Preparation, Purification, Characterization and Antioxidant Activity of Rice Bran Fermentation Broth with Hypsizigus marmoreus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Rice Bran Fermentation Broth with Hypsizigus marmoreus
Preparation of Hypsizigus marmoreus Liquid
Rice Bran Fermented with Hypsizigus marmoreus
2.2.2. Rice Bran Fermentation Broth Purification with Four Kinds of Macroporous Resin [13,14]
Pretreatment of Resin
Calculation of Adsorption Rate, Desorption Rate and Recovery Rate
2.2.3. Rice Bran Fermentation Broth Purification with D101 Resin [15,16]
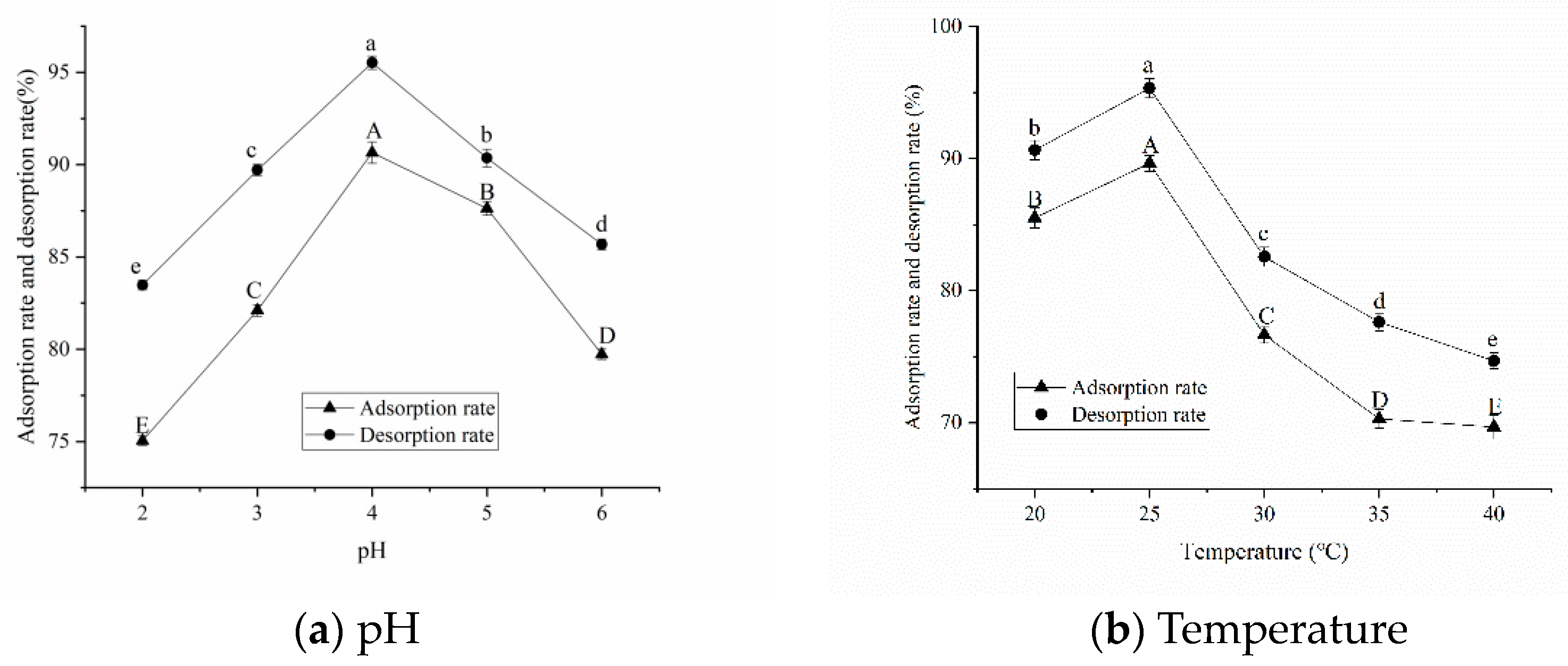
pH and Temperature
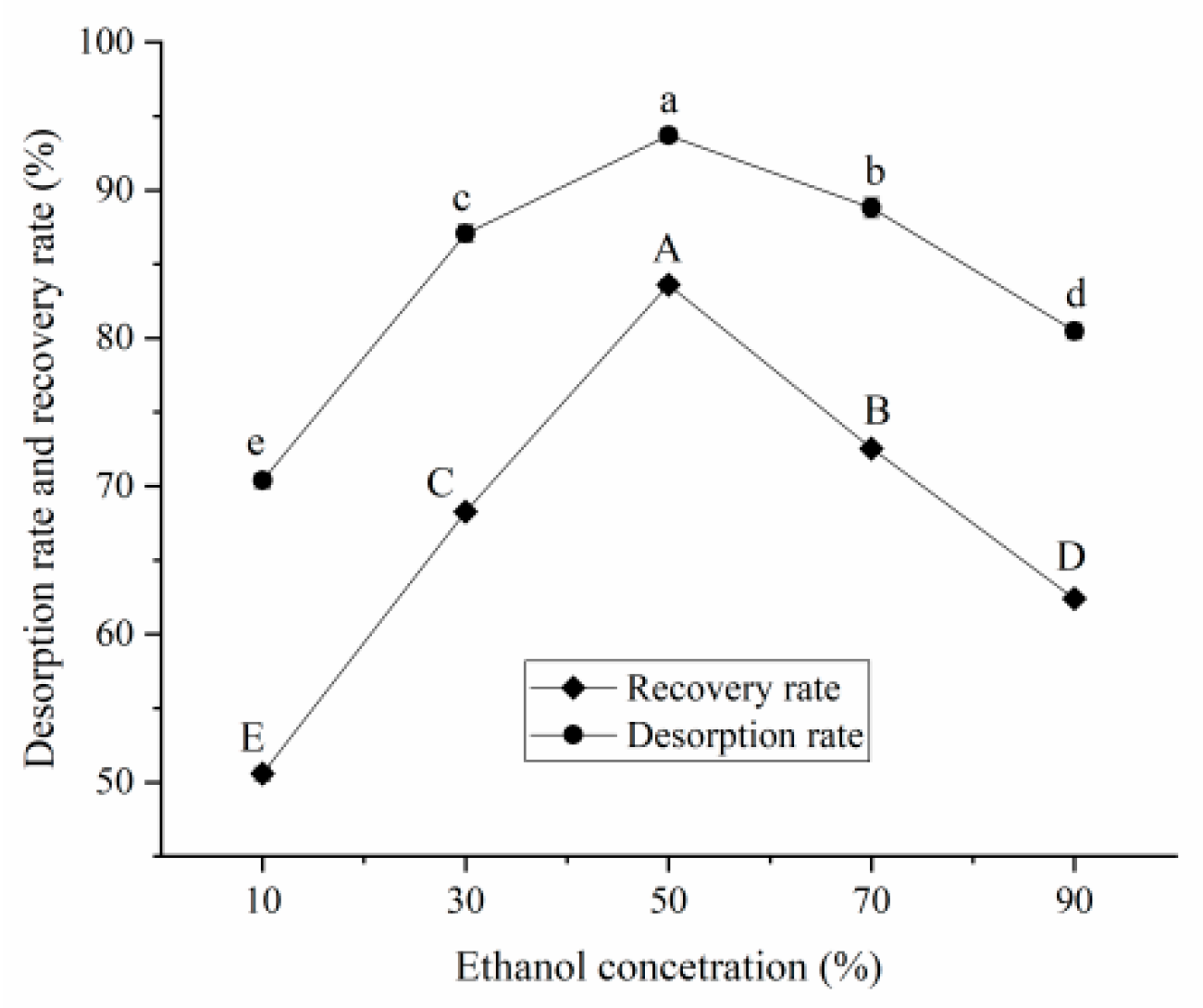
Ethanol Concentration
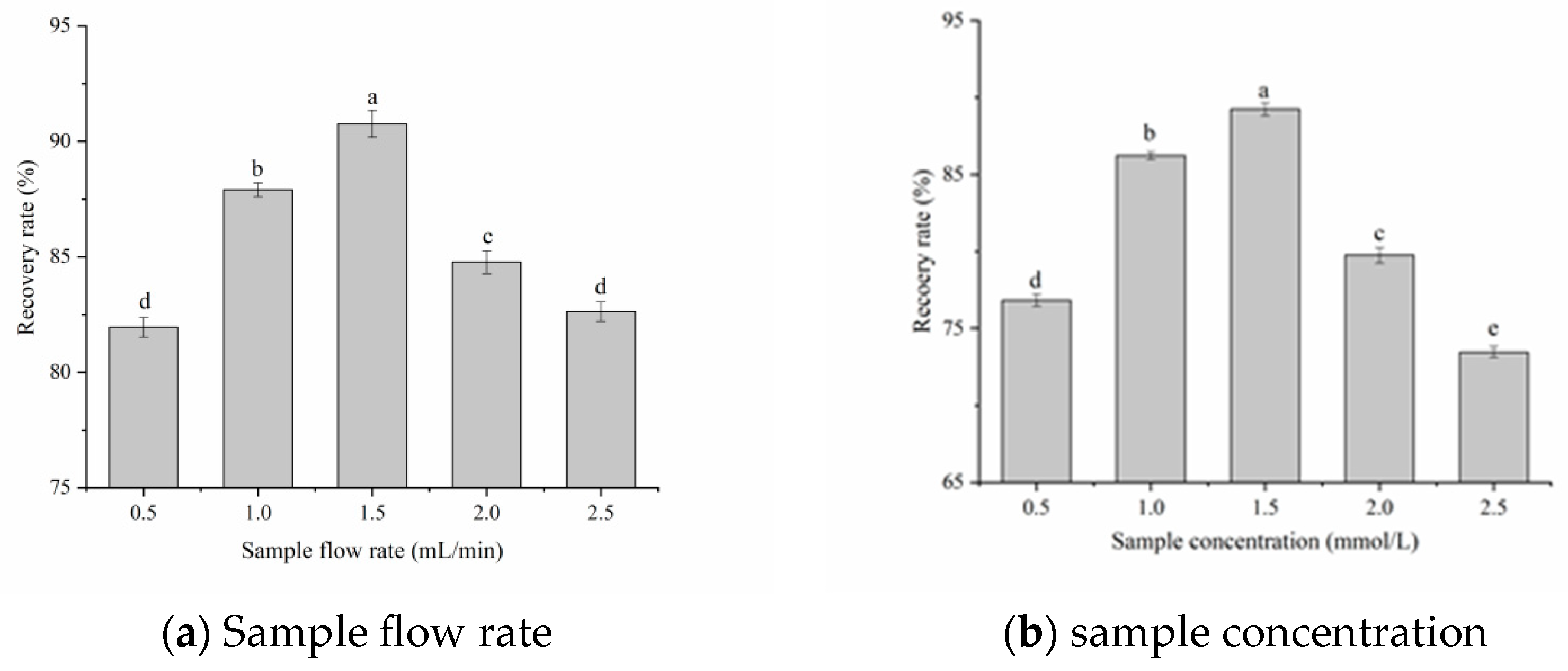
Sample Flow Rate and Sample Concentration
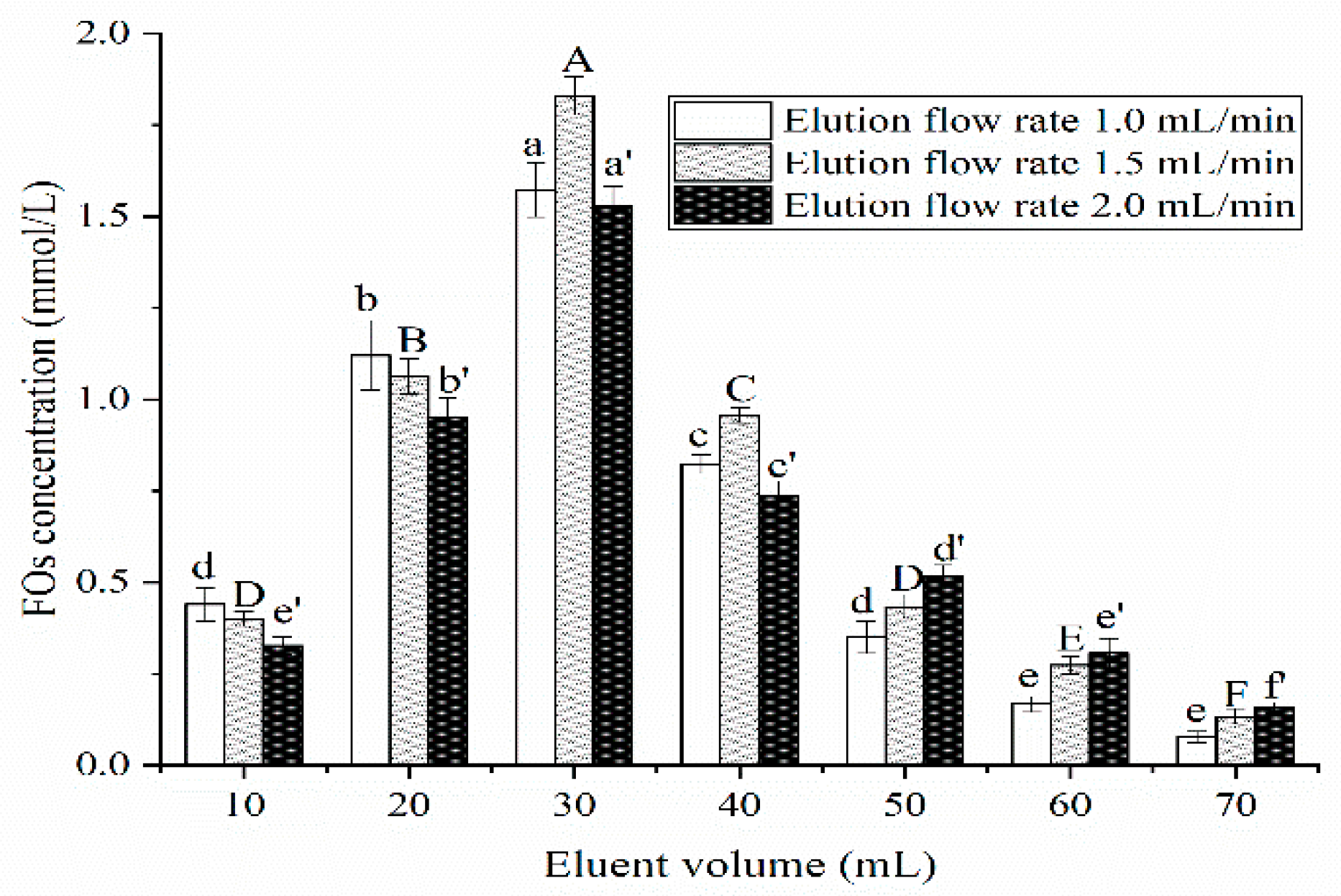
Elution Flow Rate
Orthogonal Optimization Design
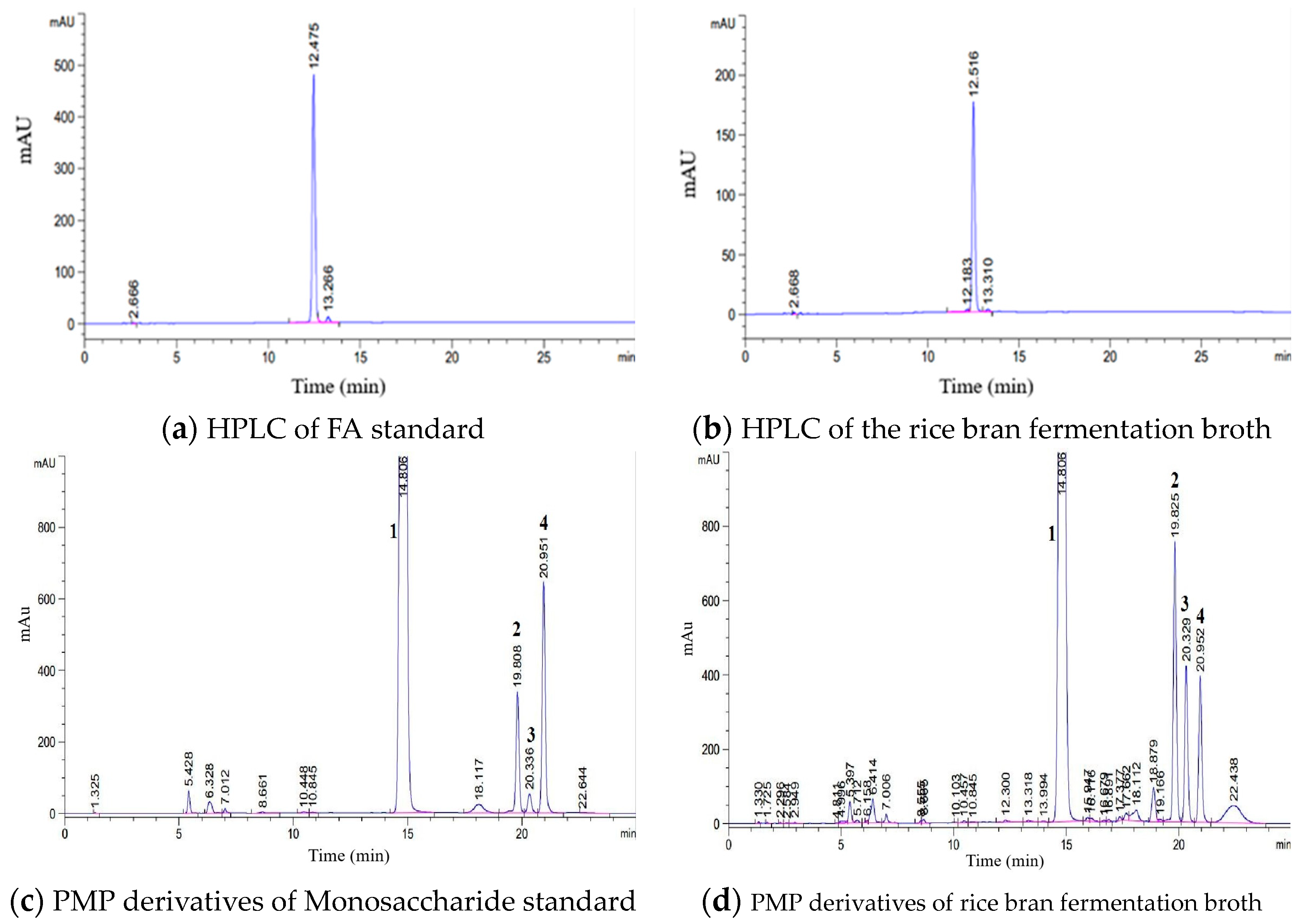
2.2.4. Determination of FOs [17,18]
2.2.5. Determination of FA [19,20]
2.2.6. Determination of Monosaccharide Composition in Rice Bran Fermentation Broth [21,22]
Preparation of Polysaccharide Sample Solution
Derivatization of Samples
Chromatographic Conditions
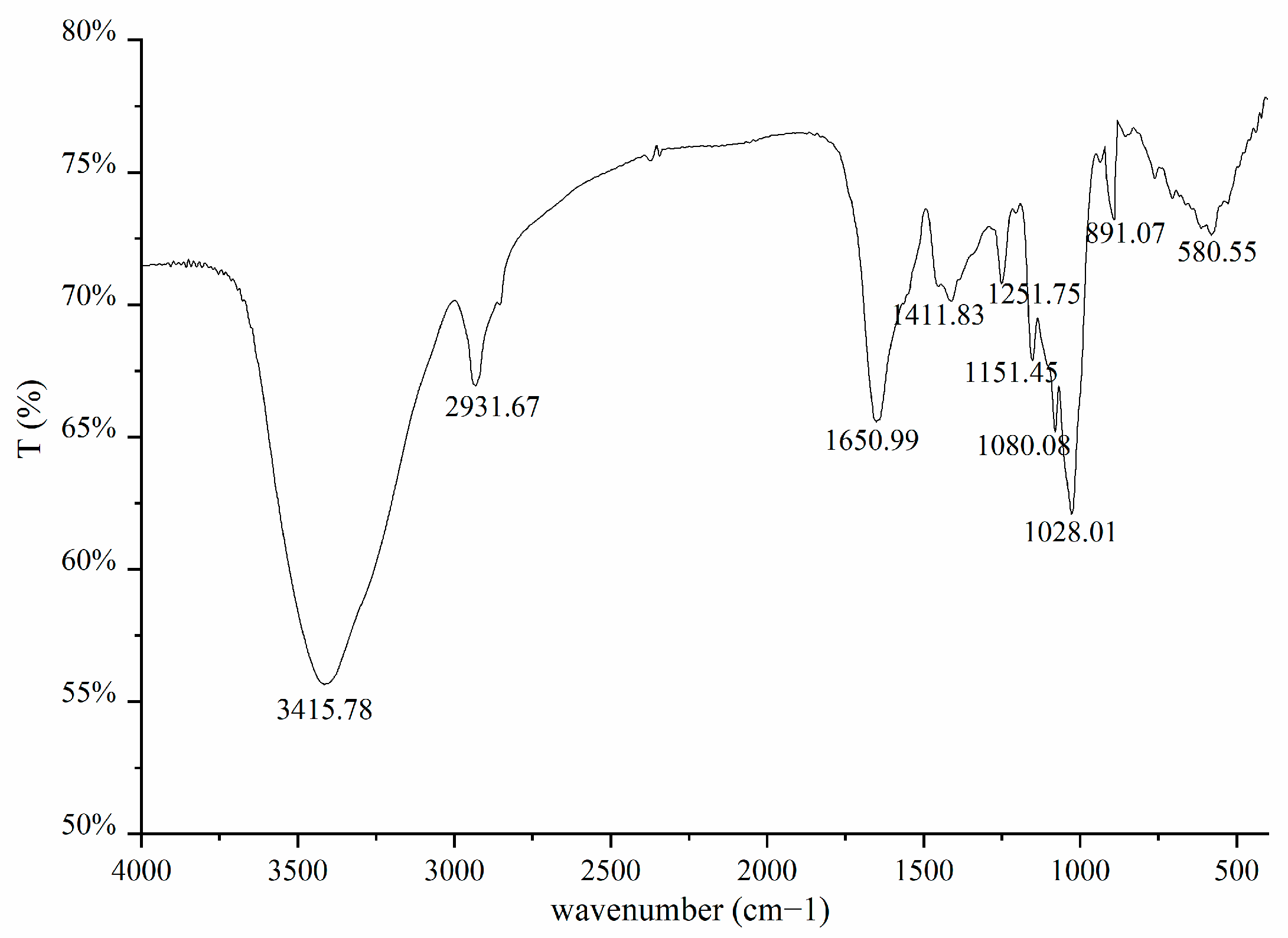
2.2.7. Determination of Rice Bran Fermentation Broth by FTIR [23]
2.2.8. Antioxidant Activity [24,25,26,27,28]
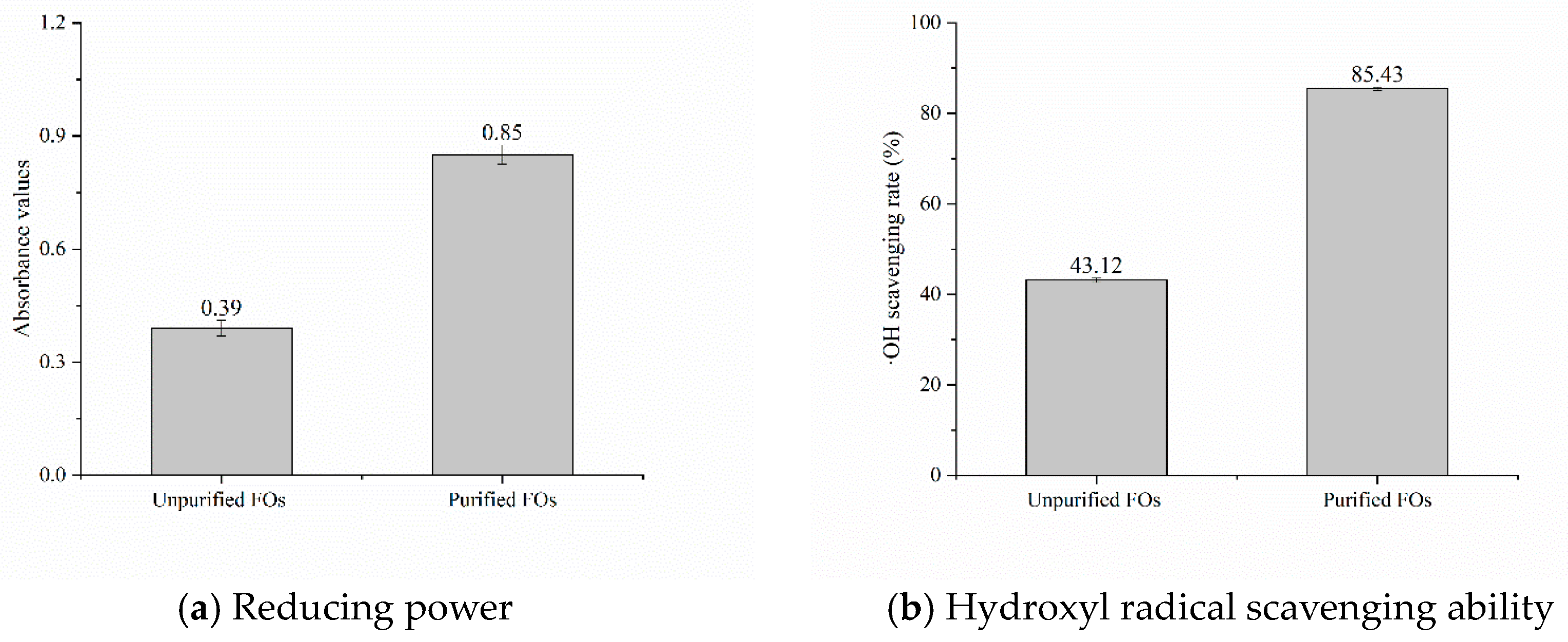
Reducing Power
Scavenging Capacity of ·OH
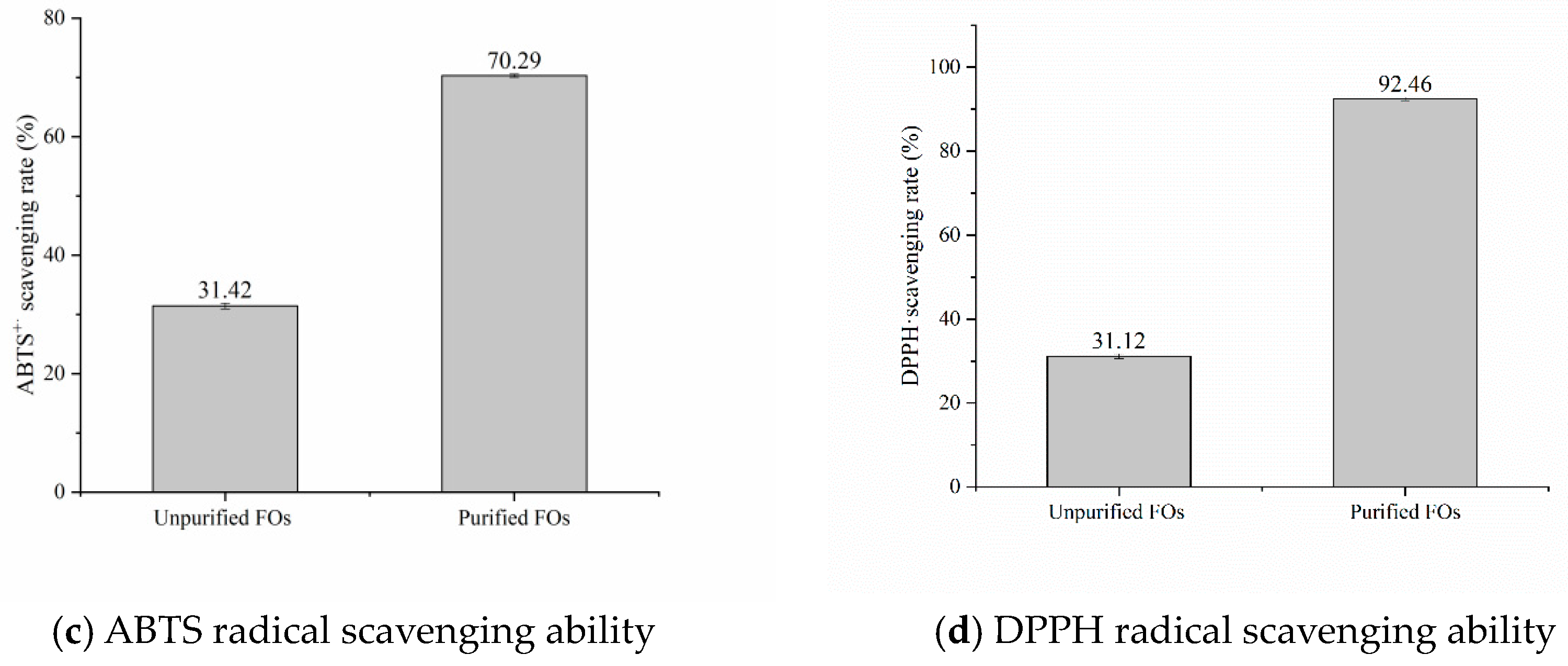
Scavenging Capacity of ABTS+·
Scavenging Ability of DPPH·
2.2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Preparation of Rice Bran Fermentation Broth with Hypsizigus marmoreus
3.2. Purification of Rice Bran Rice Bran Fermentation Broth
3.2.1. Screening of Macroporous Resin
Purification Parameters of Four Macroporous Resins
3.2.2. Single Factor Experiments on Purification of D101 Macroporous Resin
pH and Temperature
Ethanol Concentration
Sample Flow Rate and Sample Concentration
Elution Flow Rate and Eluent Volume
3.2.3. Orthogonal Test Results
3.3. Analysis of Rice Bran Fermentation Broth Composition
3.4. Infrared Spectra of Rice Bran Fermentation Broth
3.5. Antioxidant Activity of Rice Bran Fermentation Broth
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mendes, G.D.R.L.; Rodrigues, P.S.; Salas-Mellado, M.D.L.M.; Burkert, J.F.D.M.; Badiale-Furlong, E. Defatted Rice Bran as a Potential Raw Material to Improve the Nutritional and Functional Quality of Cakes. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2021, 76, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisa, K.; Rosyida, V.T.; Nurhayati, S.; Indrianingsih, A.W.; Darsih, C.; Apriyana, W. Total phenolic contents and antioxidant activity of rice bran fermented with lactic acid bacteria. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 251, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, K.; Nemoto, H.; Sakurai, A.; Yasutomo, K.; Shikanai, M. Preventive effect of fermented brown rice and rice bran on spontaneous type 1 diabetes in NOD female mice. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 78, 104356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.G.; Goncalves, L.M.; Prietto, L.; Hackbar, H.S.; Furlong, E.B. Antioxidant activity and enzyme inhibition of phenolic acids from fermented rice bran with fungus Rhizopus oryzae. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.F.; Jiang, Z.P.; Wang, C.; Xu, B.C.; Lu, Z.Q.; Wang, F.Q.; Zong, X.; Jin, M.L.; Wang, Y.Z. Dynamics of defatted rice bran in physicochemical characteristics, microbiota and metabolic functions during two-stage co-fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 362, 109489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Eligar, S.M. Feruloylated oligosaccharides-emerging natural oligosaccharides for human health: Production, structural characterization, bioactive potential, and functional food applications. Res. Technol. Adv. Food Sci. 2022, 6, 141–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wu, M.S.; Tao, G.; Lu, M.W.; Lin, J.; Huang, J.Q. Feruloylated oligosaccharides and ferulic acid alter gut microbiome to alleviate diabetic syndrome. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Liu, G.; Yu, G.; Song, Y.; Li, Q.H. Simultaneous decoloration and purification of crude oligosaccharides from pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata Duch) by macroporous adsorbent resin. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.N.; Li, H.Z.; Zhang, Z.J.; Ren, Z.Q.; Yang, F.H. Extraction, preparative monomer separation and antibacterial activity of total polyphenols from Perilla frutescens. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Jing, H.J.; Ye, X.; Jiang, C.; Shao, J.J.; Ma, C.Y.; Wang, H.X. Separation of epigallocatechin gallate and epicatechin gallate from tea polyphenols by macroporous resin and crystallization. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choukade, R.; Kango, N. Purification of Aspergillus tamarii mycelial fructosyltransferase (m-FTase), optimized FOS production, and evaluation of its anticancer potential. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 3294–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.T.; Framboisier, X.; Aymes, A.; Ropars, A.; Frippiat, J.P.; Kapel, R. Identification and Capture of Phenolic Compounds from a Rapeseed Meal Protein Isolate Production Process By-Product by Macroporous Resin and Valorization Their Antioxidant Properties. Molecules 2021, 26, 5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Fangma, Y.; Jin, W.; Jin, Z.; Li, X.; He, Y. Response surface optimization of the water immersion extraction and macroporous resin purification processes of anhydrosafflor yellow B from Carthamus tinctorius L. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 3191–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.D.; Zuo, Z.H.; Wang, Y.; Sun WPang, W.Q. Optimization of Ultrasound-Assisted Alkali Alcohol Extraction and Macroporous Resin Purification of Ferulic Acid from Corn Husk. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2023, 44, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Li, X.M.; Zhang, J.; Sun, X.; Li, Y.H.; Kan, H. Optimization of extraction and macroporous resin purification processes of total triterpenoid from boletus edulis bull.: Fr. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerakumar, S.; Manian, R. Agarase, Amylase and Xylanase from Halomonas meridiana: A Study on Optimization of Coproduction for Biomass Saccharification. Fermentation 2022, 8, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saulnier, L.; Vigouroux, J.; Thibault, J.F. Isolation and partial characterization of feruloylated oligosaccharides from maize bran. Carbohydr. Res. 1995, 272, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.Y.; Li, Y.L.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.Y.; Cao, Y. Composition and Antioxidant Activity Analysis of Feruloyl Oligosaccharides Produced from Brewer’s Grains. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2019, 40, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laddomada, B.; Blanco, A.; Mita, G.; D’Amico, L.; Singh, R.P.; Ammar, K.; Crossa, J.; Guzmán, C. Drought and heat stress impacts on phenolic acids accumulation in durum wheat cultivars. Foods 2021, 10, 2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.U.; Wang, D.L.; Huang, X.S. Simultaneous determination of six phenols in garlic skin by solid phase extraction-high performance liquid chromatography. Food Ferment. Ind. 2021, 47, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.Y.; Zhu, Z.S.; Xu, Y.J.; Wu, J.J.; Yu, Y.S. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum FM 17 fermentation on jackfruit polysaccharides: Physicochemical, structural, and bioactive properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 258, 128988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.H.; Feng, L.R.; Guan, E.Q. Structural Characterization of Feruloylated Oligosaccharides fromWheat Bran and Its Inhibitory Effects on Maillard Reaction Products. J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 2021, 36, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.N.; Zhao, C.B.; Li, S.; Qi, W.H.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zheng, M.Z.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, X.Y.; Liu, J.S. Postharvest ripening of newly harvested corn: Structural, rheological, and digestive characteristics of starch. LWT 2023, 180, 114728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudise, V.; Chowdhury, B.; Manjappa, A.S. In vitro free radical scavenging and antidiabetic activity of aqueous and ethanolic leaf extracts: A comparative evaluation of Argyreia pierreana and Matelea denticulata. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.W.; Li, X.; He, Y.F.; Peng, Y.X.; Lan, M. Colorimetric evaluation of the hydroxyl radical scavenging ability of antioxidants using carbon-confined CoOx as a highly active peroxidase mimic. Mikrochim Acta 2019, 186, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, S.; Kawakami, Y.; Kuroki MGotoh, H. Structure–antioxidant activity (oxygen radical absorbance capacity) relationships of phenolic compounds. Struct. Chem. 2022, 33, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, V.; Srivastava, M. Comparative Phytochemical Estimation and Free Radical Scavenging Activity in Leaves of Cassia Species. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 2022, 45, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.F.; Song, L.B.; Liu, H.P.; Zhang, Y.M.; Xing, H.Z. Preparation, Structural, Characterization and Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharide from Centella asiatica (L.) Urban. Food Res. Dev. 2023, 44, 1–9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.P.; Lu, M.; Hu, N.N.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Dai, Y.G.; Wang, J.H. Fermentation production for feruloyl oligosaccharides from rice bran. Storage Process 2017, 17, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, R.F.; Deng, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Huang, F.; Wen, W.; Zhang, M.W. Fermentation and complex enzyme hydrolysis enhance total phenolics and antioxidant activity of aqueous solution from rice bran pretreated by steaming with α-amylase. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Li, M.M.; Wang, W.J.; Zheng, G.D.; Yin, Z.P.; Chen, J.G.; Zhang, Q.F. Separation and purification of anthocyanins from Roselle by macroporous resins. LWT 2022, 161, 113371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erpel, F.; Camilo, C.; Mateos, R.; Ricardo P´erez-Correa, J. A macroporous resin purification process to obtain food-grade phlorotannin-rich extracts with α-glucosidase inhibitory activity from Chilean brown seaweeds: An UHPLC-MSn profiling. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhang, T.W.; Yang, F.H.; Li, H.Z.; Zhang, Z.J. Study on extraction and purification process of anthocyanins from blueberry residue. China Condiment 2024, 49, 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, J.; Zhang, L.T.; Lu, L.; Wei, J.Y.; Jin, B.; Luo, Q.; Yan, Y.M.; Cao, Y.L. Separation and Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitory Activity of Two Petunidin Anthocyanins from Lycium ruthenicum Murr. By Preparative Medium-Pressure Liquid Chromatography. Food Sci. 2023, 44, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.X.; Yin, L.J.; Wang, K.; Jia, X. Research progress of ferulic acid modified polysaccharide and its antioxidant activity. Cereals Oils 2022, 35, 23–25, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardiansyah, A.F.; Astuti, R.M.; David, W.; Shirakawa, H. Non-volatile compounds and blood pressure-lowering activity of Inpari 30 and Cempo Ireng fermented and non-fermented rice bran. AIMS Agric. Food 2021, 6, 337–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omarini, A.B.; Labuckas, D.; Zunino, M.P.; Pizzolitto, R.; Fernández-Lahore, M.; Barrionuevo, D.; Zygadlo, J.A. Upgrading the Nutritional Value of Rice Bran by Solid-State Fermentation with Pleurotus sapidus. Fermentation 2019, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No. | Factors | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A pH | B Temperature/°C | C Ethanol Concentration /% | D Sample Flow Rate /(mL/min) | E Sample Concentration /(mmol/L) | F Elution Flow Rate /(mL/min) | |
| 1 | 3.0 | 21 | 40 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.6 |
| 2 | 3.5 | 23 | 45 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.8 |
| 3 | 4.0 | 25 | 50 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 2.0 |
| 4 | 4.5 | 27 | 55 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 2.2 |
| 5 | 5.0 | 29 | 60 | 1.9 | 1.9 | 2.4 |
| Resin Type | Polarity | The Average Pore Diameter/μm | Adsorption Rate/% | Desorption Rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D101 | non-polar | 90~100 | 96.60 ± 0.30 a | 98.81 ± 0.20 a |
| HPD700 | non-polar | 90~100 | 86.54 ± 0.24 b | 90.47 ± 0.25 b |
| DA201-B | polar | 90~100 | 72.36 ± 0.53 c | 82.43 ± 0.41 c |
| DM-21 | neutral | 130~140 | 85.10 ± 0.26 d | 87.97 ± 0.15 d |
| No. | Factors | FOs Content /(mmol/L) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A pH | B Temperature | C Ethanol Concentration | D Sample Flow Rate | E Sample Concentration | F Elution | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.02 ± 0.025 q |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1.28 ± 0.015 no |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1.96 ± 0.0057 b |
| 4 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 1.80 ± 1.015 fg |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 1.55 ± 0.010 j |
| 6 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 1.58 ± 0.0057 j |
| 7 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 1.30 ± 0.015 n |
| 8 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 1.44 ± 0.0057 kl |
| 9 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1.89 ± 0.035 d |
| 10 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1.68 ± 0.015 i |
| 11 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 1.78 ± 0057 g |
| 12 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 1.72 ± 0.015 h |
| 13 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 1.68 ± 0.010 i |
| 14 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 1.82 ± 0.015 ef |
| 15 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 1.85 ± 0.015 e |
| 16 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 2.20 ± 0.015 a |
| 17 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 1.92 ± 0.057 c |
| 18 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 1.25 ± 0.057 o |
| 19 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1.28 ± 0.010 n |
| 20 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 2.21 ± 0.015 a |
| 21 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1.45 ± 0.0057 k |
| 22 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 1.72 ± 0.015 h |
| 23 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 1.42 ± 0.010 l |
| 24 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 1.10 ± 0.035 p |
| 25 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1.36 ± 0.010 m |
| k1 | 1.522 | 1.606 | 1.498 | 1.652 | 1.466 | 1.328 | |
| k2 | 1.578 | 1.588 | 1.482 | 1.588 | 1.512 | 1.498 | |
| k3 | 1.770 | 1.550 | 1.670 | 1.728 | 1.618 | 1.972 | |
| k4 | 1.772 | 1.578 | 1.704 | 1.530 | 1.798 | 1.720 | |
| k5 | 1.140 | 1.730 | 1.698 | 1.554 | 1.658 | 1.440 | |
| R | 0.362 | 0.180 | 0.222 | 0.198 | 0.332 | 0.644 | |
| optimum | A4 | B5 | C4 | D3 | E4 | F3 | |
| Number | Experimental Scheme | FOs Content |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | A4B5C4D3E4F3 | 2.38 ± 0.0153 a |
| 2 | A4B5C3D1E4F2 | 2.26 ± 0.0200 b |
| 3 | A4B1C4D2E5F3 | 2.24 ± 0.0100 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chi, Y.; Kang, L.; Liu, X.; Sun, H.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Kang, Y.; Dai, Y. Preparation, Purification, Characterization and Antioxidant Activity of Rice Bran Fermentation Broth with Hypsizigus marmoreus. Fermentation 2024, 10, 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10040188
Chi Y, Kang L, Liu X, Sun H, Meng Y, Zhang J, Kang Y, Dai Y. Preparation, Purification, Characterization and Antioxidant Activity of Rice Bran Fermentation Broth with Hypsizigus marmoreus. Fermentation. 2024; 10(4):188. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10040188
Chicago/Turabian StyleChi, Yanping, Lining Kang, Xiangying Liu, Hongrui Sun, Yue Meng, Jialin Zhang, You Kang, and Yonggang Dai. 2024. "Preparation, Purification, Characterization and Antioxidant Activity of Rice Bran Fermentation Broth with Hypsizigus marmoreus" Fermentation 10, no. 4: 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10040188
APA StyleChi, Y., Kang, L., Liu, X., Sun, H., Meng, Y., Zhang, J., Kang, Y., & Dai, Y. (2024). Preparation, Purification, Characterization and Antioxidant Activity of Rice Bran Fermentation Broth with Hypsizigus marmoreus. Fermentation, 10(4), 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10040188





