Modification of Poiseuille Flow to a Pulsating Flow Using a Periodically Expanding-Contracting Balloon
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Governing Equations
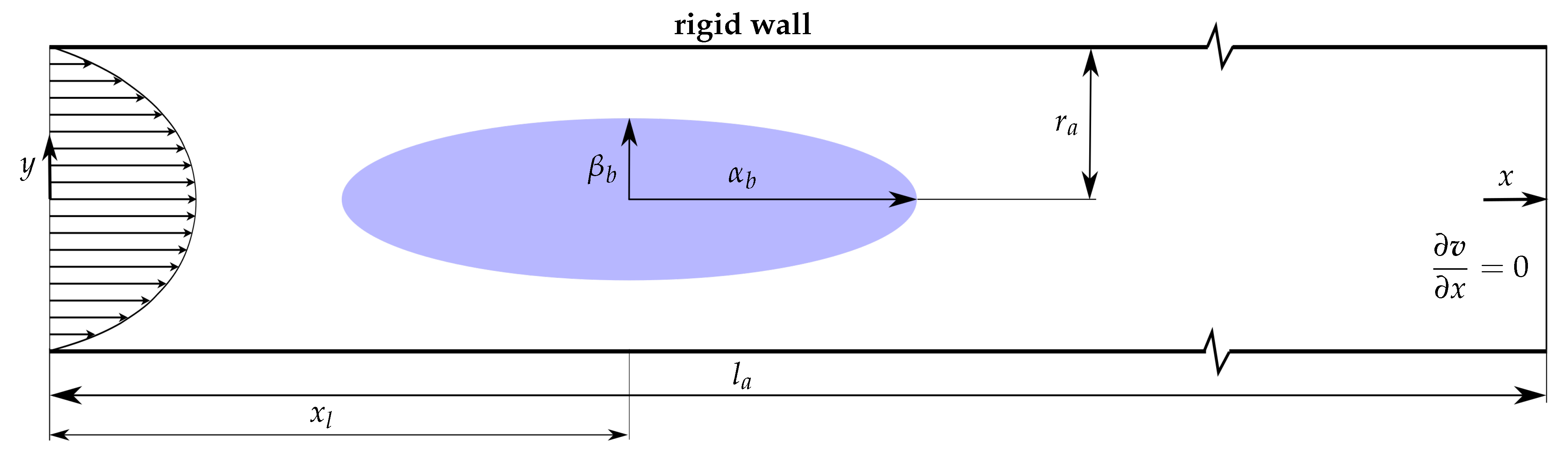
2.2. Vessel Model
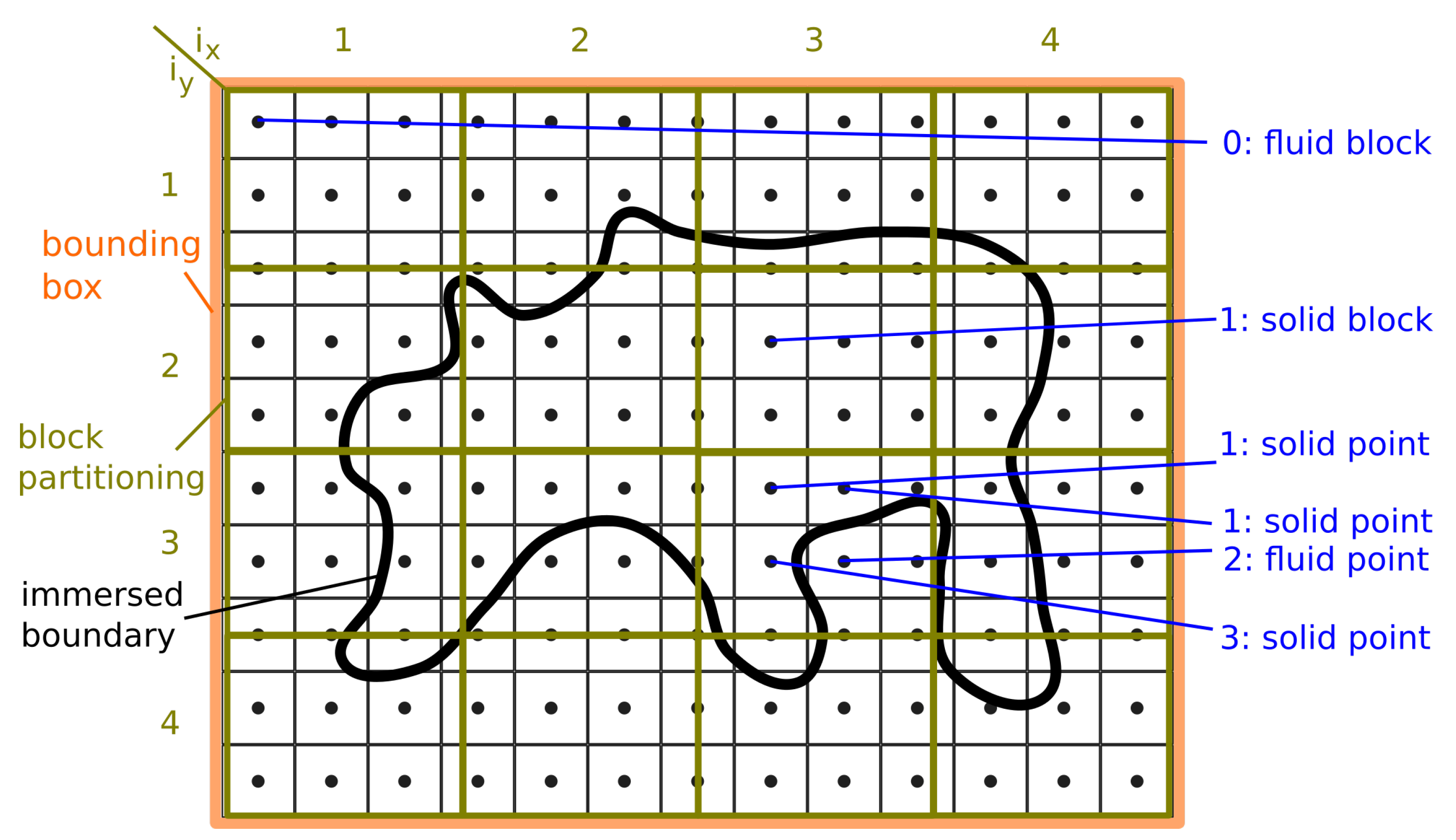
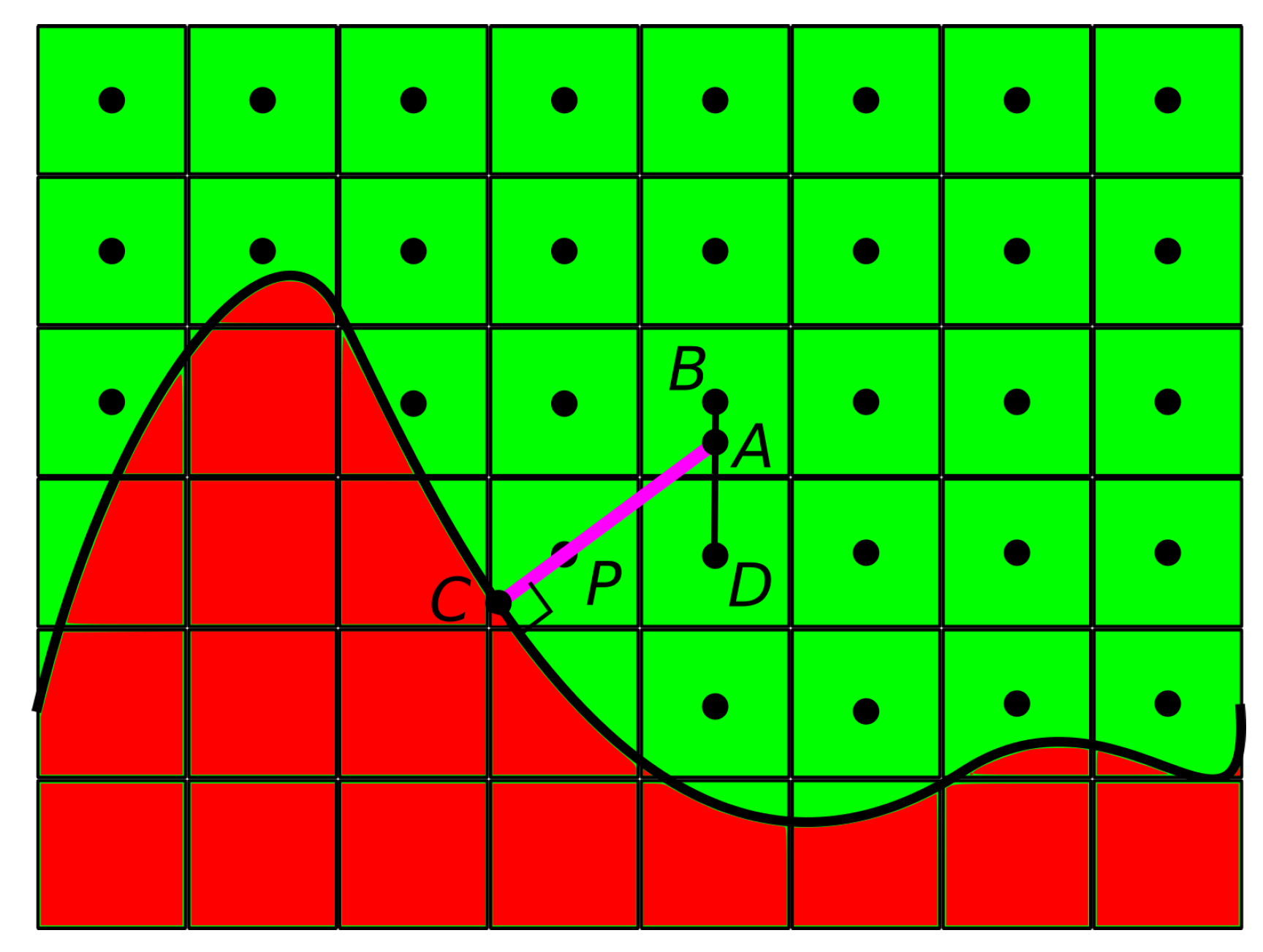
2.3. Numerical Method
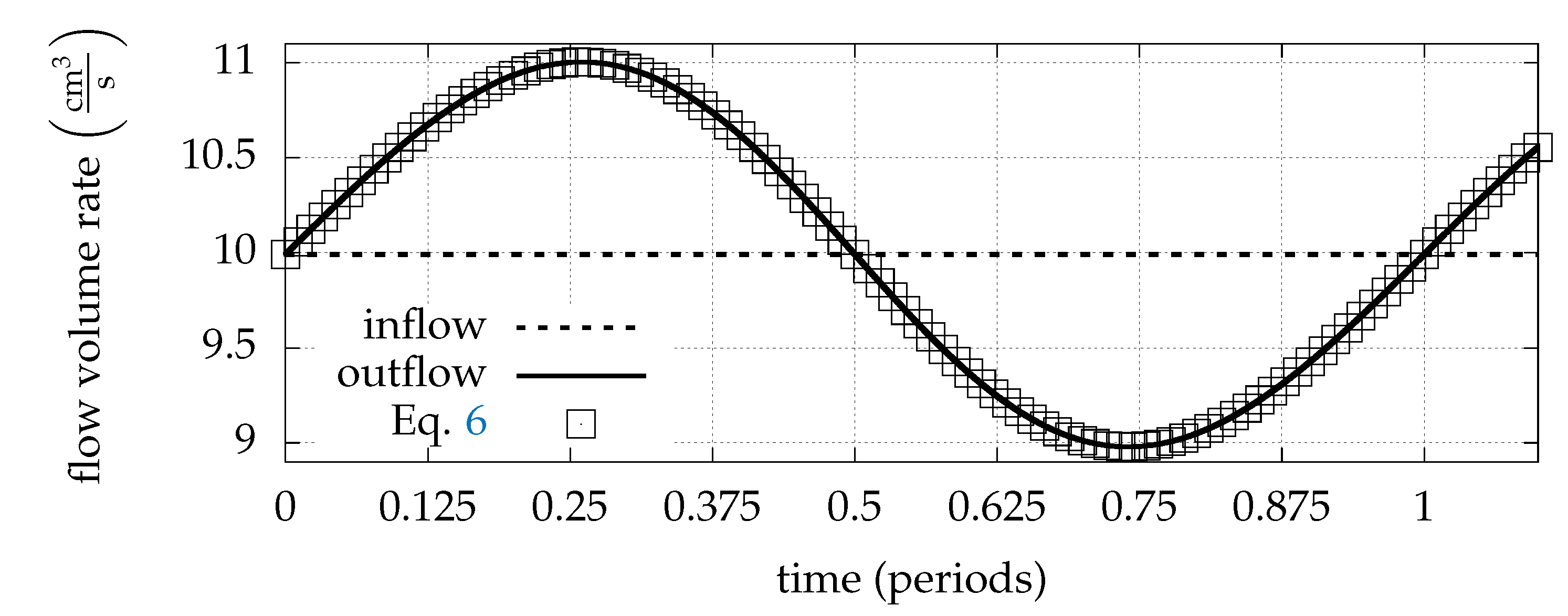
2.4. Boundary Conditions
2.5. Space and Time Domain Discretization
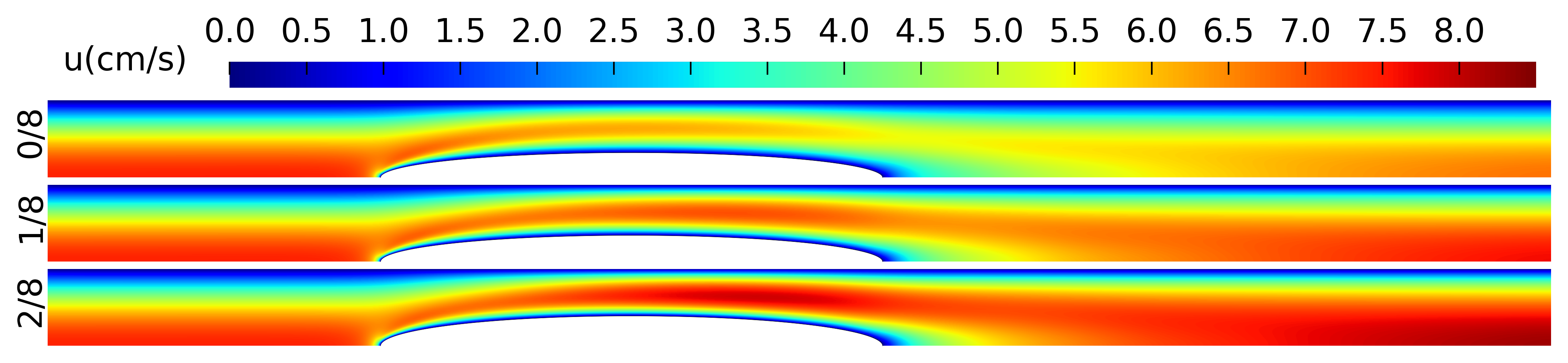
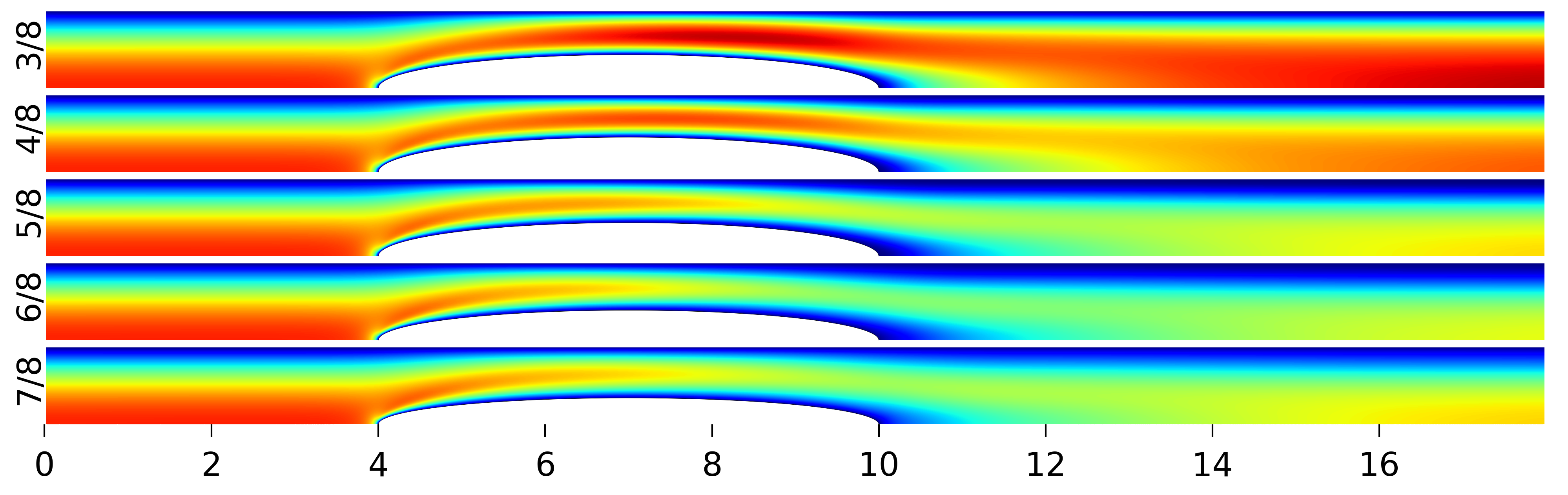
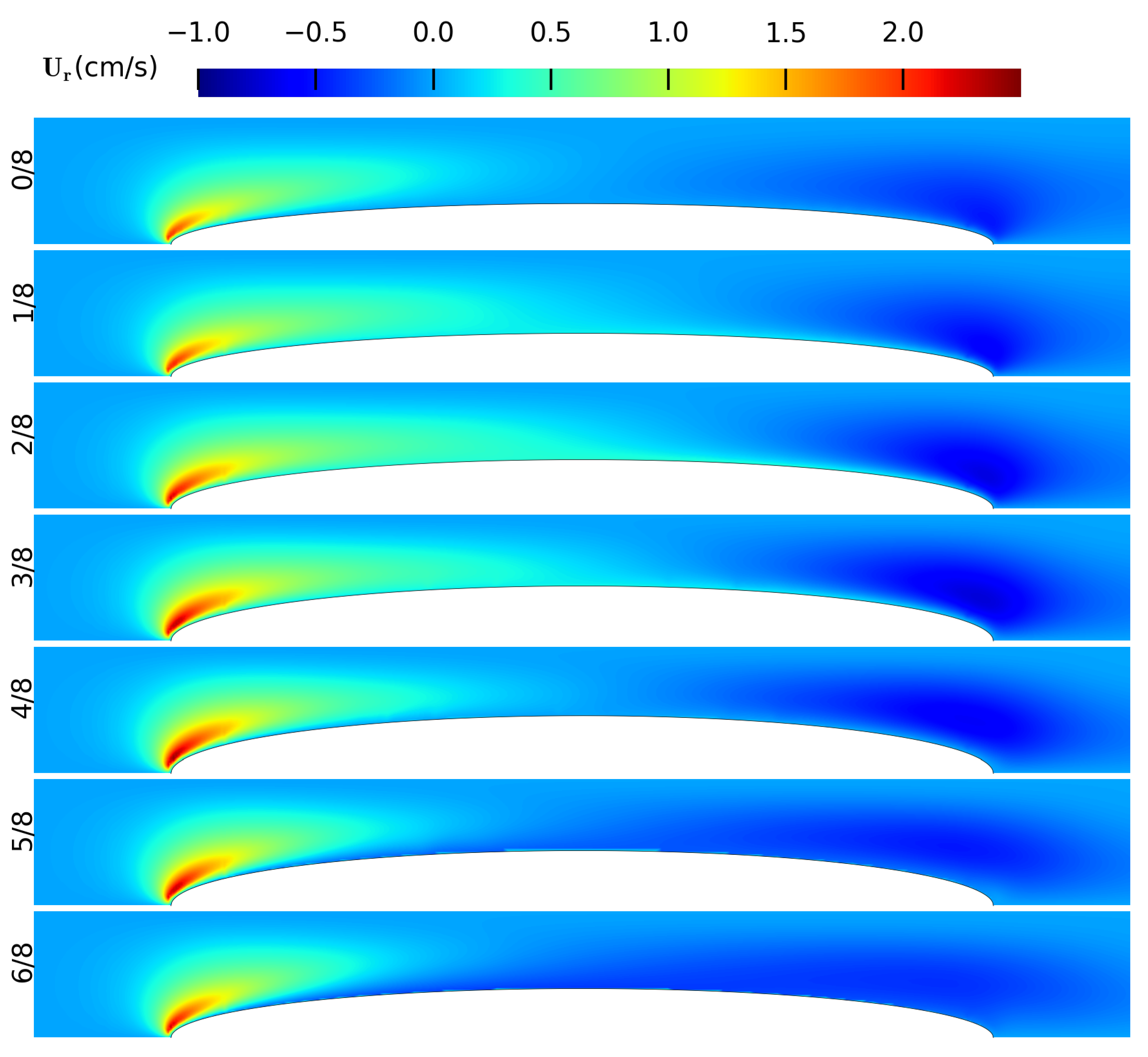
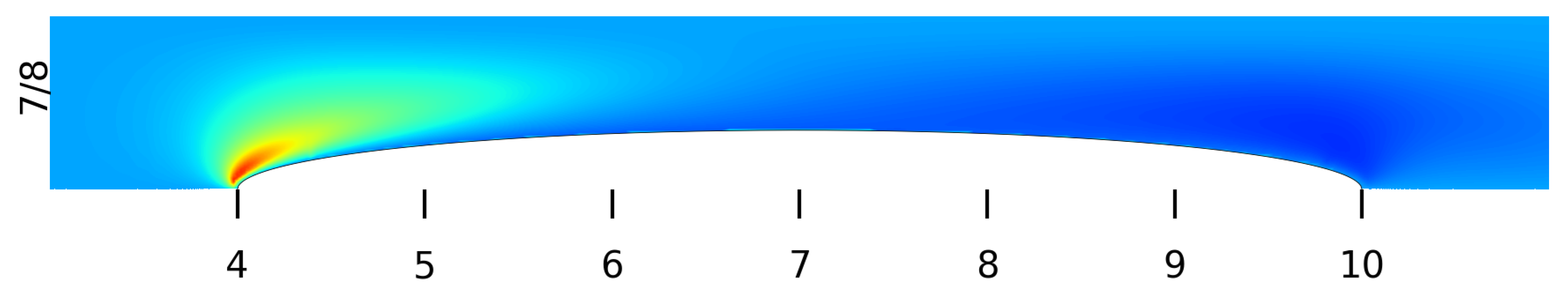
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IABP | Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump |
| PCI | Percutaneous Coronary Intervention |
| CPB | Cardiopulmonary Bypass |
| ECMO | Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation |
| Nomenclature | |
| oscillation amplitude of the equatorial radius of the prolate balloon | |
| metric tensor element, , | |
| contravariant base vector, | |
| J | Jacobian determinant |
| length of the aorta | |
| p | flow field pressure |
| inlet pressure | |
| outlet pressure | |
| inlet flow volume rate | |
| outlet flow volume rate | |
| r | radial coordinate |
| radius of the aorta | |
| central value in time of the equatorial radius of the prolate balloon | |
| t | time |
| T | period of balloon oscillation |
| u | longitudinal Cartesian velocity component |
| Cartesian velocity component, | |
| contravariant velocity component, | |
| radial velocity component | |
| angular velocity component | |
| flow field velocity vector | |
| balloon volume | |
| x | streamwise coordinate |
| Cartesian coordinate, | |
| longitudinal position of prolate balloon center of symmetry | |
| y | Cartesian cross-stream coordinate |
| z | Cartesian cross-stream coordinate |
| Womersley number | |
| length of ellipsoid major semi-axis | |
| length of ellipsoid median semi-axis | |
| length of ellipsoid minor semi-axis | |
| numerical time step | |
| numerical longitudinal step | |
| phase shift between outlet pressure and outlet volume rate | |
| angular coordinate | |
| dynamic viscosity of the fluid | |
| kinematic viscosity of the fluid | |
| curvilinear coordinate, | |
| partial derivative of with respect to | |
| density of the fluid | |
| angular frequency of balloon oscillation | |
Appendix A. The Flow Field around the Balloon for Qin = 0.01 L/s, rb0 = 0.32 cm and Ab = 0.02 cm
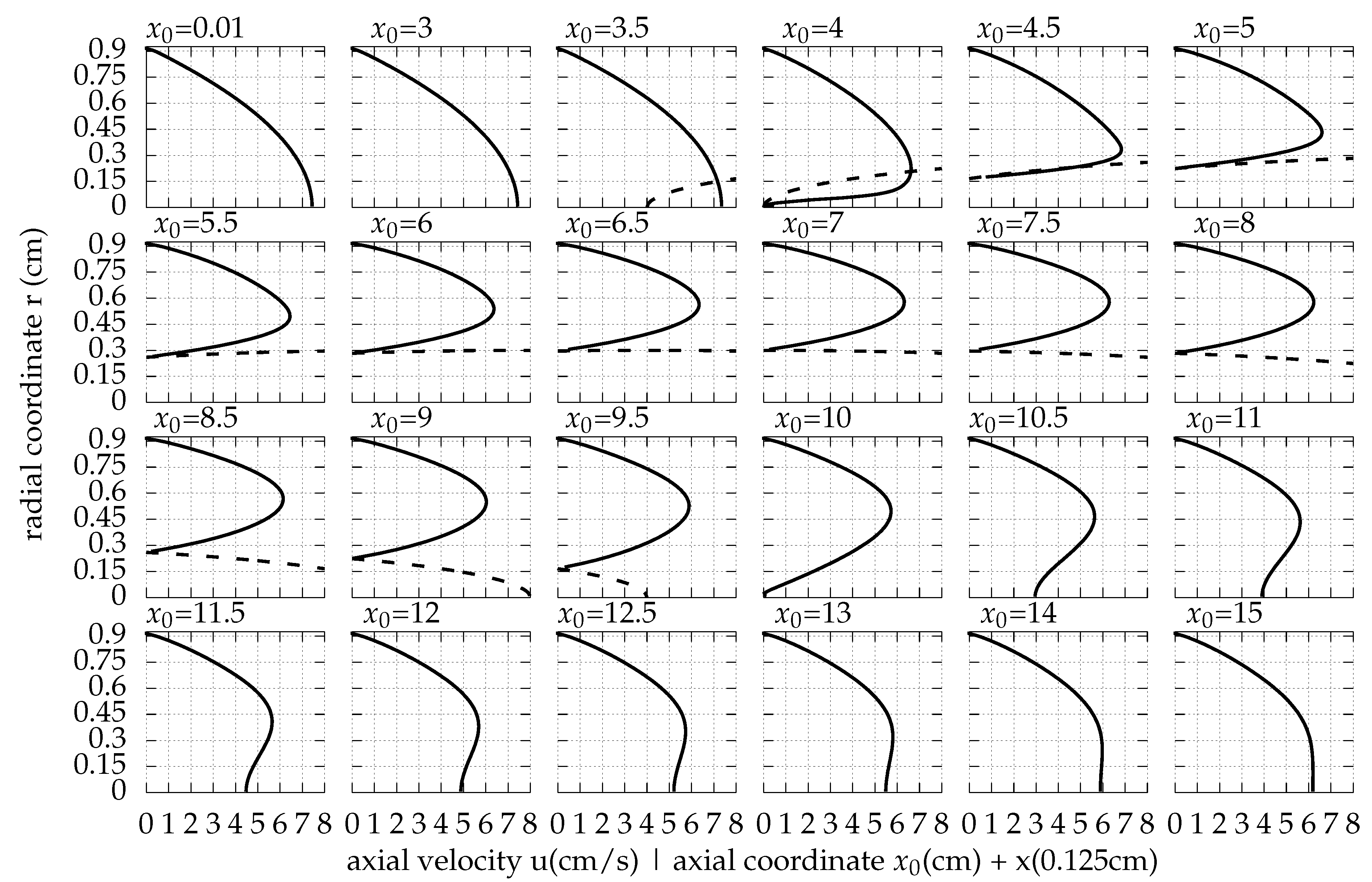
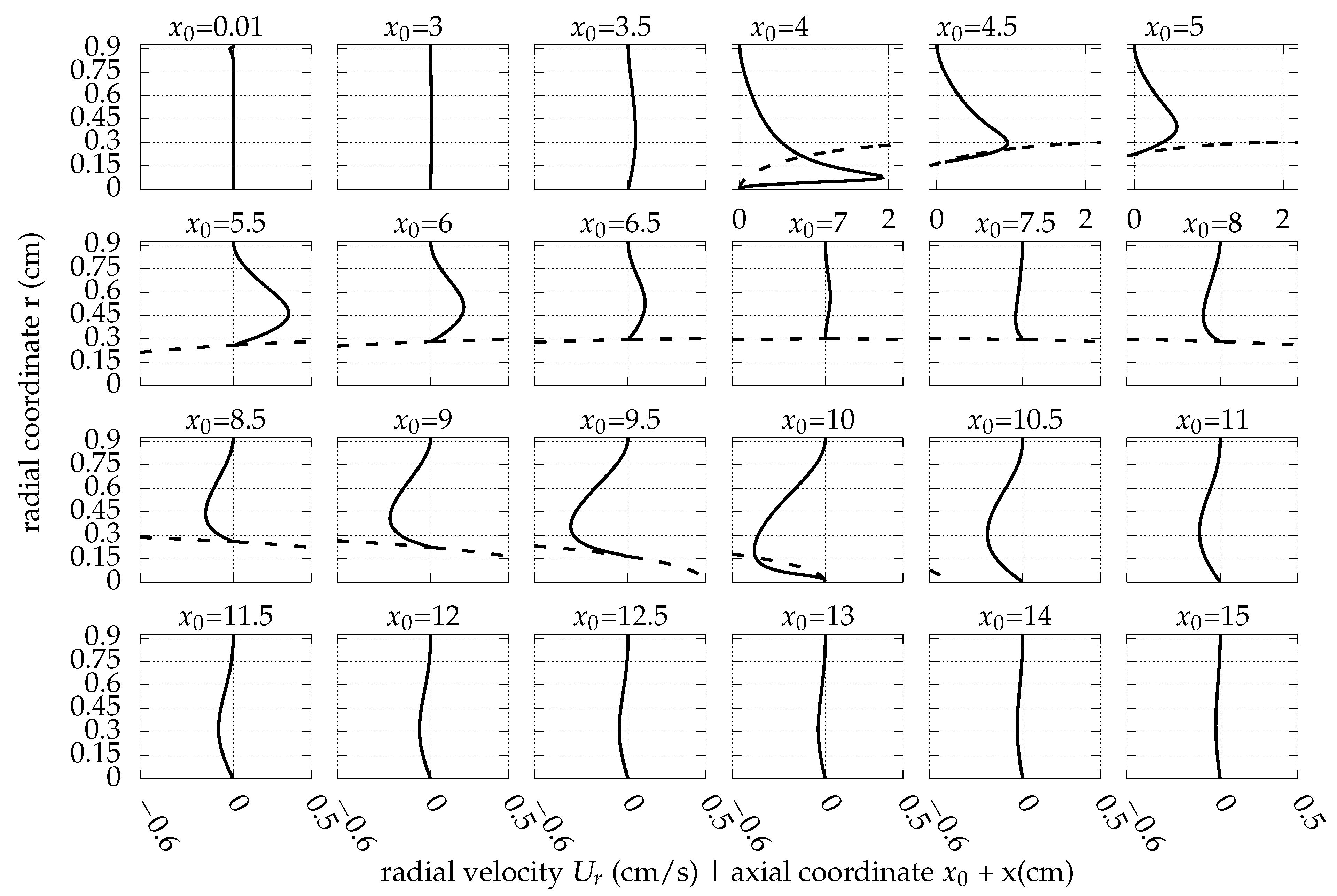
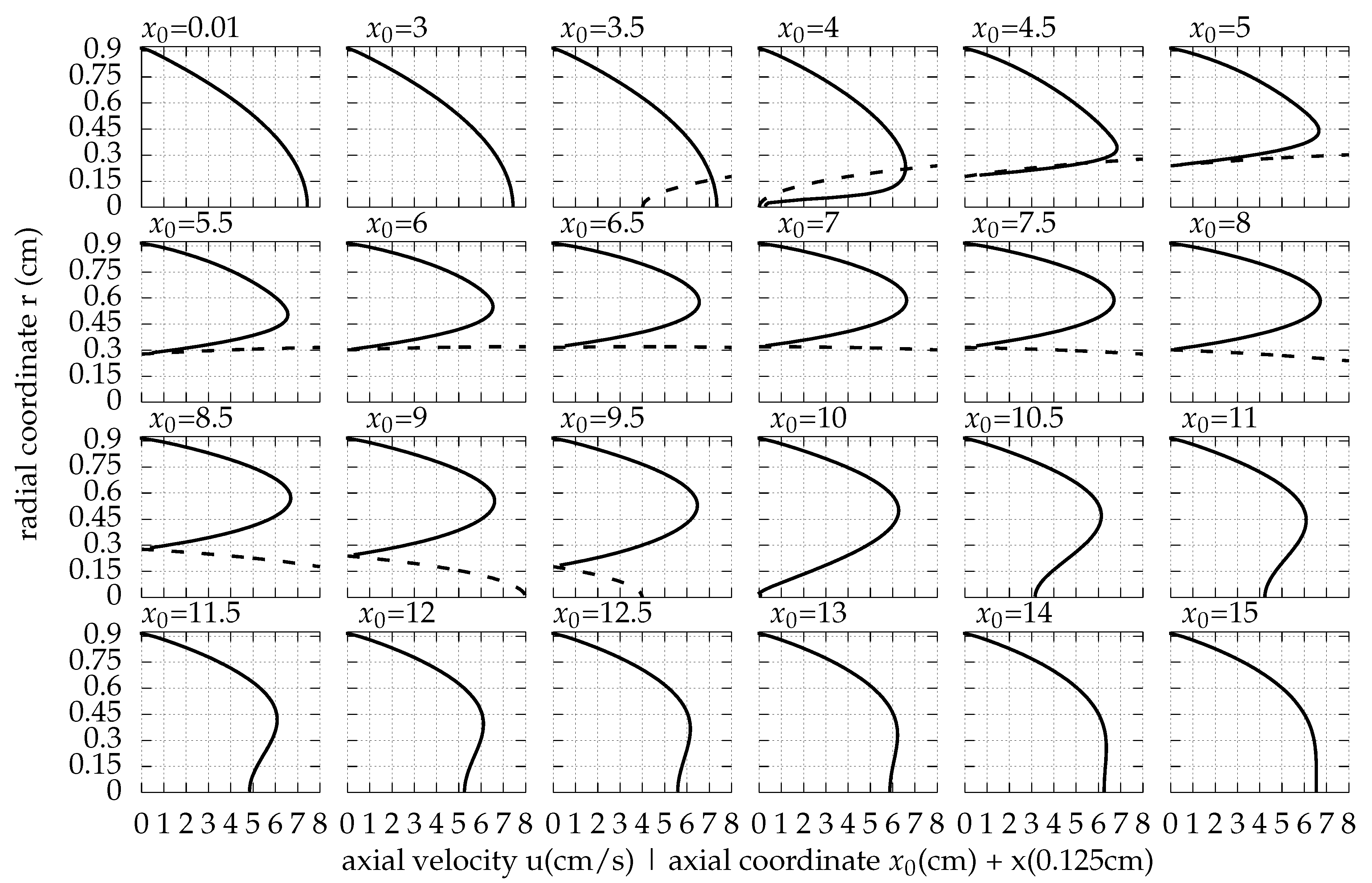
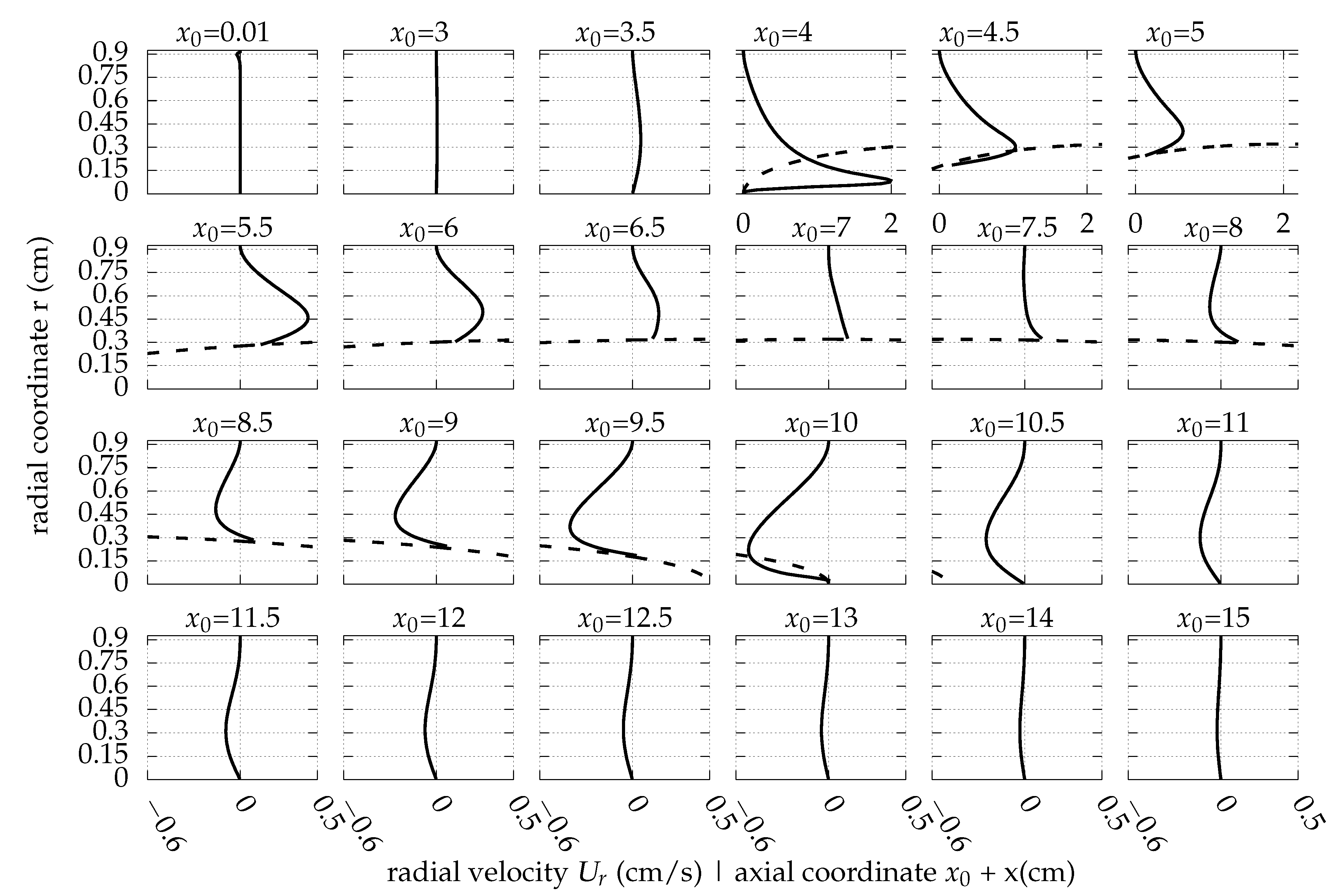
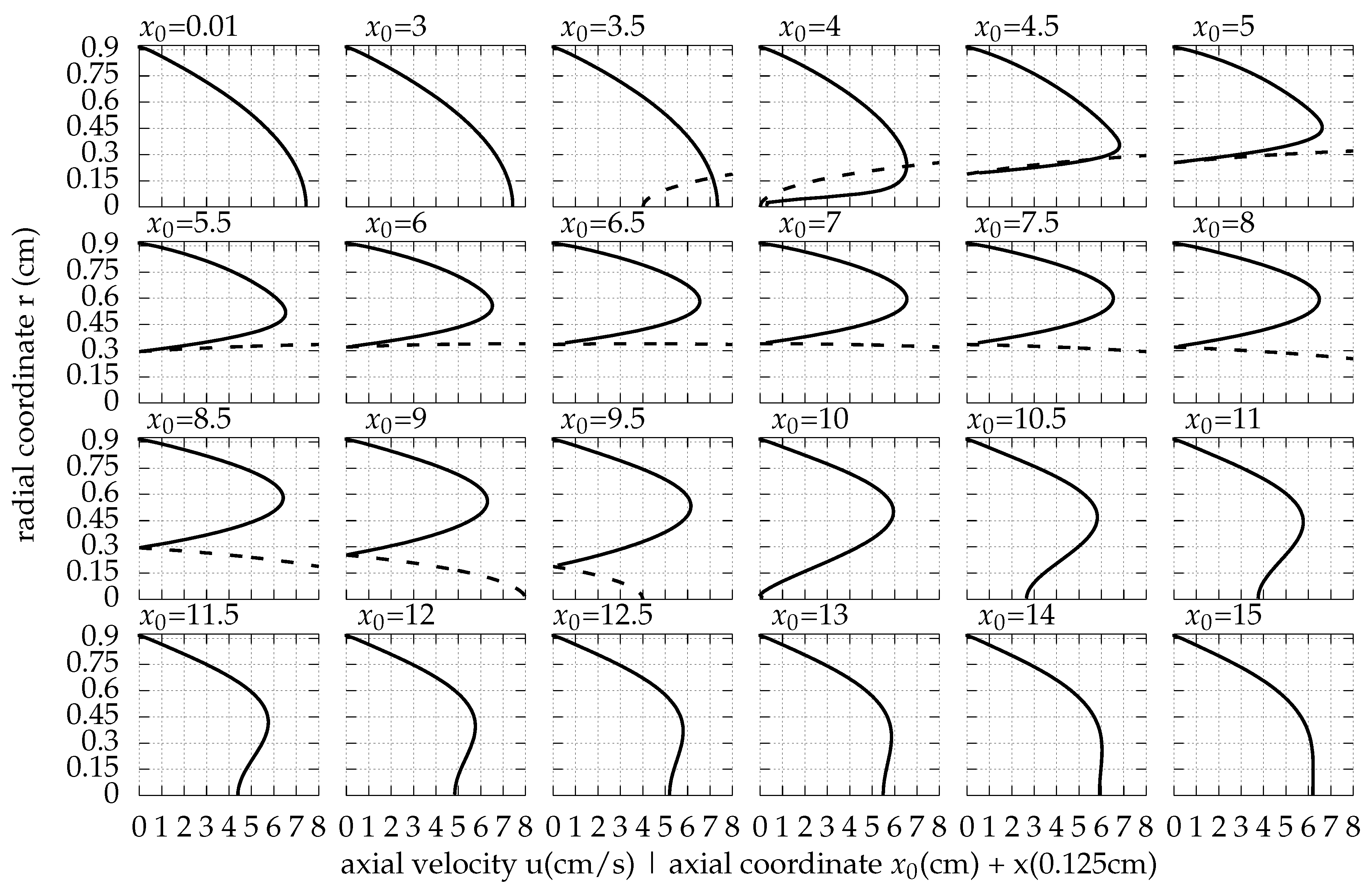
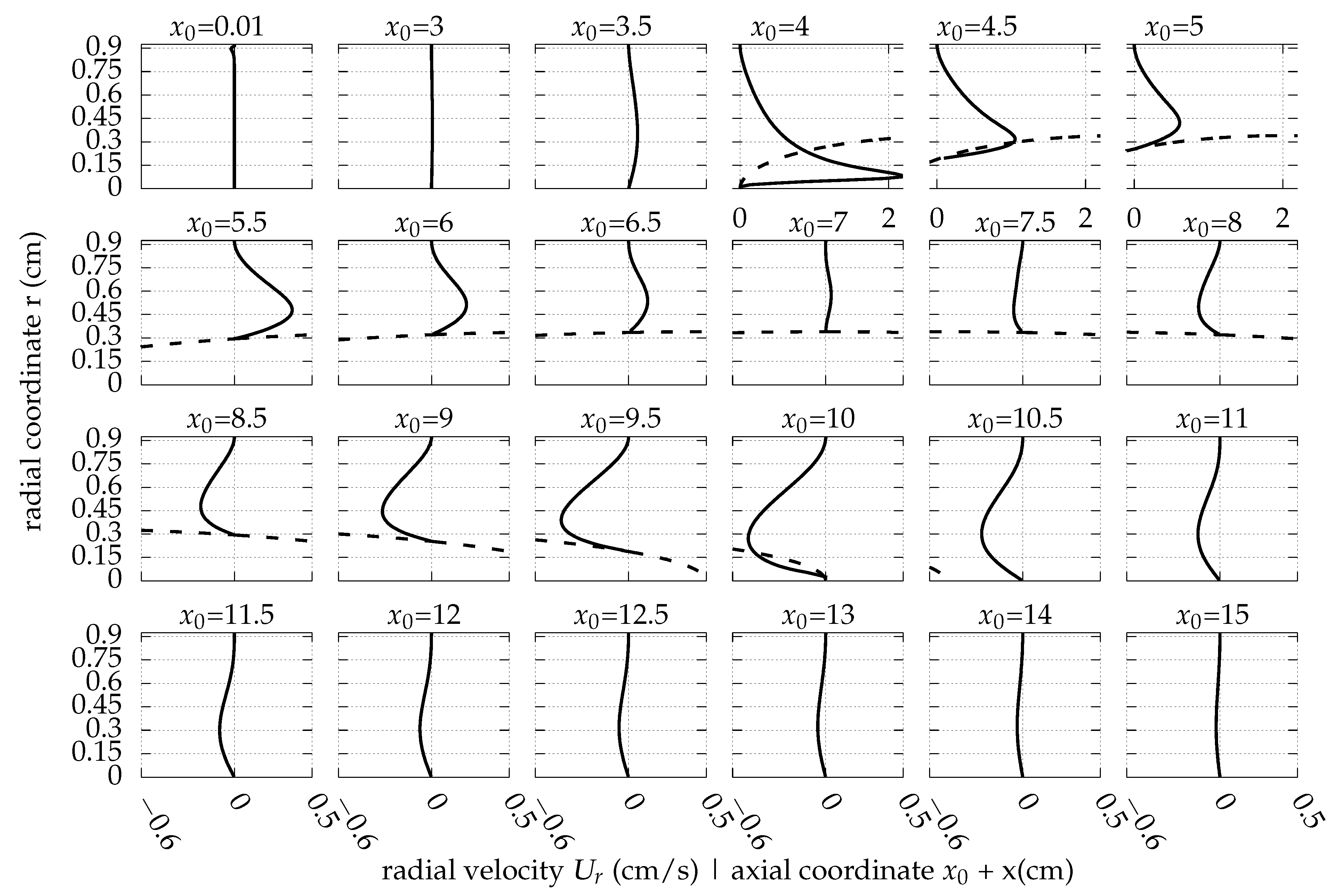
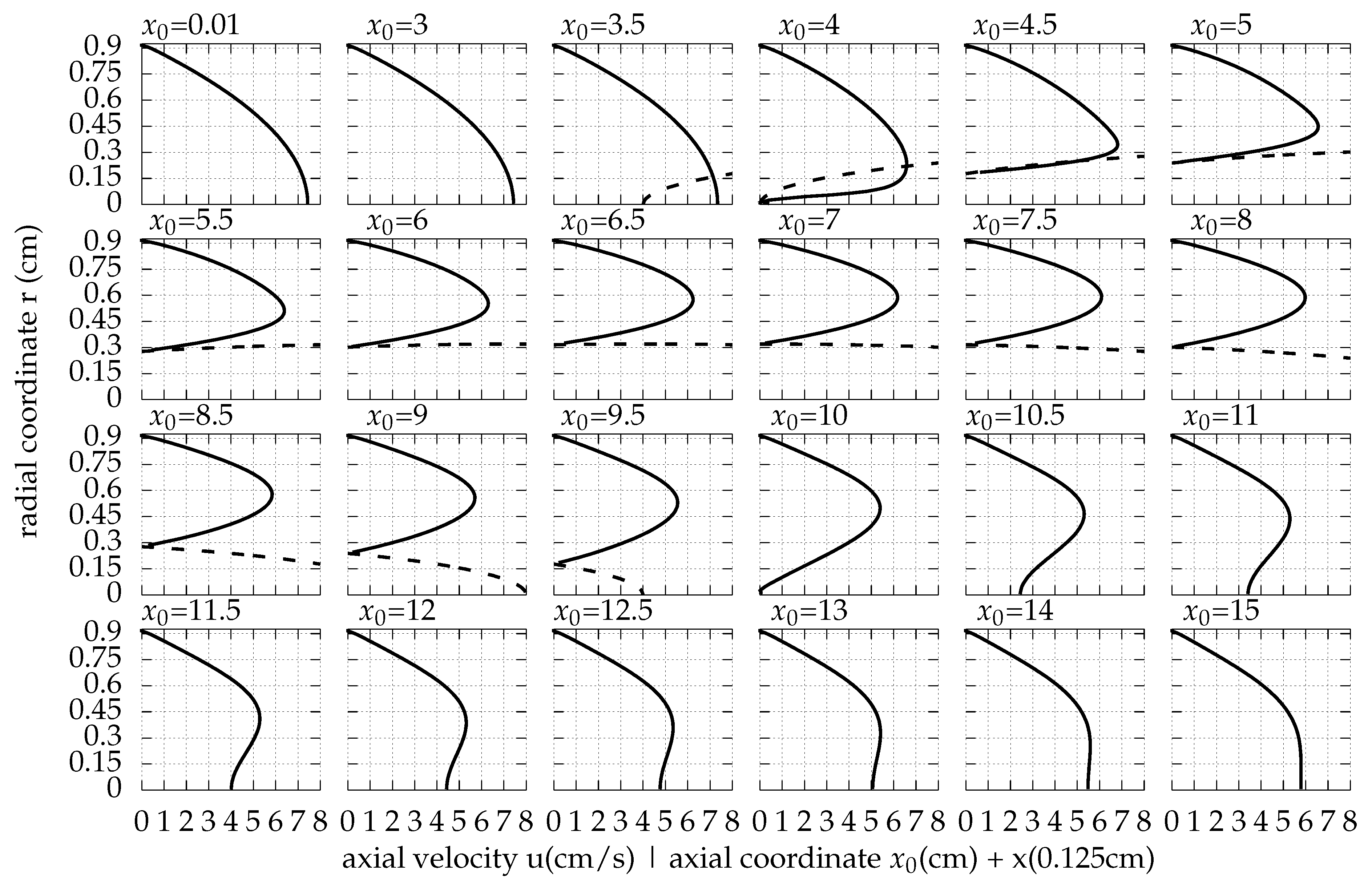

References
- McDonald, D.A. The relation of pulsatile pressure to flow in arteries. J. Physiol. 1955, 127, 533–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Womersley, J. Method for the calculation of velocity, rate of flow and viscous drag in arteries when the pressure gradient is known. J. Physiol. 1955, 127, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsangaris, S.; Stergiopulos, N. The inverse Womersley problem for pulsatile flow in a straight rigid tube. J. Biomech. 1988, 21, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parissis, H.; Graham, V.; Lampridis, S.; Lau, M.; Hooks, G.; Mhandu, P. IABP: History-evolution-pathophysiology-indications: What we need to know. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2016, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulopoulos, S.; Topaz, S.; Kollf, W. Diastolic balloon pumping (with carbon dioxide) in the aorta—A mechanical assistance to the failing circulation. Am. Heart J. 1962, 5, 154–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, T.G.; Mathioulakis, D.S.; Nanas, J.N.; Tsangaris, S.G.; Stamatelopoulos, S.F.; Moulopoulos, S.D. Arterial compliance is a main variable determining the effectiveness of intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation: Quantitative data from an in vitro study. Med. Eng. Phys. 2002, 24, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, T.; Mathioulakis, D.; Stamatelopoulos, K.; Giafalos, E.; Lekakis, J.; Nanas, J.; Stamatelopoulos, S.; Tsangaris, S. New aspects on the role of blood pressure and arterial stiffness in mechanical assistance by intra-aortic balloon pump: In-vitro data and their application in clinical practice. Artif. Organs 2004, 28, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yang, D.; Yu, H.; Wang, K.; Xie, Q. Development of Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump with Vascular Stent and Vitro Simulation Verification. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 9th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, Taiyuan, China, 25–27 May 2021; pp. 174–179. [Google Scholar]
- Bruti, G. Experimental and Computational Investigations for the Development of Intra Aortic Balloon Pump Therapy. Ph.D. Thesis, Brunel University, London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gramigna, V.; Caruso, M.V.; Rossi, M.; Serraino, G.; Renzulli, A.; Fragomeni, G. A numerical analysis of the aortic blood flow pattern during pulsed cardiopulmonary bypass. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 18, 1574–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, M.V.; Renzulli, A.; Fragomeni, G. Influence of IABP-Induced Abdominal Occlusions on Aortic Hemodynamics: A Patient-Specific Computational Evaluation. ASAIO J. 2017, 18, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, M.V.; Gramigna, V.; Fragomeni, G. A CFD investigation of intra-aortic balloon pump assist ratio effects on aortic hemodynamics. Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering. ASAIO J. 2019, 39, 224–233. [Google Scholar]
- De Lazzari, B.; Badagliacca, R.; Filomena, D.; Papa, S.; Vizza, C.D.; Capoccia, M.; De Lazzari, C. CARDIOSIM: The First Italian Software Platform for Simulation of the Cardiovascular System and Mechanical Circulatory and Ventilatory Support. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lazzari, B.; Badagliacca, R.; Filomena, D.; Papa, S.; Vizza, C.D.; Capoccia, M.; De Lazzari, C. Intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation timing: A new numerical model for programming and training in the clinical environment. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 194, 150537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, K.; Guan, Z.; Lin, X.; Feng, Y.; Feng, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chang, Y.; Ling, Y.; Wan, F. Numerical analysis of aortic hemodynamics under the support of venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and intra-aortic balloon pump. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 182, 105041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, K.; Gao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Ji, B.; Chang, Y. Hemodynamic Effect of Pulsatile on Blood Flow Distribution with VA ECMO: A Numerical Study. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formaggia, L.; Quarteroni, A.; Veneziani, A. (Eds.) Cardiovascular Mathematics: Modeling and Simulation of the Circulatory System; Springer: Milan, Italy, 2009; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ahuja, S.; Bugliarello, G. A note on the compressibility of blood. Biorheology 1971, 7, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Sotiropoulos, F. A numerical method for solving the 3D unsteady incompressible Navier—Stokes equations in curvilinear domains with complex immersed boundaries. J. Comput. Phys. 2007, 225, 1782–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderer, A.; Yang, X.; Angelidis, D.; Khosronejad, A.; Le, T.; Kang, S.; Gilmanov, A.; Ge, L.; Borazjani, I. Virtual Flow Simulator, Version 1.0; USDOE Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE): Golden, CO, USA, 2015.
- Moulinos, I.; Manopoulos, C.; Tsangaris, S. Computational Analysis of Active and Passive Flow Control for Backward Facing Step. Computation 2022, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borazjani, I.; Ge, L.; Sotiropoulos, F. Curvilinear immersed boundary method for simulating fluid structure interaction with complex 3D rigid bodies. J. Comput. Phys. 2008, 227, 7587–7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, T.; Trumbore, B. Fast, Minimum Storage Ray-Triangle Intersection. J. Graph. Tools 1997, 2, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.Q.; Habchi, S.D.; Przekwas, A.J. General strong conservation formulation of Navier-Stokes equations in nonorthogonal curvilinear coordinates. AIAA J. 1994, 32, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.K. Numerical Modeling of Turbulent Flows in Arbitrarily Complex Natural Streams. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Calderer, A.; Kang, S.; Sotiropoulos, F. Level set immersed boundary method for coupled simulation of air/water interaction with complex floating structures. J. Comput. Phys. 2014, 277, 201–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorin, A.J. Numerical solutions of the Navier-Stokes equations. Math. Comput. 1968, 22, 745–762. [Google Scholar]
- Moré, J.J.; Sorensen, D.C.; Hillstrom, K.E.; Garbow, B.S. The MINPACK Project. In Sources and Development of Mathematical Software; Cowell, W.J., Ed.; Prentice-Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1984; pp. 88–111. [Google Scholar]
- Saad, Y.; Schultz, M.H. GMRES: A Generalized Minimal Residual Algorithm for Solving Nonsymmetric Linear Systems. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput. 1986, 7, 856–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruge, J.W.; Stüben, K. Algebraic Multigrid. In Multigrid Methods; McCormick, S., Ed.; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1987; pp. 73–130. [Google Scholar]
- Cifu, D.X. (Ed.) Braddom’s Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 6th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, T.K. Unsteady flows with moving boundaries: Pulsating blood flows and earthquake hydrodynamics. In Advances in Engineering Mechanics—Reflections and Outlooks; World Scientific: Singapore, 2005; pp. 446–473. [Google Scholar]
- Tsangaris, S. Oscillatory flow of an incompressible, viscous fluid in a straight annular pipe. J. Méc.Théor. Appl. 1984, 3, 467–478. [Google Scholar]
- Zamir, M. The Physics of Coronary Blood Flow; AIP Press/Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nichols, W.; O’Rourke, M.; Elelman, E.; Vlachopoulos, C. (Eds.) McDonald’s Blood Flow in Arteries: Theoretical, Experimental and Clinical Principles, 7th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Uchida, S. The pulsating viscous flow superposed on the steady laminar motion of incompressible fluid in a circular pipe. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 1956, 3, 403–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhof, N.; Stergiopulos, N.; Noble, M.; Westerhof, B. Snapshots of Hemodynamics: An Aid for Clinical Research and Graduate Education; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, P.D. The pulsating viscous flow superposed on the steady laminar motion of incompressible fluid in a tube of elliptic section. Proc. Natl. Inst. Sci. India Part A 1960, 26, 282–297. [Google Scholar]
- Womersley, J.R. An Elastic Tube Theory of Pulse Transmission and Oscillatory Flow in Mammalian Arteries; TR 56-614; WADC: Fairborn, OH, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar]

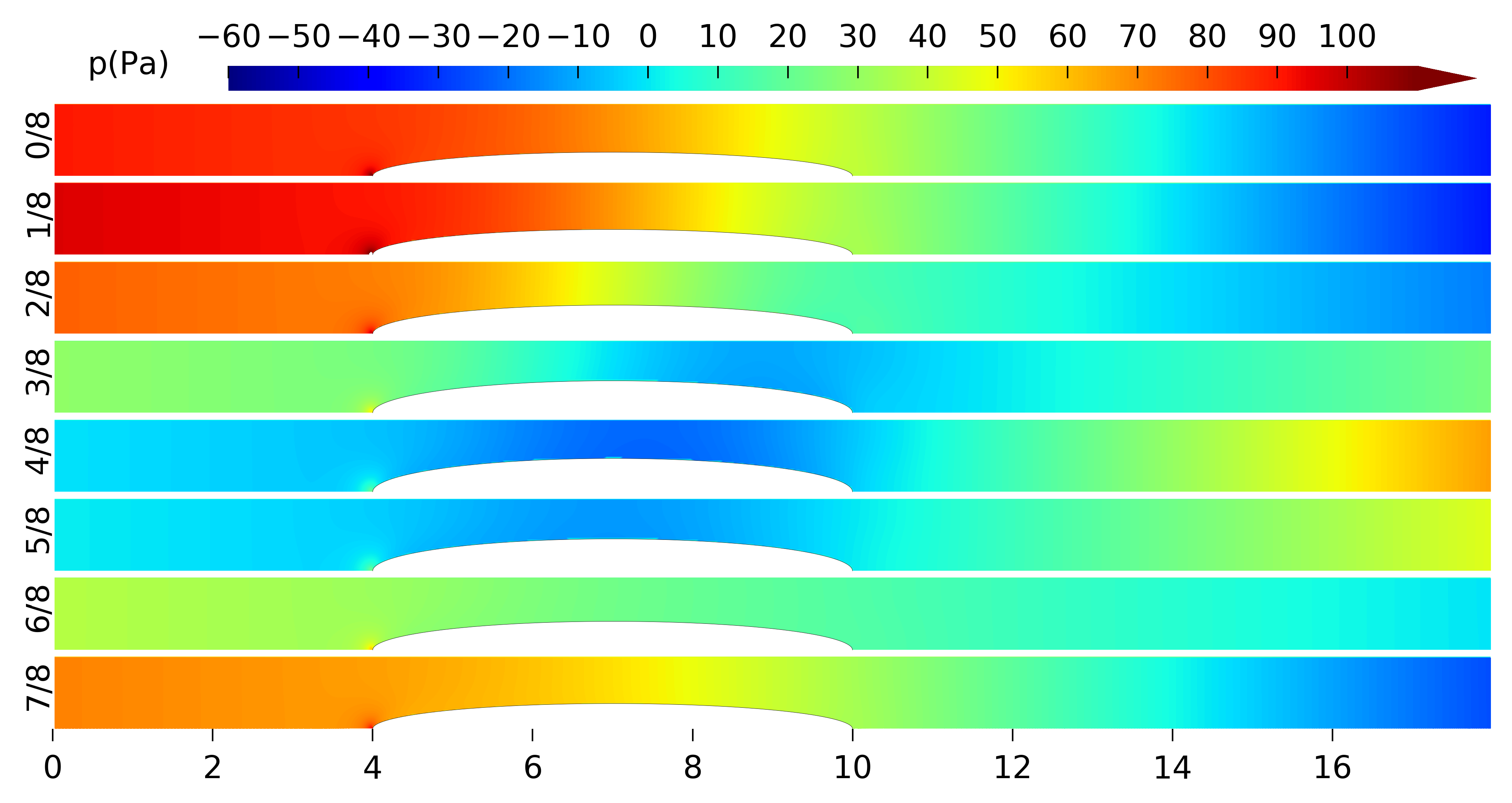
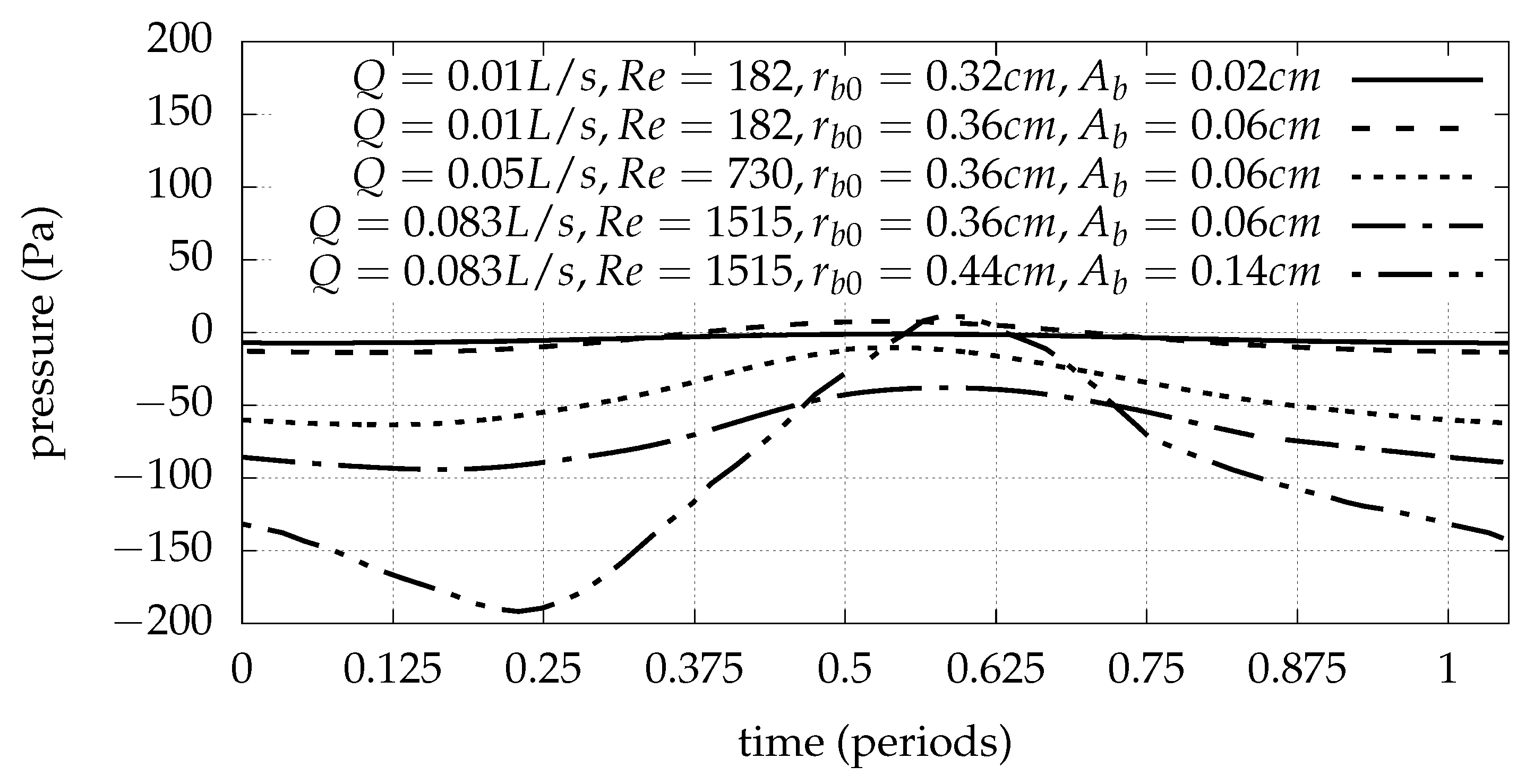
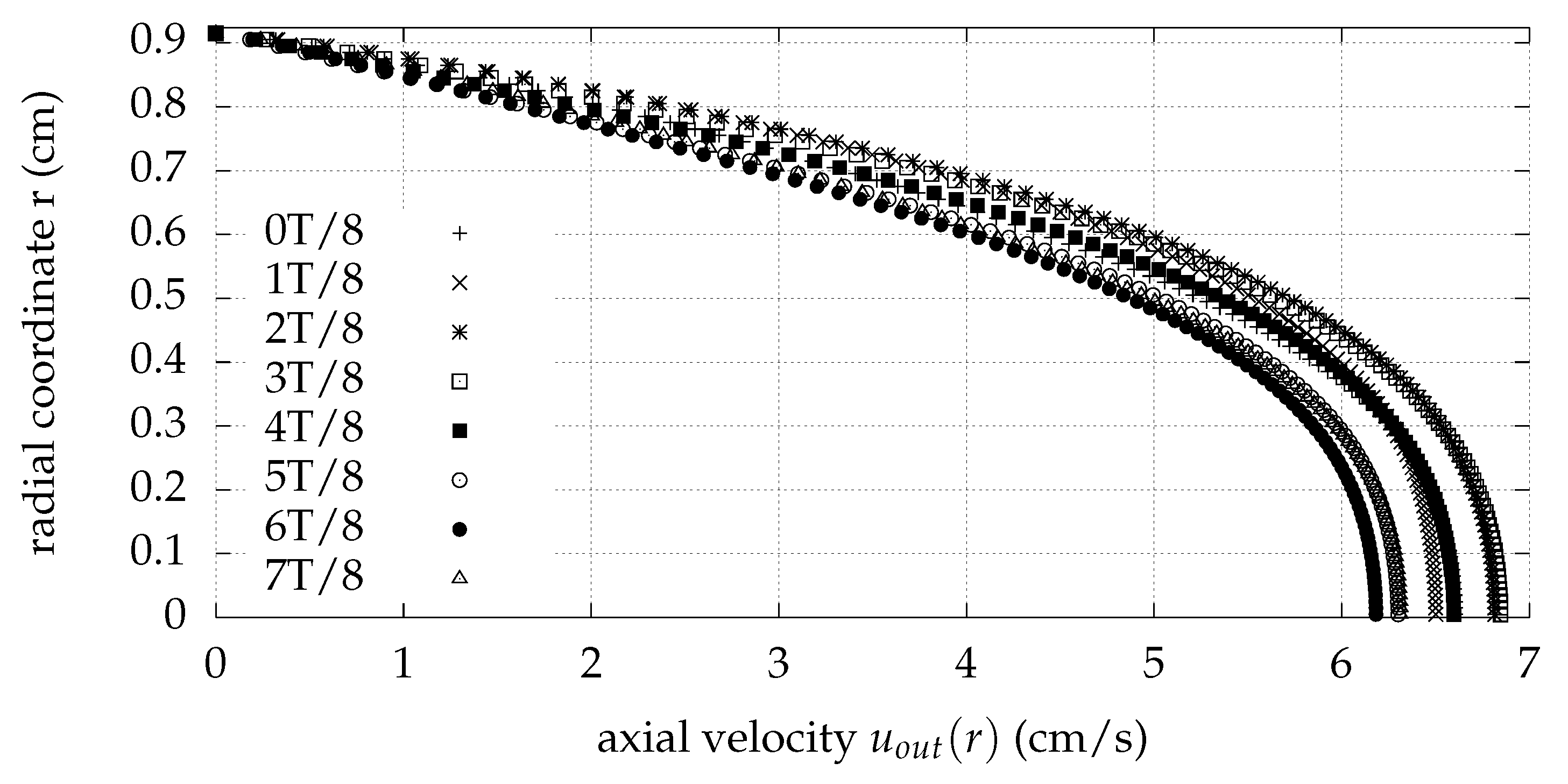
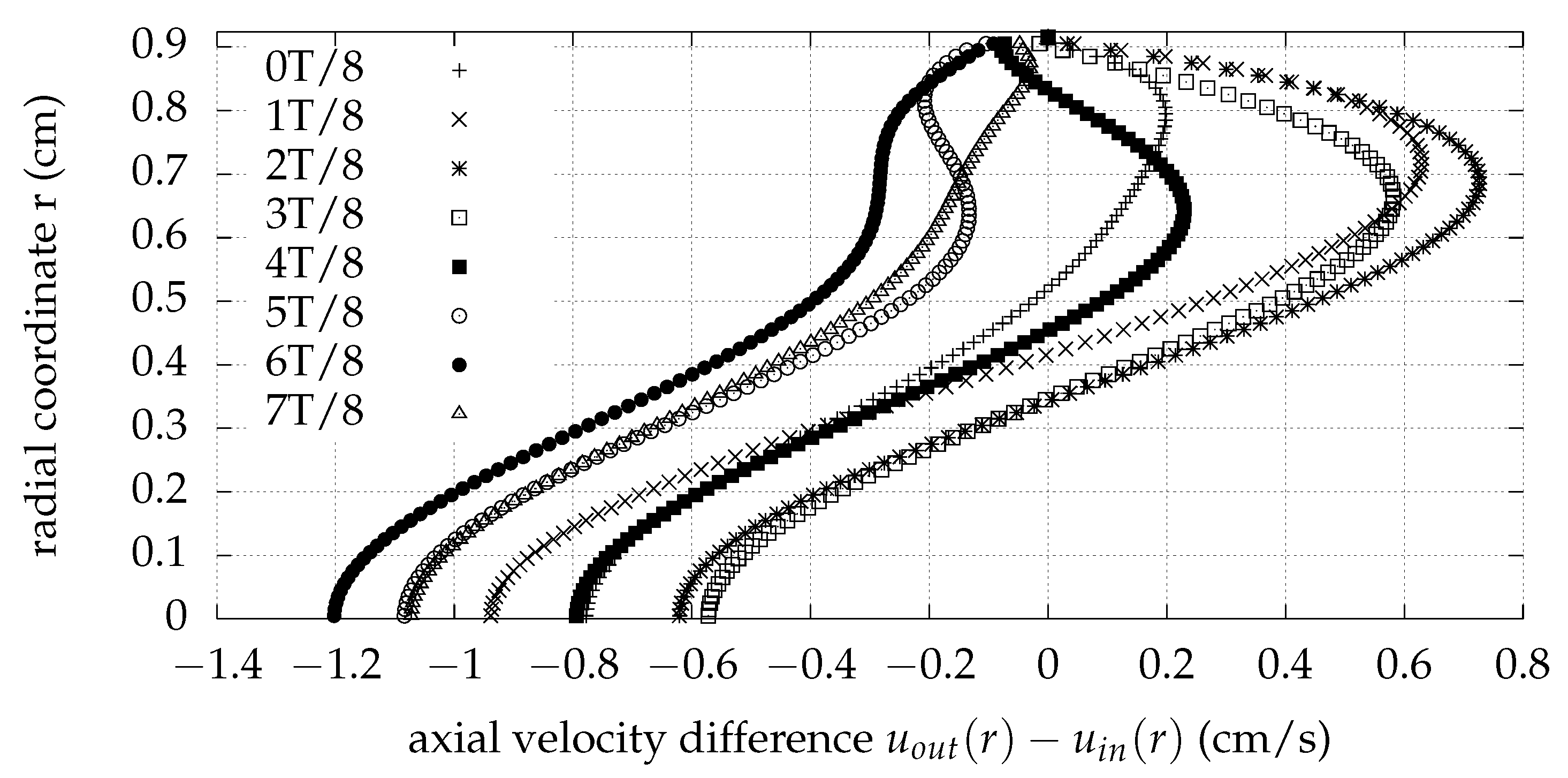
| Quantity | Value (cm) |
|---|---|
| 0.925 | |
| 18 (for L/s), 40 (for L/s) | |
| 3 | |
| 0.32, 0.36, 0.44 | |
| 0.02, 0.06, 0.14 | |
| 7 |
| Quantity | Value |
|---|---|
| dynamic viscosity | 0.04 g/(cm·s) |
| density | 1.06 g/cm3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moulinos, I.; Manopoulos, C.; Tsangaris, S. Modification of Poiseuille Flow to a Pulsating Flow Using a Periodically Expanding-Contracting Balloon. Fluids 2023, 8, 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids8040129
Moulinos I, Manopoulos C, Tsangaris S. Modification of Poiseuille Flow to a Pulsating Flow Using a Periodically Expanding-Contracting Balloon. Fluids. 2023; 8(4):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids8040129
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoulinos, Iosif, Christos Manopoulos, and Sokrates Tsangaris. 2023. "Modification of Poiseuille Flow to a Pulsating Flow Using a Periodically Expanding-Contracting Balloon" Fluids 8, no. 4: 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids8040129
APA StyleMoulinos, I., Manopoulos, C., & Tsangaris, S. (2023). Modification of Poiseuille Flow to a Pulsating Flow Using a Periodically Expanding-Contracting Balloon. Fluids, 8(4), 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids8040129








