Flow Anisotropy due to Thread-Like Nanoparticle Agglomerations in Dilute Ferrofluids
Abstract
1. Introduction
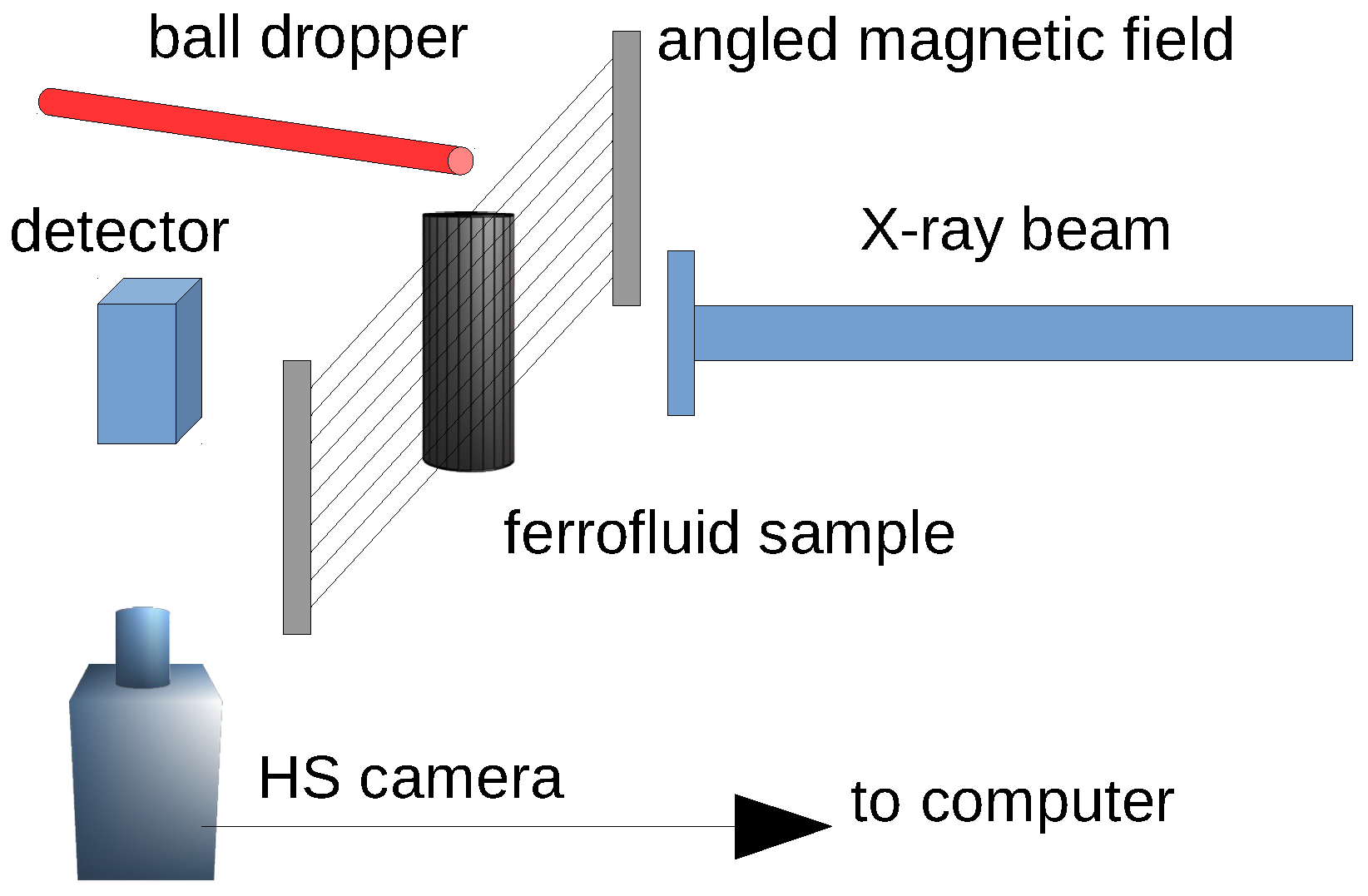
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview
2.2. Derivation of Model Predictions
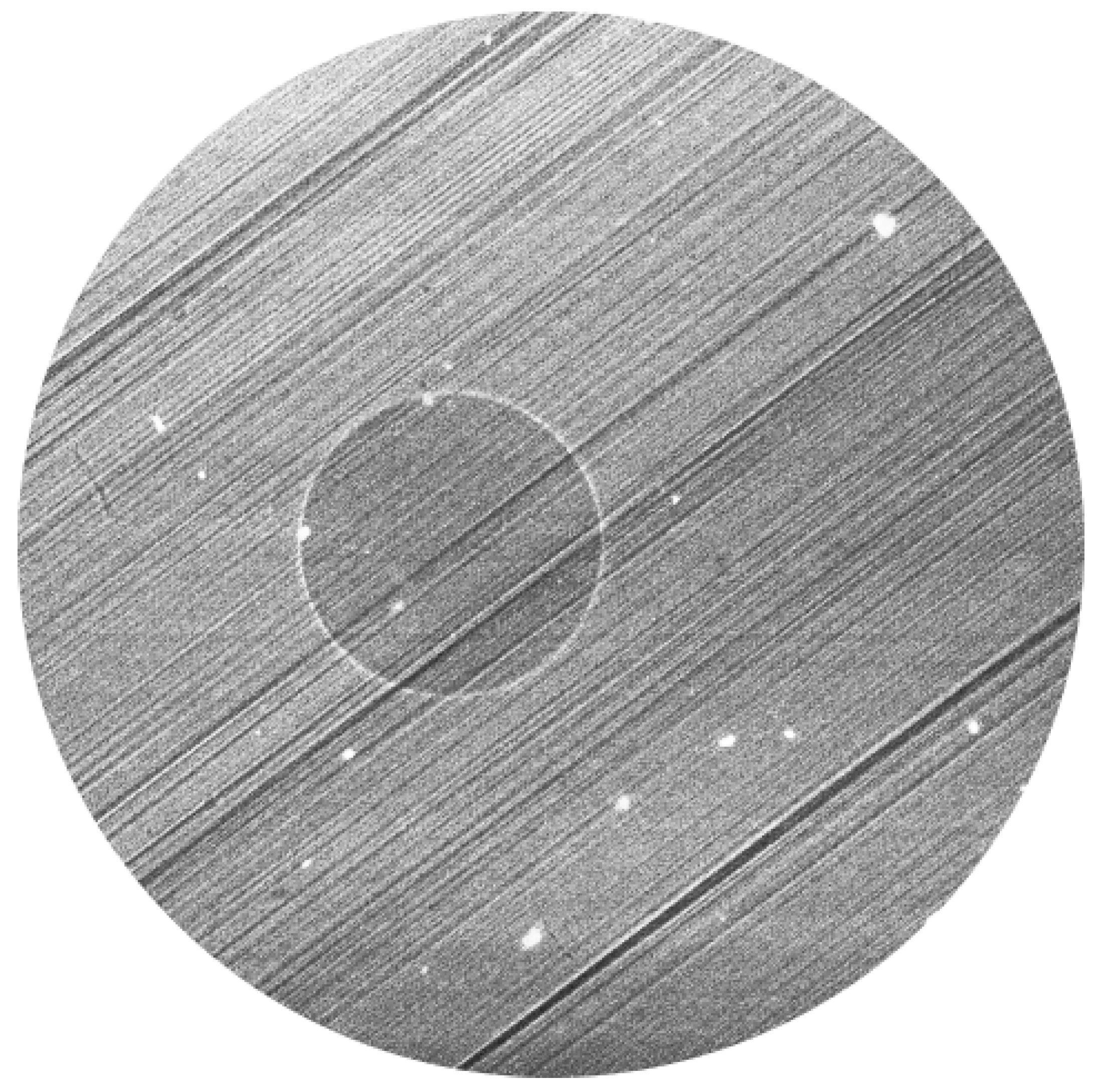
2.3. Experiment
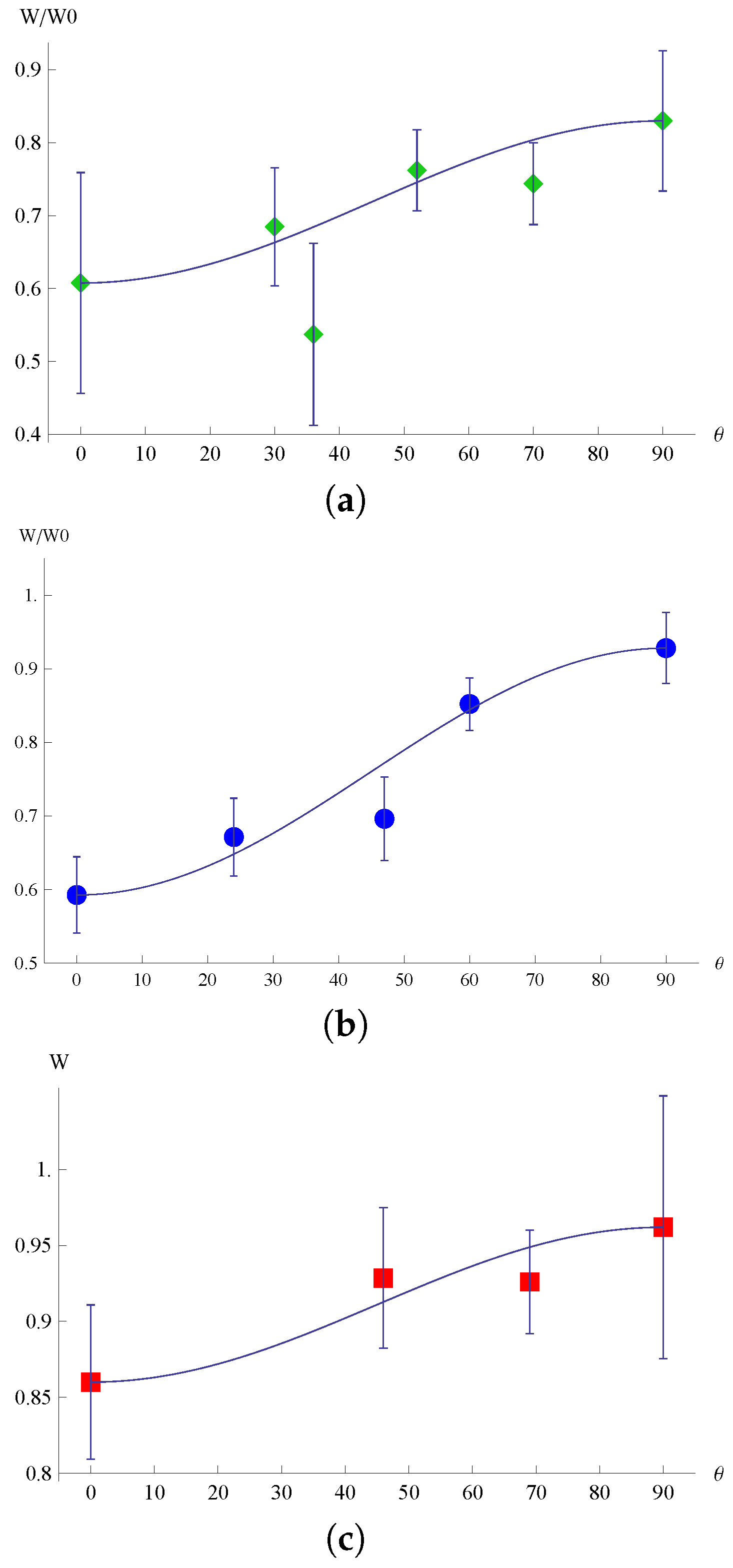
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rinaldi, C.; Chaves, A.; Elborai, S.; He, X.; Zahn, M. Magnetic fluid rheology and flows. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 10, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Diaz, I.; Rinaldi, C. Recent progress in ferrofluids research: Novel applications of magnetically controllable and tunable fluids. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 8584–8602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odenbach, S. (Ed.) Ferrofluids: Magnetically Controllable Fluids and Their Applications; Lecture Notes in Physics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; Volume 594. [Google Scholar]
- Raj, K.; Hirota, Y.; Black, T. Current and emerging applications of ferrofluids. Magnetohydrodynamics 2013, 49, 568–581. [Google Scholar]
- Trahms, L. Biomedical Applications of Magnetic Nanoparticles. In Colloidal Magnetic Fluids: Basics, Development and Application of Ferrofluids; Lecture Notes in Physics; Odenbach, S., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 763, pp. 327–358. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, J.; Wolf, D.; Odenbach, S. A rheological and microscopical characterization of biocompatible ferrofluids. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 354, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyadevan, B.; Torigoe, T.; Nakatsuka, K.; Nakatani, I.; Fujita, T.; Oka, H. X-ray image analysis and ultramicroscope study of magnetic fluids used as working liquid in heat transfer experiments. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 85, 5968–5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsuka, K.; Jeyadevan, B.; Akagami, Y.; Torigoe, T.; Asari, S. Visual observation of the effect of magnetic field on moving air and vapor bubbles in a magnetic fluid. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 201, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Scardovelli, R.; Trubatch, A.; Yecko, P. Numerical, experimental, and theoretical investigation of bubble aggregation and deformation in magnetic fluids. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 81, 016302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yecko, P.; Lee, W.K.; Trubatch, A.D.; Vieira, M. Drag enhancement due to macro-chains in uniformly magnetized ferrofluids. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 1288–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, C.F. Observation of association in a ferromagnetic colloid. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1975, 52, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horng, H.E.; Hong, C.Y.; Yang, S.Y.; Yang, H.C. Novel properties and applications in magnetic fluids. J. Phys. Chem. Sol. 2001, 62, 1749–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.A. Aggregation of water-based magnetic liquids observed with the polarizing microscope. J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 1985, 18, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taketomi, S.; Takahashi, H.; Inaba, N.; Miyajima, H. Experimental and theoretical investigations on agglomeration of magnetic colloidal particles in magnetic fluids. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1991, 60, 1689–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isimoto, J.; Okubo, M.; Higashitani, S.K.M. Bubble behavior in magnetic fluid under a nonuniform magnetic field. JSME Int. J. B Fluids Therm. Eng. 1995, 38, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashtovoi, V.; Kovalev, M.; Reks, A. Instabilities of bubbles and droplets flows in magnetic fluids. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 289, 350–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenckhan, W.; Elias, F.; Hutzler, S.; Weaire, D.; Janiaud, E.; Bacri, J.C. Bubble size control and measurement in the generation of ferrofluid foams. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 10078–10083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Holm, C.; Muller, H.W. Boundary condition effects in the simulation study of equilibrium properties of magnetic dipolar fluids. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 119, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedenmann, A.; Heinemann, A. Field-induced ordering phenomena in ferrofluids observed by small-angle neutron scattering. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 289, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, D. Review of agglomeration in ferrofluids. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1980, 16, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butter, K.; Bomans, P.; Frederik, P.; Vroege, G.; Philipse, A. Direct observation of dipolar chains in iron ferrofluids by cryogenic electron microscopy. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacri, J.C.; Salin, D. Optical scattering on ferrofluid agglomerates. J. Phys. Lett. 1982, 34, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Klokkenburg, M.; Erné, B.H.; Meeldijk, J.D.; Wiedenmann, A.; Petukhov, A.V.; Dullens, R.P.A.; Philipse, A.P. In situ imaging of field-induced hexagonal columns in magnetite ferrofluids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 185702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andelman, D.; Rosensweig, R.E. The Phenomenology of Modulated Phases: From Magnetic Solids and Fluids to Organic Films and Polymers. In Polymers, Liquids and Colloids in Electric Fields: Interfacial Instabilities, Orientation and Phase Transitions; Tsori, Y., Steiner, U., Eds.; Soft Condensed Matter; World Scientific: Singapore, 2009; Volume 2, pp. 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.K. X-ray microtomography of field-induced macro-structures in a ferrofluid. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 2525–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, K.; Doi, M. Theory of agglomeration of ferromagnetic particles in magnetic fluids. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1983, 52, 2810–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubarev, A.Y.; Iskakova, L.Y. To the theory of rheological properties of ferrofluids: Influence of drop-like aggregates. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2004, 343, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odenbach, S.; Raj, K. The influence of large particles and agglomerates on the magnetoviscous effect in ferrofluids. Magnetohydrodynamics 2000, 36, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurm, S.; Odenbach, S. Particle size distribution as key parameter for the flow behavior of ferrofluids. Phys. Fluids 2003, 15, 1658–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.K.; Ilavsky, J. Particle size distribution in ferrofluid macro-clusters. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 330, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Quinones, D.I.; Raj, K.; Rinaldi, C. A comparison of the magnetorheology of two ferrofluids with different magnetic field-dependent chaining behavior. Rheol. Acta 2013, 52, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantrell, R.; Sidhu, J.; Bissell, P.; Bates, P. Dilution induced instability in ferrofluids. J. Appl. Phys. 1982, 53, 8341–8343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerth-Noritzsch, M.; Borin, D.Y.; Odenbach, S. Anisotropy of the magnetoviscous effect in ferrofluids containing nanoparticles exhibiting magnetic dipole interaction. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2011, 23, 346002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertelj, A.; Resetic, A.; Gyergyek, S.; Makovec, D.; Copic, M. Anisotropic microrheological properties of chain-forming magnetic fluids. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Puri, I.K. Soft polymer magnetic nanocomposites: Microstructure patterning by magnetophoretic transport and self-assembly. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 2024–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosensweig, R.E.; Keiser, R.; Miskolczy, G. Viscosity of magnetic fluid in a magnetic field. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1969, 29, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shliomis, M.I. Effective viscosity of magnetic suspensions. Sov. Phys. JETP 1972, 34, 1291–1294. [Google Scholar]
- Rosensweig, R.E. Ferrohydrodynamics; Cambridge University Press (Dover): New York, NY, USA, 1984 (1997).
- De Gennes, P.G.; Pincus, P.A. Pair correlations in a ferromagnetic colloid. Z. Phys. B Condens. Matter 1970, 11, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosensweig, R. Towards ferrofluids with enhanced magnetization. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McTague, J.P. Magnetoviscosity of magnetic colloids. J. Chem. Phys. 1969, 51, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiyama, S.; Satoh, A. Rheological properties of magnetic fluids with the formation of clusters: Analysis of simple shear flow in a strong magnetic field. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1989, 127, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felicia, L.; Vinod, S.; Philip, J. Recent advances in magnetorheology of ferrofluids (magnetic nanofluids)—A critical review. J. Nanofluids 2016, 5, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, F.R.; Rosa, A.P.; Dias, N.J. Rheology of a very dilute magnetic suspension with micro-structures of nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 397, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linke, J.; Odenbach, S. Anisotropy of the magnetoviscous effect in a ferrofluid with weakly interacting magnetic nanoparticles. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2015, 27, 176001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohmen, E.; Borin, D.; Zubarev, A. Magnetic field angle dependent hysteresis of a magnetorheological suspension. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 443, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, G.K. Slender-body theory for particles of arbitrary cross-section in Stokes flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1970, 44, 419–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauga, E.; Powers, T.R. The hydrodynamics of swimming microorganisms. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2009, 72, 096601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, T.A. Ferrofluid Flow Phenomena. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, June 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cali, A. Magnetoviscous Effects of Magnetized Particle Threads in Magnetized Ferrofluids. Master’s Thesis, Montclair State University, Montclair, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
| Configuration | ||
|---|---|---|
| EFH-1 with B magnet | 0.76 | 0.58 |
| EFH-1 with C magnet | 0 .47 | 1.31 |
| P2XD with C magnet | 0.92 | 0.13 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cali, A.; Lee, W.-K.; Trubatch, A.D.; Yecko, P. Flow Anisotropy due to Thread-Like Nanoparticle Agglomerations in Dilute Ferrofluids. Fluids 2017, 2, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids2040067
Cali A, Lee W-K, Trubatch AD, Yecko P. Flow Anisotropy due to Thread-Like Nanoparticle Agglomerations in Dilute Ferrofluids. Fluids. 2017; 2(4):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids2040067
Chicago/Turabian StyleCali, Alexander, Wah-Keat Lee, A. David Trubatch, and Philip Yecko. 2017. "Flow Anisotropy due to Thread-Like Nanoparticle Agglomerations in Dilute Ferrofluids" Fluids 2, no. 4: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids2040067
APA StyleCali, A., Lee, W.-K., Trubatch, A. D., & Yecko, P. (2017). Flow Anisotropy due to Thread-Like Nanoparticle Agglomerations in Dilute Ferrofluids. Fluids, 2(4), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids2040067




