Thermodynamic Stability and Electronic Properties of Graphene Nanoflakes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
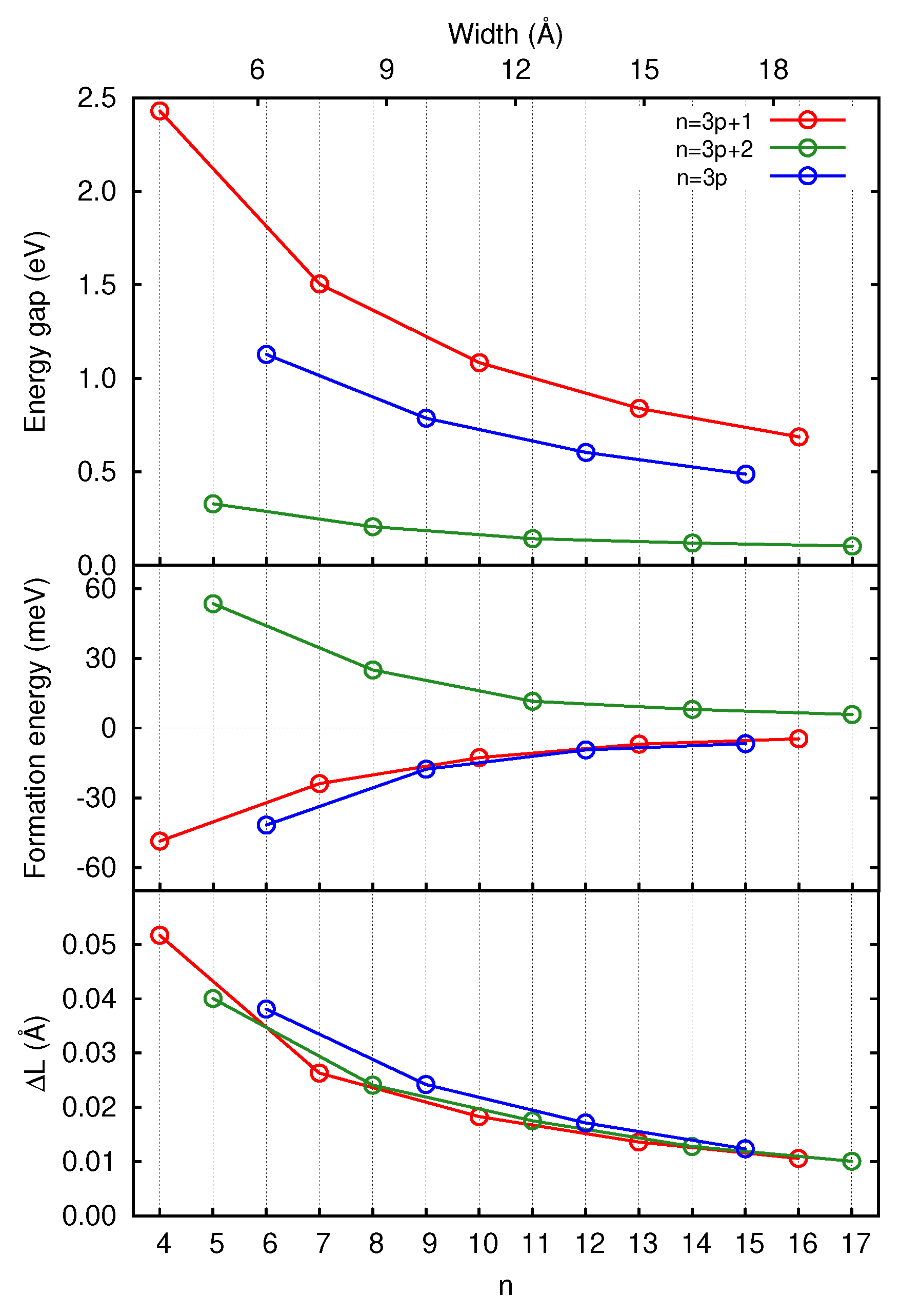
3.1. Graphene and Infinite Ribbons
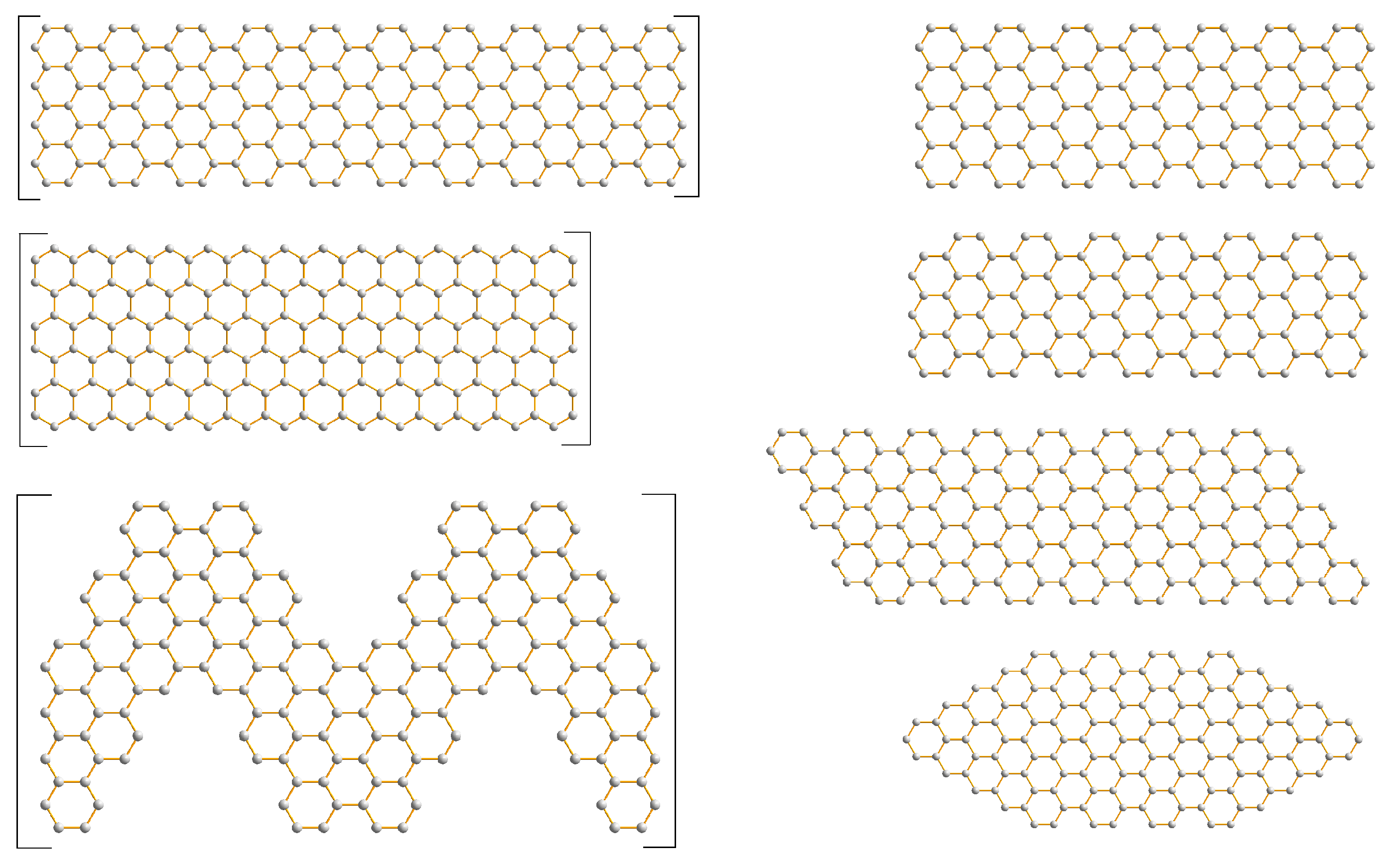
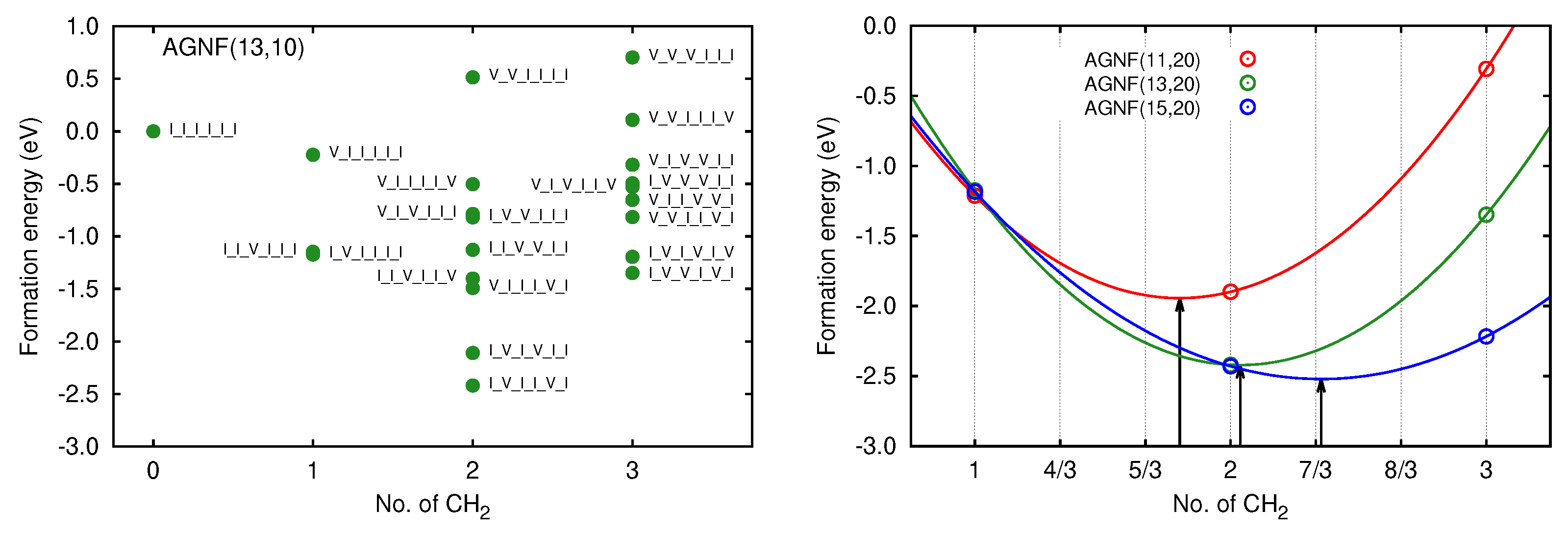
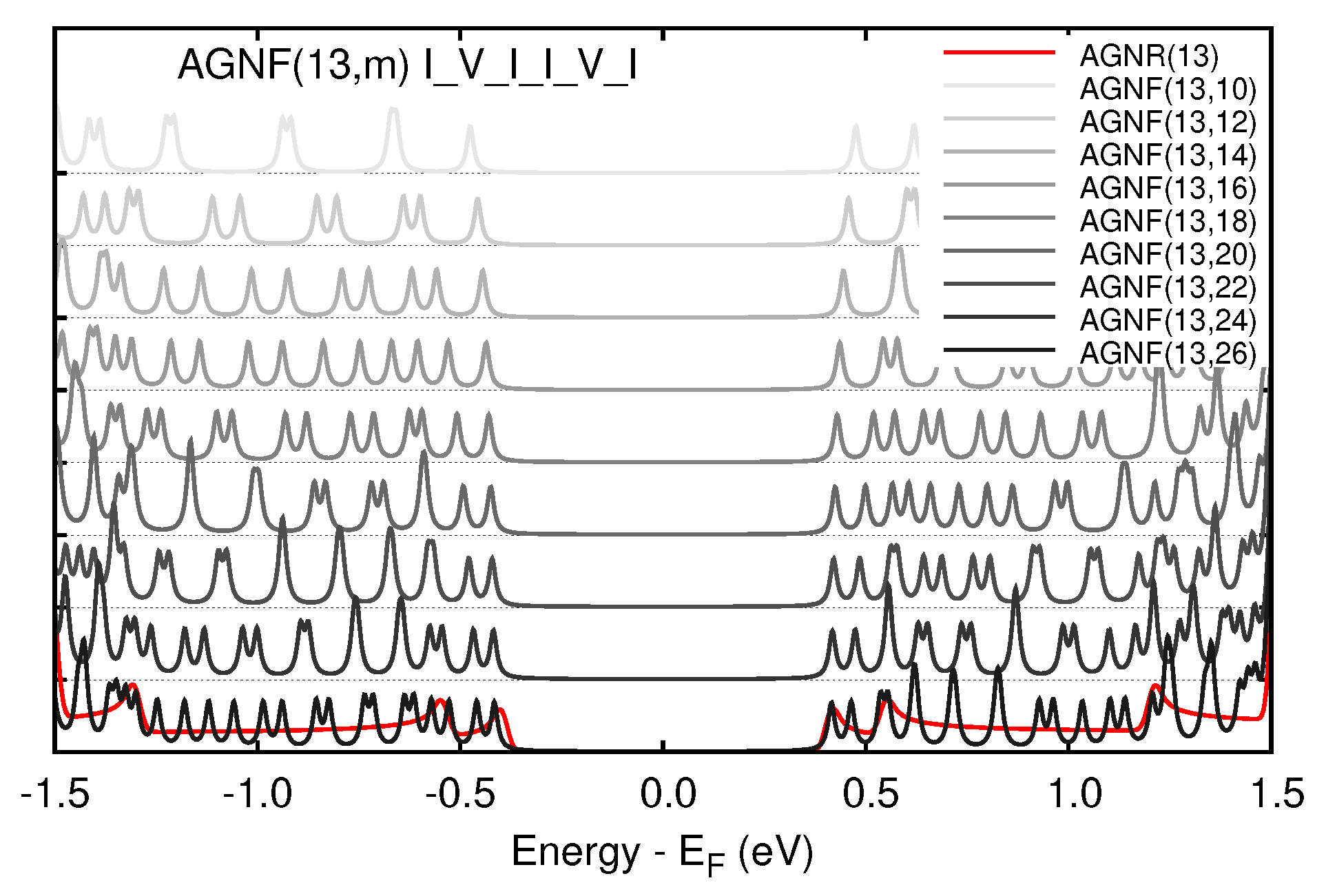
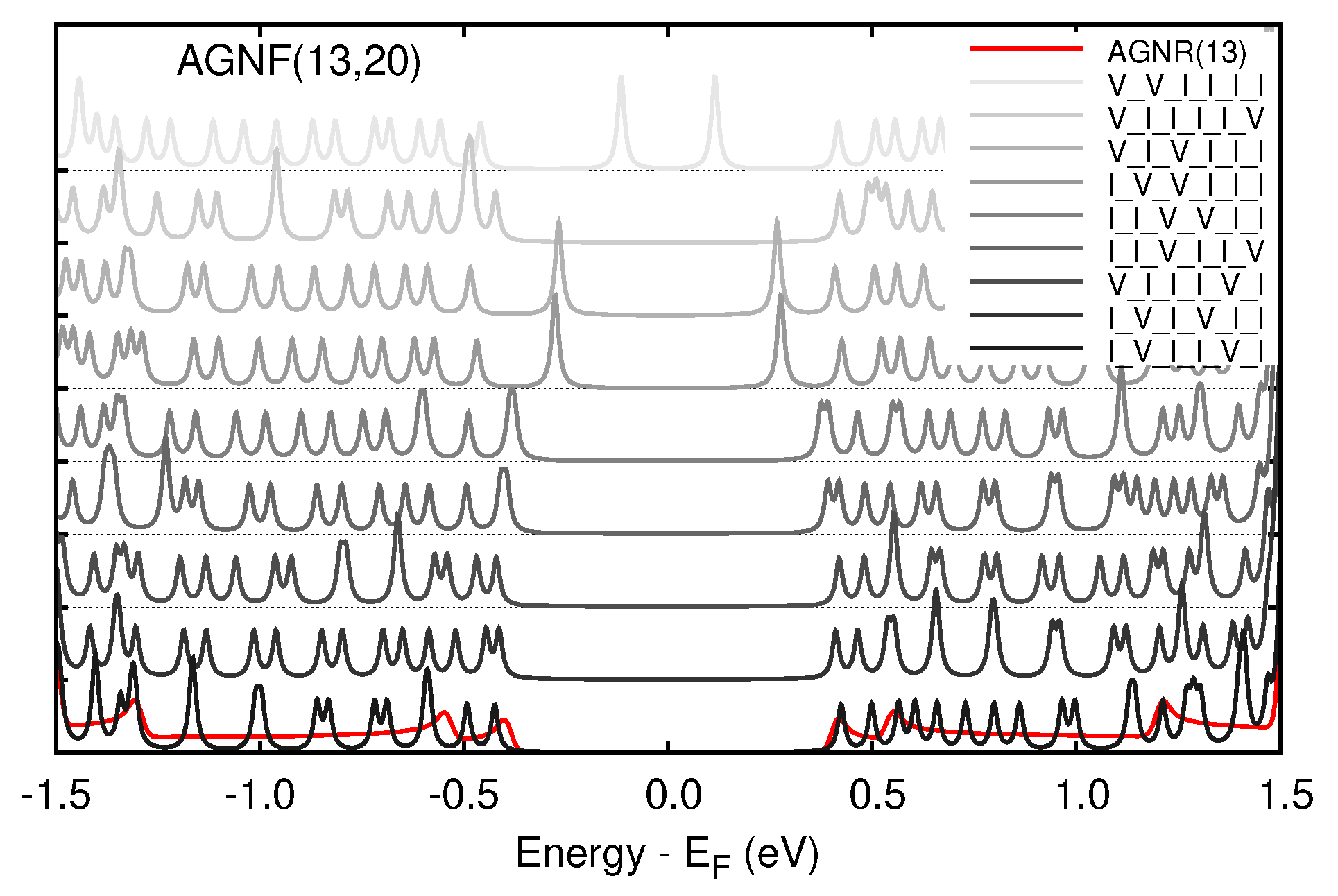
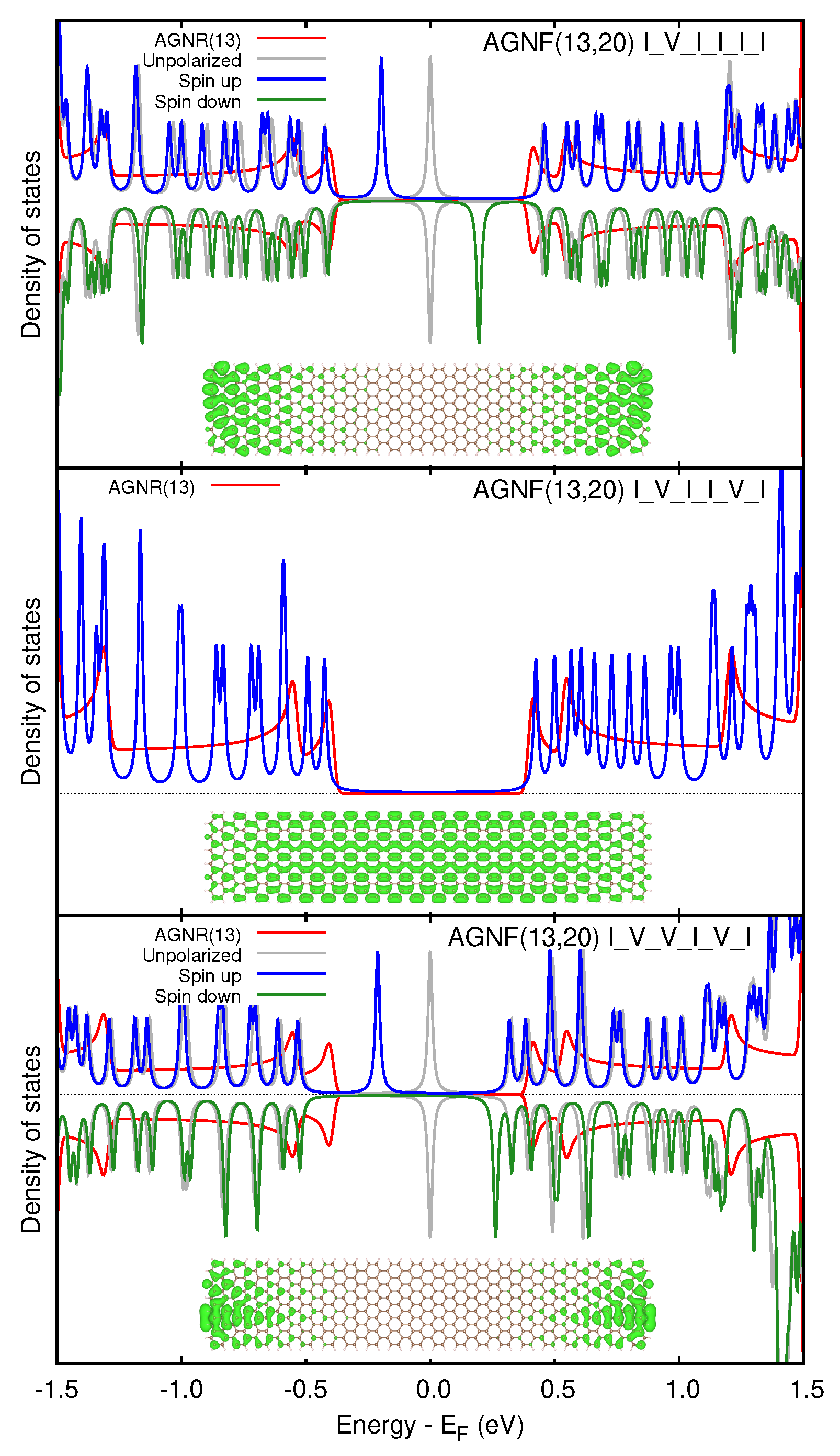
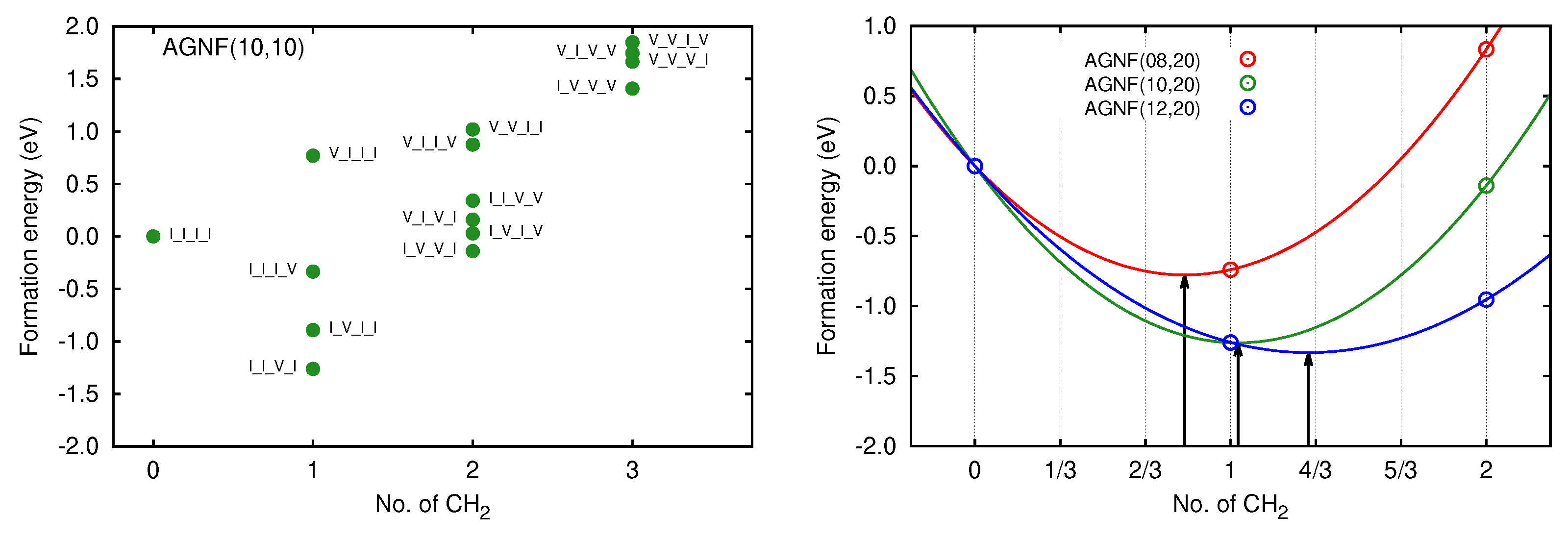
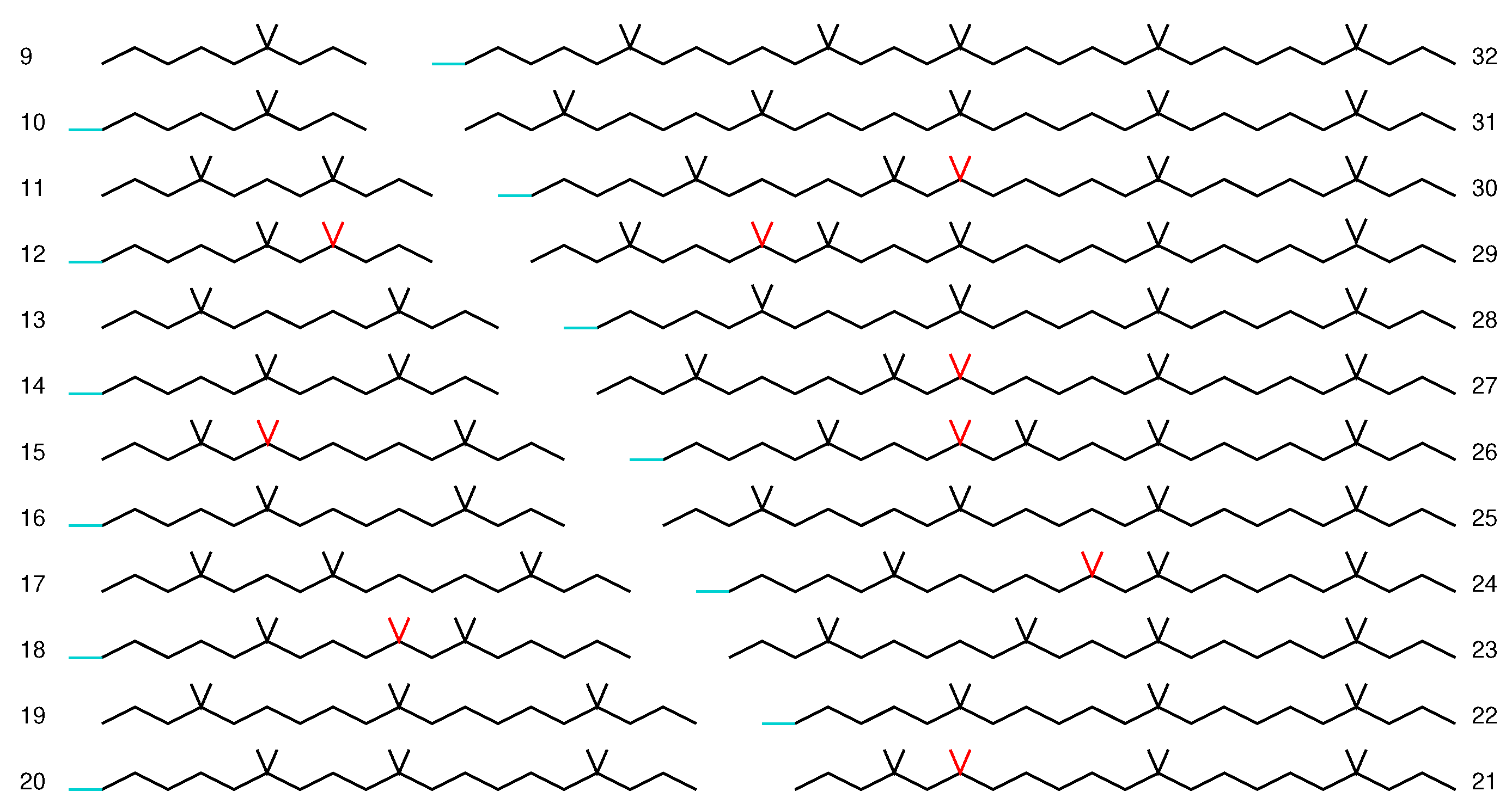
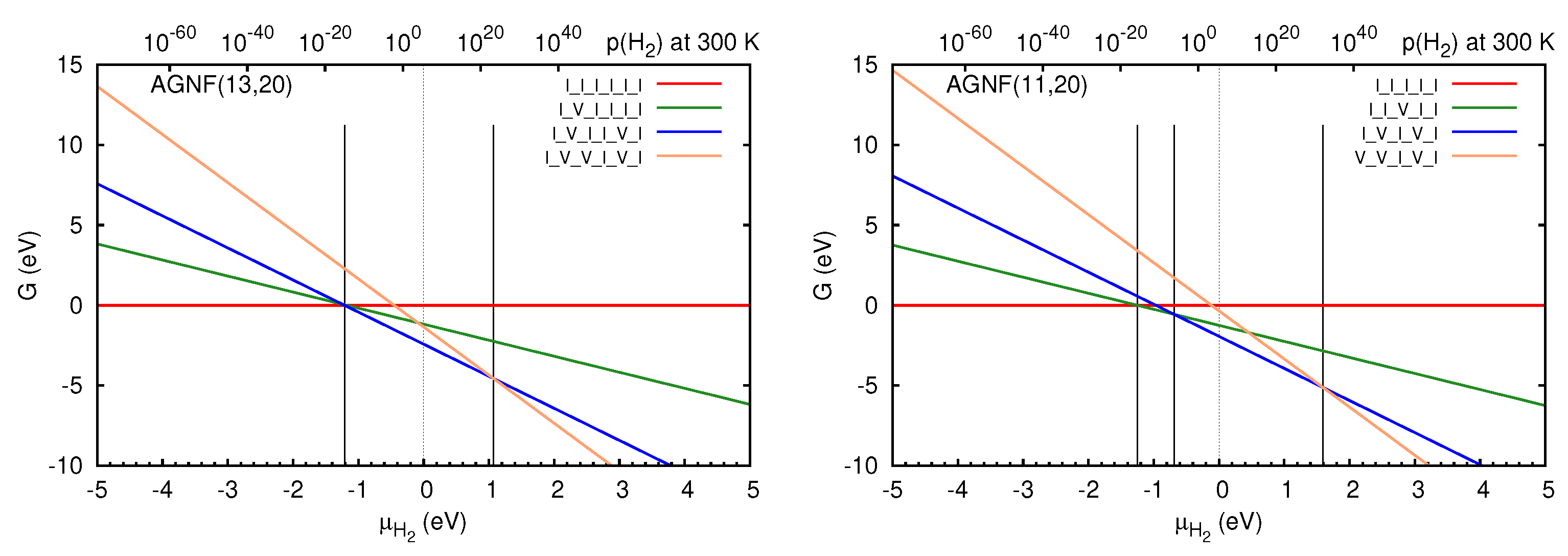
3.2. Graphene Nanoflakes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dutta, S.; Pati, S.K. Novel properties of graphene nanoribbons: A review. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 8207–8223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, H.S.; Ma, C.; Chen, L.; Jiang, C.; Chen, C.; Xie, X.; Li, A.P.; Wang, X. Graphene nanoribbons for quantum electronics. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2021, 3, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houtsma, R.S.K.; de la Rie, J.; Stohr, M. Atomically precise graphene nanoribbons: Interplay of structural and electronic properties. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 6541–6568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocchi, C.; Prezzi, D.; Ruini, A.; Caldas, M.J.; Molinari, E. Electronics and Optics of Graphene Nanoflakes: Edge Functionalization and Structural Distortions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 17328–17335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotz, A.; Wang, X.Y.; Ruini, A.; Zheng, W.; Soltani, P.; Graf, R.; Tries, A.; Li, J.; Palma, C.A.; Molinari, E.; et al. Band structure modulation by methoxy-functionalization of graphene nanoribbons. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 4173–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, L.; Chen, Z.; Mishra, N.; Barin, G.B.; Fantuzzi, P.; Ruffieux, P.; Fasel, R.; Feng, X.; Narita, A.; Coletti, C.; et al. Structure-dependent electrical properties of graphene nanoribbon devices with graphene electrodes. Carbon 2019, 146, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Mullen, K. Nanographenes and Graphene Nanoribbons as Multitalents of Present and Future Materials Science. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 11499–11524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedotov, P.V.; Obraztsova, E.D. Near infrared photoluminescence of the bottom-up produced 7-armchair graphene nanoribbons. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2023, 122, 013101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Fu, S.; Liu, X.; Narita, A.; Samorì, P.; Bonn, M.; Wang, H.I. Small Size, Big Impact: Recent Progress in Bottom-Up Synthesized Nanographenes for Optoelectronic and Energy Applications. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2106055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.Z.; Osella, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, B.; Beljonne, D.; Feng, X.; Müllen, K. Sulfur-Annulated Hexa-peri-hexabenzocoronene Decorated with Phenylthio Groups at the Periphery. Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 2970–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.Z.; Yang, B.; Parvez, K.; Narita, A.; Osella, S.; Beljonne, D.; Feng, X.; Müllen, K. Atomically precise edge chlorination of nanographenes and its application in graphene nanoribbons. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassmann, T.; Seitsonen, A.P.; Saitta, M.A.; Lazzeri, M.; Mauri, F. Structure, stability, edge states, and aromaticity of graphene ribbons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 096402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soler, J.M.; Artacho, E.; Gale, J.D.; García, A.; Junquera, J.; Ordejón, P.; Sánchez-Portal, D. The SIESTA method for ab initio order-N materials simulation. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2002, 14, 2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troullier, N.; Martins, J.L. Efficient pseudopotentials for plane-wave calculations. Phys. Rev. B 1991, 43, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chase, M.W., Jr. NIST-JANAF Thermochemical Tables; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; Volume 9, pp. 1–1951. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, R.W.; Drickamer, H.G. Effect of High Pressure on the Lattice Parameters of Diamond, Graphite, and Hexagonal Boron Nitride. J. Chem. Phys. 1966, 44, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hembacher, S.; Giessibl, F.J.; Mannhart, J.; Quate, C.F. Revealing the hidden atom in graphite by low-temperature atomic force microscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 22, 12539–12542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dappe, Y.J.; Oszwaldowski, R.; Pou, P.; Ortega, J.; Pérez, R.; Flores, F. Local-orbital occupancy formulation of density functional theory: Application to Si, C, and graphene. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 235124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, V.; Hod, O.; Scuseria, G.E. Electronic Structure and Stability of Semiconducting Graphene Nanoribbons. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 2748–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskinen, P.; Malola, S.; Häkkinen, H. Self-Passivating Edge Reconstructions of Graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 115502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Kang, S.; Koo, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.; Kwon, Y. Cohesion energetics of carbon allotropes: Quantum Monte Carlo study. J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 140, 114702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kresse, G.; Hafner, J. First-principles study of the adsorption of atomic H on Ni (111), (100) and (110). Surf. Sci. 2000, 459, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, K.P. American Institute of Physics Handbook; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, A.N.; Liu, G.; Narita, A.; Orosco, M.; Feng, X.; Müllen, K.; Zhou, C. Deposition, Characterization, and Thin-Film-Based Chemical Sensing of Ultra-long Chemically Synthesized Graphene Nanoribbons. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 7555–7558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Gemayel, M.; Narita, A.; Dössel, L.F.; Sundaram, R.S.; Kiersnowski, A.; Pisula, W.; Hansen, M.R.; Ferrari, C.; Orgiu, E.; Feng, X.; et al. Graphene nanoribbon blends with P3HT for organic electronics. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 6301–6314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candini, A.; Martini, L.; Chen, Z.; Mishra, N.; Convertino, D.; Coletti, C.; Narita, A.; Feng, X.; Müllen, K.; Affronte, M. High Photoresponsivity in Graphene Nanoribbon Field-Effect Transistor Devices Contacted with Graphene Electrodes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 10620–10625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Xiao, Z.; Puretzky, A.A.; Wang, H.; Mohsin, A.; Huang, J.; Liang, L.; Luo, Y.; Lawrie, B.J.; Gu, G.; et al. Engineering edge states of graphene nanoribbons for narrow-band photoluminescence. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5090–5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Ruffieux, P.; Jaafar, R.; Bieri, M.; Braun, T.; Blankenburg, S.; Muoth, M.; Seitsonen, A.P.; Saleh, M.; Feng, X.; et al. Atomically precise bottom-up fabrication of graphene nanoribbons. Nature 2010, 466, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wei, D.; Sun, J.; Wong, S.L.; Feng, Y.P.; Neto, A.H.C.; Wee, A.T.S. Spatially Resolved Electronic Structures of Atomically Precise Armchair Graphene Nanoribbons. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.H.; Shekhirev, M.; Kunkel, D.A.; Morton, M.D.; Berglund, E.; Kong, L.; Wilson, P.M.; Dowben, P.A.; Enders, A.; Sinitskii, A. Large-scale solution synthesis of narrow graphene nanoribbons. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, A.; Feng, X.; Müllen, K. Bottom-Up Synthesis of Chemically Precise Graphene Nanoribbons. Chem. Rec. 2015, 15, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdurakhmanova, N.; Amsharov, N.; Stepanow, S.; Jansen, M.; Kern, K.; Amsharov, K. Synthesis of wide atomically precise graphene nanoribbons from para-oligophenylene based molecular precursor. Carbon 2014, 77, 1187–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basagni, A.; Sedona, F.; Pignedoli, C.A.; Cattelan, M.; Nicolas, L.; Casarin, M.; Sambi, M. Molecules–Oligomers–Nanowires–Graphene Nanoribbons: A Bottom-Up Stepwise On-Surface Covalent Synthesis Preserving Long-Range Order. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 1802–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narita, A.; Wang, X.Y.; Feng, X.; Mullen, K. New Advances in Nanographene Chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6616–6643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, Y.W.; Cohen, M.L.; Louie, S.G. Energy gaps in graphene nanoribbons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 216803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemella, P.; Zhang, Y.; Mailman, M.; Ajayan, P.M.; Nayak, S.K. Energy gaps in zero-dimensional graphene nanoribbons. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 042101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soave, R.; Cargnoni, F.; Trioni, M.I. Thermodynamic Stability and Electronic Properties of Graphene Nanoflakes. C 2024, 10, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/c10010005
Soave R, Cargnoni F, Trioni MI. Thermodynamic Stability and Electronic Properties of Graphene Nanoflakes. C. 2024; 10(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/c10010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoave, Raffaella, Fausto Cargnoni, and Mario Italo Trioni. 2024. "Thermodynamic Stability and Electronic Properties of Graphene Nanoflakes" C 10, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/c10010005
APA StyleSoave, R., Cargnoni, F., & Trioni, M. I. (2024). Thermodynamic Stability and Electronic Properties of Graphene Nanoflakes. C, 10(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/c10010005






