Characterization of Urease from Providencia sp. LBBE and Its Application in Degrading Urea and Ethyl Carbamate in Rice Wine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmids, Strains, and Chemical Reagents
2.2. Expression and Purification of Recombinant Ps_Urease
2.3. Urease Activity Determination
2.4. Characterization of the Recombinant Ps_Urease
2.5. Elimination of Urea and EC from Rice Wine
2.6. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of the Gene Cluster and Structural Subunit of Ps_Urease
3.2. Heterologous Expression and Purification of Recombinant Ps_Urease
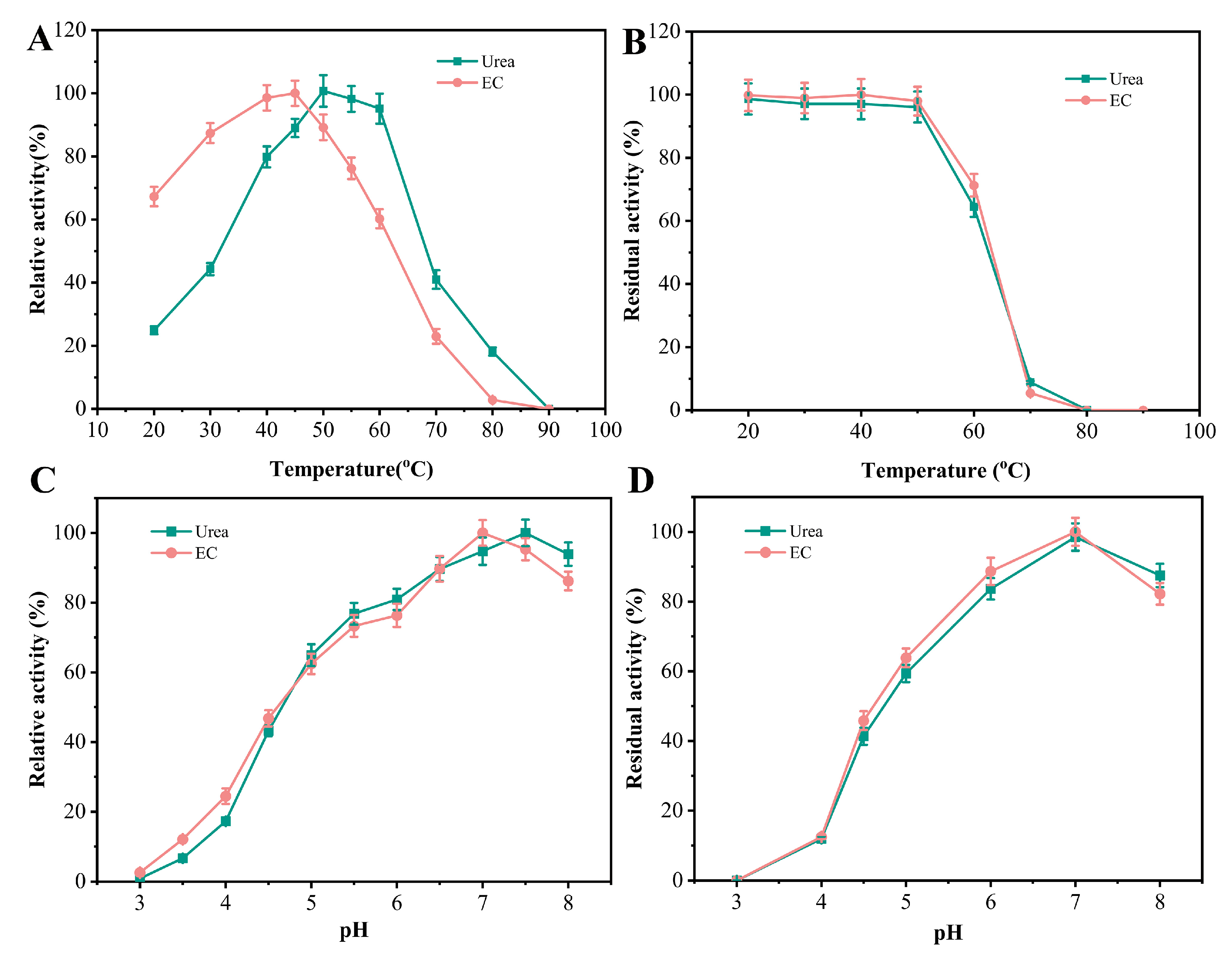
3.3. Effects of Temperature on the Activity and Stability of Ps_Urease
3.4. Effects of pH on the Activity and Stability of Ps_Urease
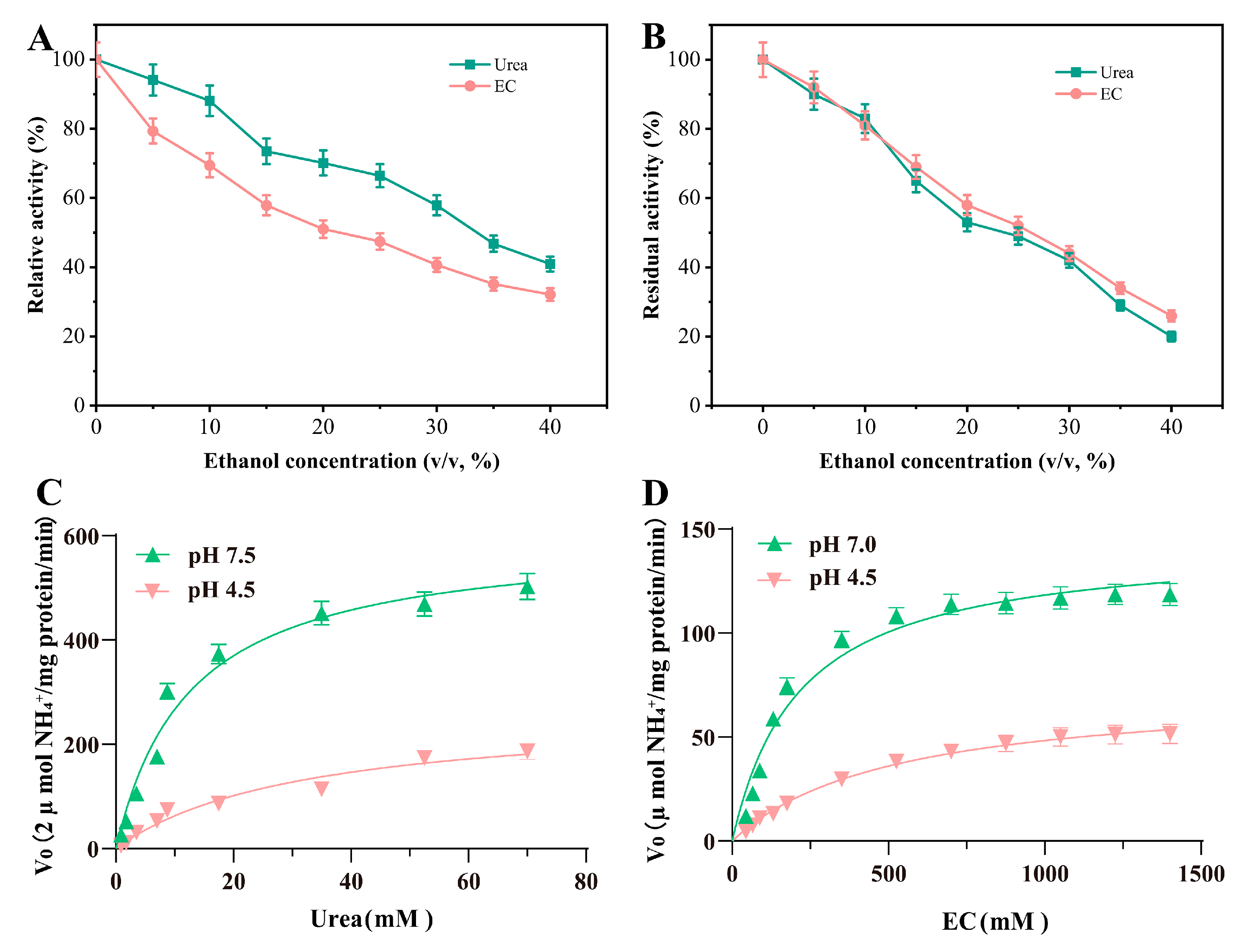
3.5. Effects of Ethanol Concentration on the Activity and Stability of Ps_Urease
3.6. Kinetic Parameters of Recombinant Ps_Urease
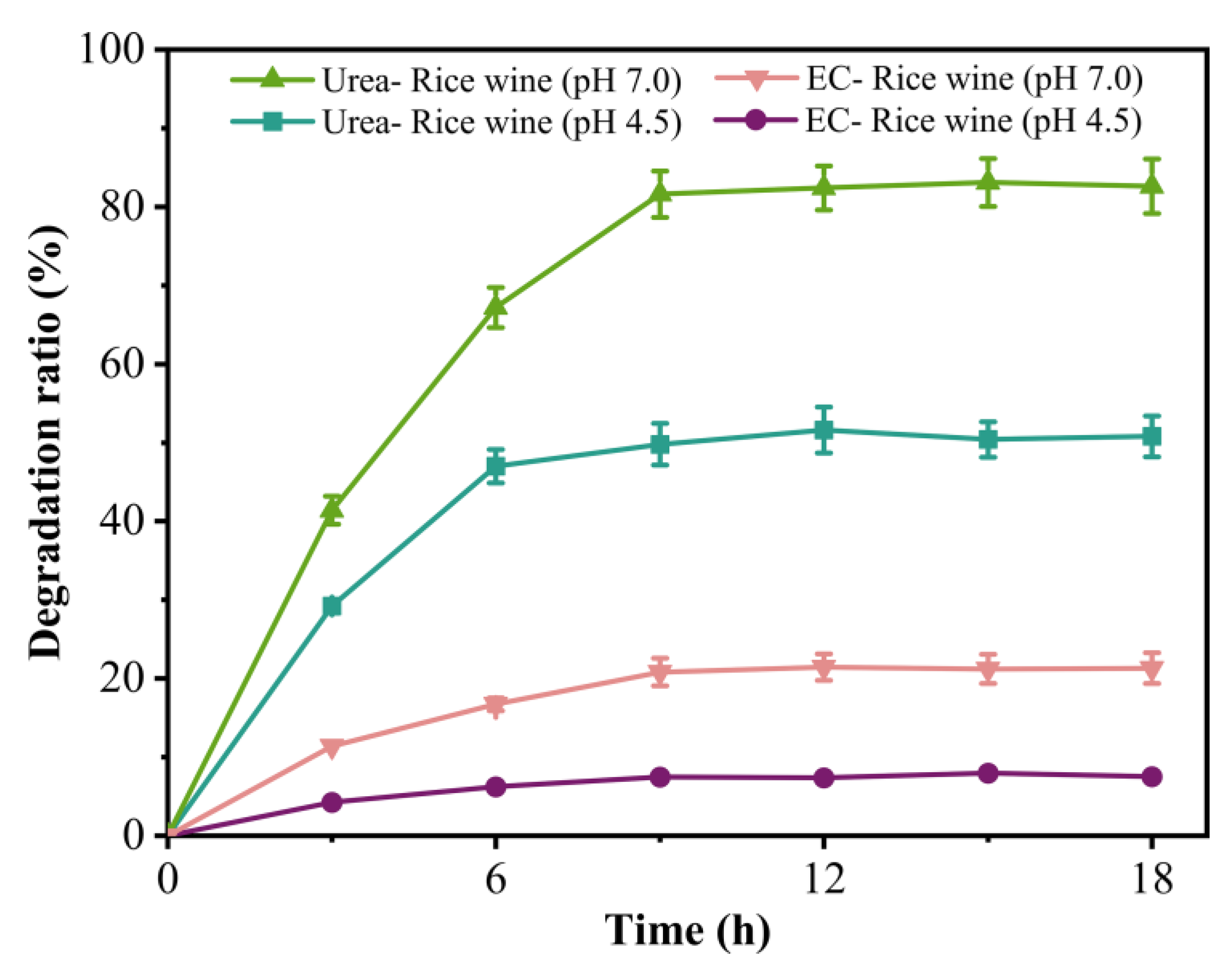
3.7. Evaluation of the Efficiency of Ps_Urease in Degrading Urea and EC from Rice Wine
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Chen, D.; Ren, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Shao, Y.; Zhao, Y.-F.; Wu, Y. Ethyl carbamate in alcoholic beverages from China: Levels, dietary intake, and risk assessment. Food Control 2017, 72, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowd, V.; Su, H.; Karlovsky, P.; Chen, W. Ethyl carbamate: An emerging food and environmental toxicant. Food Chem. 2018, 248, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, M.; Zhang, M.P. Ethyl carbamate in Chinese liquor (Baijiu): Presence, analysis, formation, and control. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 4383–4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachenmeier, D.W.; Lima, M.C.; Nóbrega, I.C.; Pereira, J.A.; Kerr-Corrêa, F.; Kanteres, F.; Rehm, J. Cancer risk assessment of ethyl carbamate in alcoholic beverages from Brazil with special consideration to the spirits cachaça and tiquira. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Yue, S.J.; Xu, D.Q.; Fu, R.J.; Han, J.Z.; Zhou, H.M.; Tang, Y.P. Research progress on flavor and quality of Chinese rice wine in the brewing process. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 32311–32330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Cai, C.; Shen, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Tan, Y.; Jiang, W.; Pan, X. Formation of ethyl carbamate and changes during fermentation and storage of yellow rice wine. Food Chem. 2014, 152, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, T.; Ji, Y.; Jiang, X.; Shi, X.; Wang, B. Origin, succession, and control of biotoxin in Wine. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 703391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Jia, W. Formation and hazard of ethyl carbamate and construction of genetically engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains in Huangjiu (Chinese grain wine). Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.; Lin, J.; Yang, L.; Wu, M. Expression, isolation, and identification of an ethanol-resistant ethyl carbamate-degrading amidase from Agrobacterium tumefaciens d(3). J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2021, 132, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaki, K. Features and application potential of microbial urethanases. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 3431–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Kang, Z.; Du, G. Advances in microbial enzymatic elimination of ethyl carbamate in Chinese rice wine. Chin. J. Biotech. 2019, 35, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.Y.; Kang, M.J.; Hwang, H.S.; Baek, K.R.; Seo, S.O. Reduction of ethyl carbamate in an alcoholic beverage by CRISPR/Cas9-based genome editing of the wild yeast. Foods 2022, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Yao, X.; Liang, Q.; Li, J.; Fang, F.; Du, G.; Kang, Z. Molecular engineering of Bacillus paralicheniformis acid urease to degrade urea and ethyl carbamate in model Chinese rice wine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 13011–13019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakimoto, S.; Sumino, Y.; Kawahara, K.; Yamazaki, E.; Nakatsui, I. Purification and characterization of acid urease from Lactobacillus fermentum. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1990, 32, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyagawa, K.; Sumida, M.; Nakao, M.; Harada, M.; Yamamoto, H.; Kusumi, T.; Yoshizawa, K.; Amachi, T.; Nakayama, T. Purification, characterization, and application of an acid urease from Arthrobacter mobilis. J. Biotechnol. 1999, 68, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Jin, X.; Fang, F.; Li, J.; Du, G.; Kang, Z. Food-grade expression of an iron-containing acid urease in Bacillus subtilis. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 293, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Kang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J.; Du, G. High-level expression and characterization of recombinant acid urease for enzymatic degradation of urea in rice wine. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Kang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Du, G.; Chen, J. Degradation of urea and ethyl carbamate in Chinese rice wine by recombinant acid urease. Chin. J. Biotech. 2016, 32, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, M.; Du, G.; Chen, J.; Kang, Z. A Bacillus paralicheniformis iron-containing urease reduces urea concentrations in rice wine. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e01258-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, N.; Tian, Y. Expression of an acid urease with urethanase activity in E. coli and analysis of urease gene. Mol. Biotechnol. 2017, 59, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhou, N.; Tian, Y. Characteristics of refold acid urease immobilized covalently by graphene oxide-chitosan composite beads. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2019, 127, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Fang, F. Improving applicability of urease from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens JP-21 by site-directed mutagenesis. Chin. J. Biotech. 2020, 36, 1640–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zhou, J.; Du, G.; Chen, J.; Fang, F. Identification of an urethanase from Lysinibacillus fusiformis for degrading ethyl carbamate in fermented foods. Food Biosci. 2020, 36, 100666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherburn, M.W. Phenol-hypochlorite reaction for determination of ammonia. Anal. Chem. 1967, 39, 971–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, S.; Tian, Y. Purification, properties, and application of a novel acid urease from Enterobacter sp. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 160, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zou, H.; Fu, J.; Zhou, J.; Du, G.; Chen, J. Metabolic engineering of the regulators in nitrogen catabolite repression to reduce the production of ethyl carbamate in a model rice wine system. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, X.; Gouet, P. Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W320–W324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappaun, K.; Piovesan, A.R.; Carlini, C.R.; Ligabue-Braun, R. Ureases: Historical aspects, catalytic, and non-catalytic properties—A review. Adv. Res. 2018, 13, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proshlyakov, D.A.; Farrugia, M.A.; Proshlyakov, Y.D.; Hausinger, R.P. Iron-containing ureases. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 448, 214190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, E.L.; Flugga, N.; Boer, J.L.; Mulrooney, S.B.; Hausinger, R.P. Interplay of metal ions and urease. Metallomics 2009, 1, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, E.L.; Tronrud, D.E.; Taber, S.R.; Karplus, P.A.; Hausinger, R.P. Iron-containing urease in a pathogenic bacterium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13095–13099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroney, M.J.; Ciurli, S. Nonredox nickel enzymes. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 4206–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, F.; Qian, S.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, S.; Wang, T.; Tian, S. High salt-resistant urethanase degrades ethyl carbamate in soy sauce. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 21266–21275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notin, P.; Rollins, N.; Gal, Y.; Sander, C.; Marks, D. Machine learning for functional protein design. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kortemme, T. De novo protein design-From new structures to programmable functions. Cell 2024, 187, 526–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.T.; Mitchell, D.A.; van der Donk, W.A. Genome mining for new enzyme chemistry. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 4536–4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Substrate | pH | Km (mM) | Vmax (µmol·mg−1·min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| EC | 4.5 | 515.6 ± 26.8 | 33.9 ± 1.8 |
| 7.0 | 214.7 ± 10.2 | 71.8 ± 2.7 | |
| Urea | 4.5 | 32.0 ± 1.4 | 263.6 ± 12.1 |
| 7.5 | 12.5 ± 0.5 | 600.2 ± 25.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Li, D.; Zhu, S.; Guo, S.; Ding, J.; Wu, C.; Liu, Q. Characterization of Urease from Providencia sp. LBBE and Its Application in Degrading Urea and Ethyl Carbamate in Rice Wine. Fermentation 2024, 10, 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10120653
Wang H, Li D, Zhu S, Guo S, Ding J, Wu C, Liu Q. Characterization of Urease from Providencia sp. LBBE and Its Application in Degrading Urea and Ethyl Carbamate in Rice Wine. Fermentation. 2024; 10(12):653. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10120653
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Han, Dandan Li, Sibao Zhu, Shuxian Guo, Jiahong Ding, Chuanchao Wu, and Qingtao Liu. 2024. "Characterization of Urease from Providencia sp. LBBE and Its Application in Degrading Urea and Ethyl Carbamate in Rice Wine" Fermentation 10, no. 12: 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10120653
APA StyleWang, H., Li, D., Zhu, S., Guo, S., Ding, J., Wu, C., & Liu, Q. (2024). Characterization of Urease from Providencia sp. LBBE and Its Application in Degrading Urea and Ethyl Carbamate in Rice Wine. Fermentation, 10(12), 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10120653






