Abstract
This study investigated the unsteady acceleration aerodynamics of bluff bodies through the study of a channel mounted square cylinder undergoing free-stream acceleration of ±20 ms−2 with Reynolds numbers spanning 3.2 × 104 to 3.6 × 105. To achieve this, a numerical simulation was created with a commercial finite volume unstructured computational fluid dynamics code, which was first validated using Improved Delayed Detached Eddy Simulation against experimental and direct numerical simulated results. Then, the free stream conditions were subjected to a periodic velocity signal where data were recorded and ensemble averaged over at least 30 distinct acceleration and deceleration data points. This enabled the comparison of body forces and flow field variations among accelerating, steady and decelerating free-stream conditions. Body force analysis determined that decelerating and accelerating drag forces varied −47% and 44%, respectively, in comparison to steady free-stream conditions. In addition, several differences were also observed and explored such as near-body flow structures, wake dynamics, Kármán vortices and vorticity production during the aforementioned conditions. The primary interest of this study was for the future application towards road vehicles for predictive dynamic modeling and aerodynamic development.
1. Introduction
Studies involving bluff body aerodynamics found in the literature primarily focus on a steady mean free-stream flow velocity. While this encompasses the majority of operating conditions, the impact of the fluid on the body due to an accelerating free-stream condition is often ignored. Analytical solutions for accelerating streamlined bodies can be obtained with potential flow analysis (see Panton [1]), but cannot be applied to bluff bodies due to separated flow regimes. The accelerating case for bluff bodies is potentially important for engineering applications where large accelerations occur, such as an automobile attempting to avoid a collision, high performance road vehicles transversing a course, and missile and aircraft maneuverability, all of which experience transient weather phenomena such as gusting and wind shear. For those engineering applications mentioned, we aimed to investigate the accelerating case and developed a numerical process with a simplified bluff body. The authors’ ultimate objectives include the characterization of a high performance street or racecar’s dynamic behavior subject to a high longitudinal acceleration or deceleration in the range of (1G), which occurs during efficient transition from high-speed straightaways to low-speed corners or vice versa. The additional effect of this longitudinal acceleration can be included in high-fidelity race-vehicle dynamics models such as the one proposed by Mohrfeld–Halterman and Uddin [2] for an improved prediction of vehicle handling characteristics. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is already used to complement steady mean free-stream flow experiments, reducing design overhead, and has the potential for applications testing accelerating free-stream conditions as well.
The existence of additional forces resulting from accelerating a body through a fluid is not a new idea. Du Baut [3] proposed adding an additional mass to spheres accelerating in air and water after his experiments in 1786 failed to agree with Newtons second law of motion. Bessel [4] also proposed an added mass in 1828 while investigating the motion of pendulums. Bessel found that an added inertia was required to complete the reduction to a vacuum for his pendulum experiments. Morison [5] experimentally measured the force distribution of surface waves on cylindrical piles, determining a coefficient (the Morison Coefficient) of = 1.96 representing the added fluid forces for a round cylinder undergoing acceleration. The coefficient of mass was determined through Equation (1) (the Morison equation) where the total instantaneous force can be broken down into two components, Part 1 representing the inertial force and Part 2 representing the drag force. Equation (1) consists of , Ɐ, , , A, and , which represent density of the fluid, volume of the test body, coefficient of mass, acceleration rate of the fluid or test body, frontal area of the test body, coefficient of drag and the velocity of the fluid or test body, respectively.
Several more recent papers have also explored acceleration of lifting devices as well as bluff bodies. Fackrell [6] investigated free falling spheres and cylinders with both experiments and numerical simulations, finding that the potential flow theory was sufficient for calculating the added-mass at initial onset of acceleration, not the total added acceleration force during sustained acceleration when separation was present. Fernando et al. [7], while investigating the acceleration of a sphere from both rest and steady-state velocity, concluded that the adverse pressure gradient at the rear of the sphere could be reduced significantly through body acceleration. Lee [8] experimentally measured the additional drag on circular and square wall mounted cylinders due to acceleration, concluding that the square cylinder would always see an increased value of drag for all Reynolds numbers tested, while other shapes may see variations depending on the location of flow separation onset. Roohani [9], while investigating the acceleration of 2D objects at both sonic and subsonic conditions, observed that, for subsonic flows over a NACA 2412 airfoil, there exist differences not only in body forces between non-accelerating and accelerating conditions but also in the stall angle of the airfoil, which varied . Zhang [10] experimentally measured the velocity front that occurs during the acceleration of spreading jets, which was found to drastically reduce the overall entrainment, leading to a decreased decay of the center-line velocity, as well as the overall jet spreading rate.
Vortex lock-on (otherwise known as wake resonance) is another example of unsteady free-stream conditions, where a forced oscillation induces specific harmonics between the forcing frequency and the natural vortex shedding of the body. Bearman, Konstantinidis and coworkers produced several in-depth studies [11,12,13,14,15,16] (both numerical and experimental) on square and circular cylinders in vortex lock-on regimes. These studies all demonstrated considerable variations in mean drag force, root mean squared (rms) lift force, wake size, vorticity, and Reynolds stresses due to their unsteady free-stream conditions. These works are similar to this paper but do not explore the same phenomenon and are included to provide insight and draw similarities in flow physics.
Herein, we focus on the differences among decelerating, constant and accelerating conditions for a square cylinder in channel flow, which is achieved by periodically forcing the inlet to drive constant acceleration and deceleration rates. We chose the square cylinder as our test article due to the simplified shape creating constant separation points, eliminating unforeseen complexities in the flow field. Data were carefully ensemble averaged at a reference velocity of 6 for each acceleration phase to extract flow fields and forces for comparison with steady free-stream results. This process is the critical first step to investigate unsteady race vehicle aerodynamics for development of advanced dynamic handling models. The work presented in this paper are based off of the PhD dissertation research work of the first author, Brett Peters [17].
2. Numerical Setup
Improved Delayed Detached Eddy Simulations (IDDES) [18,19], with Menter shear stress transport (SST) [20] turbulence modeling for the Reynolds Averaging Navier–Stokes (RANS) region, were performed on a channel mounted square cylinder using STAR-CCM+ v11.04, an unstructured finite volume commercial code. IDDES is a hybrid RANS Large Eddy Simulation (LES) model that was developed to provide a cost-effective, yet more flexible and convenient, scale-resolving simulation (SRS) methodology for high Reynolds number inherently transient flows. IDDES has been a popular tool in computational fluid dynamics research since it was proposed [21]. IDDES’s primary advantage is that it is a combination of DDES and Wall Modeled Large Eddy Simulation (WMLES) in which the SRS modeling approach depends on whether the grid resolution is sufficient to resolve dominant eddies in the boundary layer or whether the simulation contains inflow turbulence content. The literature suggests that IDDES approach has the following advantages over the standard DES model: (a) it provides shielding against Grid Induced Separation (GIS), similar to the DDES model; (b) it allows the model to run in WMLES mode in case of unsteady inlet/free-stream conditions, (c) it allows the LES simulation of wall boundary layers at much higher Reynolds numbers than standard LES models; and (d) it is self-adaptive in such a way that it reverts to DDES when the requirements/demands for WMLES are not satisfied. However, the model formulation is relatively complex and beyond the scope of the current paper, thus the interested reader is referred to the original publications of Shur et al. [19] and Gritskevich et al. [18].
Since the current study is a first step towards simulating road vehicles undergoing longitudinal acceleration, Direct Numerical Simulation (DNS) and LES approaches were not considered due to their lack of adoption in the automotive field and due to increased computational overhead. The lack of adoption is due to high Reynolds number at highway speeds requiring finer grid and temporal resolutions for both DNS and wall resolved LES simulations (see Equation (2) in the next section). Previous studies have demonstrated that fully resolving all scales of turbulence may not be required for predicting major quantities of engineering interest, such as force and moment coefficients, and the mean flow field, with a reasonable accuracy. For example, Trias [22] performed DNS on the same channel mounted cylinder as used in this paper for a Reynolds number of 2.2 × 104 and achieved very good correlation with the experimental values. In addition, the current study demonstrates in Section 2.2 that IDDES also achieves results well within acceptable accuracy using less computational overhead. Note that as there is an unavoidable increase in simulated time to obtain ensemble averaged flow fields that smooth out turbulent effects; 33 acceleration–deceleration cycles were used in this study. Based on the conclusions from the steady-mean-flow transient simulations of similar flows [23,24], this time period seems to be a good compromise between precision and computational affordability; the results of Sohankar et al. [24] and Rodi [23] were time-averaged over 20 and 10 vortex-shedding cycles , respectively. Note that the first acceleration–deceleration period was excluded in ensemble averaging due to initialization from a previous steady-mean-flow solution.
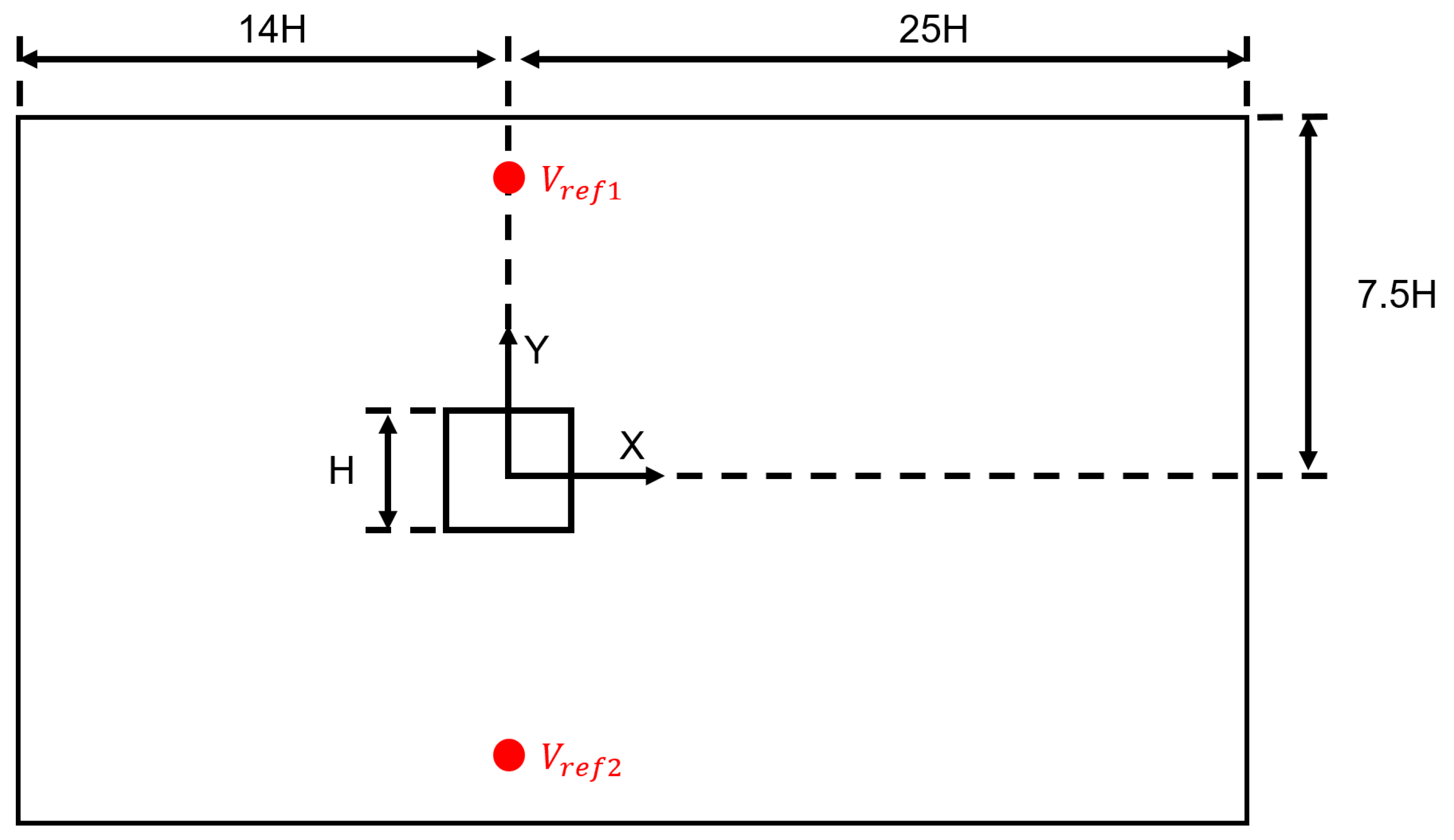
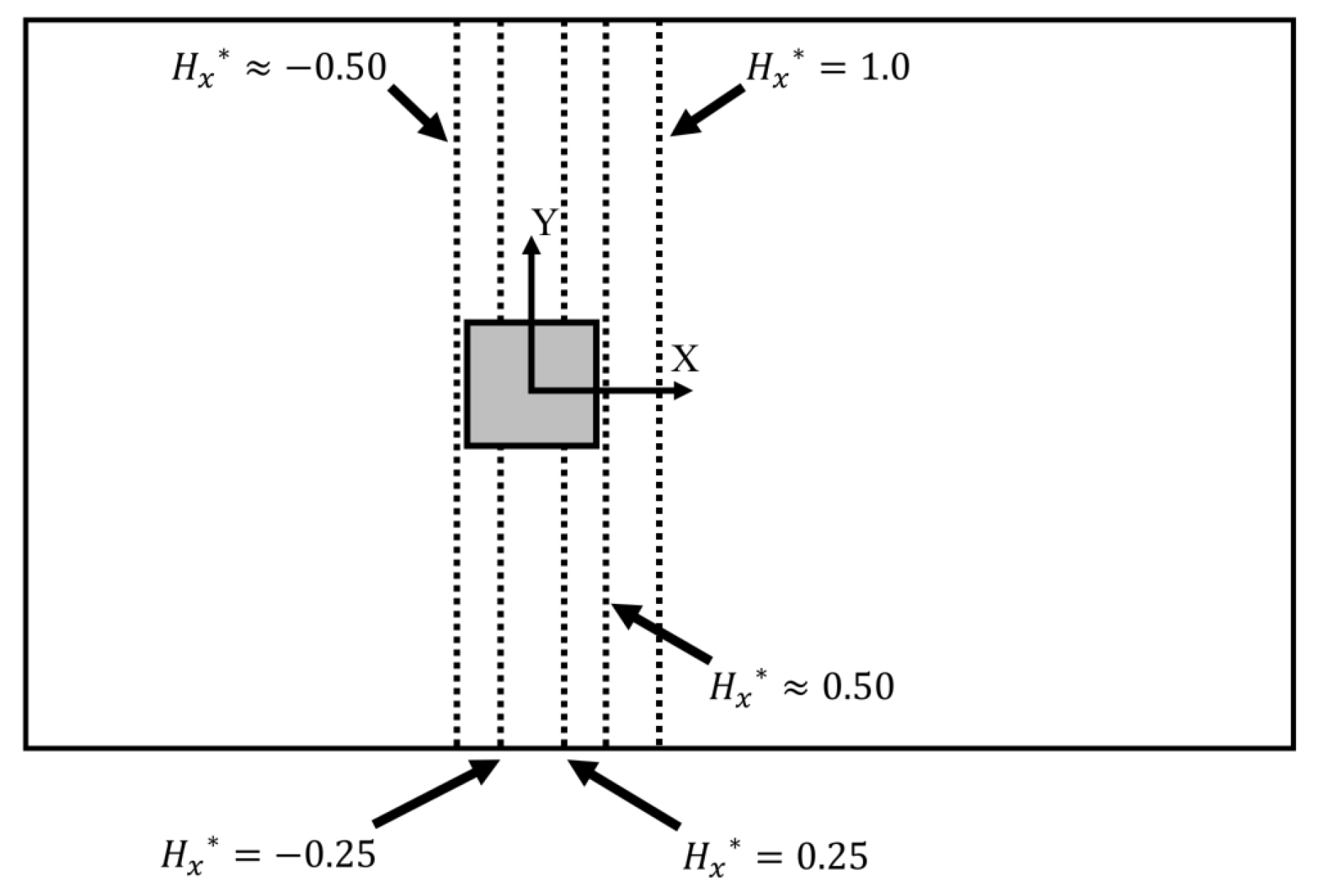
For the range of velocities investigated in this study, the Reynolds number spanned from 3.2 × 104 to 3.6 × 105, which was centered around the target Reynolds number of 1.9 × 105 based on the length scale of m and mean . The square cylinder with dimension , was mounted inside a channel, which served as the computational domain, as can be seen in Figure 1. This figure also shows the coordinate system used in this study where x, y, and z represent the streamwise, vertical and lateral directions, respectively. The origin of the coordinates system lies at the center of the cylinder on the center xy plane of the channel. Note that all length scales presented in this paper were normalized by H and are denoted by a superscript ; the subscripts x, y, and z correspond to the stream-wise, wall-normal and span-wise component of a vector quantity. All statistics in this paper are presented in the center plane (), which, according to Rodi et al. [25], for a wide channel, should be independent of span-wise extent.
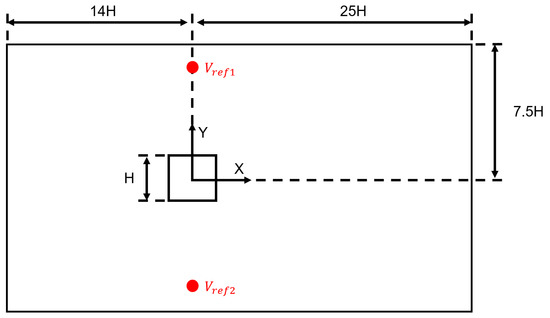
Figure 1.
Overall channel dimensions (not to scale).
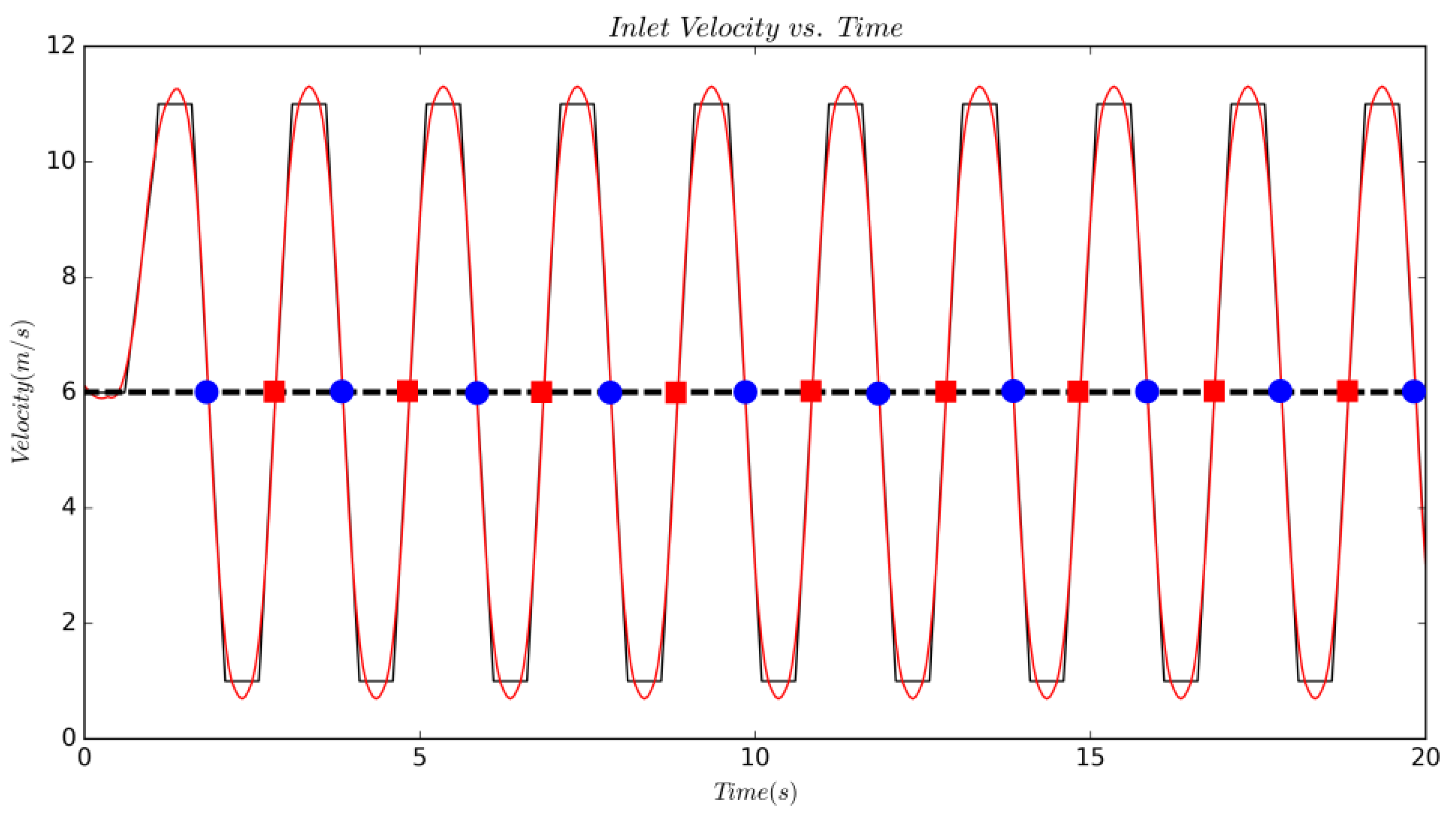
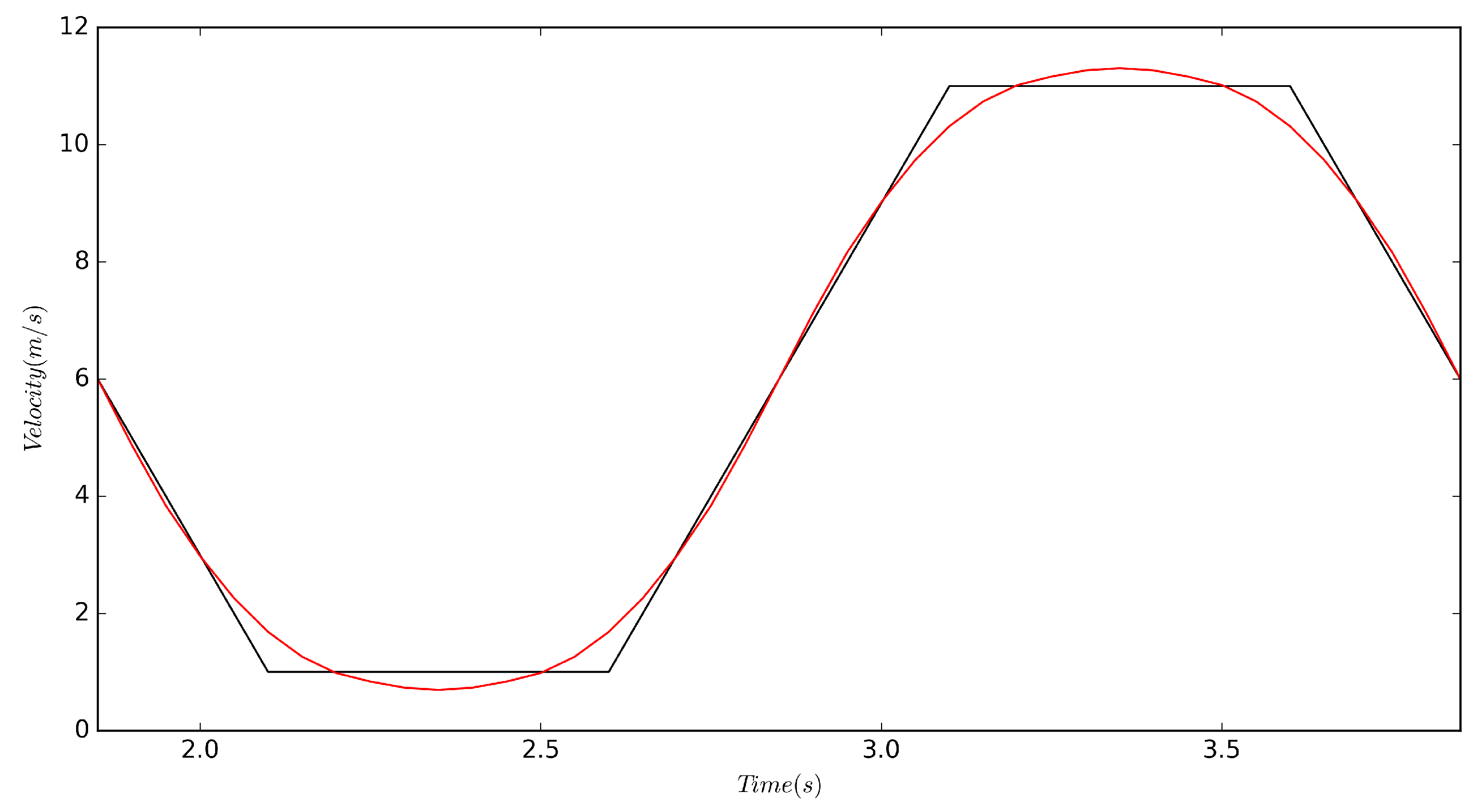
A velocity inlet was specified upstream of the cylinder; the domain outlet was held at constant pressure; top and bottom walls were set as zero-gradient boundaries while the channel side walls were set as periodic; and all surfaces of the cylinder were treated as viscous wall boundaries. The reference velocity is the average of velocities recorded at and ; the locations of these two points are marked in Figure 1 as well. Varying the inlet velocity, while keeping the object stationary, is dynamically equivalent to a body moving with an unsteady velocity in a still fluid, as determined by Wong et al. [26]. The former is a simpler method and provides an easier numerical implementation for CFD simulations. The domain was controlled through a field function driven by the linear interpolation of a file table containing the periodic signal shown in Figure 2. This table was generated from a short Python code that allowed the specification of the acceleration rate, the min/max velocity, and a coast time to aid in smoothing the turn around from acceleration to deceleration. These inputs were then concatenated together for many periods (this signal seen in black) and then smoothed via a Savitzky–Golay filter [27] within the Python signal library. The zoomed plot of in Figure 3 demonstrates that majority of the signal is consumed in changing acceleration rate, where the primary focus was to obtain constant rate of at . The inlet turbulence was specified with a non-dimensional turbulence intensity of 0.01, and turbulent length scale of 30 mm with a synthetic-eddy-method (SEM); this approach is a more flexible vortex method for realistic inlet conditions, as proposed by Jarrin et al. [28].
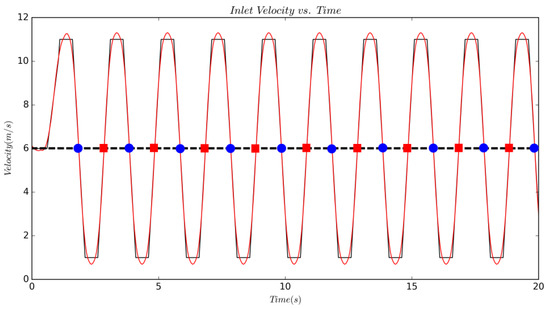
Figure 2.
The periodic signal for over 20 s. Black and red lines represent the raw user input signal and smoothed signal, respectively. The blue circles and red squares along the dotted black line indicate instances of recorded deceleration and acceleration events, respectively.
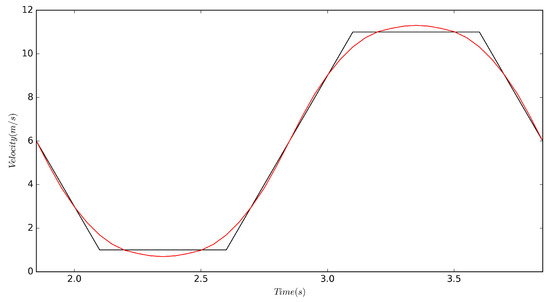
Figure 3.
A zoomed plot of the periodic signal for during one period. Black and red lines represent the raw user input signal and smoothed signal, respectively.
Simulations were carried out with a constant density fluid due to low Mach number and a first-order implicit unsteady temporal solver was utilized with coupled hybrid second-order upwind and bounded central-differencing spatial schemes for the LES and RANS regions, respectively. A time-step of 1 × 10−4 s was used at 6 , which was increased or decreased as the velocity was decreased or increased in order to maintain a constant CFL number at all time steps. The entire simulation required 520 h on 144 × 2.4 GHZ Intel Xeon E5-2665 processors (75,000 core-hours) to run through a total of 33 acceleration–deceleration periods.
The influence of time-step on the solution veracity was investigated during the initial stages of the project when the effects of mesh and time-stepping on the solution veracity were investigated. During this process, time stepping was halved, and no appreciable changes were observed in the predictions. As this simulation was very computationally intensive, time-stepping was limited to 1 × 10−4 s when the velocity was 6 for practical purposes. However, as vorticity can be viewed as another measure of the time-scale ([29]), a posterior indirect rationale for the reliability of the chosen time-step can be made by looking at the vorticity plots in figures to follow where a maximum non-dimensional vorticity of 40 is observed vorticity magnitudes presented in other figures are much smaller; these will be discussed in details later. The maximum non-dimensionalized vorticity of 40 represents a dimensional vorticity magnitude of 120 s. One of the reviewers of the paper recommended that the rule of thumb for second-order time is about 100 iterations per frequency of interest. The chosen time step of 1 × 10−4 s at 6 gives 83 time-step iterations for the highest frequency of interest, thus is very close to what the reviewer recommended as a rule of thumb requirement for a second-order time stepping.
2.1. Numerical Grid
Several techniques have been suggested in the past for la priori estimates of the minimum sufficient grid resolutions for LES. These can be grouped into four major classes: rules of thumb, techniques based on prior RANS results, single-grid estimators and multi-grid estimators (see Celik et al. [30]). According to Gant [31], single-grid estimators include: (a) ratio of the SGS to the laminar viscosity ; (b) relative effective viscosity index; (c) ratio of the cell size to the Taylor microscale; (d) the subgrid activity parameter; (e) ratio of the resolved to total turbulent kinetic energy; and (f) analysis of power spectra. Gant [31] also discussed recommended values of these parameters and examples of their use in the literature. Of these approaches, the current study opted for the Taylor microscale as the arbitrating parameter to determine the required mesh resolution for a reliable IDDES simulation.
Kuczaj et al. [32] suggested that, to obtain numerical solutions close to the experimental ones, for a the turbulent mixing flow in a T-junction, one must resolve the Taylor microscale length; they suggested that for an optimal simulation the finest mesh should be of the order of the Taylor micro-scale obtained from the RANS simulations. However, they cautioned that finer meshes must be used to accurately capture fluctuations in the shear layer close to the center of the mixing zone. In this study, the Taylor microscale () was first estimated using Equation (2) as given by Tennekes and Lumley [29], where is an undetermined constant set to 0.5, is the Reynolds number and L is the length scale; using in Equation (2) yields = 6 mm. This value of was then used as a guide to set the grid spacing required to resolve majority of the inertia driven eddies. Wilcox [33] indicated that is approximately 70 times greater than the Kolmogorov scale, thus this IDDES simulation should leave only the smallest eddies to be modeled.
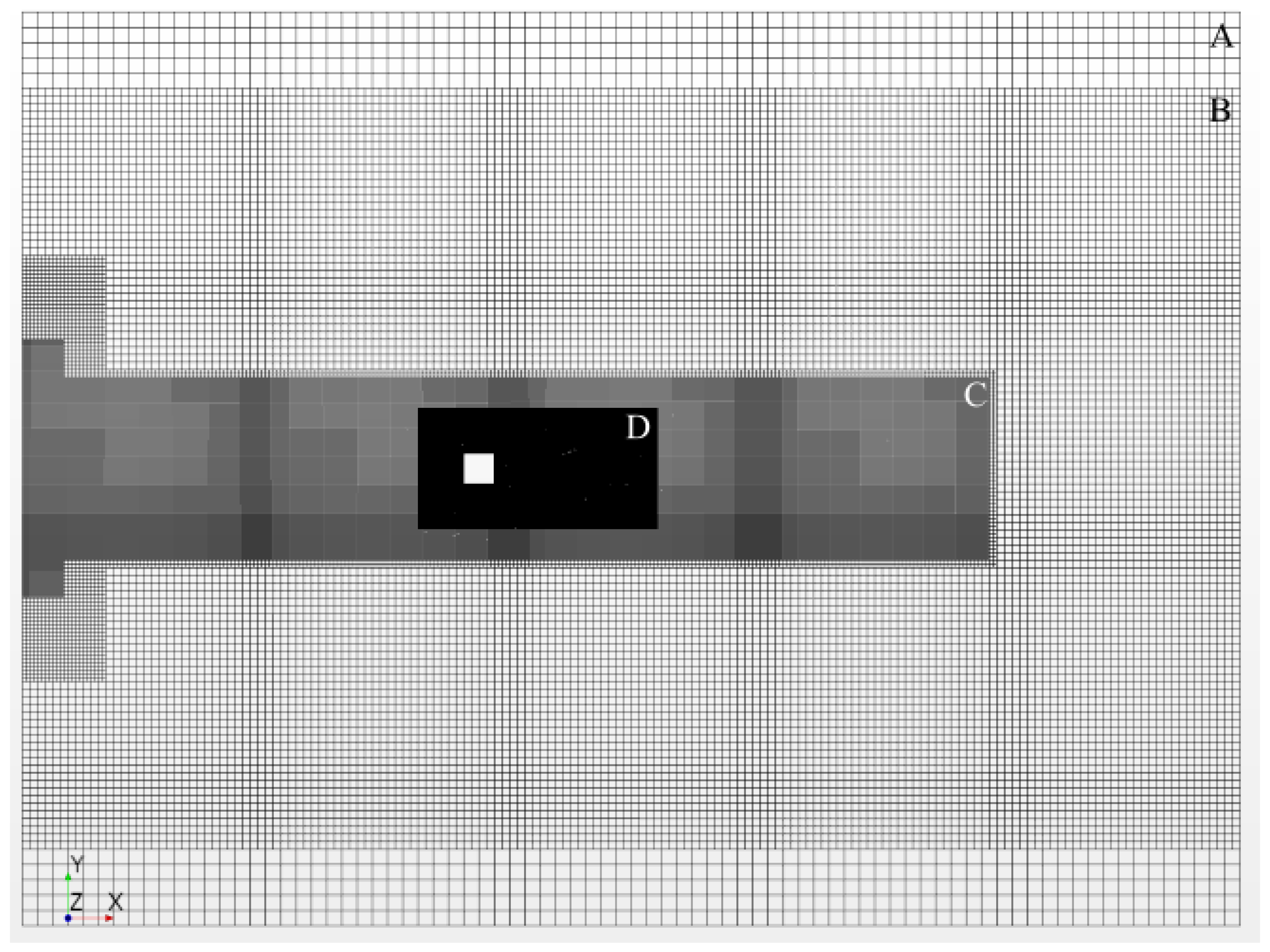
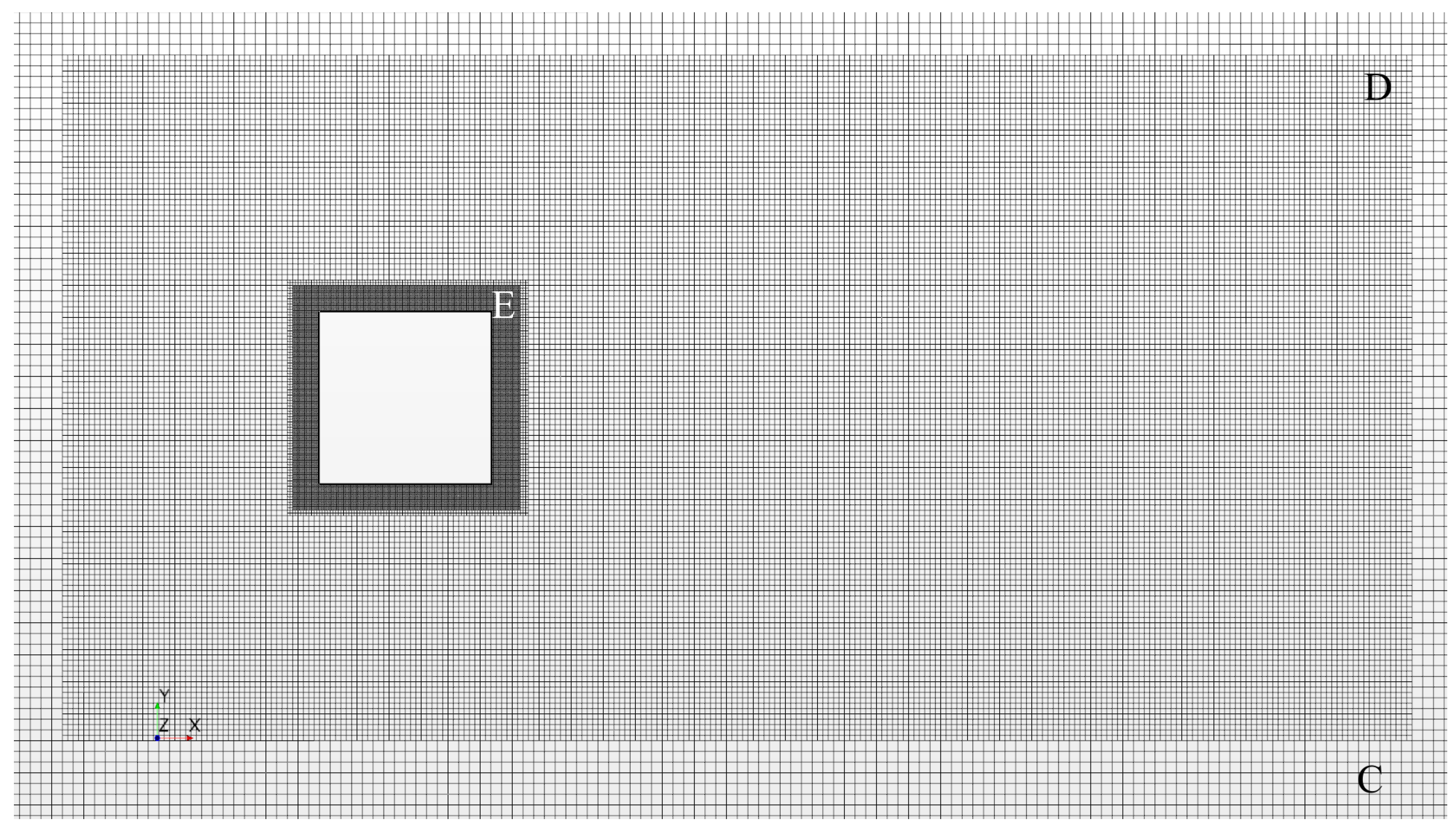
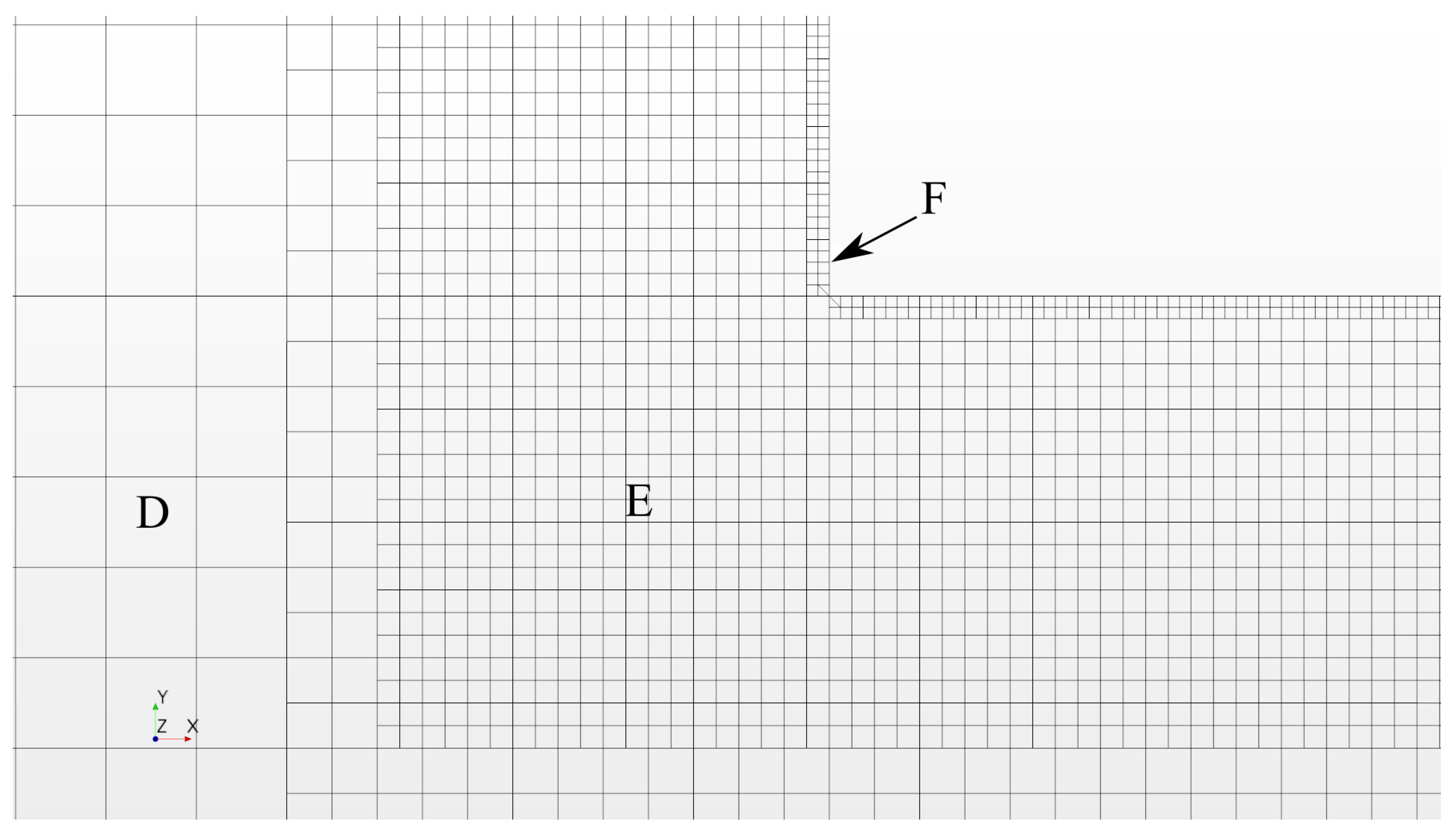
The simulation domain was discretized with hexahedral cells of varying sizes, which are summarized in Table 1. The upper bound on grid spacing was set to and can be seen in Figure 4 denoted as Region A. Region C was set to within ±3H of the cylinder in the cross stream direction to support SEM length scale advection applied at the velocity inlet. The near field region depicted as Region D in Figure 5 was set to a spacing of , which is nearly twice the calculated value of the Taylor microscale from Equation (2) and spans a region from 2H upstream and 6H downstream of the cylinder and ±2H about the cylinder in the cross-flow direction. Region E seen in Figure 6 encompasses the volume within 0.17H of the cylinder and is held to a maximum size of . Region F was created by growing two wall normal layers of equal height equal to , as shown in Figure 6.

Table 1.
Grid spacing values non-dimensionalized by cylinder height H.
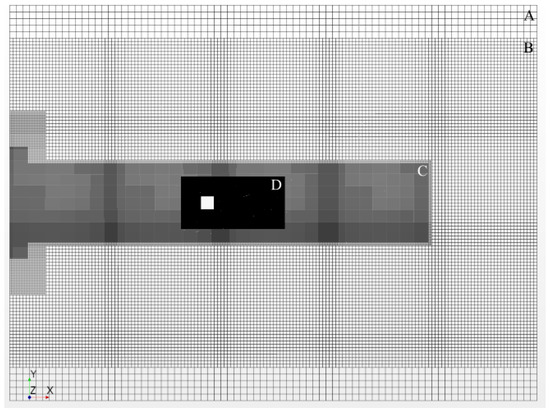
Figure 4.
Overall mesh viewed at cylinder center line.
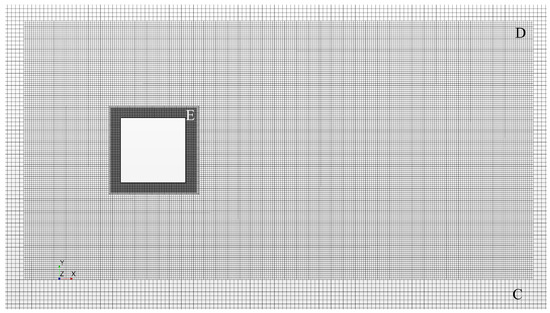
Figure 5.
Near body mesh viewed at cylinder center line.

Figure 6.
Cylinder corner mesh viewed at cylinder center line.
2.2. Model Validation
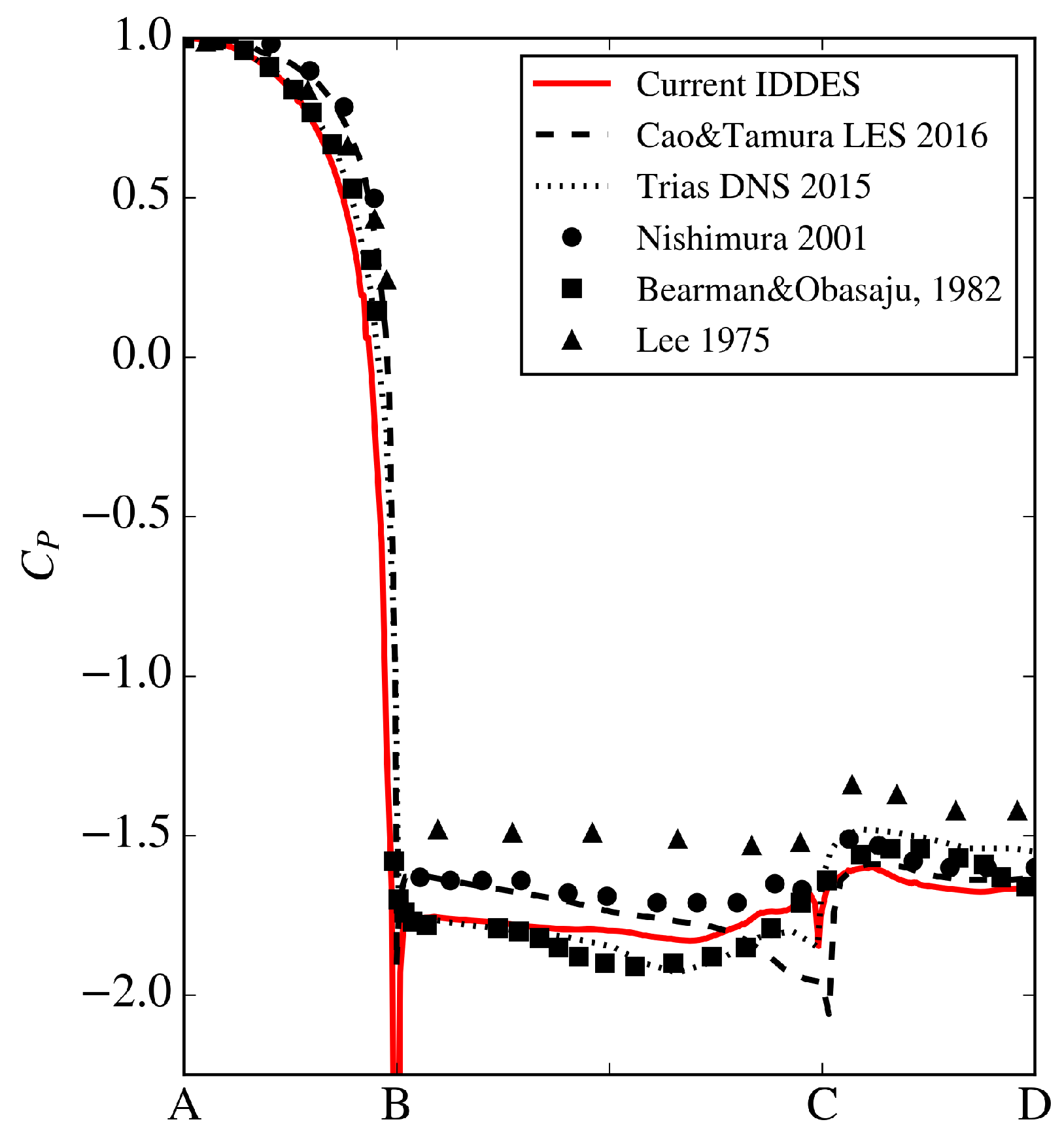
Before attempting to simulate acceleration, a validation study was performed to replicate the experimental results of Lyn and Rodi [34] for constant-velocity flow past a square cylinder at = 2.1 × 104. The previously described IDDES simulation methodology, boundary conditions and mesh specifications were first implemented for model validation, which predicted and to be 2.22 and 1.33, respectively (drag force herein was calculated from integration of both the pressure and viscous forces). Lyn and Rodi experimentally reported = 2.1, which they obtained through the momentum integral of laser-doppler velocimetry measured mean wake velocity profiles. The computed value of from the current validation study also agrees well with reported values compiled by Trias et al. [22] of 10 separate studies spanning experimental, LES and direct-numerical-simulations (DNS), where the values for the square cylinder vary from 2.01 to 2.32 and range from 1.15 to 1.79. In a recent study, Cao and Tamura [35] experimented with the effect of grid-spacing for LES predictions of flow over a square cylinder, reporting range from 2.19 to 2.24. In addition, Figure 7 shows surface pressure coefficients () at center plane along with the recent numerical LES results of Cao and Tamura [35], DNS results of Trias [22], and previous experimental results of Lee [36], Bearman and Obasaju [11] and Nishimura [37], demonstrating that current IDDES results fall well within prior studies for pressure distribution. This further supports that the IDDES methodology adopted in this study can produce results with an acceptable accuracy.
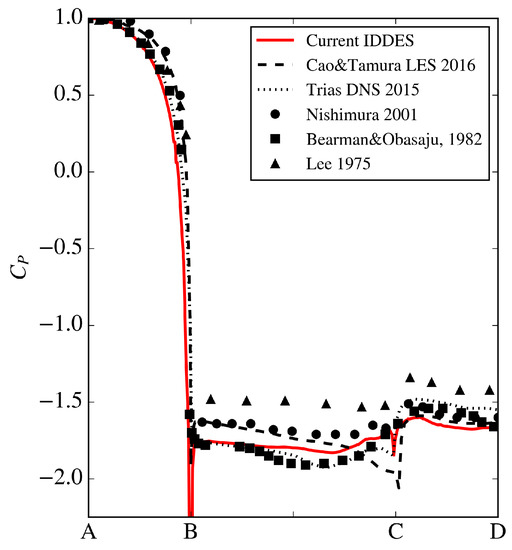
Figure 7.
Surface pressure coefficient taken at center plane () in comparison with highly resolved numerical computations and experiments.
After the validation was performed, the process was then scaled up from an H = 0.06 m to H = 0.5 m in order to increase the volume of the test object. This was done for two reasons: (1) for ease of force measurements at lower Reynolds numbers; and (2) to approach the characteristic scale of an automobile. Note that the Taylor microscale and were recalculated and scaled accordingly from validation to large scale.
3. Results and Discussion
Three specific flow cases were tested and compared with equivalent free-stream velocities while undergoing acceleration (), non-acceleration or constant-velocity () and deceleration (). Acceleration and deceleration data reported in this paper were obtained via ensemble averaging 33 total periods while non-accelerating data were obtained by holding constant and averaging for 18 large eddy turnover times in separate simulations; a total of three constant velocity simulations were run at 5, 6, and 7 . Body drag force for cases was calculated by first smoothing the transient body force data and then ensemble averaging each respective accelerating or decelerating period. was obtained through segregation of for each acceleration or deceleration period and then summed together across all periods and was left as the non-dimensional lift coefficient to not skew results due to . Ensemble averaging was utilized to obtain scalar flow field variables of velocity ( and non-dimensionalized by ) and Vorticity ( non-dimensionalized by ) at . Due to the unsteady mean free stream velocity, the overall drag force is presented as a force in Table 2, which was done intentionally as the drag coefficient is reserved for steady mean velocity flow, which is apparent in Equation (1).

Table 2.
Ensemble averaged Drag Force, rms Lift Coefficient, and Morison coefficient at for the square cylinder during , and .
3.1. Body Forces
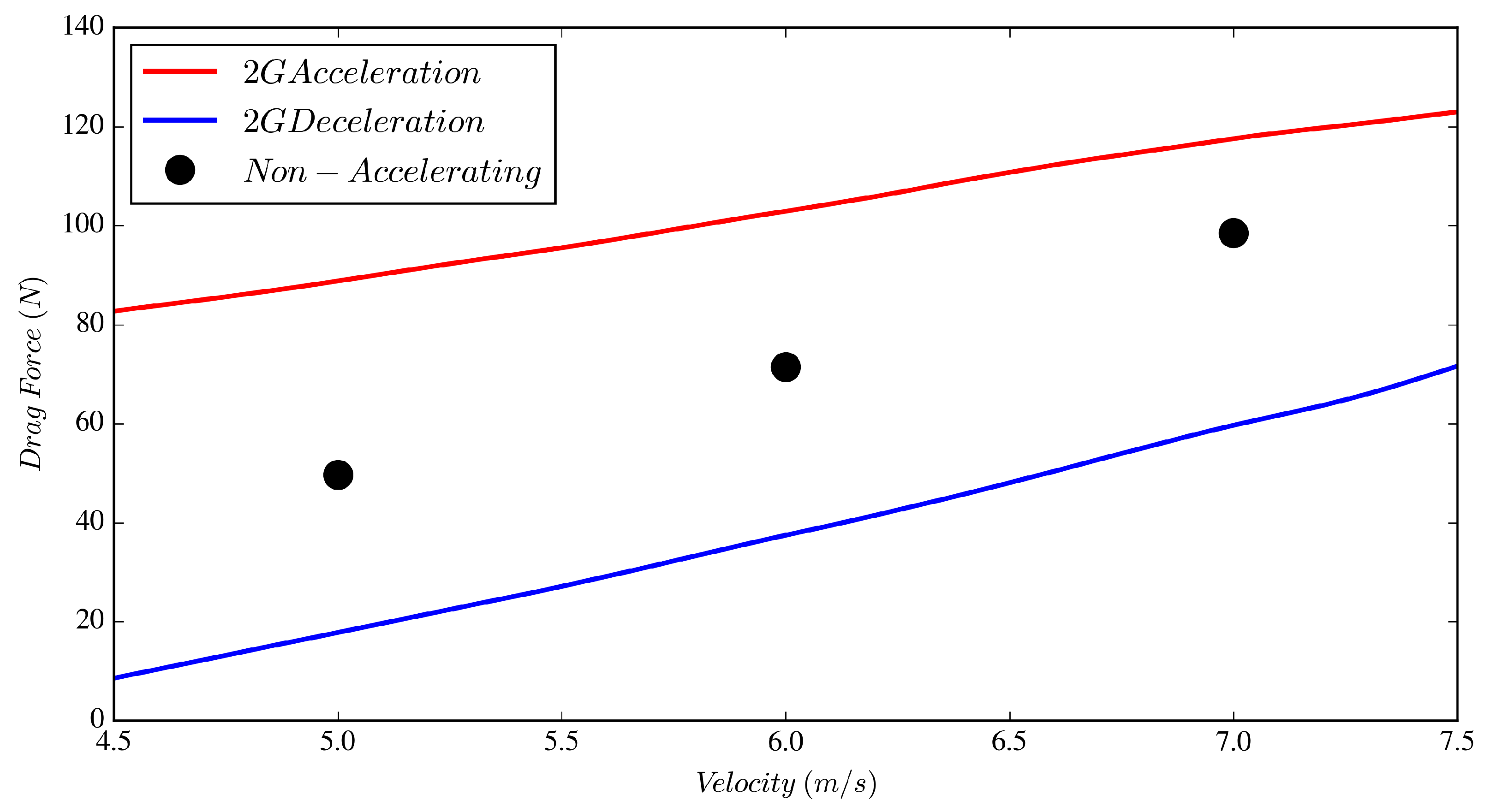
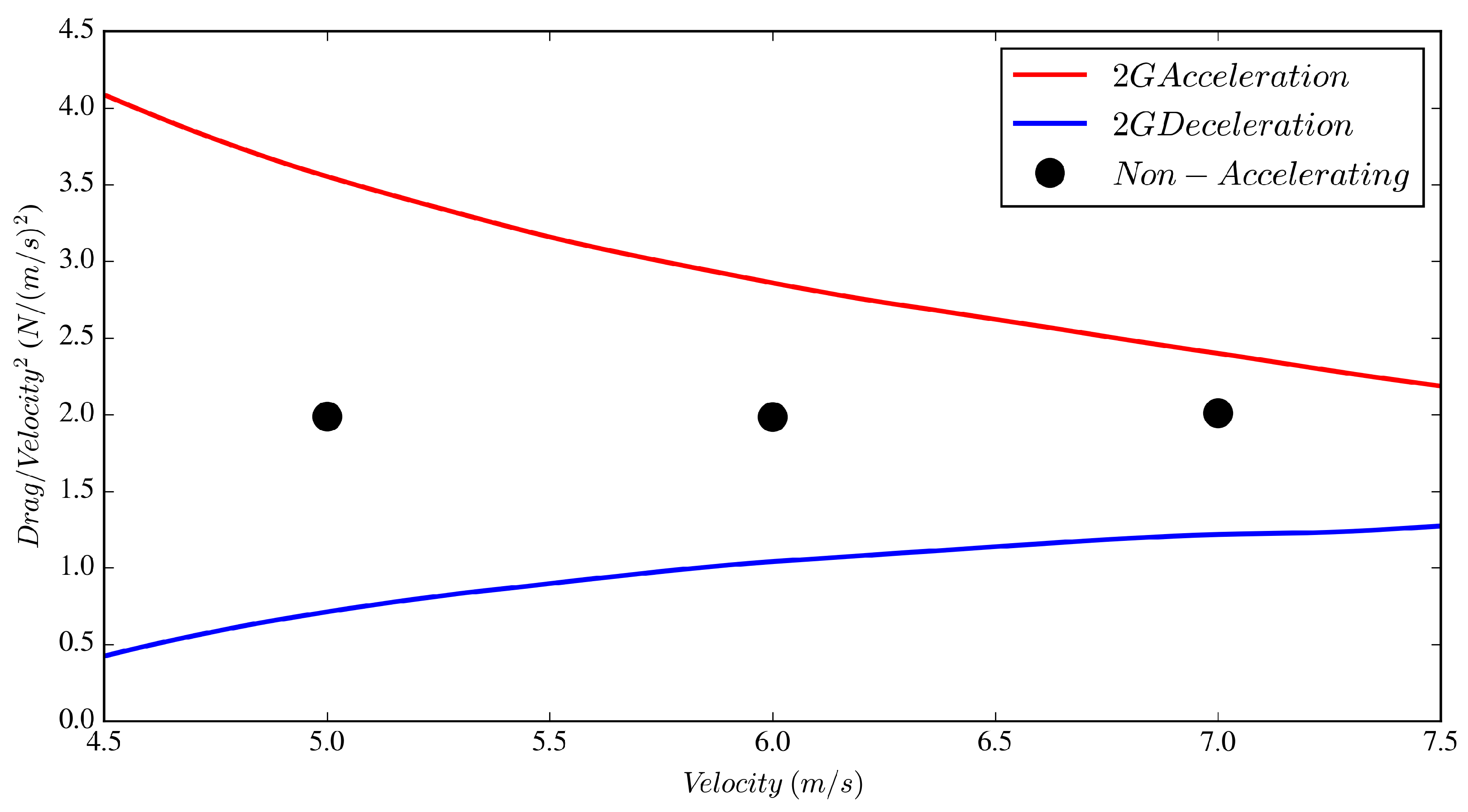
Figure 8 shows the variation of the drag force as a function of velocity for the accelerating and non-accelerating cases for . It may appear from Figure 8 that, although positive and negative accelerations have similar impacts on the drag force for , the effect of one is more dominant than the other depending on larger or smaller than 6 ; for example, the positive acceleration appears to have a larger effect on drag for , and vice versa. This may be deceiving, as this study was created to focus on the 6 velocity, and the inlet velocity was forced to vary between 0.5 and 11.5 . The closer we get to the inflection velocity ( changes sign), i.e., the further away from the mid-point velocity, the artifacts from velocity inflection may influence the results one way or the other. In support of this, Figure 3 demonstrates that the inflection velocity occurs near 5 and 7 . By non-dimensionalizing the body force by in Figure 9, the effect of the inflection velocity from the inlet signal is evident, where at the acceleration deceleration forces are nearly symmetrical and are skewed about the non-accelerating force at 5 and 7 . This further demonstrates that focus should be upon data at the intended reference velocity, however the authors concede that additional works are required. Data presented in Table 2 clearly indicate drag force deviations of −47% and +44% from the case for the , and cases, respectively, all at . values are also presented in Table 2 where the decelerating value of 1.92 is 44% larger than the non-accelerating flow and nearly four times larger than the accelerating case. These are interesting phenomena and are discussed further in Section 3.2.
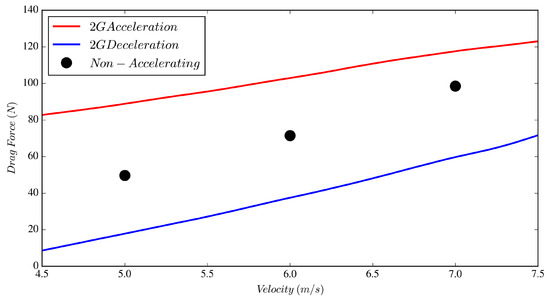
Figure 8.
Drag force on the cylinder versus for the decelerating, non-accelerating and accelerating cases.

Figure 9.
Drag force on the cylinder versus , non-dimensionalized by for the decelerating, non-accelerating and accelerating cases.
The Morison coefficient was calculated from Equation (1) by setting Part 2 of the equation equal to the non-accelerating drag force, and equal to ensemble averaged acceleration and deceleration forces, resulting in = 1.91 and = 1.77 for the decelerating and accelerating conditions, respectively. The discrepancy in the added viscous coefficients for decelerating and accelerating flow conditions (approximately 8%) is an interesting phenomenon, yet may be small enough to approximate as equivalent for vehicle dynamics modeling purposes. These discrepancies could be attributed to the body’s vorticity contribution affecting wake dynamics (vortex shedding). At this time, there is no information to support whether or not this discrepancy would be present at higher Reynolds numbers or different acceleration rates, insinuating that Equation (1) may require additional degrees of freedom to accurately model acceleration at varying Reynolds numbers.
3.2. Wake Structure
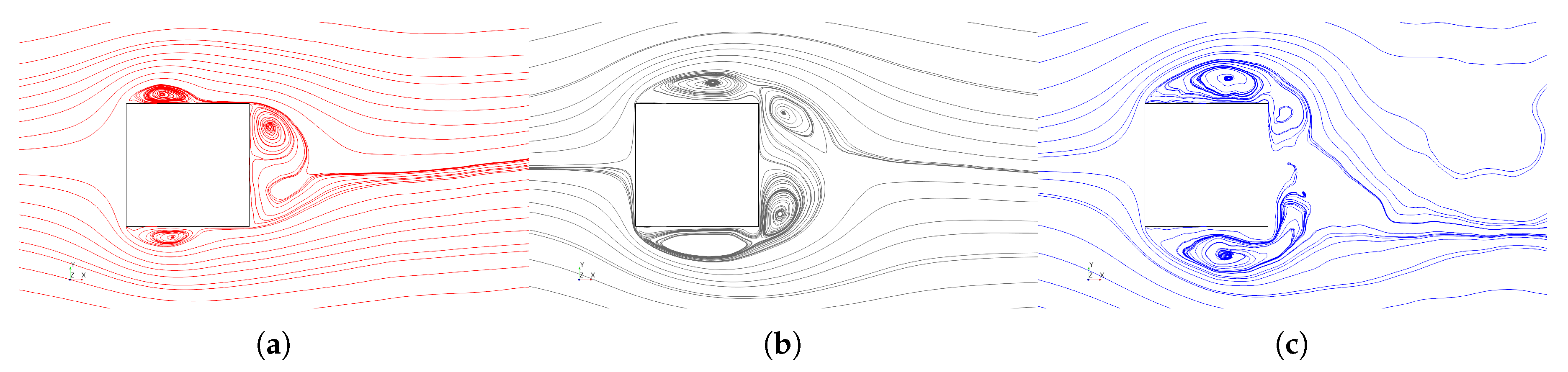
To investigate the viscous impacts of acceleration, several flow field quantities are discussed. First, Figure 10 shows ensemble averaged streamlines bounded to the center line plane of the channel () at a reference velocity of 6 corresponding to the cases , , and . Discernible differences can be observed between the accelerating (red), non-accelerating (or constant-velocity, black), and decelerating (blue) cases. Obviously, the three cases exhibit starkly different wakes; please note that the slight asymmetry observed for the zero acceleration case can be attributed to graphics rendering and seeding issues inherent to the hardware and software used in this study and can be ignored for all practical purposes. Besides this, the most noticeable differences can be observed with regard to the location and size of the leading edge vortex. The accelerating case has the smallest leading edge separation bubble with its center located at , and the recirculation at the rear of the cylinder is contained within . In addition, this case shows a reattachment of the leading edge separation on the cylinder surface making the rear recirculation in the cylinder wake clearly detached from the one off of the leading edge. Arguably, between the top and bottom vortices, the top one seems to be more dominant than the bottom one for this ensemble, and its center is slightly further upstream than the one on bottom. Compared to the accelerating case, the constant-velocity case has a larger leading edge recirculation with the center located further downstream and, at least, the top vortex is biased more towards the trailing edge. No flow reattachment on the cylinder surface is observed. The rear wake shows the presence of two alternating vortices of almost equal strength. The decelerating case has the largest leading edge separation and unlike the other two cases, the leading edge and rear re-circulations are somewhat merged.
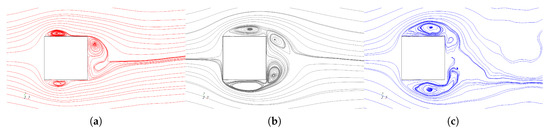
Figure 10.
Streamlines at cylinder center plane for: (a) ; (b) ; and (c) .
To complement these observations in further detail, ensemble averaged probe data were taken perpendicular to stream-wise flow at five stream-wise locations corresponding to ; these probe locations are illustrated in Figure 11.
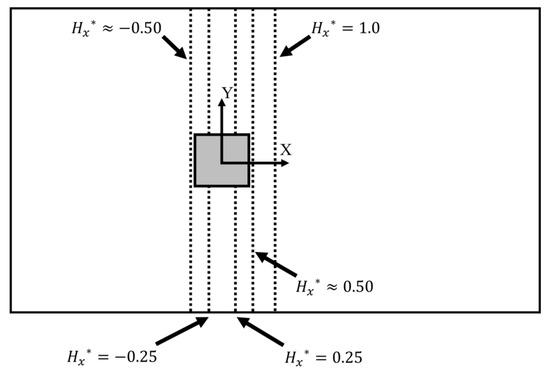
Figure 11.
Locations of the probe rakes reported. Note that dimensions are not to scale.
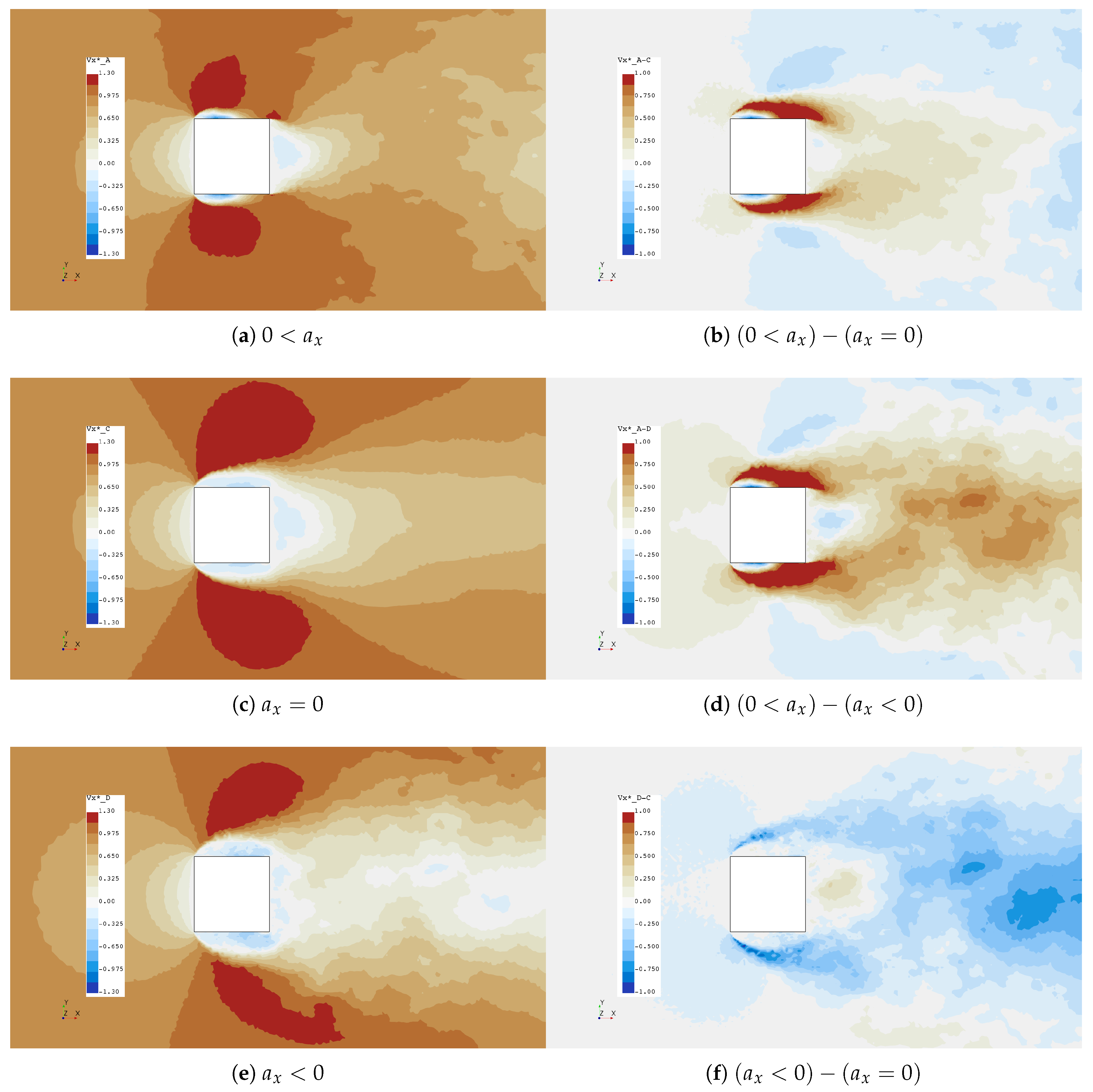
The variation in bow wake flow angle in the plane can be seen in Figure 12 where ensemble averaged data was sampled along (see Figure 11 for the location of the probe rakes) at the leading edge of the cylinder. As expected, the flow angle is orthogonal to the x-axis directly in front of the cylinder and when is , flow angles are approximately 27°, 20° and 12° for decelerating, non-accelerating and accelerating cases, respectively. Interestingly, the accelerating and non-accelerating cases have equivalent flow angle in the bow wake at approximately , and some asymmetry is also present in the accelerating bow wake. The variations in bow and downstream wakes are also apparent in Figure 13 where scalars and deltas clearly show that the accelerating case experiences reattachment on the sides of the cylinder and higher values of stream-wise velocity in the wake.
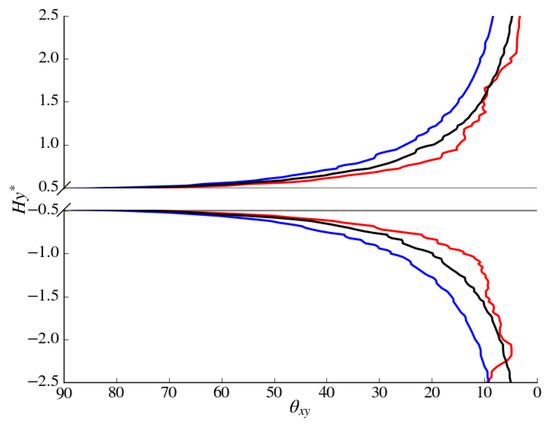
Figure 12.
Ensemble averaged flow angle in front of the cylinder at computed from and . The red, blue and black lines represent , and cases, respectively.
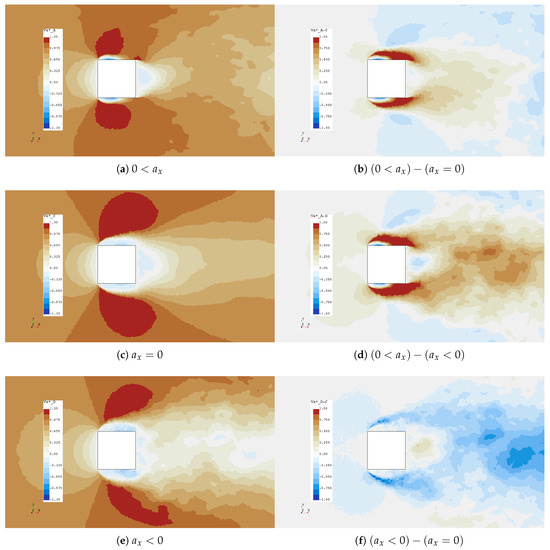
Figure 13.
scalar fields and deltas at cylinder center line.
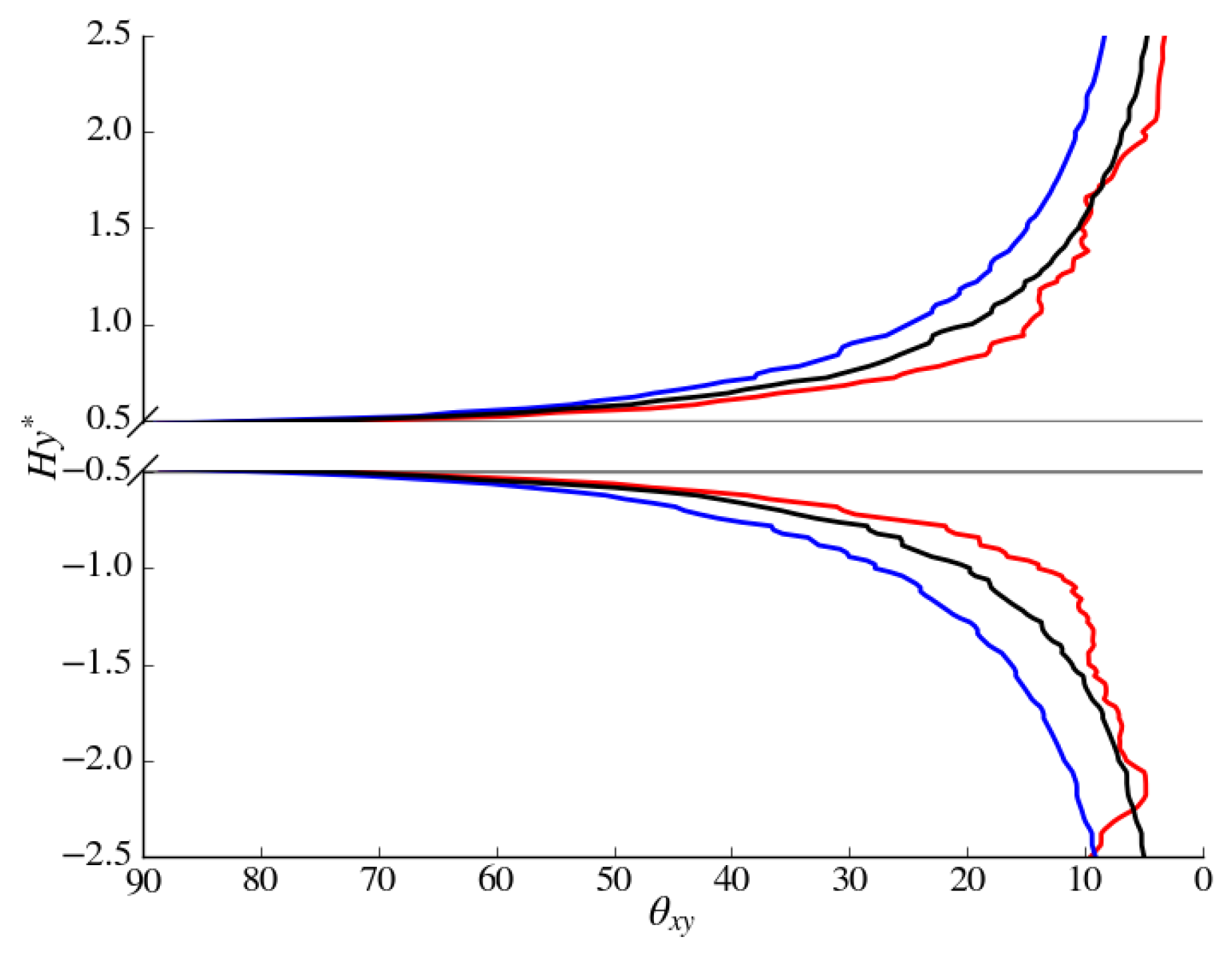
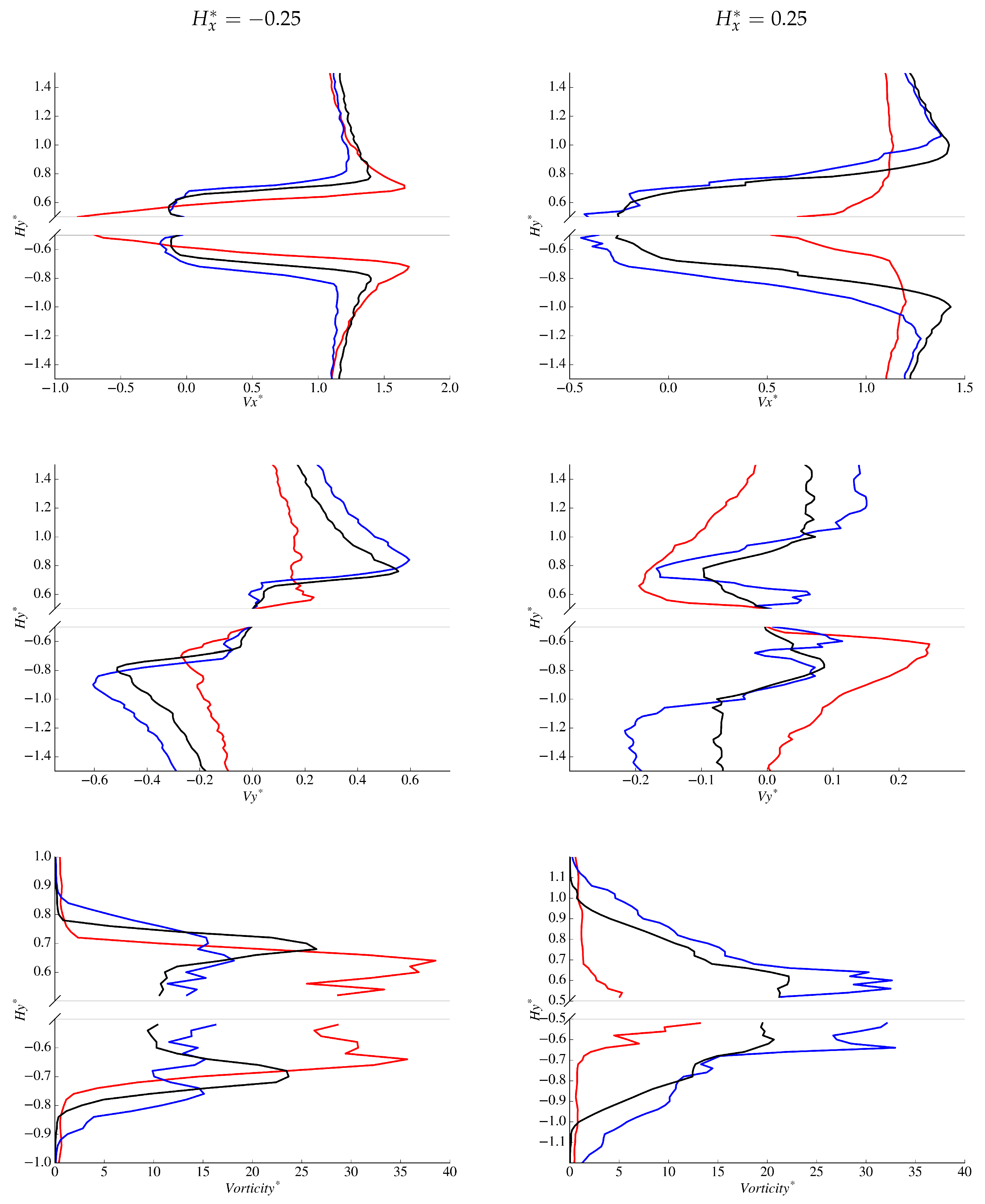
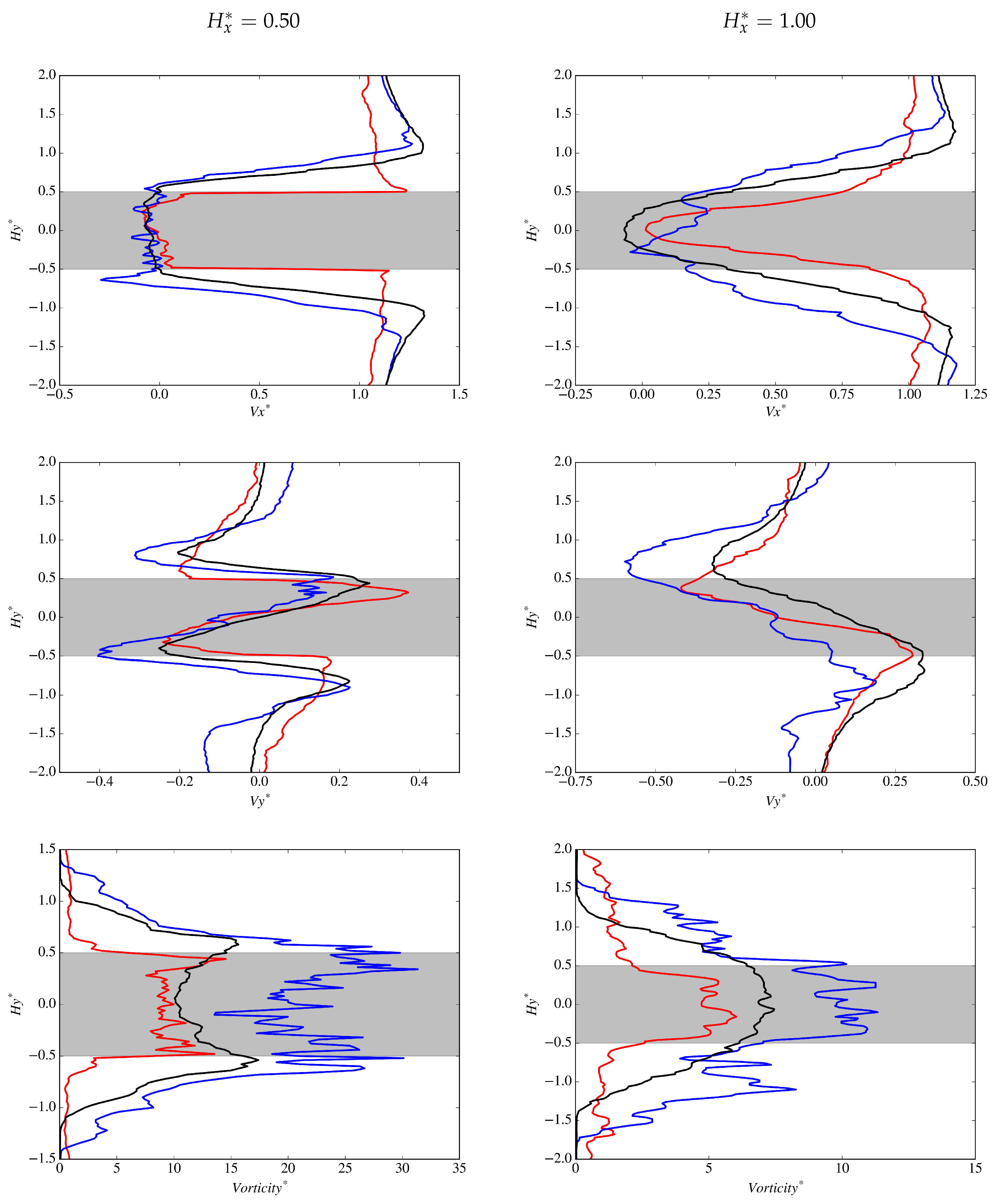
Wall-normal variations of and near the cylinder are presented in Figure 14, where a smaller bow wake is evident for the accelerating case at . In addition, has a negative component close to the wall indicating reversed flow and components are significantly smaller in comparison to other cases. At , the accelerating case appears to be nearly attached to the side walls of the cylinder as within . is small at , however the non-accelerating and decelerating cases appear to be predominately aligned with the free-stream at this location while the accelerating case has a tendency towards the cylinder. In the wake behind the cylinder (see Figure 15), the smaller accelerating wake is apparent at where values of are found very close to the cylinder walls. The decelerating wake size in comparison to the non-accelerating case is more apparent further down stream of the cylinder at for . Asymmetry of the wake is present in for both the accelerating and decelerating cases biased towards the bottom of the cylinder, although the accelerating asymmetry does appear to be smaller.

Figure 14.
Wall-normal variations of: (Top) non-dimensional streamwise velocity, ; (Middle) non-dimensional cross-stream velocity ; and (Bottom) non-dimensional vorticity magnitude at probe locations: = −0.25 (left); and = 0.25 (right). The red, blue and black lines represent , and cases, respectively.
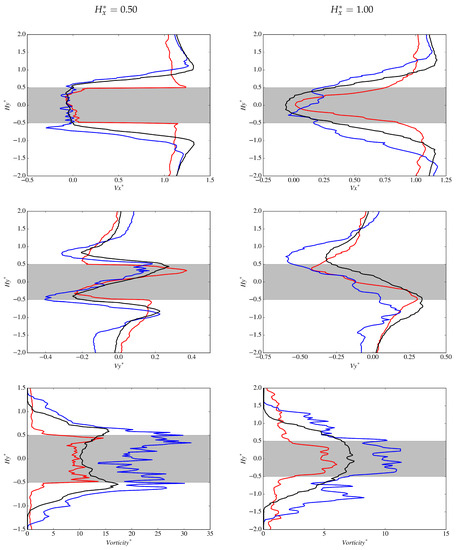
Figure 15.
Wake variations of: (Top) non-dimensional streamwise velocity, ; (Middle) non-dimensional cross-stream velocity ; and (Bottom) non-dimensional vorticity magnitude at probe location = 0.50. The red, blue and black lines represent , and cases, respectively.
The asymmetry in the ensemble averaged streamlines should not be confused with phase-averaging techniques employed by Lyn and Rodi [38], Cantwell and Coles [39] and others which were done to obtain ensemble averages of discrete vortex-shedding phases. The authors propose that the asymmetry is merely due to a slight deficiency of ensemble averaging, causing a visible shift in both the decelerating and accelerating wakes. Computational resources provided 33 total periods for this study, whereas Cantwell and Coles obtained more than 1.6 × 104 rotations at each position for their flying hotwire probe to obtain a complete phase-averaged dataset. Higher values indicate that an ideal ensemble averaged flowfield for the decelerating case could require significantly more periods than the other two cases. Furthermore, ensemble averaged vorticity scalars presented in Figure 16 appear as expected for a global mean (see Cantwell and Coles [39], Figure 21a) and do not appear to be an ensemble of constant phase (see Cantwell and Coles [39], Figure 21b). Nonetheless, the authors cannot deny the streamline asymmetries observed in Figure 10 but will carry on with further analysis and recommend this for future investigation when computational resources allow such.
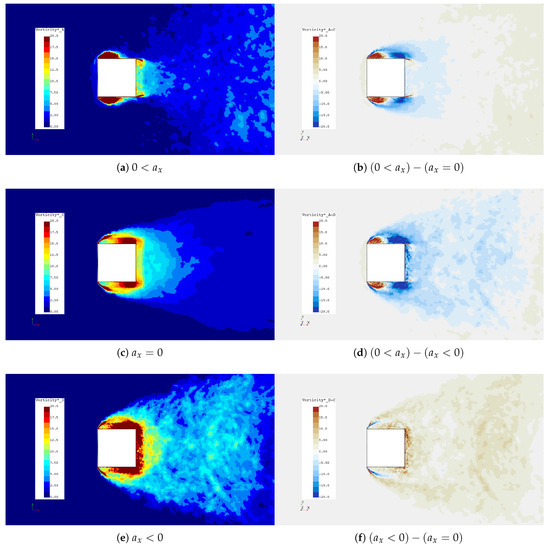
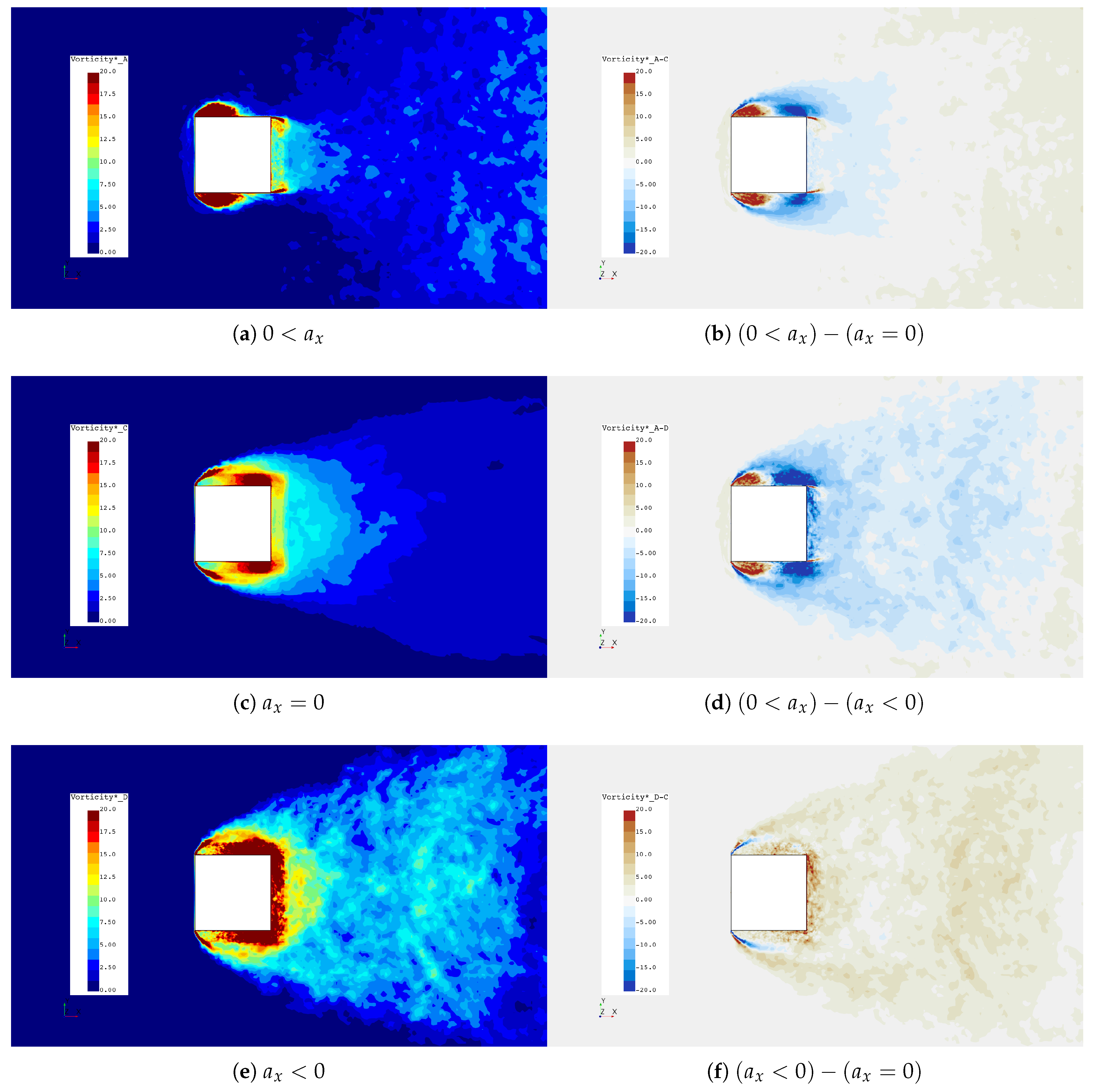
Figure 16.
scalars and deltas at cylinder center line.
Figure 16 shows that during acceleration there is a reduction in overall vorticity, while during deceleration there is an increase. This change in overall vorticity near the cylinder can be explained through flux density of vorticity at the cylinder surface, initially demonstrated by Morton [40] and recently applied by Konstantinidis and Bouris [16] to describe vortex patterns in the wakes of oscillating cylinders via Equation (3), where is the vorticity vector, is the surface-normal unit vector, p is the pressure, v is the kinematic viscosity and V is the relative velocity between the cylinder and the fluid.
Investigation of Equation (3) indicates that the vorticity flux density is dependent on both tangential pressure gradient and free stream acceleration. The former contribution is present for and the latter either decreases or increases the contribution of vorticity for and , respectively. Vorticity scalars in Figure 16 and Figure 17 support this notion where has significantly less vorticity near the faces of the cylinder and has a significant increase in vorticity. The downstream face of the cylinder also sees changes in vorticity during each case and is linked to the first component of Equation (3) through the variation of for each respective case. During , was significantly lower, thus the magnitude of vorticity on the downstream surface is lower while experienced the opposite effect. Only half of the vorticity generated at the wall ends up downstream in the Kármán vortices, as indicated by Griffin and Ramburg [41], and the deltas in Figure 16 show that only occur downstream of the cylinder between cases.
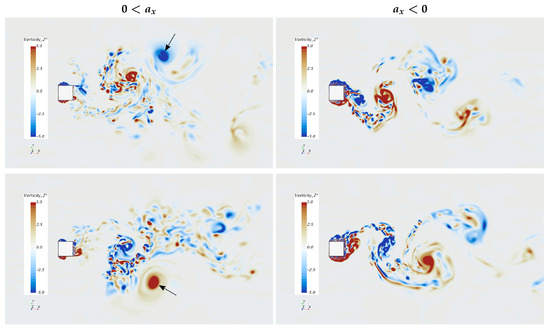
Figure 17.
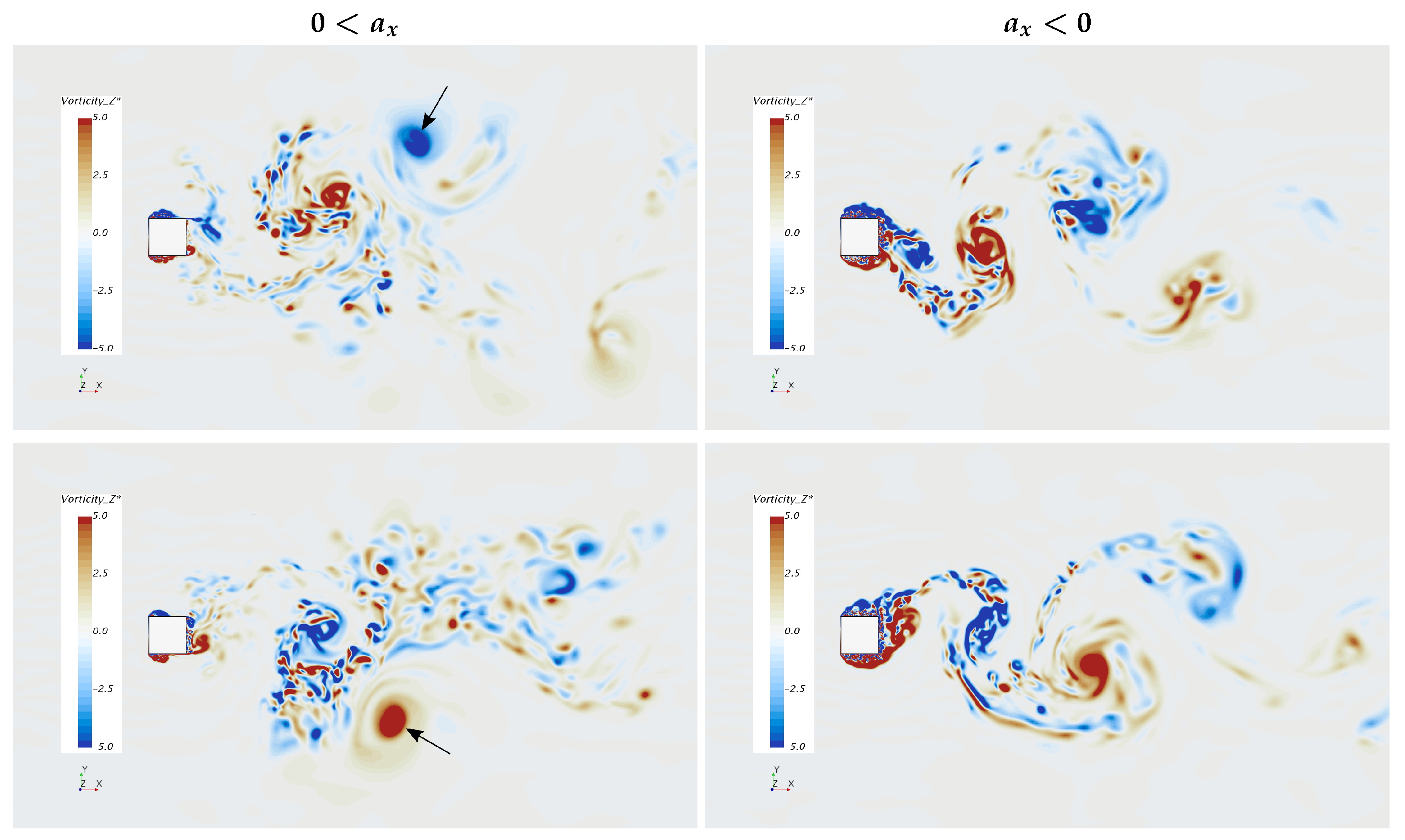
Instantaneous non-dimensional vorticity Z component at cylinder center plane () for and recorded at . The top and bottom rows represent flow approximately 180° out of phase.
Wall-normal variations of vorticity near the cylinder at in Figure 14 may seem to contradict Equation (3), but the increase of vorticity in the region for the accelerating case is merely due to a stronger leading edge circulation at this location. At , wall-normal vorticity distributions support Equation (3) with a reduction of vorticity for the accelerating case and an increase for the decelerating case. In the wake, Equation (3) continues to be supported with a reduction in ensemble averaged vorticity directly behind the cylinder at for the accelerating case and an increase for deceleration.
The formation region was defined by Bloor [42] as the point closest to the test object at which oscillating downstream wake characteristics are still detected by hot-wire. This is also the point where flow outside of the wake first crosses the x-axis, drawn cross-stream by the formation of vortices near the cylinder. According to Gerrard [43], the size of the formation region is governed by an equilibrium of entrainment into the shear layer and reversed flow replenishing free stream fluid towards the cylinder.
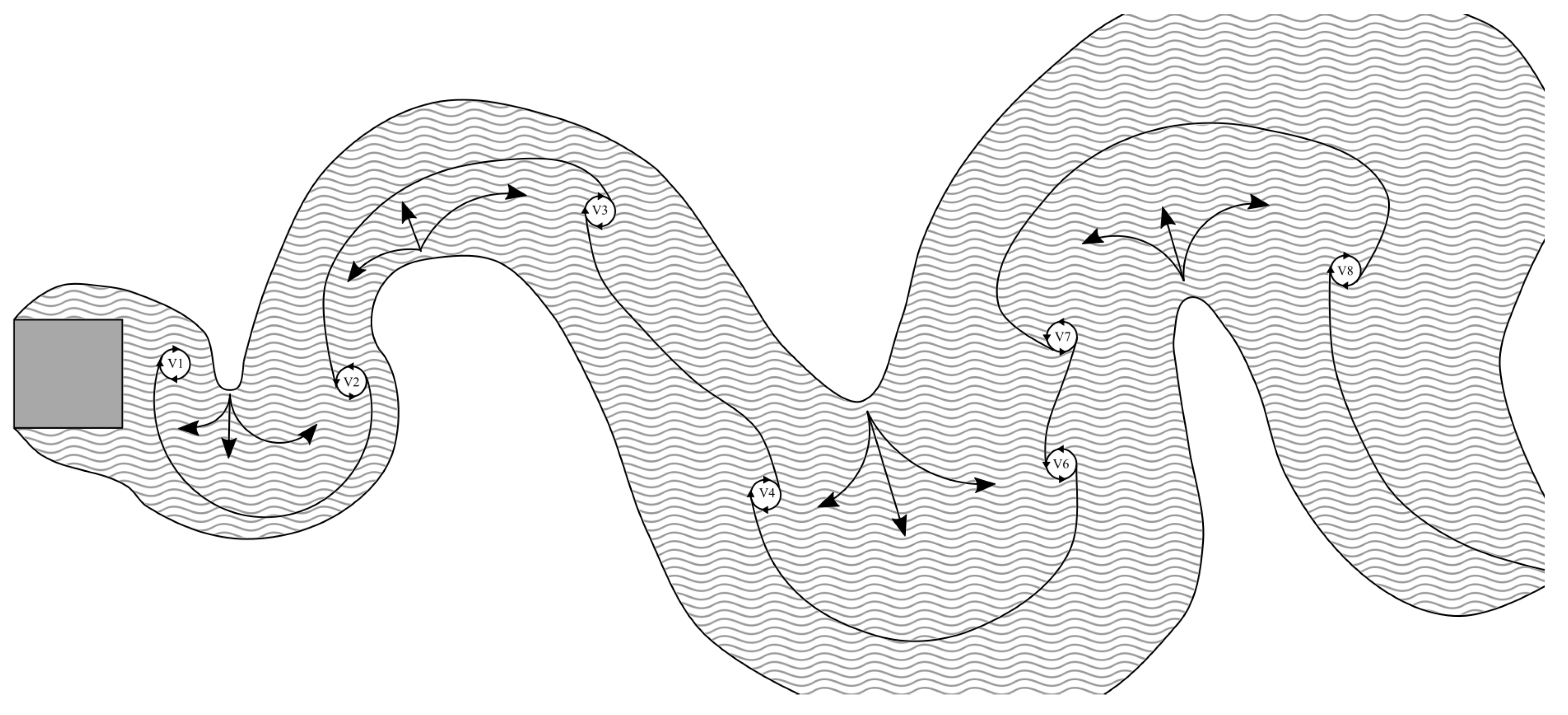
Figure 18 is a cartoon of vorticity (wavy grey area), vortex core locations (depicted as circles) and entrainment (direction depicted as arrows) during a single vortex oscillation phase. This cartoon was inspired by cartoons from both Cantwell and Coles, and Gerrard, and drawn by digitally overlaying CFD results. Liberties were taken to aid in explaining flow features. The lines connecting each vortex represent filament lines to visualize the growing and shrinking of shear layers between each vortex oscillation.
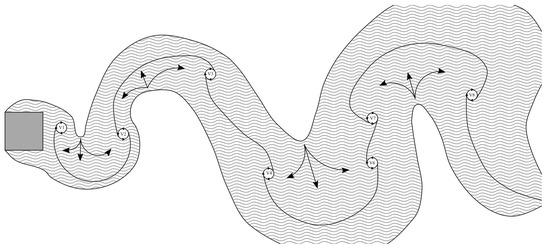
Figure 18.
A simple cartoon demonstrating a single phase of vortex shedding and the region of vorticity (depicted as grey waves) surrounding the cylinder and wake.
This led us to apply the previously discussed formation region mechanisms to the accelerating flow case. During acceleration of the free stream velocity, Vortex 1 in Figure 18 should have a higher x-component of velocity than Vortex 7 compared to the non accelerating case. Each successive vortex that is created during acceleration will have a higher x-component velocity, which should cause the vortices to stack up on one another along the x-axis. In addition, less vorticity is created by the body (see Equation (3)) and lower indicates less free stream flow crossing the x-axis near the body, provoking instability downstream of the cylinder. The accelerating cylinder has a higher drag force, yet a smaller near body wake, along with lower vorticity production. This, in conjunction with different x-component velocities of vortex cores, requires higher cross stream entrainment down stream, apparently driving every other vortex core away from the x-axis as seen in Figure 17 (indicated with an arrow).
The opposite is true for the decelerating case, where Vortex 1 of Figure 18 would have a lower stream-wise velocity than Vortex 7 and each successive vortex created near the cylinder would have even lower stream-wise components. Near body vorticity is higher ,which promotes a higher value, causing the formation region and wake to be larger. Due to these factors, vortex cores remain closer to the x-axis in comparison to the accelerating case.
4. Conclusions
This study aimed to develop a simulation technique for obtaining body forces and flow fields for a bluff body undergoing longitudinal acceleration and deceleration with an end application towards dynamic handling models of road vehicles. Oscillation of the inlet velocity via a forcing function simulated constant accelerating and decelerating free-stream conditions, which were ensemble averaged over 30 discrete instances of to obtain averaged flow fields for each respective case. In comparison to steady inlet conditions, several body force and flow field variations were observed for accelerating and decelerating conditions. First, the body drag increased 44% and decreased 47% for the accelerating and decelerating cases over steady free-stream conditions, respectively. Second, the fluctuating lift force () decreased 60% and increased 46% during acceleration and deceleration, respectively, in comparison to steady free-stream conditions, indicating that complicated turbulent phenomenon were present. Third, the near-body leading edge and downstream wake were both significantly smaller during acceleration, causing reattachment of flow on the top and bottom sides of the cylinder. During deceleration, the leading edge wake grew away from the cylinder in comparison to non-accelerating flow leading to a wider wake behind the cylinder. Fourth, further investigation revealed an imbalance of vorticity, driven by tangential pressure gradients and longitudinal free-stream acceleration conditions causing a reduction in near wall vorticity for the accelerating case and an increase for the decelerating case. These changes in the leading edge separation and vorticity along with variations in free stream velocity during vortex core formation behind the cylinder caused an imbalance in the accelerating wake, displacing every other vortex core away from the x-axis. Conversely, the surplus of vorticity during deceleration and free-stream velocity variation caused vortex cores to align with the x-axis. Finally, the Morison coefficient was calculated to be used with Equation (1) for prediction of the drag of the square cylinder undergoing acceleration and deceleration.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.P. and M.U.; methodology, B.P. and M.U.; software, B.P.; validation, B.P. and M.U.; formal analysis, B.P. and M.U.; investigation, B.P. and M.U.; resources, B.P. and M.U.; data curation, B.P.; writing—original draft preparation, B.P. and M.U.; writing—review and editing, B.P. and M.U.; visualization, B.P.; supervision, M.U.; and project administration, M.U.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge UNC Charlotte’s high performance computing group (URC) and College of Engineering MOSAIC Computing for their continuous supports.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Panton, R.L. Incompressible Flow, 3rd ed.; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mohrfeld-Halterman, J.; Uddin, M. High fidelity quasi steady-state aerodynamic model effects on race vehicle performance predictions using multi-body simulation. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2016, 54, 963–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buat, P.L.G.D. Principles D’hydraulique; F. Didot: Paris, France, 1786. [Google Scholar]
- Stokes, G.G. On the Effect of the Internal Friction of Fluids on the Motion of Pendulums. Trans. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1850, IX, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Morison, J. The Force Distribution Exerted by Surface Waves on Piles; Technical Report; California University Berkeley Wave Research Lab: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Fackrell, S.A. Study of the Added Mass of Cylinders and Spheres. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Windsor, Windsor, ON, Canada, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fernando, J.N.; Marzanek, M.; Bond, C.; Rival, D.E. On the separation mechanics of accelerating spheres. Phys. Fluids 2017, 29, 037102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Rho, J.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, D.H. Fundamental studies on free stream acceleration effects on drag force in bluff bodies. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2011, 25, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roohani, H. Aerodynamic Effects of Accelerating Object in Air. Ph.D. Thesis, University of the Witwatersand, Johannesburg, South Africa, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Johari, H. Effects of acceleration on turbulent jets. Phys. Fluids 1996, 8, 2185–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearman, P.; Obasaju, E. A Study of Forces, Circulation and Vortex Patterns around A Circular-Cylinder in Oscillating Flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1988, 119, 297–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidis, E.; Balabani, S.; Yianneskis, M. The effect of flow perturbations on the near wake characteristics of a circular cylinder. J. Fluids Struct. 2003, 18, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidis, E.; Balabani, S. Flow structure in the locked-on wake of a circular cylinder in pulsating flow: Effect of forcing amplitude. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2008, 29, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidis, E.; Bouris, D. Effect of nonharmonic forcing on bluff-body vortex dynamics. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 79, 045303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidis, E.; Liang, C. Dynamic response of a turbulent cylinder wake to sinusoidal inflow perturbations across the vortex lock-on range. Phys. Fluids 2011, 23, 075102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidis, E.; Bouris, D. Vortex synchronization in the cylinder wake due to harmonic and non-harmonic perturbations. J. Fluid Mech. 2016, 804, 248–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, B. On Accelerating Road Vehicle Aerodynamics. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of North Carolina at Charlotte, Charlotte, NC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gritskevich, M.S.; Garbaruk, A.V.; Schütze, J.; Menter, F.R. Development of DDES and IDDES Formulations for the k-ω Shear Stress Transport Model. Flow Turbul. Combust. 2012, 88, 431–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shur, M.; Spalart, P.; Travin, A. A hybrid RANS-LES approach with delayed-DES and wall-modelled LES capabilities. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2008, 29, 1638–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menter, F. Two-equation eddy-viscosity modeling for engineering applications. AIAA J. 1994, 32, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Ding, G.; He, Y.; Wu, J.; Le, J. Assessment of the IDDES method acting as wall-modeled LES in the simulation of spatially developing supersonic flat plate boundary layers. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2017, 12, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trias, F.X.; Gorobets, A.; Olivia, A. Turbulent flow around a square cylinder at Reynolds number 22000: A DNS study. Comput. Fluids 2015, 123, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodi, W. Comparison of LES and RANS calculations of the flow around bluff bodies. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1997, 69, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohankar, A.; Davidson, L.; Norberg, C. Large eddy simulation of flow past a square cylinder: Comparison of different subgrid scale models. J. Fluids Eng. 2000, 122, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodi, W.; Ferziger, J.H.; Breuer, M.; Pourquie, M. Status of large eddy simulation: Results of a workshop. J. Fluids Eng. Trans. ASME 1997, 119, 248–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; Mohebbian, A.; Kriegseis, J.; Rival, D. Rapid flow separation for transient inflow conditions versus accelerating bodies: An investigation into their equivalency. J. Fluids Struct. 2013, 40, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M. Smoothing and Differentiation of Data by Simplified Least Squares Procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrin, N.; Benhamadouche, S.; Laurence, D.; Prosser, R. A synthetic-eddy-method for generating inflow conditions for large-eddy simulations. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2006, 27, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennekes, H.; Lumley, J.L. A First Course in Turbulence; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Celik, I.; Klein, M.; Freitag, M.; Janicka, J. Assessment measures for URANS/DES/LES: An overview with applications. J. Turbul. 2006, 7, N48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gant, S. Quality and Reliability Issues with Large-Eddy Simulation; Report RR656; Health and Safety Executive: Bootle, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kuczaj, A.; Komen, E.; Loginov, M. Large-Eddy Simulation study of turbulent mixing in a T-junction. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2010, 240, 2116–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, D.C. Turbulence Modeling for CFD, 3rd ed.; DCW Industries Inc.: La Canada, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lyn, D.A.; Rodi, W. The flapping shear layer formed by flow separation from the forward corner of a square cylinder. J. Fluid Mech. 1994, 267, 353–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Tamura, T. Large-eddy simulations of flow past a square cylinder using structured and unstructured grids. Comput. Fluids 2016, 137, 36–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B. Some effects of turbulence scale on the mean forces on a bluff body. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1975, 1, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, H. Fundamental Study of Bluff Body Aerodynamics. Ph.D. Thesis, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lyn, D.A.; Einav, S.; Rodi, W.; Park, J.H. A Laser-Doppler Velocimetry Study of the Ensemble-Averaged Characteristics of the Turbulent Near Wake of a Square Cylinder. J. Fluid Mech. 1995, 304, 285–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantwell, B.; Coles, D. An experimental study of entrainment and transport in the turbulent near wake of a circular cylinder. J. Fluid Mech. 1983, 136, 321–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, B. The generation and decay of vorticity. Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn. 1984, 28, 277–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, O.M.; Ramberg, S.E. The vortex-street wakes of vibrating cylinders. J. Fluid Mech. 1974, 66, 553–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloor, M.S. The transition to turbulence in the wake of a circular cylinder. J. Fluid Mech. 1964, 19, 290–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerrard, J.H. The mechanics of the formation region of vortices behind bluff bodies. J. Fluid Mech. 1966, 25, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).