Long Non-Coding RNAs in the Regulation of Gene Expression: Physiology and Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
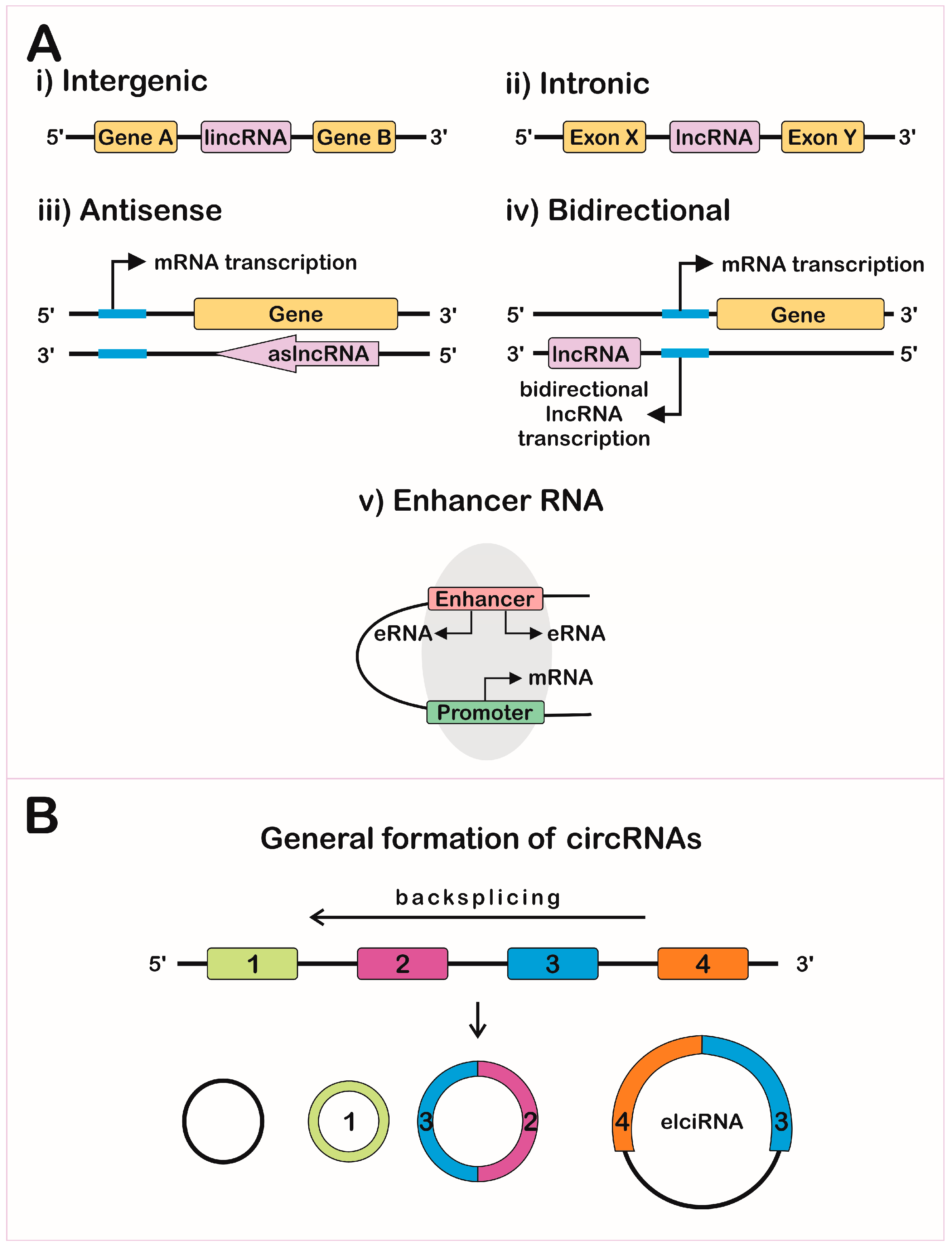
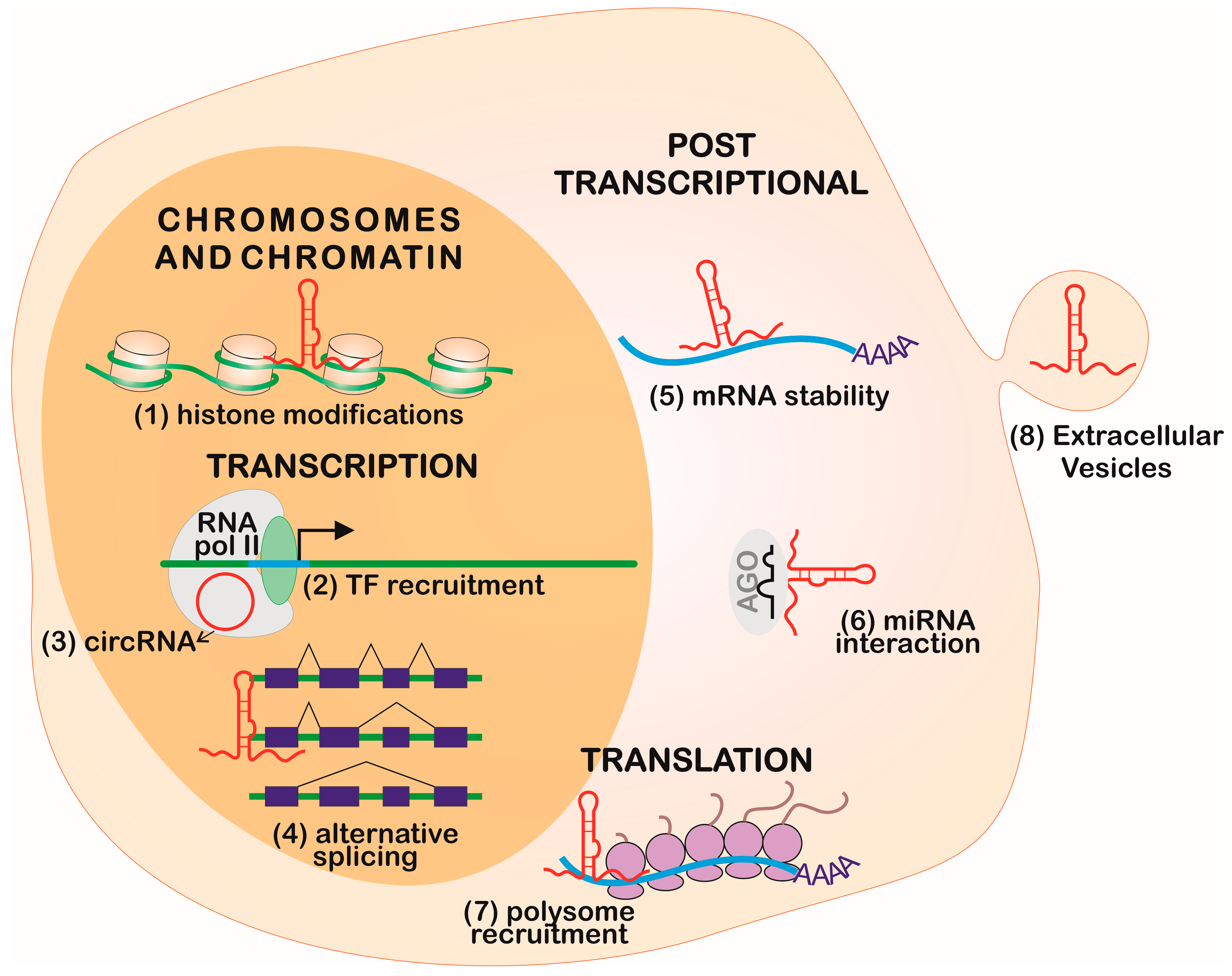
2. Gene Expression Regulation Levels
2.1. Chromosome and Chromatin Structure
2.2. Transcription
2.3. Post-Transcriptional Regulation
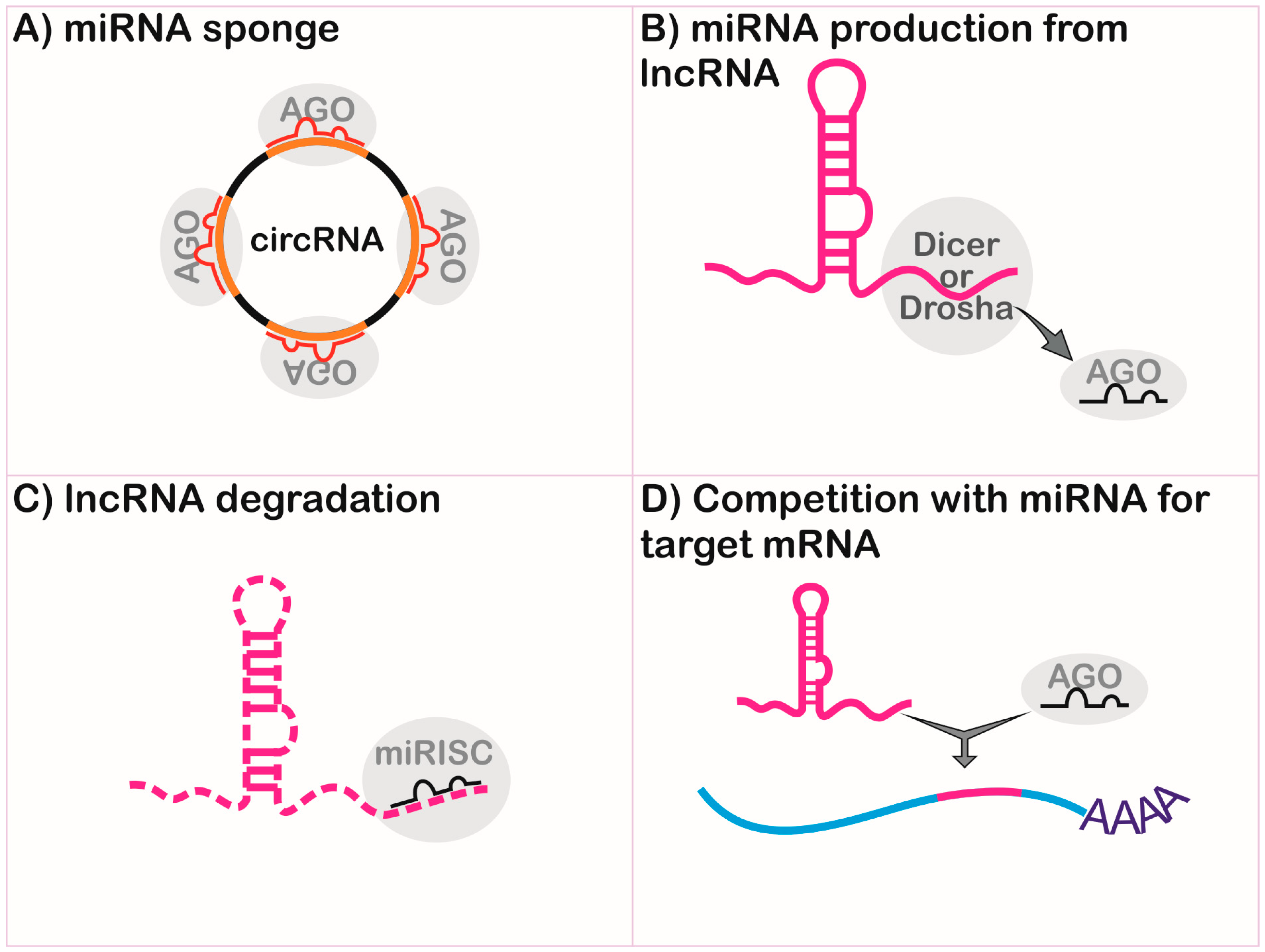
2.3.1. Long Non-Coding RNA and MicroRNA Interplay
2.3.2. Alternative Splicing
2.3.3. Messenger RNA Stability
2.4. Translation
3. Physiological Conditions and Disease
3.1. X Chromosome Dosage Compensation
3.2. Imprinting
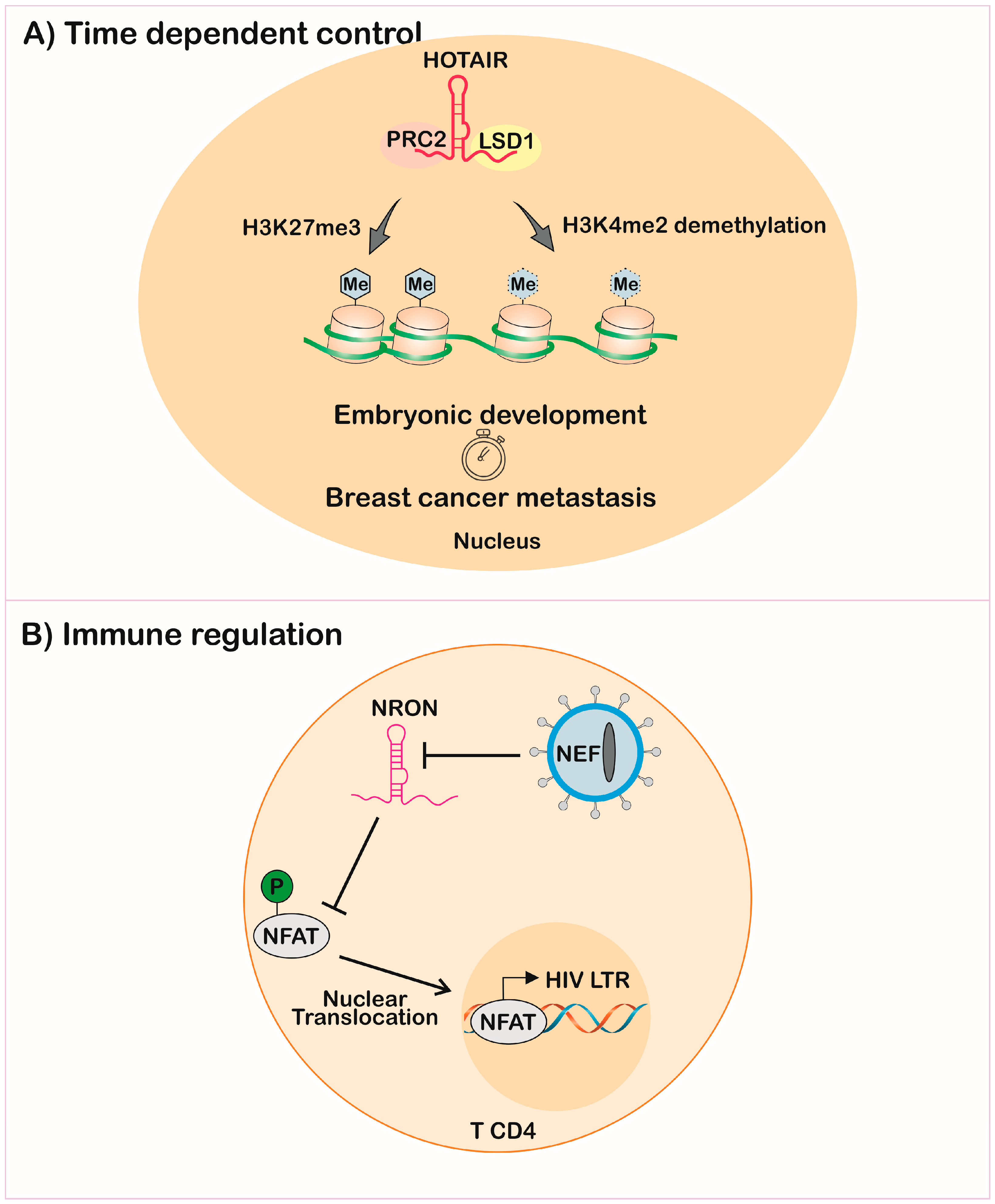
3.3. Chronic Diseases
3.4. Immune Response Against Infectious Diseases
4. Long Non-Coding RNA Expression in Pathogens
5. Novel Perspectives
5.1. Long Non-Coding RNAs as Biomarkers
5.2. Micropeptides
6. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Long, Y.; Wang, X.; Youmans, D.T.; Cech, T.R. How do lncRNAs regulate transcription? Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, eaao2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blin, N.; Stephenson, E.C.; Stafford, D.W. Isolation and some properties of a mammalian ribosomal DNA. Chromosoma 1976, 58, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, M.L.; Zamecnik, P.C. Inhibition of Rous sarcoma viral RNA translation by a specific oligodeoxyribonucleotide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1978, 75, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küpper, H.; Sekiya, T.; Rosenberg, M.; Egan, J.; Landy, A. A Rho-dependent termination site in the gene coding for tyrosine tRNA su3 of Escherichia Coli. Nature 1978, 272, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derrien, T.; Johnson, R.; Bussotti, G.; Tanzer, A.; Djebali, S.; Tilgner, H.; Guernec, G.; Martin, D.; Merkel, A.; Knowles, D.G.; et al. The gencode v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: Analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djebali, S.; Davis, C.A.; Merkel, A.; Dobin, A.; Lassmann, T.; Mortazavi, A.; Tanzer, A.; Lagarde, J.; Lin, W.; Schlesinger, F.; et al. Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature 2012, 489, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulitsky, I.; Bartel, D.P. Lincrnas: Genomics, evolution, and mechanisms. Cell 2013, 154, 26–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinn, J.L.; Chang, H.Y. Genome regulation by long noncoding RNAs. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabili, M.N.; Trapnell, C.; Goff, L.; Koziol, M.; Tazon-Vega, B.; Regev, A.; Rinn, J.L. Integrative annotation of human large intergenic noncoding rnas reveals global properties and specific subclasses. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 1915–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Ramchandran, R. Natural antisense transcript: A concomitant engagement with protein-coding transcript. Oncotarget. 2010, 1, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.J.; Chang, H.Y. Unique features of long non-coding RNA biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangauer, M.J.; Vaughn, I.W.; McManus, M.T. Pervasive transcription of the human genome produces thousands of previously unidentified long intergenic noncoding RNAs. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemczyk, M.; Ito, Y.; Huddleston, J.; Git, A.; Abu-Amero, S.; Caldas, C.; Moore, G.E.; Stojic, L.; Murrell, A. Imprinted chromatin around DIRAS3 regulates alternative splicing of GNG12-AS1, a long noncoding RNA. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 93, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, C.; Kretz, M. The more the merrier-complexity in long non-coding RNA loci. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman, M.; Amit, I.; Garber, M.; French, C.; Lin, M.F.; Feldser, D.; Huarte, M.; Zuk, O.; Carey, B.W.; Cassady, J.P.; et al. Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large non-coding RNAs in mammals. Nature 2009, 458, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.X.; Do, B.T.; Webster, D.E.; Khavari, P.A.; Chang, H.Y. Dicer-microRNA-Myc circuit promotes transcription of hundreds of long noncoding RNAs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uesaka, M.; Nishimura, O.; Go, Y.; Nakashima, K.; Agata, K.; Imamura, T. Bidirectional promoters are the major source of gene activation-associated non-coding rnas in mammals. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.S.; Liu, Q.-R.; Wei, L. Genome-wide in silico identification and analysis of cis natural antisense transcripts (cis-NATS) in ten species. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 3465–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seila, A.C.; Calabrese, J.M.; Levine, S.S.; Yeo, G.W.; Rahl, P.B.; Flynn, R.A.; Young, R.A.; Sharp, P.A. Divergent transcription from active promoters. Science 2008, 322, 1849–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Core, L.J.; Waterfall, J.J.; Lis, J.T. Nascent RNA sequencing reveals widespread pausing and divergent initiation at human promoters. Science 2008, 322, 1845–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigova, A.A.; Mullen, A.C.; Molinie, B.; Gupta, S.; Orlando, D.A.; Guenther, M.G.; Almada, A.E.; Lin, C.; Sharp, P.A.; Giallourakis, C.C.; et al. Divergent transcription of long noncoding RNA/mRNA gene pairs in embryonic stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2876–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, R.; Gebhard, C.; Miguel-Escalada, I.; Hoof, I.; Bornholdt, J.; Boyd, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Schmidl, C.; Suzuki, T.; et al. An atlas of active enhancers across human cell types and tissues. Nature 2014, 507, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.; Gardini, A.; Zhang, A.; Shiekhattar, R. Integrator mediates the biogenesis of enhancer RNAs. Nature 2015, 525, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzman, J.; Gawad, C.; Wang, P.L.; Lacayo, N.; Brown, P.O. Circular RNAs are the predominant transcript isoform from hundreds of human genes in diverse cell types. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.O.; Chen, T.; Xiang, J.F.; Yin, Q.F.; Xing, Y.H.; Zhu, S.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. Circular intronic long noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell 2013, 51, 792–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Bao, C.; Chen, L.; Lin, M.; Wang, X.; Zhong, G.; Yu, B.; Hu, W.; Dai, L.; et al. Exon-intron circular rnas regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisler, S.; Lojek, L.; Khalil, A.M.; Baker, K.E.; Coller, J. Decapping of long noncoding RNAs regulates inducible genes. Mol. Cell 2012, 45, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wery, M.; Descrimes, M.; Vogt, N.; Dallongeville, A.S.; Gautheret, D.; Morillon, A. Nonsense-mediated decay restricts lncRNA levels in yeast unless blocked by double-stranded RNA structure. Mol. Cell 2016, 61, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, Z.T.; Xing, Z.; Tran, E.J. LncRNAs: Bridging environmental sensing and gene expression. RNA Biol. 2016, 13, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Fang, S.; Kang, Y.; Wu, W.; Hao, Y.; Li, Z.; Bu, D.; Sun, N.; Zhang, M.Q.; et al. Noncode 2016: An informative and valuable data source of long non-coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D203–D208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.G.; Satpathy, A.T.; Chang, H.Y. Gene regulation in the immune system by long noncoding RNAs. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goff, L.A.; Groff, A.F.; Sauvageau, M.; Trayes-Gibson, Z.; Sanchez-Gomez, D.B.; Morse, M.; Martin, R.D.; Elcavage, L.E.; Liapis, S.C.; Gonzalez-Celeiro, M.; et al. Spatiotemporal expression and transcriptional perturbations by long noncoding RNAs in the mouse brain. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. USA 2015, 112, 6855–6862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, M.K.; Niknafs, Y.S.; Malik, R.; Singhal, U.; Sahu, A.; Hosono, Y.; Barrette, T.R.; Prensner, J.R.; Evans, J.R.; Zhao, S.; et al. The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human transcriptome. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.J.; Horlbeck, M.A.; Cho, S.W.; Birk, H.S.; Malatesta, M.; He, D.; Attenello, F.J.; Villalta, J.E.; Cho, M.Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Crispri-based genome-scale identification of functional long noncoding RNA loci in human cells. Science 2017, 355, eaah7111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, J.; Engreitz, J.M.; Konermann, S.; Abudayyeh, O.O.; Verdine, V.K.; Aguet, F.; Gootenberg, J.S.; Sanjana, N.E.; Wright, J.B.; Fulco, C.P.; et al. Genome-scale activation screen identifies a lncRNA locus regulating a gene neighbourhood. Nature 2017, 548, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Tang, Q.; Sharma, S.; Yu, F.; Escobar, T.M.; Muljo, S.A.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, K. Expression and regulation of intergenic long noncoding RNAs during t cell development and differentiation. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cech, T.R.; Steitz, J.A. The noncoding RNA revolution—trashing old rules to forge new ones. Cell 2014, 157, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rackham, O.; Shearwood, A.-M.J.; Mercer, T.R.; Davies, S.M.K.; Mattick, J.S.; Filipovska, A. Long noncoding RNAs are generated from the mitochondrial genome and regulated by nuclear-encoded proteins. RNA 2011, 17, 2085–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabili, M.N.; Dunagin, M.C.; McClanahan, P.D.; Biaesch, A.; Padovan-Merhar, O.; Regev, A.; Rinn, J.L.; Raj, A. Localization and abundance analysis of human lncRNAs at single-cell and single-molecule resolution. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlevaro-Fita, J.; Rahim, A.; Guigó, R.; Vardy, L.A.; Johnson, R. Cytoplasmic long noncoding RNAs are frequently bound to and degraded at ribosomes in human cells. RNA 2016, 22, 867–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Gunawardane, L.; Niazi, F.; Jahanbani, F.; Chen, X.; Valadkhan, S. A novel RNA motif mediates the strict nuclear localization of a long noncoding RNA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 34, 2318–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubelsky, Y.; Ulitsky, I. Sequences enriched in alu repeats drive nuclear localization of long RNAs in human cells. Nature 2018, 555, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kertesz, M.; Wan, Y.; Mazor, E.; Rinn, J.L.; Nutter, R.C.; Chang, H.Y.; Segal, E. Genome-wide measurement of RNA secondary structure in yeast. Nature 2010, 467, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, J.G.; Uzilov, A.V.; Katzman, S.; Onodera, C.S.; Mainzer, J.E.; Mathews, D.H.; Lowe, T.M.; Salama, S.R.; Haussler, D. Fragseq: Transcriptome-wide RNA structure probing using high-throughput sequencing. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegueroles, C.; Gabaldón, T. Secondary structure impacts patterns of selection in human lncRNAs. BMC Biol. 2016, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.A.; Gesell, T.; Stadler, P.F.; Mattick, J.S. Widespread purifying selection on RNA structure in mammals. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 8220–8236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diederichs, S. The four dimensions of noncoding RNA conservation. Trends Genet. 2014, 30, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Dai, Q.; Zheng, G.; He, C.; Parisien, M.; Pan, T. N(6)-methyladenosine-dependent RNA structural switches regulate RNA-protein interactions. Nature 2015, 518, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.I.; Parisien, M.; Dai, Q.; Liu, N.; Diatchenko, L.; Sachleben, J.R.; Pan, T. N(6)-methyladenosine modification in a long noncoding RNA hairpin predisposes its conformation to protein binding. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 822–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Pan, T. N6-methyladenosine-encoded epitranscriptomics. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, W.; Xiang, Y.; Diao, L.; Guo, A.-Y.; Han, L. Lncediting: A database for functional effects of RNA editing in lncRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D79–D84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, R.H.; Green, M.R. Compartmentalization of eukaryotic gene expression: Causes and effects. Cell 1997, 91, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, F.; Mendell, J.T. Functional classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 2018, 172, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewson, C.; Capraro, D.; Burdach, J.; Whitaker, N.; Morris, K.V. Extracellular vesicle associated long non-coding RNAs functionally enhance cell viability. Non-Coding RNA Res. 2016, 1, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, J.; Duerksen, J.D. Chromatin-associated rna content of heterochromatin and euchromatin. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1975, 9, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman, M.; Donaghey, J.; Carey, B.W.; Garber, M.; Grenier, J.K.; Munson, G.; Young, G.; Lucas, A.B.; Ach, R.; Bruhn, L.; et al. Lincrnas act in the circuitry controlling pluripotency and differentiation. Nature 2011, 477, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.; Orom, U.A.; Cesaroni, M.; Beringer, M.; Taatjes, D.J.; Blobel, G.A.; Shiekhattar, R. Activating RNAs associate with mediator to enhance chromatin architecture and transcription. Nature 2013, 494, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.M.; Guttman, M.; Huarte, M.; Garber, M.; Raj, A.; Rivea Morales, D.; Thomas, K.; Presser, A.; Bernstein, B.E.; van Oudenaarden, A.; et al. Many human large intergenic noncoding RNAs associate with chromatin-modifying complexes and affect gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11667–11672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engreitz, J.M.; Haines, J.E.; Perez, E.M.; Munson, G.; Chen, J.; Kane, M.; McDonel, P.E.; Guttman, M.; Lander, E.S. Local regulation of gene expression by lncRNA promoters, transcription and splicing. Nature 2016, 539, 452–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, P.G.; Morris, K.V. Transcriptional regulation of Oct4 by a long non-coding RNA antisense to Oct4-pseudogene 5. Transcription 2010, 1, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azofeifa, J.G.; Allen, M.A.; Hendrix, J.R.; Read, T.; Rubin, J.D.; Dowell, R.D. Enhancer RNA profiling predicts transcription factor activity. Genome Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.B.; Jensen, T.I.; Clausen, B.H.; Bramsen, J.B.; Finsen, B.; Damgaard, C.K.; Kjems, J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 2013, 495, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furió-Tarí, P.; Tarazona, S.; Gabaldón, T.; Enright, A.J.; Conesa, A. Spongescan: A web for detecting microrna binding elements in lncRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W176–W180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Liu, J.; Xiao, J.; Yang, L.; Cai, M.; Shen, H.; Chen, X.; Ma, Y.; Hu, S.; Wang, Z.; et al. Lnc-mg is a long non-coding RNA that promotes myogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, N.; Niu, X.; Wang, Y.; Du, H.; Wang, B.; Du, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S.; et al. Role of lncrna-activated by transforming growth factor beta in the progression of hepatitis C virus-related liver fibrosis. Discov. Med. 2016, 22, 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Dhir, A.; Dhir, S.; Proudfoot, N.J.; Jopling, C.L. Microprocessor mediates transcriptional termination of long noncoding RNA transcripts hosting microRNAs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augoff, K.; McCue, B.; Plow, E.F.; Sossey-Alaoui, K. Mir-31 and its host gene lncRNA loc554202 are regulated by promoter hypermethylation in triple-negative breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2012, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, G.A.; Dumitru, C.D.; Shimizu, M.; Bichi, R.; Zupo, S.; Noch, E.; Aldler, H.; Rattan, S.; Keating, M.; Rai, K.; et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes mir15 and mir16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15524–15529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, M.; Harada, M.; Lovén, J.; Castro, J.; Davis, Z.; Oscier, D.; Henriksson, M.; Sangfelt, O.; Grandér, D.; Corcoran, M.M. Dleu2, frequently deleted in malignancy, functions as a critical host gene of the cell cycle inhibitory microRNAs mir-15a and mir-16-1. Exp. Cell Res. 2009, 315, 2941–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Nangia-Makker, P.; Farhana, L.; Majumdar, A.P.N. A novel mechanism of lncRNA and miRNA interaction: Ccat2 regulates mir-145 expression by suppressing its maturation process in colon cancer cells. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.; Trac, C.; Jin, W.; Lanting, L.; Akbany, A.; Saetrom, P.; Schones, D.E.; Natarajan, R. Novel long noncoding RNAs are regulated by angiotensin II in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ. Res. 2013, 113, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Gorospe, M. Functional interactions among microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 34, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Ma, J.; Xue, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Xi, Z.; Teng, H.; Wang, Z.; et al. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA xist exerts tumor-suppressive functions in human glioblastoma stem cells by up-regulating mir-152. Cancer Lett. 2015, 359, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, M.; Wang, Z.; Han, S.; Tang, X.; Ge, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, C.; Yuan, Q.; Yang, M. Silencing of long noncoding RNA malat1 by mir-101 and mir-217 inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 3925–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Fang, N.; Zu, L.; Li, X.; Zhou, Q. MicroRNA-449a inhibits cell growth in lung cancer and regulates long noncoding RNA nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1. Ind. J. Cancer 2014, 51 3, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghihi, M.A.; Zhang, M.; Huang, J.; Modarresi, F.; Van der Brug, M.P.; Nalls, M.A.; Cookson, M.R.; St-Laurent, G., 3rd; Wahlestedt, C. Evidence for natural antisense transcript-mediated inhibition of microRNA function. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallen, A.N.; Zhou, X.B.; Xu, J.; Qiao, C.; Ma, J.; Yan, L.; Lu, L.; Liu, C.; Yi, J.S.; Zhang, H.; et al. The imprinted h19 lncRNA antagonizes let-7 microRNAs. Mol. Cell 2013, 52, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, B.K.; Pfeifer, K.; Dutta, A. The h19 long noncoding rna gives rise to microRNAs mir-675-3p and mir-675-5p to promote skeletal muscle differentiation and regeneration. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesana, M.; Cacchiarelli, D.; Legnini, I.; Santini, T.; Sthandier, O.; Chinappi, M.; Tramontano, A.; Bozzoni, I. A long noncoding RNA controls muscle differentiation by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell 2011, 147, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmrich, S.; Streltsov, A.; Schmidt, F.; Thangapandi, V.R.; Reinhardt, D.; Klusmann, J.H. LincRNAs monc and mir100hg act as oncogenes in acute megakaryoblastic leukemia. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Z.; Rouchka, E.C.; Gish, W.R.; States, D.J. Gene structure prediction and alternative splicing analysis using genomically aligned ests. Genome Res. 2001, 11, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Will, C.L.; Luhrmann, R. Spliceosome structure and function. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, J.N.; Ensminger, A.W.; Clemson, C.M.; Lynch, C.R.; Lawrence, J.B.; Chess, A. A screen for nuclear transcripts identifies two linked noncoding RNAs associated with Sc35 splicing domains. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, V.; Ellis, J.D.; Shen, Z.; Song, D.Y.; Pan, Q.; Watt, A.T.; Freier, S.M.; Bennett, C.F.; Sharma, A.; Bubulya, P.A.; et al. The nuclear-retained noncoding RNA MALAT1 regulates alternative splicing by modulating SR splicing factor phosphorylation. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, I.; Munita, R.; Agirre, E.; Dittmer, T.A.; Gysling, K.; Misteli, T.; Luco, R.F. A lncRNA regulates alternative splicing via establishment of a splicing-specific chromatin signature. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Barrios, N.; Legascue, M.F.; Benhamed, M.; Ariel, F.; Crespi, M. Splicing regulation by long noncoding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 2169–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamizar, O.; Chambers, C.B.; Riberdy, J.M.; Persons, D.A.; Wilber, A. Long noncoding RNA SAF and splicing factor 45 increase soluble FAS and resistance to apoptosis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 13810–13826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Maquat, L.E. LncRNAs transactivate Stau1-mediated mRNA decay by duplexing with 3′ UTRS via Alu elements. Nature 2011, 470, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerin, T.; Ramanathan, A.; Rivas, K.; Grepo, N.; Coetzee, G.A.; Campbell, D.B. A noncoding RNA antisense to Moesin at 5p14.1 in autism. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 128ra140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsson, P.; Ackley, A.; Vidarsdottir, L.; Lui, W.O.; Corcoran, M.; Grander, D.; Morris, K.V. A pseudogene long-noncoding-RNA network regulates Pten transcription and translation in human cells. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghihi, M.A.; Modarresi, F.; et al. Expression of a noncoding RNA is elevated in alzheimer’s disease and drives rapid feed-forward regulation of beta-secretase. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadaliha, M.; Gholamalamdari, O.; Tang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Petracovici, A.; Hao, Q.; Tariq, A.; Kim, T.G.; Holton, S.E.; Singh, D.K.; et al. A natural antisense lncRNA controls breast cancer progression by promoting tumor suppressor gene mRNA stability. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrieri, C.; Cimatti, L.; Biagioli, M.; Beugnet, A.; Zucchelli, S.; Fedele, S.; Pesce, E.; Ferrer, I.; Collavin, L.; Santoro, C.; et al. Long non-coding antisense RNA controls Uchl1 translation through an embedded Sineb2 repeat. Nature 2012, 491, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.C.; Yang, Y.W.; Liu, B.; Sanyal, A.; Corces-Zimmerman, R.; Chen, Y.; Lajoie, B.R.; Protacio, A.; Flyn, R.A.; Gupta, R.A.; et al. A long noncoding RNA maintains active chromatin to coordinate homeotic gene expression. Nature 2011, 472, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, F.; Shah, A.; Shan, G. Long non-coding RNAs in the cytoplasm. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2016, 14, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salviano-Silva, A.; Lobo-Alves, S.C.; Almeida, R.C.; Malheiros, D.; Petzl-Erler, M.L. Besides pathology: Long non-coding RNA in cell and tissue homeostasis. Non-Coding RNA 2018, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapranov, P.; Cheng, J.; Dike, S.; Nix, D.A.; Duttagupta, R.; Willingham, A.T.; Stadler, P.F.; Hertel, J.; Hackermuller, J.; Hofacker, I.L.; et al. Rna maps reveal new RNA classes and a possible function for pervasive transcription. Science 2007, 316, 1484–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carninci, P.; Kasukawa, T.; Katayama, S.; Gough, J.; Frith, M.C.; Maeda, N.; Oyama, R.; Ravasi, T.; Lenhard, B.; Wells, C.; et al. The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome. Science 2005, 309, 1559–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockdorff, N.; Ashworth, A.; Kay, G.F.; McCabe, V.M.; Norris, D.P.; Cooper, P.J.; Swift, S.; Rastan, S. The product of the mouse xist gene is a 15 kb inactive X-specific transcript containing no conserved Orf and located in the nucleus. Cell 1992, 71, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.J.; Hendrich, B.D.; Rupert, J.L.; Lafrenière, R.G.; Xing, Y.; Lawrence, J.; Willard, H.F. The human xist gene: Analysis of a 17 kb inactive X-specific rna that contains conserved repeats and is highly localized within the nucleus. Cell 1992, 71, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeftner, S.; Sengupta, A.K.; Kubicek, S.; Mechtler, K.; Spahn, L.; Koseki, H.; Jenuwein, T.; Wutz, A. Recruitment of prc1 function at the initiation of X inactivation independent of prc2 and silencing. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 3110–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaumeil, J.; Le Baccon, P.; Wutz, A.; Heard, E. A novel role for xist RNA in the formation of a repressive nuclear compartment into which genes are recruited when silenced. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 2223–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, K.; Levasseur, P.; Aristarkhov, A.; Lee, J.T. Locked nucleic acids (lnas) reveal sequence requirements and kinetics of xist RNA localization to the X chromosome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 22196–22201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Ciaudo, C.; Fazzari, M.J.; Mise, N.; Servant, N.; Glass, J.L.; Attreed, M.; Avner, P.; Wutz, A.; Barillot, E.; et al. Line-1 activity in facultative heterochromatin formation during X chromosome inactivation. Cell 2010, 141, 956–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.T.; Jaenisch, R. Long-range cis effects of ectopic X-inactivation centres on a mouse autosome. Nature 1997, 386, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wutz, A. Gene silencing in X-chromosome inactivation: Advances in understanding facultative heterochromatin formation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, A.; Becker, P.B. Activation of transcription through histone h4 acetylation by Mof, an acetyltransferase essential for dosage compensation in drosophila. Mol. Cell 2000, 5, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchesi, J.C. Dosage compensation indrosophila and the “Complex” World of transcriptional regulation. BioEssays 1996, 18, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.R.; Pannuti, A.; Gu, W.; Steurnagel, A.; Cook, R.G.; Allis, C.D.; Lucchesi, J.C. The drosophila Msl complex acetylates histone h4 at lysine 16, a chromatin modification linked to dosage compensation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, A.; Baker, B.S. The rox1 and rox2 rnas are essential components of the compensasome, which mediates dosage compensation in drosophila. Mol. Cell 1999, 4, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meller, V.H.; Rattner, B.P. The rox genes encode redundant male-specific lethal transcripts required for targeting of the Msl complex. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.R.; Mondal, T.; Mohammad, F.; Enroth, S.; Redrup, L.; Komorowski, J.; Nagano, T.; Mancini-DiNardo, D.; Kanduri, C. Kcnq1ot1 antisense noncoding rna mediates lineage-specific transcriptional silencing through chromatin-level regulation. Mol. Cell 2008, 32, 232–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latos, P.A.; Pauler, F.M.; Koerner, M.V.; Şenergin, H.B.; Hudson, Q.J.; Stocsits, R.R.; Allhoff, W.; Stricker, S.H.; Klement, R.M.; Warczok, K.E.; et al. Airn transcriptional overlap, but not its lncRNA products, induces imprinted IGFgf2R silencing. Science (N.Y.) 2012, 338, 1469–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipolla, G.A.; de Oliveira, J.C.; Salviano-Silva, A.; Lobo-Alves, S.C.; Lemos, D.S.; Oliveira, L.C.; Jucoski, T.S.; Mathias, C.; Pedroso, G.A.; Zambalde, E.P.; et al. Long non-coding RNAs in multifactorial diseases: Another layer of complexity. Non-Coding RNA 2018, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Qiu, C.; Liu, M.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, G.; Cui, Q. LncRNA disease: A database for long-non-coding RNA-associated diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D983–D986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magistri, M.; Velmeshev, D.; Makhmutova, M.; Faghihi, M.A. Transcriptomics profiling of Alzheimer’s disease reveal neurovascular defects, altered amyloid-β homeostasis, and deregulated expression of long noncoding RNAs. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 48, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.; Richter, N.; Jauch, R.; Gaughwin, P.M.; Zuccato, C.; Cattaneo, E.; Stanton, L.W. Human accelerated region 1 noncoding rna is repressed by rest in huntington’s disease. Physiol. Genom. 2010, 41, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Cao, M.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y. Investigation of long non-coding RNA expression profiles in the substantia Nigra of Parkinson’s disease. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 37, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Niu, W.; Kong, L.; He, M.; Jiang, K.; Chen, S.; Zhong, A.; Zhang, Q.; Li, W.; Lu, J.; et al. Long noncoding RNA as an indicator differentiating schizophrenia from major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder in nonpsychiatric hospital. Biomark. Med. 2017, 11, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, K.; Crowley, J.J. A comprehensive review of the genetic and biological evidence supports a role for microrna-137 in the etiology of schizophrenia. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2018, 177, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, B.; Campbell, D.B. Contribution of long noncoding RNAs to autism spectrum disorder risk. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2013, 113, 35–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziats, M.N.; Rennert, O.M. Aberrant expression of long noncoding rnas in autistic brain. J. Mol. Neurosci. MN 2013, 49, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumarswamy, R.; Bauters, C.; Volkmann, I.; Maury, F.; Fetisch, J.; Holzmann, A.; Lemesle, G.; de Groote, P.; Pinet, F.; Thum, T. Circulating long noncoding rna, lipcar, predicts survival in patients with heart failure. Circ. Res 2014, 114, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, W.; Jin, M.; Chen, J.; Xu, W.; Kong, X. LncRNA MIAT functions as a competing endogenous RNA to upregulate DAPK2 by sponging miR-22-3p in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.K.; Zhang, L.; Dzau, V.J.; Pratt, R.E. H19, a developmentally regulated gene, is reexpressed in RAT vascular smooth muscle cells after injury. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, N.; Qi, C.; Xiao, Y.; Tian, X.; Li, T.; Liu, B. Circulating long noncoding RNA UCA1 as a novel biomarker of acute myocardial infarction. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 8079372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Ou, C.; Xiao, Y.; Han, Q.; Li, H.; Zhou, S. LncRNAs: Key players and novel insights into diabetes mellitus. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 71325–71341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, B.; Wapinski, O.L.; Tsai, M.C.; Qu, K.; Zhang, J.; Carlson, J.C.; Lin, M.; Fang, F.; Gupta, R.A.; et al. Targeted disruption of hotair leads to homeotic transformation and gene derepression. Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amandio, A.R.; Necsulea, A.; Joye, E.; Mascrez, B.; Duboule, D. Hotair is dispensible for mouse development. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.A.; Shah, N.; Wang, K.C.; Kim, J.; Horlings, H.M.; Wong, D.J.; Tsai, M.C.; Hung, T.; Argani, P.; Rinn, J.L.; et al. Long non-coding RNA Hotair reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature 2010, 464, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemmour, D.; Pratama, A.; Loughhead, S.M.; Mathis, D.; Benoist, C. Flicr, a long noncoding RNA, modulates FOXP3 expression and autoimmunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3472–E3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, R.; Gupta, R.; Lai, K.; Chopra, N.; Arron, S.T.; Liao, W. Network analysis of psoriasis reveals biological pathways and roles for coding and long non-coding RNAs. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Qin, X.J.; Li, W.P.; Ma, R.; Wang, T.; Li, Z.Q. LncRNAs expression in adjuvant-induced arthritis rats reveals the potential role of lncRNAs contributing to rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis. Gene 2016, 593, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Liu, J.; Zhao, H.Y.; Chen, Y.P.; Xiang, Z.; Jin, X. Plasma long noncoding RNA expression profile identified by microarray in patients with Crohn’s disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 4716–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, C.L.; Conos, S.A.; Unal, B.; Tergaonkar, V. Noncoding RNAs: Master regulators of inflammatory signaling. Trends Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 66–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathy, N.W.; Chen, X.-M. Long non-coding rnas (lncrnas) and their transcriptional control of inflammatory responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 12375–12382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanucchi, S.; Fok, E.T.; Dalla, E.; Shibayama, Y.; Borner, K.; Chang, E.Y.; Stoychev, S.; Imakaev, M.; Grimm, D.; Wang, K.C.; et al. Immune genes are primed for robust transcription by proximal long noncoding rnas located in nuclear compartments. Nat. Gent. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilott, N.E.; Heward, J.A.; Roux, B.; Tsitsiou, E.; Fenwick, P.S.; Lenzi, L.; Goodhead, I.; Hertz-Fowler, C.; Heger, A.; Hall, N.; et al. Corrigendum: Long non-coding rnas and enhancer rnas regulate the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in human monocytes. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Ming, Z.; Gong, A.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Hu, G.; Zhou, R.; Shibata, A.; Swanson, P.C.; Chen, X.-M. A long noncoding RNA, lincRNA-Tnfaip3, acts as a coregulator of NF-κB to modulate inflammatory gene transcription in mouse macrophages. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 1215–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapicavoli, N.A.; Qu, K.; Zhang, J.; Mikhail, M.; Laberge, R.M.; Chang, H.Y. A mammalian pseudogene lncrna at the interface of inflammation and anti-inflammatory therapeutics. eLife 2013, 2, e00762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chao, T.C.; Chang, K.Y.; Lin, N.; Patil, V.S.; Shimizu, C.; Head, S.R.; Burns, J.C.; Rana, T.M. The long noncoding RNA THRIL regulates TNFα expression through its interaction with hnRNPL. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1002–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, M.; Emerson, B.M. P50-associated COX-2 extragenic RNA (PACER) activates COX-2 gene expression by occluding repressive NF-κB complexes. eLife 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.; Aiello, D.; Atianand, M.K.; Ricci, E.P.; Gandhi, P.; Hall, L.L.; Byron, M.; Monks, B.; Henry-Bezy, M.; Lawrence, J.B.; et al. A long noncoding RNA mediates both activation and repression of immune response genes. Science 2013, 341, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muxel, S.M.; Acuna, S.M.; Aoki, J.I.; Zampieri, R.A.; Floeter-Winter, L.M. Toll-like receptor and miRNA-Let-7e expression alter the inflammatory response in leishmania amazonensis-infected macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.; Atianand, M.; Jiang, Z.; Carpenter, S.; Aiello, D.; Elling, R.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Caffrey, D.R. Cutting edge: A natural antisense transcript, AS-IL1α, controls inducible transcription of the proinflammatory cytokine IL-1α. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 1359–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Gralinski, L.; Armour, C.D.; Ferris, M.T.; Thomas, M.J.; Proll, S.; Bradel-Tretheway, B.G.; Korth, M.J.; Castle, J.C.; Biery, M.C.; et al. Unique signatures of long noncoding RNA expression in response to virus infection and altered innate immune signaling. mBio 2010, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, S.P.; Collins, P.L.; Williams, C.L.; Boothby, M.R.; Aune, T.M. Cutting edge: Influence of Tmevpg1, a long intergenic noncoding RNA, on the expression of ifng by Th1 cells. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 2084–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muxel, S.M.; Laranjeira-Silva, M.F.; Zampieri, R.A.; Floeter-Winter, L.M. Leishmania (leishmania) amazonensis induces macrophage miR-294 and miR-721 expression and modulates infection by targeting NOS2 and L-arginine metabolism. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, M.; Cossart, P.; Lebreton, A. Mammalian microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs in the host-bacterial pathogen crosstalk. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 65, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zur Bruegge, J.; Einspanier, R.; Sharbati, S. A long journey ahead: Long non-coding RNAs in bacterial infections. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Ou, Q.; Liu, C.; Shi, L.; Zhao, C.; Xu, Y.; Kong, S.K.; Loo, J.F.C.; Li, B.; Gu, D. Differential expression of long non-coding RNAs in patients with tuberculosis infection. Tuberculosis 2017, 107, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Wen, Q.; Wang, H.; He, J.; Hu, S.; He, W.; Du, X.; Liu, S.; et al. Microarray analysis of long noncoding RNA and mrna expression profiles in human macrophages infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Li, J.; Gao, K.; Fu, Y. Identifcation of differentially expressed long non-coding RNAs in CD4+ T cells response to latent tuberculosis infection. J. Infect. 2014, 69, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Xu, X.; Xue, J.; Duan, W.; Yi, Z. Deregulated lncRNAs in B cells from patients with active tuberculosis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.T.; Wei, L.L.; Shi, L.Y.; Chen, Z.L.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.M.; Li, Z.J.; Li, J.C. Microarray expression profile analysis of mRNAs and long non-coding RNAs in pulmonary tuberculosis with different traditional chinese medicine syndromes. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westermann, A.J.; Förstner, K.U.; Amman, F.; Barquist, L.; Chao, Y.; Schulte, L.N.; Müller, L.; Reinhardt, R.; Stadler, P.F.; Vogel, J. Dual RNA-seq unveils noncoding RNA functions in host–pathogen interactions. Nature 2016, 529, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, J.A.; Wapinski, O.L.; Yang, Y.W.; Bureau, J.F.; Gopinath, S.; Monack, D.M.; Chang, H.Y.; Brahic, M.; Kirkegaard, K. The nest long ncRNA controls microbial susceptibility and epigenetic activation of the interferon-γ locus. Cell 2013, 152, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Huang, F.; Fu, J.; Dou, B.; Xu, B.; Miao, L.; Liu, W.; Yang, X.; Tan, C.; Chen, H.; et al. Differential transcription profiles of long non-coding RNAs in primary human brain microvascular endothelial cells in response to meningitic Escherichia coli. Sci. Rep-Uk 2016, 6, 38903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, Q.; Yao, Y.; Fang, J.; Sun, F.; Ni, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, H.; Shao, S. Microarray analysis of long non-coding RNA expression profiles in human gastric cells and tissues with Helicobacter Pylori infection. BMC Med. Genom. 2015, 8, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Long, Y.; Li, C.; Cao, L.; Gan, H.; Huang, K.; Jia, Y. Genome-wide analysis of long noncoding RNA profile in human gastric epithelial cell response to Helicobacter pylori. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 68, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaakoush, N.O.; Deshpande, N.P.; Man, S.M.; Burgos-Portugal, J.A.; Khattak, F.A.; Raftery, M.J.; Wilkins, M.R.; Mitchell, H.M. Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses reveal key innate immune signatures in the host response to the gastrointestinal pathogen campylobacter concisus. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 832–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, C.Y.; Yedavalli, V.S.; Jeang, K.T. Neat1 long noncoding RNA and paraspeckle bodies modulate HIV-1 posttranscriptional expression. mBio 2013, 4, e00596-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willingham, A.T.; Orth, A.P.; Batalov, S.; Peters, E.C.; Wen, B.G.; Aza-Blanc, P.; Hogenesch, J.B.; Schultz, P.G. A strategy for probing the function of noncoding RNAs finds a repressor of NFAT. Science 2005, 309, 1570–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imam, H.; Bano, A.S.; Patel, P.; Holla, P.; Jameel, S. The lncRNA NRON modulates HIV-1 replication in a NFAT-dependent manner and is differentially regulated by early and late viral proteins. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Huang, L.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, W.; Cai, L.; Liang, S. Microarray analysis of long non-coding RNA expression profiles uncovers a toxoplasma-induced negative regulation of host immune signaling. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menard, K.L.; Haskins, B.E.; Colombo, A.P.; Denkers, E.Y. Toxoplasma gondii manipulates expression of host long noncoding RNA during intracellular infection. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, E.J.R.; daSilva, L.F.; Pires, D.S.; Lavezzo, G.M.; Pereira, A.S.A.; Amaral, M.S.; Verjovski-Almeida, S. The Schistosoma mansoni genome encodes thousands of long non-coding RNAs predicted to be functional at different parasite life-cycle stages. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, J.; Dong, C.; Tao, Y.; He, A.; Liu, J.; Wu, Z. Identification of long noncoding RNAs in Schistosoma mansoni and Schistosoma japonicum. Exp. Parasitol. 2018, 191, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.F.; Moares, L.A.G.; Mota, E.A.; Jannotti-Passos, L.K.; Coelho, P.M.Z.; Mattos, A.C.A.; Couto, F.F.B.; Caffrey, B.E.; Marsico, A.; Guerra-Sa, R. Identification of 170 new long noncoding RNAs in Schistosoma mansoni. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1264697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacko, N.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, E.; Wang, L.; Cai, J.J.; Lin, X. The lncRNA RZE1 controls cryptococcal morphological transition. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patankar, S.; Munasinghe, A.; Shoaibi, A.; Cummings, L.M.; Wirth, D.F. Serial analysis of gene expression in Plasmodium Falciparum reveals the global expression profile of erythrocytic stages and the presence of anti-sense transcripts in the malarial parasite. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 3114–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Militello, K.T.; Patel, V.; Chessler, A.D.; Fisher, J.K.; Kasper, J.M.; Gunasekera, A.; Wirth, D.F. RNA polymerase II synthesizes antisense RNA in Plasmodium falciparum. RNA 2005, 11, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liniger, M.; Bodenmuller, K.; Pays, E.; Gallati, S.; Roditi, I. Overlapping sense and antisense transcription units in Trypanosoma brucei. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 40, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belli, S.I.; Monnerat, S.; Schaff, C.; Masina, S.; Noll, T.; Myler, P.J.; Stuart, K.; Fasel, N. Sense and antisense transcripts in the histone H1 (his-1) locus of Leishmania major. Int. J. Parasitol. 2003, 33, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, C.; Chow, C.; Muller, M.; Papadopoulou, B. A novel class of developmentally regulated noncoding RNAs in Leishmania. Eukaryot. Cell 2006, 5, 2033–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Allmen, N.; Bienz, M.; Hemphill, A.; Muller, N. Quantitative assessment of sense and antisense transcripts from genes involved in antigenic variation (VSP genes) and encystation (CWP 1 gene) of Giardia Lamblia clone GS/M-83-h7. Parasitology 2005, 130, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodorovic, S.; Walls, C.D.; Elmendorf, H.G. Bidirectional transcription is an inherent feature of Giardia Lamblia promoters and contributes to an abundance of sterile antisense transcripts throughout the genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 2544–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woehle, C.; Kusdian, G.; Radine, C.; Graur, D.; Landan, G.; Gould, S.B. The parasite trichomonas vaginalis expresses thousands of pseudogenes and long non-coding RNAs independently from functional neighbouring genes. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadbent, K.M.; Broadbent, J.C.; Ribacke, U.; Wirth, D.; Rinn, J.L.; Sabeti, P.C. Strand-specific RNA sequencing in Plasmodium falciparum malaria identifies developmentally regulated long non-coding RNA and circular RNA. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Shen, J.; Liu, J.; Sun, X.; Zhao, G.; Chang, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, H.; et al. Genome-wide identification and functional annotation of Plasmodium falciparum long noncoding RNAs from RNA-seq data. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 1269–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadbent, K.M.; Park, D.; Wolf, A.R.; Van Tyne, D.; Sims, J.S.; Ribacke, U.; Volkman, S.; Duraisingh, M.; Wirth, D.; Sabeti, P.C.; et al. A global transcriptional analysis of Plasmodium falciparum malaria reveals a novel family of telomere-associated lncRNAs. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vembar, S.S.; Scherf, A.; Siegel, T.N. Noncoding RNAs as emerging regulators of Plasmodium falciparum virulence gene expression. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2014, 20, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guizetti, J.; Barcons-Simon, A.; Scherf, A. Trans-acting GC-rich non-coding RNA at var expression site modulates gene counting in malaria parasite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 9710–9718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, H.; Pai, K.; Patole, M.S. A novel protein coding potential of long intergenic non-coding RNAs (lincRNAs) in the Kinetoplastid Protozoan parasite Leishmania major. Acta Trop. 2017, 167, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas Castro, F.; Ruy, P.C.; Nogueira Zeviani, K.; Freitas Santos, R.; Simoes Toledo, J.; Kaysel Cruz, A. Evidence of putative non-coding RNAs from Leishmania untranslated regions. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2017, 214, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, F.; Arias-Carrasco, R.; Caris-Maldonado, J.C.; Barral, A.; Maracaja-Coutinho, V.; De Queiroz, A.T.L. Leishdb: A database of coding gene annotation and non-coding RNAs in Leishmania braziliensis. Database (Oxford) 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laranjeira-Silva, M.F.; Zampieri, R.A.; Muxel, S.M.; Beverley, S.M.; Floeter-Winter, L.M. Leishmania amazonensis arginase compartmentalization in the glycosome is important for parasite infectivity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muxel, S.M.; Aoki, J.I.; Fernandes, J.C.R.; Laranjeira-Silva, M.F.; Zampieri, R.A.; Acuna, S.M.; Muller, K.E.; Vanderlinde, R.H.; Floeter-Winter, L.M. Arginine and polyamines fate in Leishmania infection. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, J.I.; Muxel, S.M.; Zampieri, R.A.; Laranjeira-Silva, M.F.; Muller, K.E.; Nerland, A.H.; Floeter-Winter, L.M. RNA-seq transcriptional profiling of Leishmania amazonensis reveals an arginase-dependent gene expression regulation. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0006026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolev, N.G.; Franklin, J.B.; Carmi, S.; Shi, H.; Michaeli, S.; Tschudi, C. The transcriptome of the human pathogen Trypanosoma brucei at single-nucleotide resolution. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Moss, W.; O’Grady, T.; Concha, M.; Strong, M.J.; Wang, X.; Yu, Y.; Baddoo, M.; Zhang, K.; Fewell, C.; et al. New noncoding lytic transcripts derived from the Epstein-Barr virus latency origin of replication, oriP, are hyperedited, bind the paraspeckle protein, NONO/p54nrb, and support viral lytic transcription. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 7120–7132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez-Calvillo, G.; Martin, S.; Hamm, C.; Sztuba-Solinska, J. The structure-to-function relationships of γherpesvirus-encoded long non-coding RNAs and their contributions to viral pathogenesis. Non-Coding RNA 2018, 4, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglio, S.R.; van Eijndhoven, M.A.; Koppers-Lalic, D.; Berenguer, J.; Lougheed, S.M.; Gibbs, S.; Leveille, N.; Rinkel, R.N.; Hopmans, E.S.; Swaminathan, S.; et al. Sensing of latent EBV infection through exosomal transfer of 5′pppRNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E587–E596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, M.R.; Andrews, N.C.; Miller, G.; Steitz, J.A. Two small rnas encoded by Epstein-Barr virus and complexed with protein are precipitated by antibodies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetto, C.C.; Pari, G.S. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus noncoding polyadenylated nuclear RNA interacts with virus- and host cell-encoded proteins and suppresses expression of genes involved in immune modulation. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 13290–13297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prensner, J.R.; Iyer, M.K.; Balbin, O.A.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Cao, Q.; Brenner, J.C.; Laxman, B.; Asangani, I.A.; Grasso, C.S.; Kominsky, H.D.; et al. Transcriptome sequencing across a prostate cancer cohort identifies PCAT-1, an unannotated lincRNA implicated in disease progression. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Q.; Chen, F. An integrated evolutionary analysis of miRNA-lncRNA in mammals. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasramka, M.A.; Maji, S.; Matsuda, A.; Yan, I.K.; Patel, T. Long non-coding RNAs as novel targets for therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Pharmacol. Therap. 2016, 161, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.C.; Wood, M.J.A. Therapeutic targeting of non-coding RNAs. Essays Biochem. 2013, 54, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, D.J.; Franklin, J.L.; Dou, Y.; Liu, Q.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Demory Beckler, M.; Weaver, A.M.; Vickers, K.; Prasad, N.; Levy, S.; et al. KRAS-dependent sorting of miRNA to exosomes. eLife 2015, 4, e07197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinger, S.A.; Cha, D.J.; Franklin, J.L.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Dou, Y.; Ping, J.; Shu, L.; Prasad, N.; Levy, S.; Zhang, B.; et al. Diverse long RNAs are differentially sorted into extracellular vesicles secreted by colorectal cancer cells. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 715–725.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Cha, D.J.; Franklin, J.L.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Jeppesen, D.K.; Weaver, A.M.; Prasad, N.; Levy, S.; Coffey, R.J.; Patton, J.G.; et al. Circular RNAs are down-regulated in KRAS mutant colon cancer cells and can be transferred to exosomes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Yan, I.K.; Haga, H.; Patel, T. Modulation of hypoxia-signaling pathways by extracellular linc-Ror. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 1585–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohankumar, S.; Patel, T. Extracellular vesicle long noncoding RNA as potential biomarkers of liver cancer. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2016, 15, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivas, W.M.; Muhlrad, D.; Parker, R. Analysis of the yeast genome: Identification of new non-coding and small Orf-containing RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4619–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzini, A.A.; Johnstone, T.G.; Christiano, R.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Obermayer, B.; Fleming, E.S.; Vejnar, C.E.; Lee, M.T.; Rajewsky, N.; Walther, T.C.; et al. Identification of small Orfs in vertebrates using ribosome footprinting and evolutionary conservation. EMBO J. 2014, 33, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.J.; Rothnagel, J.A. Emerging evidence for functional peptides encoded by short open reading frames. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Anderson, K.M.; Chang, C.-L.; Makarewich, C.A.; Nelson, B.R.; McAnally, J.R.; Kasaragod, P.; Shelton, J.M.; Liou, J.; Bassel-Duby, R.; et al. A micropeptide encoded by a putative long noncoding RNA regulates muscle performance. Cell 2015, 160, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, B.R.; Makarewich, C.A.; Anderson, D.M.; Winders, B.R.; Troupes, C.D.; Wu, F.; Reese, A.L.; McAnally, J.R.; Chen, X.; Kavalali, E.T.; et al. A peptide encoded by a transcript annotated as long noncoding RNA enhances serca activity in muscle. Science 2016, 351, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, A.; Pasut, A.; Matsumoto, M.; Yamashita, R.; Fung, J.; Monteleone, E.; Saghatelian, A.; Nakayama, K.I.; Clohessy, J.G.; Pandolfi, P.P. mTORC1 and muscle regeneration are regulated by the LINC00961-encoded spar polypeptide. Nature 2017, 541, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rion, N.; Rüegg, M.A. LncRNA-encoded peptides: More than translational noise? Cell Res. 2017, 27, 604–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Nair, A.; Chen, X.; Prodduturi, N.; Wang, J.; Kocher, J.-P. Uclncr: Ultrafast and comprehensive long non-coding rna detection from rna-seq. Sci. Rep-Uk 2017, 7, 14196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernandes, J.C.R.; Acuña, S.M.; Aoki, J.I.; Floeter-Winter, L.M.; Muxel, S.M. Long Non-Coding RNAs in the Regulation of Gene Expression: Physiology and Disease. Non-Coding RNA 2019, 5, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna5010017
Fernandes JCR, Acuña SM, Aoki JI, Floeter-Winter LM, Muxel SM. Long Non-Coding RNAs in the Regulation of Gene Expression: Physiology and Disease. Non-Coding RNA. 2019; 5(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna5010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernandes, Juliane C. R., Stephanie M. Acuña, Juliana I. Aoki, Lucile M. Floeter-Winter, and Sandra M. Muxel. 2019. "Long Non-Coding RNAs in the Regulation of Gene Expression: Physiology and Disease" Non-Coding RNA 5, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna5010017
APA StyleFernandes, J. C. R., Acuña, S. M., Aoki, J. I., Floeter-Winter, L. M., & Muxel, S. M. (2019). Long Non-Coding RNAs in the Regulation of Gene Expression: Physiology and Disease. Non-Coding RNA, 5(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna5010017







