Revisiting Mean Flow and Mixing Properties of Negatively Round Buoyant Jets Using the Escaping Mass Approach (EMA)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Variation of Basic Parameters
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abraham, G. Jet diffusion in stagnant ambient fluid 1963 (Vol. Tech. Rep. 29). Delft. Available online: https://resolver.tudelft.nl/uuid:6ad300a4-94d9-44f7-9b1a-787d010d2844 (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Fischer, B.H.; List, J.E.; Koh, R.C.; Imberger, J.; Brooks, N.H. Mixing in Inland and Coastal Waters; Academic Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, S.R.; Briggs, G.A.; Hosker, R.P. Handbook on Atmospheric Diffusion; U.S. Department of Energy: Washington, DC, USA, 1982. [CrossRef]
- Pasquill, F.; Smith, F.B. Atmospheric Diffusion, 3rd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Chichester, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanicolaou, P.N.; List, J.E. Investigations of round vertical turbulent buoyant jets. J. Fluid Mech. 1988, 195, 341–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Law, A.W.-K. Second-order integral model for a round turbulent buoyant jet. J. Fluid Mech. 2002, 459, 397–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirka, G.H. Integral model for turbulent buoyant jets in unbounded stratified flows. Part I: Single Round Jet. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2004, 4, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.-W.; Chu, V. Turbulent Jets and Plumes. A Lagrangian Approach; Springer US: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yannopoulos, P.C. An improved integral model for plane and round turbulent buoyant jets. J. Fluid Mech. 2006, 547, 267–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britter, R.E. Atmospheric dispersion of dense gases. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1989, 21, 317–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohba, R.; Kouchi, A.; Vieillard, V.; Nedelka, D. Validation of heavy and light gas dispersion models for the safetyanalysis of LNG tank. J. Loss Prev. Process. Ind. 2004, 17, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellasio, R.; Bianconi, R. Online simulation system for industrial accidents. Environ. Model. Softw. 2005, 20, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wei, J. Modelling and simulation of continuous dense gas leakage for emergency response application. J. Loss Prev. Process. Ind. 2017, 48, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklavounos, S.; Rigas, F. Validation of turbulence models in heavy gas dispersion over obstacles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 108, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavelli, F.; Bullister, E.; Kytomaa, H. Application of CFD (Fluent) to LNG spills into geometrically complex environments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 159, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, Y.; Stathopoulos, T. CFD simulations of near-field pollutant dispersion with different plume buoyancies. Build. Environ. 2018, 131, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezher, T.; Fath, H.; Abbas, Z.; Khaled, A. Techno-economic assessment and environmental impacts of desalination technologies. Desalination 2011, 266, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.L.; Paytan, A.; Rahav, E.; Levy, O.; Silverman, J.; Barzel, O.; Bar-Zeev, E. Impact of brine and antiscalants on reef-building corals in the Gulf of Aqaba—Potential effects from desalination plants. Water Res. 2018, 144, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, K.L.; Frank, H.; Paytan, A.; Bar-Zeev, E. Impacts of seawater desalination on coastal environment. In Sustainable Desalination Handbook. Plant Selection, Design and Implementation; Gude, V.G., Ed.; Butterworth—Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2018; pp. 437–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattemann, S.; Höpner, T. Environmental impact and impact assessment. Desalination 2008, 220, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drami, D.; Yacobi, Y.Z.; Stambler, N.; Kress, N. Seawater quality and microbial communities at a desalination plant marine outfall. A field study at the Israeli Mediterranean coast. Water Res. 2011, 45, 5449–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Chang-Chien, G.-P.; Chiang, P.-C.; Chen, W.-H.; Lin, Y.-C. Potential impacts of discharges from seawater reverse osmosis on Taiwan marine environment. Desalination 2013, 322, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, H.; Rahav, E.; Bar-Zeev, E. Short-term effects of SWRO desalination brine on benthic heterotrophic microbial communities. Desalination 2017, 417, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambridge, M.L.; Zavala-Perez, A.; Cawthray, G.R.; Mondon, J.; Kendrick, G.A. Effects of high salinity from desalination brine on growth, photosynthesis, water relations and osmolyte concentrations of seagrass Posidonia australis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambridge, M.L.; Zavala-Perez, A.; Cawthray, G.R.; Statton, J.; Mondon, J.; Gary, K.A. Effects of desalination brine and seawater with the same elevated salinity on growth, physiology and seedling development of the seagrass Posidonia australis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 140, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.A.; Johnston, E.L.; Knott, N.A. Impacts of desalination plant discharges on the marine environment. A critical review of published studies. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5117–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missimer, T.M.; Maliva, R.G. Environmental issues in seawater reverse osmosis desalination: Intakes and outfalls. Desalination 2018, 434, 198–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, H.; Fussmann, K.E.; Rahav, E.; Zeev, E.B. Chronic effects of brine discharge form large-scale seawater reverse osmosis. Water Res. 2019, 151, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, E.; Qadir, M.; van Vliet, M.T.H.; Smakhtin, V.; Kang, S.-M. The state of desalination and brine production. A global outlook. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 1343–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voutchkov, N. Overview of seawater concentrate disposal alternatives. Desalination 2011, 273, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, I.; Adams, E.E. Pre-dilution of desalination reject brine: Impact on outfall dilution in. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2019, 24, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J. Jets and plumes with negative or reversing buoyancy. J. Fluid Mech. 1966, 26, 779–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, G. Jets with Negative Buoyancy in Homogeneous Fluid. J. Hydraul. Res. 1967, 5, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomfield, L.J.; Kerr, R.C. A theoretical model of a turbulent fountain. J. Fluid Mech. 2000, 424, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, E.; Tait, S.; Carazzo, G. Turbulent entrainment in jets with arbitrary buoyancy. J. Fluid Mech. 2005, 526, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddour, R.E.; Zhang, H. Density Effect on Round Turbulent Hypersaline Fountain. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2009, 135, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Baddour, R.E. A review of sources, effects, disposal methods, and regulations of brine into marine environments. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2014, 87, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeitoun, M.A.; Mcllhenny, W.F.; Reid, R.O.; Wong, C.-M.; Savage, W.F.; Rinne, W.W.; Gransee, C.L. Conceptual Designs of Outfall Systems for Desalting Plants; Report No. 550; United States Department of the Interior: Washington, DC, USA, 1970.
- Pincince, A.B.; List, E.J. Disposal of brine into an estuary. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1973, 45, 2335–2344. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, P.J.; Toms, G. Inclined dense jets in flowing current. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1987, 113, 323–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, P.J.; Ferrier, A.; Daviero, G. Mixing in Inclined Dense Jets. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1997, 123, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane-Serff, G.F.; Linden, P.F.; Hillel, M. Forced, angled plumes. J. Hazard. Mater. 1993, 33, 75–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, W.R. Experiments on negatively buoyant jets, with and without cross-flow. In Recent Research Advances in the Fluid Mechanics of Turbulent Jets and Plumes; NATO Science Series; Davies, P.A., Valente Neves, M.J., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 131–145. [Google Scholar]
- Bloomfield, L.J.; Kerr, R.C. Inclined turbulent fountains. J. Fluid Mech. 2002, 451, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipollina, A.; Brucato, A.; Grisafi, F.; Nicosia, S. Bench-Scale Investigation of Inclined Dense Jets. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2005, 131, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.; Querzoli, G. Sea discharge of brine from desalination plants a laboratory model of negatively buoyant jets. In Proceedings of the MWWD 2004-3rd International Conference on Marine Waste Water Discharges and Marine, Catania, Italy, 27 September–2 October 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, S.; Querzoli, G. Mixing and re-entrainment in a negatively buoyant jet. J. Hydraul. Res. 2010, 48, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemlioglu, S.; Roberts, P.J. Experiments on Dense Jets Using Three-Dimensional Laser-Induced Fluorescence (3DLIF). In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Marine Wastewater Disposal and Marine Environment (MWWD), Antalya, Turkey, 6–10 November 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kikkert, G.A.; Davidson, M.J.; Nokes, R.I. Inclined Negatively Buoyant Discharges. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2007, 133, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Law, A.W.-K. Mixing and boundary interactions of 30° and 45° inclined dense jets. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2010, 10, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.C.-K.; Lee, J.H.-W. Mixing of inclined dense jets in stationary ambient. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2012, 6, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Law, A.W.-K.; Lee, J.H.-W. Mixing of 30° and 45° Inclined Dense Jets in Shallow Coastal Waters. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2014, 140, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantis, I.G.; Christodoulou, G.C.; Papanicolaou, P.N. Inclined negatively buoyant jets 1: Geometrical characteristics. J. Hydraul. Res. 2011, 49, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantis, I.G.; Christodoulou, G.C.; Papanicolaou, P.N. Inclined negatively buoyant jets 2: Concentration measurements. J. Hydraul. Res. 2011, 49, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforakis, I.K.; Stamou, A.I.; Christodoulou, G.C. A modified integral model for negatively buoyant jets in a stationary ambient. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2015, 15, 939–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantis, I.G.; Tsatsara, E.I. Trajectory characteristics of inclined turbulent dense jets. Environ. Process. 2018, 5, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantis, I.G.; Tsatsara, E.I. Mixing characteristics of inclined turbulent dense jets. Environ. Process. 2019, 6, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, C.J.; Davidson, M.J.; Nokes, R.I. Predicting the near-field mixing of desalination discharges in a stationary environment. Desalination 2013, 309, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, C.J.; Davidson, M.J.; Nokes, R.I. Removing the boundary influence on negatively buoyant jets. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2013, 13, 625–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abessi, O.; Roberts, P.J. Effect of nozzle orientation on dense jets in stagnant environments. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2015, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, A.T.; Davidson, M.J.; Nokes, R.I. Modified reduced buoyancy flux model for desalination discharges. Desalination 2016, 378, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, A.T.; Davidson, M.J.; Nokes, R.I. Velocity measurements in inclined negatively buoyant jets. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2016, 16, 503–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, I.R.; Bell, R.G.; Wilkinson, D.L. Ocean Disposal of Wastewater; Advanced series on ocean engineering; World Scientific: Singapore, 1993; Volume 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, B.R.; Taylor, G.I.; Turner, J.S. Turbulent gravitational convection from maintained and instantaneous sources. Proc. R. Soc. A 1956, 234, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanicolaou, P.N.; Papakonstantis, I.G.; Christodoulou, G.C. On the entrainment coefficient in negatively buoyant jets. J. Fluid Mech. 2008, 614, 447–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Cheung, V. Generalized Lagrangian Model for Buoyant Jets in Current. J. Environ. Eng. 1990, 116, 1085–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirka, G.H. Improved Discharge Configurations for Brine Effluents from Desalination Plants. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2008, 134, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, C.J. Near Field Mixing of Negatively Buoyant Jets. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Civil and Natural Resources Engineering, University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Crowe, A.T. Inclined Negatively Buoyant Jets and Boundary Interaction. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Civil and Natural Resources Engineering, University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Besalduch, L.A.; Badas, M.G.; Ferrari, S.; Querzoli, G. Experimental studies for the characterization of the mixing processes in negative buoyant jets. EPJ Web Conf. 2013, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besalduch, L.A.; Badas, M.G.; Ferrari, S.; Querzoli, G. On the near field behavior of inclined negatively buoyant jets. EPJ Web Conf. 2014, 67, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Law, A.W.-K.; Lai, A.C. Turbulence characteristics of 45° inclined dense jets. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2019, 19, 27–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakanth, A. Quantifying Boundary Interaction of Negatively Buoyant Jets. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Civil and Natural Resources Engineering, University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yannopoulos, P.C.; Bloutsos, A.A. Escaping mass approach for inclined plane and round buoyant jets. J. Fluid Mech. 2012, 695, 81–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafeiadou, P.; Papakonstantis, I.; Christodoulou, G. Numerical simulation of inclined negatively buoyant jets. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, Rhodes, Greece, 1–3 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, C.J.; Davidson, M.J.; Nokes, R.I. k-ε Predictions of the initial mixing of desalination discharges. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2008, 8, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gildeh, H.K.; Mohammadian, A.; Nistor, I.; Qiblawey, H. Numerical Modeling of Turbulent Buoyant Wall Jets in Stationary Ambient Water. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2014, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gildeh, H.K.; Mohammadian, A.; Nistor, I.; Qiblawey, H. Numerical modeling of 30° and 45° inclined dense turbulent jets in stationary ambient. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2015, 15, 537–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gildeh, H.K.; Mohammadian, A.; Nistor, I.; Qiblawey, H.; Yan, X. CFD modeling and analysis of the behavior of 30° and 45° inclined dense jets—New numerical insights. J. Appl. Water Eng. Res. 2016, 4, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardalan, H.; Vafaei, F. CFD and Experimental Study of 45° Inclined Thermal-Saline Reversible Buoyant Jets in Stationary Ambient. Environ. Process. 2019, 6, 219–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jiang, B.; Law, A.W.-K.; Zhao, B. Large eddy simulations of 45° inclined dense jets. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2016, 16, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Law, A.W.-K.; Jiang, M. Large eddy simulations of 45° and 60° inclined dense jets with bottom. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2017, 15, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cintolesi, C.; Petronio, A.; Armenio, V. Turbulent structures of buoyant jet in cross-flow studied through large-eddy simulation. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2019, 19, 401–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloutsos, A.A.; Yannopoulos, P.C. Curvilinear Coordinate System for Mathematical Analysis of Inclined Buoyant Jets Using the Integral Method. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yannopoulos, P.C. Advanced integral model for groups of interacting round turbulent buoyant jets. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2010, 10, 415–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreyszig, E. Advanced Engineering Mathematics, 10th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bosanquet, C.H.; Horn, G.; Thring, M.W.; Taylor, G.I. The effect of density differences on the path of jets. Proc. R. Soc. A 1961, 263, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashitialshaaer, R.; Larson, M.; Persson, K.M. An Experimental Investigation on Inclined Negatively Buoyant Jets. Water 2012, 2012, 720–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforakis, I.K.; Christodoulou, G.C.; Stamou, A.I. Bottom concentration field due to impingement of inclined dense jet on a slope. In Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium of Environmental Hydraulics, Singapore, 7–8 January 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Baines, W.; Turner, J.; Campbell, I. Turbulent fountains in an open chamber. J. Fluid Mech. 1990, 212, 557–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Law, A.W.-K.; Song, J. Mixing characteristics of inclined dense jets with different nozzle geometries. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2019, 27, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, C.L.; Antenucci, J.P.; Luketina, D.; Okely, P.; Imberger, J. Near-Field Dilution Characteristics of a Negatively Buoyant Hypersaline Jet Generated by a Desalination Plant. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2011, 137, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantis, I.; Kampourelli, M.; Christodoulou, G. Height of rise of inclined and vertical negatively buoyant. In Proceedings of the 32nd IAHR Congress, Venice, Italy, 1–6 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ramaprian, R.B.; Chandrasekhara, M. Study of Vertical Plane Turbulent Jets and Plumes; Tech. Rep. IIHR No. 257; Iowa Institute of Hydraulic Research, University of Iowa: Iowa City, IA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Christodoulou, G.C.; Papakonstantis, I.G. Simplified estimates of trajectory of inclined negatively buoyant jets. In Environmental Hydraulics, Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Environmental Hydraulics, Athens, Greece, 23–25 June 2005; Christodoulou, G.C., Stamou, A.I., Eds.; Taylor and Francis Group: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]

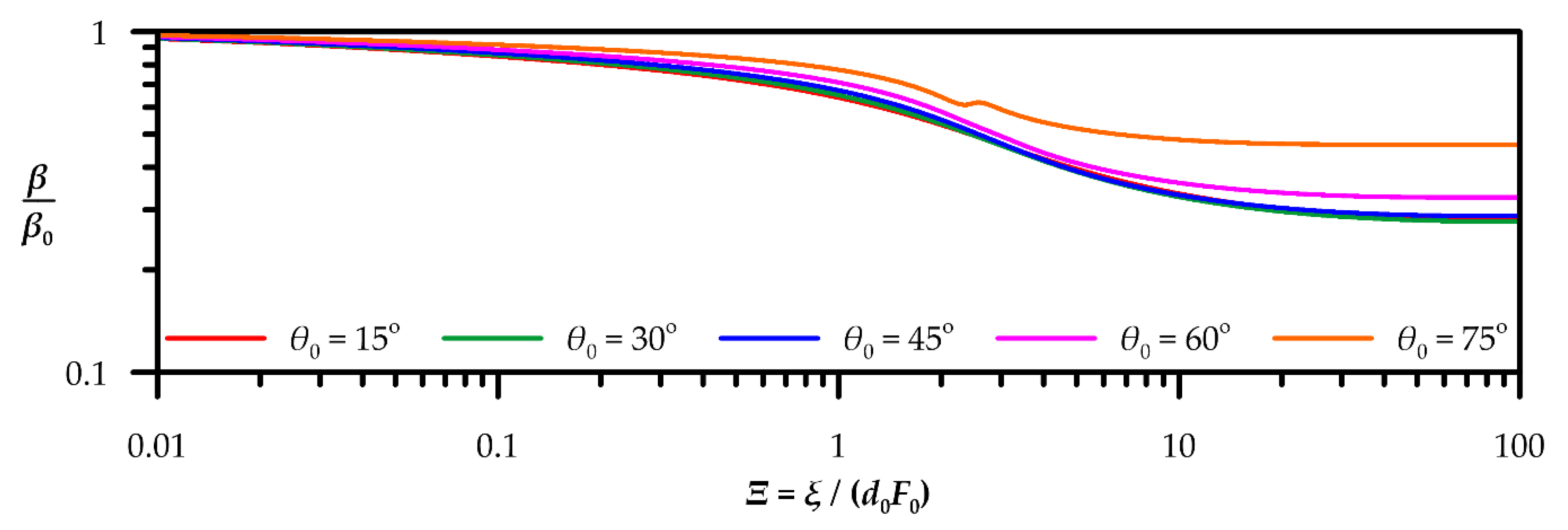
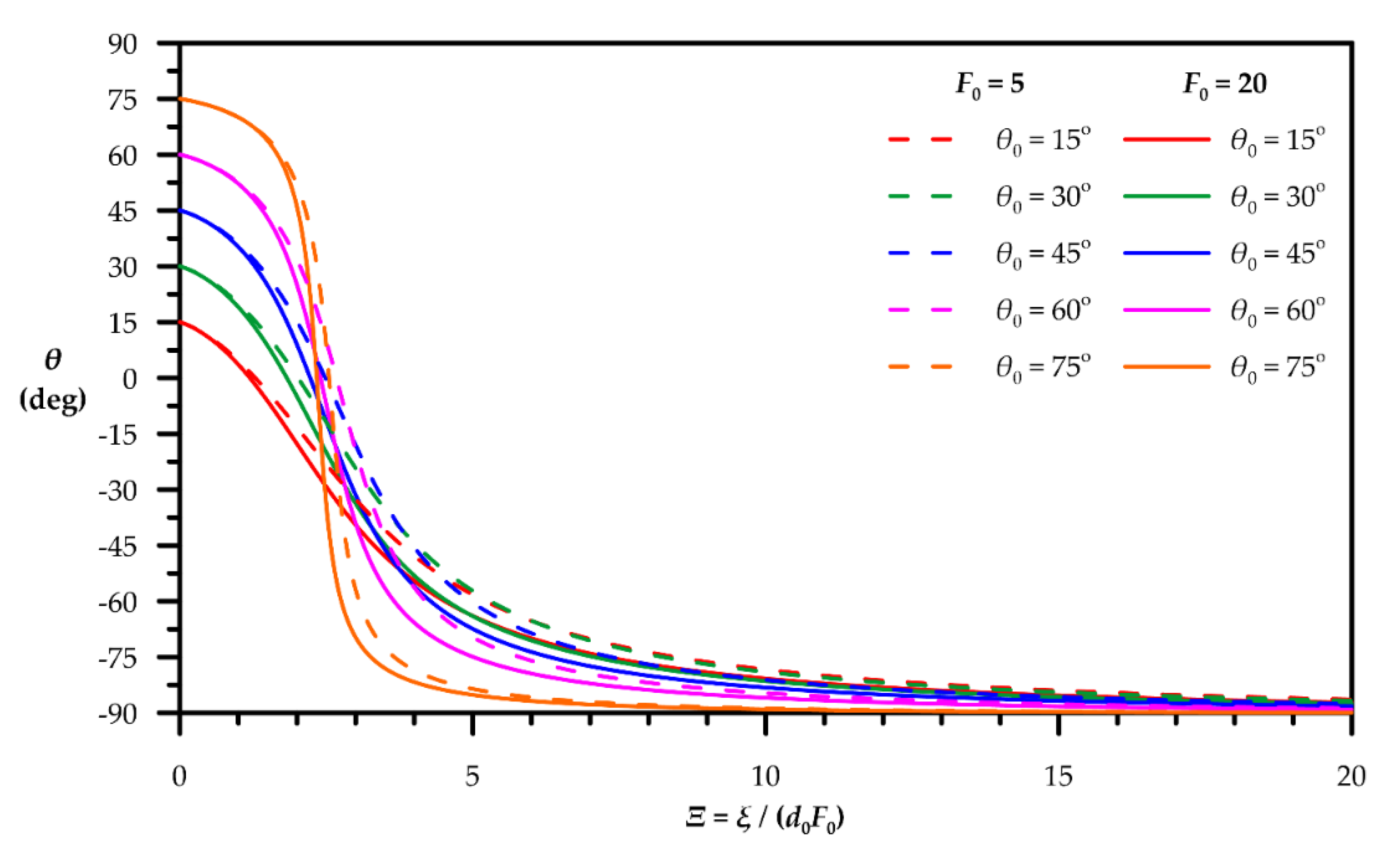
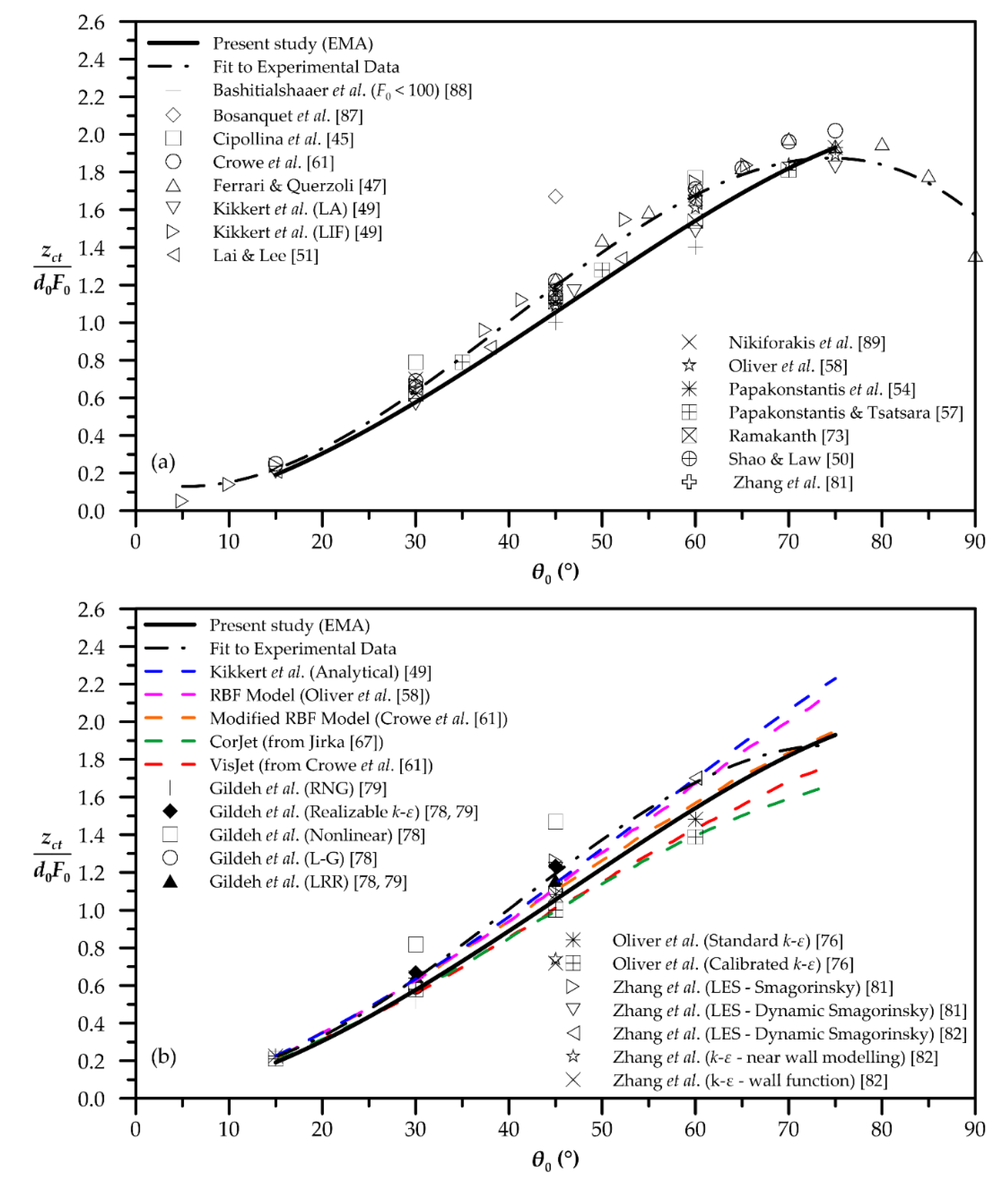
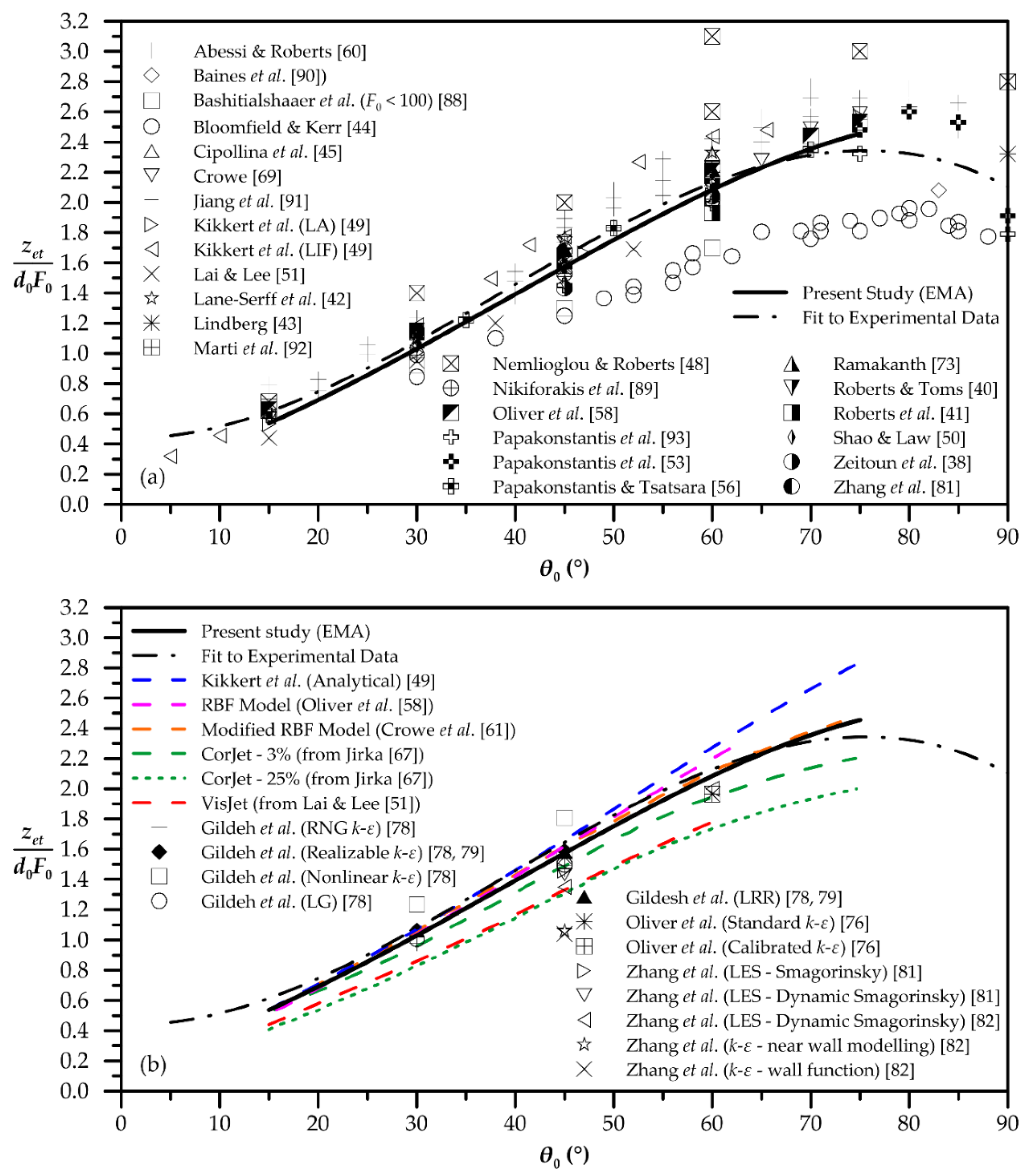
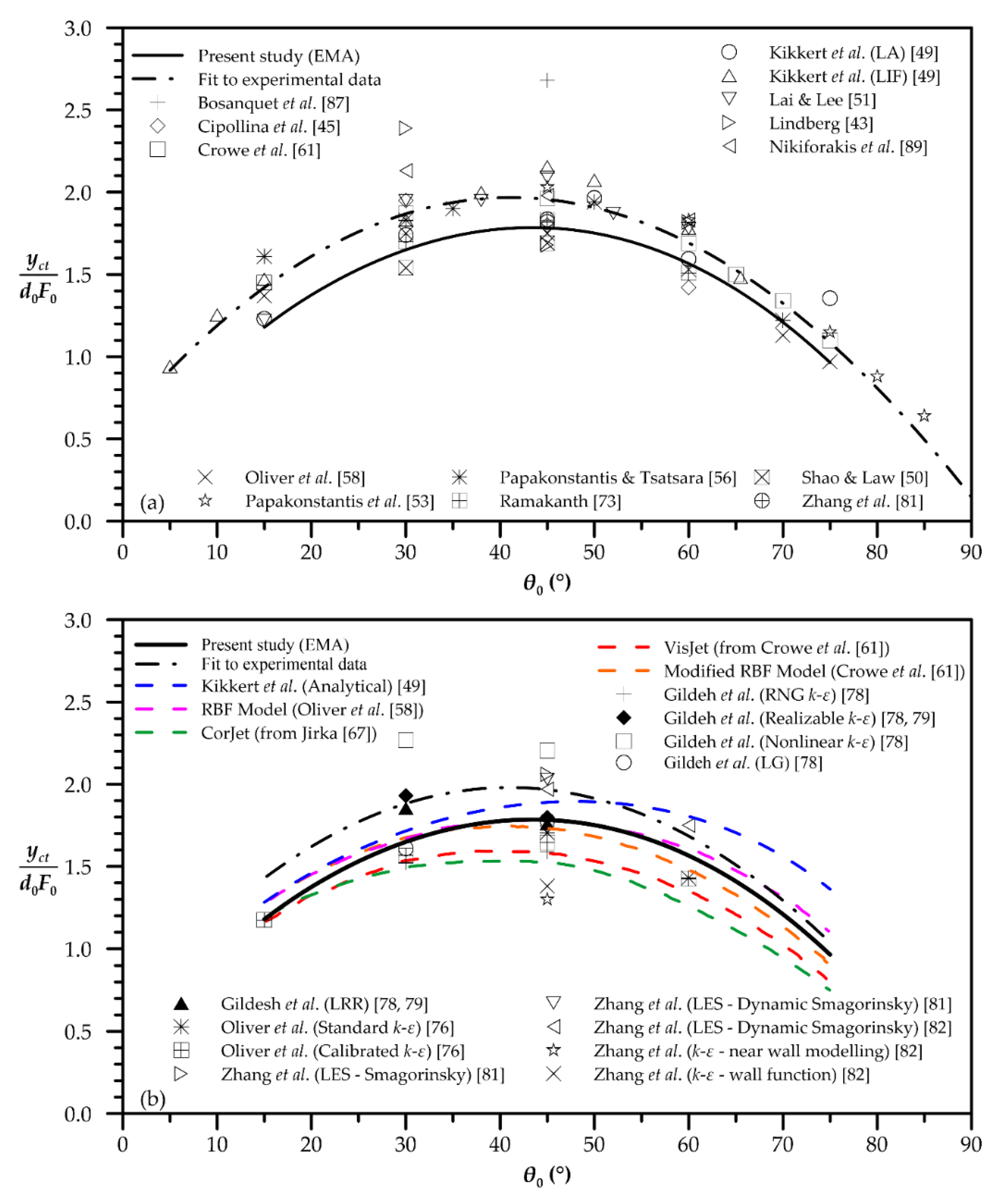
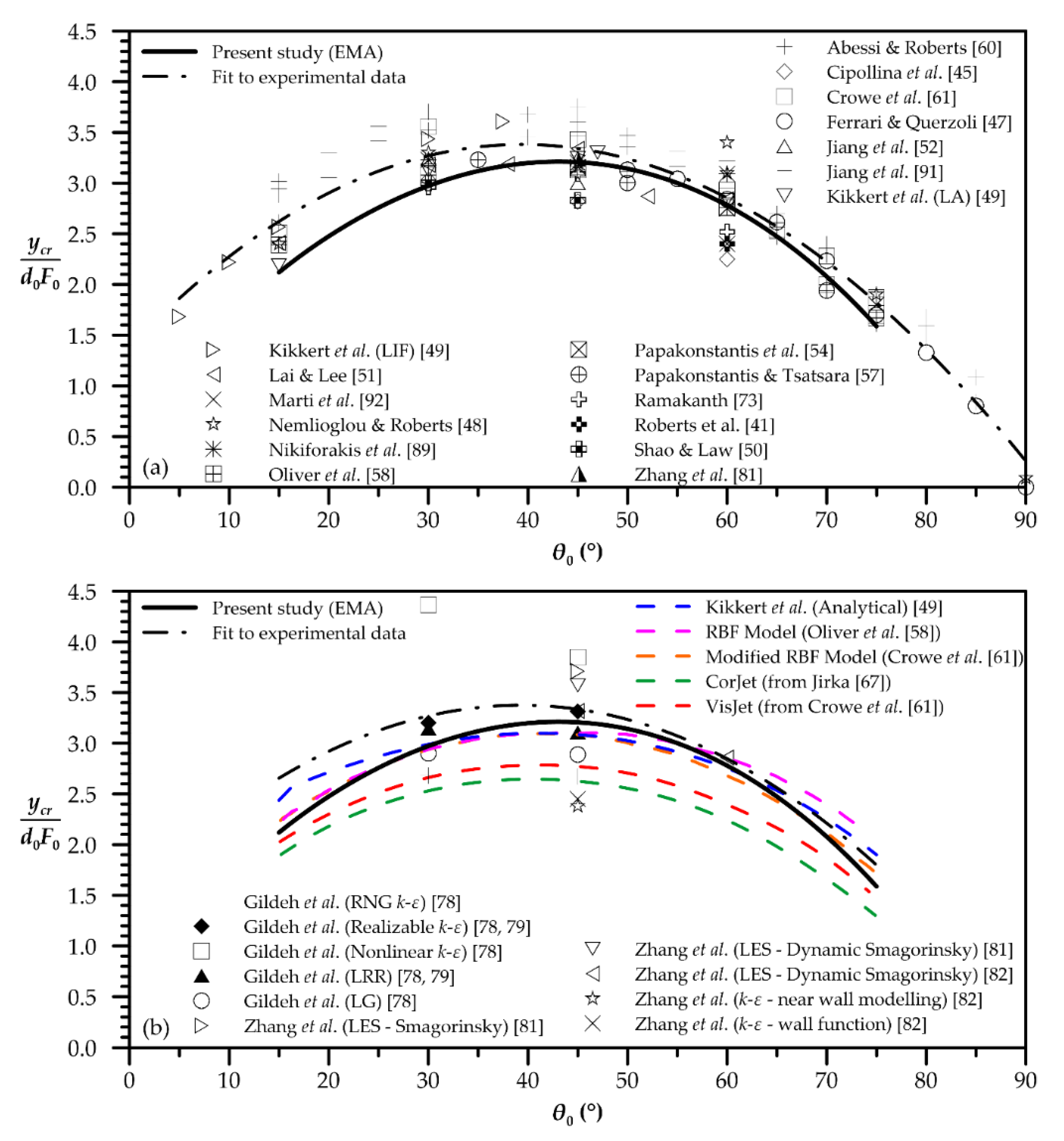
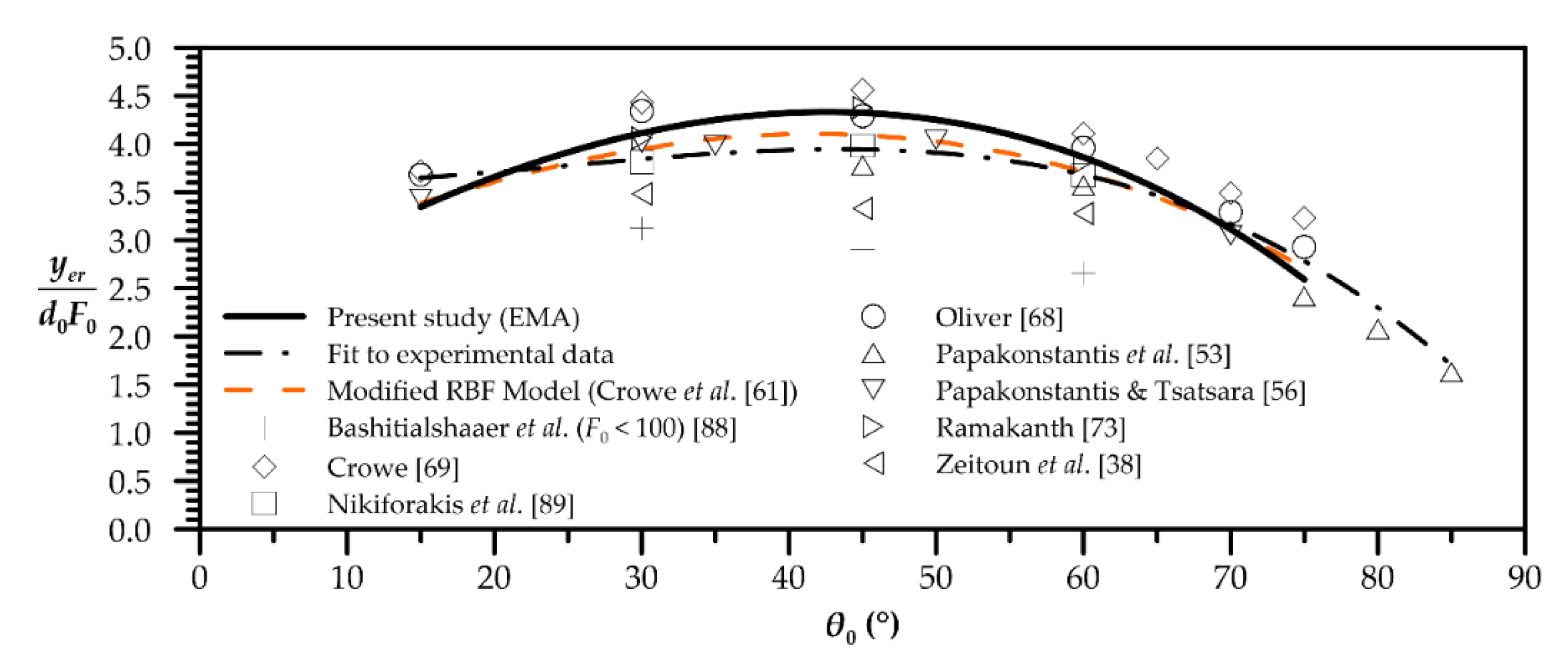
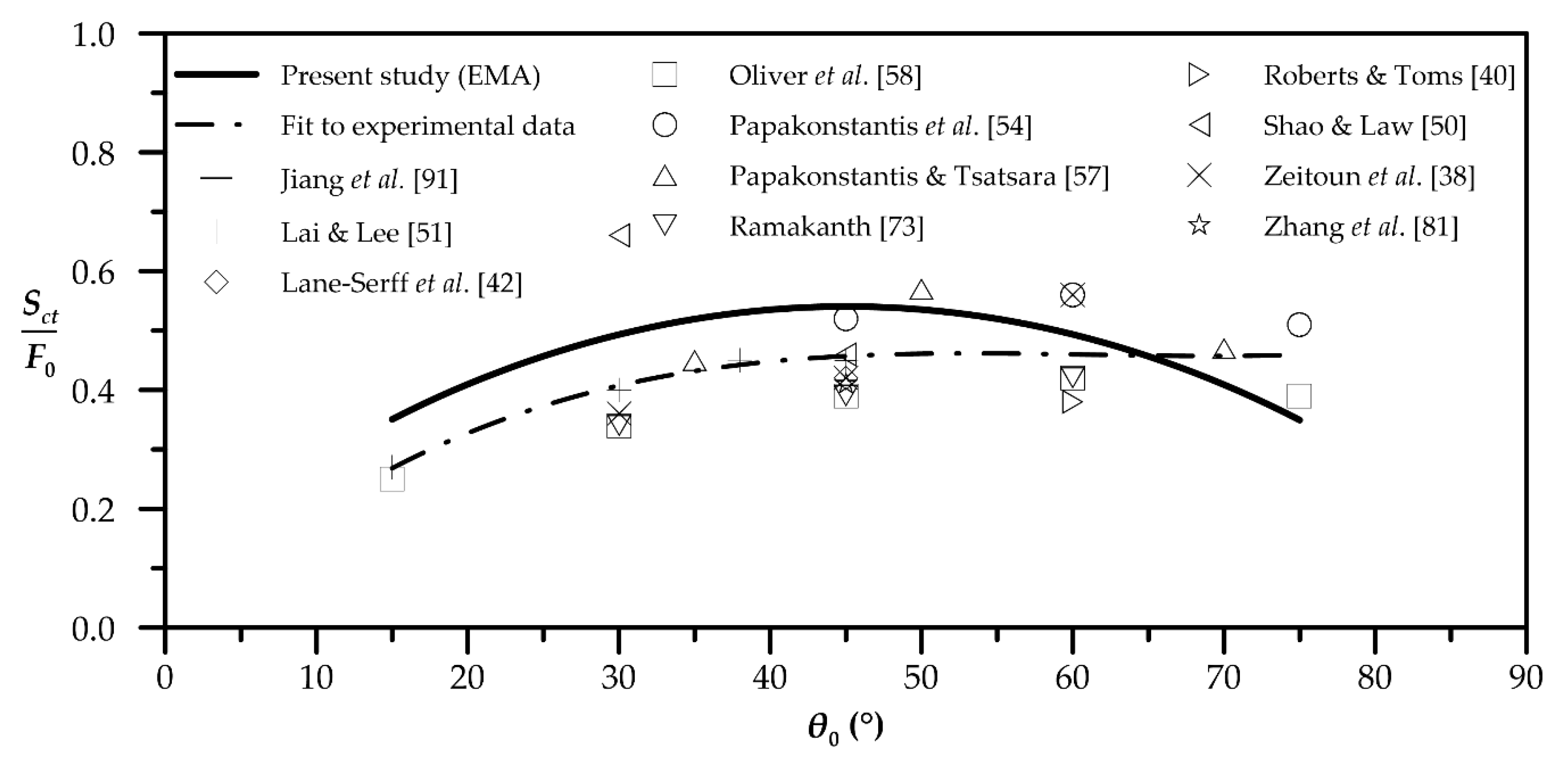
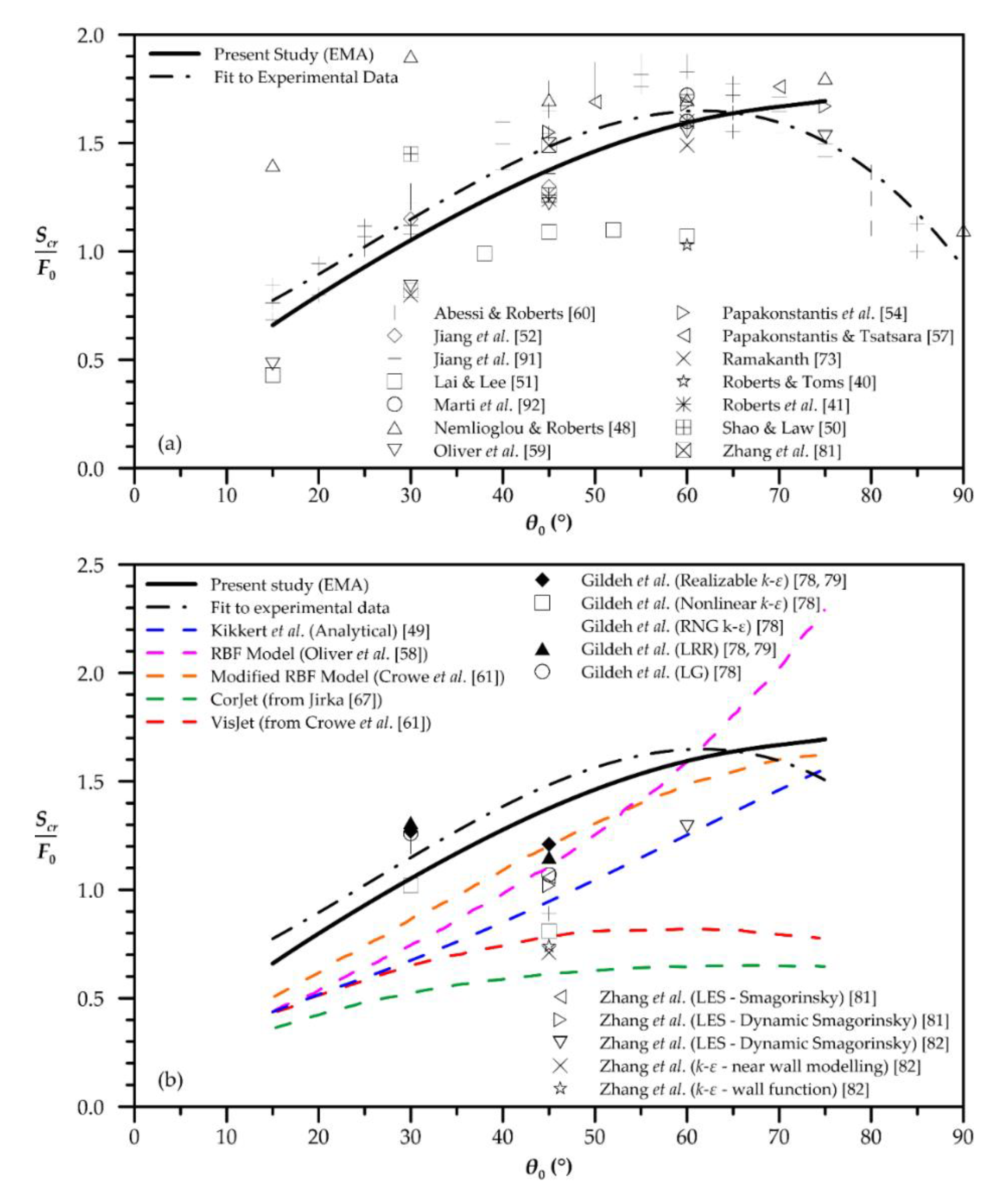
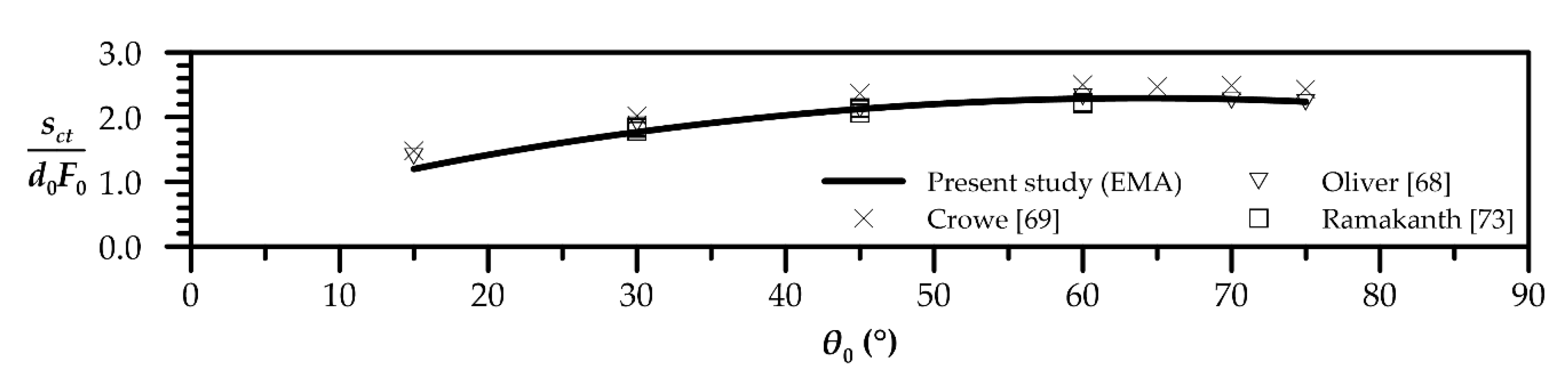
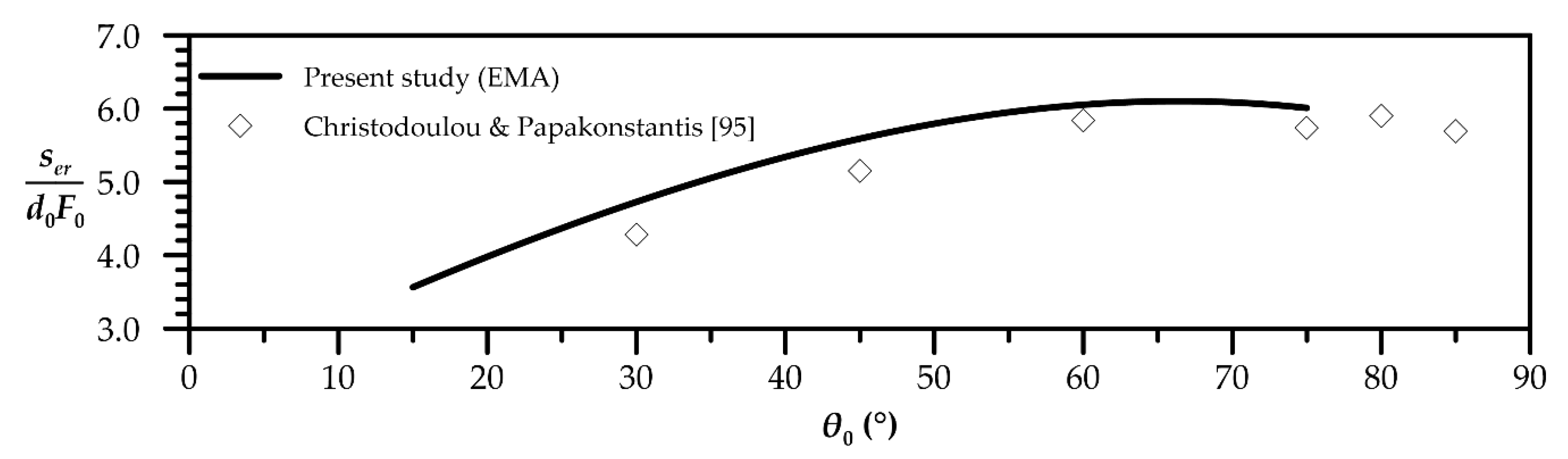
| Quantity | Figure | Polynomial Fit |
|---|---|---|
| Centerline terminal height | 2 | |
| External edge terminal height | 3 | |
| Horizontal distance to terminal height | 4 | |
| Horizontal distance to centerline return point | 5 | |
| Horizontal distance to external edge’s return point | 6 | |
| Minimum dilution at terminal height | 7 | |
| Minimum dilution at return point | 8 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bloutsos, A.A.; Yannopoulos, P.C. Revisiting Mean Flow and Mixing Properties of Negatively Round Buoyant Jets Using the Escaping Mass Approach (EMA). Fluids 2020, 5, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids5030131
Bloutsos AA, Yannopoulos PC. Revisiting Mean Flow and Mixing Properties of Negatively Round Buoyant Jets Using the Escaping Mass Approach (EMA). Fluids. 2020; 5(3):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids5030131
Chicago/Turabian StyleBloutsos, Aristeidis A., and Panayotis C. Yannopoulos. 2020. "Revisiting Mean Flow and Mixing Properties of Negatively Round Buoyant Jets Using the Escaping Mass Approach (EMA)" Fluids 5, no. 3: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids5030131
APA StyleBloutsos, A. A., & Yannopoulos, P. C. (2020). Revisiting Mean Flow and Mixing Properties of Negatively Round Buoyant Jets Using the Escaping Mass Approach (EMA). Fluids, 5(3), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids5030131





