Phytosterol Recognition via Rationally Designed Molecularly Imprinted Polymers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Selection of the Molecular Template
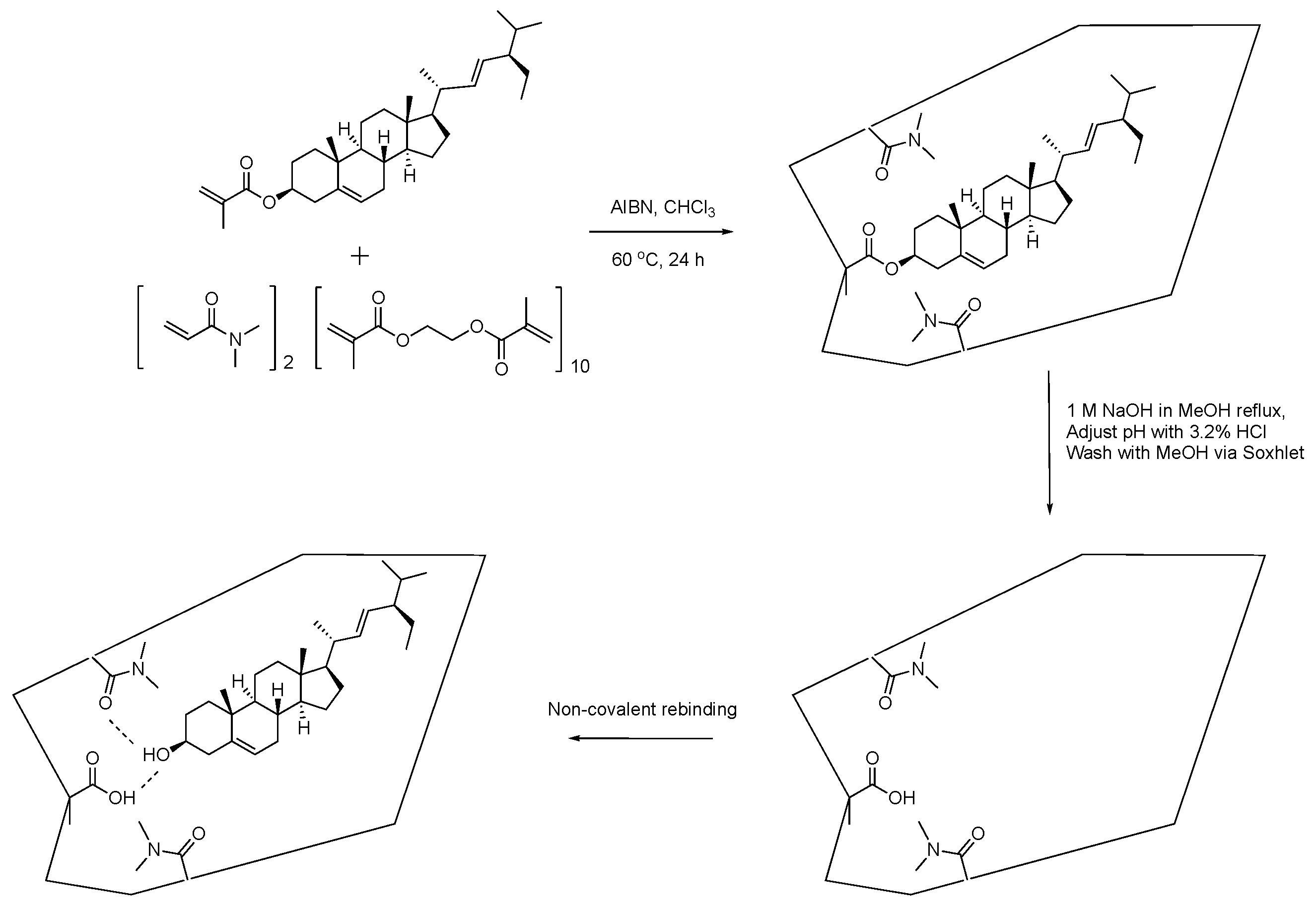
2.2. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Design
2.3. Preparation of the Molecularly Imprinted Polymers
2.4. Evaluation of the Molecularly Imprinted Polymers
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. LC Equipment and Methods
3.2. Molecular Modelling
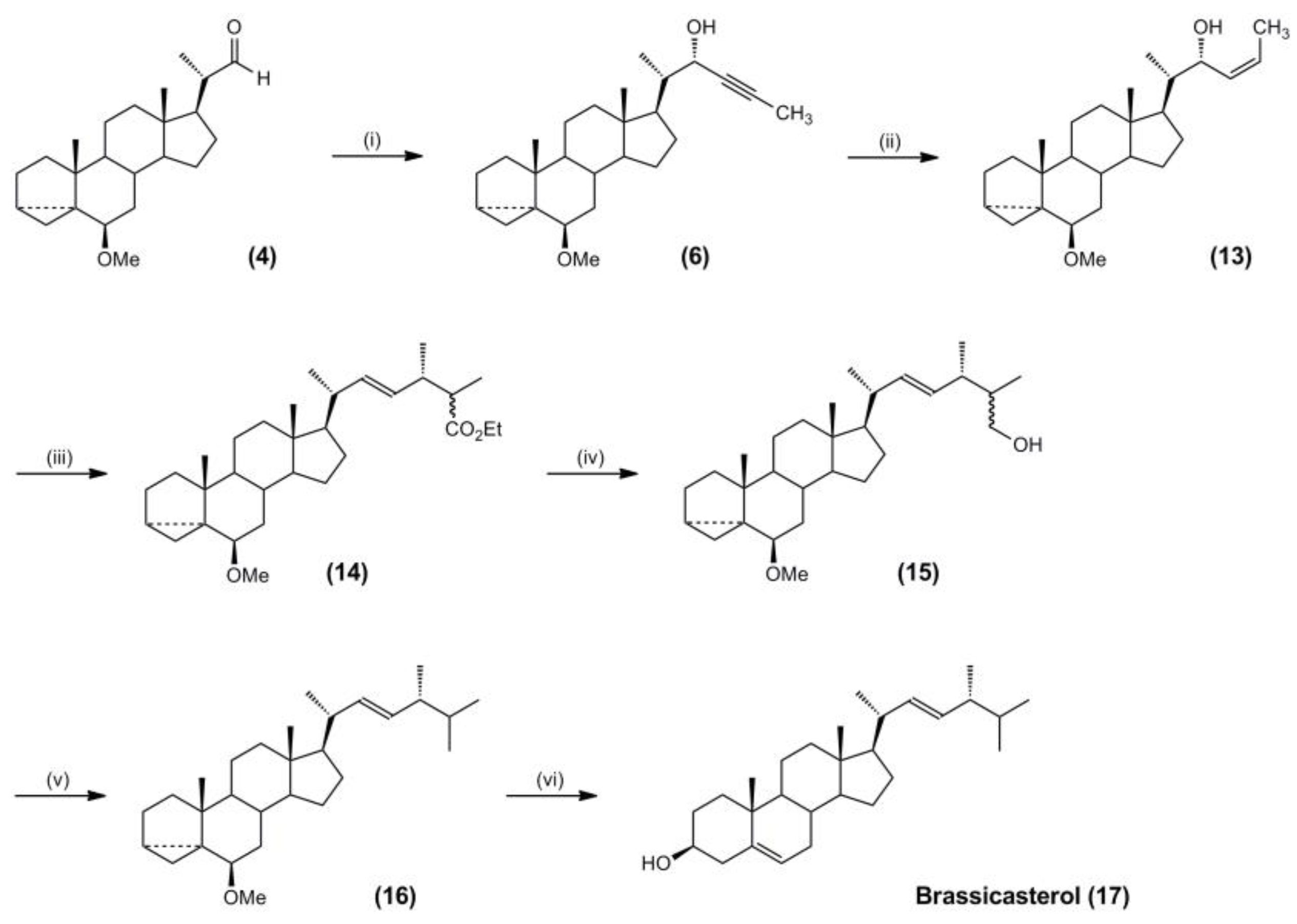
3.3. Synthesis of Molecular Targets and Templates
3.4. Synthesis of Campesterol and Brassicasterol Targets
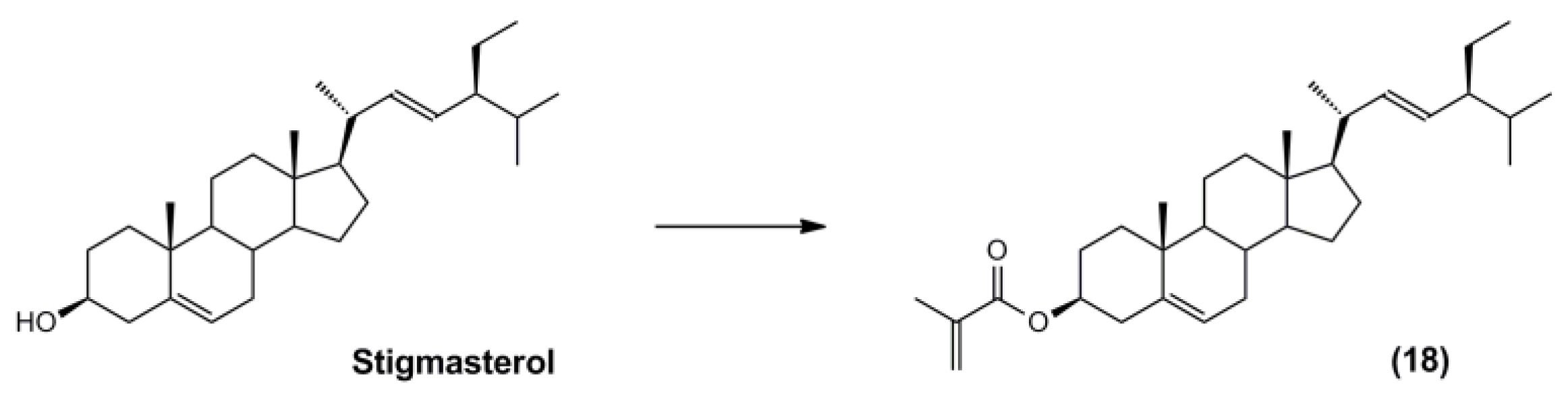
3.5. Synthesis of the Polymerisable Molecular Template
3.6. MIP Preparation
3.7. MIP Batch Binding Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abidi, S.L. Chromatographic analysis of plant sterols in foods and vegetable oils. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 935, 173–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P.; Cabral, J.M.S. Phytosterols: Applications and recovery methods. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 2335–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, M.; Vetter, W. High-speed counter-current chromatographic separation of phytosterols. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 3615–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Wang, H. Optimization of phytosterols recovery from soybean oil deodorizer distillate. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2012, 89, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosello-Soto, E.; Koubaa, M.; Moubarik, A.; Lopes, R.P.; Saraiva, J.A.; Boussetta, N.; Grimi, N.; Barba, F.J. Emerging opportunities for the effective valorization of wastes and by-products generated during olive oil production process: Non-conventional methods for the recovery of high-added value compounds. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.S.; Sarker, M.Z.I.; Ferdosh, S.; Akanda, M.J.H.; Easmin, S.; Bt Shamsudin, S.H.; Yunus, K.B. Phytosterols and their extraction from various plant matrices using supercritical carbon dioxide: A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, W.J.; Yang, S.H.; Ali, F. Molecular imprinted polymers for separation science: A review of reviews. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 609–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, L.J.; Danylec, B.; Harris, S.J.; Boysen, R.I.; Hearn, M.T.W. Sequential molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction methods for the analysis of resveratrol and other polyphenols. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1438, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashim, S.N.N.S.; Schwarz, L.J.; Danylec, B.; Mitri, K.; Yang, Y.; Boysen, R.I.; Hearn, M.T.W. Recovery of ergosterol from the medicinal mushroom, Ganoderma tsugae var. Janniae, with a molecularly imprinted polymer derived from a cleavable monomer-template composite. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1468, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danylec, B.; Schwarz, L.J.; Harris, S.J.; Boysen, R.I.; Hearn, M.T.W. The application of template selectophores for the preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers. Molecules 2015, 20, 17601–17613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickert, F.L.; Hayden, O. Molecular imprinting in chemical sensing. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 1999, 18, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitcombe, M.J.; Kirsch, N.; Nicholls, I.A. Molecular imprinting science and technology: A survey of the literature for the years 2004–2011. J. Mol. Recognit. 2014, 27, 297–401. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boysen, R.I.; Schwarz, L.J.; Nicolau, D.V.; Hearn, M.T.W. Molecularly imprinted polymer membranes and thin films for the separation and sensing of biomacromolecules. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 314–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitcombe, M.J.; Rodriguez, M.E.; Villar, P.; Vulfson, E.N. A new method for the introduction of recognition site functionality into polymers prepared by molecular imprinting: Synthesis and characterisation of polymeric receptors for cholesterol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 7105–7111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellergren, B.; Wieschemeyer, J.; Boos, K.S.; Seidel, D. Imprinted polymers for selective adsorption of cholesterol from gastrointestinal fluids. Chem. Mater. 1998, 10, 4037–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Ahn, K.D.; Wulff, G. Cholesterol esterase activity of a molecularly imprinted polymer. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2001, 202, 1105–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.C.; Lee, W.C. Chromatographic characteristics of cholesterol-imprinted polymers prepared by covalent and non-covalent imprinting methods. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 962, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, M.A.; Karmalkar, R.N.; Kulkarni, M.G. Enhanced capacities and selectivities for cholesterol in aqueous media by molecular imprinting: Role of novel cross-linkers. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 804, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciardelli, G.; Borrelli, C.; Silvestri, D.; Cristallini, C.; Barbani, N.; Giusti, P. Supported imprinted nanospheres for the selective recognition of cholesterol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 2329–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puoci, F.; Curcio, M.; Cirillo, G.; Iemma, F.; Spizzirri, U.G.; Picci, N. Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction for cholesterol determination in cheese products. Food Chem. 2008, 106, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaei, A.; Milani Hosseini, M.R.; Najafi, M. A novel capacitive biosensor for cholesterol assay that uses an electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymer. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 1503–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitahara, K.I.; Yoshihama, I.; Hanada, T.; Kokuba, H.; Arai, S. Synthesis of monodispersed molecularly imprinted polymer particles for high-performance liquid chromatographic separation of cholesterol using templating polymerization in porous silica gel bound with cholesterol molecules on its surface. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 7249–7254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, S.; Chen, L.; Zhou, N.; Xiong, H.; Peng, H. Label-free colorimetric detection of trace cholesterol based on molecularly imprinted photonic hydrogels. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 19267–19274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Weiss, R.; Mosbach, K. Synthesis and characterization of molecularly imprinted microspheres. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 8239–8245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Yu, Y.H.; Mosbach, K. Towards the development of molecularly imprinted artificial receptors for the screening of estrogenic chemicals. Analyst 2001, 126, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szumski, M.; Buszewski, B. Molecularly imprinted polymers: A new tool for separation of steroid isomers. J. Sep. Sci. 2004, 27, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Wang, L.; Wu, S.; Joseph, W.; Gu, X.; Tang, J. Selectivity of molecularly imprinted solid phase extraction for sterol compounds. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, S.N.N.S.; Boysen, R.I.; Schwarz, L.J.; Danylec, B.; Hearn, M.T.W. A comparison of covalent and non-covalent imprinting strategies for the synthesis of stigmasterol imprinted polymers. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1359, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boysen, R.I.; Schwarz, L.J.; Li, S.; Chowdhury, J.; Hearn, M.T.W. Photolithographic patterning of biomimetic molecularly imprinted polymer thin films onto silicon wafers. Microsyst. Technol. 2014, 20, 2037–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.K.; Ryoo, C.H.; Yang, H.W.; Shim, J.Y.; Kang, M.G.; Lee, K.W.; Kang, H.I. Synthesis and bioactivities of steroid derivatives as antifungal agents. Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 15899–15914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, Y.; Kimura, M.; Khalifa, F.A.M.; Ikekawa, N. Side chain structural requirement for utilization of sterols by the silkworm for growth and development. Non-stereoselective utilization of the 24-stereoisomeric pairs of 24-alkylsterols. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1984, 32, 4372–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, R.F.N.; Thompson, M.J.; Svoboda, J.A. The synthesis and the mass and nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of side chain isomers of cholesta-5,22-dien-3β-ol and cholesta-5,22,24-trien-3β-ol. Steroids 1970, 15, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, J.J.; Faber, S.; Uskoković, M.R. Vitamin D3 metabolites I. Synthesis of 25-hydroxycholesterol. Helv. Chim. Acta 1974, 57, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, J.A.; Mosettig, E. The solvolysis of stigmasteryl tosylate. J. Org. Chem. 1963, 28, 571–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

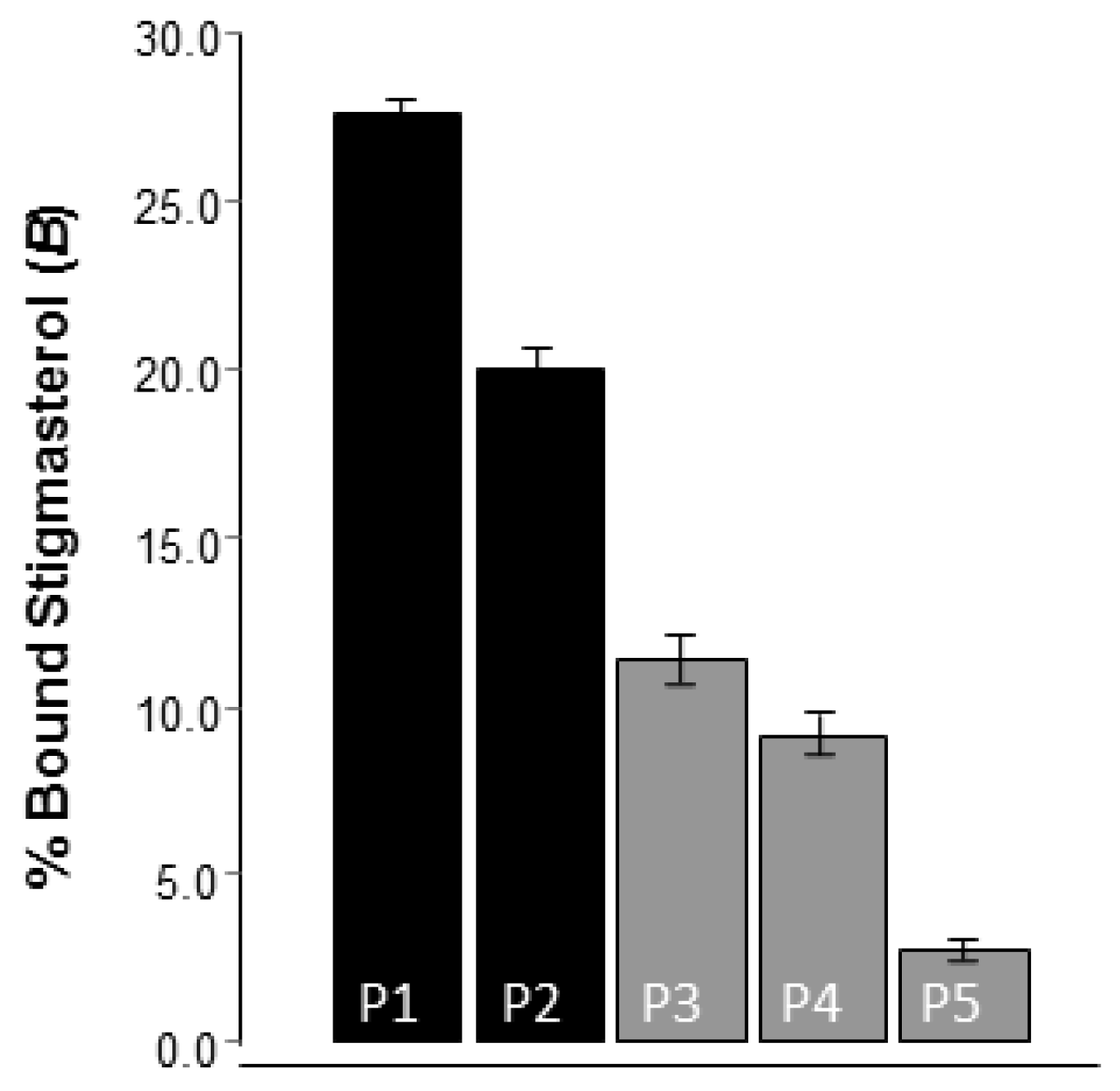
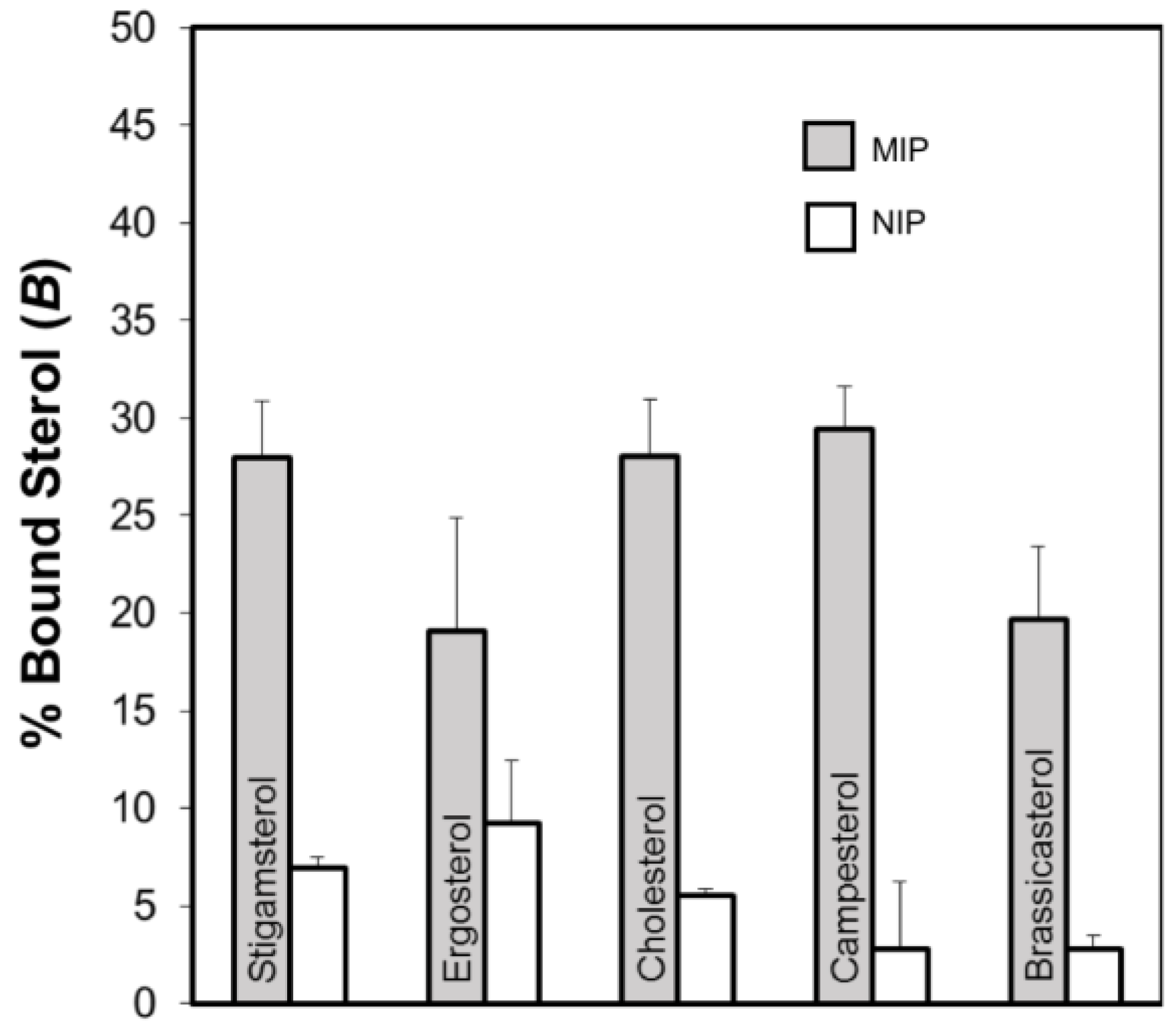
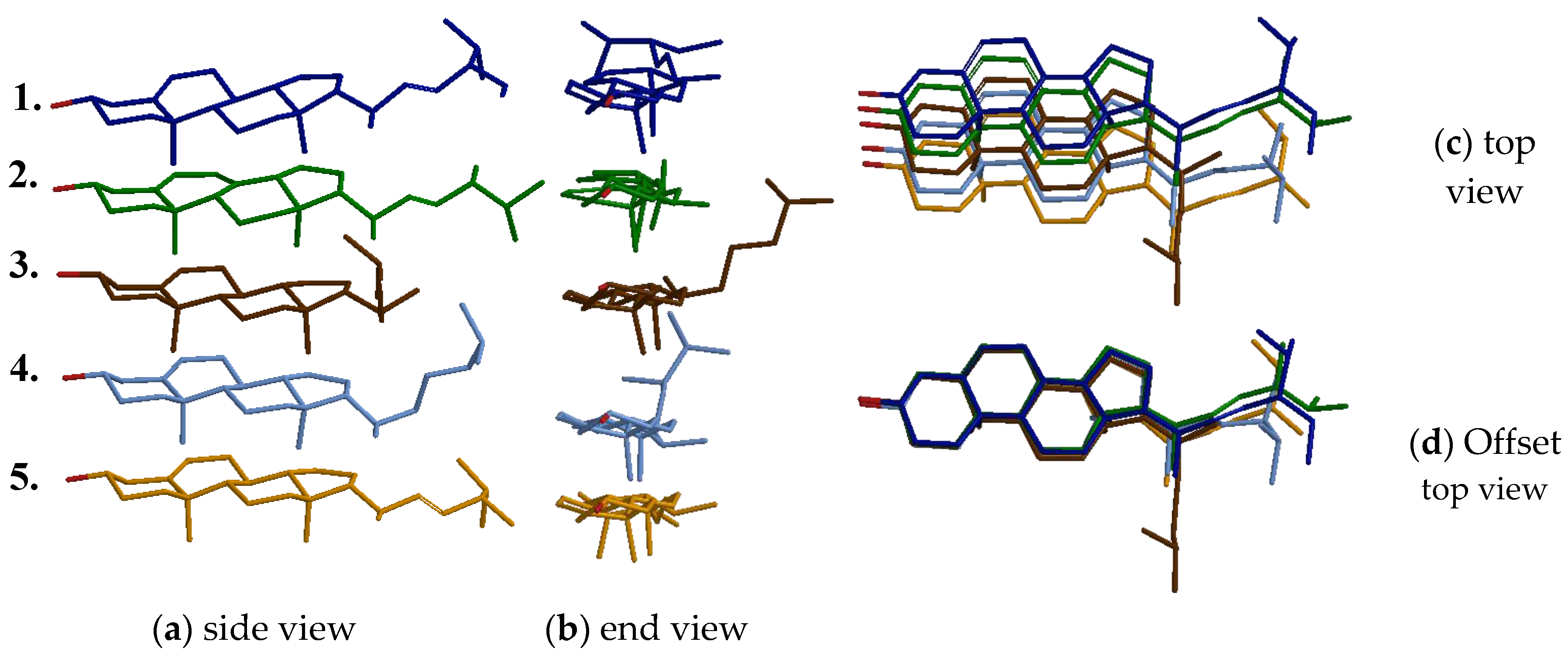
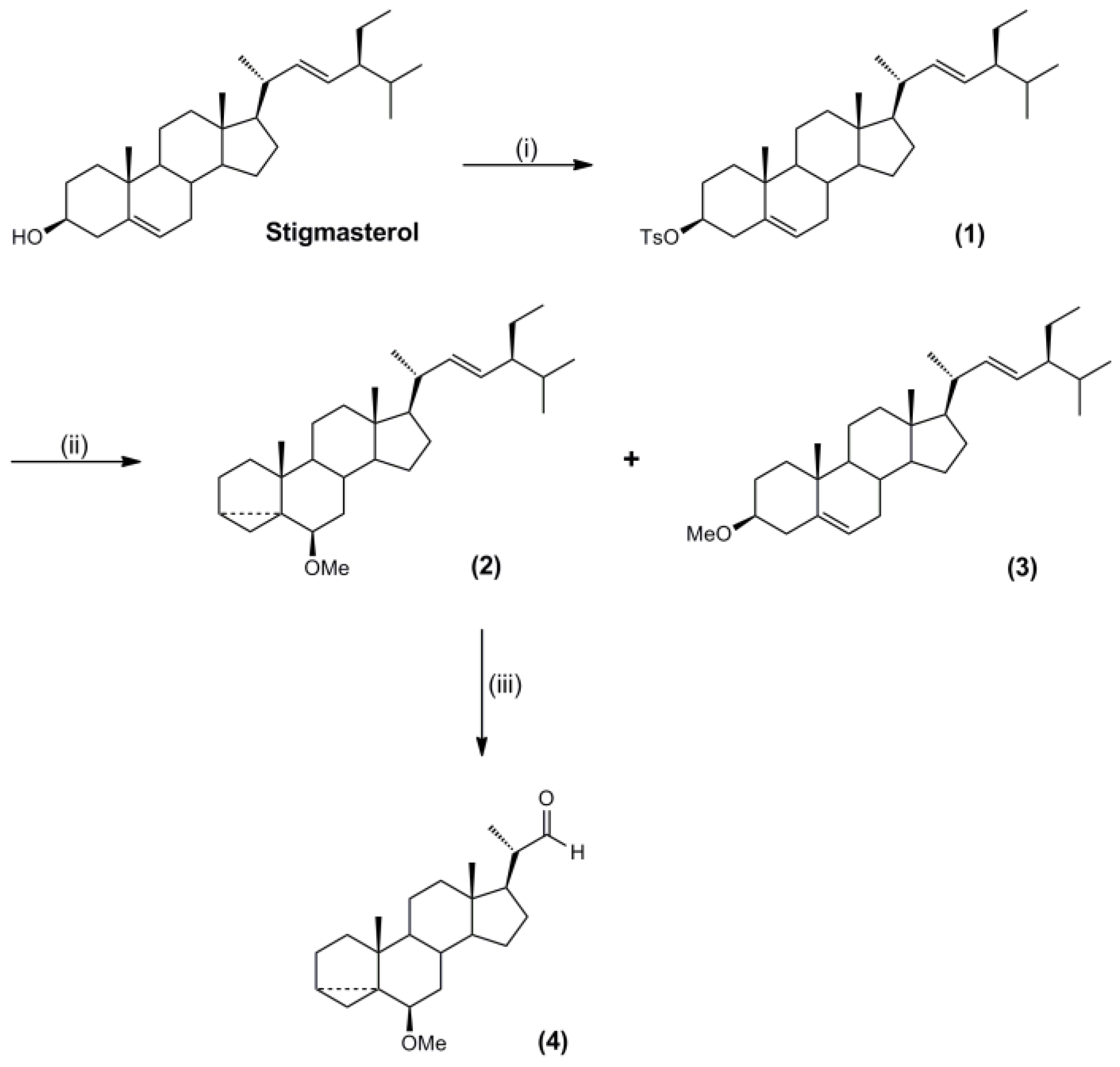

| Polymer Code | Template (mmol) | DMAAM (FM) (mmol) | MAA (FM) (mmol) | EGDMA (Cross-Linker) (mmol) | Porogen (6 mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 1 | 2 | - | 10 | CHCl3 |
| P2 | 1 | - | - | 10 | CHCl3 |
| P3 | - | 2 | - | 10 | CHCl3 |
| P4 | - | - | 2 | 10 | CHCl3 |
| P5 | - | - | - | 10 | CHCl3 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schwarz, L.J.; Leung, B.K.Y.; Danylec, B.; Harris, S.J.; Boysen, R.I.; Hearn, M.T.W. Phytosterol Recognition via Rationally Designed Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. C 2018, 4, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/c4010013
Schwarz LJ, Leung BKY, Danylec B, Harris SJ, Boysen RI, Hearn MTW. Phytosterol Recognition via Rationally Designed Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. C. 2018; 4(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/c4010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchwarz, Lachlan J., Brenda K. Y. Leung, Basil Danylec, Simon J. Harris, Reinhard I. Boysen, and Milton T. W. Hearn. 2018. "Phytosterol Recognition via Rationally Designed Molecularly Imprinted Polymers" C 4, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/c4010013
APA StyleSchwarz, L. J., Leung, B. K. Y., Danylec, B., Harris, S. J., Boysen, R. I., & Hearn, M. T. W. (2018). Phytosterol Recognition via Rationally Designed Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. C, 4(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/c4010013







