Enhancing Organic Contaminant Removal from Wool Scouring Wastewater Using Chemically Modified Biochars
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pristine Biochar
2.2. Post-Treatment of Biochar
2.3. Synthetic Wool Scouring Wastewater
2.4. Biochar-Based COD Removal from Wastewater
2.5. Chemical Analysis
2.6. Biochar Characterization
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
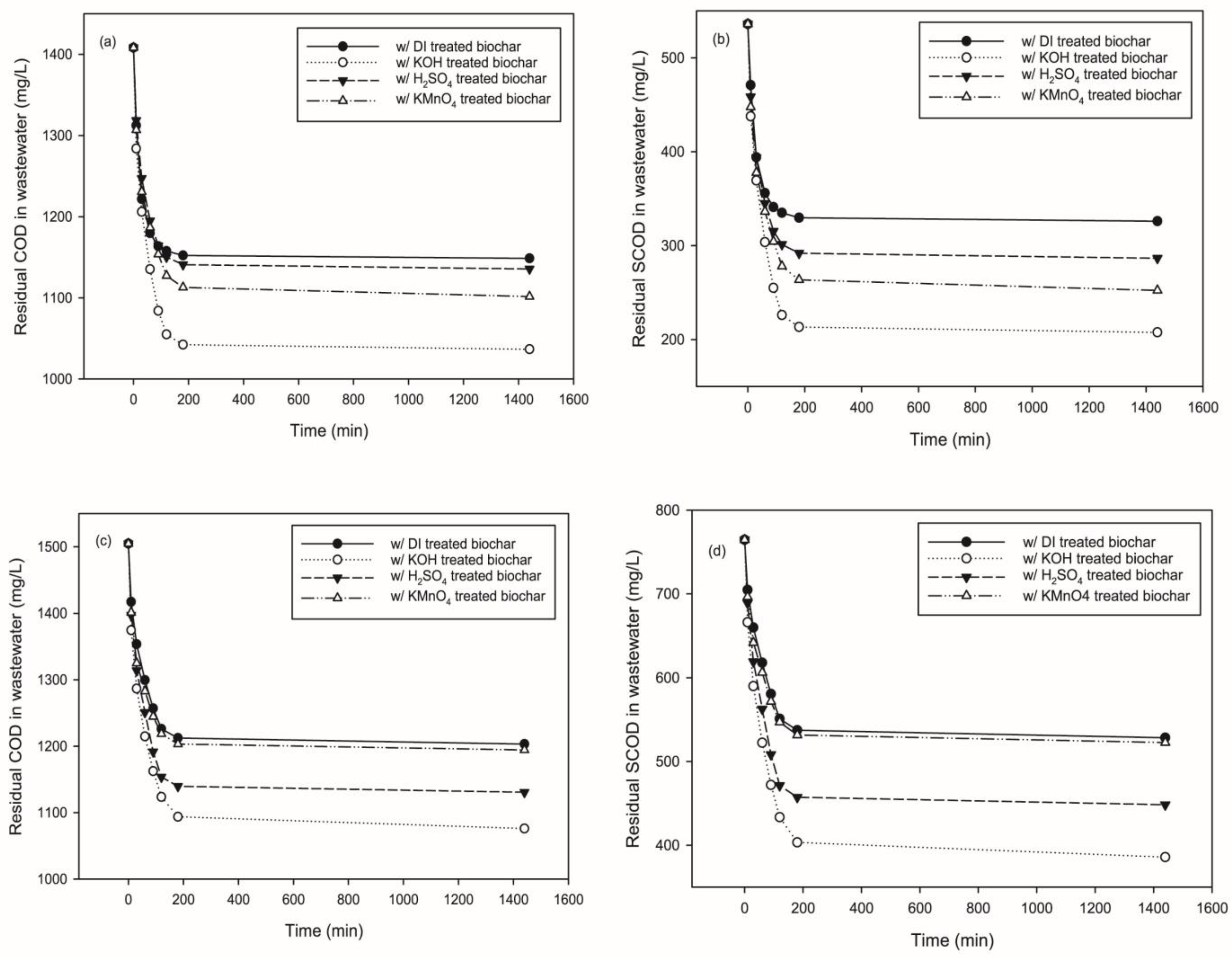
3.1. Residual COD and SCOD in Treated Wastewater
3.2. Removal of COD and SCOD from Wool Scouring Wastewater
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics
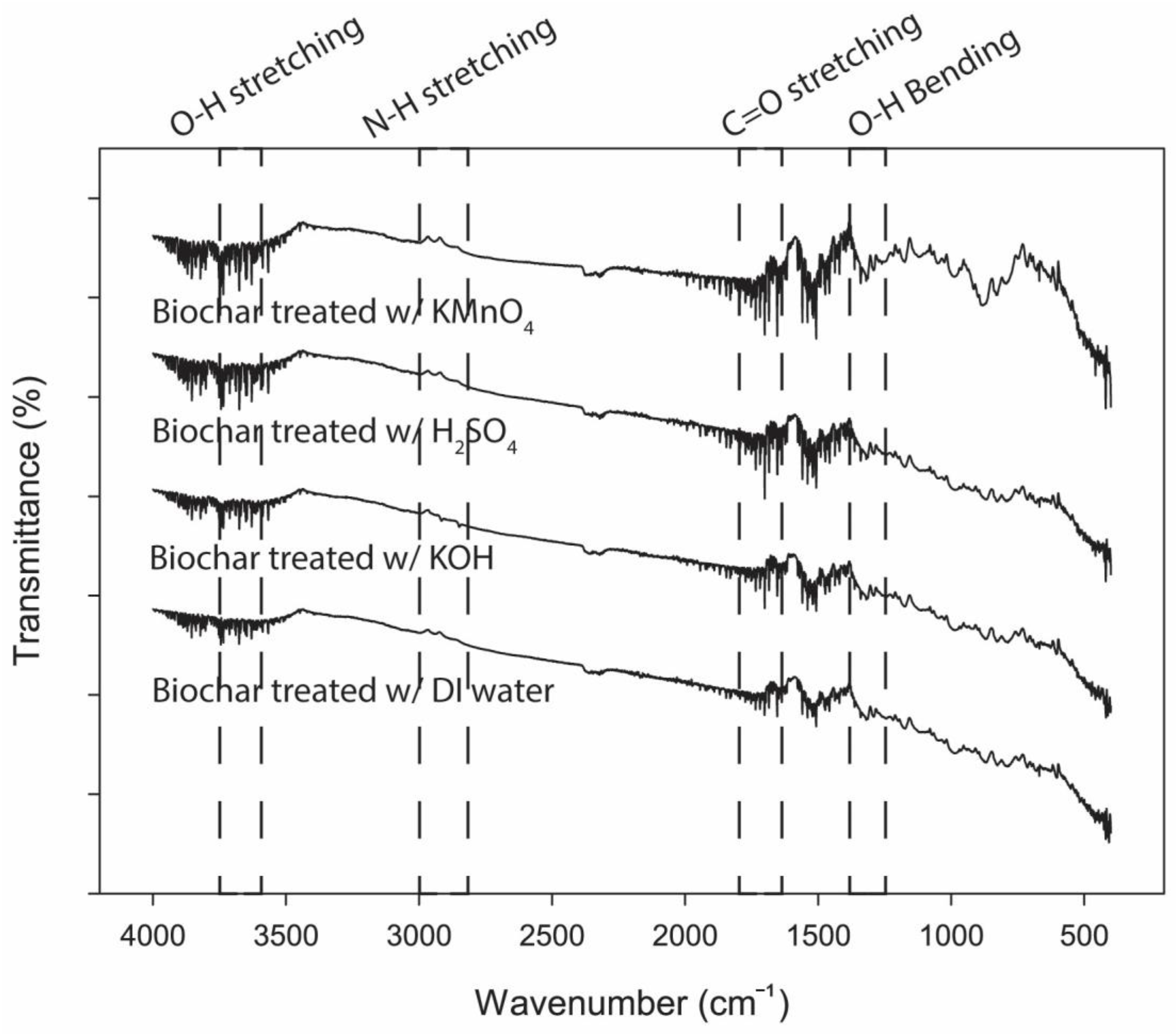
3.4. Surface Functional Groups of Biochar
3.5. Surface Area and Pore Properties of Biochar
3.6. Proximate and Elemental Analysis of Biochar
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhavsar, P.; Zoccola, M.; Dalla Fontana, G.; Pallavicini, M.; Roda, G.; Bolchi, C. Sustainable Routes for Wool Grease Removal Using Green Solvent Cyclopentyl Methyl Ether in Solvent Extraction and Biosurfactant Wool Protein Hydrolyzate in Scouring. Processes 2023, 11, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Hao, Z.; Liu, J.; Han, J.; Wang, A.; Ouyang, Q.; Fu, F. Molecular probing of dissolved organic matter and its transformation in a woolen textile wastewater treatment station. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 457, 131807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allafi, F.A.; Hossain, M.S.; Shaah, M.; Lalung, J.; Ab Kadir, M.O.; Ahmad, M.I. A review on characterization of sheep wool impurities and existing techniques of cleaning: Industrial and environmental challenges. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 8669–8687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaupin, M. Wool Scouring in Europe: Urgent and Ecological Solutions. In Advances in Fibre Production Science in South American Camelids and Other Fibre Animals; Gerken, M., Renieri, C., Allain, D., Galbraith, H., Gutiérrez, J.P., McKenna, L., Niznikowski, R., Wurzinger, M., Eds.; Universitätsverlag Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 2019; p. 301. [Google Scholar]
- Saran, R.K.; Kumar, R.; Yadav, S. Environmental issues in textiles. In Advanced Functional Textiles and Polymers: Fabrication, Processing and Applications; Wiley-Scrivener: Austin, TX, USA, 2019; pp. 129–151. [Google Scholar]
- Awchat, G.D. Upgradation of wool scouring plant for efficient wastewater treatment. Ecol. Eng. Environ. Technol. 2022, 23, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattnaik, P.; Dangayach, G.S. Sustainability of wastewater management in textile sectors: A conceptual framework. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2019, 18, 1947–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugasundaram, O.; Pandit, P. Conclusion on biotechnology in textile production and future scope. In Applications of Biotechnology for Sustainable Textile Production; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 241–249. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, D.; Zeng, B.; Liu, Q.; Cui, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. Inorganic composite coagulant for wool scouring wastewater treatment: Performance, kinetics and coagulation mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 313, 123482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwuozor, K.O. Prospects and challenges of using coagulation-flocculation method in the treatment of effluents. Adv. J. Chem. Sect. A 2019, 2, 105–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinperi, N.C.; Ozturk, E.; Yigit, N.O.; Kitis, M. Treatment of woolen textile wastewater using membrane bioreactor, nanofiltration and reverse osmosis for reuse in production processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 223, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.N.R.; Ang, W.L.; Teow, Y.H.; Mohammad, A.W.; Hilal, N. Nanofiltration membrane processes for water recycling, reuse and product recovery within various industries: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 45, 102478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.-F.; Yang, D.-S.; Liao, J.-W.; Chen, S.-T. Treating high COD dyeing wastewater via a regenerative sorption-oxidation process using a nano-pored activated carbon. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, B.; Niu, A.; Cheng, N.; Chen, M.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Z.; Wang, S. Application of biochar immobilized microorganisms for pollutants removal from wastewater: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Chan, C.Y.; Sharbatmaleki, M.; Trejo, H.; Delagah, S. Engineered Biochar Production and Its Potential Benefits in a Closed-Loop Water-Reuse Agriculture System. Water 2020, 12, 2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotito, A.M.; De Sanctis, M.; Di Iaconi, C.; Bergna, G. Textile wastewater treatment: Aerobic granular sludge vs activated sludge systems. Water Res. 2014, 54, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brickler, C.A.; Wu, Y.; Li, S.; Anandhi, A.; Chen, G. Comparing Physicochemical Properties and Sorption Behaviors of Pyrolysis-Derived and Microwave-Mediated Biochar. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Skelly, S. Physicochemical properties and applications of biochars derived from municipal solid waste: A review. Environ. Adv. 2023, 13, 100395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Galoustian, T.; Trejo, H. Biochar pyrolyzed with concentrated solar radiation for enhanced nitrate adsorption. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2023, 174, 106131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, A.; Kondracki, B.; Szewczuk-Karpisz, K. Chemical modification of biochars as a method to improve its surface properties and efficiency in removing xenobiotics from aqueous media. Chemosphere 2023, 312, 137238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Xu, L.; Buyong, F.; Chay, T.C.; Li, Z.; Cai, Y.; Hu, B.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X. Modified biochar: Synthesis and mechanism for removal of environmental heavy metals. Carbon Res. 2022, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmi, A.H.; Jol, H.; Singh, D. Physical modification of biochar to expose the inner pores and their functional groups to enhance lead adsorption. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 38270–38280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Westholm, L.J.; Carvalho, L.; Thorin, E.; Yu, Z.; Yu, X.; Skreiberg, Ø. A critical review on production, modification and utilization of biochar. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2022, 161, 105405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Niu, D.; Sang, W.; Verpoort, F. Investigating the sorption behavior of cadmium from aqueous solution by potassium permanganate-modified biochar: Quantify mechanism and evaluate the modification method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 8330–8339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Liu, C.; Lu, Y.; Lin, X.; Zheng, Z. Insight into the KOH/KMnO4 activation mechanism of oxygen-enriched hierarchical porous biochar derived from biomass waste by in-situ pyrolysis for methylene blue enhanced adsorption. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 158, 105269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Fang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhou, N.; Fan, S. Effects of KMnO4 pre-and post-treatments on biochar properties and its adsorption of tetracycline. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 373, 121257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, Z.; Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Xie, X. Enhanced adsorption of ciprofloxacin by KOH modified biochar derived from potato stems and leaves. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Luo, L.; He, J.; Feng, B.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, K.; Ren, H. Subsurface constructed wetlands with modified biochar added for advanced treatment of tailwater: Performance and microbial communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Chen, G. Thermogravimetric, thermochemical, and infrared spectral characterization of feedstocks and biochar derived at different pyrolysis temperatures. Waste Manag. 2018, 78, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.-F.; Zhu, S.-S.; Wang, R.-P.; Chen, Y.-D.; Show, P.-L.; Zhang, F.-F.; Ho, S.-H. Role of biochar surface characteristics in the adsorption of aromatic compounds: Pore structure and functional groups. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 2939–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, G.; Fan, Q.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Sun, J.; Cui, L.; Wang, H.; Gao, B.; Yan, J. Effects of laboratory biotic aging on the characteristics of biochar and its water-soluble organic products. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 382, 121071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakout, S.M. Monitoring the changes of chemical properties of rice straw–derived biochars modified by different oxidizing agents and their adsorptive performance for organics. Bioremediation J. 2015, 19, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zheng, H.; Zhai, X.; Wang, Z. Characteristics and mechanisms of microcystin-LR adsorption by giant reed-derived biochars: Role of minerals, pores, and functional groups. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 176, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Bhattacharya, T.; Shaikh, W.A.; Chakraborty, S.; Sarkar, D.; Biswas, J.K. Biochar modification methods for augmenting sorption of contaminants. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2022, 8, 519–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Ma, J.; Li, Z.; Xia, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y. Highly enhanced adsorption performance of tetracycline antibiotics on KOH-activated biochar derived from reed plants. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 5066–5076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Shang, H.; Cao, Y.; Yang, C.; Hu, W.; Feng, Y.; Yu, Y. Influence of adsorption sites of biochar on its adsorption performance for sulfamethoxazole. Chemosphere 2023, 326, 138408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herath, A.; Layne, C.A.; Perez, F.; Hassan, E.I.B.; Pittman, C.U.; Mlsna, T.E. KOH-activated high surface area Douglas Fir biochar for adsorbing aqueous Cr(VI), Pb(II) and Cd(II). Chemosphere 2021, 269, 128409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Capareda, S.; Chang, Z.; Gao, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J. Biochar pyrolytically produced from municipal solid wastes for aqueous As(V) removal: Adsorption property and its improvement with KOH activation. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Zhu, J.; Fu, Q.; Hu, H. Comparing the adsorption mechanism of Cd by rice straw pristine and KOH-modified biochar. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 11875–11883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jawad, A.H.; Abdulhameed, A.S.; Wilson, L.D.; Syed-Hassan, S.S.A.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Khan, M.R. High surface area and mesoporous activated carbon from KOH-activated dragon fruit peels for methylene blue dye adsorption: Optimization and mechanism study. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 32, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhu, L.; Yang, J.; Lin, D. Adsorption and correlations of selected aromatic compounds on a KOH-activated carbon with large surface area. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 1677–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Sun, S.; Wang, Y.; Guo, L. Efficient toluene adsorption/desorption on biochar derived from in situ acid-treated sugarcane bagasse. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 62616–62627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yue, X.; Li, F.; Xiao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, D. Preparation of rice straw-derived biochar for efficient cadmium removal by modification of oxygen-containing functional groups. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, P.K.; Kataria, N.; Khoo, K.S.; Narwal, N.; Dhull, S.B.; Kumar, R.; Rani, S.; Kumar, P. Pristine and Modified Biochar for Pharmaceuticals Removal from Aquatic Systems. In Pharmaceuticals in Aquatic Environments; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 145–172. [Google Scholar]
- Murtaza, G.; Ahmed, Z.; Usman, M. Feedstock type, pyrolysis temperature and acid modification effects on physiochemical attributes of biochar and soil quality. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; McNamara, P.J.; Mayer, B.K. Adsorption of organic micropollutants onto biochar: A review of relevant kinetics, mechanisms and equilibrium. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 821–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revellame, E.D.; Fortela, D.L.; Sharp, W.; Hernandez, R.; Zappi, M.E. Adsorption kinetic modeling using pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws: A review. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2020, 1, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.M.; Clouse, J.A.; Longo, J.M. Adsorption of organic compounds on carbonate minerals: 1. Model compounds and their influence on mineral wettability. Chem. Geol. 1993, 109, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanassova, I.; Doerr, S. Organic compounds of different extractability in total solvent extracts from soils of contrasting water repellency. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2010, 61, 298–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzetta, A.; Łuczak, J.; Woch, J.; Chiappe, C.; Nowicki, J.; Guazzelli, L. Surface active fatty acid ILs: Influence of the hydrophobic tail and/or the imidazolium hydroxyl functionalization on aggregates formation. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 289, 111155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadeesh, N.; Sundaram, B. Adsorption of pollutants from wastewater by biochar: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 9, 100226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.-Y.; Wei, Z.-J.; Wang, Y.; Deng, Y.-P.; Li, M.-Y.; Wang, B. Effects of biochar properties on the bioremediation of the petroleum-contaminated soil from a shale-gas field. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 36427–36438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Harris, S.; Anandhi, A.; Chen, G. Predicting biochar properties and functions based on feedstock and pyrolysis temperature: A review and data syntheses. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 890–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurav, R.; Bhatia, S.K.; Choi, T.-R.; Choi, Y.-K.; Kim, H.J.; Song, H.-S.; Park, S.L.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, S.M.; Choi, K.-Y. Adsorptive removal of crude petroleum oil from water using floating pinewood biochar decorated with coconut oil-derived fatty acids. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, L.; Sengupta, S.; Das, P.; Bhowal, A.; Bhattacharjee, C. Experimental and Numerical modeling on dye adsorption using pyrolyzed mesoporous biochar in Batch and fixed-bed column reactor: Isotherm, Thermodynamics, Mass transfer, Kinetic analysis. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 23, 100985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardestani, R.; Patience, G.S.; Kaliaguine, S. Experimental methods in chemical engineering: Specific surface area and pore size distribution measurements—BET, BJH, and DFT. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 2781–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhao, N.; Tong, L.; Lv, Y. Structural and adsorption characteristics of potassium carbonate activated biochar. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 21012–21019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, S.; Ishak, S.; Lee, D.-E.; Park, T. Optimization of eco-friendly Pinus resinosa biochar-dodecanoic acid phase change composite for the cleaner environment. J. Energy Storage 2022, 55, 105414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Qiu, L.; Tang, G.; Chen, W.; Li, Y.; Gao, B.; He, F. Ultrafast sequestration of cadmium and lead from water by manganese oxide supported on a macro-mesoporous biochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 387, 124095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Barreto, V.; Li, R.; Chen, G.; Hsieh, Y.P. Nitrogen retention of biochar derived from different feedstocks at variable pyrolysis temperatures. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2018, 133, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

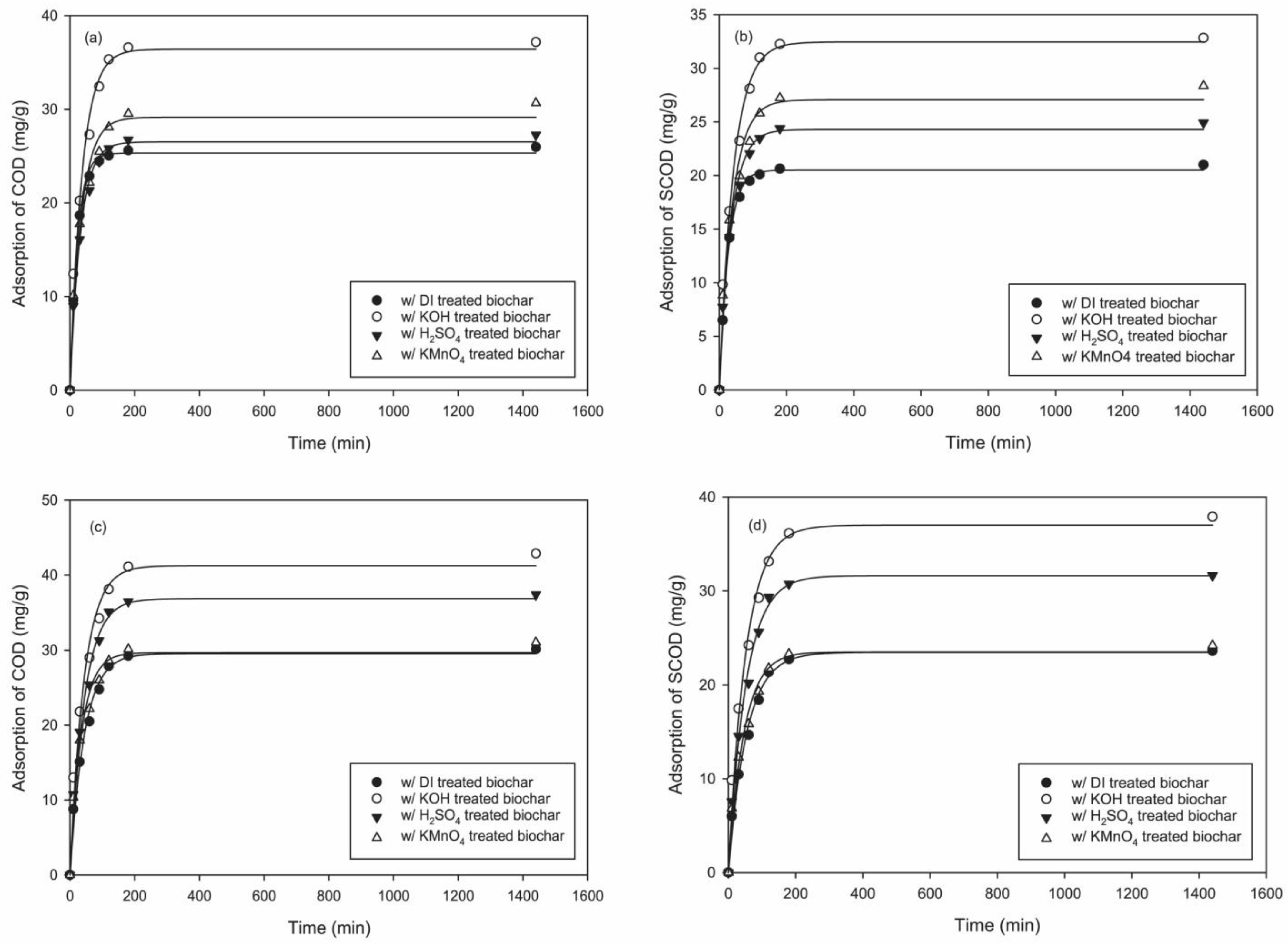
| Wastewater | Contaminant Type | Parameters | DI Water Biochar | KOH Biochar | H2SO4 Biochar | KMnO4 Biochar |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dorset | COD | (mg/g) | 25.318 | 36.419 | 26.520 | 29.150 |
| Dorset | COD | (min−1) | 0.0444 | 0.0272 | 0.0312 | 0.0292 |
| Dorset | COD | R2 | 0.9977 | 0.9843 | 0.9917 | 0.9789 |
| Dorset | SCOD | (mg/g) | 20.524 | 32.460 | 24.307 | 27.076 |
| Dorset | SCOD | (min−1) | 0.0376 | 0.0239 | 0.0290 | 0.0266 |
| Dorset | SCOD | R2 | 0.9985 | 0.9885 | 0.9927 | 0.9802 |
| BFL | COD | (mg/g) | 29.538 | 41.238 | 36.878 | 29.672 |
| BFL | COD | (min−1) | 0.0226 | 0.0231 | 0.0228 | 0.0286 |
| BFL | COD | R2 | 0.9861 | 0.9798 | 0.9869 | 0.9778 |
| BFL | SCOD | (mg/g) | 23.466 | 37.012 | 31.611 | 23.522 |
| BFL | SCOD | (min−1) | 0.0185 | 0.0194 | 0.0194 | 0.0218 |
| BFL | SCOD | R2 | 0.9880 | 0.9872 | 0.9921 | 0.9825 |
| BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Micropore (<2 nm) | Mesopore (2–50 nm) | Macropore (>50 nm) | Total Pore Volume (cm3/g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DI water-treated biochar | 24.6 | 14% | 71% | 15% | 0.062 |
| KOH-treated biochar | 724.4 | 94% | 4% | 2% | 0.746 |
| H2SO4-treated biochar | 339.2 | 39% | 48% | 13% | 1.061 |
| KMnO4-treated biochar | 238.7 | 78% | 20% | 1% | 0.224 |
| Volatile Matter | Fixed Carbon | Ash | C | H | O | N | S | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DI water treated biochar | 57.31% | 34.03% | 8.66% | 74.52% | 4.43% | 9.81% | 2.56% | 0.02% |
| KOH treated biochar | 40.73% | 49.58% | 9.69% | 81.53% | 2.88% | 3.23% | 2.64% | 0.03% |
| H2SO4 treated biochar | 43.87% | 51.31% | 4.82% | 91.32% | 1.58% | 1.66% | 0.53% | 0.09% |
| KMnO4 treated biochar | 52.15% | 40.38% | 7.47% | 84.61% | 2.53% | 4.31% | 1.03% | 0.05% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Tasnady, D.; Skelley, S.; Calderon, B.; Jiang, S. Enhancing Organic Contaminant Removal from Wool Scouring Wastewater Using Chemically Modified Biochars. C 2024, 10, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/c10010006
Li S, Tasnady D, Skelley S, Calderon B, Jiang S. Enhancing Organic Contaminant Removal from Wool Scouring Wastewater Using Chemically Modified Biochars. C. 2024; 10(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/c10010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Simeng, Desarae Tasnady, Shannon Skelley, Blanca Calderon, and Sherine Jiang. 2024. "Enhancing Organic Contaminant Removal from Wool Scouring Wastewater Using Chemically Modified Biochars" C 10, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/c10010006
APA StyleLi, S., Tasnady, D., Skelley, S., Calderon, B., & Jiang, S. (2024). Enhancing Organic Contaminant Removal from Wool Scouring Wastewater Using Chemically Modified Biochars. C, 10(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/c10010006