N, S-Doped Carbon Dots (N, S-CDs) for Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid (PFOS) Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Methods
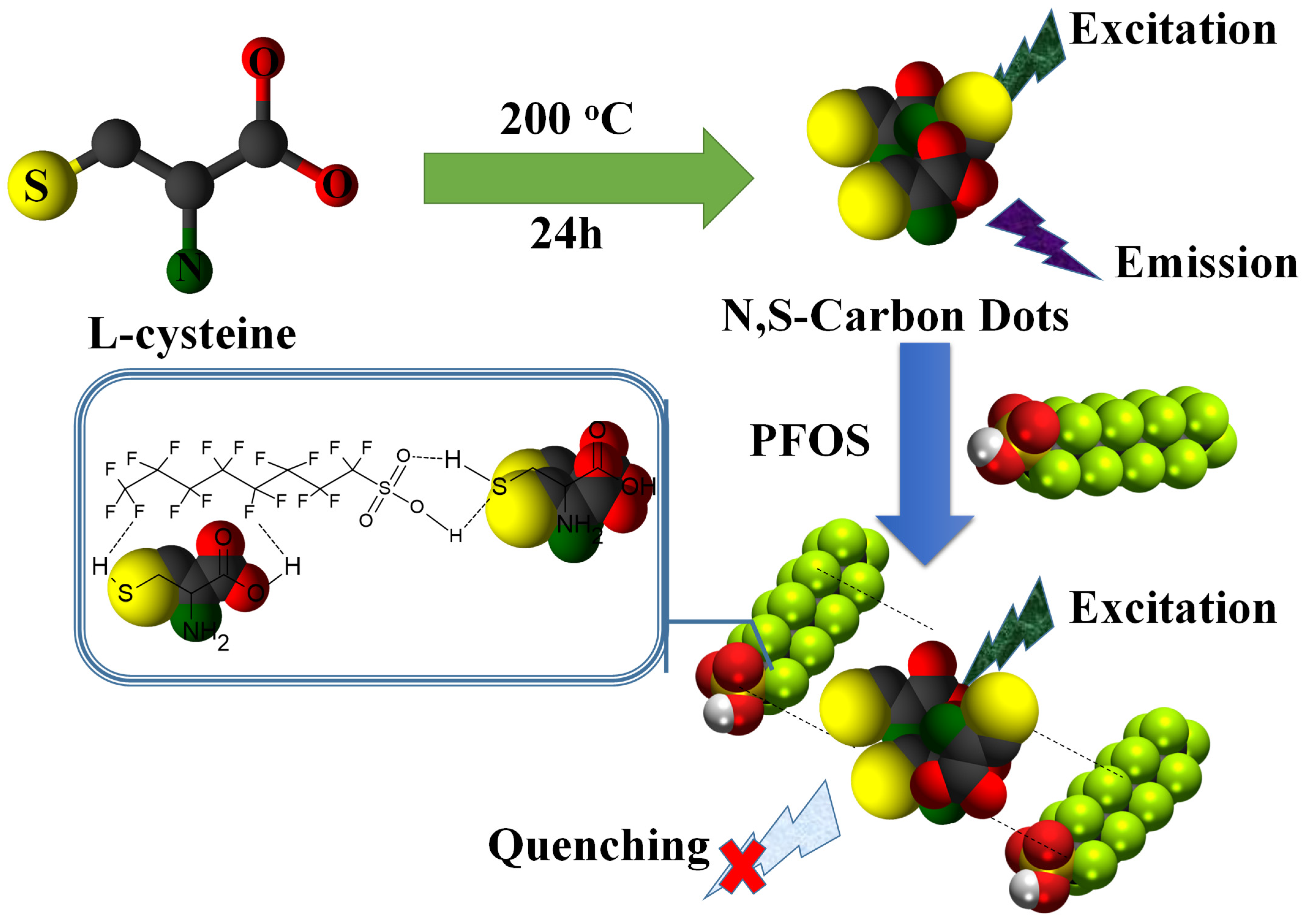
2.2. Synthesis of N, S-Doped CDs
2.3. Characterization Instruments
2.4. Fluorescence Measurements
2.5. UV-Vis Spectroscopy
3. Results and Discussion
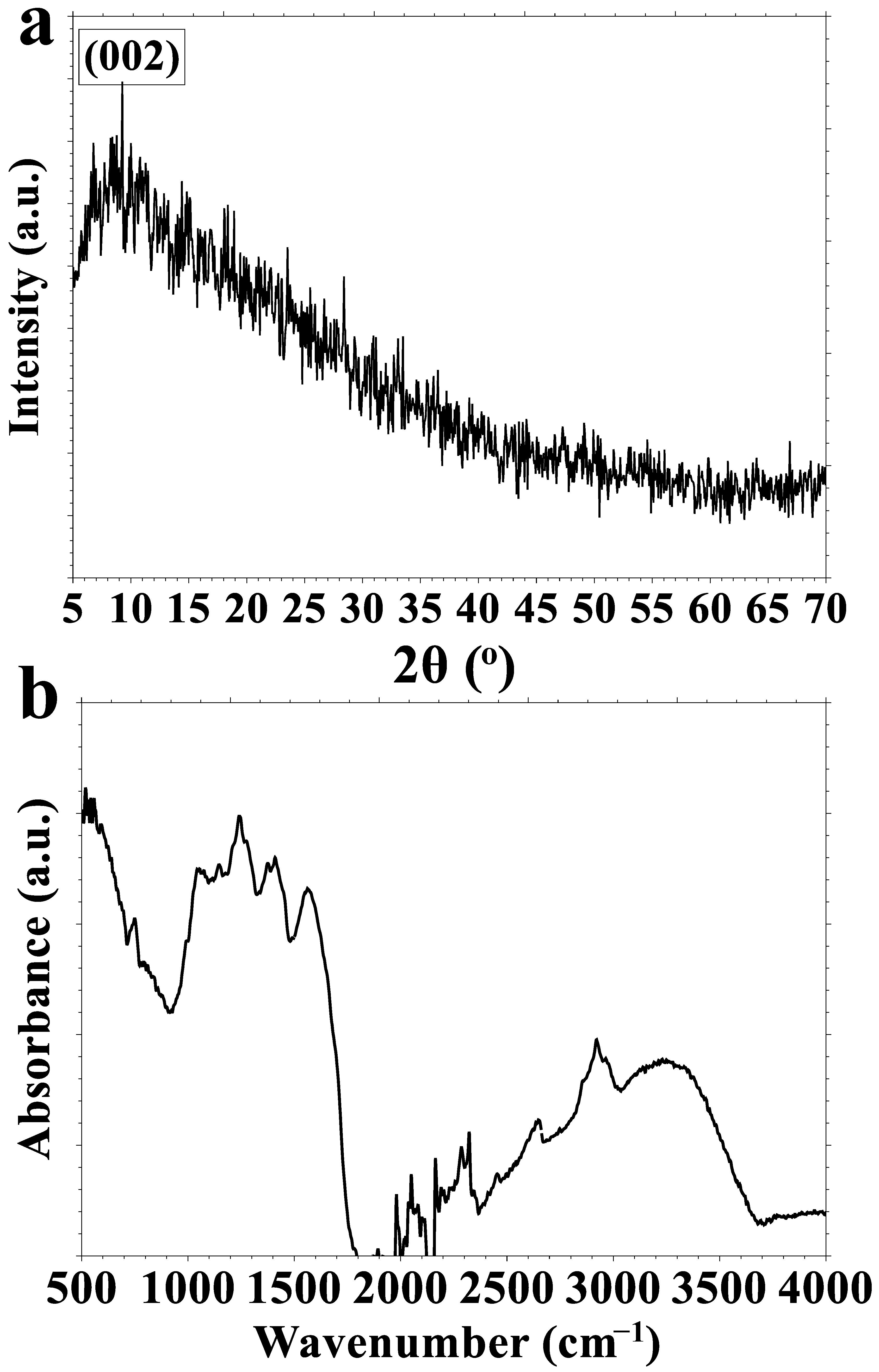
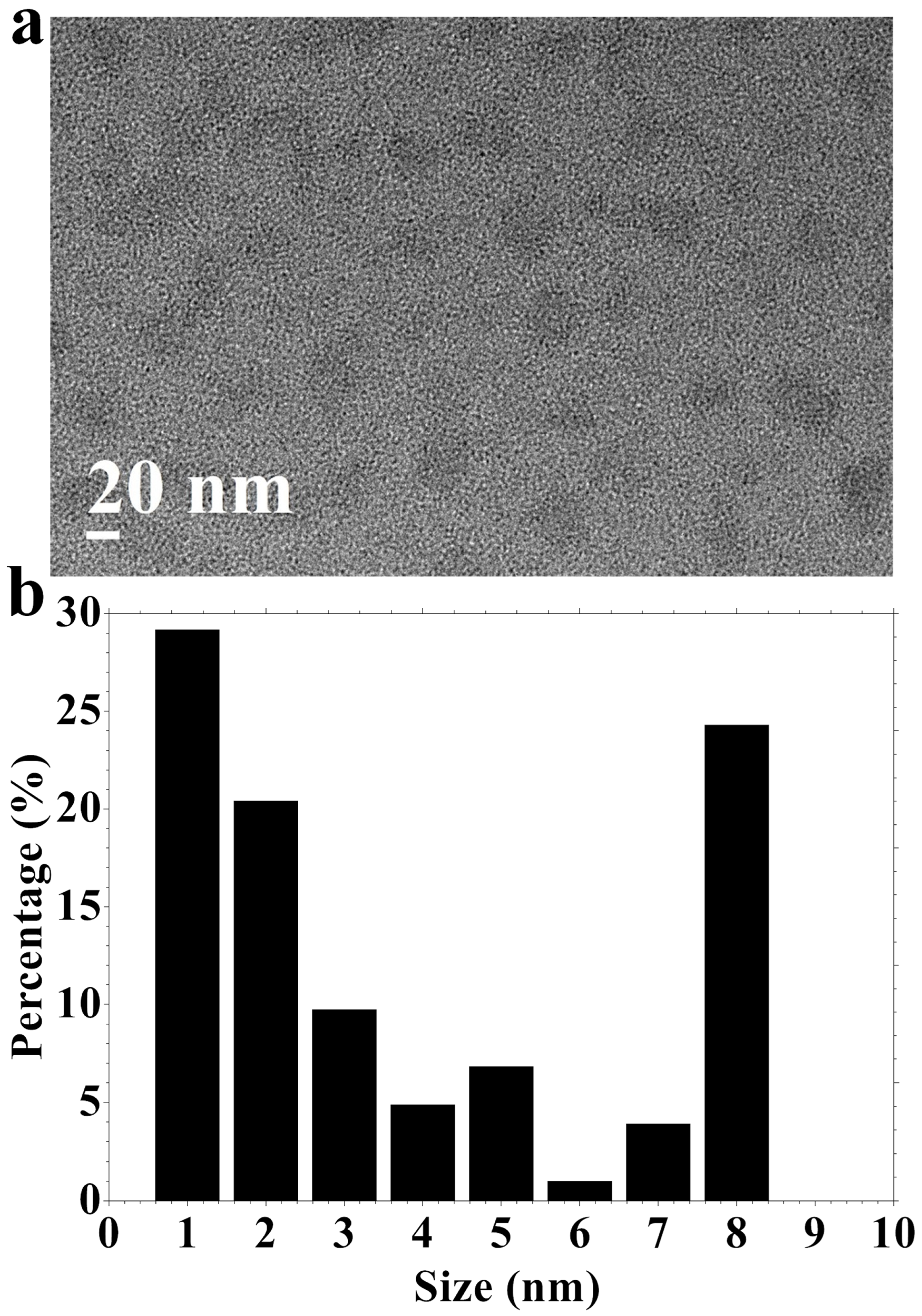
3.1. N, S-CDs Synthesis and Characterization
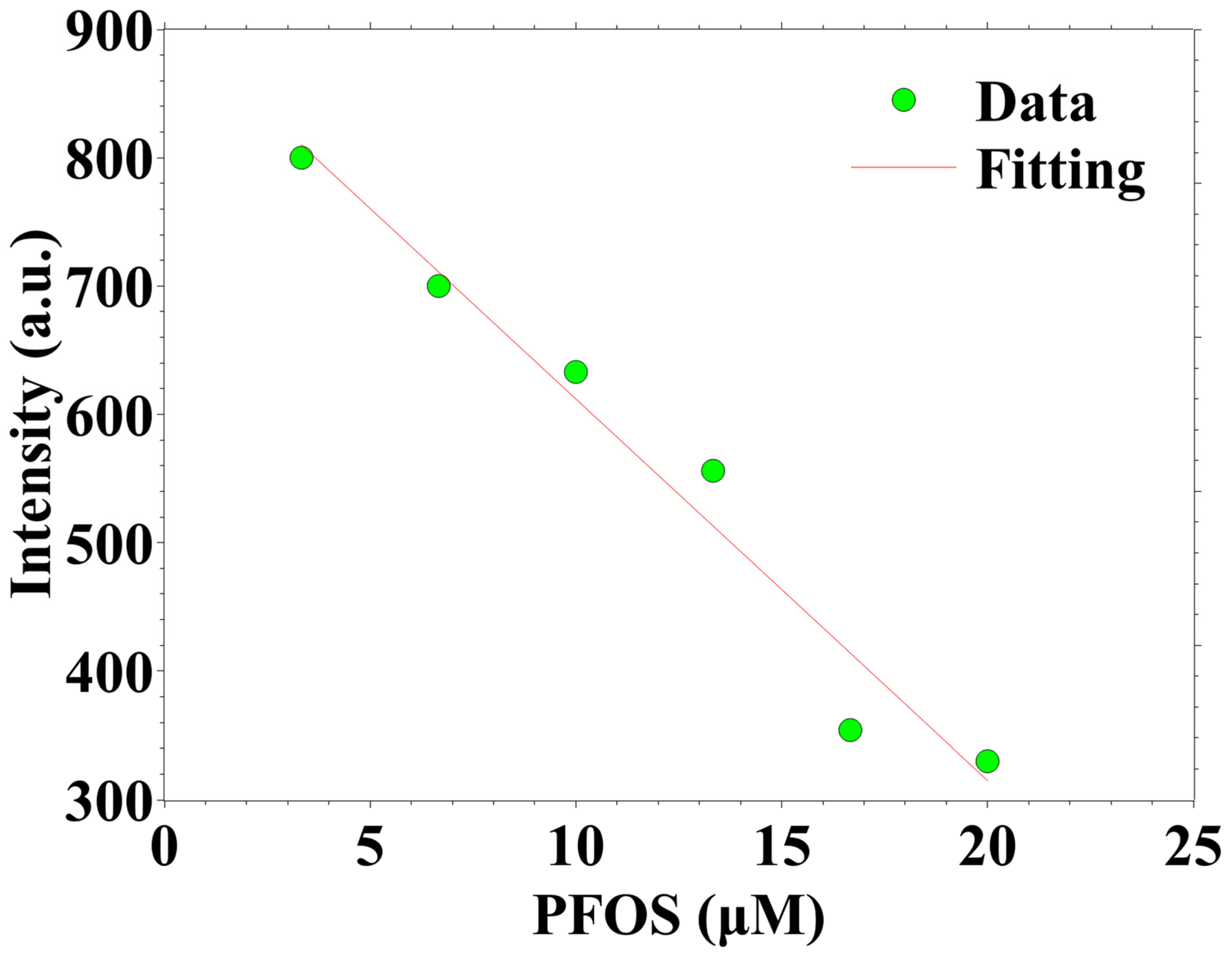
3.2. Analysis of PFOS
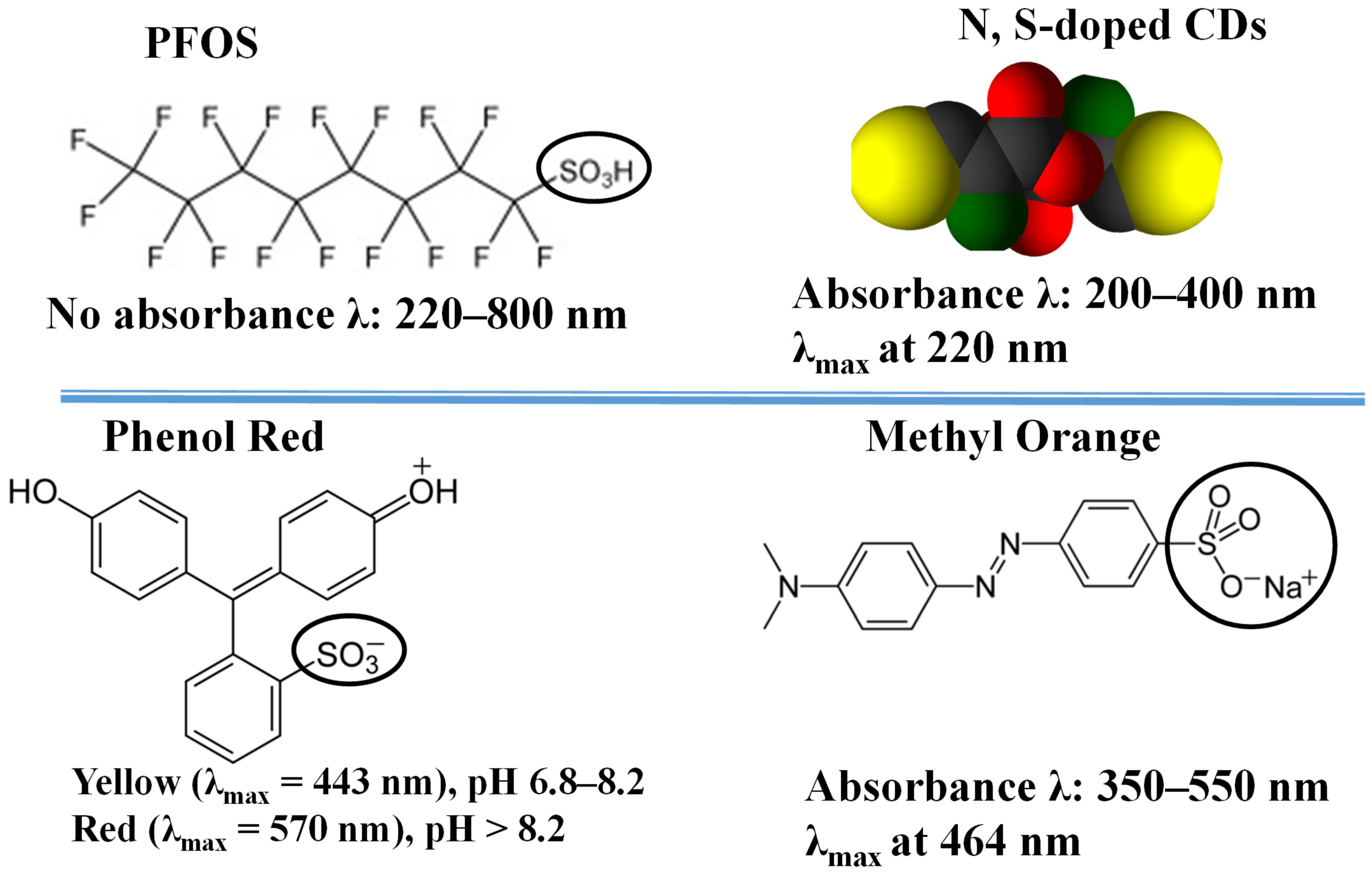
3.3. Mechanism of Interaction and Sensing: Dye-CD Interactions
| Materials | Method | LOD | Linear Range | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic dyes MBD SF | Electrochemical Fluorescence Colorimetric | 0.08 μM 0.64 μM 0.03 μM | 0.1–15 μM (MBD) 0.75–20 (SF) | [13] |
| Fe/Zn-BDC | Colorimetric | 100 nM | 0–75 μM | [18] |
| Molecular Nanocages | Fluorescence | 0.105 nM | 0–20 µM | [59] |
| M1-EB | 2.7–4.65 μM | 0–40 µM | [62] | |
| CQDs | 18.27 nM | 0–12 µM | [63] | |
| CQDs | 5 nM | 0.05–1.0 μM | [64] | |
| EB/N-CDs | 27.8 nM | 0–2.0 μM | [66] | |
| BH/CD | 21.7 nM | 0.22–50.0 μM | [67] | |
| CDs | 2 μM | 3–20 µM | Here |
4. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Dong, H.; Li, J. Reproductive toxicity of PFOA, PFOS and their substitutes: A review based on epidemiological and toxicological evidence. Environ. Res. 2024, 250, 118485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.; Yin, R.; Wang, J.; You, M.; Wang, N.; Wong, Y.J.; Xiao, T. Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) in the Surface Waters of China: A Meta-Analysis. Water 2025, 17, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Hao, G.; Zhou, D.; Fan, Y.; Wei, Z.; Li, D.; Shen, Y.; Fang, H.; Lin, F.; Zhao, M.; et al. Hepatotoxicity in Carp (Carassius auratus) Exposed to Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS): Integrative Histopathology and Transcriptomics Analysis. Animals 2025, 15, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, A.U.; Crimi, M.; Andreescu, S. Current and emerging analytical techniques for the determination of PFAS in environmental samples. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2023, 37, e00198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, K.; Zulkarnain, N.A.; Niven, R.K. A Review of Analytical Methods and Technologies for Monitoring Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Water. Water 2023, 15, 3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, T.; Shingu, A.; Kato, S.; Nagatomo, R.; Tsutsumi, T.; Inoue, K. Countermeasure for interfered monitoring ion of perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) from intrinsic food samples based on LC-MS/MS analysis of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 133, 106436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menger, R.F.; Funk, E.; Henry, C.S.; Borch, T. Sensors for detecting per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): A critical review of development challenges, current sensors, and commercialization obstacles. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 129133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Amin, M.; Sobhani, Z.; Liu, Y.; Dharmaraja, R.; Chadalavada, S.; Naidu, R.; Chalker, J.M.; Fang, C. Recent advances in the analysis of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)—A review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 100879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Bui, B.; Tang, L.; Xue, J.; Chen, M.; Chen, W. The Latest Sensor Detection Methods for per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2025, 55, 542–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Darling, S.B.; Chen, J. Selectivity of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Sensors and Sorbents in Water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 60789–60814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Li, B.; De Guise, S.; McCutcheon, J.; Lei, Y. Recent progress in the detection of emerging contaminants PFASs. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, S.; Kumar, P.; Greene, G.W.; Mishra, V.; Avisar, D.; Sharma, R.S.; Dumée, L.F. Nano-enabled sensing of per-/poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from aqueous systems—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 308, 114655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, A.U.; Locke, E.; Andreescu, S. Spectroelectrochemical investigation of the interaction of perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) with organic dyes. Microchem. J. 2025, 209, 112683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Jin, X.; Chau, C.V.; Yang, J.; Henkelman, G.; Chi, X.; Gong, H.; Hooley, R.J.; Sessler, J.L. Readily Visualized Perfluorooctanoic Acid Detection Using a Small Molecule Chemosensor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202501245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; An, Z.; Zhang, B.; Hong, W.; Ye, C.; Li, M.; Guo, L.-H. Colorimetric visualization detection of perfluorooctanoic acid based on host–guest interactions with cyclodextrin-modified gold nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Nano 2025, 12, 1581–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Cheng, C.; Qin, X.; Wang, Y. β-cyclodextrin imprinted film embedded with methylene blue: A host-guest sensitive electrochemical strategy for PFAS detection. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 485, 136870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hussain, S.; Tang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Gao, R.; Wang, S.; Hao, Y. Two-in-one platform based on conjugated polymer for ultrasensitive ratiometric detection and efficient removal of perfluoroalkyl substances from environmental water. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Tong, Y.-J.; Zou, X.; Zheng, X.; Gong, Z. Tailoring the Coordination Environment of Fe/Zn-BDC to Boost Peroxidase-like Activity for Highly Selective Detection of PFOS. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 4673–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalapati, R.; Hunter, M.; SK, M.; Yang, X.; Zang, L. Fluorescence Turn-on Detection of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) by Perylene Diimide-Based Metal–Organic Framework. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 32344–32356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Zhu, D.Z.; Gan, H.; Yao, Z.; Luo, J.; Yu, S.; Kurup, P. An ultra-sensitive molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) and gold nanostars (AuNS) modified voltammetric sensor for facile detection of perfluorooctance sulfonate (PFOS) in drinking water. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 352, 131055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Luo, R.; Yang, D.; Gao, Y.; Chen, X.; Xu, L.; Hu, X. A sustainable photoelectrochemical sensing platform for effective detection of perfluorooctane sulfonate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2025, 426, 137095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, G.R.; Venelinov, T.; Marinov, Y.G.; Hadjichristov, G.B.; Terfort, A.; David, M.; Florescu, M.; Karakuş, S. First Direct Gravimetric Detection of Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid (PFOS) Water Contaminants, Combination with Electrical Measurements on the Same Device—Proof of Concepts. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yin, Q.; Du, N.; Yi, Y.; Zhu, G. An innovative homogeneous electrochemistry coupled with colorimetry dual-model sensing strategy for perfluorooctane sulfonate based on Cu@CuO aerogel nanozyme. Microchim. Acta 2024, 191, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Uygun, Z.O.; Andreescu, D.; Andreescu, S. Sensitive Detection of Perfluoroalkyl Substances Using MXene-AgNP-Based Electrochemical Sensors. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 3403–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimian, N.; Stortini, A.M.; Moretto, L.M.; Costantino, C.; Bogialli, S.; Ugo, P. Electrochemosensor for Trace Analysis of Perfluorooctanesulfonate in Water Based on a Molecularly Imprinted Poly(o-phenylenediamine) Polymer. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walekar, L.S.; Zheng, M.; Zheng, L.; Long, M. Selenium and nitrogen co-doped carbon quantum dots as a fluorescent probe for perfluorooctanoic acid. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liao, M.; Xiao, K.; Zhuang, K.; Zheng, W.; Yao, Z. A water-soluble fluorescence probe based on perylene diimide for rapid and selective detection of perfluorooctane sulfonate in 100% aqueous media. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 350, 130851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.-Y.; Duncan, C.L.; Li, H.-W.; Zhang, C.-X.; Mocerino, M.; Wu, Y. Calixarene-based supramolecular assembly with fluorescent gold-nanoclusters for highly selective determination of perfluorooctane sulfonic acid. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 302, 123127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Kiey, S.A.; Abdelhamid, H.N. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs)-derived Co3O4@N-doped carbon as an electrode materials for supercapacitor. J. Energy Storage 2022, 55, 105449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, H.N.; Khan, M.S.; Wu, H.F. Graphene oxide as a nanocarrier for gramicidin (GOGD) for high antibacterial performance. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 50035–50046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, H.N.; Wu, H.-F. Ultrasensitive, Rapid, and Selective Detection of Mercury Using Graphene Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 25, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, H.N.; Wu, H.-F. Reduced graphene oxide conjugate thymine as a new probe for ultrasensitive and selective fluorometric determination of mercury(II) ions. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Abdelhamid, H.N.; Abuelftooh, A.M.; Mohamed, S.G.; Wen, Z.; Sun, X. Covalent organic frameworks (COFs)-derived nitrogen-doped carbon/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite as electrodes materials for supercapacitors. J. Energy Storage 2022, 55, 105375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Q.; Zhang, M.; Tang, B.; Hou, W.; Wang, K.; Guo, H.; Zhang, J.; Han, T.; Wu, M.; Wang, L. Rapid synthesis of carbon quantum dot-integrated metal–organic framework nanosheets via electron beam irradiation for selective 5-hydroxymethylfurfural electrooxidation. Adv. Powder Mater. 2025, 4, 100267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Luo, K.; Xie, C.; Zhou, L. Nanotechnology of carbon dots with their hybrids for biomedical applications: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 153915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Opoku, H.; Tang, S.; Edman, L.; Wang, J. Carbon Dots: A Review with Focus on Sustainability. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2405472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Bhankar, V.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, K. Biomass-derived carbon dots as significant biological tools in the medicinal field: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 328, 103182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Han, Y.; Bianco, A.; Ji, D.-K. Recent Progress on Second Near-Infrared Emitting Carbon Dots in Biomedicine. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 11560–11572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Qu, S. Recent advances in photo-responsive carbon dots for tumor therapy. Responsive Mater. 2024, 2, e20240012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Jing, M.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zou, G.; Wu, T.; Hou, H.; Ji, X. Recent Developments of Carbon Dots for Advanced Zinc-Based Batteries: A Review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2400001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, T.; Wang, J.; Liang, Y.; Daoudi, W.; Dong, W.; Li, R.; Chen, X.; Liu, S.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, K. Carbon Dots for Anti-Corrosion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2411456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Ma, J.; Chen, C.; Ding, J.; Liu, Y.; He, H.; Liu, Q.; Hu, G.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X. Cutting-edge innovations in red carbon dots: Synthesis, perfection, and breakthroughs in optoelectronics and electrocatalysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, B.; Yu, S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X. Multicolor Afterglow Carbon Dots: Luminescence Regulation, Preparation, and Application. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2315366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, H.; Qiu, H.; Yan, Y.; Wang, X.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Z. Phosphorescent carbon dots: Intermolecular interactions, properties, and applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 503, 215642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Cheng, H.-L.; Huang, Y.-L.; Ni, C.; Shi, Y.; Xu, Z.-H.; Zhang, G.-Q. Achieving ultrasensitive detection of glyphosate in fruits and vegetables using a triple-mode strategy based on carbon dots nanozymes derived from expired drugs. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2025, 326, 125214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y. Developing oxygen vacancy-rich CuMn2O4/carbon dots dual-function nanozymes via Chan-Lam coupling reaction for the colorimetric/fluorescent determination of D-penicillamine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 267, 116864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, H.N.; Talib, A.; Wu, H.-F. One pot synthesis of gold—Carbon dots nanocomposite and its application for cytosensing of metals for cancer cells. Talanta 2017, 166, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sendão, R.M.S.; Esteves da Silva, J.C.G.; Pinto da Silva, L. Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) Detection Via Carbon Dots: A Review. Sustain. Chem. 2023, 4, 339–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algethami, F.K.; Abdelhamid, H.N. Heteroatoms-doped carbon dots as dual probes for heavy metal detection. Talanta 2024, 273, 125893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Dorado, Z.N.; Sharifan, H. Nanoscale Fluorinated Carbon Dots for the Detection of Perfluorooctanoic Acid in Aqueous Systems: A Fluorescence Assay Enhanced by Fluorophilic Interactions. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 21410–21419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, H.N.; Wu, H.-F. Multifunctional graphene magnetic nanosheet decorated with chitosan for highly sensitive detection of pathogenic bacteria. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 3950–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahnawaz Khan, M.; Abdelhamid, H.N.; Wu, H.-F. Near infrared (NIR) laser mediated surface activation of graphene oxide nanoflakes for efficient antibacterial, antifungal and wound healing treatment. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 127C, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowaidar, M.; Abdelhamid, H.N.; Hällbrink, M.; Zou, X.; Langel, Ü. Graphene oxide nanosheets in complex with cell penetrating peptides for oligonucleotides delivery. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 2334–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, M.; Sadek, A.A.; Abdelhamid, H.N.; Hussein, K. Graphene oxide-cellulose nanocomposite accelerates skin wound healing. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 137, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, K.H.; Abdelhamid, H.N.; Zou, X.; Woo, H.-M. Ultrasonicated graphene oxide enhances bone and skin wound regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 94, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, M.; Jiang, J.; Liu, S.; Yang, J.; Tan, K.; Zhu, J.; Shi, Y.; Hu, X. Triple-wavelength overlapping resonance Rayleigh scattering method for facile and rapid assay of perfluorooctane sulfonate. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, S.C.E.; Wanninayake, D.; Chen, D.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Li, Q. Physicochemical properties and interactions of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)—Challenges and opportunities in sensing and remediation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 166764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Su, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wu, F.; Bai, Y. A chitosan-mediated “turn-on” strategy for rapid fluorometric detection of perfluorooctane sulfonate. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 105030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lu, Y.-L.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Cheng, P.; Yang, S.; Shi, W. Efficient Recognition and Removal of Persistent Organic Pollutants by a Bifunctional Molecular Material. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalapati, R.; Manickam, S.; Shi, J.; Hunter, M.; Zang, L. Perylene diimide based fluorescent sensors for aqueous detection of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS). Anal. Chim. Acta 2025, 1341, 343670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Ma, S.; Sui, B.; Zhang, L.; Yu, A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Ouyang, G. Exploring an indirect quantification strategy for PFOA in rat tissues via efficient degradation and fluorescence spectroscopy. Microchem. J. 2024, 207, 112108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Z.; Wang, A.; Zhang, X.; Zuo, Y.; Lin, W. Multi-head cationic siloxane based “turn on” fluorescent system for selective detection of perfluorooctanoic sulfonate (PFOS). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 367, 132017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhu, P.; Xiong, J.; Gao, L.; Tan, K. A sensitive and selective triple-channel optical assay based on red-emissive carbon dots for the determination of PFOS. Microchem. J. 2019, 145, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, J.; Swihart, M.T.; Tan, K.; Dong, L. One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of high quantum yield orange-emitting carbon quantum dots for sensitive detection of perfluorinated compounds. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 19658–19666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zhou, S.; Guo, H.; Chen, Y.; Lin, S.; Yan, L.; Li, K.; Li, J. Nitrogen-doped carbon dots as an effective fluorescence enhancing system for the determination of perfluorooctyl sulfonate. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Zhu, P.; Xiong, J.; Gao, L.; Tan, K. A new dual-recognition strategy for hybrid ratiometric and ratiometric sensing perfluorooctane sulfonic acid based on high fluorescent carbon dots with ethidium bromide. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 224, 117362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Dong, H.; Liang, J.; Zhang, F.; Chen, X.; Du, L.; Tan, K. Highly selective fluorescent visual detection of perfluorooctane sulfonate via blue fluorescent carbon dots and berberine chloride hydrate. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 207, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelhamid, H.N. N, S-Doped Carbon Dots (N, S-CDs) for Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid (PFOS) Detection. C 2025, 11, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/c11020036
Abdelhamid HN. N, S-Doped Carbon Dots (N, S-CDs) for Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid (PFOS) Detection. C. 2025; 11(2):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/c11020036
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelhamid, Hani Nasser. 2025. "N, S-Doped Carbon Dots (N, S-CDs) for Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid (PFOS) Detection" C 11, no. 2: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/c11020036
APA StyleAbdelhamid, H. N. (2025). N, S-Doped Carbon Dots (N, S-CDs) for Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid (PFOS) Detection. C, 11(2), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/c11020036








