Solid-State Fermentation of Mucuna deeringiana Seed Flour Using Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Legumes | Treatment | Nutritional Modification | Ref. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein (%) | Total Phenolic Contents (g/100 g Sample) | Tannins (g/100 g Sample) | L-DOPA (g/100 g Sample) | |||||||
| Raw | Proccesed | Raw | Proccesed | Raw | Proccesed | Raw | Proccesed | |||
| Mucuna cochinchinensis | Fermentation | 22.19 | 36.41 | NR | NR | 1.07 | 1.35 | NR | NR | [23] |
| Mucuna pruriens | Soaked | 25.34 | 25.27 | 1.82 | 0.73 | 0.38 | 0.30 | 6.83 | 4.26 | [20] |
| Cooked | 25.34 | 24.25 | 1.82 | 0.69 | 0.38 | 0.12 | 6.83 | 1.27 | ||
| Roasted | 25.34 | 25.90 | 1.82 | 0.69 | 0.38 | 0.29 | 6.83 | 5.19 | ||
| Germinated | 25.34 | 26.90 | 1.82 | 1.82 | 0.38 | 0.20 | 6.83 | 1.30 | ||
| Fermented | 25.34 | 29.50 | 1.82 | 3.02 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 6.83 | 1.30 | ||
| Soaked + cooked | 25.34 | 24.10 | 1.82 | 2.89 | 0.38 | 0.14 | 6.83 | 2.10 | ||
| Germinated + roasted | 25.34 | 28.78 | 1.82 | 3.49 | 0.38 | 0.12 | 6.83 | 1.23 | ||
| Fermented + roasted | 25.34 | 30.40 | 1.82 | 1.71 | 0.30 | 0.11 | 6.83 | 0.01 | ||
| Mucuna pruriens | Fermented (L. acidophilus) | 29.37 | 37.36 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | [22] |
| Fermented (Rhizopus oligosporus) | 30.48 | 36.85 | NR | NR | NR | NR | 6.36 | 1.00 | ||
| Mucuna deeringiana | Toasted | 29.23 | 29.71 | 11.80 | 8.51 | 2.19 | 1.26 | 5.17 | 2.05 | [19] |
| Hydratation water | NR | NR | 11.80 | 9.19 | 2.19 | 1.06 | 5.17 | 3.19 | ||
| Hydratation NaHCO3 | NR | NR | 11.80 | 9.48 | 2.19 | 0.79 | 5.17 | 3.27 | ||
| Hydratation Ca(OH)2 | 29.23 | 30.14 | 11.80 | 9.67 | 2.19 | 0.66 | 5.17 | 2.69 | ||
| Hydratation NaCl | 29.23 | 30.02 | 11.80 | 8.99 | 2.19 | 0.99 | 5.17 | 3.12 | ||
| Hydratation + cooked | 29.23 | 32.55 | 11.80 | 8.70 | 2.19 | 1.33 | 5.17 | 2.08 | ||
| Germinated | NR | NR | 11.80 | 11.02 | 2.19 | 1.06 | 5.17 | 3.80 | ||
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Experimental Screening
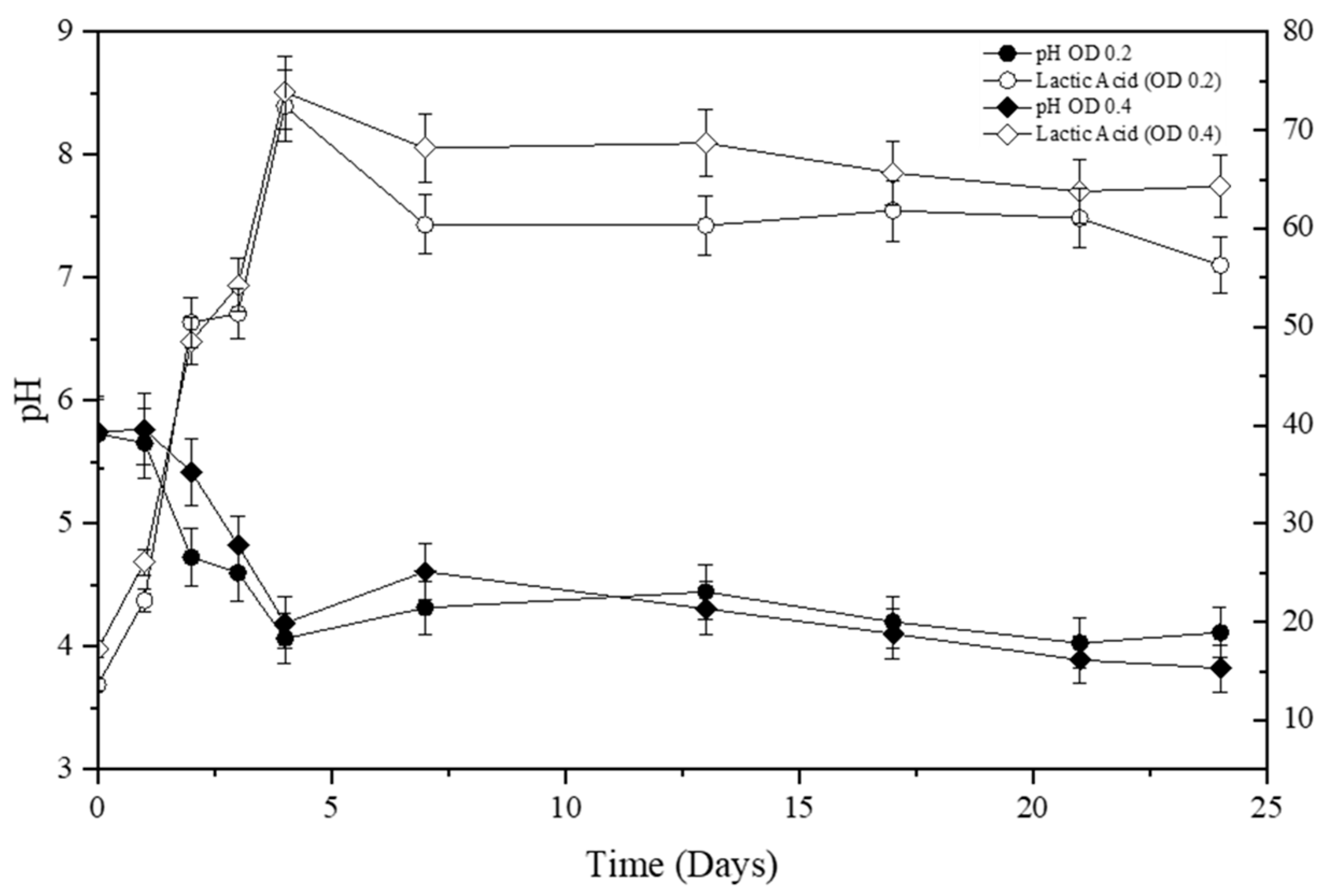
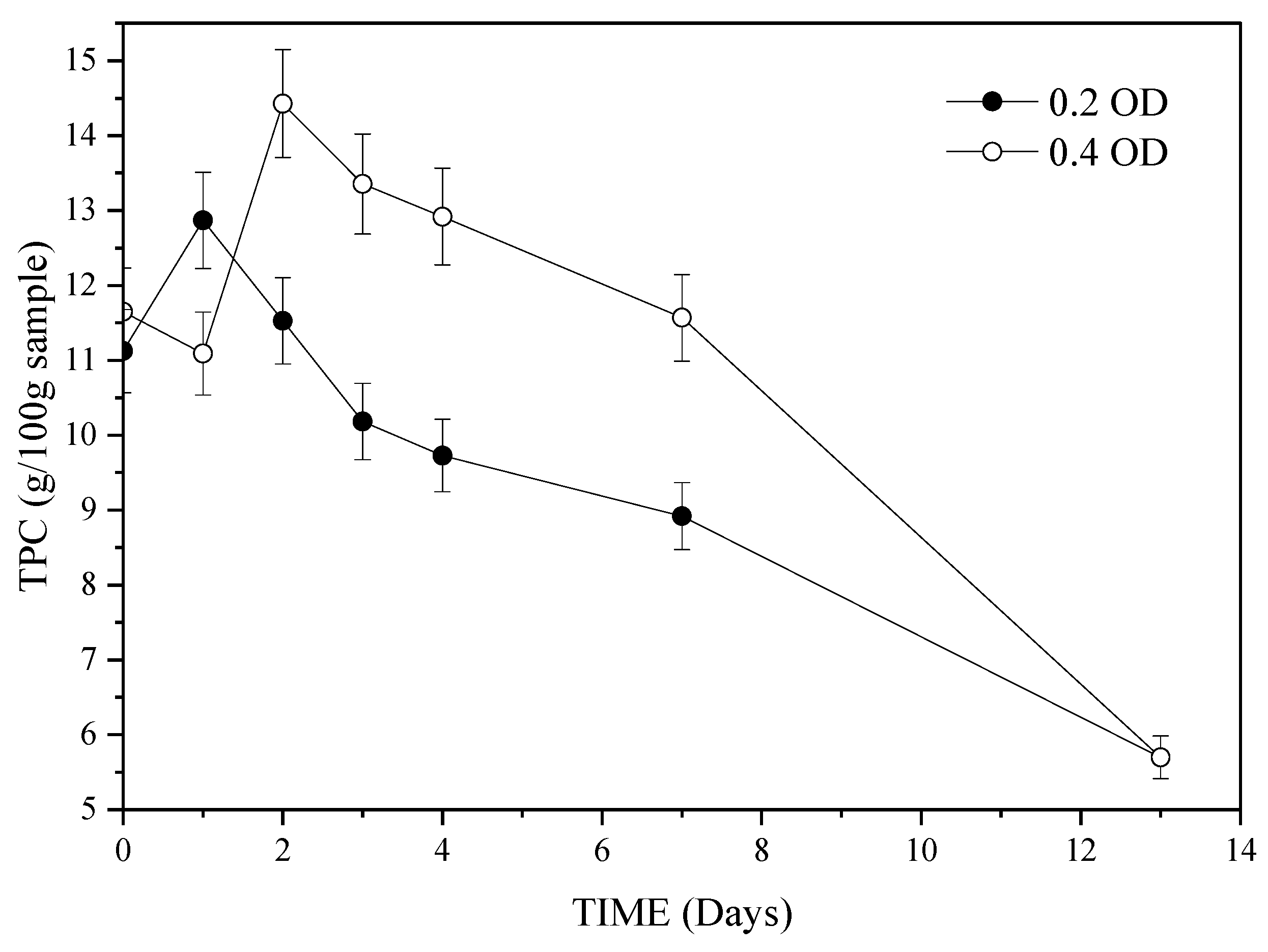
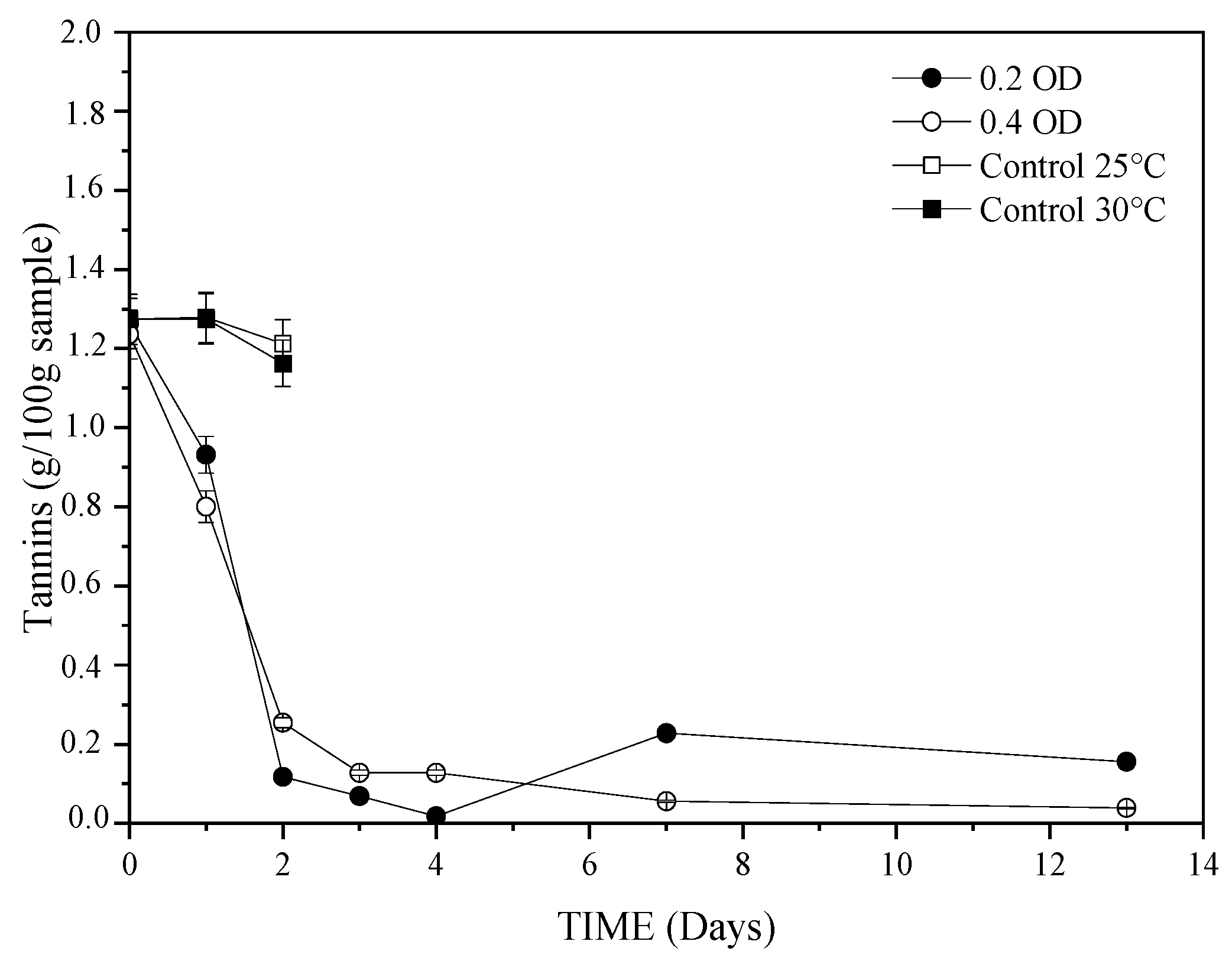
3.2. The Effect of Fermentation Time on SSF
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Śmiglak-Krajewska, M. Fabaceae as an Alternative Source of Protein in the Production of Compound Feeds in the Opinion of Poultry Producers and Pig Producers. Ann. Pol. Assoc. Agric. Aribus. 2022, XXIV, 180–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida Sá, A.G.; Franco, Y.M.; Mattar, B.A. Plant Proteins as High-Quality Nutritional Source for Human Diet. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 97, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandi, B.; Zurlini, C.; Maria, C.L.; Cutroneo, S.; Di Massimo, M.; Bondi, M.; Brutti, A.; Sforza, S.; Tedeschi, T. Targeting the Nutritional Value of Proteins From Legumes By-Products Through Mild Extraction Technologies. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 695793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, L.A.; Molina, E. Las Leguminosas en Alimentación Animal. Arbo 2016, 192, a315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedilla Alonso, B.; Farré Rovir, R.; Asensio Vegas, C.; Martín Pedrosa, M. Papel de las Leguminosas en la Alimentación Actual. Act. Dietética 2010, 14, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sońta, M.; Rekiel, A. Legumes—Use for Nutritional and Feeding Purposes. J. Elem. 2020, 25, 835–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Cabrejas, M.A. Chapter 1. Legumes: An Overview. In Legumes: Nutritional Quality, Processing and Potential Health Benefits; Ebook Collection; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maure, O.B.; Borrás Sandoval, L.M.; Rache Cardenal, L.Y. Fermentación en estado sólido como método para reducir factores antinutricionales en la harina de frutos de Artocarpus altilis. Cienc. Desarro. 2023, 13, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, G.; Makkar, H.P.; Becker, K. Antinutritional Factors Present in Plant-Derived Alternate Fish Feed Ingredients and Their Effects in Fish. Aquaculture 2001, 199, 197–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopan, A.; Lalappan, S.; Varghese, T.; Maiti, M.K.; Peter, R.M. Anti-Nutritional Factors in Plant-Based Aquafeed Ingredients: Effects on Fish and Amelioration Strategies. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Commun. 2020, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- De Deurwaerdère, P.; Di Giovanni, G.; Millan, M.J. Expanding the repertoire of L-DOPA’s actions: A comprehensive review of its functional neurochemistry. Prog. Neurobiol. 2017, 151, 57–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, W.G.; Vivonia, C.A.; Menon, M.K.; Kurtz, S.M.; Mattis, P.A.; Suzuki, Y.; Page, J.G.; Cotzias, G.C. The acute toxicity of L-dopa. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 1974, 28, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matenga, V.R.; Ngongoni, N.T.; Titterton, M.; Maasdorp, B.V. Mucuna Seed as a Feed Ingredient for Small Ruminants and Effect of Ensiling on Its Nutritive Value. Trop. Subtrop. Agroecosyst. 2003, 1, 97–105. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahim, H.; Negussie, F. Effect of Secondary Compounds on Nutrients Utilization and Productivity of Ruminant Animals: A review. J. Agric. Sci. Pract. 2020, 5, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed Hassan, Z.; Manyelo, T.G.; Selaledi, L.; Mabelebele, M. The Effects of Tannins in Monogastric Animals with Special Reference to Alternative Feed Ingredients. Molecules 2020, 25, 4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echegaray, N.; Munekata, P.E.; Centeno, J.A.; Domínguez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Carballo, J.; Lorenzo, J.M. Total Phenol Content and Antioxidant Activity of Different Celta Pig Carcass Locations as Affected by the Finishing Diet (Chestnuts or Commercial Feed). Antioxidants 2021, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes-Herrera, P.B.; Herrera-Cabrera, B.E.; Martínez-Ayala, A.L.; Zamilpa, A.; Delgado-Alvarado, A. Content and Yield of L-DOPA and Bioactive Compounds of Broad Bean Plants: Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activity In Vitro. Plants 2023, 12, 3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randhir, R.; Shetty, K. Microwave-Induced Stimulation of L-DOPA, Phenolics and Antioxidant Activity in Fava bean (Vicia faba) for Parkinson’s Diet. Process Biochem. 2004, 39, 1775–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro Acuña, S.P.; Aristizabal Torres, I.D.; Gil González, J.H. Reducción de Factores Antinutricionales de la Semilla de Vitabosa (Mucuna deeringiana) Mediante Procesos Físico—Químicos. Rev. Fac. Nac. Agron. Medellín 2009, 62, 5157–5164. Available online: https://revistas.unal.edu.co/index.php/refame/article/view/24927 (accessed on 5 June 2024).
- Wanjekeche, E.; Wakasa, V.; Mureithi, J.G. Effect of Germination, Alkaline and Acid Soaking and Boiling on The Nutritional Value of Mature and Immature Mucuna (Mucuna pruriens) Beans. Trop. Subtrop. Agroecosyst. 2003, 1, 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- Vadivel, V.; Pugalenthi, M. Effect of Various Processing Methods on the Levels of Antinutritional Constituents and Protein Digestibility of Mucuna pruriens (L.) dc. var. Utilis (Wall. Ex Wight) Baker Ex Burck (Velvet bean) Seeds. J. Food Biochem. 2008, 32, 795–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezegbe, C.C.; Nwosu, J.N.; Owuamanam, C.I.; Victor-Aduloju, T.A.; Nkhata, S.G. Proximate Composition and Anti-Nutritional Factors in Mucuna pruriens (Velvet Bean) Seed Flour as Affected by Several Processing Methods. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curiel, J.A.; Coda, R.; Centomani, I.; Summo, C.; Gobbetti, M.; Rizzello, C.G. Exploitation of the Nutritional and Functional Characteristics of Traditional Italian Legumes: The Potential of Sourdough Fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 196, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polanowska, K.; Szwengiel, A.; Kuligowski, M.; Nowak, J. Degradation of Pyrimidine Glycosides and L-DOPA in the Faba bean by Rhizopus oligosporus. LWT 2020, 127, 109353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro, S. Efecto de Diferentes Procesos Fisicoquímicos en la Reducción de Factores Antinutricionales de la Semilla de Vitabosa (Mucuna deeringiana). Master’s Thesis, Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Medellín, Colombia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Amadou, I.; Amza, T.; Foh, M.B.K.; Kamara, M.T.; Le, G.W. Influence of Lactobacillus plantarum Lp6 Fermentation on the Functional Properties of Soybean Protein Meal. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2010, 22, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaleye, H.T.; Oresanya, T.O.; Ogundipe, O.O. Comparative Study on Proximate and Antinutritional Factors of Dehulled and Undehulled Fermented Lyon Bean (Mucuna cochinchinensis). Food Res. 2020, 4, 1611–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartkiene, E.; Krungleviciute, V.; Juodeikiene, G.; Vidmantiene, D.; Maknickiene, Z. Solid State Fermentation with Lactic Acid Bacteria to Improve the Nutritional Quality of Lupin and Soya Bean. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 1336–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doblado, R.; Frias, J.; Muñoz, R.; Vidal-Valverde, C. Fermentation of Vigna sinensis Var. carilla Flours by Natural Microflora and Lactobacillus species. J. Food Prot. 2003, 66, 2313–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Wittouck, S.; Salvetti, E.; Franz, C.M.; Harris, H.M.; Mattarelli, P.; O’toole, P.W.; Pot, B.; Vandamme, P.; Walter, J.; et al. A taxonomic note on the genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 novel genera, emended description of the genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2782–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukalova, T.F.; García-Martínez, M.D.; Raigón, M.D. Nutritional Composition, Bioactive Compounds, and Volatiles Profile Characterization of Two Edible Undervalued Plants: Portulaca oleracea L. and Porophyllum ruderale (Jacq.). Cass. Plants 2022, 11, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, R.; Sridhar, K.R.; Tomita-Yokotani, K. Effect of Ionizing Radiation on Antinutritional Features of Velvet bean seeds (Mucuna pruriens). Food Chem. 2007, 103, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.Z.; Alhebsi, M.S.R.; Ghnimi, S.; Kamal-Eldin, A. Inability of Total Antioxidant Activity Assays to Accurately Assess the Phenolic Compounds of Date Palm Fruit (Phoenix dactylifera L.). NFS J. 2021, 22, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Sattar, E.; Mahrous, E.A.; Thabet, M.M.; Yousry Elnaggar, D.M.; Youssef, A.M.; Elhawary, R.; Zaitone, S.A.; Rodríguez-Pérez, C.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Mekky, R.H. Methanolic Extracts of a Selected Egyptian Vicia faba Cultivar Mitigate the Oxidative/Inflammatory Burden and Afford Neuroprotection in a Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Inflammopharmacology 2021, 29, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banica, F.; Bungau, S.; Mirela Tit, D.; Behl, T.; Otrisal, P.; Nechifor, A.C.; Gitea, D.; Pavel, F.-M.; Nemeth, S. Determination of the Total Polyphenols Content and Antioxidant Activity of Echinacea purpurea Extracts Using Newly Manufactured Glassy Carbon Electrodes Modified with Carbon Nanotubes. Processes 2020, 8, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Hayasaka, Y.; Iland, P.G.; Sefton, M.; Høj, P.; Waters, E.J. Quantitative Analysis of Polymeric Procyanidins (Tannins) from Grape (Vitis vinifera) Seeds by Reverse Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouveia, S.; Castilho, P.C. Antioxidant Potential of Artemisia argentea L’Hér Alcoholic Extract and its Relation with the Phenolic Composition. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1620–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiex, N.; Novotny, L.; Crawford, A. Determination of Ash in Animal Feed: AOAC Official Method 942.05 Revisited. J. AOAC Int. 2012, 95, 1392–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olukomaiya, O.O.; Adiamo, O.Q.; Fernando, W.C.; Mereddy, R.; Li, X.; Sultanbawa, Y. Effect of Solid-State Fermentation on Proximate Composition, Anti-nutritional Factor, Microbiological and Functional Properties of Lupin Flour. Food Chem. 2020, 315, 126238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitessa, D.A.; Bacha, K.; Tola, Y.B.; Murimi, M. Effect of Fermentation Time and Blending Ratio on Microbial Dynamics, Nutritional Quality and Sensory Acceptability of Shameta: A Traditional Cereal-Based Fermented Porridge for Lactating Mothers in Ethiopia. Fermentation 2024, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez de Olmos, A.; Correa Deza, M.A.; Garro, M.S. Selected Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria Development in Solid State Fermentation Using Soybean Paste. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2017, 49, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakil, S.M.; Onilude, A.A. Microbiological and Chemical Changes During Production of Malted and Fermented Cereal-Legume Weaning Foods. Adv. Food Sci. 2009, 31, 139–145. [Google Scholar]
- Akao, S.; Tsuno, H.; Horie, T.; Mori, S. Effects of pH and Temperature on Products and Bacterial Community in L-lactate Batch Fermentation of Garbage Under Unsterile Condition. Water Res. 2007, 41, 2636–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emkani, M.; Oliete, B.; Saurel, R. Effect of Lactic Acid Fermentation on Legume Protein Properties, a Review. Fermentation 2022, 8, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Lazim, M.I.; Mohamad, S.; Abdul Rahman, I.; Koh, S.P.; Abdul Manan, M.; Mohd Asri, M.A. Optimization of Process Parameters for GABA and L-DOPA Production on Fermented Coconut Drink. Food Res. 2023, 6, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Xie, C.; He, Q.; Sun, J.; Bai, W. Improvement in Color Expression and Antioxidant Activity of Strawberry Juice Fermented with Lactic Acid Bacteria: A Phenolic-based Research. Food Chem. X 2023, 17, 100535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pasquale, I.; Pontonio, E.; Gobbetti, M.; Rizzello, C.G. Nutritional and Functional Effects of the Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermentation on Gelatinized Legume Flours. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 316, 108426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knez, E.; Kadac-Czapska, K.; Grembecka, M. Effect of Fermentation on the Nutritional Quality of the Selected Vegetables and Legumes and Their Health Effects. Life 2023, 13, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samadi, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Najafpour, G.D. Production of Single Cell Protein from Sugarcane Bagasse by Saccharomyces cerevisiae in Tray Bioreactor. Int. J. Eng. 2016, 29, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Organisms | Anti-Nutritional Compounds (g/100 g Sample) | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tannins | Total Phenol Compound | L-DOPA | ||
| Bovine | 1.70–3.50 | <0.002 | 2000 | [10,13,14] |
| Ovine | 1.30–1.40 | <0.002 | NR | [10,14] |
| Pig | 1.00–3.00 | 18.60–21.43 | NR | [15,16] |
| Rats | NR | NR | 0.8 | [12] |
| Chickens | 0.07–0.20 | 4.88–9.56 | NR | [15,16] |
| OD | Time (Days) | Temperature (°C) | pH | Lactic Acid (g/100 g Sample) | L-DOPA (g/100 g Sample) | Phenols (g/100 g Sample) | DPPH (%Inhibition) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 1 | 25 | 5.92 ± 0.01 | 47.25 ± 0.015 | 7.08 ± 0.01 | 1.82 ± 0.01 | 87.64 ± 0.70 |
| 0.4 | 1 | 25 | 6.02 ± 0.01 | 16.11 ± 0.06 | 5.56 ± 0.01 | 6.77 ± 0.01 | 86.20 ± 0.00 |
| 0.6 | 1 | 25 | 5.96 ± 0.01 | 59.22 ± 0.010 | 3.47 ± 0.02 | 0.74 ± 0.01 | 86.82 ± 0.02 |
| 0.2 | 3 | 25 | 5.60 ± 0.01 | 18.54 ± 0.035 | 2.75 ± 0.01 | 7.08 ± 0.00 | 97.12 ± 0.12 |
| 0.4 | 3 | 25 | 6.96 ± 0.00 | 31.86± 0.105 | 3.95 ± 0.10 | 6.23 ± 0.02 | 97.11 ± 0.03 |
| 0.6 | 3 | 25 | 6.25 ± 0.03 | 18.18 ± 0.025 | 3.38 ± 0.04 | 6.20 ± 0.10 | 97.08 ± 0.02 |
| 0.2 | 1 | 30 | 6.01 ± 0.01 | 67.68 ± 0.015 | 5.33 ± 0.05 | 2.50 ± 0.05 | 88.36 ± 0.01 |
| 0.4 | 1 | 30 | 6.14 ± 0.01 | 15.16 ± 0.135 | 4.62 ± 0.01 | 8.66 ± 0.01 | 88.46 ± 0.02 |
| 0.6 | 1 | 30 | 6.02 ± 0.02 | 78.21 ± 0.006 | 4.59 ± 0.02 | 0.64 ± 0.06 | 87.84 ± 0.01 |
| 0.2 | 3 | 30 | 5.69 ± 0.00 | 23.40 ± 0.025 | 2.62 ± 0.01 | 9.61 ± 0.03 | 97.06 ± 0.02 |
| 0.4 | 3 | 30 | 4.51 ±0.01 | 11.34 ± 0.015 | 2.57 ± 0.09 | 6.79 ± 0.20 | 97.09 ± 0.01 |
| 0.6 | 3 | 30 | 4.99 ± 0.01 | 22.68 ± 0.025 | 3.52 ± 0.01 | 8.32 ±0.00 | 97.11 ±0.10 |
| 0.2 | 1 | 35 | 5.97 ± 0.06 | 46.89 ± 0.125 | 4.24 ± 0.02 | 11.89 ± 0.03 | 88.47 ±0.02 |
| 0.4 | 1 | 35 | 6.23 ± 0.02 | 12.78 ± 0.025 | 4.02 ± 0.02 | 0.43 ±0.05 | 88.05 ± 0.00 |
| 0.6 | 1 | 35 | 6.00 ± 0.00 | 35.37 ± 0.000 | 4.67 ± 0.07 | 7.10 ± 0.10 | 88.05 ± 0.00 |
| 0.2 | 3 | 35 | 6.09 ± 0.01 | 36.00 ± 0.100 | 2.65 ± 0.05 | 5.89 ± 0.01 | 97.10 ± 0.03 |
| 0.4 | 3 | 35 | 5.73 ± 0.01 | 59.13 ± 0.000 | 2.97 ± 0.00 | 2.18 ± 0.00 | 97.13 ±0.03 |
| 0.6 | 3 | 35 | 4.51 ± 0.00 | 30.33 ± 0.015 | 3.01 ± 0.02 | 5.49 ± 0.02 | 95.30 ± 0.10 |
| Treatment | Crude Protein (%) | Dry Matter (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 Day Without L. rhamnosus 25 °C and 30 °C | 24.9 ± 0.00 | 88.8 ± 0.00 |
| 1 Day 0.2 OD. 25 °C | 27.8 ± 0.01 | 72.2 ± 0.10 |
| 4 Days 0.2 OD. 25 °C | 27.2 ± 0.10 | 71.9 ± 0.02 |
| 7 Days 0.2 OD. 25 °C | 26.2 ± 0.05 | 75.7 ± 0.00 |
| 1 Day 0.4 OD. 30 °C | 23.0 ± 0.02 | 62.2 ± 0.05 |
| 4 Days 0.4 OD. 30 °C | 26.9± 0.01 | 77.5 ± 0.02 |
| 7 Days 0.4 OD. 30 °C | 26.0 ± 0.00 | 75.5 ± 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Álvarez, A.; Rache, L.Y.; Chaparro, S.; Brijaldo, M.H.; Borras, L.M.; Martínez, J.J. Solid-State Fermentation of Mucuna deeringiana Seed Flour Using Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus. Fermentation 2024, 10, 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10080396
Álvarez A, Rache LY, Chaparro S, Brijaldo MH, Borras LM, Martínez JJ. Solid-State Fermentation of Mucuna deeringiana Seed Flour Using Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus. Fermentation. 2024; 10(8):396. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10080396
Chicago/Turabian StyleÁlvarez, Andrés, Leidy Y. Rache, Sandra Chaparro, María H. Brijaldo, Luis Miguel Borras, and José J. Martínez. 2024. "Solid-State Fermentation of Mucuna deeringiana Seed Flour Using Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus" Fermentation 10, no. 8: 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10080396
APA StyleÁlvarez, A., Rache, L. Y., Chaparro, S., Brijaldo, M. H., Borras, L. M., & Martínez, J. J. (2024). Solid-State Fermentation of Mucuna deeringiana Seed Flour Using Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus. Fermentation, 10(8), 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10080396







