Identification of Genomic Loci Responsible for the Formation of Nuclear Domains Using Lampbrush Chromosomes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
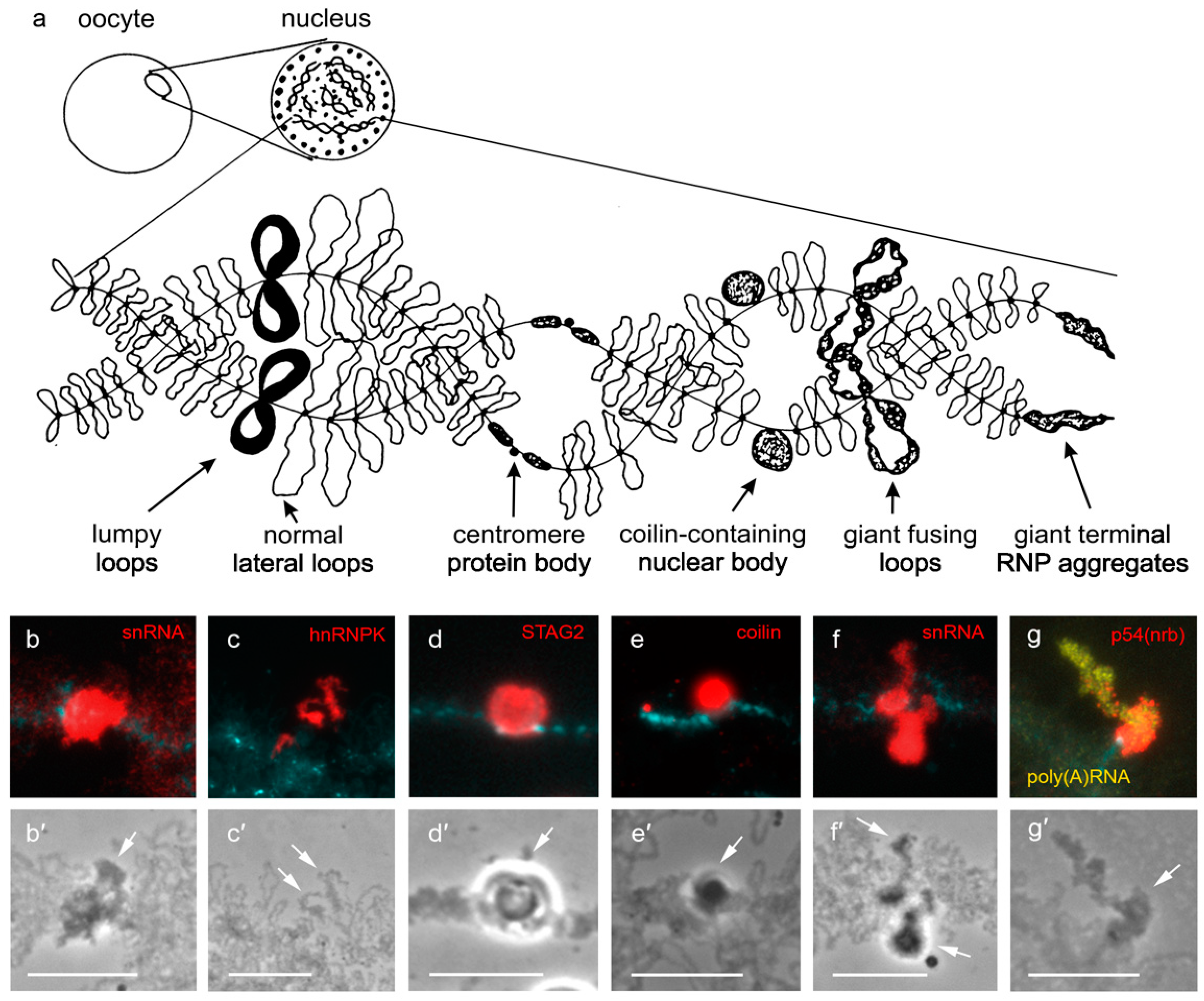
2. Locus-Specific Nuclear Domains on Lampbrush Chromosomes
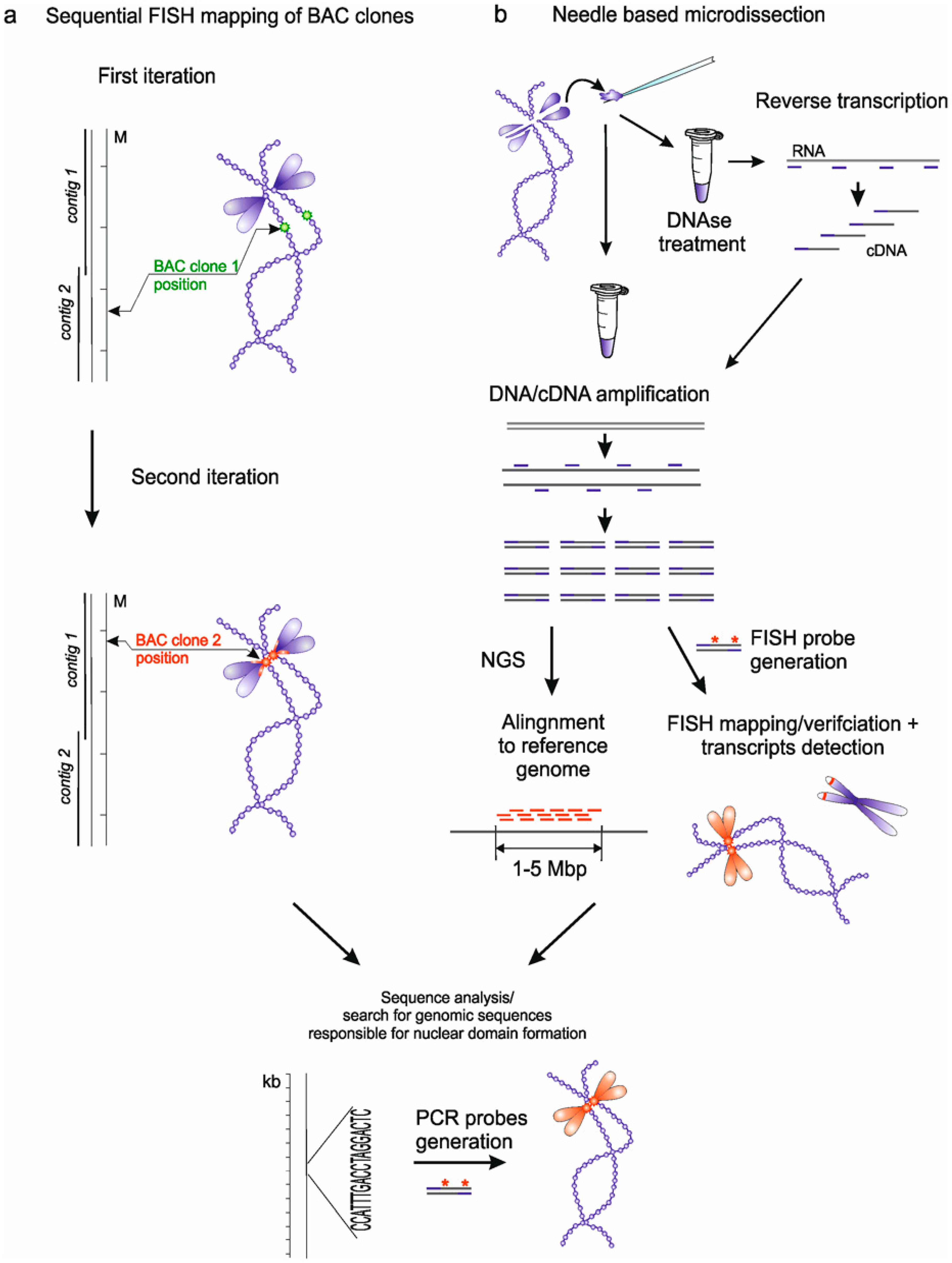
3. Approaches to Identification of Genomic Loci Responsible for Nuclear Domains Formation
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mao, Y.S.; Sunwoo, H.; Zhang, B.; Spector, D.L. Direct visualization of the co-transcriptional assembly of a nuclear body by noncoding RNAs. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevtsov, S.P.; Dundr, M. Nucleation of nuclear bodies by RNA. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chujo, T.; Hirose, T. Nuclear bodies built on architectural long noncoding RNAs: Unifying principles of their construction and function. Mol. Cells 2017, 40, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveed, A.; Fortini, E.; Li, R.; Fox, A.H. Long Non-coding RNAs and Nuclear Body Formation and Function. In Molecular Biology of Long Non-coding RNAs, 1st ed.; Khalil, A., Coller, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Vale, R.D. RNA phase transitions in repeat expansion disorders. Nature 2017, 546, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maharana, S.; Wang, J.; Papadopoulos, D.K.; Richter, D.; Pozniakovsky, A.; Poser, I.; Bickle, M.; Rizk, S.; Guillén-Boixet, J.; Franzmann, T.M.; et al. RNA buffers the phase separation behavior of prion-like RNA binding proteins. Science 2018, 360, 918–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Musinova, Y.R.; Lisitsyna, O.M.; Sorokin, D.V.; Arifulin, E.A.; Smirnova, T.A.; Zinovkin, R.A.; Potashnikova, D.M.; Vassetzky, Y.S.; Sheval, E.V. RNA-dependent disassembly of nuclear bodies. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 4509–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caudron-Herger, M.; Pankert, T.; Seiler, J.; Németh, A.; Voit, R.; Grummt, I.; Rippe, K. Alu element-containing RNAs maintain nucleolar structure and function. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 2758–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fox, A.H.; Nakagawa, S.; Hirose, T.; Bond, C.S. Paraspeckles: Where long noncoding RNA meets phase separation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2018, 43, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prasanth, K.V.; Rajendra, T.K.; Lal, A.K.; Lakhotia, S.C. Omega speckles-a novel class of nuclear speckles containing hnRNPs associated with noncoding hsr-omega RNA in Drosophila. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113, 3485–3497. [Google Scholar]
- Jolly, C.; Metz, A.; Govin, J.; Vigneron, M.; Turner, B.M.; Khochbin, S.; Vourc’h, C. Stress-induced transcription of satellite III repeats. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 164, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsuiji, H.; Yoshimoto, R.; Hasegawa, Y.; Furuno, M.; Yoshida, M.; Nakagawa, S. Competition between a noncoding exon and introns: Gomafu contains tandem UACUAAC repeats and associates with splicing factor-1. Genes Cells 2011, 16, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yap, K.; Mukhina, S.; Zhang, G.; Tan, J.S.; Ong, H.S.; Makeyev, E.V. A short tandem repeat-enriched RNA assembles a nuclear compartment to control alternative splicing and promote cell survival. Mol. Cell 2018, 72, 525–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumbović, G.; Biayna, J.; Banús, J.; Samuelsson, J.; Roth, A.; Diederichs, S.; Alonso, S.; Buschbeck, M.; Perucho, M.; Forcales, S.V. A novel long non-coding RNA from NBL2 pericentromeric macrosatellite forms a perinucleolar aggregate structure in colon cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 5504–5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, M.K.; Ninomiya, K.; Adachi, S.; Natsume, T.; Hirose, T. Two distinct nuclear stress bodies containing different sets of RNA-binding proteins are formed with HSATIII architectural noncoding RNAs upon thermal stress exposure. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 516, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, A. meiRNA, A Polyvalent Player in Fission Yeast Meiosis. ncRNA 2019, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sawyer, I.A.; Hager, G.L.; Dundr, M. Specific genomic cues regulate Cajal body assembly. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callan, H.G. Lampbrush Chromosomes, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaginskaya, E.; Kulikova, T.; Krasikova, A. Avian lampbrush chromosomes: A powerful tool for exploration of genome expression. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2009, 124, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derjusheva, S.; Kurganova, A.; Krasikova, A.; Saifitdinova, A.; Habermann, F.A.; Gaginskaya, E. Precise identification of chicken chromosomes in the lampbrush form using chromosome painting probes. Chromosome Res. 2003, 11, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galkina, S.; Deryusheva, S.; Fillon, V.; Vignal, A.; Crooijmans, R.; Groenen, M.; Rodionov, A.; Gaginskaya, E. FISH on avian lampbrush chromosomes produces higher resolution gene mapping. Genetica 2006, 128, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krasikova, A.; Deryusheva, S.; Galkina, S.; Kurganova, A.; Evteev, A.; Gaginskaya, E. On the positions of centromeres in chicken lampbrush chromosomes. Chromosome Res. 2006, 14, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, R.; Cremer, C.; Gall, J.G. Superresolution imaging of transcription units on newt lampbrush chromosomes. Chromosome Res. 2012, 20, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morgan, G.T. Imaging the dynamics of transcription loops in living chromosomes. Chromosoma 2018, 127, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khutinaeva, M.A.; Kropotova, E.V.; Gaginskaia, E.R. The characteristics of the morphofunctional organization of the lampbrush chromosomes from the oocytes of the rock dove. Tsitologiia 1989, 10, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar]
- Chelysheva, L.A.; Solovei, I.V.; Rodionov, A.V.; Yakovlev, A.F.; Gaginskaya, E.R. The lampbrush chromosomes of the chicken. The cytological map of macrobivalents. Tsitologiia 1990, 32, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Solovei, I.V.; Joffe, B.I.; Gaginskaya, E.R.; Macgregor, H.C. Transcription on lampbrush chromosomes of a centromerically localized highly repeated DNA in pigeon (Columba) relates to sequence arrangement. Chromosome Res. 1996, 8, 588–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikova, T.; Chervyakova, D.; Zlotina, A.; Krasikova, A.; Gaginskaya, E. Giant poly (A)-rich RNP aggregates form at terminal regions of avian lampbrush chromosomes. Chromosoma 2016, 125, 709–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizami, Z.F.; Gall, J.G. Pearls are novel Cajal body-like structures in the Xenopus germinal vesicle that are dependent on RNA pol III transcription. Chromosome Res. 2012, 20, 953–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrade, L.E.; Chan, E.K.; Raska, I.; Peebles, C.L.; Roos, G.; Tan, E.M. Human autoantibody to a novel protein of the nuclear coiled body: Immunological characterization and cDNA cloning of p80-coilin. J. Exp. Med. 1991, 173, 1407–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zlotina, A.; Kulikova, T.; Kosyakova, N.; Liehr, T.; Krasikova, A. Microdissection of lampbrush chromosomes as an approach for generation of locus-specific FISH-probes and samples for high-throughput sequencing. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gall, J.G.; Stephenson, E.C.; Erba, H.P.; Diaz, M.O.; Barsacchi-Pilone, G. Histone genes are located at the sphere loci of newt lampbrush chromosomes. Chromosoma 1981, 84, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callan, H.G.; Gall, J.G.; Murphy, C. Histone genes are located at the sphere loci of Xenopus lampbrush chromosomes. Chromosoma 1991, 101, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasikova, A.; Kulikova, T.; Saifitdinova, A.; Derjusheva, S.; Gaginskaya, E. Centromeric protein bodies on avian lampbrush chromosomes contain a protein detectable with an antibody against DNA topoisomerase II. Chromosoma 2004, 113, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasikova, A.; Barbero, J.L.; Gaginskaya, E. Cohesion proteins are present in centromere protein bodies associated with avian lampbrush chromosomes. Chromosome Res. 2005, 13, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krasikova, A.V.; Gaginskaia, E.R. Organization of centromere regions of chromosomes in the lampbrush phase. Tsitologiia 2010, 52, 515–533. [Google Scholar]
- Krasikova, A.; Fukagawa, T.; Zlotina, A. High-resolution mapping and transcriptional activity analysis of chicken centromere sequences on giant lampbrush chromosomes. Chromosome Res. 2012, 20, 995–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krasikova, A.; Khodyuchenko, T.; Maslova, A.; Vasilevskaya, E. Three-dimensional organisation of RNA-processing machinery in avian growing oocyte nucleus. Chromosome Res. 2012, 20, 979–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deryusheva, S.; Krasikova, A.; Kulikova, T.; Gaginskaya, E. Tandem 41-bp repeats in chicken and Japanese quail genomes: FISH mapping and transcription analysis on lampbrush chromosomes. Chromosoma 2007, 116, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimova, I.; Popova, D.; Vasilevskaya, E.; Krasikova, A. Non-coding RNA derived from a conservative subtelomeric tandem repeat in chicken and Japanese quail somatic cells. Mol. Cytogenet. 2014, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trofimova, I.; Chervyakova, D.; Krasikova, A. Transcription of subtelomere tandemly repetitive DNA in chicken embryogenesis. Chromosome Res. 2015, 23, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Brinkman, E.K.; Adam, S.A.; Goldman, R.; Van Steensel, B.; Ma, J.; Belmont, A.S. Mapping 3D genome organization relative to nuclear compartments using TSA-Seq as a cytological ruler. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 4025–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Yan, Z.; Li, S.; Huang, N.; Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, S. RNAs as proximity-labeling media for identifying nuclear speckle positions relative to the genome. iScience 2018, 4, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinodoz, S.A.; Ollikainen, N.; Tabak, B.; Palla, A.; Schmidt, J.M.; Detmar, E.; Lai, M.M.; Shishkin, A.A.; Bhat, P.; Takei, Y.; et al. Higher-order inter-chromosomal hubs shape 3D genome organization in the nucleus. Cell 2018, 174, 744–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Sawyer, I.A.; Sung, M.H.; Sturgill, D.; Shevtsov, S.P.; Pegoraro, G.; Hakim, O.; Baek, S.; Hager, G.L.; Dundr, M. Cajal bodies are linked to genome conformation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ching, R.W.; Ahmed, K.; Boutros, P.C.; Penn, L.Z.; Bazett-Jones, D.P. Identifying gene locus associations with promyelocytic leukemia nuclear bodies using immuno-TRAP. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 201, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.K.; Anchel, D.; Gong, Z.; Cotton, R.; Li, R.; Sun, Y.; Bazett-Jones, D.P. Nano-Dissection and Sequencing of DNA at Single Sub-Nuclear Structures. Small 2014, 10, 3267–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anchel, D.; Ching, R.W.; Cotton, R.; Li, R.; Bazett-Jones, D.P. A novel single cell method to identify the genetic composition at a single nuclear body. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasikova, A.V.; Vasilevskaya, E.V.; Gaginskaya, E.R. Chicken lampbrush chromosomes: Transcription of tandemly repetitive DNA sequences. Russ. J. Genet. 2010, 46, 1173–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotina, A.; Maslova, A.; Pavlova, O.; Kosyakova, N.; Al-Rikabi, A.B.; Liehr, T.; Krasikova, A. New insights into chromomere organization provided by lampbrush chromosome microdissection and high-throughput sequencing. Front. Genet. 2019. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.L.; Gall, J.G. Induction of human lampbrush chromosomes. Chromosome Res. 2012, 20, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krasikova, A.; Kulikova, T. Identification of Genomic Loci Responsible for the Formation of Nuclear Domains Using Lampbrush Chromosomes. Non-Coding RNA 2020, 6, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna6010001
Krasikova A, Kulikova T. Identification of Genomic Loci Responsible for the Formation of Nuclear Domains Using Lampbrush Chromosomes. Non-Coding RNA. 2020; 6(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna6010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrasikova, Alla, and Tatiana Kulikova. 2020. "Identification of Genomic Loci Responsible for the Formation of Nuclear Domains Using Lampbrush Chromosomes" Non-Coding RNA 6, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna6010001
APA StyleKrasikova, A., & Kulikova, T. (2020). Identification of Genomic Loci Responsible for the Formation of Nuclear Domains Using Lampbrush Chromosomes. Non-Coding RNA, 6(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna6010001



