Sponge Long Non-Coding RNAs Are Expressed in Specific Cell Types and Conserved Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
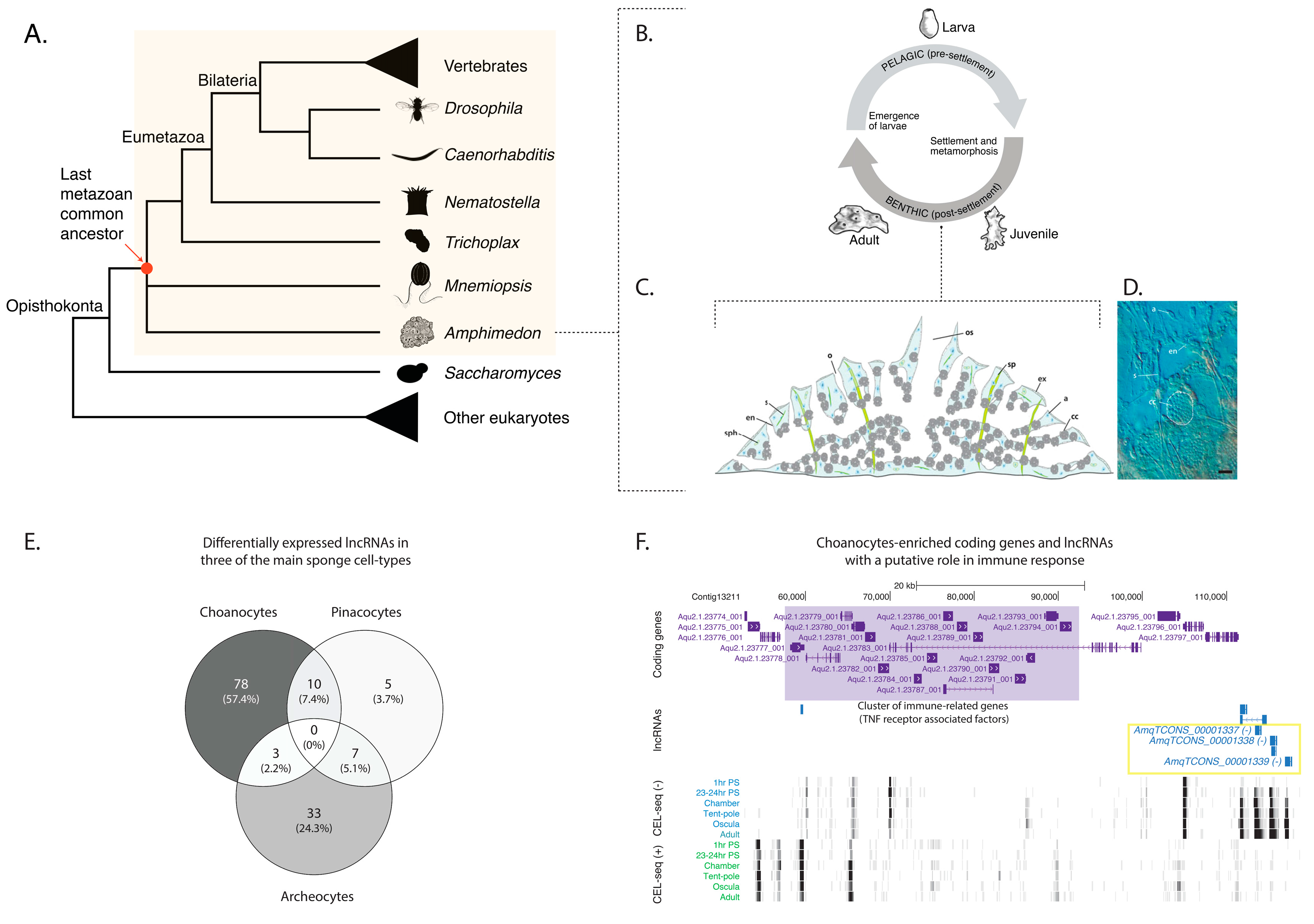
2.1. Sponge lncRNAs Are Enriched in Specific Cell Types
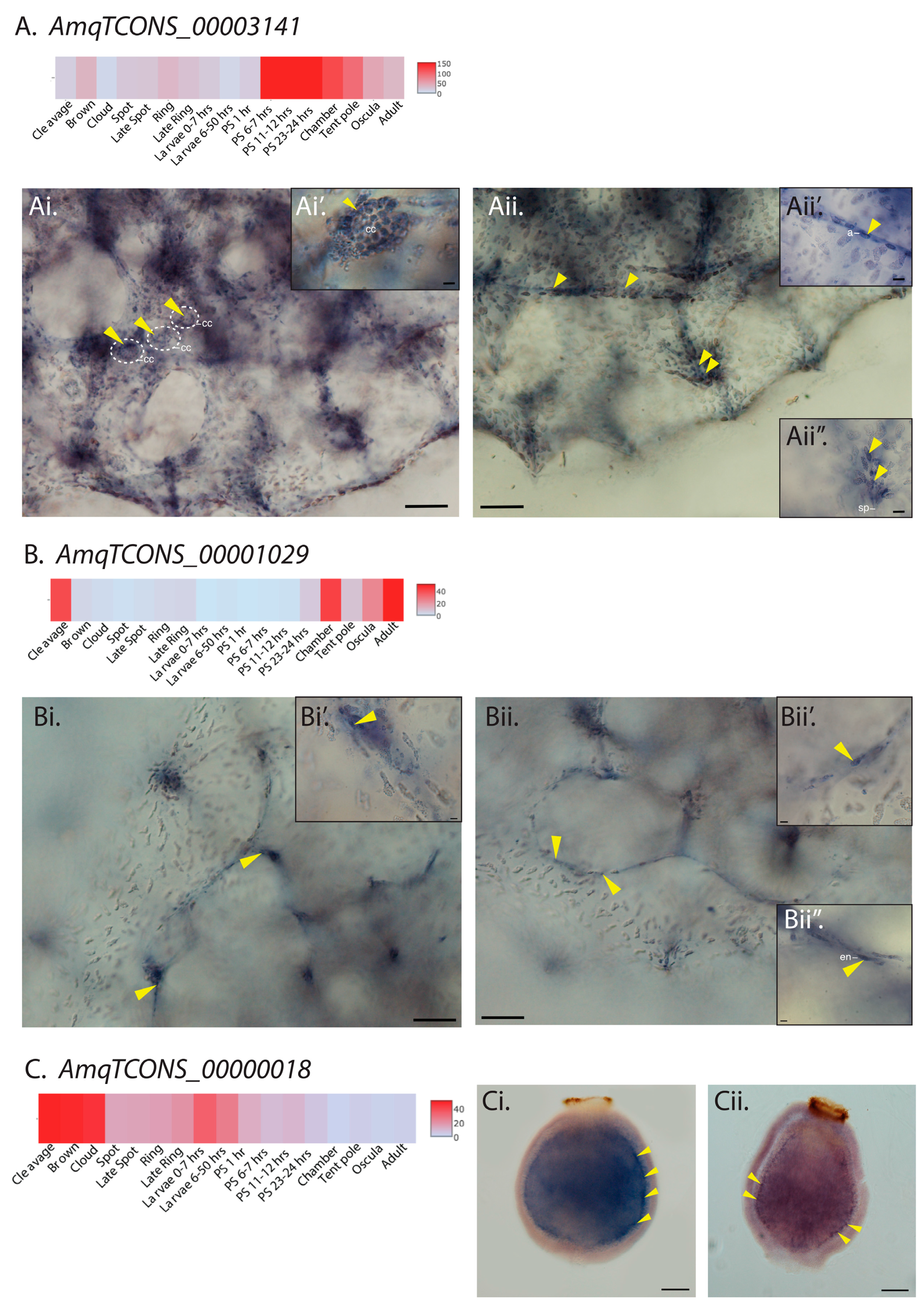
2.2. Sponge lncRNAs Show Cell Type-Specific Restricted Expression Patterns
2.3. Amphimedon and Sycon lncRNAs Are Co-Expressed with Similar Sets of Protein-Coding Genes
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell-Type Specific Transcriptome Analysis
4.2. Gene Isolation and Whole Mount In Situ Hybridization
4.3. Co-Expression Network Analysis
4.4. Data Access
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bertone, P.; Stolc, V.; Royce, T.E.; Rozowsky, J.S.; Urban, A.E.; Zhu, X.; Rinn, J.L.; Tongprasit, W.; Samanta, M.; Weissman, S.; et al. Global identification of human transcribed sequences with genome tiling arrays. Science 2004, 306, 2242–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabili, M.N.; Trapnell, C.; Goff, L.; Koziol, M.; Tazon-Vega, B.; Regev, A.; Rinn, J.L. Integrative annotation of human large intergenic noncoding RNAs reveals global properties and specific subclasses. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 1915–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carninci, P.; Kasukawa, T.; Katayama, S.; Gough, J.; Frith, M.C.; Maeda, N.; Oyama, R.; Ravasi, T.; Lenhard, B.; Wells, C.; et al. The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome. Science 2005, 309, 1559–1563. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Derrien, T.; Johnson, R.; Bussotti, G.; Tanzer, A.; Djebali, S.; Tilgner, H.; Guernec, G.; Martin, D.; Merkel, A.; Knowles, D.G.; et al. The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long non-coding RNAs: Analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djebali, S.; Davis, C.A.; Merkel, A.; Dobin, A.; Lassmann, T.; Mortazavi, A.; Tanzer, A.; Lagarde, J.; Lin, W.; Schlesinger, F.; et al. Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature 2012, 489, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman, M.; Russell, P.; Ingolia, N.T.; Weissman, J.S.; Lander, E.S. Ribosome profiling provides evidence that large noncoding RNAs do not encode proteins. Cell 2013, 154, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Housman, G.; Ulitsky, I. Methods for distinguishing between protein-coding and long noncoding RNAs and the elusive biological purpose of translation of long noncoding RNAs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2016, 1859, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingolia, N.T.; Brar, G.A.; Stern-Ginossar, N.; Harris, M.S.; Talhouarne, G.J.S.; Jackson, S.E.; Wills, M.R.; Weissman, J.S. Ribosome profiling reveals pervasive translation outside of annotated protein-coding genes. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 1365–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapranov, P.; Cheng, J.; Dike, S.; Nix, D.A.; Duttagupta, R.; Willingham, A.T.; Stadler, P.F.; Hertel, J.; Hackermuller, J.; Hofacker, I.L.; et al. RNA maps reveal new RNA classes and a possible function for pervasive transcription. Science 2007, 316, 1484–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, A.M.; Guttman, M.; Huarte, M.; Garber, M.; Raj, A.; Rivea Morales, D.; Thomas, K.; Presser, A.; Bernstein, B.E.; van Oudenaarden, A.; et al. Many human large intergenic noncoding RNAs associate with chromatin-modifying complexes and affect gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11667–11672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagarde, J.; Uszczynska-Ratajczak, B.; Carbonell, S.; Pérez-Lluch, S.; Abad, A.; Davis, C.; Gingeras, T.R.; Frankish, A.; Harrow, J.; Guigo, R.; et al. High-throughput annotation of full-length long noncoding RNAs with capture long-read sequencing. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, Y.; RIKEN Genome Exploration Research Group Phase I & II Team. Analysis of the mouse transcriptome based on functional annotation of 60,770 full-length cDNAs. Nature 2002, 420, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ponting, C.P.; Oliver, P.L.; Reik, W. Evolution and functions of long non-coding RNAs. Cell 2009, 136, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravasi, T.; Suzuki, H.; Pang, K.C.; Katayama, S.; Furuno, M.; Okunishi, R.; Fukuda, S.; Ru, K.; Frith, M.C.; Gongora, M.M.; et al. Experimental validation of the regulated expression of large numbers of non-coding RNAs from the mouse genome. Genome Res. 2006, 16, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman, M.; Amit, I.; Garber, M.; French, C.; Lin, M.F.; Feldser, D.; Huarte, M.; Zuk, O.; Carey, B.W.; Cassady, J.P.; et al. Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large non-coding RNAs in mammals. Nature 2009, 458, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, J.J.; Chang, H.Y. Unique features of long non-coding RNA biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.J.; Nowakowski, T.J.; Pollen, A.A.; Lui, J.H.; Horlbeck, M.A.; Attenello, F.J.; He, D.; Weissman, J.S.; Kriegstein, A.R.; Diaz, A.A.; et al. Single-cell analysis of long non-coding RNAs in the developing human neocortex. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bråte, J.; Adamski, M.; Neumann, R.S.; Shalchian-Tabrizi, K.; Adamska, M. Regulatory RNA at the root of animals: Dynamic expression of developmental lincRNAs in the calcisponge Sycon ciliatum. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20151746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabili, M.N.; Dunagin, M.C.; McClanahan, P.D.; Biaesch, A.; Padovan-Merhar, O.; Regev, A.; Rinn, J.L.; Raj, A. Localization and abundance analysis of human lncRNAs at single-cell and single-molecule resolution. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaiti, F.; Fernandez-Valverde, S.L.; Nakanishi, N.; Calcino, A.D.; Yanai, I.; Tanurdzic, M.; Degnan, B.M. Dynamic and widespread lncRNA expression in a sponge and the origin of animal complexity. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 2367–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, T.R.; Dinger, M.E.; Sunkin, S.M.; Mehler, M.F.; Mattick, J.S. Specific expression of long noncoding RNAs in the mouse brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauli, A.; Valen, E.; Lin, M.F.; Garber, M.; Vastenhouw, N.L.; Levin, J.Z.; Fan, L.; Sandelin, A.; Rinn, J.L.; Regev, A.; et al. Systematic identification of long non-coding RNAs expressed during zebrafish embryogenesis. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponjavic, J.; Oliver, P.L.; Lunter, G.; Ponting, C.P. Genomic and transcriptional co-localization of protein-coding and long non-coding RNA pairs in the developing brain. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zappulo, A.; van den Bruck, D.; Ciolli Mattioli, C.; Franke, V.; Imami, K.; McShane, E.; Moreno-Estelles, M.; Calviello, L.; Filipchyk, A.; Peguero-Sanchez, E.; et al. RNA localization is a key determinant of neurite-enriched proteome. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauli, A.; Rinn, J.L.; Schier, A.F. Non-coding RNAs as regulators of embryogenesis. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulitsky, I. Evolution to the rescue: Using comparative genomics to understand long non-coding RNAs. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.B.; Boley, N.; Eisman, R.; May, G.E.; Stoiber, M.H.; Duff, M.O.; Booth, B.W.; Wen, J.; Park, S.; Suzuki, A.M.; et al. Diversity and dynamics of the Drosophila transcriptome. Nature 2014, 512, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jia, S.; Chen, S.; Kang, L. Genome-wide identification and developmental expression profiling of long noncoding RNAs during Drosophila metamorphosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forouzmand, E.; Owens, N.D.L.; Blitz, I.L.; Paraiso, K.D.; Khokha, M.K.; Gilchrist, M.J.; Xie, X.; Cho, K.W.Y. Developmentally regulated long non-coding RNAs in Xenopus tropicalis. Dev. Biol. 2017, 426, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Morlighem, J.-É.R.L.; Cai, J.; Liao, Q.; Perez, C.D.; Gomes, P.B.; Guo, M.; Rádis-Baptista, G.; Lee, S.M.-Y. Identification of long non-coding RNAs in two anthozoan species and their possible implications for coral bleaching. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakodi, M.; Jung, J.W.; Park, D.; Ahn, Y.-J.; Lee, S.-C.; Shin, S.-Y.; Shin, C.; Yang, T.-J.; Kwon, H.W. Genome-wide characterization of long intergenic non-coding RNAs (lincRNAs) provides new insight into viral diseases in honey bees Apis cerana and Apis mellifera. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, A.M.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Muskavitch, M.A.T. Long non-coding RNA discovery across the genus anopheles reveals conserved secondary structures within and beyond the Gambiae complex. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, C.; Wang, R.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Tian, M.; Jiao, W.; Huang, X.; Zhang, L.; Hu, X.; Wang, S.; et al. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) of sea cucumber: Large-scale prediction, expression profiling, non-coding network construction, and lncRNA-microRNA-gene interaction analysis of lncRNAs in Apostichopus japonicus and Holothuria glaberrima during LPS challenge and radial organ complex regeneration. Mar. Biotechnol. 2016, 18, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nam, J.W.; Bartel, D.P. Long noncoding RNAs in C. elegans. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 2529–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Necsulea, A.; Soumillon, M.; Warnefors, M.; Liechti, A.; Daish, T.; Zeller, U.; Baker, J.C.; Grutzner, F.; Kaessmann, H. The evolution of lncRNA repertoires and expression patterns in tetrapods. Nature 2014, 505, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, J.J.; Zhang, Q.C.; Georgiev, P.; Ilik, I.A.; Akhtar, A.; Chang, H.Y. Rapid evolutionary turnover underlies conserved lncRNA–genome interactions. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauvageau, M.; Goff, L.A.; Lodato, S.; Bonev, B.; Groff, A.F.; Gerhardinger, C.; Sanchez-Gomez, D.B.; Hacisuleyman, E.; Li, E.; Spence, M.; et al. Multiple knockout mouse models reveal lincRNAs are required for life and brain development. eLife 2013, 2, e01749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.H.; Au, K.F.; Yablonovitch, A.L.; Wills, A.E.; Chuang, J.; Baker, J.C.; Wong, W.H.; Li, J.B. RNA sequencing reveals a diverse and dynamic repertoire of the Xenopus tropicalis transcriptome over development. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulitsky, I.; Shkumatava, A.; Jan, C.H.; Sive, H.; Bartel, D.P. Conserved function of lincRNAs in vertebrate embryonic development despite rapid sequence evolution. Cell 2011, 147, 1537–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Cheng, T.; Liu, C.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Long, R.; Zhao, P.; Xia, Q. Systematic identification and characterization of long non-coding RNAs in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, R.S.; Marques, A.C.; Tibbit, C.; Haerty, W.; Bassett, A.R.; Liu, J.L.; Ponting, C.P. Identification and properties of 1119 candidate lincRNA loci in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Genome Biol. Evol. 2012, 4, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, J.; Mahadevaiah, S.K.; Khil, P.; Sangrithi, M.N.; Royo, H.; Duckworth, J.; McCarrey, J.R.; VandeBerg, J.L.; Renfree, M.B.; Taylor, W.; et al. Rsx is a metatherian RNA with Xist-like properties in X-chromosome inactivation. Nature 2012, 487, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heard, E.; Mongelard, F.; Arnaud, D.; Chureau, C.; Vourc’h, C.; Avner, P. Human XIST yeast artificial chromosome transgenes show partial X inactivation center function in mouse embryonic stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 6841–6846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migeon, B.R.; Kazi, E.; Haisley-Royster, C.; Hu, J.; Reeves, R.; Call, L.; Lawler, A.; Moore, C.S.; Morrison, H.; Jeppesen, P. Human X inactivation center induces random X chromosome inactivation in male transgenic mice. Genomics 1999, 59, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erwin, D.H.; Laflamme, M.; Tweedt, S.M.; Sperling, E.A.; Pisani, D.; Peterson, K.J. The Cambrian conundrum: Early divergence and later ecological success in the early history of animals. Science 2011, 334, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazave, E.; Lapébie, P.; Ereskovsky, A.V.; Vacelet, J.; Renard, E.; Cárdenas, P.; Borchiellini, C. No longer Demospongiae: Homoscleromorpha formal nomination as a fourth class of Porifera. Hydrobiologia 2012, 687, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.S.; Hill, A.L.; Lopez, J.; Peterson, K.J.; Pomponi, S.; Diaz, M.C.; Thacker, R.W.; Adamska, M.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Cardenas, P.; et al. Reconstruction of family-level phylogenetic relationships within Demospongiae (Porifera) using nuclear encoded housekeeping genes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e50437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worheide, G.; Dohrmann, M.; Erpenbeck, D.; Larroux, C.; Maldonado, M.; Voigt, O.; Borchiellini, C.; Lavrov, D.V. Deep phylogeny and evolution of sponges (phylum Porifera). Adv. Mar. Biol. 2012, 61, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Degnan, B.M.; Adamska, M.; Richards, G.S.; Larroux, C.; Leininger, S.; Bergum, B.; Calcino, A.; Taylor, K.; Nakanishi, N.; Degnan, S.M. Porifera. In Evolutionary Developmental Biology of Invertebrates 1: Introduction, Non-Bilateria, Acoelomorpha, Xenoturbellida, Chaetognatha; Wanninger, A., Ed.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2015; pp. 65–106. [Google Scholar]
- Ereskovsky, A.V. The Comparative Embryology of Sponges; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Heidelberg, Germany; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Leys, S.P.; Degnan, B.M. Embryogenesis and metamorphosis in a haplosclerid demosponge: Gastrulation and transdifferentiation of larval ciliated cells to choanocytes. Invertebr. Biol. 2002, 121, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simion, P.; Philippe, H.; Baurain, D.; Jager, M.; Richter, D.J.; Di Franco, A.; Roure, B.; Satoh, N.; Quéinnec, É.; Ereskovsky, A.; et al. A large and consistent phylogenomic dataset supports sponges as the sister group to all other animals. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelan, N.V.; Kocot, K.M.; Moroz, T.P.; Mukherjee, K.; Williams, P.; Paulay, G.; Moroz, L.L.; Halanych, K.M. Ctenophore relationships and their placement as the sister group to all other animals. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 1737–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, R.M.; Haussler, D.; Kent, W.J. The UCSC genome browser and associated tools. Brief. Bioinform. 2013, 14, 144–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chodroff, R.A.; Goodstadt, L.; Sirey, T.M.; Oliver, P.L.; Davies, K.E.; Green, E.D.; Molnar, Z.; Ponting, C.P. Long noncoding RNA genes: Conservation of sequence and brain expression among diverse amniotes. Genome Boil. 2010, 11, R72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hezroni, H.; Koppstein, D.; Schwartz, M.G.; Avrutin, A.; Bartel, D.P.; Ulitsky, I. Principles of long noncoding RNA evolution derived from direct comparison of transcriptomes in 17 species. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 1110–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washietl, S.; Kellis, M.; Garber, M. Evolutionary dynamics and tissue specificity of human long noncoding RNAs in six mammals. Genome Res. 2014, 24, 616–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sogabe, S. The Biology of Choanocytes and Choanocyte Chambers and Their Role in the Sponge Stem Cell System. Ph.D. Thesis, School of Biological Sciences, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yuen, B. Deciphering the Genomic Tool-Kit Underlying Animal-Bacteria Interactions: Insights through the Demosponge Amphimedon queenslandica. Ph.D. Thesis, School of Biological Sciences, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, T.; Seridi, L.; Moitinho-Silva, L.; Oates, M.; Liew, Y.J.; Mavromatis, C.; Wang, X.; Haywood, A.; Lafi, F.F.; Kupresanin, M.; et al. Hologenome analysis of two marine sponges with different microbiomes. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, B.; Bayes, J.M.; Degnan, S.M. The characterization of sponge NLRs provides insight into the origin and evolution of this innate immune gene family in animals. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degnan, S.M. The surprisingly complex immune gene repertoire of a simple sponge, exemplified by the NLR genes: A capacity for specificity? Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 48, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detournay, O.; Schnitzler, C.E.; Poole, A.; Weis, V.M. Regulation of cnidarian–dinoflagellate mutualisms: Evidence that activation of a host TGF-β innate immune pathway promotes tolerance of the symbiont. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 38, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, C.J.C.; Smyth, D.J.; Dresser, D.W.; Maizels, R.M. TGF-β in tolerance, development and regulation of immunity. Cell. Immunol. 2016, 299, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamska, M.; Degnan, S.M.; Green, K.M.; Adamski, M.; Craigie, A.; Larroux, C.; Degnan, B.M. Wnt and TGF-beta expression in the sponge Amphimedon queenslandica and the origin of metazoan embryonic patterning. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sogabe, S.; Nakanishi, N.; Degnan, B.M. The ontogeny of choanocyte chambers during metamorphosis in the demosponge Amphimedon queenslandica. EvoDevo 2016, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaiti, F.; Jindrich, K.; Fernandez-Valverde, S.L.; Roper, K.E.; Degnan, B.M.; Tanurdzic, M. Landscape of histone modifications in a sponge reveals the origin of animal cis-regulatory complexity. eLife 2017, 6, e22194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, G.S.; Degnan, B.M. The expression of Delta ligands in the sponge Amphimedon queenslandica suggests an ancient role for Notch signaling in metazoan development. EvoDevo 2012, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goff, L.A.; Groff, A.F.; Sauvageau, M.; Trayes-Gibson, Z.; Sanchez-Gomez, D.B.; Morse, M.; Martin, R.D.; Elcavage, L.E.; Liapis, S.C.; Gonzalez-Celeiro, M.; et al. Spatiotemporal expression and transcriptional perturbations by long non-coding RNAs in the mouse brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 6855–6862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatica, A.; Bozzoni, I. Long non-coding RNAs: New players in cell differentiation and development. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalei, V.; Sansom, S.N.; Kong, L.; Lee, S.; Montiel, J.F.; Vance, K.W.; Ponting, C.P. The long non-coding RNA Dali is an epigenetic regulator of neural differentiation. eLife 2014, 3, e04530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinger, M.E.; Amaral, P.P.; Mercer, T.R.; Pang, K.C.; Bruce, S.J.; Gardiner, B.B.; Askarian-Amiri, M.E.; Ru, K.; Solda, G.; Simons, C.; et al. Long non-coding RNAs in mouse embryonic stem cell pluripotency and differentiation. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 1433–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman, M.; Donaghey, J.; Carey, B.W.; Garber, M.; Grenier, J.K.; Munson, G.; Young, G.; Lucas, A.B.; Ach, R.; Bruhn, L.; et al. lincRNAs act in the circuitry controlling pluripotency and differentiation. Nature 2011, 477, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Lu, J.Y.; Liu, L.; Yin, Y.; Chen, C.; Han, X.; Wu, B.; Xu, R.; Liu, W.; Yan, P.; et al. Divergent lncRNAs regulate gene expression and lineage differentiation in pluripotent cells. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 18, 637–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Yan, P.; Lu, J.; Song, G.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, B.; Huang, X.; Zhu, H.; et al. Opposing roles for the lncRNA Haunt and its genomic locus in regulating HoxA gene activation during embryonic stem cell differentiation. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 16, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, E.H.; Erwin, D.H. Gene regulatory networks and the evolution of animal body plans. Science 2006, 311, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erwin, D.H.; Davidson, E.H. The evolution of hierarchical gene regulatory networks. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, I.S.; Davidson, E.H. Evolution of gene regulatory networks controlling body plan development. Cell 2011, 144, 970–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, M.; Simakov, O.; Chapman, J.; Fahey, B.; Gauthier, M.E.; Mitros, T.; Richards, G.S.; Conaco, C.; Dacre, M.; Hellsten, U.; et al. The Amphimedon queenslandica genome and the evolution of animal complexity. Nature 2010, 466, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimshony, T.; Wagner, F.; Sher, N.; Yanai, I. CEL-Seq: Single-cell RNA-Seq by multiplexed linear amplification. Cell Rep. 2012, 2, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larroux, C.; Fahey, B.; Adamska, M.; Richards, G.S.; Gauthier, M.; Green, K.; Lovas, E.; Degnan, B.M. Whole-mount in situ hybridization in Amphimedon. Cold Spring Harbor Protoc. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Valverde, S.L.; Calcino, A.D.; Degnan, B.M. Deep developmental transcriptome sequencing uncovers numerous new genes and enhances gene annotation in the sponge Amphimedon queenslandica. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, B.J.; Papanicolaou, A.; Yassour, M.; Grabherr, M.; Blood, P.D.; Bowden, J.; Couger, M.B.; Eccles, D.; Li, B.; Lieber, M.; et al. De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-Seq: Reference generation and analysis with Trinity. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.; Domrachev, M.; Lash, A.E. Gene Expression Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anavy, L.; Levin, M.; Khair, S.; Nakanishi, N.; Fernandez-Valverde, S.L.; Degnan, B.M.; Yanai, I. BLIND ordering of large-scale transcriptomic developmental timecourses. Development 2014, 141, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
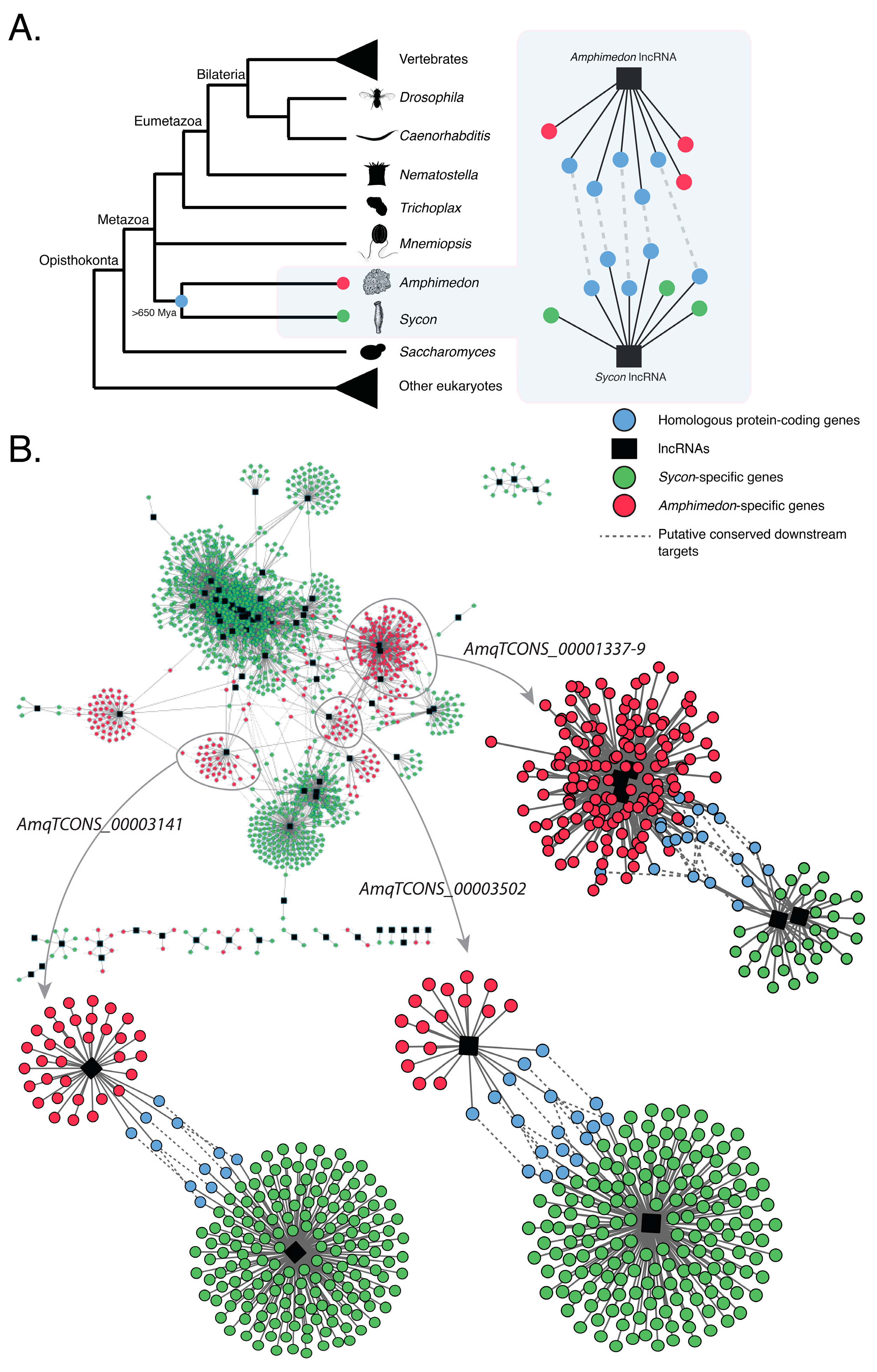
| AmqTCONS_00003141 | |
| Homologous gene pairs | Description |
| scigt010895-Aqu2.1.43387_001 | mitochondrial dicarboxylate carrier |
| scigt017797-Aqu2.1.41074_001 | protein disulfide-isomerase a5-like |
| scigt001771-Aqu2.1.30885_001 | sh3 and px domain-containing protein 2a-like |
| scigt016036-Aqu2.1.36626_001 | adp-ribosylation factor gtpase-activating protein 2-like |
| scigt018255-Aqu2.1.30885_001 | sh3 and px domain-containing protein 2a-like |
| scigt000612-Aqu2.1.41568_001 | tgf-beta receptor type-1 |
| scigt008994-Aqu2.1.41568_001 | tgf-beta receptor type-1 |
| AmqTCONS_00001337-9 | |
| Homologous gene pairs | Description |
| scigt017951-Aqu2.1.43947_001 | arylsulfatase b-like |
| scigt017951-Aqu2.1.24502_001 | arylsulfatase b-like |
| scigt017951-Aqu2.1.39727_001 | arylsulfatase |
| scigt017951-Aqu2.1.41029_001 | arylsulfatase |
| scigt017951-Aqu2.1.37909_001 | sulfatase |
| scigt014545-Aqu2.1.37909_001 | sulfatase |
| scigt014545-Aqu2.1.41029_001 | arylsulfatase |
| scigt014545-Aqu2.1.39727_001 | arylsulfatase |
| scigt017997-Aqu2.1.32274_001 | usherin |
| scigt020120-Aqu2.1.28087_001 | lysosomal alpha-glucosidase-like isoform x2 |
| scigt020423-Aqu2.1.35119_001 | filamin-c-like isoform x3 |
| scigt000557-Aqu2.1.32241_001 | myosin-i heavy chain |
| scigt008273-Aqu2.1.36394_001 | deleted in malignant brain tumors 1 |
| scigt017951-Aqu2.1.42755_001 | arylsulfatase b-like |
| AmqTCONS_00003502 | |
| Homologous gene pairs | Description |
| scigt000138-Aqu2.1.44676_001 | actin family protein |
| scigt001771-Aqu2.1.38758_001 | tyrosine-protein kinase lck |
| scigt005362-Aqu2.1.44676_001 | actin family protein |
| scigt004922-Aqu2.1.40987_001 | unconventional myosin-viia |
| scigt008792-Aqu2.1.24982_001 | adenylyl cyclase-associated protein 1 |
| scigt012572-Aqu2.1.40987_001 | unconventional myosin-viia |
| scigt014349-Aqu2.1.32914_001 | pleckstrin homology domain-containing family g member 1-like |
| scigt016045-Aqu2.1.28519_001 | ap-2 complex subunit alpha-1-like |
| scigt020995-Aqu2.1.43989_001 | protein plant cadmium resistance 3-like |
| scigt021992-Aqu2.1.44676_001 | actin family protein |
| scigt022018-Aqu2.1.44676_001 | actin family protein |
| scigt025009-Aqu2.1.40987_001 | unconventional myosin-viia |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gaiti, F.; Hatleberg, W.L.; Tanurdžić, M.; Degnan, B.M. Sponge Long Non-Coding RNAs Are Expressed in Specific Cell Types and Conserved Networks. Non-Coding RNA 2018, 4, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna4010006
Gaiti F, Hatleberg WL, Tanurdžić M, Degnan BM. Sponge Long Non-Coding RNAs Are Expressed in Specific Cell Types and Conserved Networks. Non-Coding RNA. 2018; 4(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna4010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaiti, Federico, William L. Hatleberg, Miloš Tanurdžić, and Bernard M. Degnan. 2018. "Sponge Long Non-Coding RNAs Are Expressed in Specific Cell Types and Conserved Networks" Non-Coding RNA 4, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna4010006
APA StyleGaiti, F., Hatleberg, W. L., Tanurdžić, M., & Degnan, B. M. (2018). Sponge Long Non-Coding RNAs Are Expressed in Specific Cell Types and Conserved Networks. Non-Coding RNA, 4(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna4010006





