Abstract
Allergy is a type 2 immune reaction triggered by antigens known as allergens, including food and environmental substances such as peanuts, plant pollen, fungal spores, and the feces and debris of mites and insects. Macrophages are myeloid immune cells with phagocytic abilities that process exogenous and endogenous antigens. Upon activation, they can produce effector molecules such as cytokines as well as anti-inflammatory molecules. The dysregulation of macrophage function can lead to excessive type 1 inflammation as well as type 2 inflammation, which includes allergic reactions. Thus, it is important to better understand how macrophages are regulated in the pathogenesis of allergies. Emerging evidence highlights the role of noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) in macrophage polarization, which in turn can modify the pathogenesis of various immune-mediated diseases, including allergies. This review summarizes the current knowledge regarding this topic and considers three classes of ncRNAs: microRNAs, long ncRNAs, and circular ncRNAs. Understanding the roles of these ncRNAs in macrophage polarization will provide new insights into the pathogenesis of allergies and identify potential novel therapeutic targets.
1. Introduction
Allergies affect millions of people worldwide and are characterized by an excessive type 2 immune response to normally harmless substances, generally known as antigens or allergens, specifically [1,2]. Consequently, this response leads to the development of various allergic symptoms, including asthma, allergic rhinitis, and atopic dermatitis. In the most severe cases, it can result in anaphylaxis and possibly death. According to the World Allergy Organization, the prevalence of allergic diseases has been continuously increasing in the industrialized world [3,4]. In addition, according to the World Health Organization, the number of asthma patients is expected to increase to 400 million by 2025 [4]. The process by which the immune system becomes sensitive to a particular allergen is called sensitization and is typically accompanied by the development of immunoglobulin E (IgE), a specific subclass of antibodies, against the allergen. Sensitization rates to one or more common allergens among schoolchildren are reported to be between 40% and 50% [5]. Since antigen E was isolated from the pollen of common ragweed (Ambrosia artemisiifolia) as the first antigen in 1962 [6], a variety of environmental and food allergens have been identified, including 106 allergens that have recently (between January 2019 and March 2021) been accepted by the Allergen Nomenclature Sub-Committee (http://allergen.org/committee.php, accessed on 5 July 2023) [7]. For example, one of the authors (O.I.), together with colleagues, identified Liposcelis bostrychophila, a booklouse species commonly found in house dust, as a potent environmental allergen source based on IgE inhibition analysis, which demonstrated that approximately 20% of the studied patients with asthma were sensitized by the L. bostrychophila-specific antigen Lip b 1 [8,9]. It should be noted that sensitization to booklice antigens may lead to the misdiagnosis of food-induced allergies. Babaie et al. recently reported that a patient developed anaphylaxis after ingesting oatmeal. However, the results of the skin prick test and serologic testing for oats were negative, and the cause was ultimately identified as booklice contamination of the oatmeal [10]. As insects may become a popular food source in the future, it is important to consider their potential to harbor known and novel allergens [11].
Antihistamines are widely used for symptomatic treatment of many allergic diseases with variable efficacy. Despite the identification of increasing varieties of antigens, there is no fundamental treatment to overcome allergic symptoms except for allergen immunotherapy or desensitization, whereby long-term remission is expected, against a few food and environmental allergens, e.g., cedar pollen [12]. Desensitization therapy is actively investigated because of its clinical potential; however, it harbors the intrinsic risk of inducing severe side effects such as anaphylaxis [13]. Thus, desensitization shots are co-administered with antihistamines. A drug that promotes immune tolerance by targeting macrophages, for instance, could make allergen desensitization safer and even more effective. In 2003, omalizumab, an IgE-blocking antibody received approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), but it is not approved for all allergic conditions, and it is expensive [14]. Alternatively, blocking antibodies against specific allergens are being developed, but these will be even more expensive for patients that are allergic to multiple allergens. Therefore, an alternative remedy based on a new concept is desirable for this growing patient population.
Immune cells such as mast cells, basophils, dendritic cells, B cells, and specific T-cell subsets are well recognized as key players in allergic reactions. In contrast, to date, macrophages are not commonly associated with allergies. In the future, it would be key for the field to provide credible in vivo evidence that macrophages also play a role in modulating allergy first using mouse models but ultimately in human patients. However, several lines of evidence have recently revealed the crucial role of macrophages in developing and modulating these allergic responses [15,16,17,18,19,20]. For example, macrophages are the most abundant immune cells present in the lungs (approximately 70% of the immune cells) and play a crucial role in asthma caused by environmental-allergen-induced airway inflammation [21,22], suggesting that macrophages, together with other immune cells could play a role in immune responses. Therefore, the role of macrophages in allergic diseases and the mechanism underlying their functional regulation deserve further study.
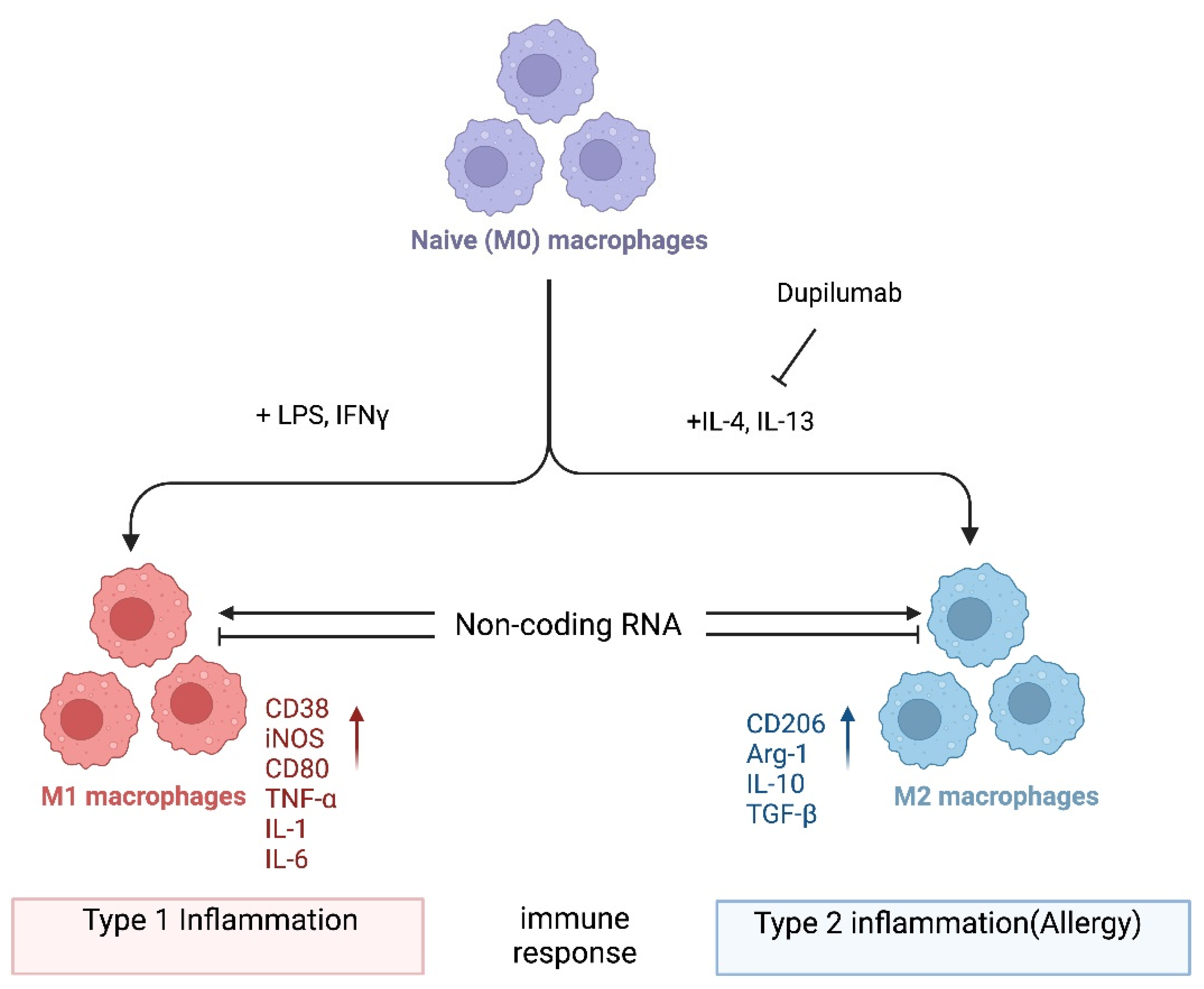
In one popular paradigm, macrophages can be divided into two major subclasses, i.e., M1 and M2, based on the inflammatory responses that they mediate, and the process by which macrophages differentiate in response to challenge is called macrophage polarization. Macrophage polarization is determined by the microenvironment (Figure 1). However, the mechanisms underlying in vivo macrophage polarization are complicated and remain largely unclarified, but various intracellular molecules, including signaling molecules and enzymes, and receptors have been shown to regulate macrophage polarization [23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34]. For example, it is not known whether dupilumab, a clinically approved biologic drug that blocks IL4Rα signaling [35], leads to an in vivo reduction in M2 macrophages in patients receiving this drug. In the future, it would be important to investigate which immune cells are in fact being inhibited by dupilumab. Alternatively, it is possible that dupilumab switches macrophages into a tolerant state, for instance, by turning on the expression of anti-inflammatory molecules. Thus, it is crucial that the mechanism of action of dupilumab be investigated systematically at the cellular and molecular levels. Here, we provide a consideration of macrophages and noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs). Accumulating evidence has revealed that ncRNAs, a class of functional RNAs not translated into proteins and associated with various pathological events, are associated with both macrophage polarization and allergies. ncRNAs are typically classified into two major types that have distinct functions, i.e., housekeeping ncRNAs and regulatory ncRNAs. The detailed classification of ncRNAs is discussed elsewhere [36,37]. Emerging evidence shows that these ncRNAs play roles in macrophage polarization related to allergies [38,39]. Herein, we summarize the current knowledge on ncRNA-regulated macrophage functions related to allergies, focusing on microRNAs (miRNAs), long ncRNAs (lncRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs), and discuss the possibility of identifying novel potential targets for allergy treatment. In general, we hypothesize that noncoding RNAs could serve as druggable targets to manipulate macrophage plasticity in immune-mediated diseases. With regard to treating allergy specifically, we hypothesize that inhibiting M2 polarization could be a fruitful avenue as exemplified by dupilumab (Figure 1). However, systemic blockade of IL4Rα signaling may have pleiotropic effects in patients, and a target such as a ncRNA that is more specific to M2 could have fewer side effects.
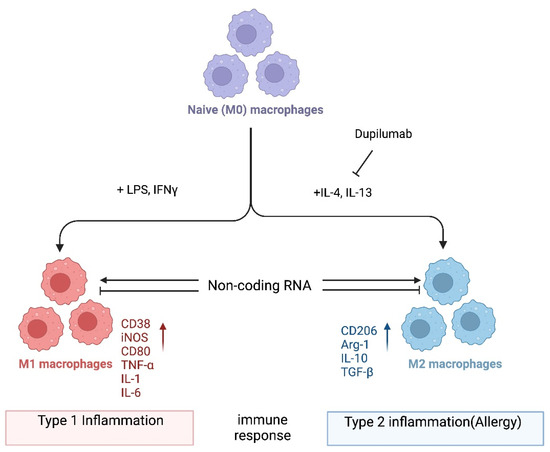
Figure 1.
Macrophage polarization. Naïve (M0) macrophages in their inactive state can be polarized into either of two types of activated macrophages with distinct functions, M1 and M2 macrophages (also termed “classically activated” or “alternatively activated” macrophages, respectively), after exposure to certain stimuli. M1 and M2 macrophages are functionally associated with type 1 and type 2 immune reactions, respectively. Several mRNAs and proteins are used as markers to differentiate between these macrophages: i.e., arginase-1 (Arg-1) and CD206 for M2; CD38, CD80, and iNOS for M1 macrophages. However, the criteria for the subclassification of macrophages in vivo in different tissues still require further investigation. Noncoding RNAs might regulate the differentiation of macrophages and/or the function of M1 and M2 macrophages by modifying gene expression programs. Dupilumab is a currently available monoclonal antibody that blocks IL-4 and IL-13 signaling by targeting IL4Rα [35]. This biologic drug is FDA-approved for allergic diseases such as eczema, asthma, and nasal polyps, which result in chronic sinusitis. Hypothetically, its mechanism of action is in part to inhibit M2 polarization. Tralokinumab, another FDA-approved monoclonal antibody, used for the treatment of atopic dermatitis, targets just the cytokine IL-13 (not depicted). Again, it is not well understood which cell types are being affected by this biologic drug. It would be interesting to directly compare dupilumab versus tralokinumab and assess the in vivo effects of each on macrophages and their noncoding transcriptome. Image created with BioRender.com (accessed on 28 November 2023).
2. M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization
Macrophages are evolutionarily ancient white blood cells crucial for the immune system to function properly. They are characterized by high plasticity, which allows them to functionally adapt depending on their microenvironment. Two major macrophage polarization states exist: classically activated macrophages (M1 macrophages) and alternatively activated macrophages (M2 macrophages) (Figure 1). The T helper (Th)1/Th2 balance of T cells affects the balance between the two macrophage polarization states and is critical for maintaining healthy immune functionality [32,33].
M1 macrophages collaborate with Th1 immune responses and play a proinflammatory role in host defense against infection with viruses and intracellular microbes [20,40,41,42]. Polarization of M1 macrophages is typically activated by factors such as interferon (IFN)-γ, a Th1 cytokine, and bacterial products like lipopolysaccharides (LPSs) [24,25,28]. They initiate immune responses by phagocytosing and destroying foreign elements that enter the body, including microorganisms and viruses [40,41,42]. M1 macrophages can also react against endogenous substances in the body. This reaction involves critical physiological functions such as removing cancer cells that are generated in the body [31]; however, they can also cause pathological states such as autoimmune diseases [43,44].
The effector functions of the M1 macrophages are characterized by the production of proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, and IL-6, and the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), which recruits other types of immune cells to the infection or injury site [25,26,27,28,29,30]. In addition to these molecules, some cell-surface proteins, such as CD80 and CD38, serve as M1 macrophage markers [25]. Furthermore, it has been reported that M1 macrophages are involved in forming granulomas, which are masses of immune cells that wall-off infected tissue [45].
In contrast, M2 macrophages are associated with Th2 immune responses and activated by Th2 cytokines, such as IL-4 and IL-13 [2,26,27,28,29,30]. In general, M2 and Th2 cells are associated with allergic reactions. They typically produce anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-10 and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, which help suppress the immune response and promote wound healing, tissue repair, tissue remodeling, resistance to parasites (e.g., helminths), and tumor growth [46,47]. Additionally, M2 macrophages are involved in clearing apoptotic cells and tissue debris as well as promoting angiogenesis [48]. Compared to M1 macrophages, M2 macrophages show more diverse characteristics. They can be subdivided into several subclasses such as M2a, M2b, M2c, and M2d macrophages based on their functions and the signals they receive [16,28,29] (M2d macrophages are alternatively termed tumor-associated macrophages). However, it is important to know that the validity of the classification and markers remains controversial.
As mentioned above, macrophages in the M1 and M2 states play distinct physiological roles; therefore, an imbalance in these states can lead to various pathological conditions such as chronic inflammation, autoimmune diseases, cancer, metabolic disorders, and infections [34,40,42,44,49,50,51,52,53,54]. Thus, we believe that macrophage polarization is a promising target for drug discovery.
3. Association of M2 Macrophages with Immune Tolerance or Suppression in Allergy
The M1 and M2 polarization of macrophages is closely associated with the balance of Th1 and Th2 cells, and it is thought that M2 and Th2 cells are directly linked to allergy [33]. However, macrophages can modulate allergic reactions through their phenotypic plasticity. For example, it has been demonstrated that M2 macrophages regulate allergic responses by suppressing the activity of effector lymphocytes [15,17] and that M2 macrophages can produce resistin-like molecule α (RELMα), which correlates with the appearance of Foxp3-expressing regulatory T cells [32].
As such, various allergic diseases can occur when macrophage functions are dysregulated. Nonetheless, the linkage between macrophage polarization and allergies is still not fully understood. Several studies have explained that dysregulated macrophage functions in the lung and nasal tissues can cause allergic asthma and allergic rhinitis [5,16,18,19,55,56,57,58]. Recent studies have demonstrated the involvement of macrophages in the development of food allergies. For example, chitinase 3-like 1, which is known to be associated with various chronic diseases including allergic disease, plays a pivotal role in M2 macrophage polarization in food allergy [59].
Considering the above-mentioned knowledge, it seems reasonable to propose that targeting macrophage plasticity could be an opportunity to promote immune tolerance and suppress exaggerated immune reactions. However, the anti-inflammatory property of M2 macrophages contradicts previous reports that they are associated with allergic diseases. This contradiction might be explained by differences in the tissue microenvironment and/or their developmental origins, i.e., yolk sac, fetal liver, or adult bone marrow.
4. ncRNAs in Macrophage Polarization
As mentioned earlier, ncRNAs are RNA molecules that do not encode proteins and are essential in regulating gene expression at both transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels, which includes epigenetic regulation [60]. There are at least three classes of ncRNAs that regulate gene expression: microRNAs (miRNAs), long ncRNAs (lncRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs). Furthermore, ncRNAs that regulate protein activity have been described [61,62]. While miRNA-mediated regulation of gene expression occurs at the post-transcriptional level, lncRNAs and circRNAs may utilize diverse mechanisms of action. Emerging evidence has highlighted the critical role of ncRNAs in regulating macrophage polarization, which may lead to the development of allergies [63]. Although the mechanisms through which ncRNAs regulate macrophage polarization are diverse and complex, several studies have shown that ncRNAs potentially regulate M1 and M2 macrophage polarization by targeting the regulators of proinflammatory signaling pathways or regulating the expression of anti- or proinflammatory cytokines.
Although published studies have thus far highlighted the functional association between ncRNAs and macrophage polarization or that between ncRNAs and allergic diseases, few reports have described the ncRNA–macrophage polarization–allergy axis. Therefore, in the following sections, we summarize these previous studies on how the individual ncRNA classes are involved in macrophage polarization and how that may relate to allergic diseases.
4.1. miRNA-Mediated Regulation of Macrophage Polarization
miRNAs are small (typically ~22 nt in length) ncRNAs that post-transcriptionally regulate gene and protein expression by binding to the 3′-untranslated region of the target mRNAs, which induces mRNA degradation and translational repression [39,64]. Several miRNAs have been demonstrated to regulate macrophage polarization related to allergic diseases (Table 1). For example, it was reported that miR-155-5p directly targeted the IL-13 receptor alpha1. Given that IL-13 signaling is associated with M2-mediated allergic diseases like asthma, miR-155-5p could regulate the M1/M2 balance [65]. Furthermore, the enhanced proinflammatory response of RAW264.7 macrophage-like cells to IL-33, another proinflammatory cytokine associated with allergic diseases, correlated with increased miR-155-5p expression [66]. Thus, it would be of interest to check the miR-155-5p expression in macrophages from patients with allergies.
In addition, Jaiswal et al. found that lentiviral overexpression of let-7c and miR-99a-5p in mouse bone-marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) promoted M2 macrophage polarization [67]. Although let-7c was previously demonstrated to target C/EBP-δ, thus inhibiting M1 polarization [68], this study identified TNF-α as the target of miR-99a-5p as another mechanism to suppress M1 macrophage differentiation [67]. In contrast, it was reported that angiotensin II enhanced M1 macrophage polarization by abrogating miR-99a-5p activation [67]. A different study by Wang et al. illustrates that M2 macrophage polarization in allergic rhinitis was promoted by the miR-202-5p–Matrilin-2 axis [69]. Furthermore, recently, Lee et al. found, using an ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma mouse model, that the inhibition of miR-21 suppresses alveolar M2 macrophage polarization [70]. These findings will need to be independently, thoughtfully validated before an allergy drug development strategy is worth considering.
The mannose receptor MRC1/CD206 is expressed in immune cells, and its expression level is pronouncedly elevated in M2 macrophages; therefore, it is generally accepted as an M2 macrophage marker [29]. MRC1/CD206 recognizes an extensive range of surface glycoproteins and plays a crucial role in a variety of immunological events, both physiologically and pathologically [71]. Interestingly, miR-511-3p is an miRNA that is transcribed from an intron of the MRC1 gene. The expressions of miR-511-3p and MRC1/CD206 have been shown to be coregulated in macrophages [72,73]. In studies with the MRC1 knockout mouse model in which miR-511-3p expression is also deficient, Zhou et al. demonstrated that miR-511-3p downregulated M1 macrophage polarization, upregulated M2 macrophage polarization, and protected against cockroach allergen-induced lung inflammation [73]. In addition, it was reported by Do et al. that miR-511-3p promoted M2 macrophage polarization and attenuated cockroach-allergen-induced lung inflammation by targeting CCL2 [74]. Alternatively, Heinsbroek et al. demonstrated that miR-511-3p regulated intestinal inflammation by controlling macrophage-mediated microbial responses via the indirect upregulation of TLR-4 expression [75]. These findings suggest that miR-511-3p regulates macrophage functions and polarization by targeting multiple mRNAs.
Using an allergen-induced asthma knockout mouse model, Chung et al. reported that miR-451a negatively affects IL-4-induced M2 macrophage polarization by targeting and silencing the expression of Sirtuin 2 and promoting asthmatic inflammation [76]. Additionally, a few other studies were conducted using ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma mouse models to identify miRNAs in macrophage polarization. For example, Veremeyko et al. demonstrated that miR-124 expression was upregulated in the lung alveolar macrophages of an ovalbumin-induced allergic lung inflammation mouse model and contributed to the development of M2, but not M1, macrophage polarization [77]. Another study by Shi et al. highlighted the involvement of miR-142-5p and miR-130a-3p in pulmonary macrophage polarization and asthma airway remodeling in ovalbumin-sensitized mice [78]. Additionally, Su et al. reported that miR-142-5p and miR-130a-3p functioned by targeting suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ, respectively [79]. Notably, this study revealed that SOCS1 had a negative impact on the M2 macrophage polarization in mice [79], while the M2 polarization of human macrophages is enhanced by SOCS1 [80]. Again, such contradiction will need to be resolved before ncRNAs can be selected as allergy drug targets.

Table 1.
MicroRNAs that regulate macrophage polarization in allergy.
Table 1.
MicroRNAs that regulate macrophage polarization in allergy.
| miRNA *1 | Materials Used | Affecting Polarization *2 | Target | Related Pathophysiology | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-155-5p | Blood monocytes from healthy donors and the human monocytic cell line THP1 | M2 (−) | IL13R | Allergic asthma | [65] |
| miR-99a-5p | Mouse bone-marrow-derived macrophages | M1 (−) M2 (+) | TNF | Allergic airway inflammation | [67] |
| miR-202-5p | Mucus-derived macrophages from allergic rhinitis patients | M2 (+) | MATN2 | Allergic rhinitis | [69] |
| miR-21-5p | Ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma mouse model | M2 (+) | Possibly IRF5 | Allergic asthma | [70] |
| miR-511-3p | Lung macrophages and an allergen-induced lung inflammation mouse model | M1 (−) M2 (+) | HPGDS | Allergic lung inflammation | [73] |
| miR-511-3p | Lung macrophages and an allergen-induced lung inflammation mouse model | M1 (−) M2 (+) | CCL2 | Allergic lung inflammation | [74] |
| miR-451a | Allergen-induced mouse asthma model | M2 (+) | SIRT2 | Allergic asthma | [76] |
| miR-124-3p | Ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma mouse model | M2 (+) | CEBPA | Allergic asthma | [77] |
| miR-130a-3p | Ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma mouse model | M2 (−) | PPARG | Allergic asthma | [78,79] |
| miR-142-5p | Ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma mouse model | M2 (+) | SOCS1 | Allergic asthma | [78,79] |
*1 miRNAs are indicated as current miRBase identifiers; *2 plus and minus signs indicate positive and negative regulation, respectively.
4.2. lncRNA-Mediated Regulation of Macrophage Polarization
lncRNAs are long (generally defined to be >200 nt in length) ncRNAs that regulate gene expression at various levels, which include chromatin remodeling, transcriptional regulation, and post-transcriptional regulation [62,63]. Several lncRNAs have been shown to regulate M2 macrophage polarization related to allergies (Table 2). For example, the knockdown of receptor-type tyrosine protein phosphatase ε (PTPRE)-AS1, a lncRNA selectively expressed in IL-4-stimulated macrophages, was shown to promote M2 macrophage activation via the MAPK/ERK 1/2 pathway [81]. Wen et al. recently demonstrated that MIR222HG acts on the miR146a-5p/TRAF6/NF-κB axis, leading to the attenuation of macrophage M2 polarization and allergic inflammation in allergic rhinitis [82]. The few studies investigating the lncRNA AK085865 have also highlighted its role in macrophage polarization [83,84]. In particular, the study conducted by Pei et al. showed that AK085865-deficient mice were protected from the allergic airway inflammation induced by Der f 1, a major mite allergen component of Dermatophagoides farinae [83]. They also found that AK085865 deletion suppressed M2 macrophage polarization, which subsequently decreased their susceptibility to Der f 1-induced airway inflammation. In addition, Zhang et al. demonstrated that AK085865 specifically interacted with interleukin-enhancer-binding factor (ILF)-2 and functioned as a negative regulator of the ILF2–ILF3-complex-mediated biosynthesis of miR-192, which promotes M2 macrophage polarization through the direct targeting of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) 1 [84].
lnc-BAZ2B, a lncRNA dominantly expressed in monocytes and significantly upregulated in children with asthma, was also demonstrated to promote M2 macrophage polarization. Mechanistically, lnc-BAZ2B promotes the expression of BAZ2B mRNA by stabilizing its pre-mRNA, leading to enhanced IRF4 expression and M2 macrophage polarization [85]. Another lncRNA reported to regulate the pathological state of allergies is NKILA [86]. This lncRNA was demonstrated to limit the asthmatic airway inflammation, enhancing M2 macrophage polarization and inhibiting the NF-κB pathway in a mouse asthmatic model.
In contrast to many reports on the lncRNA-mediated regulation of M2 macrophage polarization in allergy, there are few reports on the lncRNA–M1 macrophage polarization-allergy axis. One of the few such studies, reported by Jiang et al., describes the contribution of lncRNA MEG8-sponging of miR-181a-5p to M1 macrophage polarization via regulating SHP2 expression in a rat model of IgA purpura, which is a type 3 allergic disease triggered by allergens such as drugs, food, or insect bites [87]. In another study, Zhu et al. demonstrated that lncRNA growth-arrest-specific transcript 5 (GAS5) is upregulated in exosomes isolated from the nasal mucus of allergic rhinitis patients and promotes M1 macrophage polarization by restraining autophagy and subsequently activating NF-κB signaling [88].
4.3. circRNA-Mediated Regulation of Macrophage Polarization
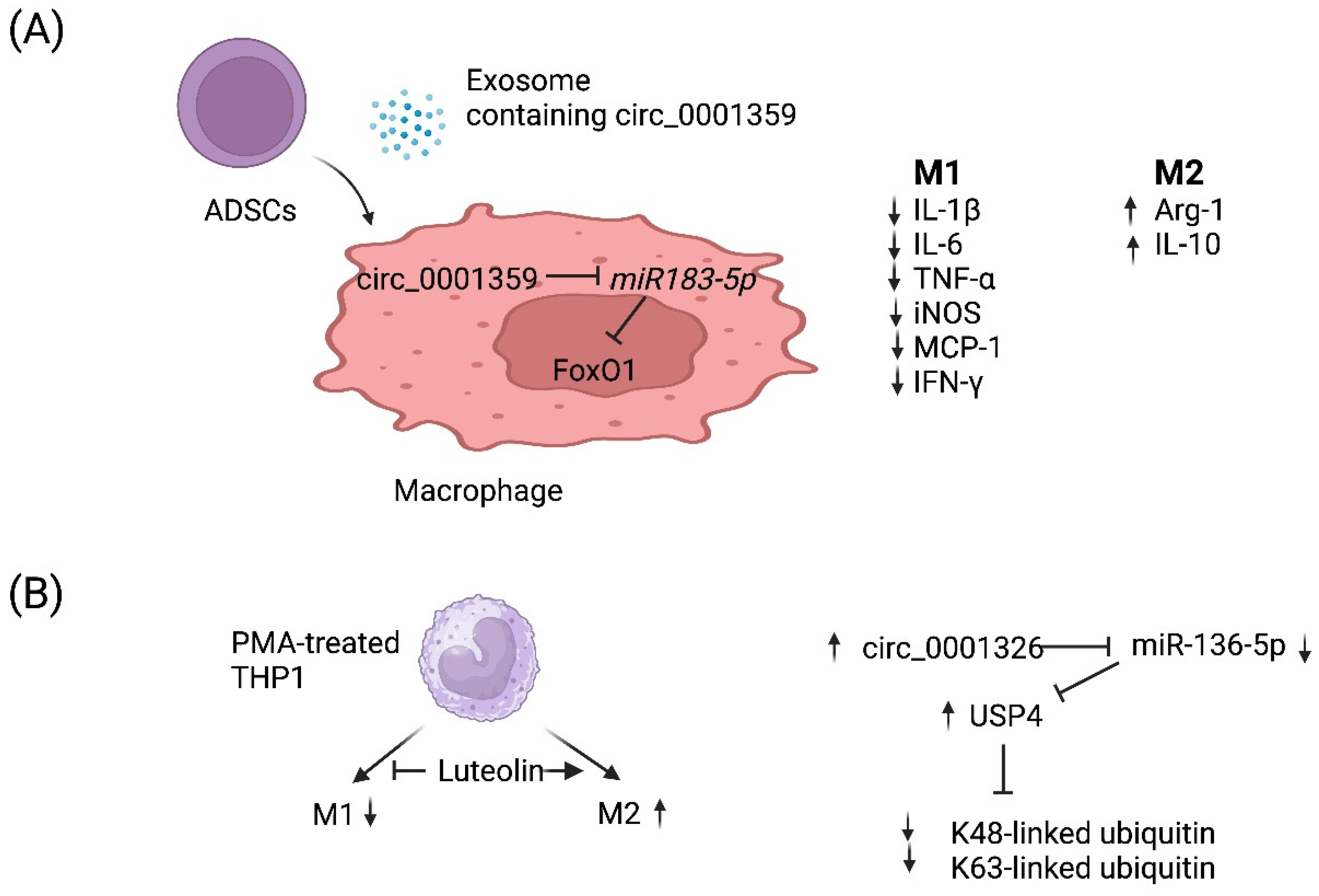
circRNAs are a recently discovered product of back splicing, and a subset of them do not encode for protein. Thus, they comprise a new category of ncRNAs that form covalently closed circular structures, which make them resistant to degradation by RNA exonucleases [89,90]. Since they are long-lived, a few circRNAs have been shown to act as molecular “sponges” that sequester miRNAs and/or RNA-binding proteins [91]. Although the function of most circRNAs remains poorly understood, a few circRNAs have been demonstrated to regulate the macrophage polarization associated with allergy (Table 2). For example, Shang et al. reported that circ_0001359 was downregulated in ovalbumin-induced asthmatic mice compared with normal mice and circ_0001359-enriched exosomes secreted from adipose-derived stem-cells-attenuated airway remodeling via promoting polarization into M2-like macrophages [92]. Mechanistically, circ_0001359 was shown to regulate macrophage polarization by enhancing FoxO1 signaling via sponging miR-183-5p (Figure 2A) [92]. Recently, luteolin, a flavone reported to have a protective role in asthma, was shown to activate M2 and suppress M1 macrophage polarization via upregulating circ_0001326 in the human macrophage cell line THP-1 [93]. The same study also elucidated the underlying mechanism of how circ_0001326 regulates downstream gene expression, including miR-136-5p and USP4 (Figure 2B). Finally, it is also conceivable that synthetic circRNAs could be rationally designed to inhibit specific miRNAs to treat diseases such as allergy. Once miRNAs that promote allergy have been identified and validated, then one could simply multimerize the binding sites for miRNA(s) of interest into a synthetic circRNA that will serve to inhibit them and, in turn, allergy.
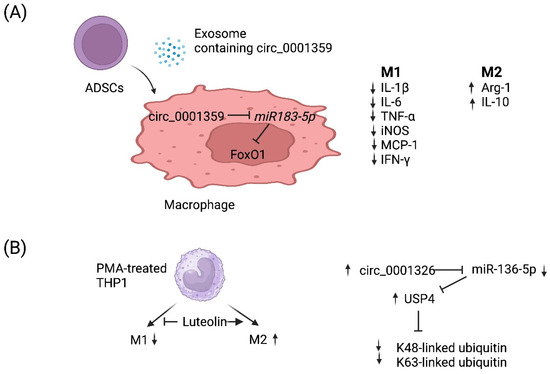
Figure 2.
Working models of how two circRNAs regulate M1 vs. M2 macrophage polarization. (A) Adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) secrete exosomes that contain circ_0001359. Upon fusion with macrophages, circ_0001359 is released into the cytoplasm and promotes M2-like macrophage polarization in an ovalbumin-induced asthma mouse model and lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 macrophages cells as evidenced by Arg-1 and IL-10 expression. In contrast, the expression of the following M1 effector molecules is suppressed by circ_0001359: IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, iNOS, MCP-1, and IFN-γ. Mechanistically, circ_0001359 inhibits miR-183-5p via base pairing. Since Foxo1 mRNA is directly repressed by miR-183-5p, FoxO1 activity is enhanced as a result and may be in part responsible for reprogramming macrophage cell fate. Image created with BioRender.com (accessed on 28 November 2023). (B) Luteolin (a naturally occurring flavonoid found in plants), known for its protective role in asthma, inhibits M1 macrophage polarization and promotes M2 activation in THP-1-derived macrophages. Luteolin-treated THP-1 macrophages induce expression of circ_0001326, inhibiting miR-136-5p via base pairing. Consequently, ubiquitin-specific protease 4 (USP4) is upregulated since it is directly repressed by miR-136-5p, and ultimately K48-linked and K63-linked ubiquitin is metabolized by USP4 since it is a deubiquitinase enzyme. Image created with BioRender.com (accessed on 28 November 2023).

Table 2.
Long noncoding and circular RNAs that regulate macrophage polarization in allergy.
Table 2.
Long noncoding and circular RNAs that regulate macrophage polarization in allergy.
| LncRNA | Materials Used | Affecting Polarization | Target | Related Pathophysiology | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTPRE-AS1 | Mouse bone-marrow-derived macrophages | M2 (−) | MAPK/ERK-1/2 pathway | Allergic asthma | [81] |
| MIR222HG | Mouse RAW264.7 cell line | M2 (−) | miR146a-5p/TRAF6/NF-κB axis | Allergic rhinitis | [82] |
| AK085865 | AK085865-deficient mice | M2 (+) | Not determined | Asthmatic airway inflammation | [83,84] |
| lnc-BAZ2B | Peripheral blood mononuclear cells of asthma patients | M2 (+) | IRF4 | Allergic asthma | [85] |
| NKILA | Asthmatic mouse model | M2 (+) | NF-κB pathway | Asthmatic airway inflammation | [86] |
| MEG8 | Rat peripheral blood cells | M1 (+) | miR-181a-5p | IgA purpura (Henoch-Schonlein purpura) | [87] |
| GAS5 | Asthmatic rat model Human ASM culture | M1 (+) | mTORC1/ULK1/ATG13 axis | Allergic rhinitis | [88] |
| circ_0001359 | Asthmatic mouse model | M2 (+) | FoxO1 signaling via sponging miR-183-5p | Allergic asthma | [92] |
| circ_0001326 | Human THP-1 cell line | M2 (+) M1 (−) | miR-136-5p and USP4 | Allergic asthma | [93] |
5. Therapeutic Implications of the ncRNA–Allergy Axis
Individual ncRNAs regulate the expression of multiple genes and proteins; therefore, they are involved in diverse biological processes including those associated with allergic diseases. Since the dysregulation of macrophage polarization is a primary feature of many allergic diseases, targeting the ncRNAs that regulate macrophage polarization represents a promising therapeutic approach for treating these diseases. As described above, several studies have shown that modulating the expression of specific ncRNAs can alter macrophage polarization and ameliorate allergic symptoms. Of the ncRNAs, miRNAs have particularly attracted attention as promising therapeutic targets of allergic diseases, as is the case for many diseases, e.g., cancer [72].
Of several types of molecules that modulate ncRNA functions, synthetic oligonucleotides such as small interfering (si) RNAs and antisense RNAs are widely used as tools to inactivate specific ncRNAs and are being developed into drugs. For example, patisiran is an FDA-approved siRNA therapeutic [94]. Inotersen is an FDA-approved antisense RNA for the same indication [95]. Thus, in principle, both classes of oligonucleotides can be developed into safe and effective drugs. Synthetic miRNA mimics are frequently used in miRNA studies, as well as antisense RNAs that bind target miRNAs, thus inhibiting their function (antagomirs). For example, a previous in vitro study demonstrated that miR-155-5p overexpression via transfection of a synthetic miR-155-5p mimic reprogrammed macrophages from the M2 phenotype into M1 phenotype. If this could be accomplished in vivo, then it could be a potential avenue for treating allergies. Conversely, targeting miR-155-5p with antisense oligonucleotides restored the defect in M2-like macrophage polarization in rheumatoid arthritis, suggesting that a miR-155-5p antagomir may serve as a drug for rheumatoid arthritis treatment [79].
Although several antagomirs and miRNA mimics have been developed as promising oligonucleotide therapeutics, they have yet to reach the market. Conceivably, the major limitation is a difficulty in delivering sufficient amounts of these molecules into the targeted cells. In addition, small RNA molecules that are chemically modified to enhance their specificity and/or stability have been reported to potently induce unfavorable immune responses such as the interferon response in a cell-type-dependent manner [96]. Thus, further research will be necessary to develop oligonucleotide therapeutics with both high efficacy and safety.
In addition to miRNAs, some lncRNAs and circRNAs have been shown to regulate macrophage polarization as mentioned above; thus, they can also be potent therapeutic targets. However, compared with miRNA research, lncRNA and circRNA research has not yet progressed from bench to clinical application. A hurdle to be overcome is the difficulty experienced with the delivery of RNA molecules. As is the case for COVID-19 vaccines, the use of lipid nanoparticles as an RNA carrier is a promising option. In addition, exosomes have been recently highlighted as a promising carrier of RNA molecules including ncRNAs due to their high stability, high biocompatibility, and low immunogenicity [97]. For example, Huang et al. reported that exosomes engineered for the tumor-targeted delivery lncRNA MEG3 had high therapeutic efficacy against osteosarcoma [98]. Exosomes are naturally derived lipid nanoparticles that deliver RNA and/or protein cargo to cells. Therefore, exosomes carrying ncRNAs that regulate macrophage polarization could be less-toxic allergy medications.
6. Concluding Remarks
In summary, we discussed how the ncRNA-mediated regulation of macrophage polarization and function could be associated with allergies. However, current knowledge on ncRNA–macrophage–allergy connections is limited; therefore, more mechanistic as well as in vivo studies are needed using either human subjects or animal models that better mimic human allergy. In other human diseases, genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have led to the identification of important drug targets [99,100]. Furthermore, most of the identified associations map to noncoding regions of the human genome [101]. While not all such loci are ncRNA genes, at least a subset of them are [102]. Some are regulatory elements including 3′-untranslated regions (UTRs). It stands to reason that if miRNAs can regulate disease pathogenesis, then variation in their binding site within a 3′ UTR could also have a significant biological effect [103,104]. These targets of natural variation in some cases can also be modulated pharmacologically.
Since M1 and M2 macrophages have been mainly defined and characterized based on the results of simplified in vitro studies, their in vivo roles, where the environment is more heterogeneous and complicated, have yet to be fully elucidated. This might explain why there is no consensus on whether inhibiting or promoting M2 macrophage polarization is associated with allergic diseases. Until this issue is resolved, it will be challenging to rationally design a drug development strategy for allergy. Nonetheless, it is widely accepted that macrophages are an attractive therapeutic target for immune-mediated diseases, and there is no reason to think that allergy is an exception. Moreover, ncRNAs have been considered promising therapeutic targets in addition to biomarkers. Regulatory networks involving cytokines, chemokines, signaling molecules, and transcription factors, as well as epigenetic events such as DNA methylation and histone modifications through methylation and acetylation, are essential for macrophage polarization [54]. Currently, the options available to treat or cure allergic diseases are limited; therefore, many allergic patients continuously receive treatments such as antihistamines, which do not completely relieve their symptoms. In this context, an improved understanding of how these ncRNAs are associated with the complicated networks between macrophage polarization and allergic diseases is required to reveal novel targets for drug discovery and development.
Author Contributions
O.I. wrote the first draft; Z.I. and S.A.M. substantially edited the manuscript. Z.I. made the figures in BioRender with input from O.I. and S.A.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI grant number 19K05954. (O.I.) and in part by the Intramural Research Program of NIAID (Z.I. and. S.A.M.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We thank anonymous reviewers, Alia Welsh (NIAID), and Patrick T. Smith (NIAID) for reading our manuscript and providing useful feedback.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lee, T.H. Allergy: The unmet need. Clin. Med. 2003, 3, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulendran, B.; Artis, D. New Paradigms in Type 2 Immunity. Science 2012, 337, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawankar, R.; Canonica, G.W.; Holgate, S.T.; Lockey, R.F.; Blaiss, M.S. WAO White Book on Allergy: Update 2013 Executive Summary; World Allergy Organization: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pawankar, R.; Canonica, G.W.; Holgate, S.T.; Lockey, R.F. Allergic diseases and asthma: A major global health concern. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 12, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawankar, R.; Mori, S.; Ozu, C.; Kimura, S. Overview on the pathomechanisms of allergic rhinitis. Asia Pac. Allergy 2011, 1, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, T.P.; Norman, P.S. Isolation studies of allergens from regweed pollen. Biochemistry 1962, 1, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudharson, S.; Kalic, T.; Hafner, C.; Breiteneder, H. Newly defined allergens in the WHO/IUIS Allergen Nomenclature Database during 01/2019-03/2021. Allergy 2021, 76, 3359–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukutomi, Y.; Kawakami, Y.; Taniguchi, M.; Saito, A.; Fukuda, A.; Yasueda, H.; Nakazawa, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Nakamura, H.; Akiyama, K. Allergenicity and cross-reactivity of booklice (Liposcelis bostrichophila): A common household insect pest in Japan. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 157, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishibashi, O.; Sakuragi, K.; Fukutomi, Y.; Kawakami, Y.; Kamata, Y.; Sakurai, M.; Nakayama, S.; Uchiyama, H.; Kobayashi, H.; Kojima, H.; et al. Lip b 1 is a novel allergenic protein isolated from the booklouse, Liposcelis bostrychophila. Allergy 2017, 72, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, D.; Vadas, P. Anaphylaxis to Oatmeal and Psocid Crisps. Iran J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020, 19, 200–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnana Moorthy Eswaran, U.; Karunanithi, S.; Gupta, R.K.; Rout, S.; Srivastav, P.P. Edible insects as emerging food products-processing and product development perspective. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 60, 2105–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.P.; Silvers, S.; Shapiro, M.A. Intralymphatic immunotherapy for mountain cedar pollinosis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020, 125, 311–318.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, C.; Bernstein, D.I. Allergen immunotherapy: An updated review of safety. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 17, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, W.; Corren, J.; Lanier, B.Q.; McAlary, M.; Fowler-Taylor, A.; Cioppa, G.D.; van As, A.; Gupta, N. Omalizumab, anti-IgE recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody, for the treatment of severe allergic asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 108, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girodet, P.O.; Nguyen, D.; Mancini, J.D.; Hundal, M.; Zhou, X.; Israel, E.; Cernadas, M. Alternative Macrophage Activation Is Increased in Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 55, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, M.H.; Abdelwahab, S.F.; Wan, J.; Cai, W.; Huixuan, W.; Jianjun, C.; Kumar, K.D.; Vasudevan, A.; Sadek, A.; Su, Z.; et al. Alternatively activated macrophages; a double-edged sword in allergic asthma. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balhara, J.; Gounni, A.S. The alveolar macrophages in asthma: A double-edged sword. Mucosal Immunol. 2012, 5, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Veen, T.A.; de Groot, L.E.; Melgert, B.N. The different faces of the macrophage in asthma. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2020, 26, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wei, D.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y. FABP5 controls macrophage alternative activation and allergic asthma by selectively programming long-chain unsaturated fatty acid metabolism. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackaness, G.B. Cellular resistance to infection. J. Exp. Med. 1962, 116, 381–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbe, P.; Draijer, C.; Borg, T.R.; Luinge, M.; Timens, W.; Wouters, I.M.; Melgert, B.N.; Hylkema, M.N. Distinct macrophage phenotypes in allergic and nonallergic lung inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2015, 308, L358–L367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draijer, C.; Robbe, P.; Boorsma, C.E.; Hylkema, M.N.; Melgert, B.N. Dual role of YM1+ M2 macrophages in allergic lung inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, T.; Ding, W.; Zhao, Y. Cellular metabolism and macrophage functional polarization. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 34, 82–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertani, F.R.; Mozetic, P.; Fioramonti, M.; Iuliani, M.; Ribelli, G.; Pantano, F.; Santini, D.; Tonini, G.; Trombetta, M.; Businaro, L.; et al. Classification of M1/M2-polarized human macrophages by label-free hyperspectral reflectance confocal microscopy and multivariate analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosser, D.M.; Edwards, J.P. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 958–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, Z.; Inui, T.; Ishibashi, O. Gpr137b is an orphan G-protein-coupled receptor associated with M2 macrophage polarization. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 509, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, C.F.; Murray, H.W.; Wiebe, M.E.; Rubin, B.Y. Identification of interferon-gamma as the lymphokine that activates human macrophage oxidative metabolism and antimicrobial activity. J. Exp. Med. 1983, 158, 670–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, F.O.; Gordon, S. The M1 and M2 paradigm of macrophage activation: Time for reassessment. F1000Prime Rep. 2014, 6, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, P.J.; Allen, J.E.; Biswas, S.K.; Fisher, E.A.; Gilroy, D.W.; Goerdt, S.; Gordon, S.; Hamilton, J.A.; Ivashkiv, L.B.; Lawrence, T.; et al. Macrophage activation and polarization: Nomenclature and experimental guidelines. Immunity 2014, 41, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sica, A.; Mantovani, A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization: In vivo veritas. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutilier, A.J.; Elsawa, S.F. Macrophage Polarization States in the Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Lainez, N.M.; Coss, D.; Nair, M.G. Macrophage-Regulatory T Cell Interactions Promote Type 2 Immune Homeostasis Through Resistin-Like Molecule α. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 710406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Liang, H.; Zen, K. Molecular mechanisms that influence the macrophage m1-m2 polarization balance. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Geng, X.; Hou, J.; Wu, G. New insights into M1/M2 macrophages: Key modulators in cancer progression. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Floc’h, A.; Allinne, J.; Nagashima, K.; Scott, G.; Birchard, D.; Asrat, S.; Bai, Y.; Lim, W.K.; Martin, J.; Huang, T.; et al. Dual blockade of IL-4 and IL-13 with dupilumab, an IL-4Rα antibody, is required to broadly inhibit type 2 inflammation. Allergy 2020, 75, 1188–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahariya, S.; Paddibhatla, I.; Kumar, S.; Raghuwanshi, S.; Pallepati, A.; Gutti, R.K. Long non-coding RNA: Classification, biogenesis and functions in blood cells. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 112, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, W.; Chen, Q.; Chen, M. Non-Coding RNAs and their Integrated Networks. J. Integr. Bioinform. 2019, 16, 2019-0027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, C.; Gao, J.; Yang, L.; Yuan, X. Non-coding RNA regulation of macrophage function in asthma. Cell. Signal. 2023, 112, 110926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feketea, G.; Bocsan, C.I.; Popescu, C.; Gaman, M.; Stanciu, L.A.; Zdrenghea, M.T. A Review of Macrophage MicroRNAs’ Role in Human Asthma. Cells 2019, 8, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atri, C.; Guerfali, F.Z.; Laouini, D. Role of Human Macrophage Polarization in Inflammation during Infectious Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, M.; Desnues, B.; Mege, J.-L. Macrophage Polarization in Bacterial Infections. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 3733–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassol, E.; Cassetta, L.; Alfano, M.; Poli, G. Macrophage polarization and HIV-1 infection. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 87, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Sugimoto, C.; Arainga, M.; Alvarez, X.; Didier, E.S.; Kuroda, M.J. In vivo characterization of alveolar and interstitial lung macrophages in rhesus macaques: Implications for understanding lung disease in humans. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 2821–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Benedetto, P.; Ruscitti, P.; Vadasz, Z.; Toubi, E.; Giacomelli, R. Macrophages with regulatory functions, a possible new therapeutic perspective in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 102369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilhorst, M.; Shirai, T.; Berry, G.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. T cell-macrophage interactions and granuloma formation in vasculitis. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskin, D.L.; Sunil, V.R.; Gardner, C.R.; Laskin, J.D. Macrophages and tissue injury: Agents of defense or destruction? Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2011, 51, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sica, A.; Erreni, M.; Allavena, P.; Porta, C. Macrophage polarization in pathology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 4111–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Nair, M.G. Macrophages in wound healing: Activation and plasticity. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2019, 97, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Xu, X.-H.; Jin, L. Macrophage Polarization in Physiological and Pathological Pregnancy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiseleva, V.; Vishnyakova, P.; Elchaninov, A.; Fatkhudinov, T.; Sukhikh, G. Biochemical and molecular inducers and modulators of M2 macrophage polarization in clinical perspective. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 122, 110583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labonte, A.C.; Tosello-Trampont, A.-C.; Hahn, Y.S. The role of macrophage polarization in infectious and inflammatory diseases. Mol. Cells 2014, 37, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Fessler, M.B.; Qu, P.; Heymann, J.; Kopp, J.B. Macrophage polarization in innate immune responses contributing to pathogenesis of chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol. 2020, 21, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.; Zou, X.B.; Chai, Y.F.; Yao, Y.M. Macrophage polarization in inflammatory diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Locati, M. Tumor-associated macrophages as a paradigm of macrophage plasticity, diversity, and polarization: Lessons and open questions. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 1478–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fricker, M.; Gibson, P.G. Macrophage dysfunction in the pathogenesis and treatment of asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffery, P.K.; Haahtela, T. Allergic rhinitis and asthma: Inflammation in a one-airway condition. BMC Pulm. Med. 2006, 6 (Suppl. 1), S5–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Huang, Y.; Chu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L. M2 Macrophages Upregulated by Allergen Exposure in Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2023, 184, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Akkoyunlu, M.; Rabin, R.L. Macrophages—common culprit in obesity and asthma. Allergy 2018, 73, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.G.; Kim, M.N.; Hong, J.Y.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, K.W.; Lee, C.G.; Elias, J.A.; Song, T.W.; Sohn, M.H. Chitinase 3-Like 1 Contributes to Food Allergy via M2 Macrophage Polarization. Allergy, Asthma Immunol. Res. 2020, 12, 1012–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peschansky, V.J.; Wahlestedt, C. Non-coding RNAs as direct and indirect modulators of epigenetic regulation. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statello, L.; Guo, C.J.; Chen, L.L.; Huarte, M. Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattick, J.S.; Amaral, P.P.; Carninci, P.; Carpenter, S.; Chang, H.Y.; Chen, L.L.; Chen, R.; Dean, C.; Dinger, M.E.; Fitzgerald, K.A. Long non-coding RNAs: Definitions, functions, challenges and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 430–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodarzi, V.; Nouri, S.; Nassaj, Z.S.; Bighash, M.; Abbasian, S.; Hagh, R.A. Long non coding RNAs reveal important pathways in childhood asthma: A future perspective. Histochem. J. 2023, 54, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squadrito, M.L.; Etzrodt, M.; De Palma, M.; Pittet, M.J. MicroRNA-mediated control of macrophages and its implications for cancer. Trends Immunol. 2013, 34, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Nunez, R.T.; Louafi, F.; Sanchez-Elsner, T. The interleukin 13 (IL-13) pathway in human macrophages is modulated by microRNA-155 via direct targeting of interleukin 13 receptor alpha1 (IL13Ralpha1). J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 1786–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, N.; Kumar, R.K.; Foster, P.S.; Herbert, C. Enhanced Pro-Inflammatory Response of Macrophages to Interleukin-33 in an Allergic Environment. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 176, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, A.; Maurya, M.; Maurya, P.; Barthwal, M.K. Lin28B Regulates Angiotensin II-Mediated Let-7c/miR-99a MicroRNA Formation Consequently Affecting Macrophage Polarization and Allergic Inflammation. Inflammation 2020, 43, 1846–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Xie, N.; Cui, H.; Tan, Z.; Yang, S.; Icyuz, M.; Abraham, E.; Liu, G. MicroRNA let-7c regulates macrophage polarization. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 6542–6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Song, X.; Dong, L.; Liu, D. MiR-202-5p Promotes M2 Polarization in Allergic Rhinitis by Targeting MATN2. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 178, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Hur, J.; Kang, J.Y.; Rhee, C.K.; Lee, S.Y. MicroRNA-21 Inhibition Suppresses Alveolar M2 Macrophages in an Ovalbumin-Induced Allergic Asthma Mice Model. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2021, 13, 312–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Pomares, L. The mannose receptor. J. Leukoc Biol. 2012, 92, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squadrito, M.L.; Pucci, F.; Magri, L.; Moi, D.; Gilfillan, G.D.; Ranghetti, A.; Casazza, A.; Mazzone, M.; Lyle, R.; Naldini, L.; et al. miR-511-3p modulates genetic programs of tumor-associated macrophages. Cell Rep. 2012, 1, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Do, D.C.; Ishmael, F.T.; Squadrito, M.L.; Tang, H.M.; Tang, H.L.; Hsu, M.H.; Qiu, L.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Mannose receptor modulates macrophage polarization and allergic inflammation through miR-511-3p. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 350–364.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, D.C.; Mu, J.; Ke, X.; Sachdeva, K.; Qin, Z.; Wan, M.; Ishmael, F.T.; Gao, P. miR-511-3p protects against cockroach allergen-induced lung inflammation by antagonizing CCL2. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 4, e126832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinsbroek, S.E.; Squadrito, M.L.; Schilderink, R.; Hilbers, F.W.; Verseijden, C.; Hofmann, M.; Helmke, A.; Boon, L.; Wildenberg, M.E.; Roelofs, J.J.; et al. miR-511-3p, embedded in the macrophage mannose receptor gene, contributes to intestinal inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 2016, 9, 960–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.; Lee, Y.G.; Karpurapu, M.; Englert, J.A.; Ballinger, M.N.; Davis, I.C.; Park, G.Y.; Christman, J.W. Depletion of microRNA-451 in response to allergen exposure accentuates asthmatic inflammation by regulating Sirtuin2. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2020, 318, L921–L930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veremeyko, T.; Siddiqui, S.; Sotnikov, I.; Yung, A.; Ponomarev, E.D. IL-4/IL-13-dependent and independent expression of miR-124 and its contribution to M2 phenotype of monocytic cells in normal conditions and during allergic inflammation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Chen, M.; Ouyang, L.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Huang, L.; Jiang, S. miR-142-5p and miR-130a-3p regulate pulmonary macrophage polarization and asthma airway remodeling. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2020, 98, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.; Zhao, Q.; He, C.; Huang, D.; Liu, J.; Chen, F.; Chen, J.; Liao, J.Y.; Cui, X.; Zeng, Y.; et al. miR-142-5p and miR-130a-3p are regulated by IL-4 and IL-13 and control profibrogenic macrophage program. Nat Commun. 2015, 6, 8523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, A.; Rohmer, J.; Ly, B.; Pascaud, J.; Rivière, E.; Seror, R.; Le Goff, B.; Nocturne, G.; Mariette, X. Monocyte/Macrophage Abnormalities Specific to Rheumatoid Arthritis Are Linked to miR-155 and Are Differentially Modulated by Different TNF Inhibitors. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 1766–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Huang, S.; Xue, P.; Fu, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; Yang, L.; Xia, L.; Sun, L.; Huang, S.K.; et al. LncRNA PTPRE-AS1 modulates M2 macrophage activation and inflammatory diseases by epigenetic promotion of PTPRE. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax9230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Li, F.; Tang, Y.; Dong, L.; He, Y.; Deng, Y.; Tao, Z. MIR222HG attenuates macrophage M2 polarization and allergic inflammation in allergic rhinitis by targeting the miR146a-5p/TRAF6/NF-κB axis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1168920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Luo, M.; Chen, T.; Zhang, M.; Zhong, M.; Lv, K. LncRNA AK085865 depletion ameliorates asthmatic airway inflammation by modulating macrophage polarization. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 83, 106450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, M.; Yang, H.; Lv, K. lncRNA AK085865 Promotes Macrophage M2 Polarization in CVB3-Induced VM by Regulating ILF2-ILF3 Complex-Mediated miRNA-192 Biogenesis. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 21, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Fu, J.; Xiao, W.; Liang, Q.; Han, X.; Huang, S.; Sun, L.; Gao, Y.; et al. lnc-BAZ2B promotes M2 macrophage activation and inflammation in children with asthma through stabilizing BAZ2B pre-mRNA. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 921–932.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Lu, L.; Li, X.; Lu, S. Long non-coding RNA NKILA alleviates airway inflammation in asthmatic mice by promoting M2 macrophage polarization and inhibiting the NF-κB pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 571, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Dai, J.; Yin, M.; Jiang, C.; Ren, M.; Tian, L. LncRNA MEG8 sponging miR-181a-5p contributes to M1 macrophage polarization by regulating SHP2 expression in Henoch-Schonlein purpura rats. Ann. Med. 2021, 53, 1576–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Sun, Y.; Yu, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Exosomal lncRNA GAS5 promotes M1 macrophage polarization in allergic rhinitis via restraining mTORC1/ULK1/ATG13-mediated autophagy and subsequently activating NF-κB signaling. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 121, 110450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.-Y.; Kuo, H.-C. The emerging roles and functions of circular RNAs and their generation. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memczak, S.; Jens, M.; Elefsinioti, A.; Torti, F.; Krueger, J.; Rybak, A.; Maier, L.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Gregersen, L.H.; Munschauer, M.; et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 2013, 495, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, J.; Lu, D.; Xu, A. The interaction of circRNAs and RNA binding proteins: An important part of circRNA maintenance and function. J. Neurosci. Res. 2020, 98, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xu, J.; Ge, X.; Hu, Z.; Xiao, J.; Ning, Y.; Dong, Y.; Bai, C. Exosomes from mmu_circ_0001359-Modified ADSCs Attenuate Airway Remodeling by Enhancing FoxO1 Signaling-Mediated M2-like Macrophage Activation. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 19, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, B.; Zheng, Y.; Li, J.; Lei, H.; Liu, K.; Tang, J.; Peng, Y. Luteolin activates M2 macrophages and suppresses M1 macrophages by upregulation of hsa_circ_0001326 in THP-1 derived macrophages. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 5079–5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.; Gonzalez-Duarte, A.; O’Riordan, W.D.; Yang, C.C.; Ueda, M.; Kristen, A.V.; Tournev, I.; Schmidt, H.H.; Coelho, T.; Berk, J.L.; et al. Patisiran, an RNAi Therapeutic, for Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, M.D.; Waddington-Cruz, M.; Berk, J.L.; Polydefkis, M.; Dyck, P.J.; Wang, A.K.; Planté-Bordeneuve, V.; Barroso, F.A.; Merlini, G.; Obici, L.; et al. Inotersen Treatment for Patients with Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishibashi, O.; Ali, M.M.; Luo, S.S.; Ohba, T.; Katabuchi, H.; Takeshita, T.; Takizawa, T. Short RNA duplexes elicit RIG-I-mediated apoptosis in a cell type- and length-dependent manner. Sci. Signal. 2011, 4, ra74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Huang, W.; Li, M.; Zhang, A. Exosome-Based Carrier for RNA Delivery: Progress and Challenges. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Wu, W.; Jing, D.; Yang, L.; Guo, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Pu, F.; Shao, Z. Engineered exosome as targeted lncRNA MEG3 delivery vehicles for osteosarcoma therapy. J. Control. Release 2022, 343, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teslovich, T.M.; Musunuru, K.; Smith, A.V.; Edmondson, A.C.; Stylianou, I.M.; Koseki, M.; Pirruccello, J.P.; Ripatti, S.; Chasman, D.I.; Willer, C.J.; et al. Biological, clinical and population relevance of 95 loci for blood lipids. Nature 2010, 466, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, D.I.; Preiss, D.; Kuchenbaecker, K.B.; Holmes, M.V.; Engmann, J.E.; Shah, T.; Sofat, R.; Stender, S.; Johnson, P.C.; Scott, R.A.; et al. HMG-coenzyme A reductase inhibition, type 2 diabetes, and bodyweight: Evidence from genetic analysis and randomised trials. Lancet 2015, 385, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurano, M.T.; Humbert, R.; Rynes, E.; Thurman, R.E.; Haugen, E.; Wang, H.; Reynolds, A.P.; Sandstrom, R.; Qu, H.; Brody, J.; et al. Systematic localization of common disease-associated variation in regulatory DNA. Science 2012, 337, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos-Rubio, A.; Ghosh, S. Disease-Associated SNPs in Inflammation-Related lncRNAs. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wightman, B.; Ha, I.; Ruvkun, G. Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell 1993, 75, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, C.; Hemann, M.T.; Bartel, D.P. Disrupting the pairing between let-7 and Hmga2 enhances oncogenic transformation. Science 2007, 315, 1576–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).