciosek, P. Monitoring of beer fermentation based on hybrid electronic tongue. Bioelectrochemistry 2012, 87, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowler, A.; Escrig, J.; Pound, M.; Watson, N. Predicting alcohol concentration during beer fermentation using ultrasonic measurements and machine learning. Fermentation 2021, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowler, A.L.; Pound, M.P.; Watson, N.J. Domain adaptation and federated learning for ultrasonic monitoring of beer fermentation. Fermentation 2021, 7, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovenzana, V.; Beghi, R.; Guidetti, R. Rapid evaluation of craft beer quality during fermentation process by vis/NIR spectroscopy. J. Food Eng. 2014, 142, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, D.; Zinellu, M.; Fanari, M.; Porcu, M.C.; Scognamillo, S.; Puggioni, G.M.; Rocchitta, G.; Serra, P.A.; Pretti, L. Development of a biosensor telemetry system for monitoring fermentation in craft breweries. Food Chem. 2017, 218, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, S.L.; Herberts, R.A.; Hollatz, C.; Trichez, D.; Miletti, L.C.; de Araujo, P.S.; Stambuk, B.U. Molecular Analysis of Maltotriose Active Transport and Fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae Reveals a Determinant Role for the AGT1 Permease. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 1494–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parcunev, I.; Naydenova, V.; Kostov, G.; Yanakiev, Y.; Popova, Z.; Kaneva, M.; Ignatov, I. Modeling Of Alcohol Fermentation In Brewing—Some Practical Approaches. In Proceedings of the 26th European Conference on Modelling and Simulation, Shaping Reality through Simulation, Koblenz, Germany, 29 May–1 June 2012; Troitzsch, K.G., Moehring, M., Lotzmann, U., Eds.; European Council for Modeling and Simulation: Koblenz, Germany, 2012; pp. 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Maicas, S. The role of yeasts in fermentation processes. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutaia, A.J.; Reid, A.J.; Speers, R.A. Examination of the relationships between original, real and apparent extracts, and alcohol in pilot plant and commercially produced beers. J. Inst. Brew. 2009, 115, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbelen, P.J.; Dekoninck, T.M.; Saerens, S.M.; Van Mulders, S.E.; Thevelein, J.M.; Delvaux, F.R. Impact of pitching rate on yeast fermentation performance and beer flavour. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 82, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shopska, V.; Denkova-Kostova, R.; Kostov, G. Modeling in brewing—A review. Processes 2022, 10, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, R.; Power, A.; Chapman, J.; Chandra, S.; Cozzolino, D. A review on the source of lipids and their interactions during beer fermentation that affect beer quality. Fermentation 2018, 4, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonocore, D.; Ciavolino, G.; Iacono, S.D.; Di Leo, G.; Pietrosanto, A. Mesh Overlay for wM-Bus Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Measurements & Networking (M&N), Padua, Italy, 18–20 July 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fix, G. Principles of Brewing Science, 2nd ed.; Brewers Publications: Boulder, CO, USA, 1999; ISBN 10: 0937381748/13: 978-0937381748. [Google Scholar]
- Grassi, S.; Amigo, J.M.; Lyndgaard, C.B.; Foschino, R.; Casiraghi, E. Beer fermentation: Monitoring of process parameters by FT-NIR and multivariate data analysis. Food Chem. 2014, 155, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarkiainen, V.; Kotiaho, T.; Mattila, I.; Virkajärvi, I.; Aristidou, A.; Ketola, R.A. On-line monitoring of continuous beer fermentation process using automatic membrane inlet mass spectrometric system. Talanta 2005, 65, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, V.A.; Barbero, A.P.L.; Sphaier, L.A.; Santos, A.B.D.; Peixoto, F.C.; Silva, V.N.H. Real-Time Fermentation Monitoring of Synthetic Beer Wort Using Etched Fiber Bragg Grating. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 7006707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Beer Type | Yeast Strain | OG (g/cm3) | FG (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| British Golden Ale | SafAle™ S-04 | 1.045 | 1.010 |
| Apple Wit Ale | Lalbrew Wit™ | 1.048 | 1.010 |
| Lemon Ale | SafAle™ S-04 | 1.036 | 1.010 |
| Belgian Pale Ale | Safbrew™ BE-256 | 1.054 | 1.014 |
| English IPA | SafAle™ S-04 | 1.058 | 1.012 |
| British Strong Ale | Safale™ S-04 | 1.073 | 1.018 |
| Working Temperature | [−10,40] °C, max humidity (85%) |
| Full scale | 150 kg |
| Linearity | <0.01% of full scale |
| Resolution | 15 gr |
| Cell Supply | 5 Vcc 150 mA |
| Max cell number | 4 (350 Ω), 8 (700 Ω) |
| Sampling frequency | 20 Hz |
| Serial Port | RS232 |
| Baud Rate | 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600 |
| Figure | Weight Loss [kg] | OG [g/cm3] | FG [g/cm3] | ABV [%] | CO2 Produced [kg] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lemon Ale | Figure 6a | 2.64 | 1.036 | 1.010 | 3.413 | 2.347 |
| Belgian Pale Ale | Figure 6b | 3.95 | 1.054 | 1.014 | 5.250 | 3.611 |
| British Pale Ale | Figure 6c | 3.31 | 1.045 | 1.010 | 4.594 | 3.160 |
| Apple Wit Ale | Figure 6d | 3.54 | 1.048 | 1.010 | 4.988 | 3.431 |
| Lemon Ale | Figure 6e | 2.37 | 1.036 | 1.010 | 3.413 | 2.347 |
| British Pale Ale | Figure 6f | 3.43 | 1.045 | 1.010 | 4.594 | 3.160 |
| Batch1: Belgian Pale Ale | Batch2: British Golden Ale | Batch3: IPA | Batch4: British Strong Ale | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yeast | SafAle™ S-04 | SafAle™ S-04 | Safbrew™ BE-256 | SafAle™ S-04 |
| Original gravity | 1.054 g/cm3 | 1.045 g/cm3 | 1.058 g/cm3 | 1.073 g/cm3 |
| Weight [kg] | Density [g/m3] |
|---|---|
| 25.08 | 54 |
| 24.93 | 50 |
| 24.89 | 47 |
| 24.80 | 43 |
| 24.28 | 19 |
| 24.18 | 16 |
| 24.08 | 14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buonocore, D.; Ciavolino, G.; Dello Iacono, S.; Liguori, C. Online Identification of Beer Fermentation Phases. Fermentation 2024, 10, 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10080399
Buonocore D, Ciavolino G, Dello Iacono S, Liguori C. Online Identification of Beer Fermentation Phases. Fermentation. 2024; 10(8):399. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10080399
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuonocore, Daniele, Giuseppe Ciavolino, Salvatore Dello Iacono, and Consolatina Liguori. 2024. "Online Identification of Beer Fermentation Phases" Fermentation 10, no. 8: 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10080399
APA StyleBuonocore, D., Ciavolino, G., Dello Iacono, S., & Liguori, C. (2024). Online Identification of Beer Fermentation Phases. Fermentation, 10(8), 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10080399






