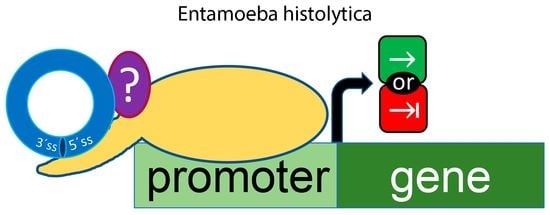
Promoter-Bound Full-Length Intronic Circular RNAs-RNA Polymerase II Complexes Regulate Gene Expression in the Human Parasite Entamoeba histolytica
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
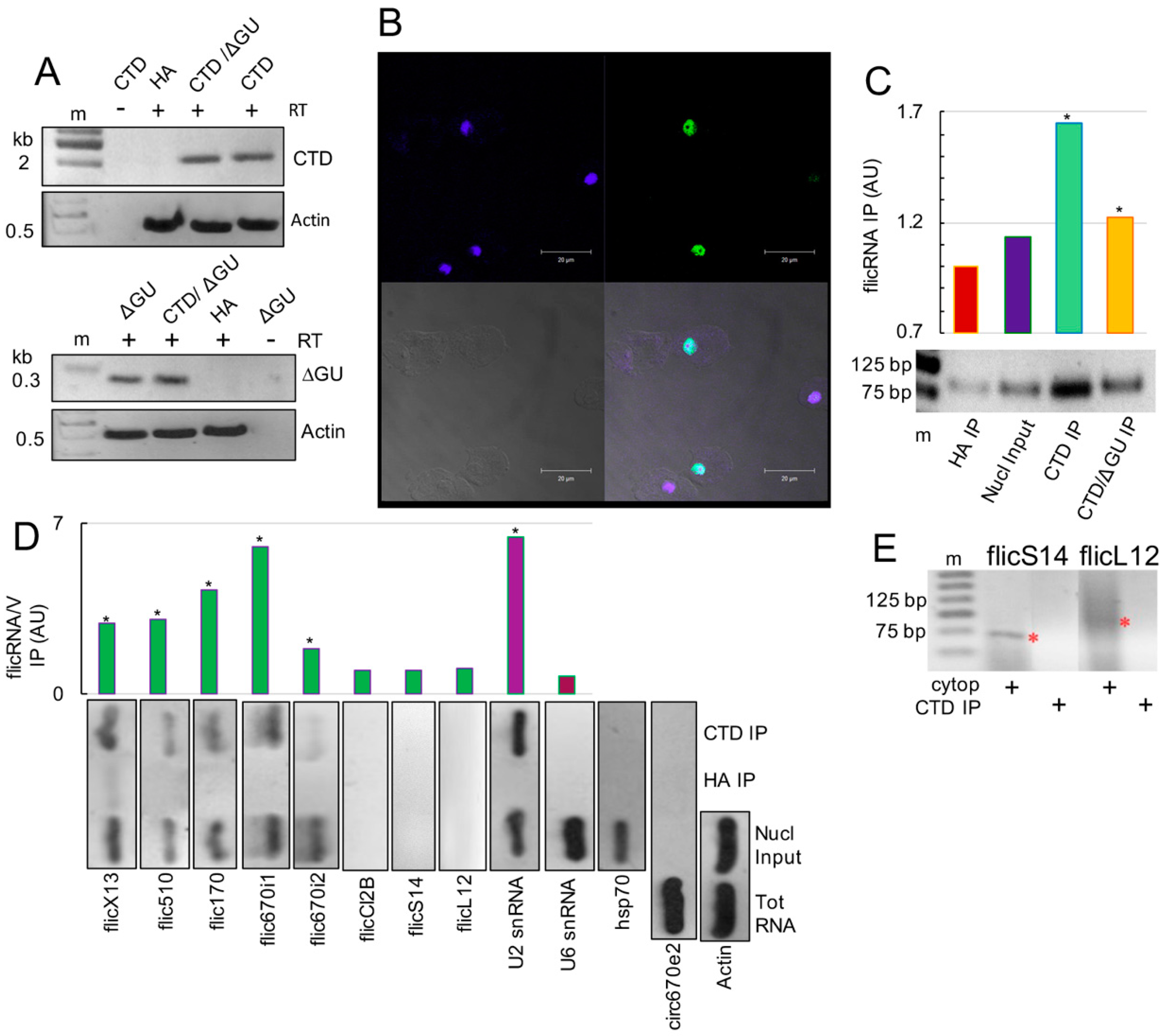
2.1. CLIP Assays Reveal flicRNAs-RNA Polymerase II Interactions
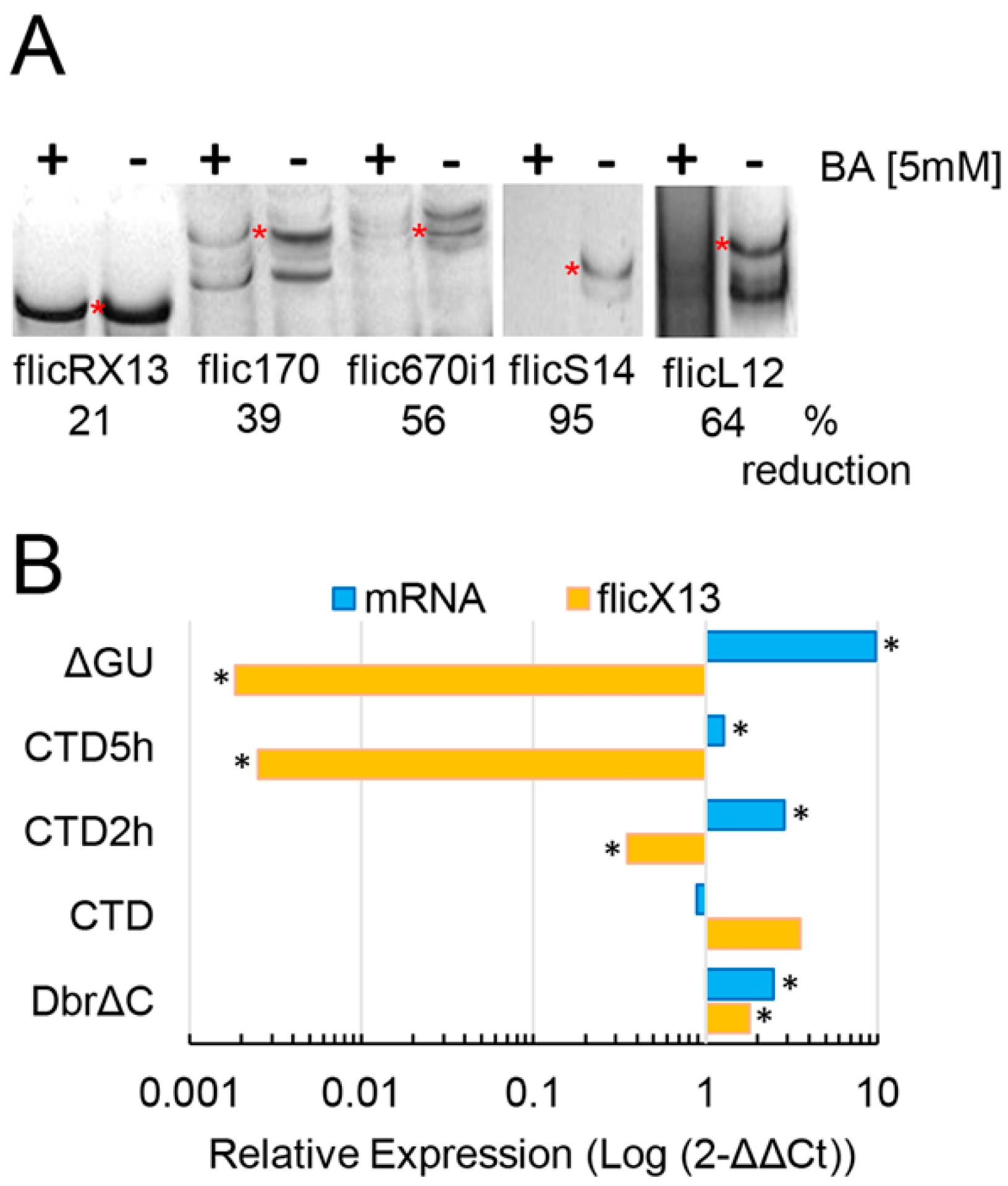
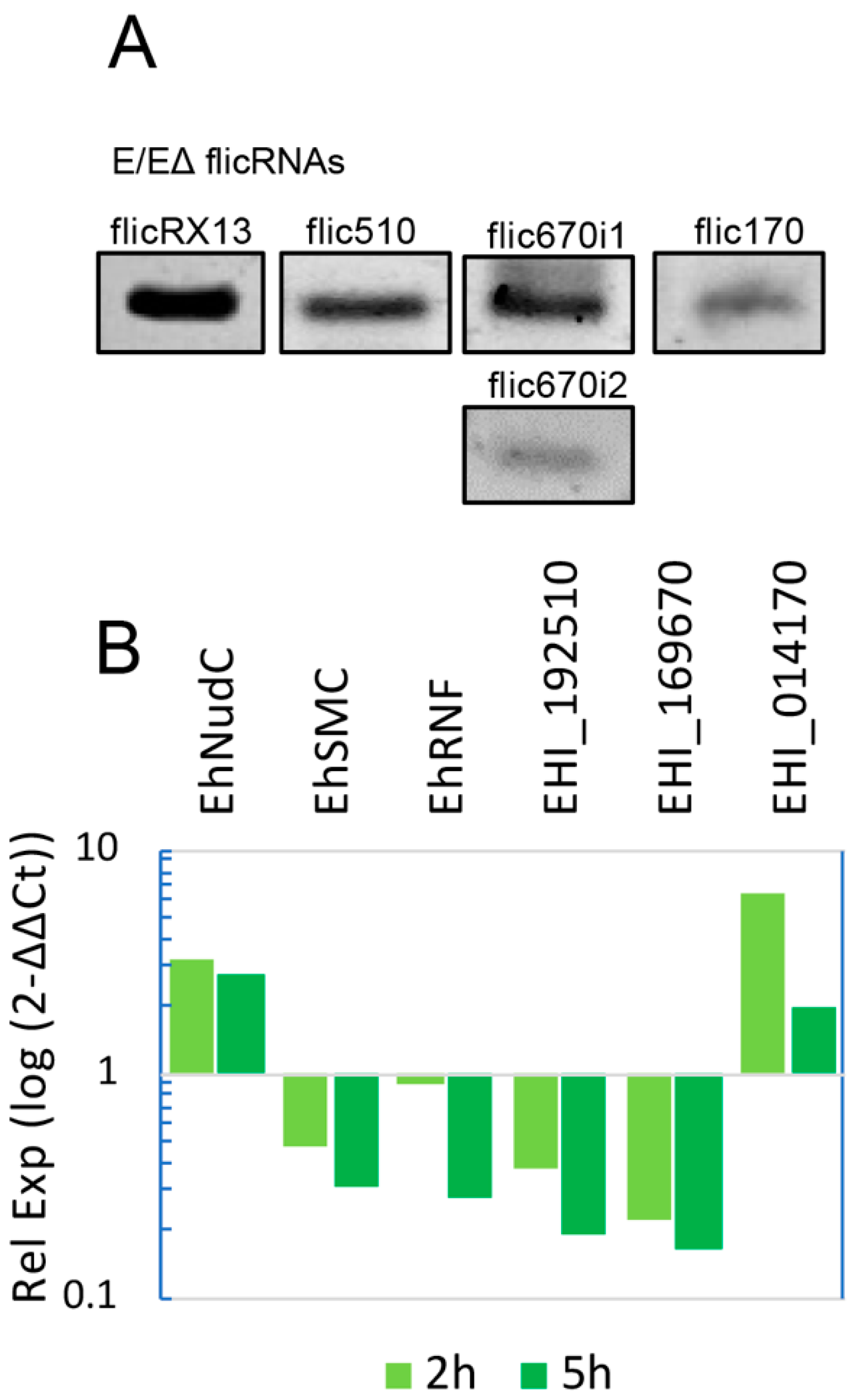
2.2. flicRNAs Modify Gene Expression
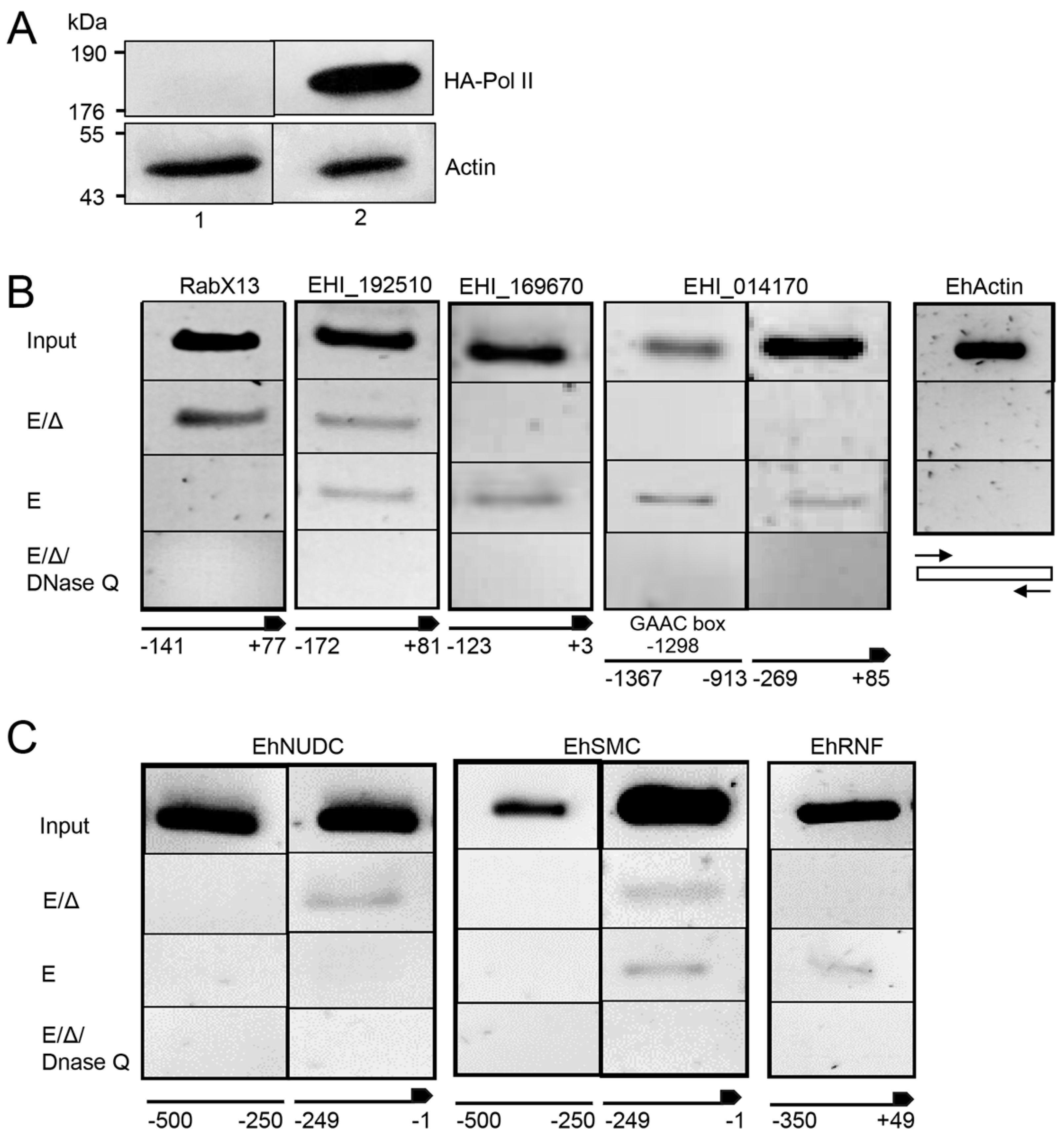
2.3. ChIP Identifies Promoter-Associated flicRNA-Pol II Complexes
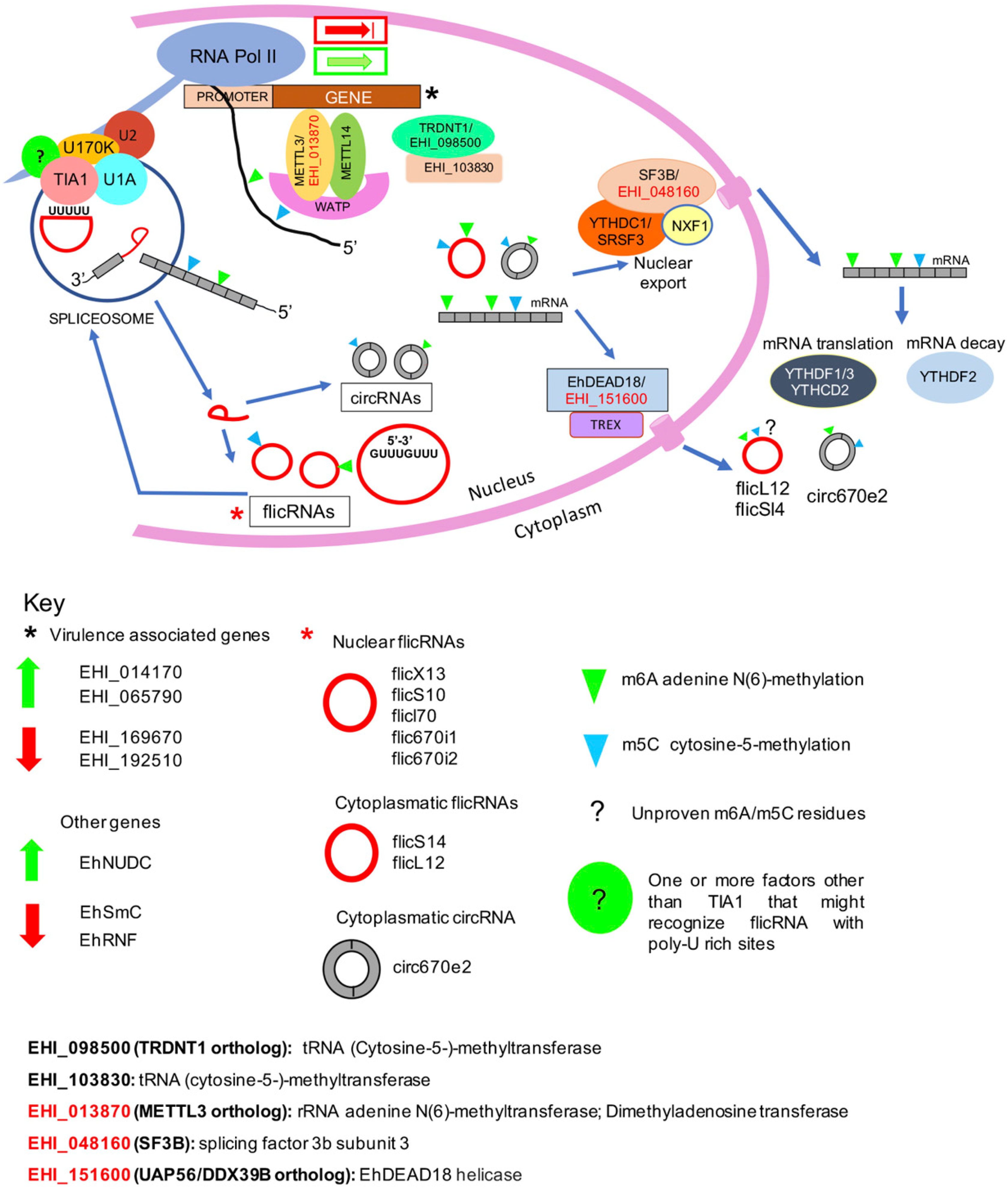
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanger, H.L.; Klotz, G.; Riesner, D.; Gross, H.J.; Kleinschmidt, A.K. Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 3852–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, M.T.; Coca-Prados, M. Electron microscopic evidence for the circular form of RNA in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Nature 1979, 280, 339–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasda, E.; Parker, R. Circular RNAs: Diversity of form and function. RNA 2014, 20, 1829–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Bao, C.; Chen, L.; Lin, M.; Wang, X.; Zhong, G.; Yu, B.; Hu, W.; Dai, L.; et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.L. The biogenesis and emerging roles of circular RNAs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdt, L.M.; Kohlmaier, A.; Teupser, D. Molecular roles and function of circular RNAs in eukaryotic cells. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 1071–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasman, Z.; Been, M.D.; Garcia-Blanco, M.A. Exon circularization in mammalian nuclear extracts. RNA 1996, 2, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.; Wilusz, J.E. Short intronic repeat sequences facilitate circular RNA production. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 2233–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xue, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.L.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.-L. The Biogenesis of Nascent Circular RNAs. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwal-Fluss, R.; Meyer, M.; Pamudurti, N.R.; Ivanov, A.; Bartok, O.; Hanan, M.; Evantal, N.; Memczak, S.; Rajewsky, N.; Kadener, S. circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, S.J.; Pillman, K.A.; Toubia, J.; Conn, V.M.; Salmanidis, M.; Phillips, C.A.; Roslan, S.; Schreiber, A.W.; Gregory, P.A.; Goodall, G.J. The RNA binding protein quaking regulates formation of circRNAs. Cell 2015, 160, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebbesen, K.K.; Hansen, T.B.; Kjems, J. Insights into circular RNA biology. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 1035–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talhouarne, G.J.; Gall, J.G. Lariat intronic RNAs in the cytoplasm of Xenopus tropicalis oocytes. RNA 2014, 20, 1476–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memczak, S.; Jens, M.; Elefsinioti, A.; Torti, F.; Krueger, J.; Rybak, A.; Maier, L.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Gregersen, L.H.; Munschauer, M.; et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 2013, 495, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmohsen, K.; Panda, A.C.; Munk, R.; Grammatikakis, I.; Dudekula, D.B.; De, S.; Kim, J.; Noh, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; Martindale, J.L.; et al. Identification of HuR target circular RNAs uncovers suppression of PABPN1 translation by CircPABPN1. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legnini, I.; Di Timoteo, G.; Rossi, F.; Morlando, M.; Briganti, F.; Sthandier, O.; Fatica, A.; Santini, T.; Andronache, A.; Wade, M.; et al. Circ-ZNF609 Is a Circular RNA that Can Be Translated and Functions in Myogenesis. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Feng, C.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, J.; Irwin, D.M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S. Identification of Candidate Circular RNAs Underlying Intramuscular Fat Content in the Donkey. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 587559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Xiao, L.; Chung, H.K.; Ma, X.X.; Liu, X.; Song, J.L.; Bao, C.; Chen, L.; Lin, M. Interaction between HuR and circPABPN1 Modulates Autophagy in the Intestinal Epithelium by Altering ATG16L1 Translation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2020, 40, e00492-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talhouarne, G.J.S.; Gall, J.G. Lariat intronic RNAs in the cytoplasm of vertebrate cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E7970–E7977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.C.; De, S.; Grammatikakis, I.; Munk, R.; Yang, X.; Piao, Y.; Dudekula, D.B.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Gorospe, M. High-purity circular RNA isolation method (RPAD) reveals a vast collection of intronic circRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.O.; Chen, T.; Xiang, J.F.; Yin, Q.F.; Xing, Y.H.; Nakada-Tsukui, K.; Sato, D.; Nozaki, T. Circular intronic long noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell 2013, 51, 792–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza-Figueroa, M.S.; Alfonso-Maqueira, E.E.; Velez, C.; Azuara-Liceaga, E.I.; Zarate, S.; Villegas-Sepulveda, N.; Saucedo-Cárdenas, O.; Valdés, J. Postsplicing-Derived Full-Length Intron Circles in the Protozoan Parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taggart, A.J.; Lin, C.L.; Shrestha, B.; Heintzelman, C.; Kim, S.; Fairbrother, W.G. Large-scale analysis of branchpoint usage across species and cell lines. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, J.; Hess, W.R.; Borner, T. Precise branch point mapping and quantification of splicing intermediates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 2030–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Luis, M.A. In Silico Identification and Characterization of circRNAs with miRNA-Sponge Potential in Virulent and Non-Virulent Strains of Entamoeba Histolytica and Entamoeba Invadens. Master’s Thesis, Escuela Nacional de Ciencias Biológicas del Instituto Politécnico Nacional, Mexico City, Mexico, 21 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- McKay, S.L.; Johnson, T.L. An investigation of a role for U2 snRNP spliceosomal components in regulating transcription. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojima, T.; Rebelo, K.; Gomes, T.; Grosso, A.R.; Proudfoot, N.J.; Carmo-Fonseca, M. RNA Polymerase II Phosphorylated on CTD Serine 5 Interacts with the Spliceosome during Co-transcriptional Splicing. Mol. Cell 2018, 72, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, D.J.; Friesen, J.D. Functionally redundant interactions between U2 and U6 spliceosomal snRNAs. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesler, C.; Rigo, N.; Anokhina, M.M.; Tauchert, M.J.; Agafonov, D.E.; Kastner, B.; Urlaub, H.; Ficner, R.; Will, C.L.; Lührmann, R. A spliceosome intermediate with loosely associated tri-snRNP accumulates in the absence of Prp28 ATPase activity. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davila Lopez, M.; Rosenblad, M.A.; Samuelsson, T. Computational screen for spliceosomal RNA genes aids in defining the phylogenetic distribution of major and minor spliceosomal components. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 3001–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdes, J.; Nozaki, T.; Sato, E.; Chiba, Y.; Nakada-Tsukui, K.; Villegas-Sepulveda, N.; Winkler, R.; Azuara-Liceaga, E.; Mendoza-Figueroa, M.S.; Watanabe, N.; et al. Proteomic analysis of Entamoeba histolytica in vivo assembled pre-mRNA splicing complexes. J. Proteom. 2014, 111, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waris, S.; Garcia-Maurino, S.M.; Sivakumaran, A.; Beckham, S.A.; Loughlin, F.E.; Gorospe, M.; Diaz-Moreno, I.; Wilce, M.C.; Wilce, J.A. TIA-1 RRM23 binding and recognition of target oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 4944–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weedall, G.D.; Hall, N. Evolutionary genomics of Entamoeba. Res. Microbiol. 2011, 162, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, I.; Kosti, I.; Ares, M., Jr.; Cline, M.; Mandel-Gutfreund, Y. RBPmap: A web server for mapping binding sites of RNA-binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W361–W367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Aibara, S.; Vos, S.M.; Agafonov, D.E.; Luhrmann, R.; Cramer, P. Structure of a transcribing RNA polymerase II-U1 snRNP complex. Science 2021, 371, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.W.; Zhang, C.; Yang, W.; Yong, T.; Awan, F.M.; Yang, B.B. Identifying and Characterizing circRNA-Protein Interaction. Theranostics 2017, 7, 4183–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alpert, T.; Herzel, L.; Neugebauer, K.M. Perfect timing: Splicing and transcription rates in living cells. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2017, 8, e1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oesterreich, F.C.; Herzel, L.; Straube, K.; Hujer, K.; Howard, J.; Neugebauer, K.M. Splicing of Nascent RNA Coincides with Intron Exit from RNA Polymerase II. Cell 2016, 165, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijsen, A.J.; Cocera Ortega, L.; Reckman, Y.J.; Zhang, X.; van der Made, I.; Aufiero, S.; Li, J.; Kamps, S.C.; Bout, A.V.D.; Devalla, H.D.; et al. Titin Circular RNAs Create a Back-Splice Motif Essential for SRSF10 Splicing. Circulation 2021, 143, 1502–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.; Xiao, W.; Zhao, Y.L.; Yang, Y.G. m(6)A: Signaling for mRNA splicing. RNA Biol. 2016, 13, 756–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendel, M.; Delaney, K.; Pandey, R.R.; Chen, K.M.; Wenda, J.M.; Vagbo, C.B.; Steiner, F.A.; Homolka, D.; Pillai, R.S. Splice site m(6)A methylation prevents binding of U2AF35 to inhibit RNA splicing. Cell 2021, 184, 3125–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lei, X.; Meng, J.; Wei, Z. WITMSG: Large-scale Prediction of Human Intronic m(6)A RNA Methylation Sites from Sequence and Genomic Features. Curr. Genom. 2020, 21, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Liang, D.; Tatomer, D.C.; Wilusz, J.E. A length-dependent evolutionarily conserved pathway controls nuclear export of circular RNAs. Genes Dev. 2018, 32, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Kearse, M.G.; Huang, C. The nuclear export of circular RNAs is primarily defined by their length. RNA Biol. 2019, 16, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Shu, Y.; He, J.; Gao, W. Interaction between N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) modification and noncoding RNAs in cancer. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Li, X.; Tang, H.; Jiang, B.; Dou, Y.; Gorospe, M.; Wang, W. NSUN2-Mediated m5C Methylation and METTL3/METTL14-Mediated m6A Methylation Cooperatively Enhance p21 Translation. J. Cell Biochem. 2017, 118, 2587–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jin, M.; Wang, J. The crosstalk between m(6)A RNA methylation and other epigenetic regulators: A novel perspective in epigenetic remodeling. Theranostics 2021, 11, 4549–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yuan, W.; Zhou, Q.; Shao, B.; Guo, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, L.; Dang, Q.; et al. N6-methyladenosine-induced circ1662 promotes metastasis of colorectal cancer by accelerating YAP1 nuclear localization. Theranostics 2021, 11, 4298–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesbirel, S.; Viphakone, N.; Parker, M.; Parker, J.; Heath, C.; Sudbery, I.; Wilson, S.A. The m(6)A-methylase complex recruits TREX and regulates mRNA export. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henze, K.; Badr, A.; Wettern, M.; Cerff, R.; Martin, W. A nuclear gene of eubacterial origin in Euglena gracilis reflects cryptic endosymbioses during protist evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 9122–9126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morf, L.; Singh, U. Entamoeba histolytica: A snapshot of current research and methods for genetic analysis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guminska, N.; Zakrys, B.; Milanowski, R. A New Type of Circular RNA derived from Nonconventional Introns in Nuclear Genes of Euglenids. J. Mol. Biol. 2021, 433, 166758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shomron, N.; Ast, G. Boric acid reversibly inhibits the second step of pre-mRNA splicing. FEBS Lett. 2003, 552, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brittingham, A.; Wilson, W.A. The antimicrobial effect of boric acid on Trichomonas vaginalis. Sex Transm. Dis. 2014, 41, 718–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdy, J.E.; Pho, L.T.; Mann, B.J.; Petri, W.A., Jr. Upstream regulatory elements controlling expression of the Entamoeba histolytica lectin. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1996, 78, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.; Rogers, J.B.; Mann, B.J.; Petri, W.A., Jr. Transcription initiation is controlled by three core promoter elements in the hgl5 gene of the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 8812–8817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanasamy, R.K.; Castanon-Sanchez, C.A.; Luna-Arias, J.P.; Garcia-Rivera, G.; Avendano-Borromeo, B.; Labra-Barrios, M.L.; Valdés, J.; Herrera-Aguirre, M.E.; Orozco, E. The Entamoeba histolytica TBP and TRF1 transcription factors are GAAC-box binding proteins, which display differential gene expression under different stress stimuli and during the interaction with mammalian cells. Parasit Vectors 2018, 11, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Diaz, M.; Gomez, C.; Lopez-Reyes, I.; Martinez, M.B.; Orozco, E.; Rodriguez, M.A. Structural and functional analysis of the Entamoeba histolytica EhrabB gene promoter. BMC Mol. Biol. 2007, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.C.; Wong, M.C.; Liao, W.T.; Chen, C.J.; Lee, S.C.; Yen, J.H.; Chang, S.-J. Genetic Variants in Transcription Factor Binding Sites in Humans: Triggered by Natural Selection and Triggers of Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, V.M.; Hugouvieux, V.; Nayak, A.; Conos, S.A.; Capovilla, G.; Cildir, G.; Jourdain, A.; Tergaonkar, V.; Schmid, M.; Zubieta, C.; et al. A circRNA from SEPALLATA3 regulates splicing of its cognate mRNA through R-loop formation. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 17053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenkaufer, G.M.; Weedall, G.D.; Williams, D.; Lorenzi, H.A.; Caler, E.; Hall, N.; Singh, U. The genome and transcriptome of the enteric parasite Entamoeba invadens, a model for encystation. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, L.S.; Clark, C.G.; Cunnick, C.C. YI-S, a casein-free medium for axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica, related Entamoeba, Giardia intestinalis and Trichomonas vaginalis. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1995, 42, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houseley, J.; Tollervey, D. Apparent non-canonical trans-splicing is generated by reverse transcriptase in vitro. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito-Nakano, Y.; Mitra, B.N.; Nakada-Tsukui, K.; Sato, D.; Nozaki, T. Two Rab7 isotypes, EhRab7A and EhRab7B, play distinct roles in biogenesis of lysosomes and phagosomes in the enteric protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Cell Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, T.; Asai, T.; Sanchez, L.B.; Kobayashi, S.; Nakazawa, M.; Takeuchi, T. Characterization of the gene encoding serine acetyltransferase, a regulated enzyme of cysteine biosynthesis from the protist parasites Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba dispar: Regulation and possible function of the cysteine biosynthetic pathway in Entamoeba. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 32445–32452. [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa, A.; Nakada-Tsukui, K.; Nozaki, T. Novel transmembrane receptor involved in phagosome transport of lysozymes and beta-hexosaminidase in the enteric protozoan Entamoeba histolytica. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez de la Cruz, O.; Marchat, L.A.; Guillen, N.; Weber, C.; Lopez Rosas, I.; Diaz-Chavez, J.; Herrera, L.; Rojo-Domínguez, A.; Orozco, E.; Lopez, K. Multinucleation and Polykaryon Formation is Promoted by the EhPC4 Transcription Factor in Entamoeba histolytica. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Lerena, J.A.; González-Blanco, G.; Saucedo-Cárdenas, O.; Valdés, J. Promoter-Bound Full-Length Intronic Circular RNAs-RNA Polymerase II Complexes Regulate Gene Expression in the Human Parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Non-Coding RNA 2022, 8, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8010012
García-Lerena JA, González-Blanco G, Saucedo-Cárdenas O, Valdés J. Promoter-Bound Full-Length Intronic Circular RNAs-RNA Polymerase II Complexes Regulate Gene Expression in the Human Parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Non-Coding RNA. 2022; 8(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Lerena, Jesús Alberto, Gretter González-Blanco, Odila Saucedo-Cárdenas, and Jesús Valdés. 2022. "Promoter-Bound Full-Length Intronic Circular RNAs-RNA Polymerase II Complexes Regulate Gene Expression in the Human Parasite Entamoeba histolytica" Non-Coding RNA 8, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8010012
APA StyleGarcía-Lerena, J. A., González-Blanco, G., Saucedo-Cárdenas, O., & Valdés, J. (2022). Promoter-Bound Full-Length Intronic Circular RNAs-RNA Polymerase II Complexes Regulate Gene Expression in the Human Parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Non-Coding RNA, 8(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8010012