Towards Controlled Degradation of Poly(lactic) Acid in Technical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
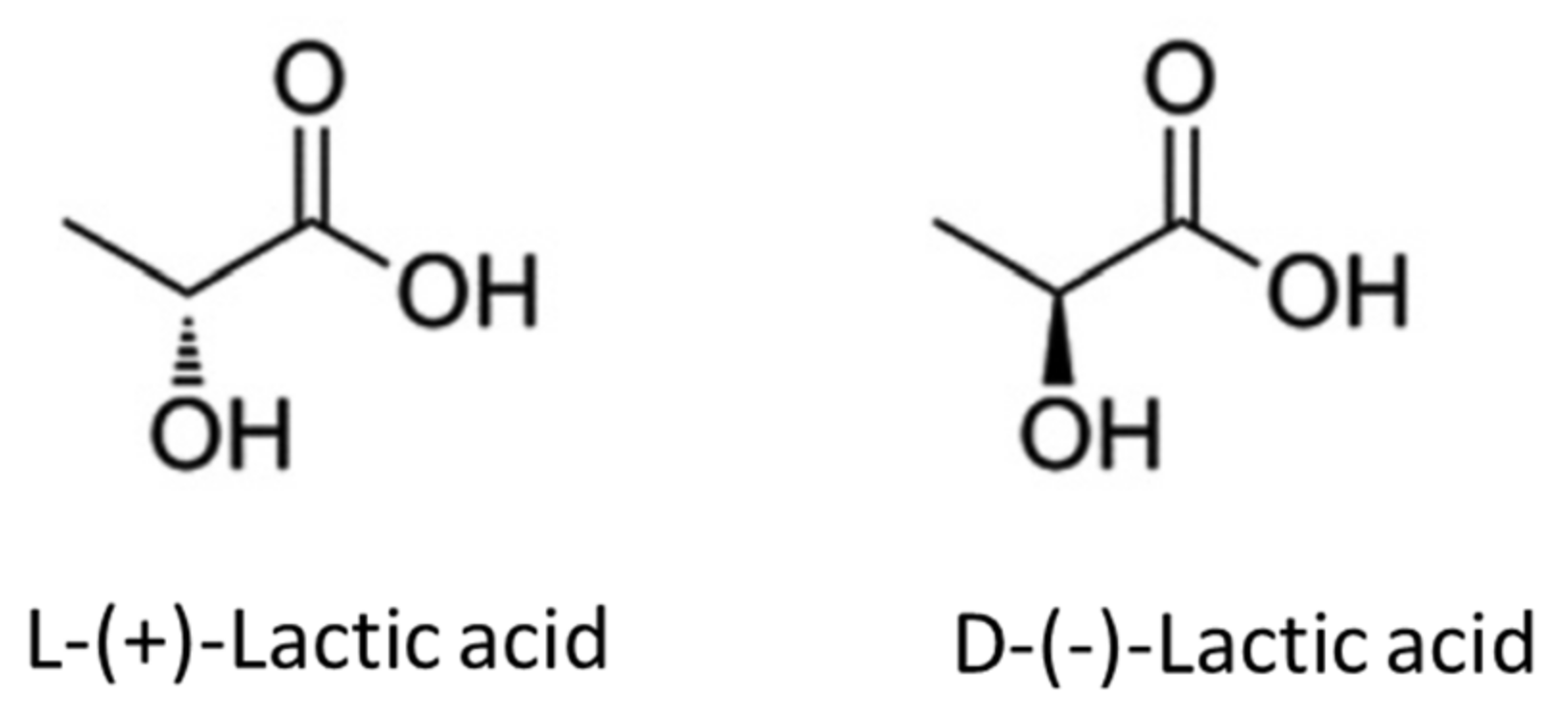
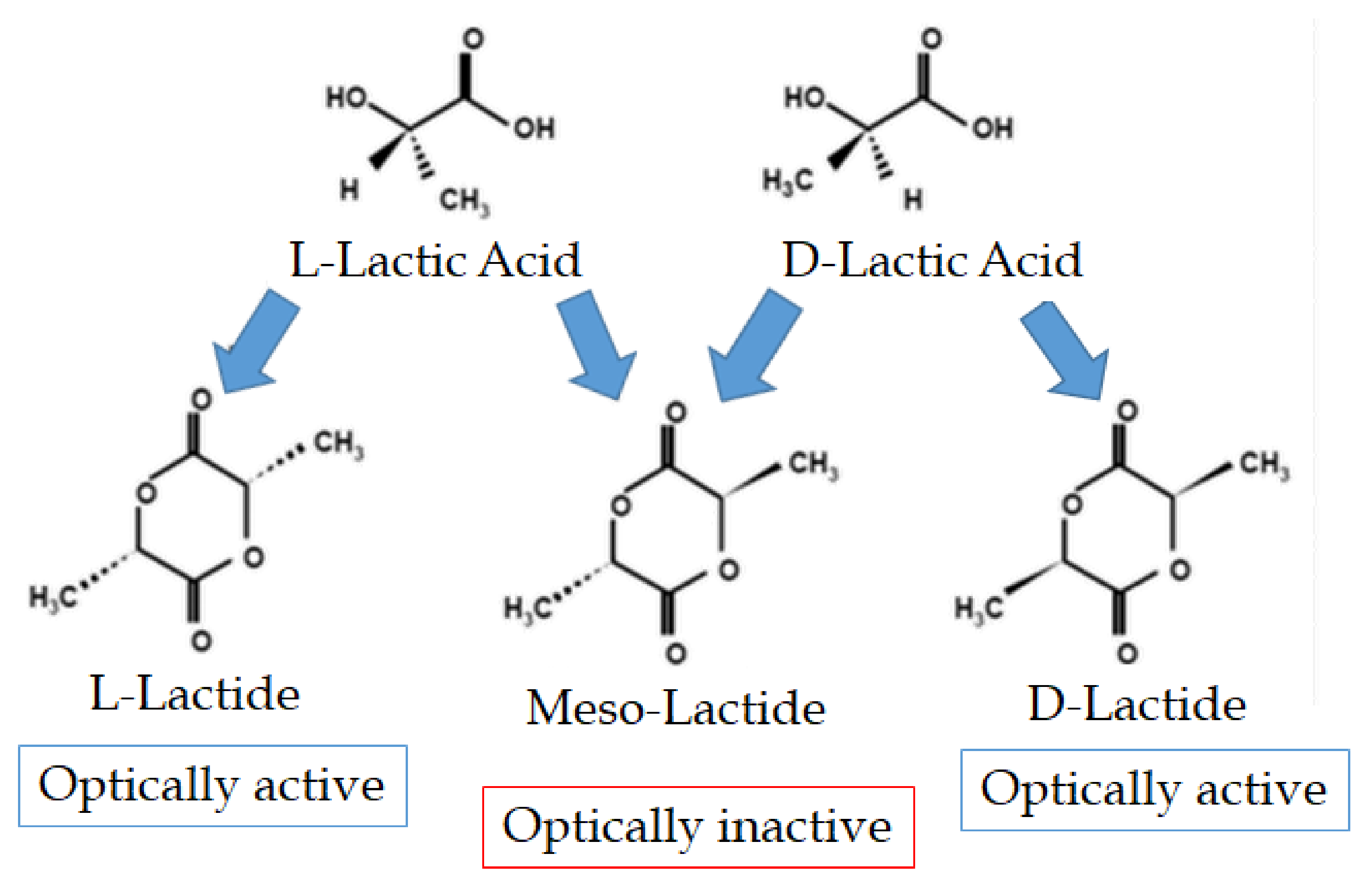
2. Properties of Lactic Acid and Lactides
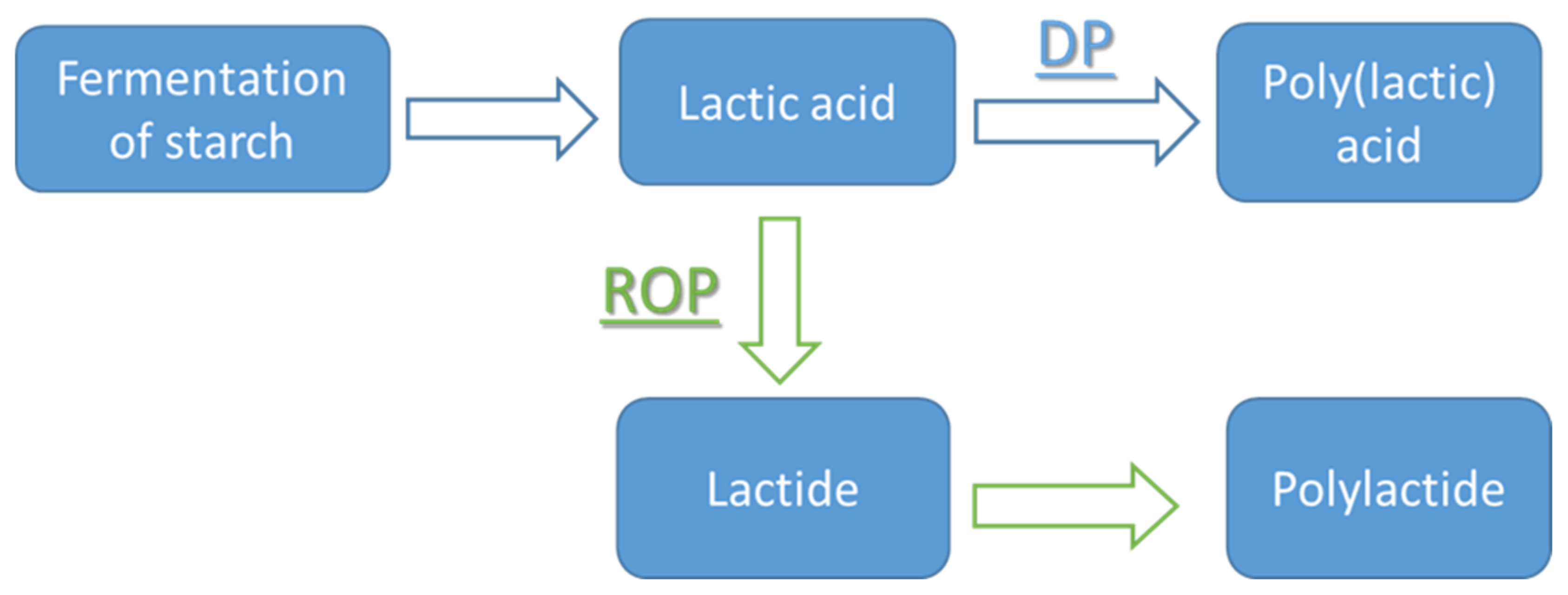
3. Methods of PLA Production
4. Properties of PLA
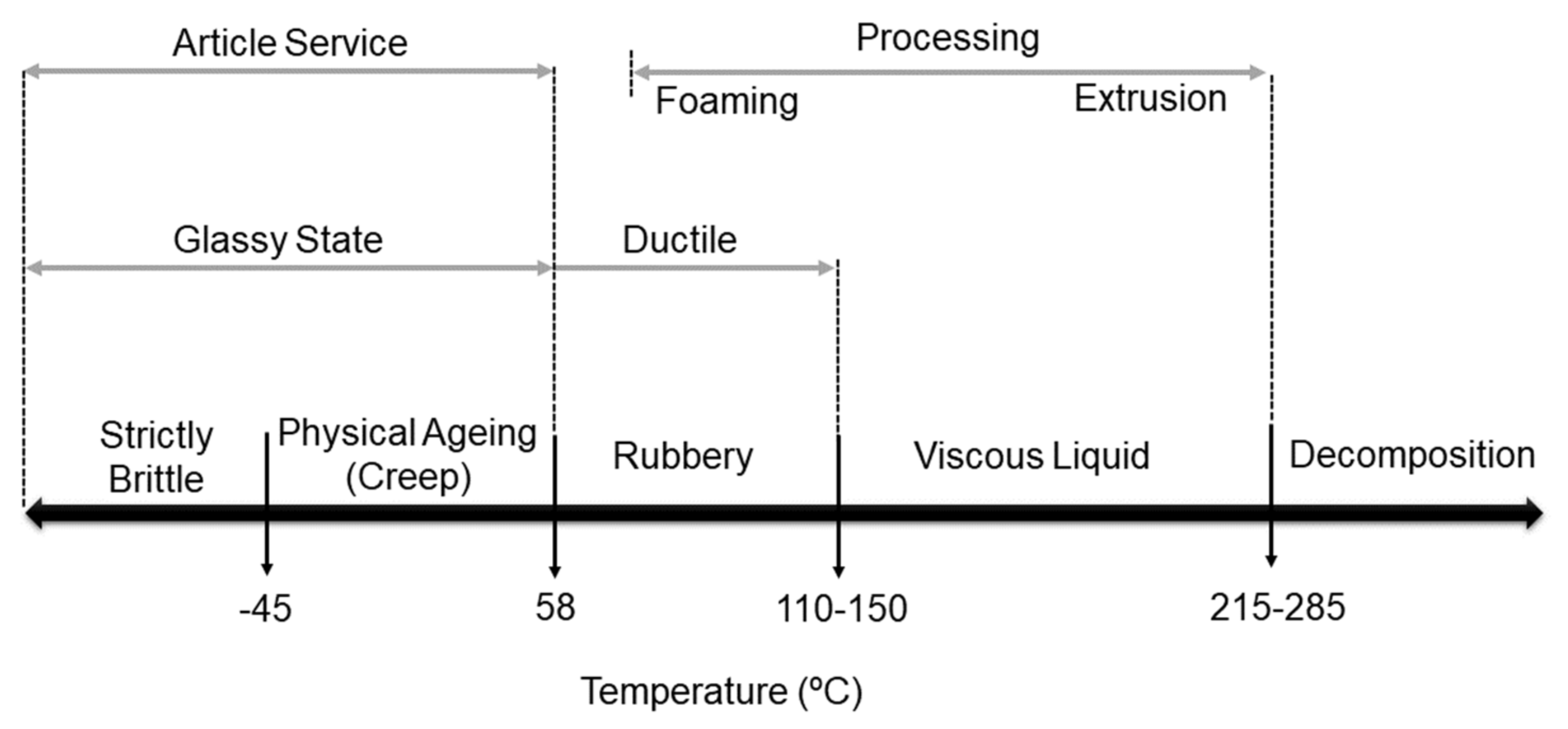
4.1. Thermophysical Properties and Crystallinity
4.2. Miscibility with Other Polymers
5. Degradation of PLA
- Biogenic or biobased plastic, originating from renewable sources;
- Biodegradable plastics, in terms of their functionality;
- Biocompatible plastics, in medical applications only.
5.1. Hydrolytic Degradation
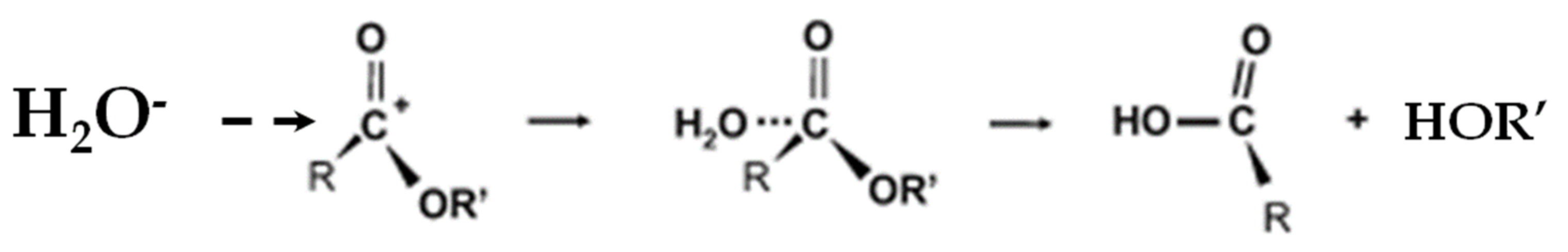
5.1.1. Hydrolysis Mechanism
5.1.2. Erosion
5.1.3. Factors Affecting Hydrolytic Degradation of PLA
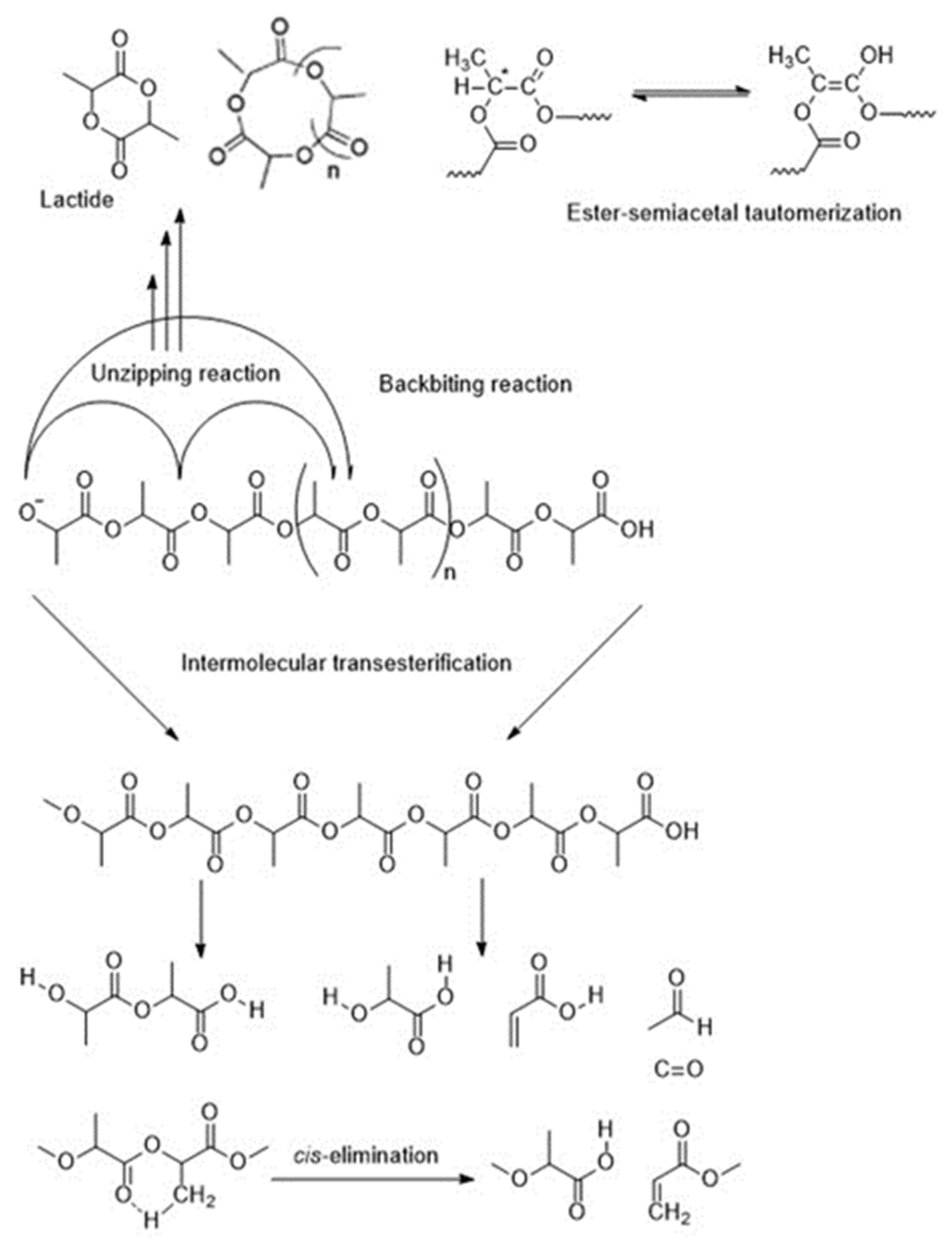
5.2. Thermal Degradation
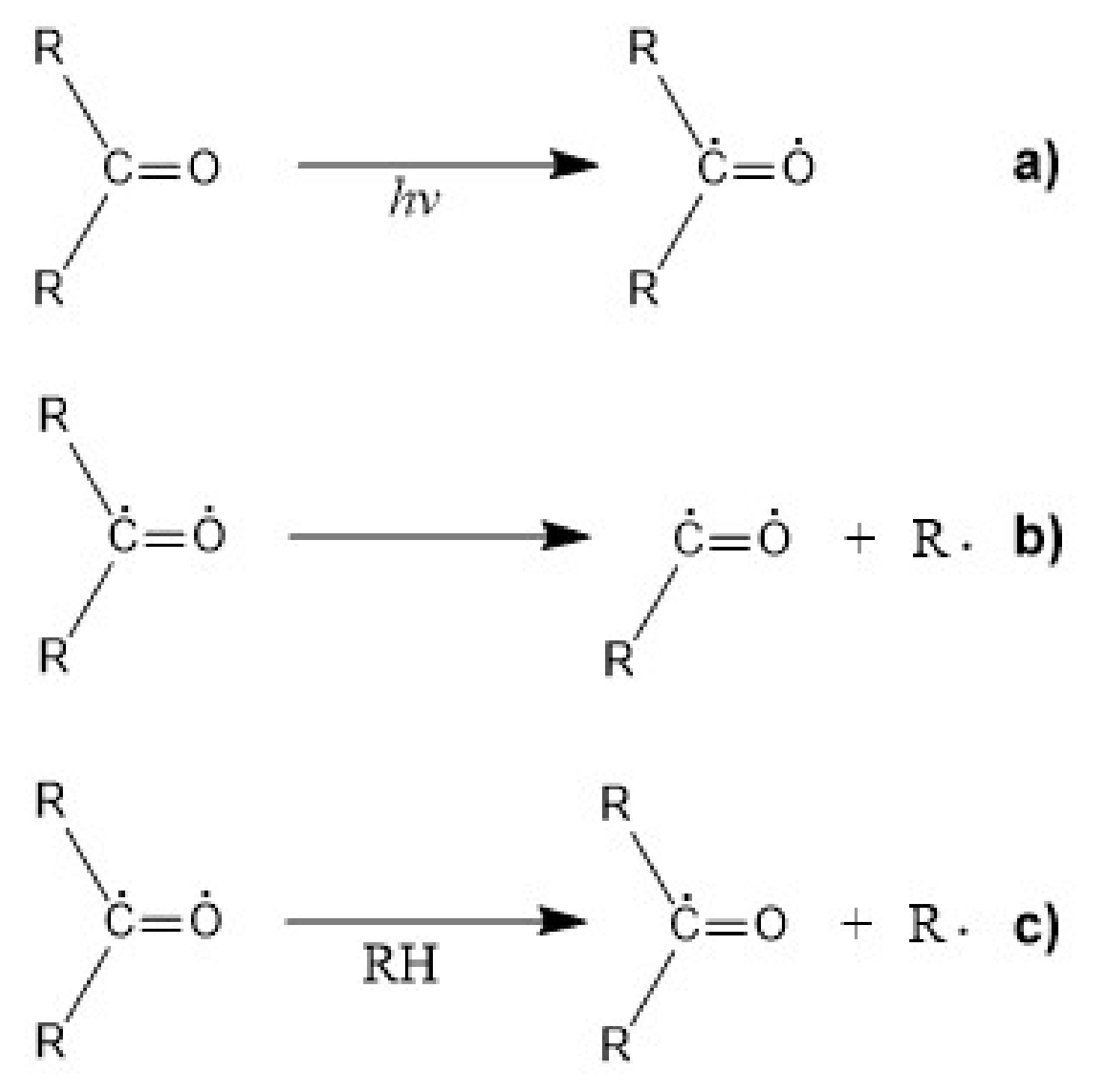
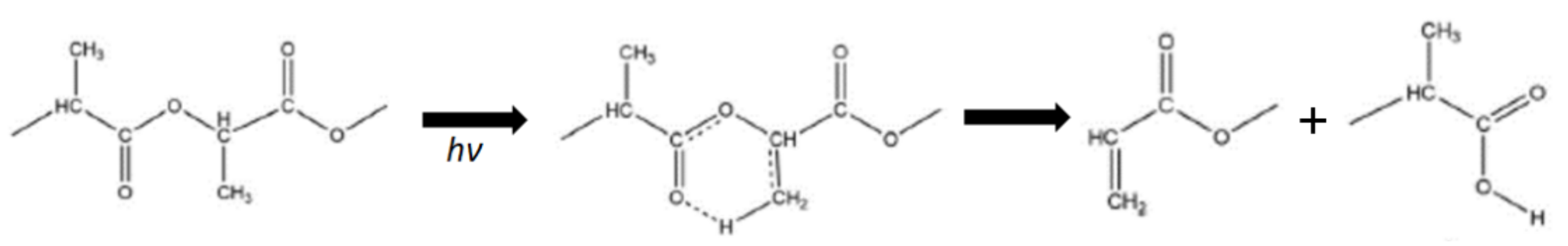
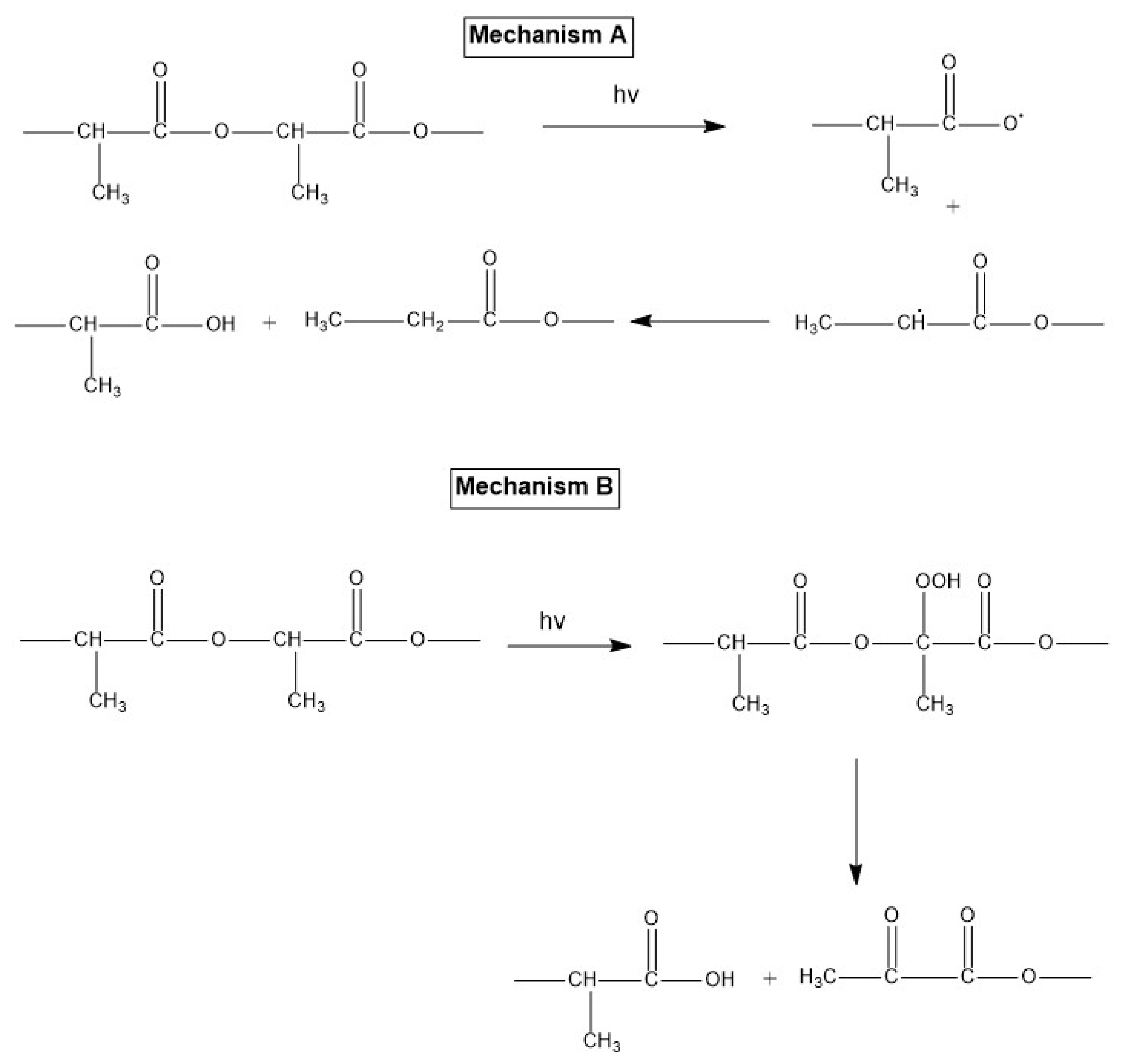
5.3. Photodegradation
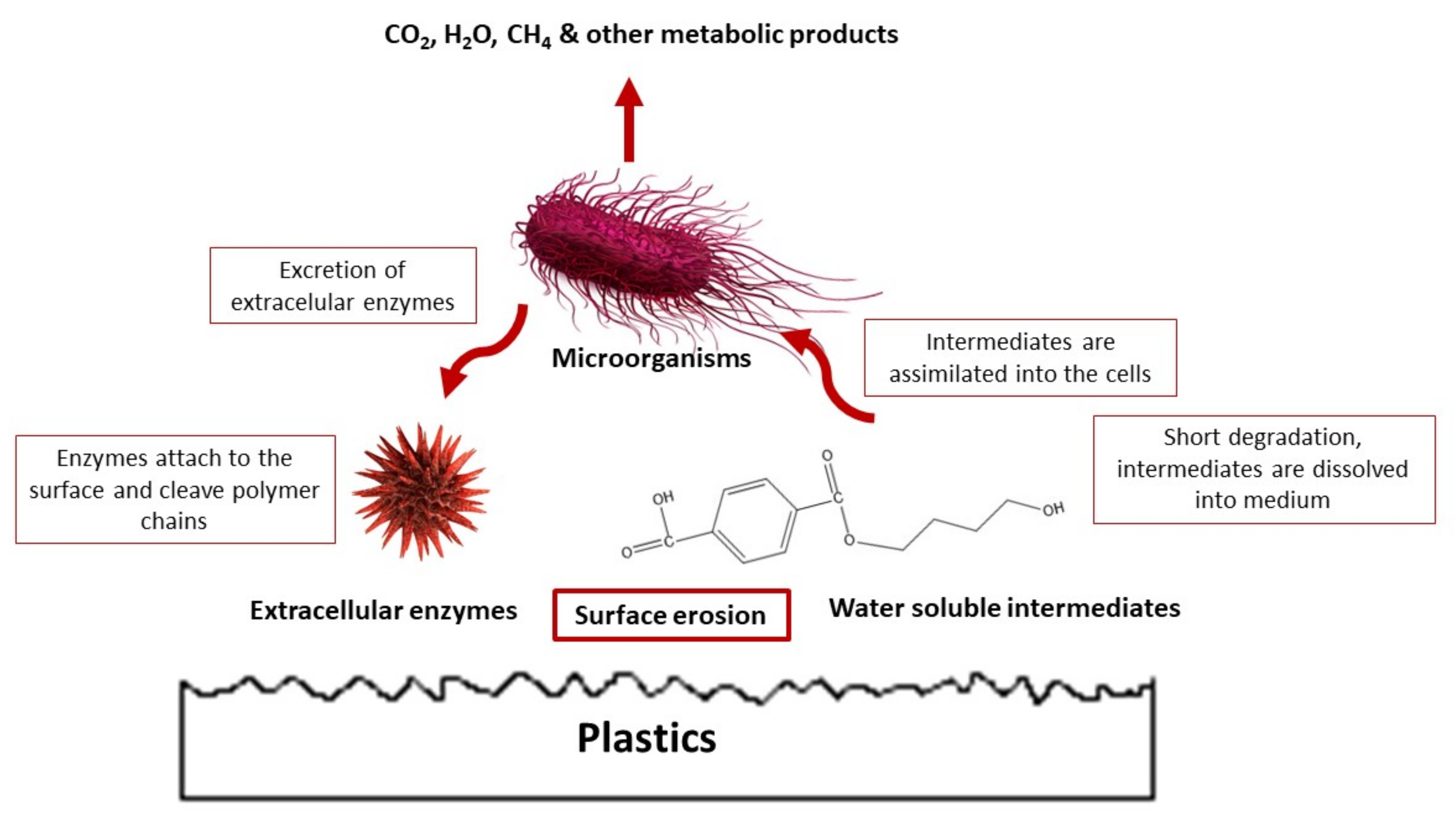
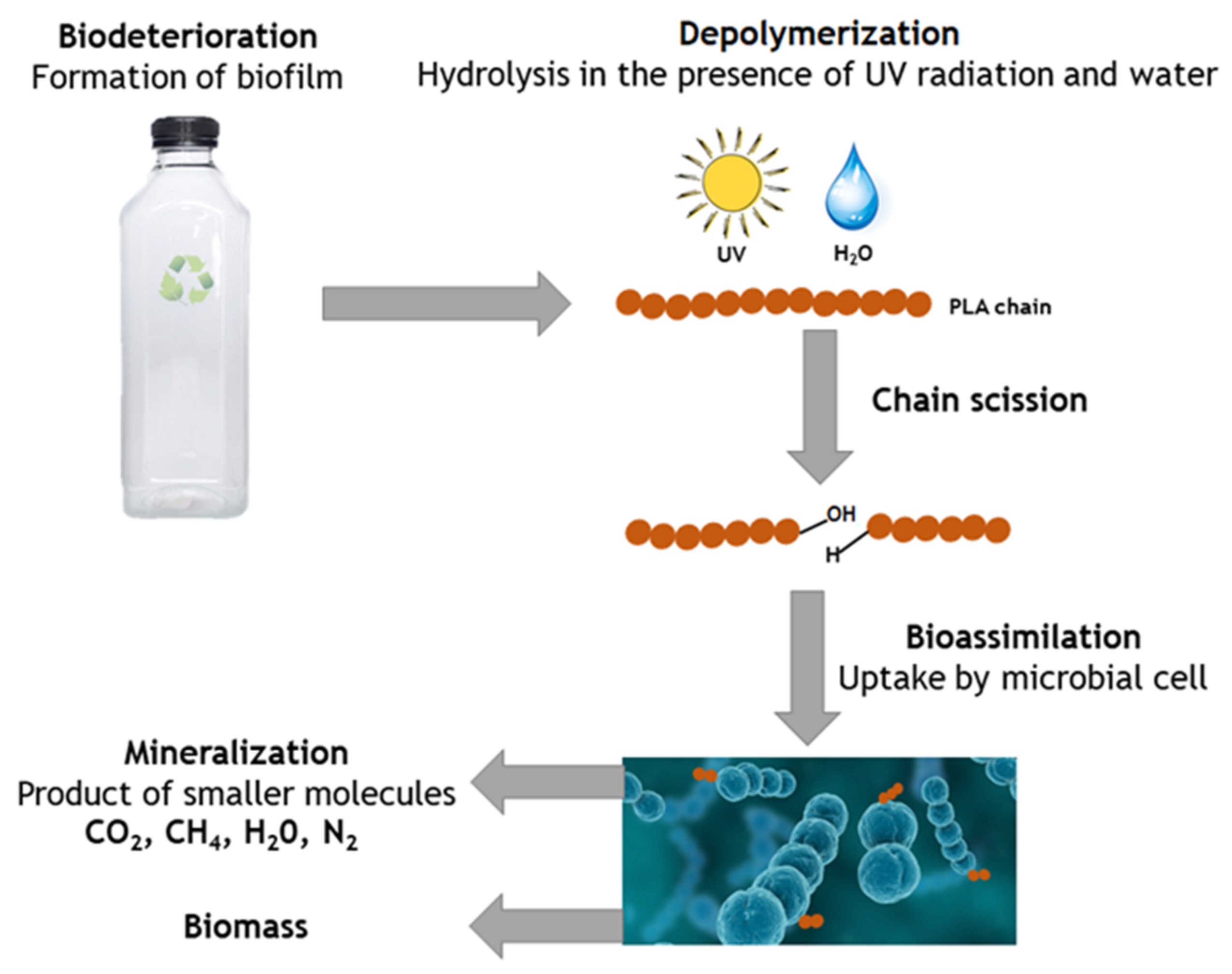
5.4. Microbial Degradation
6. Degradation of PLA in Different Environments
6.1. Composting Conditions
6.2. Soils
6.3. Aquatic Environment
7. Control and Improvement of PLA Biodegradation
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alexis, F. Factors affecting the degradation and drug-release mechanism of poly(lactic acid) and poly[(lactic acid)-co-(glycolic acid)]. Polym. Int. 2004, 54, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, A.; Oliveira, M.; Oliveira, R.; Botelho, G.; Machado, A.V. Biodegradation assessment of PLA and its nanocomposites. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 21, 9477–9486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aso, Y.; Yoshioka, S.; Liwanpo, A.; Terao, T. Effect of temperature on mechanisms of drug release and matrix degradation of poly(d,l-lactide) microspheres. J. Control. Release 1994, 31, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Aguirre, E.; Iñiguez-Franco, F.; Samsudin, H.; Fang, X.; Auras, R. Poly(lactic acid)—Mass production, processing, industrial applications, and end of life. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 333–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidian, M.; Tehrany, E.A.; Imran, M.; Jacquot, M.; Desobry, S. Poly-Lactic Acid: Production, Applications, Nanocomposites, and Release Studies. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2010, 9, 552–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.A.; Hasan, F.; Hameed, A.; Ahmed, S. Biological degradation of plastics: A comprehensive review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 246–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsawy, M.A.; Kim, K.-H.; Park, J.-W.; Deep, A. Hydrolytic degradation of polylactic acid (PLA) and its composites. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 1346–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nampoothiri, K.M.; Nair, N.R.; John, R.P. An overview of the recent developments in polylactide (PLA) research. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8493–8501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murariu, M.; Dubois, P. PLA composites: From production to properties. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 17–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vink, E.T.; Rábago, K.R.; Glassner, D.A.; Gruber, P.R. Applications of life cycle assessment to NatureWorks™ polylactide (PLA) production. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2003, 80, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platel, R.H.; Hodgson, L.M.; Williams, C.K. Biocompatible Initiators for Lactide Polymerization. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 11–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinconico, M. Soil Degradable Bioplastics for a Sustainable Modern Agriculture; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, L.; Zhang, Y. Jointly modified mechanical properties and accelerated hydrolytic degradation of PLA by interface reinforcement of PLA-WF. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 88, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.; Kumar, V.; Bhunia, H.; Upadhyay, S.N. Synthesis of Poly(Lactic Acid): A Review. J. Macromol. Sci. Part C 2005, 45, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.-T.; Auras, R.; Rubino, M. Processing technologies for poly(lactic acid). Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 820–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, L.T.; Rahmat, A.R.; Rahman, W.A.W.A. (Eds.) 3-Thermal Properties of Poly(lactic Acid). In Polylactic Acid; William Andrew Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 109–141. [Google Scholar]
- Fambri, L.; Migliaresi, C.; Kesenci, K.; Pişkin, E. Biodegradable Polymers. In Integrated Biomaterials Science; J.B. Metzler: Stuttgart, Germany, 2005; pp. 119–187. [Google Scholar]
- Farah, S.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R. Physical and mechanical properties of PLA, and their functions in widespread applications—A comprehensive review. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 367–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Revagade, N.; Hilborn, J. Poly(lactic acid) fiber: An overview. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 455–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Södergård, A.; Stolt, M. Properties of lactic acid based polymers and their correlation with composition. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2002, 27, 1123–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanlioglu, M.; Preziosi, R.; Robson, G.D. Abiotic and biotic environmental degradation of the bioplastic polymer poly(lactic acid): A review. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 137, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergsma, J.E.; de Bruijn, W.C.; Rozema, F.R.; Bos, R.R.M.; Boering, G. Late degradation tissue response to poly(l-lactide) bone plates and screws. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.pressreleasefinder.com/NatureWorks/NWPR005/en/ (accessed on 22 December 2020).
- Available online: https://www.natureworksllc.com/News-and-Events/Press-Releases/2020 (accessed on 12 November 2020).
- Momani, B. Assessment of the Impacts of Bioplastics: Energy Usage, Fossil Fuel Usage, Pollution, Health Effects, Effects on the Food Supply, and Economic Effects Compared to Petroleum Based Plastics. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/212988946.pdf (accessed on 28 November 2020).
- Momani, B. Assessment of the Impacts of Bioplastics: Energy Usage, Fossil Fuel Usage, Pollution, Health Effects, Effects on the Food Supply, and Economic Effects Compared to Petroleum Based Plastics; An Interactive Qualifying Project Report; Worcester Polytechnic Institute: Worcester, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, H.; Kong, L.; Zhao, X.; Miao, G.; Zhu, L.; Li, S.; Sun, Y. Highly efficient production of lactic acid from xylose using Sn-beta catalysts. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 7333–7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komesu, A.; Oliveira, J.A.R.d.; Martins, L.H.d.S.; Wolf Maciel, M.R.; Maciel Filho, R. Lactic Acid Production to Purification: A Review. BioResources 2017, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xiu, Z. Efficient production of lactic acid from sugarcane molasses by a newly microbial consortium CEE-DL15. Process. Biochem. 2019, 81, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhavaram, N.K.; Fan, Z. Production of lactic acid from paper sludge using acid-tolerant, thermophilic Bacillus coagulan strains. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5966–5972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Padukone, N. Production of lactic acid from wastepaper as a cellulosic feedstock. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1997, 18, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullón, B.; Yáñez, R.; Alonso, J.L.; Parajó, J. l-Lactic acid production from apple pomace by sequential hydrolysis and fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlotta, D. A Literature Review of Poly(Lactic Acid). J. Polym. Environ. 2001, 9, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasal, R.M.; Janorkar, A.V.; Hirt, D.E. Poly(lactic acid) modifications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 338–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, L.T.; Rahmat, A.R.; Rahman, W.A.W.A. Synthesis and Production of Poly(lactic Acid). In Polylactic Acid; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 71–107. [Google Scholar]
- Drumright, R.E.; Gruber, P.R.; Henton, D.E. Polylactic Acid Technology. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 1841–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botvin, V.; Karaseva, S.; Salikova, D.; Dusselier, M. Syntheses and chemical transformations of glycolide and lactide as monomers for biodegradable polymers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2021, 183, 109427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.H. High Molecular Weight Polylactic Acid Polymers. In Biopolymers from Renewable Resources; Kaplan, D.L., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 367–411. [Google Scholar]
- Dechy-Cabaret, O.; Martin-Vaca, B.; Bourissou, D. Controlled Ring-Opening Polymerization of Lactide and Glycolide. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 6147–6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendix, D. Chemical synthesis of polylactide and its copolymers for medical applications. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1998, 59, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Ren, Y.; Wang, X. New advances in the biodegradation of Poly(lactic) acid. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegradation 2017, 117, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metkar, S.; Sathe, V.; Rahman, I.; Idage, B.; Idage, S. Ring opening polymerization of lactide: Kinetics and modeling. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2019, 206, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Lisowski, M.S.; Runt, J.; Hall, E.S.; Kean, R.T.; Buehler, N.; Lin, J.S. Crystallization and Microstructure of Poly(l-lactide-co-meso-lactide) Copolymers. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 2593–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanthakumari, R.; Pennings, A. Crystallization kinetics of poly(l-lactic acid). Polymer 1983, 24, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marega, C.; Marigo, A.; Noto, V.; Zannetti, R.; Martorana, A.; Paganetto, G. Structure and crystallization kinetics of poly(L-Lactic Acid). Die Makromolekulare Chemie 1992, 193, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzullo, S.; Paganetto, G.; Celli, A. Regime III crystallization in poly-(l-lactic) acid. Solidif. Process. Polym. 2007, 34, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolstad, J.J. Crystallization kinetics of poly(L-lactide-co-meso-lactide). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 62, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zell, M.T.; Padden, B.E.; Paterick, A.J.; Hillmyer, M.A.; Kean, R.T.; Thakur, K.A.M.; Munson, E.J. Direct Observation of Stereodefect Sites in Semicrystalline Poly(lactide) Using 13C Solid-State NMR. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 12672–12673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratian, S.; Hall, E.S.; Lin, J.S.; Xu, R.; Runt, J. Crystallization and Solid-State Structure of Random Polylactide Copolymers: Poly(l-lactide-co-d-lactide)s. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 4857–4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, M.L. Crystallization behavior of poly(l-lactic acid). Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.S.; Jardini, A.; Filho, R.M. Poly (Lactic Acid) Production for Tissue Engineering Applications. Procedia Eng. 2012, 42, 1402–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunt, J. Large-scale production, properties and commercial applications of polylactic acid polymers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1998, 59, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eling, B.; Gogolewski, S.; Pennings, A. Biodegradable materials of poly(l-lactic acid): 1. Melt-spun and solution-spun fibres. Polymer 1982, 23, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.hitachi-hightech.com/file/global/pdf/products/science/appli/ana/thermal/application_TA_081e.pdf (accessed on 13 December 2020).
- Auras, R.; Harte, B.; Selke, S. An Overview of Polylactides as Packaging Materials. Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4, 835–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H. Poly(lactide) Stereocomplexes: Formation, Structure, Properties, Degradation, and Applications. Macromol. Biosci. 2005, 5, 569–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Horii, F.; Hyon, S.H.; Ikada, Y. Stereocomplex formation between enantiomeric poly(lactic acid)s. 2. Stereocomplex formation in concentrated solutions. Macromolecules 1991, 24, 2719–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, K.; Hyon, S.-H.; Ikada, Y. Thermal characterization of polylactides. Polymer 1988, 29, 2229–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Deng, S.; Chen, P.; Ruan, R. Polylactic acid (PLA) synthesis and modifications: A review. Front. Chem. China 2009, 4, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Z.; Xu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Lu, C.; Cheng, S. Novel polyethylene glycol-based polyester-toughened polylactide. Mater. Lett. 2012, 71, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Zheng, Y.; Tian, J. Study on the biodegradability of modified starch/polylactic acid (PLA) composite materials. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 26298–26307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meaurio, E.; Hernandez-Montero, N.; Zuza, E.; Sarasua, J.R. Miscible Blends Based on Biodegradable Polymers. In Characterization of Polymer Blends: Miscibility, Morphology and Interfaces; Thomas, S., Grohens, Y., Jyotishkumar, P., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2015; pp. 7–86. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Goh, S.; Lee, S. Miscibility and crystallization behaviour of poly(l-lactide)/poly(p-vinylphenol) blends. Polymer 1998, 39, 4841–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-L.; Liu, H.-H.; Lin, J.S. Microstructure of Semicrystalline Poly(l-lactide)/Poly(4-vinylphenol) Blends Evaluated from SAXS Absolute Intensity Measurement. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 4856–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, G.; Cha, Y.; Shah, S.; Zhu, K. Blends of PVA and PGLA: Control of the permeability and degradability of hydrogels by blending. J. Control. Release 1992, 19, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajria, A.M.; Davé, V.; Gross, R.A.; McCarthy, S.P. Miscibility and biodegradability of blends of poly(lactic acid) and poly(vinyl acetate). Polymer 1996, 37, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedl, B.; Prud’Homme, R.E. Thermodynamic study of poly(vinyl chloride)/polyester blends by inverse-phase gas chromatography at 120 °C. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1986, 24, 2565–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hillmyer, M.A. Polyethylene-poly(L-lactide) diblock copolymers: Synthesis and compatibilization of poly(L-lactide)/polyethylene blends. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2001, 39, 2755–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakafuku, C.; Sakoda, M. Melting and Crystallization of Poly(L-lactic acid) and Poly(ethylene oxide) Binary Mixture. Polym. J. 1993, 25, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.G.; Cohen, S.; Langer, R. Poly(L-lactic acid)/Pluronic blends: Characterization of phase separation behavior, degradation, and morphology and use as protein-releasing matrixes. Macromolecules 1992, 25, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-M.; Chen, H.-L.; You, J.-W.; Hwang, J.C. Miscibility and Crystallization of Poly(L-lactide)/Poly(ethylene glycol) and Poly(L-lactide)/Poly(ε-caprolactone) Blends. Polym. J. 1997, 29, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.-S.; Oh, S.-H.; Kim, M.-N.; Chin, I.-J.; Kim, Y.-H. Thermal and mechanical properties of poly(l-lactic acid)–poly (ethylene-co-vinyl acetate) blends1Dedicated to Professor Ick-Sam Noh on the occasion of his retirement from Inha University.1. Polymer 1999, 40, 2303–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.-J.; Chin, I.-J.; Kim, M.-N.; Kim, S.-H.; Yoon, J.-S. Blending of poly(L-lactic acid) with poly(cis-1,4-isoprene). Eur. Polym. J. 2000, 36, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikos, A.G.; Thorsen, A.J.; Czerwonka, L.A.; Bao, Y.; Langer, R.; Winslow, D.N.; Vacanti, J.P. Preparation and characterization of poly(l-lactic acid) foams. Polymer 1994, 35, 1068–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avella, M.; Errico, M.; Immirzi, B.; Malinconico, M.; Martuscelli, E.; Paolillo, L.; Falcigno, L. Radical polymerization of poly(butyl acrylate) in the presence of poly(L-lactic acid), 1. Synthesis, characterization and properties of blends. Angew. Makromol. Chem. Appl. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1997, 246, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguiburu, J.; Iruin, J.; Fernandez-Berridi, M.; Román, J.S. Blends of amorphous and crystalline polylactides with poly(methyl methacrylate) and poly(methyl acrylate): A miscibility study. Polymer 1998, 39, 6891–6897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avella, M.; Errico, M.E.; Immirzi, B.; Malinconico, M.; Falcigno, L.; Paolillo, L. Radical polymerization of methyl methacrylate in the presence of biodegradable poly(L-lactic acid). Preparation of blends, chemical-physical characterization and morphology. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2000, 201, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-X.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, E.-S.; Yoon, J.-S. Compatibilization-like effect of reactive organoclay on the poly(l-lactide)/poly(butylene succinate) blends. Polymer 2005, 46, 11829–11836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grijpma, D.W.; Van Hofslot, R.D.A.; Supèr, H.; Nijenhuis, A.J.; Pennings, A.J. Rubber toughening of poly(lactide) by blending and block copolymerization. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1994, 34, 1674–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, N.; Jimenez, G.; Kawai, H.; Ogihara, T. Structure and thermal/mechanical properties of poly(l-lactide)-clay blend. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1997, 35, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.; Pitt, C. The biodegradability of polyester blends. Biomaterials 1990, 11, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joziasse, C.; Veenstra, H.; Topp, M.; Grijpma, D.; Pennings, A. Rubber toughened linear and star-shaped poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide): Synthesis, properties and in vitro degradation. Polymer 1998, 39, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérard, T.; Budtova, T. PLA-PHA blends: Morphology, thermal and mechanical properties. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biodegradable and Biobased Polymers—BIOPOL 2011, Strasbourg, France, 29–31 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Amass, W.; Amass, A.; Tighe, B. A review of biodegradable polymers: Uses, current developments in the synthesis and characterization of biodegradable polyesters, blends of biodegradable polymers and recent advances in biodegradation studies. Polym. Int. 1999, 47, 89–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, W.; Gross, R.; McCarthy, S. Reactive compatibilization of biodegradable blends of poly(lactic acid) and poly(ε-caprolactone). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1998, 59, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, N.R.; Sekhar, V.C.; Nampoothiri, K.M.; Pandey, A. 32-Biodegradation of Biopolymers. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Pandey, A., Negi, S., Soccol, C.R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 739–755. [Google Scholar]
- Zaaba, N.F.; Jaafar, M. A review on degradation mechanisms of polylactic acid: Hydrolytic, photodegradative, microbial, and enzymatic degradation. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2020, 60, 2061–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malwela, T.; Ray, S.S. Enzymatic degradation behavior of nanoclay reinforced biodegradable PLA/PBSA blend composites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 77, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikiaris, D.N. Nanocomposites of aliphatic polyesters: An overview of the effect of different nanofillers on enzymatic hydrolysis and biodegradation of polyesters. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 1908–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Hiyama, M.; Kabe, T.; Kimura, S.; Iwata, T. Enzymatic Self-Biodegradation of Poly(l-lactic acid) Films by Embedded Heat-Treated and Immobilized Proteinase K. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 3301–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jong, S.; Arias, E.; Rijkers, D.; van Nostrum, C.; Bosch, J.K.-V.D.; Hennink, W. New insights into the hydrolytic degradation of poly(lactic acid): Participation of the alcohol terminus. Polymer 2001, 42, 2795–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engineer, C.; Parikh, J.; Raval, A. Review on hydrolytic degradation behavior of biodegradable polymers from controlled drug delivery system. Trends. Biomater. Artif. Organs 2011, 25, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Laycock, B.; Nikolić, M.; Colwell, J.M.; Gauthier, E.; Halley, P.; Bottle, S.; George, G. Lifetime prediction of biodegradable polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 71, 144–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husárová, L.; Pekařová, S.; Stloukal, P.; Kucharzcyk, P.; Verney, V.; Commereuc, S.; Ramone, A.; Koutny, M. Identification of important abiotic and biotic factors in the biodegradation of poly(l-lactic acid). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 71, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasco, L.S.; Ribes-Greus, A.; Alamo, R. Comparative thermal, biological and photodegradation kinetics of polylactide and effect on crystallization rates. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, G.; Kijchavengkul, T.; Auras, R.; Rubino, M.; Selke, S.E.; Singh, S.P. Compostability of Bioplastic Packaging Materials: An Overview. Macromol. Biosci. 2007, 7, 255–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasaka, F.; Miyazaki, H.; Ohya, A.Y.; Ouchi, T. Synthesis of Comb-Type Biodegradable Polylactide through Depsipeptide−Lactide Copolymer Containing Serine Residues. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 6386–6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polman, E.M.; Gruter, G.-J.M.; Parsons, J.R.; Tietema, A. Comparison of the aerobic biodegradation of biopolymers and the corresponding bioplastics: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 141953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siparsky, G.L.; Voorhees, K.J.; Miao, F. Hydrolysis of Polylactic Acid (PLA) and Polycaprolactone (PCL) in Aqueous Acetonitrile Solutions: Autocatalysis. J. Polym. Environ. 1998, 6, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirao, K.; Nakatsuchi, Y.; Ohara, H. Alcoholysis of Poly(l-lactic acid) under microwave irradiation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 925–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iñiguez-Franco, F.; Auras, R.; Burgess, G.; Holmes, D.; Fang, X.; Rubino, M.; Soto-Valdez, H. Concurrent solvent induced crystallization and hydrolytic degradation of PLA by water-ethanol solutions. Polymer 2016, 99, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Gondo, D.; Wada, T.; Kanehashi, S.; Nagai, K. Effects of various liquid organic solvents on solvent-induced crystallization of amorphous poly(lactic acid) film. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 129, 1607–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, I.; Leiper, H. Degradation studies of some polyesters and polycarbonates—2. Polylactide: Degradation under isothermal conditions, thermal degradation mechanism and photolysis of the polymer. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1985, 11, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Ikada, Y. Properties and morphology of poly(L-lactide). II. hydrolysis in alkaline solution. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1998, 36, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-M.; Shen, Y.; Yang, J.-H.; Huang, T.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.-W. Molecular ordering and α′-form formation of poly(l-lactide) during the hydrolytic degradation. Polymer 2013, 54, 6644–6653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suuronen, R.; Pohjonen, T.; Hietanen, J.; Lindqvist, C. A 5-year in vitro and in vivo study of the biodegradation of polylactide plates. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1998, 56, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, D.; Kaduri, M.; Poley, M.; Adir, O.; Krinsky, N.; Shainsky-Roitman, J.; Schroeder, A. Biocompatibility, biodegradation and excretion of polylactic acid (PLA) in medical implants and theranostic systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 340, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, D.H. Biodegradable Polymers as Drug Delivery Systems. In Biomedical Polymers; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, S.; Schley, J.; Loy, B.; Lind, D.; Hobot, C.; Sparer, R.; Untereker, D. Kinetics and Time−Temperature Equivalence of Polymer Degradation. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2301–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schliecker, G.; Schmidt, C.; Fuchs, S.; Kissel, T. Characterization of a homologous series of d,l-lactic acid oligomers; a mechanistic study on the degradation kinetics in vitro. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 3835–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C. Chain-end scission in acid catalyzed hydrolysis of poly (d,l-lactide) in solution. J. Control. Release 1995, 34, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, C.G.; Chasalow, F.I.; Hibionada, Y.M.; Klimas, D.M.; Schindler, A. Aliphatic polyesters. I. The degradation of poly(ϵ-caprolactone) in vivo. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1981, 26, 3779–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.M.; Garreau, H.; Vert, M. Structure-property relationships in the case of the degradation of massive poly(α-hydroxy acids) in aqueous media. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1990, 1, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henton, D.; Gruber, P.; Lunt, J.; Randall, J. Polylactic Acid Technology. In Natural Fibers, Biopolymers, and Biocomposites; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gajjar, C.R.; King, M.W. Resorbable Fiber-Forming Polymers for Biotextile Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kronenthal, R.L. Biodegradable Polymers in Medicine and Surgery. In Polymers in Medicine and Surgery; Kronenthal, R.L., Oser, Z., Martin, E., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1975; pp. 119–137. [Google Scholar]
- Göpferich, A. Mechanisms of polymer degradation and erosion. Biomaterials 1996, 17, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.; Sparer, R.; Untereker, D. Analytical solutions to mathematical models of the surface and bulk erosion of solid polymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2005, 43, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, G.; Auras, R.; Singh, S.P. Comparison of the degradability of poly(lactide) packages in composting and ambient exposure conditions. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2007, 20, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepmann, J.; Göpferich, A. Mathematical modeling of bioerodible, polymeric drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 48, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Cha, Y.; Pitt, C. Poly (glycolic acid-co-dl-lactic acid): Diffusion or degradation controlled drug delivery? J. Control. Release 1992, 18, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Burkersroda, F.; Schedl, L.; Göpferich, A. Why degradable polymers undergo surface erosion or bulk erosion. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4221–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, T.; Kishita, M.; Sun, Y.; Sako, T.; Okajima, I. Degradation of Polylactic Acid Using Sub-Critical Water for Compost. Polymer 2020, 12, 2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Pan, J.; Buchanan, F.; Weir, N.; Farrar, D. Analysis of degradation data of poly(l-lactide–co-l,d-lactide) and poly(l-lactide) obtained at elevated and physiological temperatures using mathematical models. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 3882–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Pan, J. A model for simultaneous crystallisation and biodegradation of biodegradable polymers. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coszach, P.; Bogaert, J.-C.; Willocq, J. Chemical Recycling of Pla by Hydrolysis; GALACTIC, S.A.: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2012; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Gorrasi, G.; Pantani, P. Hydrolysis and Biodegradation of Poly(lactic acid). In Synthesis, Structure and Properties of Poly(lactic acid); Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, S.; Untereker, D. Degradability of Polymers for Implantable Biomedical Devices. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 4033–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Ree, M.; Kim, H. Acid- and base-catalyzed hydrolyses of aliphatic polycarbonates and polyesters. Catal. Today 2006, 115, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca-Smith, J.; Chau, N.; Champion, D.; Brachais, C.-H.; Marcuzzo, E.; Sensidoni, A.; Piasente, F.; Karbowiak, T.; Debeaufort, F. Effect of the state of water and relative humidity on ageing of PLA films. Food Chem. 2017, 236, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höglund, A.; Odelius, K.; Albertsson, A.-C. Crucial Differences in the Hydrolytic Degradation between Industrial Polylactide and Laboratory-Scale Poly(L-lactide). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 2788–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limsukon, W.; Auras, R.; Selke, S. Hydrolytic degradation and lifetime prediction of poly(lactic acid) modified with a multifunctional epoxy-based chain extender. Polym. Test. 2019, 80, 106108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.C.; Deshmukh, V.G. Thermal oxidative degradation of poly-lactic acid Part I. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1982, 260, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Santos, E.; Araújo, A.; Fechine, G.J.; Machado, A.V.; Botelho, G. The role of shear and stabilizer on PLA degradation. Polym. Test. 2016, 51, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadri, A.; Martín-Alfonso, J. Thermal, thermo-oxidative and thermomechanical degradation of PLA: A comparative study based on rheological, chemical and thermal properties. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 150, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, N.; Bienaime, C.; Belloy, C.; Queneudec, M.; Silvestre, F.; Nava-Saucedo, J.-E. Polymer biodegradation: Mechanisms and estimation techniques—A review. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Yi, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Xu, W. Thermal degradation of poly(lactic acid) measured by thermogravimetry coupled to Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2009, 97, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopinke, F.-D.; Mackenzie, K. Mechanistic aspects of the thermal degradation of poly(lactic acid) and poly(β-hydroxybutyric acid). J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 1997, 40–41, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopinke, F.-D.; Remmler, M.; Mackenzie, K.; Möder, M.; Wachsen, O. Thermal decomposition of biodegradable polyesters—II. Poly(lactic acid). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1996, 53, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kricheldorf, H.R.; Lüderwald, I. Strukturuntersuchung von polyestern durch direkten abbau im massenspektrometer, 3. Poly-β-propiolacton, poly-β-pivalolacton und poly-δ-valerolacton. Die Makromol. Chem. 1978, 179, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auras, R.; Lim, L.-T.; Selke, S.; Tsuji, H. Poly (lactic acid): Synthesis, Structures, Properties, Processing, and Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco, F.; Pagès, P.; Gámez-Pérez, J.; Santana, O.; Maspoch, M. Kinetics of the thermal decomposition of processed poly(lactic acid). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 2508–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babanalbandi, A.; Hill, D.; O’Donnell, J.; Pomery, P.; Whittaker, A. An electron spin resonance study on γ-irradiated poly(l-lactic acid) and poly(d,l-lactic acid). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1995, 50, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, H. Thermal Degradation, Poly (lactic acid): Synthesis, Structures, Properties, Processing, and Applications; Auras, R.A., Lim, T.-K., Selke, S.E.M., Tsuji, H., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 401–412. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.; Heuzey, M.-C.; Carreau, P.J. Control of thermal degradation of polylactide/clay nanocomposites during melt processing by chain extension reaction. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 2010–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, N.; Heuzey, M.; Carreau, P.; Wood-Adams, P.M. Control of thermal degradation of polylactide (PLA)-clay nanocomposites using chain extenders. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
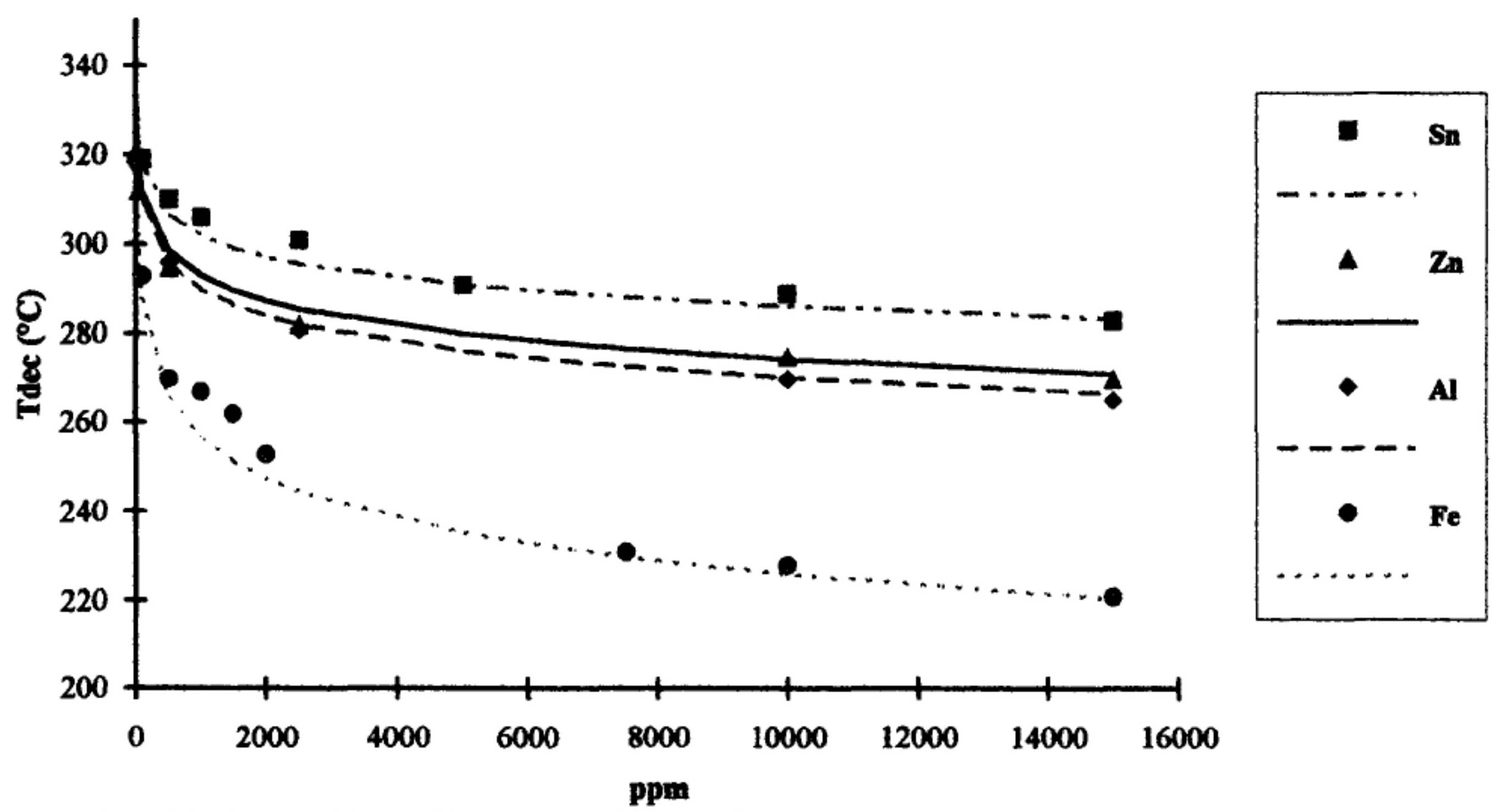
- Cam, D.; Marucci, M. Influence of residual monomers and metals on poly (l-lactide) thermal stability. Polymer 1997, 38, 1879–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, H.; Takahashi, N.; Kim, K.J.; Mochizuki, M.; Doi, Y. Thermal Degradation Processes of End-Capped Poly(l-lactide)s in the Presence and Absence of Residual Zinc Catalyst. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 1606–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kricheldorf, H.R.; Serra, A. Polylactones. Polym. Bull. 1985, 14, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijenhuis, A.J.; Grijpma, D.W.; Pennings, A.J. Lewis acid catalyzed polymerization of L-lactide. Kinetics and mechanism of the bulk polymerization. Macromolecules 1992, 25, 6419–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorin, N.S.Q.S.; Rosa, G.; Alves, J.F.; Gonçalves, S.P.C.; Franchetti, S.M.M.; Fechine, G.J.M. Study of thermodegradation and thermostabilization of poly(lactide acid) using subsequent extrusion cycles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, G.; Kerr, G. Thermal degradation of polystyrene—I. Chain scission at low temperatures. Eur. Polym. J. 1968, 4, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasselet, D.; Ruellan, A.; Guinault, A.; Miquelard-Garnier, G.; Sollogoub, C.; Fayolle, B. Oxidative degradation of polylactide (PLA) and its effects on physical and mechanical properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 50, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zou, Y.; Li, W.; Cao, G.; Chen, W. Kinetics of thermo-oxidative and thermal degradation of poly(d,l-lactide) (PDLLA) at processing temperature. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 3259–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.C.; Deshmukh, V.G. Thermal oxidative degradation of poly-lactic acid part II. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1982, 260, 514–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.J.; Kim, M.N. Biodegradation of poly(l-lactide) (PLA) exposed to UV irradiation by a mesophilic bacterium. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 85, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wataru Sakai, N. Tsutsumi, Photodegradation and Radiation Degradation, Poly (lactic acid); John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 413–422. [Google Scholar]
- Ikada, E. Photo- and Bio-degradable Polyesters. Photodegradation Behaviors of Aliphatic Polyesters. J. Photopolym. Sci. Technol. 1997, 10, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Echizen, Y.; Saha, S.K.; Nishimura, Y. Photodegradation of Poly(L-lactic acid): Effects of Photosensitizer. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2005, 290, 1192–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Echizen, Y.; Nishimura, Y. Photodegradation of biodegradable polyesters: A comprehensive study on poly(l-lactide) and poly(ɛ-caprolactone). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janorkar, A.V.; Metters, A.T.; Hirt, D.E. Degradation of poly(L-lactide) films under ultraviolet-induced photografting and sterilization conditions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 106, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchini, S.; Fukushima, K.; Di Blasio, A.; Fina, A.; Frache, A.; Geobaldo, F. Polylactic Acid and Polylactic Acid-Based Nanocomposite Photooxidation. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 2919–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benyathiar, P.; Selke, S.E.; Harte, B.R.; Mishra, D.K. The Effect of Irradiation Sterilization on Poly(Lactic) Acid Films. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantoǧlu, Ö.; Güven, O. Radiation induced crystallinity damage in poly(L-lactic acid). Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interactions Mater. Atoms 2002, 197, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkinshaw, C.; Buggy, M.; Henn, G.; Jones, E. Irradiation of poly-d,l-lactide. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1992, 38, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, L.F.; Welt, B.A.; Pullammanappallil, P.; Teixeira, A.A.; Balaban, M.O.; Beatty, C.L. Effect of electron beam treatments on degradation kinetics of polylactic acid (PLA) plastic waste under backyard composting conditions. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2009, 22, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Sasaki, H.; Sato, H.; Gotoh, Y.; Ishikawa, J. Neuron attachment properties of carbon negative-ion implanted bioabsorbable polymer of poly-lactic acid. Nuclear Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2002, 191, 815–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, G.-H.; Jang, J. Surface modification of poly(lactic acid) by UV/Ozone irradiation. Fibers Polym. 2008, 9, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.M.; Yang, Y.; Marton, D.; Carnes, D.L.; Ong, J.L.; Sylvia, V.L.; Dean, D.D.; Reis, R.L.; Agrawal, C.M. Plasma surface modification of poly(D,L-lactic acid) as a tool to enhance protein adsorption and the attachment of different cell types. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2008, 87, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, N.; Kaneda, A.; Kanazawa, S.; Yagi, T.; Mitomo, H.; Yoshii, F.; Tamada, M. Application of poly(lactic acid) modified by radiation crosslinking. Nuclear Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms. 2005, 236, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Gao, C.; Ji, J.; Shen, J. Protein immobilization on the surface of poly-L-lactic acid films for improvement of cellular interactions. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 2279–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadi, Z.; Rasmont, A.; Cesar, G.; Bewa, H.; Benguigui, L. Fungal Degradation of Poly(l-lactide) in Soil and in Compost. J. Polym. Environ. 2011, 20, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, A.V.; Araújo, A.; Oliveira, M. Assessment of polymer-based nanocomposites biodegradability. In Biodegradable Polymers: Advancement in Biodegradation Study and Applications; Chu, C.-C., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2015; p. 26. [Google Scholar]
- Tomita, K.; Tsuji, H.; Nakajima, T.; Kikuchi, Y.; Ikarashi, K.; Ikeda, N. Degradation of poly(d-lactic acid) by a thermophile. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2003, 81, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butbunchu, N.; Pathom-Aree, W. Actinobacteria as Promising Candidate for Polylactic Acid Type Bioplastic Degradation. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankhla, I.S.; Sharma, G.; Tak, A. Chapter 4—Fungal degradation of bioplastics: An overview. In New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Singh, J., Gehlot, P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 35–47. [Google Scholar]
- Maqbool, Z.; Hussain, S.; Imran, M.; Mahmood, F.; Shahzad, T.; Ahmed, Z.; Azeem, F.; Muzammil, S. Perspectives of using fungi as bioresource for bioremediation of pesticides in the environment: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 16904–16925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzi, F.; Fortunati, E.; Puglia, D.; Petrucci, R.; Kenny, J.; Torre, L. Study of disintegrability in compost and enzymatic degradation of PLA and PLA nanocomposites reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals extracted from Posidonia Oceanica. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 121, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedstrom, L. Serine Protease Mechanism and Specificity. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4501–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattanasuttichonlakul, W.; Sombatsompop, N.; Prapagdee, B. Accelerating biodegradation of PLA using microbial consortium from dairy wastewater sludge combined with PLA-degrading bacterium. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 132, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwan, P.; Wu, D.Y. New Insights into Polylactide Biodegradation from Molecular Ecological Techniques. Macromol. Biosci. 2008, 8, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorpade, V.M.; Gennadios, A.; Hanna, M.A. Laboratory composting of extruded poly(lactic acid) sheets. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 76, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, N.K.; Bhasney, S.M.; Mudenur, C.; Kalamdhad, A.; Katiyar, V. End-of-life evaluation and biodegradation of Poly(lactic acid) (PLA)/Polycaprolactone (PCL)/Microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) polyblends under composting conditions. Chemosphere 2020, 247, 125875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajalakshmi, S.; Abbasi, S.A. Solid Waste Management by Composting: State of the Art. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 38, 311–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooperband, L.R. Composting: Art and Science of Organic Waste Conversion to a Valuable Soil Resource. Lab. Med. 2000, 31, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Liu, X.; Gu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Tan, H.; Zhang, Y. Microstructure analysis of polylactic acid-based composites during degradation in soil. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 122, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.-L.G.; Iii, A.L.P.; Gadea-Rivas, A.; Briceño, J.A.; Rojas, A. Degradation of Polylactic Acid (PLA) Plastic in Costa Rican Soil and Iowa State University Compost Rows. J. Polym. Environ. 1999, 7, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanlioglu, M.; Robson, G.D. The influence of biotic and abiotic factors on the rate of degradation of poly(lactic) acid (PLA) coupons buried in compost and soil. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 2063–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calmon, A.; Guillaume, S.; Bellon-Maurel, V.; Feuilloley, P.; Silvestre, F. Evaluation of Material Biodegradability in Real Conditions–Development of a Burial Test and an Analysis Methodology Based on Numerical Vision. J. Polym. Environ. 1999, 7, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanlioglu, M.; Houlden, A.; Robson, G.D. Isolation and characterisation of fungal communities associated with degradation and growth on the surface of poly(lactic) acid (PLA) in soil and compost. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 95, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shogren, R.; Doane, W.; Garlotta, D.; Lawton, J.; Willett, J. Biodegradation of starch/polylactic acid/poly(hydroxyester-ether) composite bars in soil. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2003, 79, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolstad, J.J.; Vink, E.T.; De Wilde, B.; Debeer, L. Assessment of anaerobic degradation of Ingeo™ polylactides under accelerated landfill conditions. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnik, E.; Briassoulis, D. Comparative Biodegradation in Soil Behaviour of two Biodegradable Polymers Based on Renewable Resources. J. Polym. Environ. 2011, 19, 18–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasile, C.; Pamfil, D.; Râpă, M.; Darie-Niţă, R.N.; Mitelut, A.C.; Popa, E.E.; Popescu, P.A.; Draghici, M.C.; Popa, M.E. Study of the soil burial degradation of some PLA/CS biocomposites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 142, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santonja-Blasco, L.; Moriana, R.; Badía, J.; Ribes-Greus, A. Thermal analysis applied to the characterization of degradation in soil of polylactide: I. Calorimetric and viscoelastic analyses. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 2185–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.-X.; Jin, Y.-J.; Meng, Q.-Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.-Z. Biodegradation behavior of poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT), poly(lactic acid) (PLA), and their blend under soil conditions. Polym. Test. 2013, 32, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itävaara, M.; Karjomaa, S.; Selin, J.-F. Biodegradation of polylactide in aerobic and anaerobic thermophilic conditions. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musioł, M.; Sikorska, W.; Adamus, G.; Janeczek, H.; Richert, J.; Malinowski, R.; Jiang, G.; Kowalczuk, M. Forensic engineering of advanced polymeric materials. Part III—Biodegradation of thermoformed rigid PLA packaging under industrial composting conditions. Waste Manag. 2016, 52, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deroiné, M.; le Duigou, A.; Corre, Y.-M.; le Gac, P.-Y.; Davies, P.; César, G.; Bruzaud, S. Accelerated ageing of polylactide in aqueous environments: Comparative study between distilled water and seawater. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 108, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Duigou, A.; Davies, P.; Baley, C. Seawater ageing of flax/poly(lactic acid) biocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2009, 94, 1151–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Suzuyoshi, K. Environmental degradation of biodegradable polyesters 1. Poly(ε-caprolactone), poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], and poly(L-lactide) films in controlled static seawater. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2002, 75, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Suzuyoshi, K. Environmental degradation of biodegradable polyesters 2. Poly(ε-caprolactone), poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], and poly(L-lactide) films in natural dynamic seawater. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2002, 75, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, K.; Tabuani, D.; Dottori, M.; Armentano, I.; Kenny, J.; Camino, G. Effect of temperature and nanoparticle type on hydrolytic degradation of poly(lactic acid) nanocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 2120–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brebu, M. Environmental Degradation of Plastic Composites with Natural Fillers—A Review. Polymer 2020, 12, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, M.-P.; Lau, K.-T.; Wang, H.; Hui, D. Improvement on the properties of polylactic acid (PLA) using bamboo charcoal particles. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 81, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegyesi, N.; Zhang, Y.; Kohári, A.; Polyák, P.; Sui, X.; Pukánszky, B. Enzymatic degradation of PLA/cellulose nanocrystal composites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 141, 111799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaguer, M.P.; Aliaga, C.; Fito, C.; Hortal, M. Compostability assessment of nano-reinforced poly(lactic acid) films. Waste Manag. 2016, 48, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.S.; Bousmina, M. Biodegradable polymers and their layered silicate nanocomposites: In greening the 21st century materials world. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2005, 50, 962–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, K.; Abbate, C.; Tabuani, D.; Gennari, M.; Camino, G. Biodegradation of poly(lactic acid) and its nanocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2009, 94, 1646–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neppalli, R.; Causin, V.; Marega, C.; Modesti, M.; Adhikari, R.; Scholtyssek, S.; Ray, S.S.; Marigo, A. The effect of different clays on the structure, morphology and degradation behavior of poly(lactic acid). Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 87, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stloukal, P.; Pekařová, S.; Kalendova, A.; Mattausch, H.; Laske, S.; Holzer, C.; Chitu, L.; Bodner, S.; Maier, G.; Slouf, M.; et al. Kinetics and mechanism of the biodegradation of PLA/clay nanocomposites during thermophilic phase of composting process. Waste Manag. 2015, 42, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Xie, Y.-N.; Yang, J.-H.; Huang, T.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.-H. Graphene oxide induced hydrolytic degradation behavior changes of poly(l-lactide) in different mediums. Polym. Test. 2016, 56, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anžlovar, A.; Kržan, A.; Žagar, E. Degradation of PLA/ZnO and PHBV/ZnO composites prepared by melt processing. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Xue, B.; Yang, S.; Huo, K.; Liao, X.; Li, X.; Xie, L.; Qin, S.; Zheng, Q. Structural conversion of PLLA/ZnO composites facilitated by interfacial crystallization to potential application in oil-water separation. Appl. Surface Sci. 2020, 517, 146135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-J.; Huang, Z.; Wei, M.-Y.; Lu, T.; Nong, D.-D.; Zhao, J.-X.; Gao, X.-Y.; Teng, L.-J. Catalytic effect of nanosized ZnO and TiO2 on thermal degradation of poly(lactic acid) and isoconversional kinetic analysis. Thermochim. Acta 2019, 672, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, N.; Hayashi, T. Preparation and characterization of poly(l-lactic acid)/TiO2 nanoparticle nanocomposite films with high transparency and efficient photodegradability. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaseem, M.; Hamad, K.; Rehman, Z.U. Review of Recent Advances in Polylactic Acid/TiO2 Composites. Materials 2019, 12, 3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Lin, Z.; Guo, G. Biodegradation Assessment of Poly (Lactic Acid) Filled with Functionalized Titania Nanoparticles (PLA/TiO2) under Compost Conditions. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.-B.; Wang, X.-L.; Wang, Y.-Z. Effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on the long-term hydrolytic degradation behavior of PLA. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Nishida, H.; Mori, T.; Shirai, Y.; Endo, T. Thermal degradation of poly(l-lactide): Effect of alkali earth metal oxides for selective l,l-lactide formation. Polymer 2004, 45, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, J.; Tan, H. Biodegradation behavior and modelling of soil burial effect on degradation rate of PLA blended with starch and wood flour. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2017, 159, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, C.A.; Tofanello, A.; Nantes, I.L.; Rosa, D.S. Biological Oxidative Mechanisms for Degradation of Poly(lactic acid) Blended with Thermoplastic Starch. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2756–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petinakis, E.; Liu, X.; Yu, L.; Way, C.; Sangwan, P.; Dean, K.; Bateman, S.; Edward, G. Biodegradation and thermal decomposition of poly(lactic acid)-based materials reinforced by hydrophilic fillers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 1704–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.F.; Gu, J.; Qiao, Z.; Tan, H.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y. Effects of dry method esterification of starch on the degradation characteristics of starch/polylactic acid composites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, R.; Misra, M.; Erickson, L.; Mohanty, A. Compostability and biodegradation study of PLA–wheat straw and PLA–soy straw based green composites in simulated composting bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8489–8491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iovino, R.; Zullo, R.; Rao, M.; Cassar, L.; Gianfreda, L. Biodegradation of poly(lactic acid)/starch/coir biocomposites under controlled composting conditions. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoda, H.; Asou, Y.; Kashima, T.; Kato, T.; Tseng, Y.; Yagi, T. Amphiphilic biodegradable copolymer, poly(aspartic acid-co-lactide): Acceleration of degradation rate and improvement of thermal stability for poly(lactic acid), poly(butylene succinate) and poly(ε-caprolactone). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2003, 80, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höglund, A.; Hakkarainen, M.; Edlund, U.; Albertsson, A.-C. Surface Modification Changes the Degradation Process and Degradation Product Pattern of Polylactide. Langmuir 2010, 26, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Microorganism | Representative Species | Enzyme | Temperature of Digestion (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Actinomycetes | Amycolotopsis strain K104-1 | Protease | 55–60 |
| Amycolotopsis strain 41 | 37–45 | ||
| Amycolotopsis strain orientalis | 30 | ||
| Actinomadura strain T16-1 | 70 | ||
| Bacteria | Bacillus smithii strain PL21 | Esterase | 60 |
| Alcanivorax borkumenesis ABO2449 | 30–37 | ||
| Rhodopseudomonas palustris RPA1511 | 55–60 | ||
| Paenibacillus amylolyticus strain TB-13 | Lipase | 50 | |
| Alcaligenes sp. | 55 | ||
| Pseudomonas tamsuii TKU015 | 60 | ||
| Fungus | Tritirachium album ATCC 22563 | Protease | 37 |
| Cryptococcus sp. strain S-2 | Cutinase | 37 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teixeira, S.; Eblagon, K.M.; Miranda, F.; R. Pereira, M.F.; Figueiredo, J.L. Towards Controlled Degradation of Poly(lactic) Acid in Technical Applications. C 2021, 7, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/c7020042
Teixeira S, Eblagon KM, Miranda F, R. Pereira MF, Figueiredo JL. Towards Controlled Degradation of Poly(lactic) Acid in Technical Applications. C. 2021; 7(2):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/c7020042
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeixeira, Stefanie, Katarzyna Morawa Eblagon, Filipa Miranda, M. Fernando R. Pereira, and José Luis Figueiredo. 2021. "Towards Controlled Degradation of Poly(lactic) Acid in Technical Applications" C 7, no. 2: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/c7020042
APA StyleTeixeira, S., Eblagon, K. M., Miranda, F., R. Pereira, M. F., & Figueiredo, J. L. (2021). Towards Controlled Degradation of Poly(lactic) Acid in Technical Applications. C, 7(2), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/c7020042