Multi-Omics Analysis of the Co-Regulation of Wood Alcohol Accumulation in Baijiu Fermentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Preprocessing
2.2. Chemical Indicator Detection
2.3. Total DNA and Total RNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.4. DNA Extraction, Amplification, and Sequencing
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
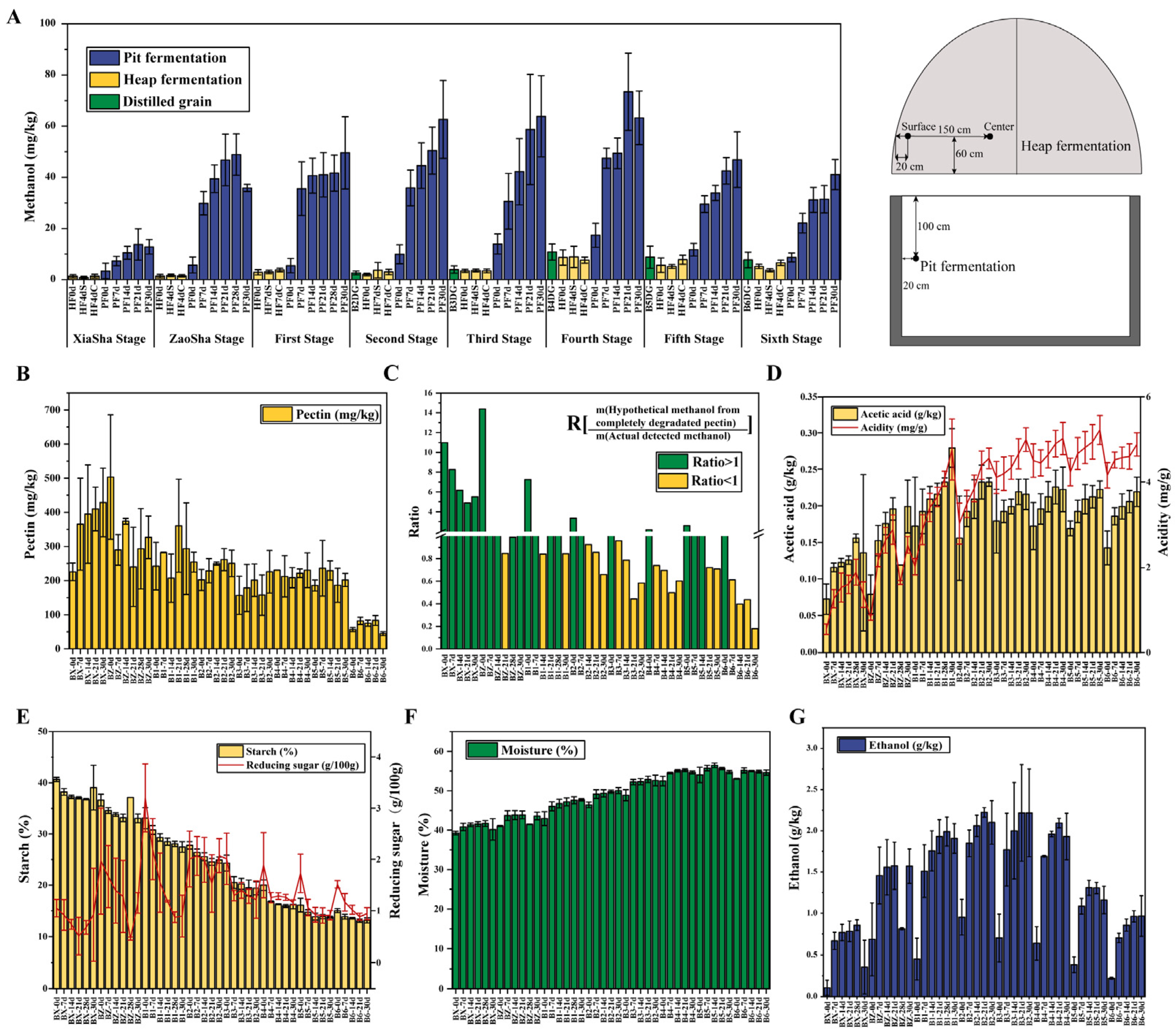
3.1. Trends in Methanol Content and Environmental Factors Variation during Fermentation across the Baijiu Production Cycles
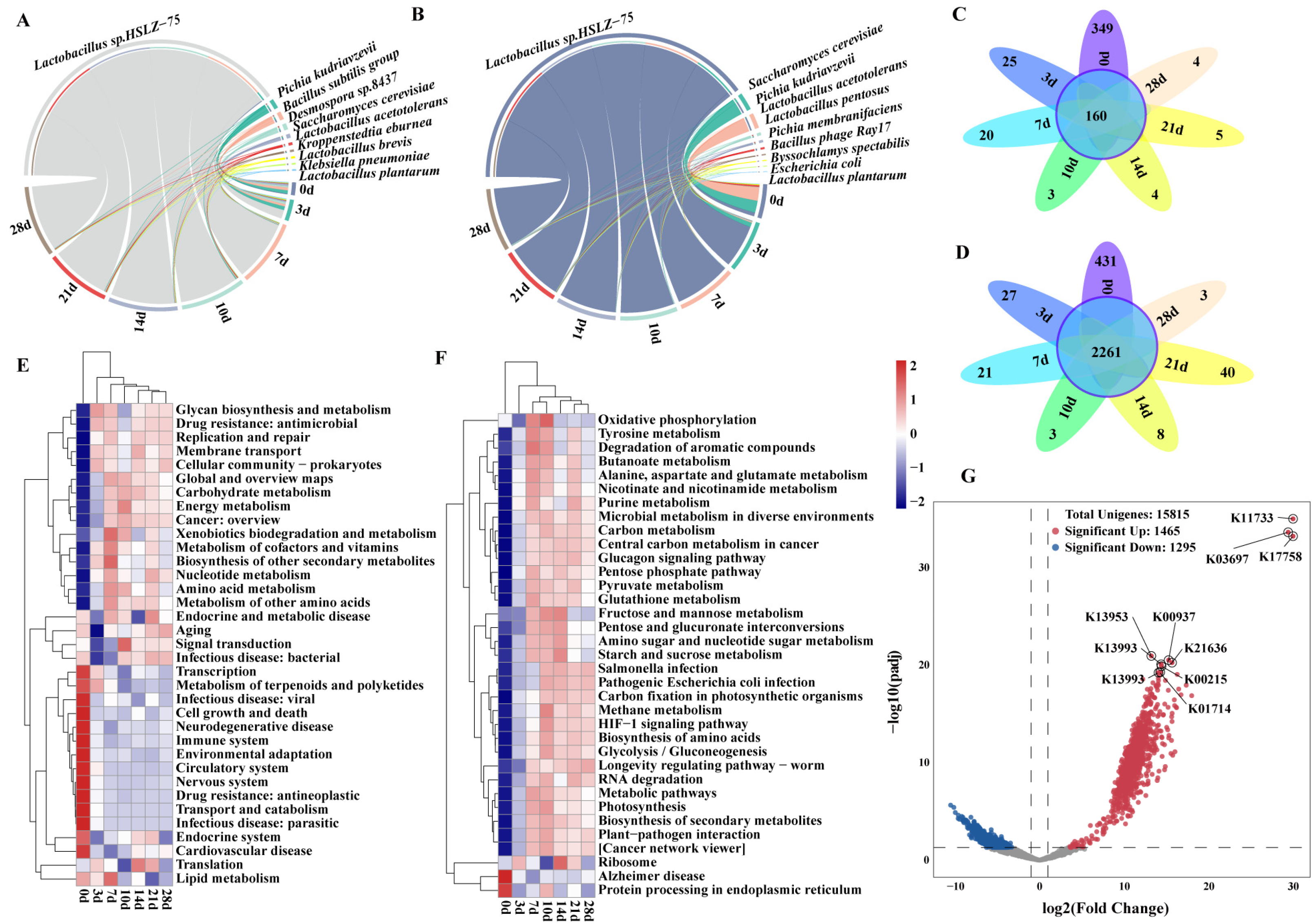
3.2. Analysis of the Changes in Dominant Species and Functions during Pit Fermentation
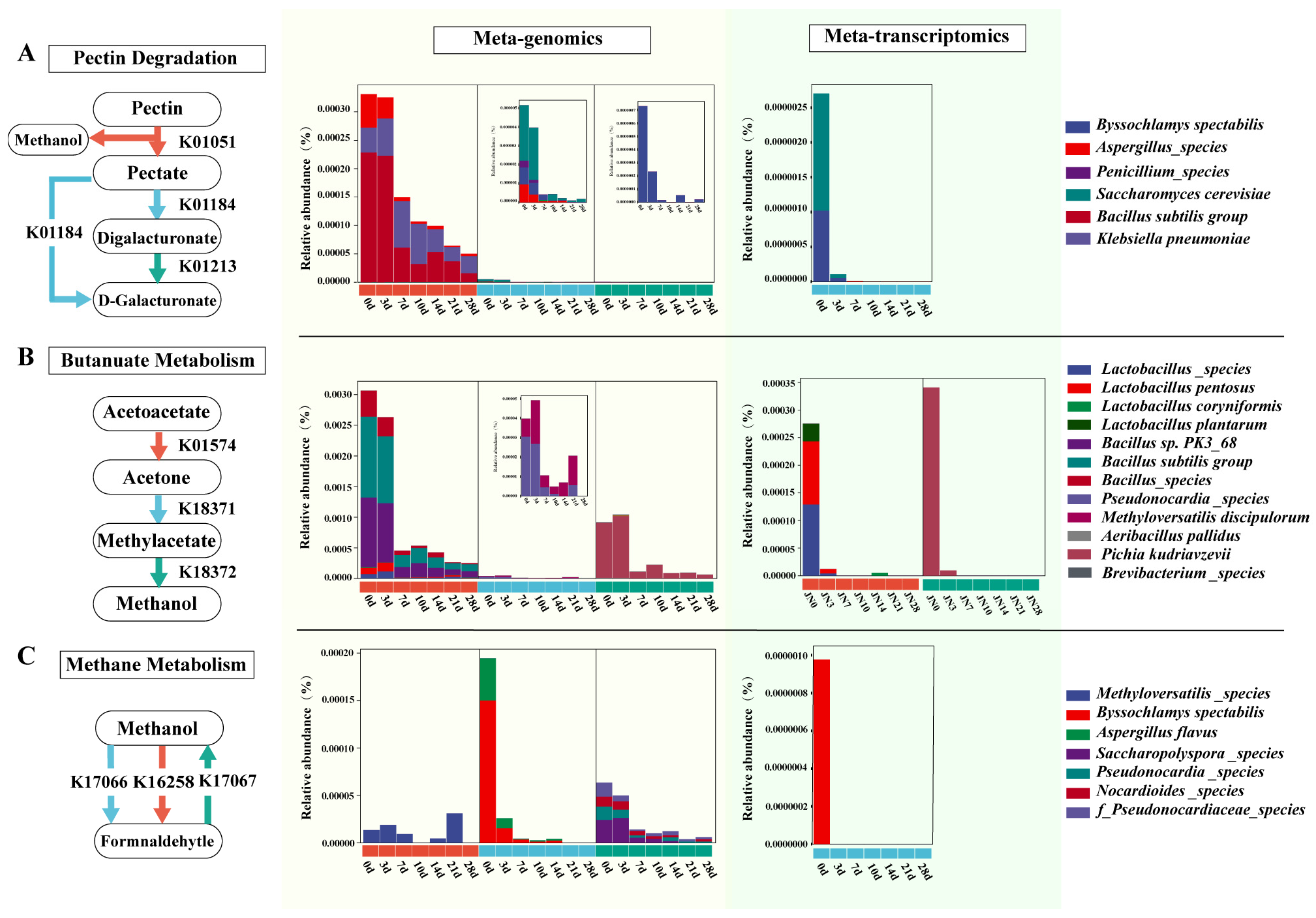
3.3. Analysis of Methanol Metabolism Pathways and Participating Microorganisms during Pit Fermentation
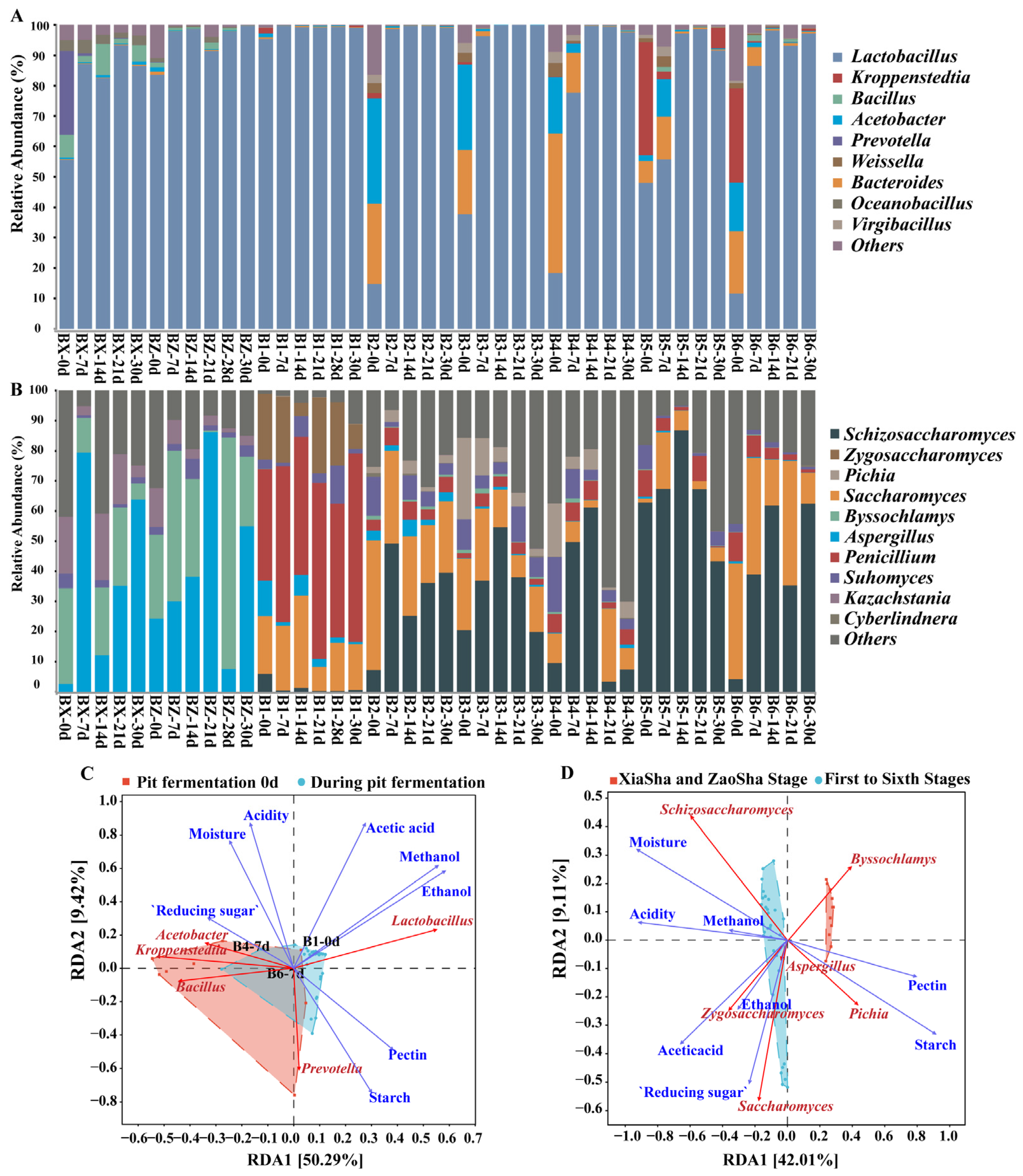
3.4. Microbial Succession and Driving Environmental Factors during Pit Fermentation across the Baijiu Production Cycles
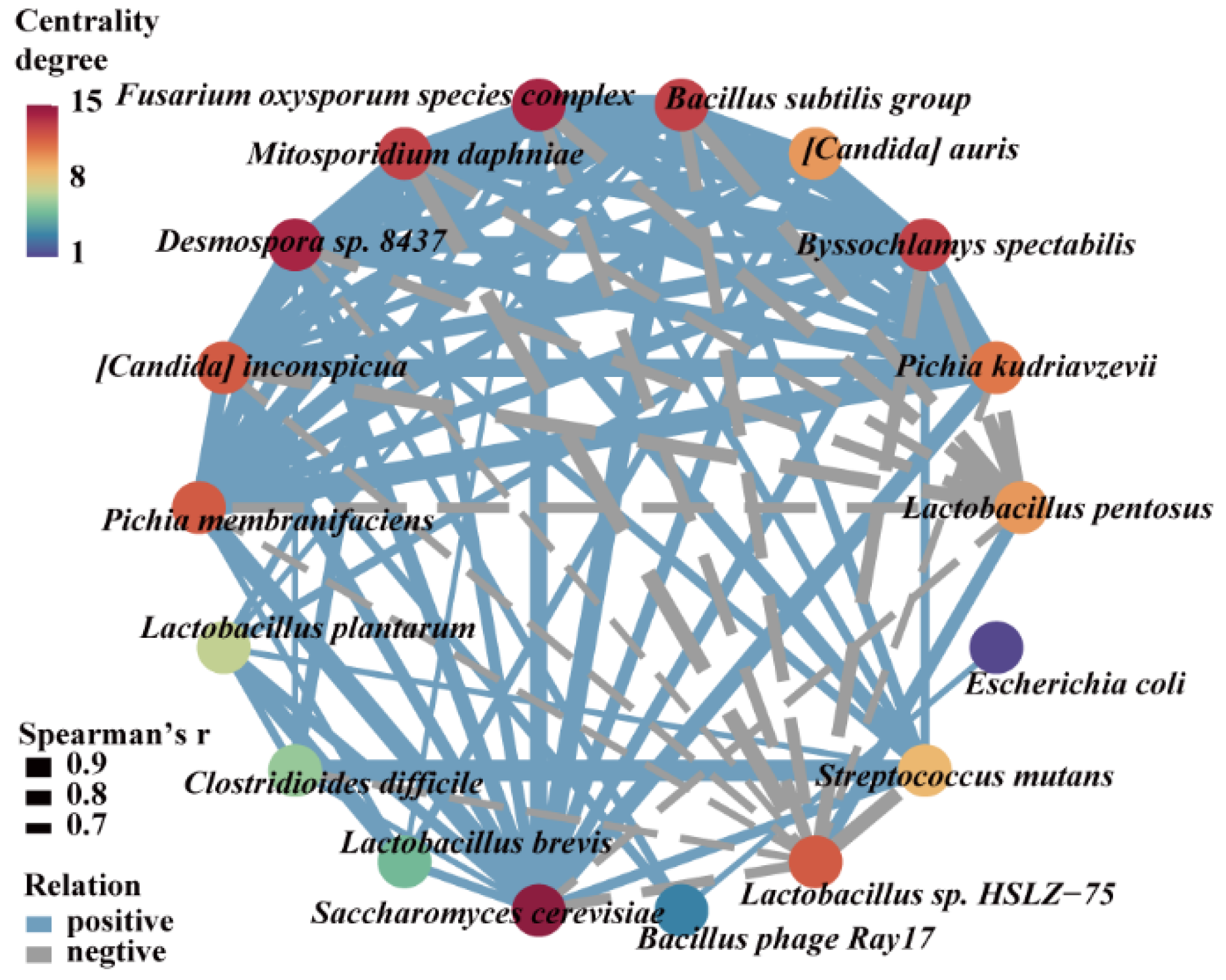
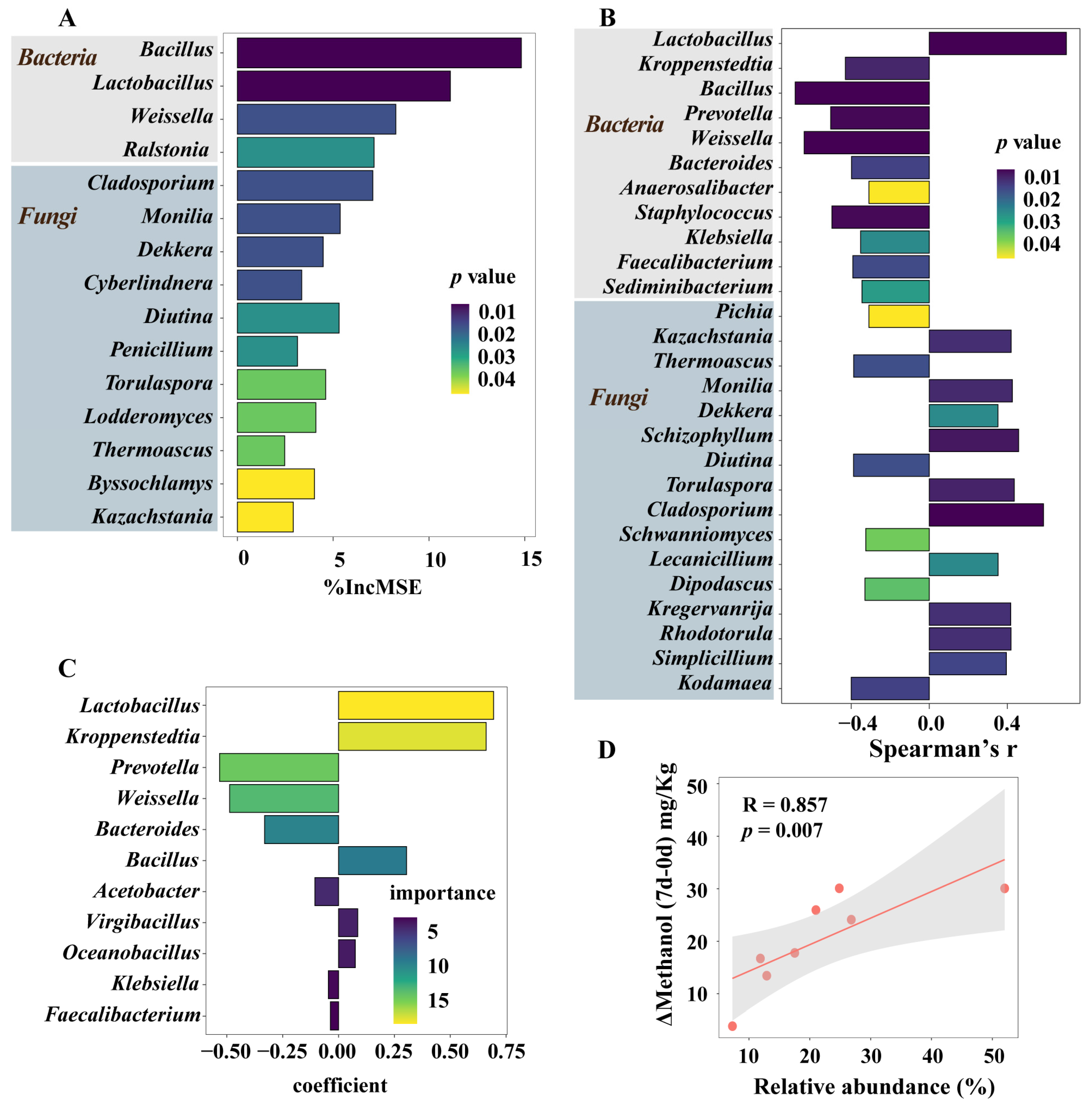
3.5. Microorganisms Having a Significant Impact on Methanol Accumulation during Pit Fermentation across the Baijiu Production Cycles
3.6. Integrated Impact of Environmental Factors and Microorganisms on Methanol Content Changes during Pit Fermentation across the Baijiu Production Cycles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gurler, M.; Martz, W.; Tastekin, B.; Najafova, T.; Dettmeyer, R.B. Estimates of Non-Alcoholic Food-Derived Ethanol and Methanol Exposure in Humans. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2022, 46, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, M.M.; Zeren, C.; Aydin, Z.; Akcan, R.; Dokuyucu, R.; Keten, A.; Cekin, N. Analysis of methanol and its derivatives in illegally produced alcoholic beverages. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2015, 33, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, X.-N.; Li, Z.-J.; Chen, J.-Y.; Gao, L.-J.; Han, B.-Z. A Comprehensive Review of Spirit Drink Safety Standards and Regulations from an International Perspective. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohimain, E.I. Methanol contamination in traditionally fermented alcoholic beverages: The microbial dimension. Springerplus 2016, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez Espitia, P.J.; Du, W.-X.; Avena-Bustillos, R.d.J.; Ferreira Soares, N.d.F.; McHugh, T.H. Edible films from pectin: Physical-mechanical and antimicrobial properties—A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haile, S.; Ayele, A. Pectinase from Microorganisms and Its Industrial Applications. Sci. World J. 2022, 2022, 1881305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsouko, E.; Maina, S.; Ladakis, D.; Kookos, I.K.; Koutinas, A. Integrated biorefinery development for the extraction of value-added components and bacterial cellulose production from orange peel waste streams. Renew. Energy 2020, 160, 944–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenthal, P.; Steger, M.C.; Einfalt, D.; Rieke-Zapp, J.; Bellucci, A.Q.; Sommerfeld, K.; Schwarz, S.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Methanol Mitigation during Manufacturing of Fruit Spirits with Special Consideration of Novel Coffee Cherry Spirits. Molecules 2021, 26, 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Tovar, J.A.; Flores-Gallegos, A.C.; Contreras-Esquivel, J.C.; Escobedo-Garcia, S.; Morlett-Chavez, J.A.; Rodriguez-Herrera, R. Analytical Methods for Pectin Methylesterase Activity Determination: A Review. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 3634–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, O.; Kakizono, D.; Takahashi, T.; Mukai, N.; Fukuda, H.; Yamada, O. The effect of Aspergillus luchuensis pectin methylesterase genes pmeA and pmeB on methanol production in sweet potato shochu. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2023, 87, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Francoise, U.; Qin, M.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Fang, Y.-L. Effects of different fermentation and storage conditions on methanol content in Chinese spine grape (Vitis davidii Foex) wine. CyTA-J. Food 2020, 18, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, Y. Mystery behind Chinese liquor fermentation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 63, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. Research trends in Jiang-flavor baijiu fermentation: From fermentation microecology to environmental ecology. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 1362–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, W.; Cao, X.; Cheng, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, T.; Wu, Q.; Xiang, P.; Shen, C.; Li, Q. Chinese Baijiu: The Perfect Works of Microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Zhang, L.; Yu, X.; Chen, F.; Guo, F.; Wu, Q.; Xu, Y. Selection of initial microbial community for the alcoholic fermentation of sesame flavor-type baijiu. Food Res. Int. 2023, 172, 113141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Du, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y. Unraveling Core Functional Microbiota in Traditional Solid-State Fermentation by High-Throughput Amplicons and Metatranscriptomics Sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Ma, D.; Yang, C.; Yin, Q.; Liu, S.; Shen, C.; Mao, J. Microbial community succession patterns and drivers of Luxiang-flavor Jiupei during long fermentation. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1109719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Li, X.; Sun, B. Flavor mystery of Chinese traditional fermented baijiu: The great contribution of ester compounds. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zhong, H.; Zhao, D.; Du, H.; Xu, Y. Succession rate of microbial community causes flavor difference in strong-aroma Baijiu making process. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 311, 108350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Q.; Chen, S.; Tang, J.; Xu, Y. Modeling and Regulation of Higher Alcohol Production through the Combined Effects of the C/N Ratio and Microbial Interaction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 10694–10701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, C.-I.; Ye, F.; Shyr, Y. Evaluation of read count based RNAseq analysis methods. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Du, J. Relationship of the methanol production, pectin and pectinase activity during apple wine fermentation and aging. Food Res. Int. 2022, 159, 111645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, L.; Qian, W.; Zhong, X.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Shen, C.; Shi, J.; Xu, Z. Distribution of archaeal community in the mud pit during strong-flavor baijiu fermentation. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao = Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 2635–2643. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, T.D.; Zhang, J.H.; Wang, T.R.; Bai, B.Q.; Hou, Z.X.; Cheng, J.F.; Bo, T.; Fan, S.H. Reveal the microbial communities and functional prediction during the fermentation of Fen-flavor Baijiu via metagenome combining amplicon sequencing. Ann. Microbiol. 2023, 73, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xiong, Y.; Xie, Y.H.; Zhang, H.X.; Jiang, K.X.; Pang, X.N.; Huang, M.Q. Metabolic characteristics of lactic acid bacteria and interaction with yeast isolated from light-flavor Baijiu fermentation. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 102102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zeng, X.; Chen, L.; Yan, F.; Du, H.; Huang, X. Microbial intervention to reduce lactic acid in Moutai-flavor liquor brewing. Food Ferment. Ind. 2023, 49, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J.; Li, X.; Xie, S.; Yu, P.; Chen, J. Interaction between lactic acid bacteria and yeasts in light-aroma liquor. Microbiol. China 2017, 44, 1767–1776. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Huang, Y.; Tu, H.; Hu, F.; Cheng, P.; You, X. Bacterial Diversity Structure during the First Round of Pile and Pit Fermentation of Moutai-flavor Baijiu. Food Sci. 2020, 41, 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Ding, H.; Lang, Y.; Xu, P.; Wang, C.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Qiu, S. Airborne microorganisms and key environmental factors shaping their community patterns in the core production area of the Maotai-flavor Baijiu. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 912, 169010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klepach, H.M.; Zakalskiy, A.E.; Zakalska, O.M.; Gayda, G.Z.; Smutok, O.V.; Gonchar, M.V. Alcohol Oxidase from the Methylotrophic Yeast Ogataea polymorpha: Isolation, Purification, and Bioanalytical Application. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2280, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Hao, W.J.; Zhou, S.; Duan, C.B.; Li, Q.S.; Wei, J.W.; Liu, G. Exploring the Role of Active Functional Microbiota in Flavor Generation by Integrated Metatranscriptomics and Metabolomics during Niulanshan Baijiu Fermentation. Foods 2023, 12, 4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Jia, F.; Wang, L.; Chang, F. The initial composition and structure of microbial community determined the yield and quality of Baijiu during the spontaneous fermentation. Int. Microbiol. 2023, 27, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.W.; Yu, Q.L.; Su, W.H.; Wang, S.J.; Wang, X.C.; Han, Q.; Qu, J.P.; Li, H. Metagenomics reveals elevated temperature causes nitrogen accumulation mainly by inhibiting nitrate reduction process in polluted water. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 882, 163631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, T.; Yamada, K.; Fujimura, S.; Ito, T.; Miyaji, T.; Tomizuka, N. Pectin utilization by the methylotrophic yeast Pichia methanolica. Microbiology 2005, 151, 2047–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Jianlan, C.; Kejia, W.; Dounan, L.; Xiaoye, L.; Jie, C.; Shuyi, Q. Progress in understanding the effect of sorghum on the quality of maotai-flavor Baijiu. Food Sci. China 2022, 43, 356–364. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Zheng, H.; Chai, L.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Z. Research progress on the nutritional components and brewing performance of brewing sorghum. Food Ferment. Ind. 2022, 48, 307–317. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Zhang, L.-Q.; Ran, M.-F.; Wang, S.-T.; Yang, J.-G.; Shen, C.-H. Investigation on fresh bamboo replacing rice husks for brewing light-aroma Baijiu. J. Food Sci. 2023, 88, 1224–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Fan, E.; Ma, B.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, D. Research progress in functional bacteria in solid-state fermented Baijiu in China. Food Ferment. Ind. 2020, 46, 280–286. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, W.; Jian, L.; Qian, W.; Xueli, P.; Qifa, Z.; Wei, L.; Dewen, H.; Yang, N. Research Progress on the effect of Bacillus on flavor substances of Maotai flavor Baijiu. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 43, e101422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liqin, Q.; Jinghao, M.; Erhao, L.; Yang, Z.; Bosi, Y.; Yuting, Z.; Qiuhua, W.; Jinying, T.; Xiuting, L.; Guangsen, F. Solation and identification of an amylase-producing bacterium from Beipai sauce-flavor Baijiu brewing environment and its characteristics research. China Brew. 2021, 40, 154–160. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Yang, Q.; Jiang, W.; Li, Q.; Lin, B.; Tang, J.; Chen, S. Mold communities and enzyme activity characteristics in light-flavor Xiaoqu Baijiu. Food Ferment. Ind. 2022, 48, 70–77. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, X.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, J.; Qiao, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z. Isolation and identification of cultivable molds in the air of Baijiu-making environment of Wuliangye and their enzyme producing ability. Food Ferment. Ind. 2022, 48, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- He, M.; Jin, Y.; Liu, M.; Yang, G.; Zhou, R.; Zhao, J.; Wu, C. Metaproteomic investigation of enzyme profile in daqu used for the production of Nongxiangxing baijiu. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 400, 110250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Ao, R.; Huang, H.; Hong, J.; Zhao, D.; et al. “Key Factor” for Baijiu Quality: Research Progress on Acid Substances in Baijiu. Foods 2022, 11, 2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Li, Z.; Tian, Z. Enzyme activity of fermented grains of sauce-flavor Baijiu and analysis of physical and chemical index of rounds Baijiu. China Brew. 2019, 38, 31–36. [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, T.; Cao, Q.; Yang, F.; Lu, J.; Zeng, X.; Li, J.; Du, G.; Tu, H.; Liu, Y. Multi-Omics Analysis of the Co-Regulation of Wood Alcohol Accumulation in Baijiu Fermentation. Fermentation 2024, 10, 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10040175
Liu T, Cao Q, Yang F, Lu J, Zeng X, Li J, Du G, Tu H, Liu Y. Multi-Omics Analysis of the Co-Regulation of Wood Alcohol Accumulation in Baijiu Fermentation. Fermentation. 2024; 10(4):175. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10040175
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Tong, Qingqing Cao, Fan Yang, Jianjun Lu, Xianglian Zeng, Jianghua Li, Guocheng Du, Huabin Tu, and Yanfeng Liu. 2024. "Multi-Omics Analysis of the Co-Regulation of Wood Alcohol Accumulation in Baijiu Fermentation" Fermentation 10, no. 4: 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10040175
APA StyleLiu, T., Cao, Q., Yang, F., Lu, J., Zeng, X., Li, J., Du, G., Tu, H., & Liu, Y. (2024). Multi-Omics Analysis of the Co-Regulation of Wood Alcohol Accumulation in Baijiu Fermentation. Fermentation, 10(4), 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10040175






