Silage Making of Napier Grass and Sugarcane Top at Different Proportions: Evolution of Natural Fermentation Characteristics, Chemical Composition, and Microbiological Profile
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ensiling Materials and Silage Preparation
2.2. Chemical Analysis
2.3. Fermentation Analysis
2.4. Microbial Populations and Bacterial Community Analyses
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Compositions
3.2. Fermentation Quality
3.3. Microbial Populations
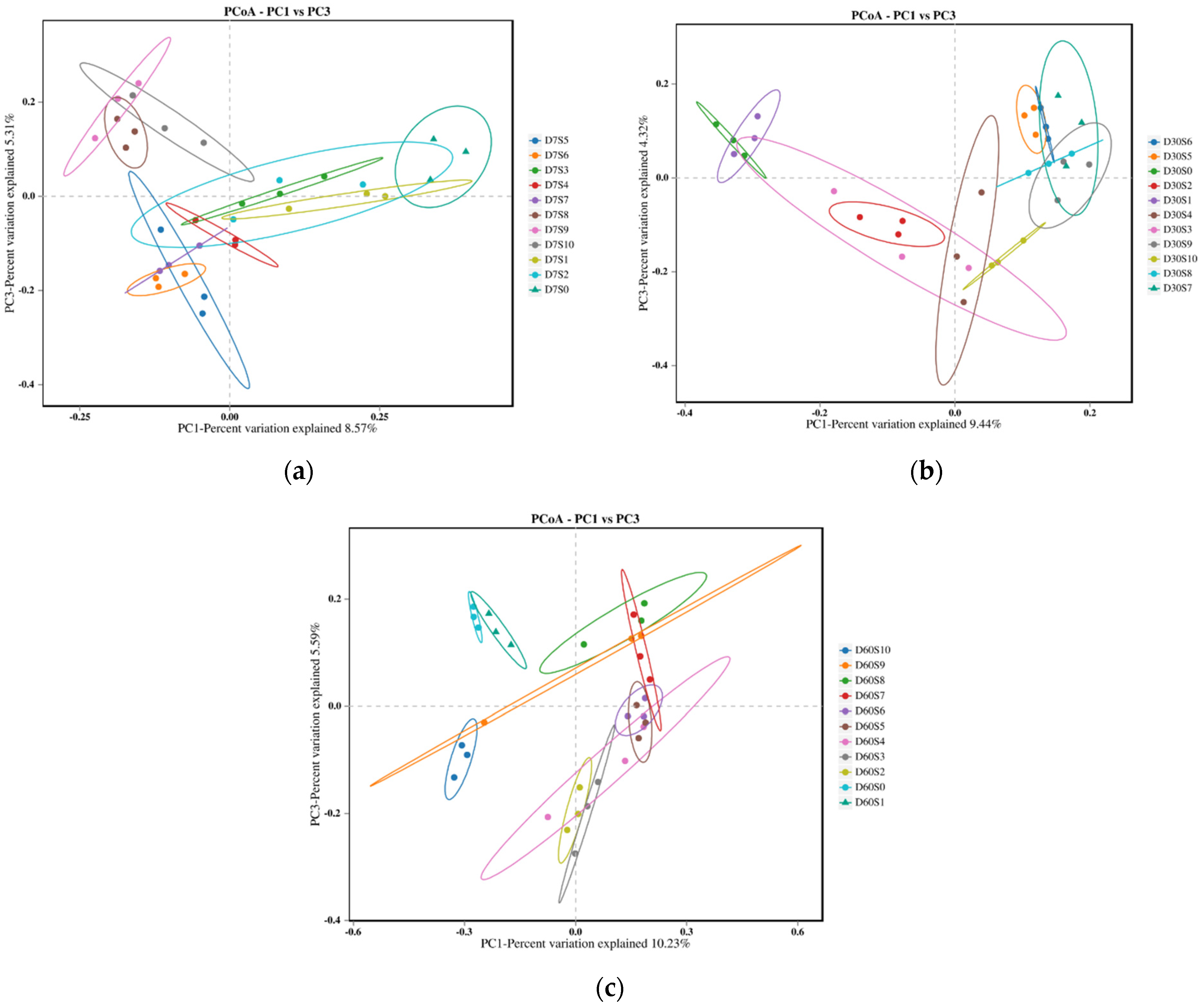
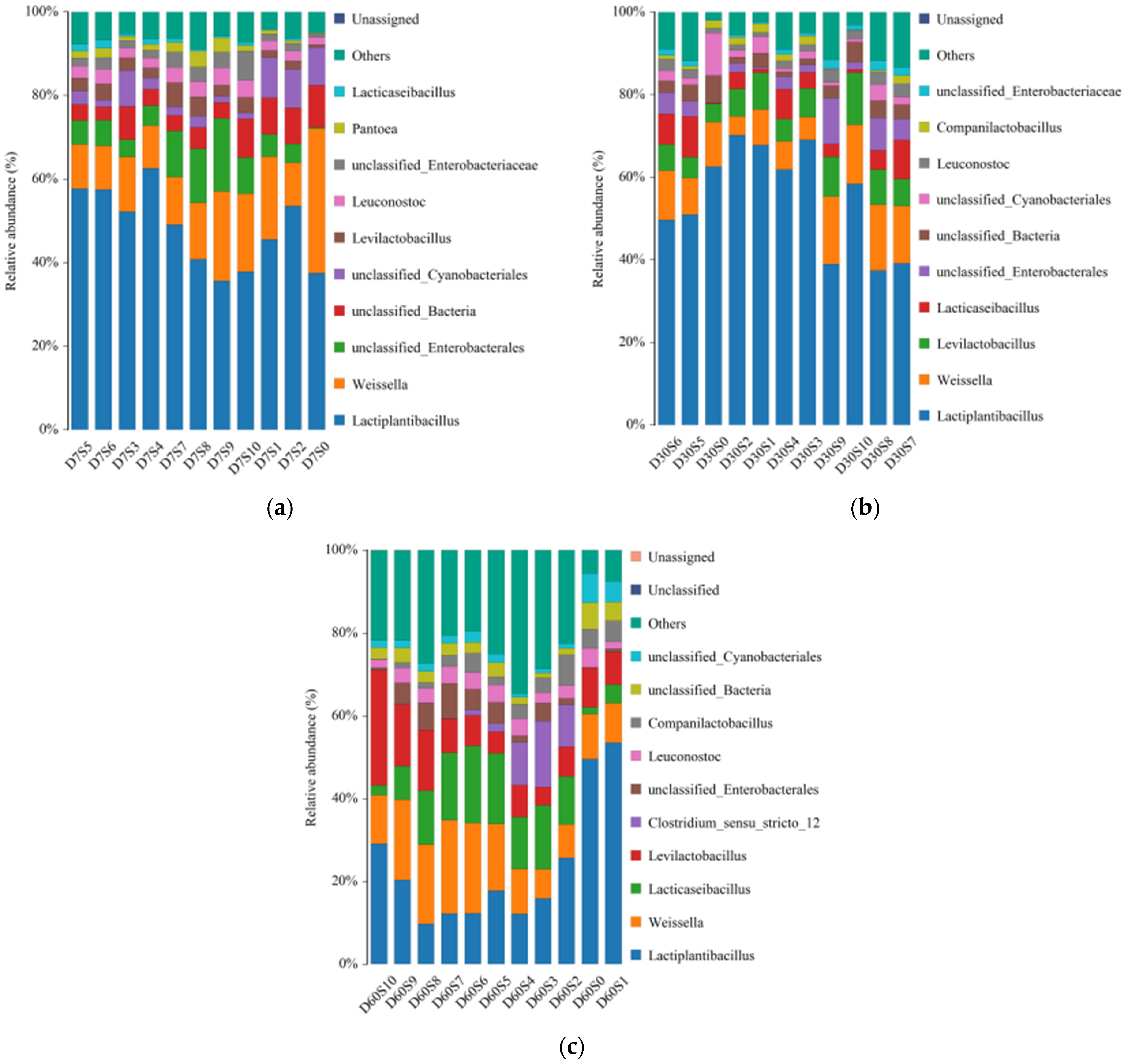
3.4. Bacterial Community
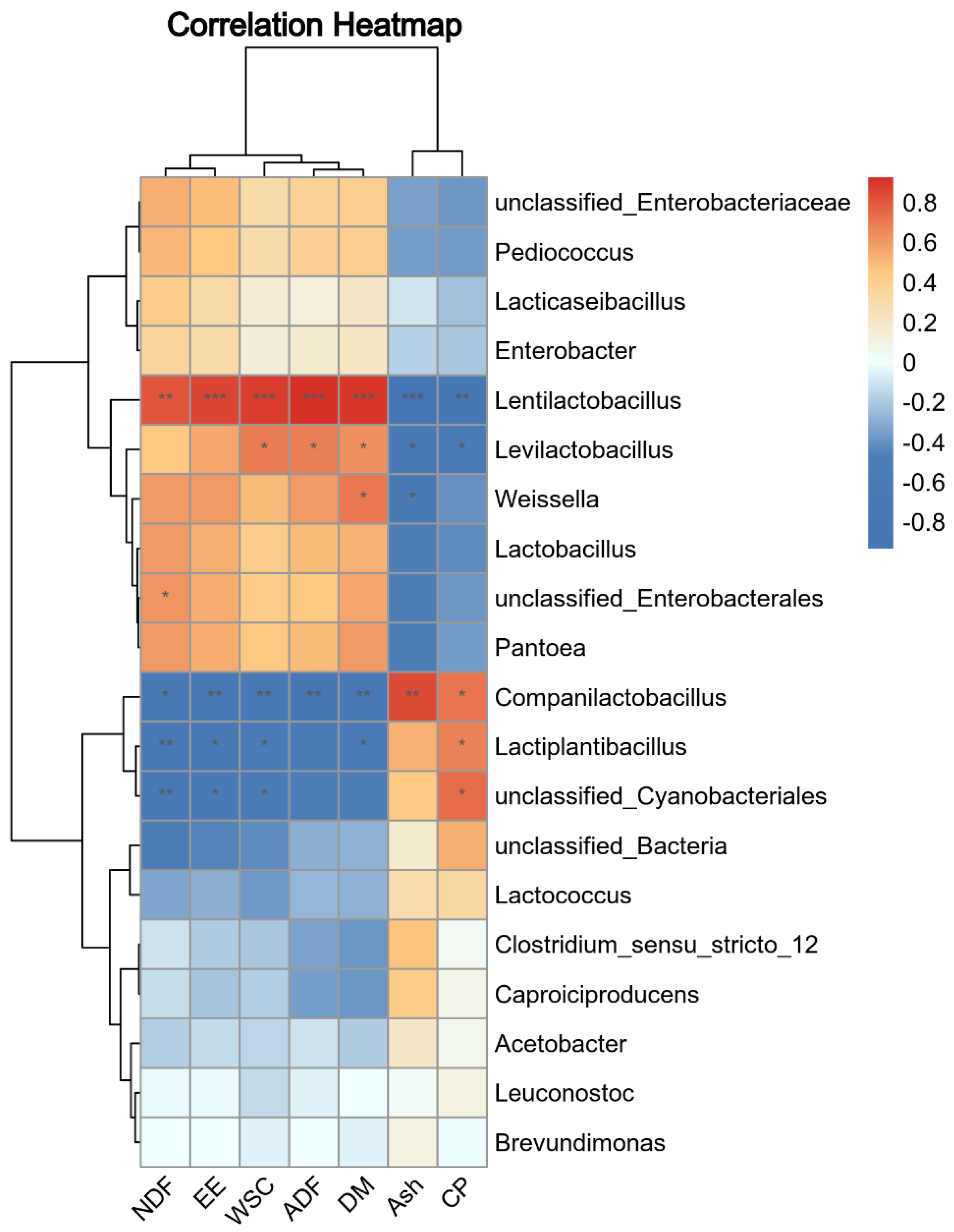
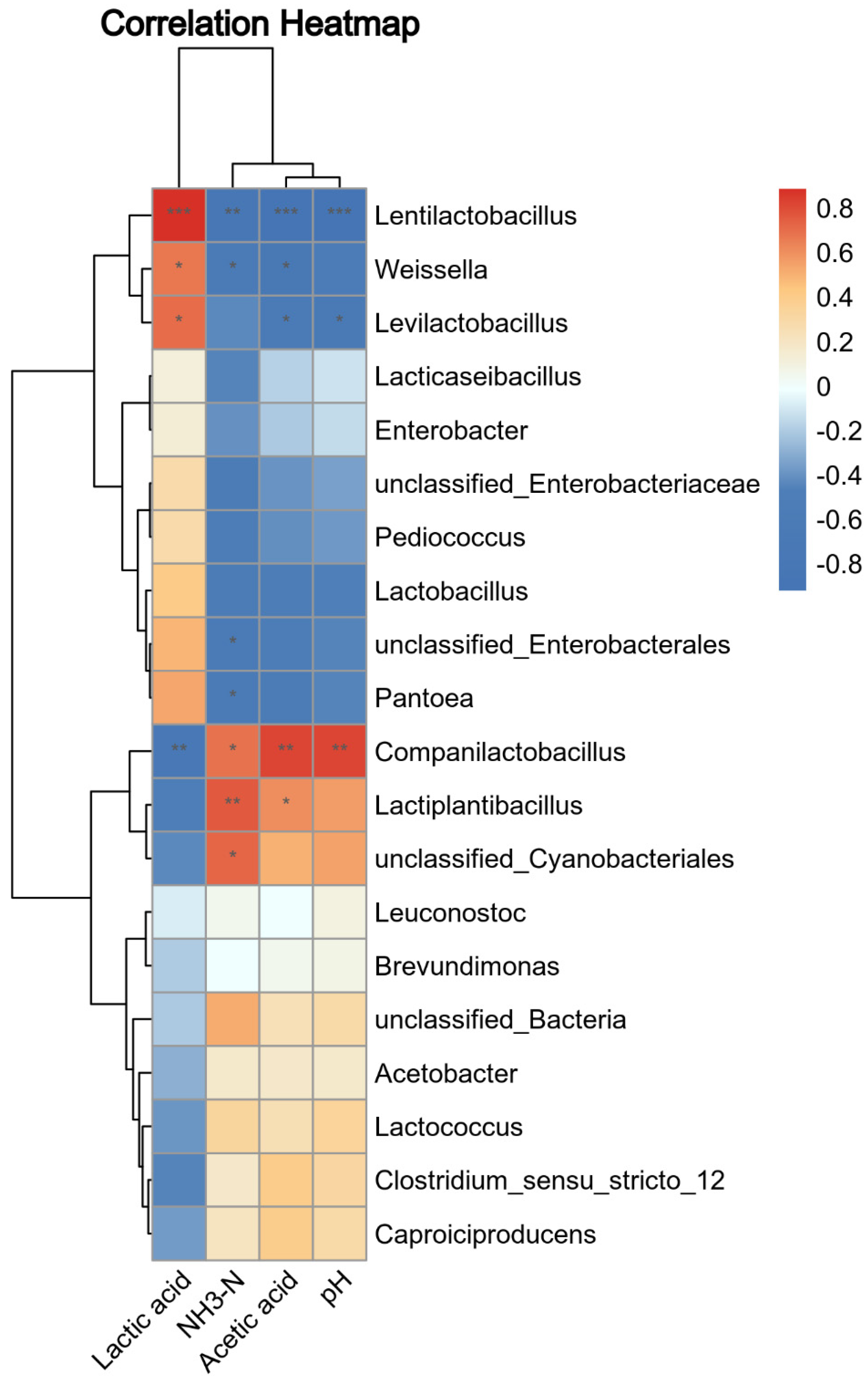
3.5. Association among Silage Bacteria, Chemical Composition, and Fermentation Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thorat, B.S.; Pawar, G.R.; Sushir, K.V.; Talekar, S.D.; Repale, J.M.; Kadlag, A.D. Sugarcane: A Climate Resilient Devine Crop. Int. J. Environ. Clim. Chang. 2024, 14, 555–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Xu, D.; Li, F.; Bai, J.; Su, R. Current approaches on the roles of lactic acid bacteria in crop silage. Microb. Biotechnol. 2022, 16, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, J.L.P.; Jacovaci, F.A.; Junges, D.; Santos, M.C.; Lima, J.R.; Anjos, I.A.; Landell, M.G.A.; Huhtanen, P.; Nussio, L.G. Fibre digestibility and its relationships with chemical and morphological traits in thirty-two sugarcane varieties. Grass Forage Sci. 2016, 72, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. NBS: China Statistical Yearbook, 12th, ed.; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Zi, X.; Yang, H.; Ji, F.; Tang, J.; Lv, R.; Zhou, H. Effects of king grass and sugarcane top in the absence or presence of exogenous enzymes on the growth performance and rumen microbiota diversity of goats. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, F.; Eichler, P.; Machado, G.; De Mattia, J.; De Souza, G. By-Products of the Sugarcane Industry. In Sugarcane Biorefinery, Technology and Perspectives; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 21–48. [Google Scholar]
- Salinas-Chavira, J.; Almaguer, L.J.; Aguilera-Aceves, C.E.; Zinn, R.A.; Mellado, M.; Ruiz-Barrera, O. Effect of substitution of sorghum stover with sugarcane top silage on ruminal dry matter degradability of diets and growth performance of feedlot hair lambs. Small Rumin. Res. 2013, 112, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Peng, L.; Li, M.; Guo, Y.; Liang, X.; Peng, K.; Yang, C. Effects of mixed sugarcane tops and napiergrass silages on fermentative quality, nutritional value, and milk yield in water buffaloes. Anim. Sci. J. 2023, 94, e13824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraro, G.B.; de Almeida Carvalho-Estrada, P.; de Oliveira Pasetti, M.H.; Santos, M.C.; Nussio, L.G. Bacterial dynamics of sugarcane silage in the tropics. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 5979–5991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Garcia, S.C.; Islam, M.A.; Bashar, M.K.; Roy, A.; Roy, B.K.; Sarker, N.R.; Clark, C.E.F. Ruminant Production from Napier Grass (Pennisetum purpureum Schum): A Review. Animals 2024, 14, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazar, M.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Ali Kaka, N.; Shao, T. Effects of various epiphytic microbiota inoculation on the fermentation quality and microbial community dynamics during the ensiling of sterile Napier grass. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 130, 1466–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wu, H.; Li, L.; He, J.; Hu, Z.; Yang, X.; Xie, X. Effects of applying cellulase and starch on the fermentation characteristics and microbial communities of Napier grass (Pennisetum purpureum Schum.) silage. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 1301–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tang, X.; Zhao, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, S.; Shao, T. Improvement of fermentation quality and cellulose convertibility of Napier grass silage by inoculation of cellulolytic bacteria from Tibetan yak (Bos grunniens). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 130, 1857–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, T.R.; da Silva Filho, J.R.V.; Pereira, G.A.; Meira, T.M.; de Sá, M.K.N.; Gois, G.C.; de Souza Silva, C.; Campos, F.S.; Yamamoto, S.M.; de Araújo, G.G.L. Potential use of vitiviniculture waste in mixed cactus pear silages with elephant grass in lamb diet. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2024, 307, 115824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zheng, M.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, W. Improving the quality of Napier grass silage with pyroligneous acid: Fermentation, aerobic stability, and microbial communities. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1034198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Guerra, N.A.; Gonzalez-Ronquillo, M.; Anderson, R.C.; Hume, M.E.; Ruiz-Albarrán, M.; Bautista-Martínez, Y.; Zúñiga-Serrano, A.; Nájera-Pedraza, O.G.; Salinas-Chavira, J. Improvements in fermentation and nutritive quality of elephant grass [Cenchrus purpureus (Schumach.) Morrone] silages: A review. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2024, 56, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ran, Q.; Jia, Z.; Shuai, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Guan, H. Effect of different dry matter content on fermentation characteristics and nutritional quality of Napier grass silage with novel lactic acid bacteria strains. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 76, ovad018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaipolsaen, N.; Sangsritavong, S.; Uengwetwanit, T.; Angthong, P.; Plengvidhya, V.; Rungrassamee, W.; Yammuenart, S. Comparison of the Effects of Microbial Inoculants on Fermentation Quality and Microbiota in Napier Grass (Pennisetum purpureum) and Corn (Zea mays L.) Silage. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 784535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitiku, A.A.; Andeta, A.F.; Borremans, A.; Lievens, B.; Bossaert, S.; Crauwels, S.; Aernouts, B.; Kechero, Y.; Van Campenhout, L. Silage making of maize stover and banana pseudostem under South Ethiopian conditions: Evolution of pH, dry matter and microbiological profile. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 1477–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Ding, Z.; Ke, W.; Xu, D.; Wang, M.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Guo, X. Different lactic acid bacteria and their combinations regulated the fermentation process of ensiled alfalfa: Ensiling characteristics, dynamics of bacterial community and their functional shifts. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.J.; Chaudhry, A.S.; Osman, A.; Shi, C.Q.; Edwards, G.R.; Dewhurst, R.J.; Cheng, L. Associative effects of ensiling mixtures of sweet sorghum and alfalfa on nutritive value, fermentation and methane characteristics. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2015, 206, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Feng, Y.; Liu, T.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Fu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Peng, Z. Effects of different simulated seasonal temperatures on the fermentation characteristics and microbial community diversities of the maize straw and cabbage waste co-ensiling system. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Ahmadi, F.; Kim, Y.I.; Oh, Y.K.; Kwak, W.S. Co-ensiling garlic stalk with citrus pulp improves the fermentation quality and feed-nutritional value. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 33, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, S.U.; Hjort-Gregersen, K.; Vazifehkhoran, A.H.; Triolo, J.M. Co-ensiling of straw with sugar beet leaves increases the methane yield from straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillion, M.L.; Moscoviz, R.; Trably, E.; Leblanc, Y.; Bernet, N.; Torrijos, M.; Escudié, R. Co-ensiling as a new technique for long-term storage of agro-industrial waste with low sugar content prior to anaerobic digestion. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, G.; Zhang, G.; Shi, J.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Z.; Liu, X.; Yuan, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, B. Keystone Taxa lactiplantibacillus and Lacticaseibacillus Directly Improve the Ensiling Performance and Microflora Profile in Co-Ensiling Cabbage Byproduct and Rice Straw. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Li, P.; Xiao, B.; Yang, F.; Li, D.; Ge, G.; Jia, Y.; Bai, S. Effects of LAB inoculant and cellulase on the fermentation quality and chemical composition of forage soybean silage prepared with corn stover. Grassl. Sci. 2021, 67, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Gou, W.; Cheng, Q.; Bai, S.; Cai, Y. Silage fermentation and bacterial community of bur clover, annual ryegrass and their mixtures prepared with microbial inoculant and chemical additive. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2019, 247, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wang, N.; Rinne, M.; Ke, W.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Da, M.; Bai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Guo, X. The bacterial community and metabolome dynamics and their interactions modulate fermentation process of whole crop corn silage prepared with or without inoculants. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 14, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC: Official Methods of Analysis. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 15th ed.; AOAC: Arlington, VA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for Dietary Fiber, Neutral Detergent Fiber, and Nonstarch Polysaccharides in Relation to Animal Nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udén, P. In vitro studies on microbial efficiency from two cuts of ryegrass (Lolium perenne, cv. Aberdart) with different proportions of sugars and protein. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2006, 126, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y. Analysis Method for Silage. In Japanese Society of Grassland Science; Field and Laboratory Methods for Grassland Science. Tosho Printing Co., Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 2004; pp. 279–282. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Xie, F.; Guo, Y.; Liang, X.; Peng, L.; Li, M.; Tang, Z.; Peng, K.; Yang, C. Fermentation quality, nutritive value and in vitro ruminal digestion of Napier grass, sugarcane top and their mixed silages prepared using lactic acid bacteria and formic acid. Grassl. Sci. 2023, 69, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, G.A.; Kang, J.H. Automated Simultaneous Determination of Ammonia and Total Amino Acids in Ruminal Fluid and In Vitro Media. J. Dairy Sci. 1980, 63, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Hirakubo, T.; Fukui, H.; Matsuyama, H. Fermentation characteristics and microorganism composition of total mixed ration silage with local food by-products in different seasons. Anim. Sci. J. 2011, 82, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borreani, G.I.O.R.G.I.O.; Tabacco, E.R.N.E.S.T.O.; Schmidt, R.J.; Holmes, B.J.; Muck, R.A. Factors affecting dry matter and quality losses in silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3952–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Xu, Y.; Pan, X.; Shao, T. Effect of Sorbic Acid, Ethanol, Molasses, Previously Fermented Juice and Combined Additives on Ensiling Characteristics and Nutritive Value of Napiergrass (Pennisetum purpureum) Silage. Fermentation 2022, 8, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Chen, S.; Zhao, J.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Sun, F.; Shao, T. Fermentation and aerobic stability of Napier grass silage treated with different levels of citric acid residue. Grassl. Sci. 2021, 67, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Du, Z.; Yamasaki, S.; Nguluve, D.; Tinga, B.; Macome, F.; Oya, T. Influence of microbial additive on microbial populations, ensiling characteristics, and spoilage loss of delayed sealing silage of Napier grass. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2020, 33, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugabe, W.; Shao, T.; Li, J.; Dong, Z.; Yuan, X. Effect of hexanoic acid, Lactobacillus plantarum and their combination on the aerobic stability of napier grass silage. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureenok, S.; Yuangklang, C.; Vasupen, K.; Schonewille, J.T.; Kawamoto, Y. The effects of additives in napier grass silages on chemical composition, feed intake, nutrient digestibility and rumen fermentation. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 25, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; He, L.; Xing, Y.; Zhou, W.; Yang, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Effects of mixing Neolamarckia cadamba leaves on fermentation quality, microbial community of high moisture alfalfa and stylo silage. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bao, J.; Zhao, M.; Si, Q.; Sun, P.; Ge, G.; Jia, Y. Effects of Different Types of LAB on Dynamic Fermentation Quality and Microbial Community of Native Grass Silage during Anaerobic Fermentation and Aerobic Exposure. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatlı Seven, P.; Yıldırım, E.N.; Seven, İ.; Kaya, C.A.; İflazoğlu Mutlu, S. An evaluation of the effectiveness of sumac and molasses as additives for alfalfa silage: Influence on nutrient composition, in vitro degradability and fermentation quality. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2024, 108, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Lee, K.D.; Choi, K.C. Role of LAB in silage fermentation: Effect on nutritional quality and organic acid production—An overview. AIMS Agric. Food 2021, 6, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broberg, A.; Jacobsson, K.; Ström, K.; Schnürer, J. Metabolite profiles of lactic acid bacteria in grass silage. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5547–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guan, L.; Fang, J.; Cai, Y.; Cao, Y. Fermentation characteristics and in vitro ruminal digestion of yacon residue silage with lactic acid bacteria inoculant or beet pulp. Rev. Bras. Zootec. 2019, 48, e20180152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Yoshida, N.; Tohno, M.; Uegaki, R.; Nonaka, K.; Terada, F. Effect of lactic acid bacteria inoculant and beet pulp addition on fermentation characteristics and in vitro ruminal digestion of vegetable residue silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 3902–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, B.; Su, R.; Pan, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhou, G.; Tao, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhong, J. Assessing the fermentation quality and microbial community of the mixed silage of forage soybean with crop corn or sorghum. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Li, L.; Jiang, J.; Sun, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Feng, X.; Guo, Y. Effects of fermentative and non-fermentative additives on silage quality and anaerobic digestion performance of Pennisetum purpureum. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moura Zanine, A.; de Sene, O.A.; de Jesus Ferreira, D.; Parente, H.N.; de Oliveira Maia Parente, M.; Pinho, R.M.A.; Santos, E.M.; Nascimento, T.V.C.; de Oliveira Lima, A.G.V.; Perazzo, A.F.; et al. Fermentative profile, losses and chemical composition of silage soybean genotypes amended with sugarcane levels. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Liao, C.; Huang, X.; Chen, C.; Xu, D.; Chen, C. Epiphytic microbiota source stimulates the fermentation profile and bacterial community of alfalfa-corn mixed silage. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1247254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharechahi, J.; Kharazian, Z.A.; Sarikhan, S.; Jouzani, G.S.; Aghdasi, M.; Hosseini Salekdeh, G. The dynamics of the bacterial communities developed in maize silage. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1663–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshri, J.; Chen, Y.; Pinto, R.; Kroupitski, Y.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Sela Saldinger, S. Bacterial Dynamics of Wheat Silage. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mpanza, T.D.E.; Mani, S. Effects of Vachellia mearnsii Tannin Extract as an Additive on Fermentation Quality, Aerobic Stability, and Microbial Modulation of Maize Silage. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margalho, L.P.; Jorge, G.P.; Noleto, D.A.; Silva, C.E.; Abreu, J.S.; Piran, M.V.; Brocchi, M.; Sant’Ana, A.S. Biopreservation and probiotic potential of a large set of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Brazilian artisanal cheeses: From screening to in product approach. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 242, 126622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonda, H.; Nikodinoska, I.; Le Cocq, K.; Moran, C.A. Efficacy of six lactic acid bacteria strains as silage inoculants in forages with different dry matter and water-soluble carbohydrate content. Grass Forage Sci. 2023, 78, 636–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xie, H.; Zeng, F.; Luo, X.; Peng, L.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, C. An Assessment on the Fermentation Quality and Bacterial Community of Corn Straw Silagewith Pineapple Residue. Fermentation 2024, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Item | DM | CP | EE | Ash | NDF | ADF | WSC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (% DM) | ||||||
| NG | 16.71 | 12.89 | 1.32 | 11.91 | 69.58 | 36.15 | 3.46 |
| ST | 26.11 | 7.33 | 2.59 | 6.79 | 74.15 | 42.98 | 11.66 |
| Item | DM | CP | EE | Ash | NDF | ADF | WSC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (% DM) | ||||||
| S0 † | 11.02 j | 9.45 a | 1.08 g | 10.65 a | 66.81 e | 34.15 g | 1.51 f |
| S1 | 12.42 i | 9.34 a | 1.20 g | 10.30 ab | 67.83 e | 34.81 fg | 2.02 f |
| S2 | 13.21 h | 8.21 b | 1.45 f | 10.21 ab | 69.67 d | 35.42 f | 3.67 e |
| S3 | 14.74 g | 7.86 bc | 1.63 ef | 9.87 b | 70.16 cd | 36.37 e | 4.46 de |
| S4 | 16.54 f | 7.80 bc | 1.71 de | 9.20 c | 70.30 cd | 37.80 d | 4.54 de |
| S5 | 17.34 e | 7.74 bc | 1.79 cde | 8.45 d | 70.78 bcd | 38.02 d | 4.73 cde |
| S6 | 19.53 d | 7.64 bc | 1.88 bcd | 8.37 d | 71.12 abc | 38.39 dc | 5.38 cd |
| S7 | 20.90 c | 7.57 c | 1.94 bcd | 7.38 e | 71.75 ab | 39.06 c | 5.98 bc |
| S8 | 21.85 b | 7.47 cd | 1.99 abc | 6.91 e | 71.86 ab | 40.19 b | 6.71 b |
| S9 | 22.14 b | 6.98 d | 2.09 ab | 6.78 ef | 72.17 a | 40.90 ab | 7.14 b |
| S10 | 23.24 a | 6.27 e | 2.21 a | 6.22 f | 72.31 a | 41.75 a | 8.65 a |
| SEM | 0.2438 | 0.1896 | 0.0771 | 0.2122 | 0.4031 | 0.3064 | 0.4257 |
| p-Value | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Item | pH | Lactic Acid | Acetic Acid | Propionic Acid | Butyric Acid | NH3-N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g/kg DM) | ||||||
| Ensiling days mean (ED) | ||||||
| 1 | 6.23 a | 2.73 f | 0.70 f | ND | ND | 0.16 g |
| 3 | 6.01 b | 3.18 f | 0.86 ef | ND | ND | 0.18 f |
| 5 | 5.88 c | 7.59 e | 1.28 e | ND | ND | 0.24 e |
| 7 | 5.15 d | 8.54 d | 3.70 d | ND | ND | 0.35 d |
| 15 | 4.69 e | 12.41 c | 11.50 c | ND | 0.62 b | 0.40 c |
| 30 | 4.30 f | 25.69 b | 15.45 b | ND | 0.83 a | 0.48 b |
| 60 | 4.19 g | 27.54 a | 18.78 a | ND | 0.85 a | 0.53 a |
| Mixture ratios mean (MR) | ||||||
| S0 † | 5.62 a | 7.56 i | 12.25 a | ND | 3.61 a | 0.45 a |
| S1 | 5.56 b | 8.87 h | 11.48 ab | ND | ND | 0.40 b |
| S2 | 5.47 c | 10.08 g | 10.81 b | ND | ND | 0.38 b |
| S3 | 5.38 d | 10.89 fg | 9.41 c | ND | ND | 0.36 c |
| S4 | 5.26 e | 11.35 f | 8.00 d | ND | ND | 0.34 cd |
| S5 | 5.19 f | 12.53 e | 7.04 e | ND | ND | 0.32 de |
| S6 | 5.09 g | 13.78 d | 6.00 f | ND | ND | 0.30 ef |
| S7 | 5.03 h | 14.40 cd | 5.09 g | ND | ND | 0.29 fg |
| S8 | 4.97 i | 15.15 bc | 4.37 gh | ND | ND | 0.28 fg |
| S9 | 4.88 j | 15.95 b | 3.93 h | ND | ND | 0.27 gh |
| S10 | 4.83 k | 17.19 a | 3.73 h | ND | ND | 0.26 h |
| SEM | 0.0277 | 0.5742 | 0.4516 | - | 0.0362 | 0.013 |
| Significance of main effects and interactions | ||||||
| ED | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | - | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| MR | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | - | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| ED × MR | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | - | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Item | Lactic Acid Bacteria | Yeasts | Molds |
|---|---|---|---|
| log cfu/g FM | |||
| Ensiling days mean (ED) | |||
| 1 | 4.41 e | 4.35 e | ND |
| 3 | 4.47 d | 4.38 e | ND |
| 5 | 4.49 d | 4.56 c | ND |
| 7 | 4.61 c | 4.60 b | ND |
| 15 | 4.99 b | 4.87 a | ND |
| 30 | 6.51 a | 4.43 d | ND |
| 60 | 6.52 a | 4.45 d | ND |
| Mixture ratios mean (MR) | |||
| S0 † | 4.95 e | 4.52 | ND |
| S1 | 5.08 d | 4.52 | ND |
| S2 | 5.09 d | 4.52 | ND |
| S3 | 5.13 bcd | 4.54 | ND |
| S4 | 5.18 abc | 4.52 | ND |
| S5 | 5.15 abcd | 4.54 | ND |
| S6 | 5.22 a | 4.5 | ND |
| S7 | 5.23 a | 4.5 | ND |
| S8 | 5.22 a | 4.51 | ND |
| S9 | 5.21 ab | 4.52 | ND |
| S10 | 5.12 cd | 4.51 | ND |
| SEM | 0.0741 | 0.0391 | - |
| Significance of main effects and interactions | |||
| ED | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | - |
| MR | <0.0001 | 0.6832 | - |
| ED × MR | <0.0001 | 0.2111 | - |
| Ensiling Days | Mixture Rations | ACE | Chao1 | Simpson | Shannon | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | S0 † | 193.89 ab | 204.58 a | 0.78 abc | 2.95 d | 0.9998 |
| S1 | 195.23 ab | 202.68 a | 0.78 abc | 3.30 cd | 0.9998 | |
| S2 | 205.91 a | 219.40 a | 0.75 bcd | 3.34 bcd | 0.9998 | |
| S3 | 154.62 ab | 163.00 ab | 0.75 bcd | 3.25 d | 0.9999 | |
| S4 | 133.30 b | 137.25 b | 0.68 d | 3.09 d | 0.9999 | |
| S5 | 197.71 ab | 203.94 a | 0.73 cd | 3.38 bcd | 0.9999 | |
| S6 | 171.89 ab | 175.29 ab | 0.72 cd | 3.34 bcd | 0.9998 | |
| S7 | 188.47 ab | 190.35 ab | 0.80 abc | 3.77 ab | 0.9999 | |
| S8 | 169.81 ab | 177.46 ab | 0.84 a | 3.86 a | 0.9998 | |
| S9 | 152.70 ab | 156.42 ab | 0.84 a | 3.75 ab | 0.9999 | |
| S10 | 187.04 ab | 200.50 a | 0.83 ab | 3.73 abc | 0.9998 | |
| p-Value | 0.2424 | 0.1208 | 0.0034 | 0.0009 | 0.1526 | |
| 30 | S0 | 126.04 c | 133.30 d | 0.67 c | 2.54 d | 0.9998 |
| S1 | 129.69 c | 133.56 d | 0.63 c | 2.55 d | 0.9999 | |
| S2 | 154.05 bc | 158.66 bcd | 0.60 c | 2.67 d | 0.9998 | |
| S3 | 151.74 bc | 153.76 cd | 0.62 c | 2.76 cd | 0.9999 | |
| S4 | 171.84 ab | 176.57 abcd | 0.69 bc | 3.23 bc | 0.9998 | |
| S5 | 191.17 ab | 195.10 abc | 0.77 ab | 3.67 ab | 0.9998 | |
| S6 | 187.60 ab | 195.98 abc | 0.78 ab | 3.69 ab | 0.9998 | |
| S7 | 197.78 a | 202.49 ab | 0.85 a | 4.12 a | 0.9997 | |
| S8 | 205.04 a | 216.09 a | 0.85 a | 4.07 a | 0.9998 | |
| S9 | 179.04 ab | 189.14 abc | 0.85 a | 4.03 a | 0.9998 | |
| S10 | 154.35 bc | 157.39 bcd | 0.69 bc | 2.81 cd | 0.9998 | |
| p-Value | 0.0018 | 0.0021 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.1633 | |
| 60 | S0 | 178.94 b | 184.60 b | 0.78 c | 3.32 c | 0.9998 |
| S1 | 186.81 b | 196.33 b | 0.75 c | 3.42 c | 0.9998 | |
| S2 | 204.11 b | 207.90 b | 0.91 ab | 4.73 b | 0.9999 | |
| S3 | 211.96 b | 215.75 b | 0.93 ab | 4.89 ab | 0.9998 | |
| S4 | 234.16 b | 234.45 b | 0.95 a | 5.37 a | 0.9999 | |
| S5 | 178.18 b | 182.56 b | 0.94 a | 5.05 ab | 0.9999 | |
| S6 | 202.07 b | 202.96 b | 0.93 ab | 5.03 ab | 0.9999 | |
| S7 | 190.13 b | 194.28 b | 0.93 ab | 4.98 ab | 0.9999 | |
| S8 | 209.27 b | 212.53 b | 0.94 a | 5.18 ab | 0.9999 | |
| S9 | 318.48 b | 322.32 b | 0.91 ab | 4.92 ab | 0.9999 | |
| S10 | 667.09 a | 677.17 a | 0.89 b | 4.91 ab | 0.9999 | |
| p-Value | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.3009 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, H.; Zeng, F.; Luo, X.; Li, Z.; Pan, Y.; Guo, Y.; Peng, L.; Liang, L.; Li, J.; Liang, Y.; et al. Silage Making of Napier Grass and Sugarcane Top at Different Proportions: Evolution of Natural Fermentation Characteristics, Chemical Composition, and Microbiological Profile. Fermentation 2024, 10, 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10100525
Xie H, Zeng F, Luo X, Li Z, Pan Y, Guo Y, Peng L, Liang L, Li J, Liang Y, et al. Silage Making of Napier Grass and Sugarcane Top at Different Proportions: Evolution of Natural Fermentation Characteristics, Chemical Composition, and Microbiological Profile. Fermentation. 2024; 10(10):525. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10100525
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Huade, Fanquan Zeng, Xianqing Luo, Zhipei Li, Yuhong Pan, Yanxia Guo, Lijuan Peng, Li Liang, Jingzhen Li, Yuchen Liang, and et al. 2024. "Silage Making of Napier Grass and Sugarcane Top at Different Proportions: Evolution of Natural Fermentation Characteristics, Chemical Composition, and Microbiological Profile" Fermentation 10, no. 10: 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10100525
APA StyleXie, H., Zeng, F., Luo, X., Li, Z., Pan, Y., Guo, Y., Peng, L., Liang, L., Li, J., Liang, Y., & Yang, C. (2024). Silage Making of Napier Grass and Sugarcane Top at Different Proportions: Evolution of Natural Fermentation Characteristics, Chemical Composition, and Microbiological Profile. Fermentation, 10(10), 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation10100525







