N-Alkylhydantoins as New Organogelators and Their Ability to Create Thixotropic Mixed Molecular Organogels
Abstract
1. Introduction
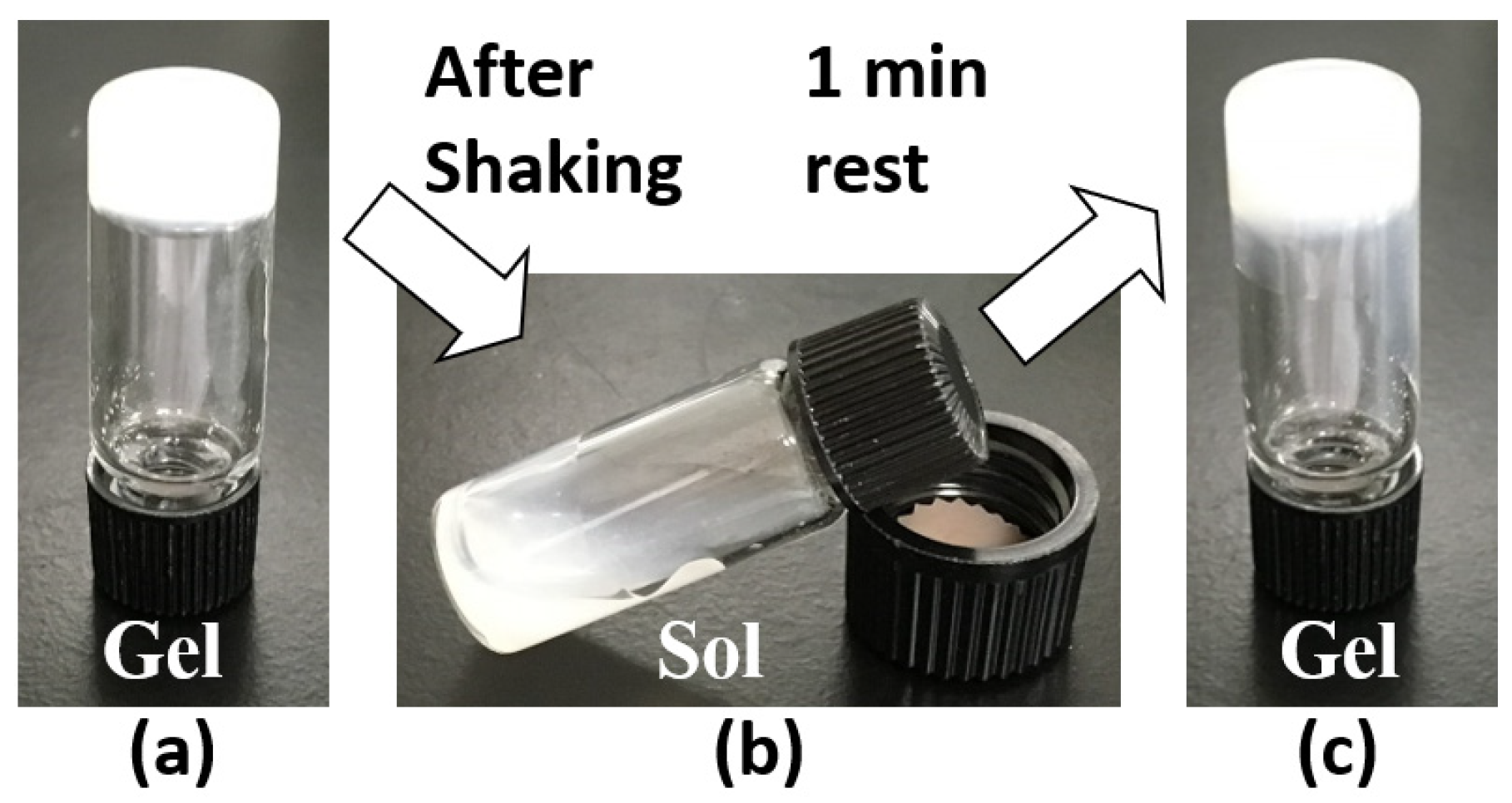
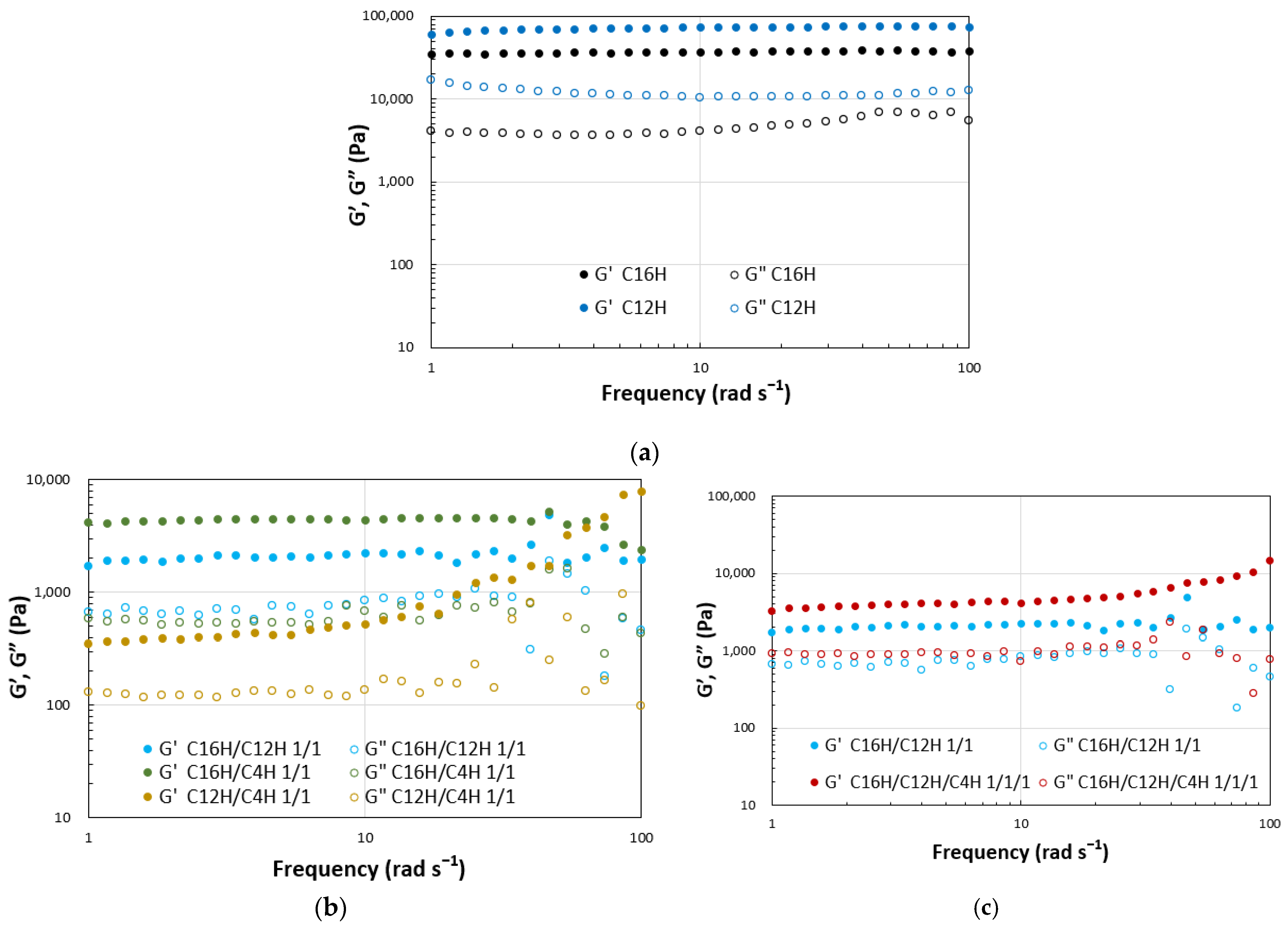
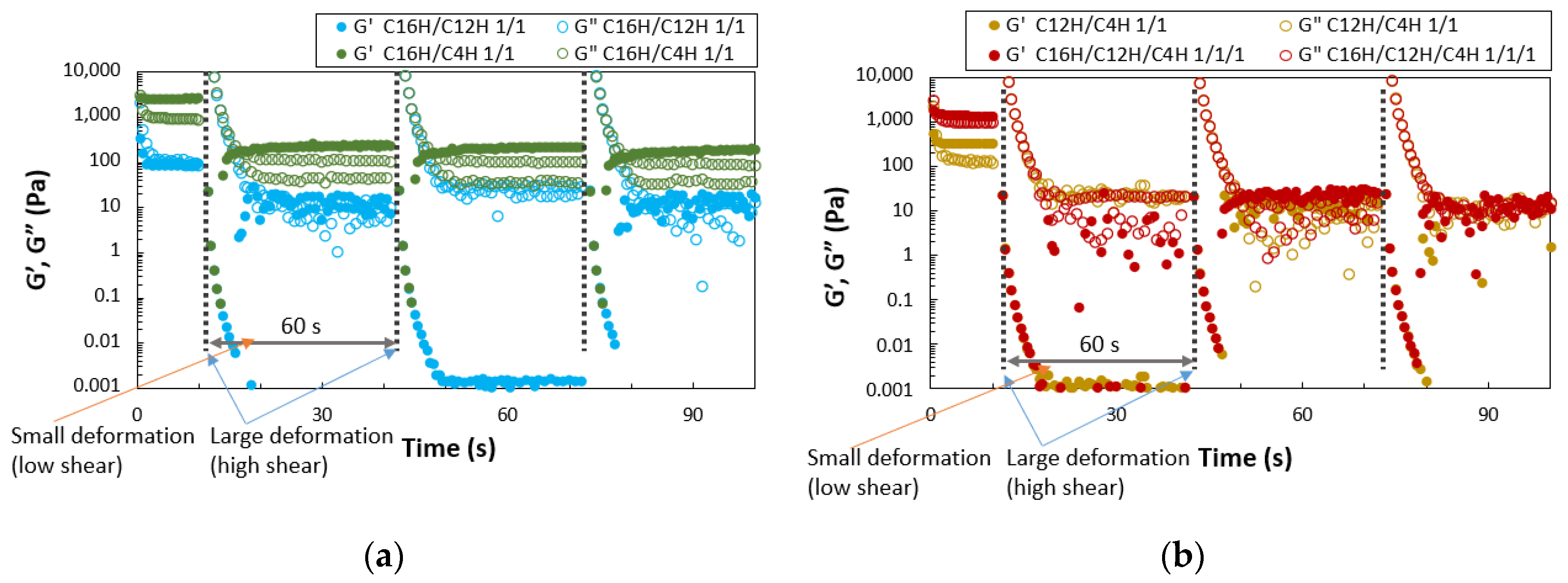
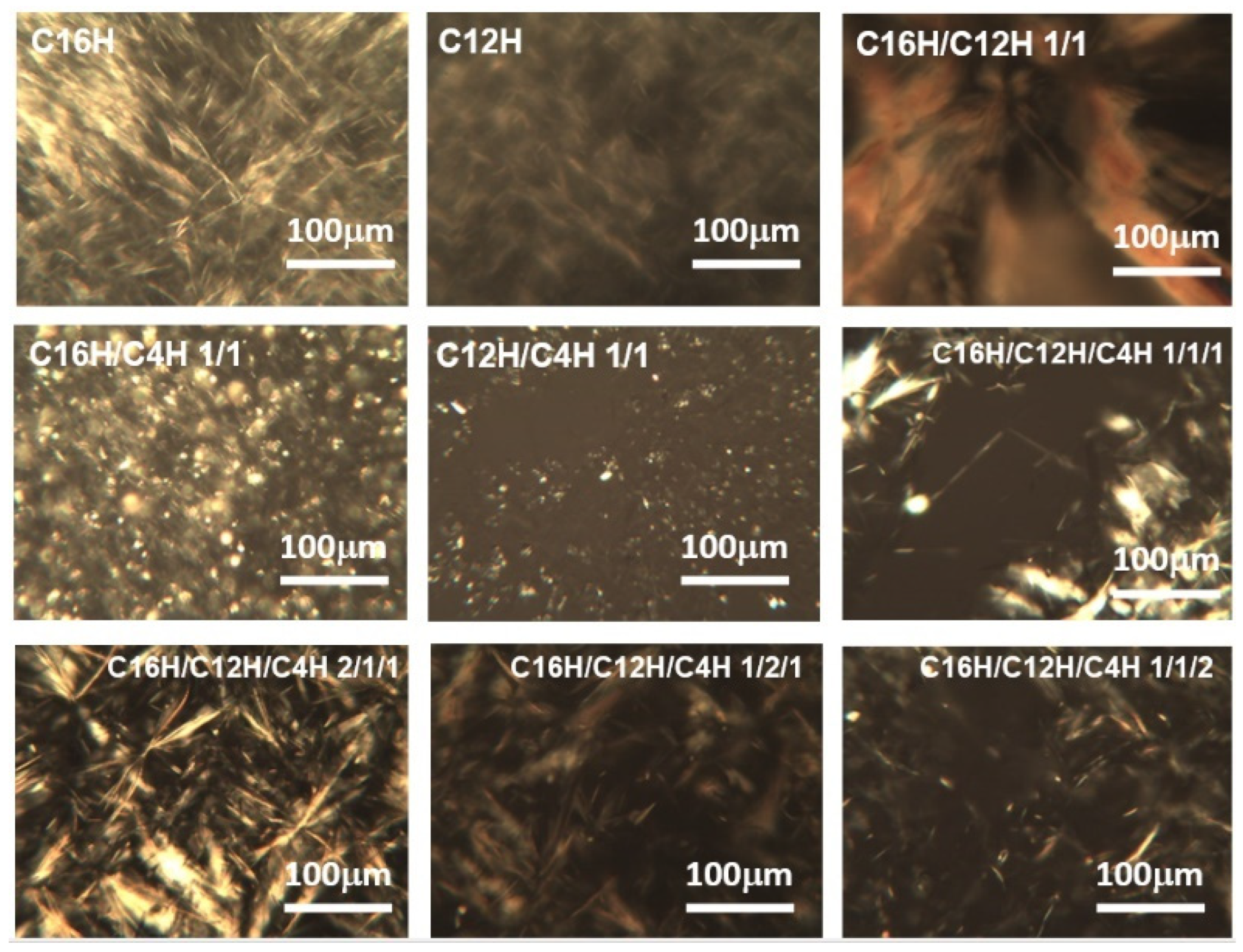
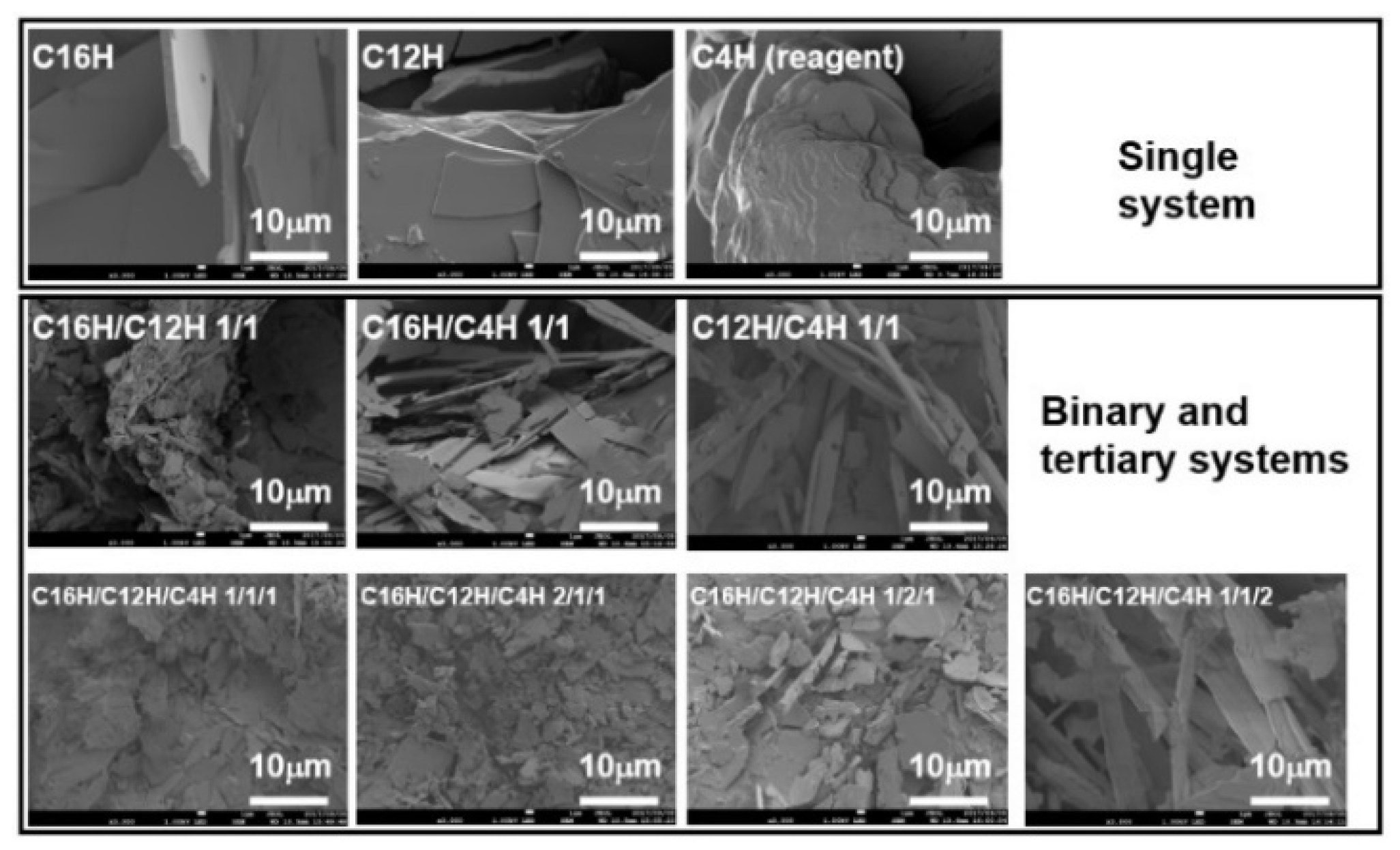
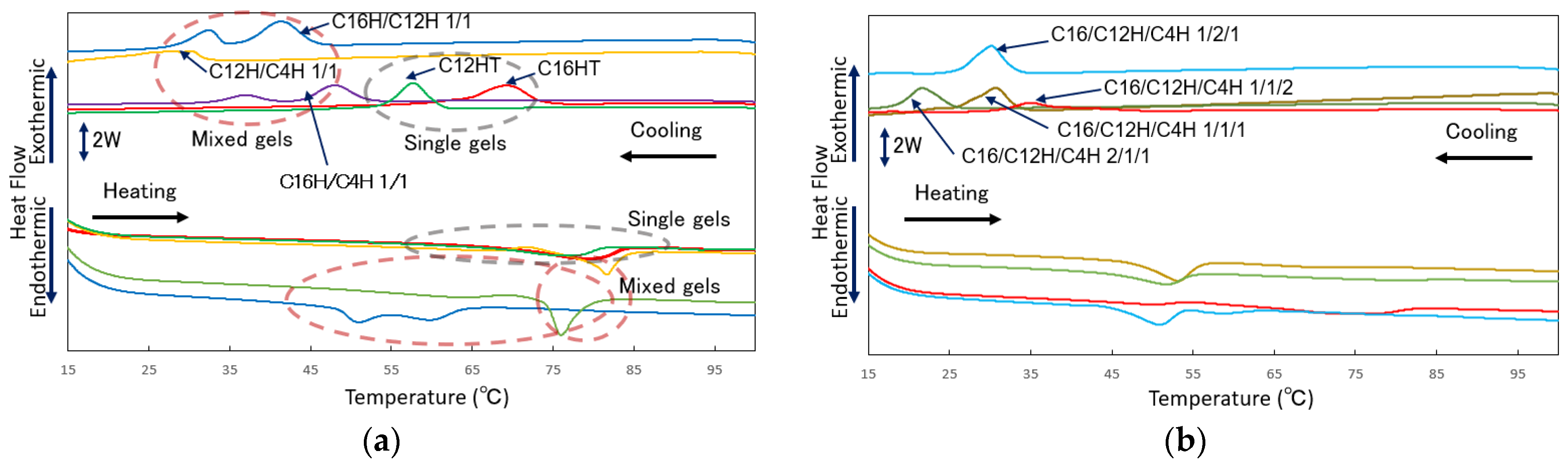
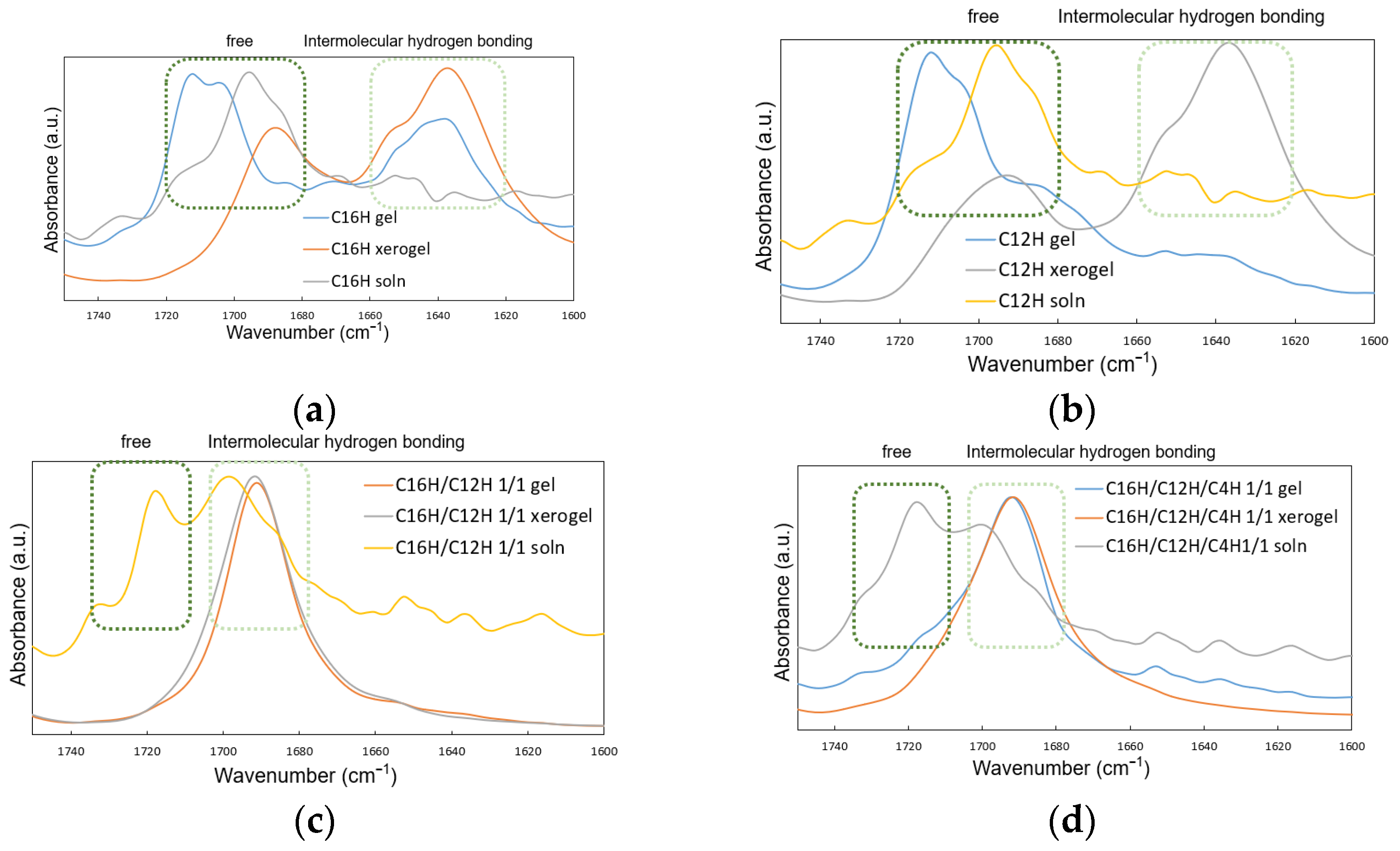
2. Results and Discussion
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- López, C.A.; Trigo, G.G. The Chemistry of Hydantoins. Adv. Heterocycl. Chem. 1985, 38, 177–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Shin, D. Recent Applications of Hydantoin and Thiohydantoin in Medicinal Chemistry. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 164, 517–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thenmozhiyal, J.C.; Wong, P.T.H.; Chui, W.K. Anticonvulsant Activity of Phenylmethylenehydantoins: A Structure-Activity Relationship Study. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1527–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, N.; Suzuki, K. Discovery and Development of Pyrethroid Insecticides. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2019, 95, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, H.; Lee, J.H.; Seok, J.H.; Jung, K.; Yang, J.Y.; Jeong, J.; Lee, J.K. Single- and Repeated-Dose 28-Day Oral Toxicity Study of MDM Hydantoin in Sprague–Dawley Rats. Toxicol. Res. 2021, 37, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konnert, L.; Lamaty, F.; Martinez, J.; Colacino, E. Recent Advances in the Synthesis of Hydantoins: The State of the Art of a Valuable Scaffold. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 13757–13809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Sun, Y. N-Halamine-Based Antimicrobial Additives for Polymers: Preparation, Characterization, and Antimicrobial Activity. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 2634–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Yang, X.; Ma, Y.; Shao, J.; Yang, X.; Chen, Z. Alkyl Substituted Hydantoin-Based N-Halamine: Preparation, Characterization, and Structure-Antibacterial Efficacy Relationship. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 9344–9351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, E. The Chemistry of the Hydantoins. Chem. Rev. 1950, 46, 403–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, R.G.; Terech, P. Molecular Gels: Materials with Self-Assembled Fibrillar Networks; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Guenet, J.-M. Organogels Thermodynamics, Structure, Solvent Role, and Properties; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, R.G. Molecular Gels, Structure and Dynamics; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wojtecki, R.J.; Meador, M.A.; Rowan, S.J. Using the Dynamic Bond to Access Macroscopically Responsive Structurally Dynamic Polymers. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, M. Development of C 3-Symmetric Tris-Urea Low-Molecular-Weight Gelators. Chem. Rec. 2016, 16, 768–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amabilino, D.B.; Smith, D.K.; Steed, J.W. Supramolecular Materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 2404–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, R.; Peng, J.; Fang, Y. Molecular Gels as Intermediates in the Synthesis of Porous Materials and Fluorescent Films: Concepts and Applications. Langmuir 2017, 33, 10419–10428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, R.G. Controlling Variables in Molecular Gel Science: How Can We Improve the State of the Art? Gels 2018, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, J.; Saldías, C.; Díaz Díaz, D. Release of Small Bioactive Molecules from Physical Gels. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 1484–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivers, P.R.A.; Smith, D.K. Shaping and Structuring Supramolecular Gels. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panja, S.; Adams, D.J. Stimuli Responsive Dynamic Transformations in Supramolecular Gels. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 5165–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, J.; Hughes, R. Rheology for Chemists: An Introduction, 2nd ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cornwell, D.J.; Smith, D.K. Expanding the scope of gels—Combining polymers with low-molecular-weight gelators to yield modified self-assembling smart materials with high-tech applications. Mater. Horiz. 2015, 2, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawn, A.; Shiraki, T.; Haraguchi, S.; Tamaru, S.; Shinkai, S. What Kind of “Soft Materials” Can We Design from Molecular Gels? Chem. Asian J. 2011, 6, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, R.G. The Past, Present, and Future of Molecular Gels. What Is the Status of the Field, and Where Is It Going? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 7519–7530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, S.S.; Praveen, V.K.; Ajayaghosh, A. Functional π-Gelators and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 1973–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, M.A.; Weiss, R.G. Systematic Modifications of Alkane-Based Molecular Gelators and the Consequences to the Struc-tures and Properties of Their Gels. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 785–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsedo, Y. Low-Molecular-Weight Organogelators as Functional Materials for Oil Spill Remediation. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2016, 27, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsedo, Y. Low-Molecular-Weight Gelators as Base Materials for Ointments. Gels 2016, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, N. Delivery System Design in Topically Applied Formulations: An Overview. In Delivery System Handbook for Personal Care and Cosmetic Products, Technology, Applications, and Formulations; Rosen, M.R., Ed.; William Andrew, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 101–118. [Google Scholar]
- Sugibayashi, K.; Morimoto, Y. Transdermal Patches. In Gels Handbook, The Fundamentals; Osada, Y., Kajiwara, K., Fushimi, T., Irasa, O., Hirokawa, Y., Matsunaga, T., Shimomura, T., Wang, L., Ishida, H., Eds.; Section 6; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 3, pp. 201–210. [Google Scholar]
- Boekhoven, J.; Stupp, S.I. 25th Anniversary Article: Supramolecular Materials for Regenerative Medicine. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 1642–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, J.; Du, X.; Xu, B. Supramolecular Biofunctional Materials. Biomaterials 2017, 129, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohsedo, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Oono, M.; Tanaka, A. Mixing Enhancement Effect of Low-Molecular-Weight Organogelators for Thixotropic Organogel Creation. Chem. Lett. 2013, 42, 363–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsedo, Y.; Oono, M.; Tanaka, A.; Watanabe, H. Mixing Induced Thixotropy of a Two-Component System of Alkylurea Or-ganogelators Having Different Alkyl Chains. New J. Chem. 2013, 37, 2250–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsedo, Y.; Taniguchi, M.; Oono, M.; Saruhashi, K.; Watanabe, H. Creation of Thixotropic Multicomponent Alkylamide Organogels Containing Non-Volatile Oil as Potential Drug Release Host Materials. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 35484–35488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirst, A.R.; Smith, D.K. Two-Component Gel-Phase Materials—Highly Tunable Self-Assembling Systems. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2005, 11, 5496–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buerkle, L.E.; Rowan, S.J. Supramolecular Gels Formed from Multi-Component Low Molecular Weight Species. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 6089–6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draper, E.R.; Wallace, M.; Schweins, R.; Poole, R.J.; Adams, D.J. Nonlinear Effects in Multicomponent Supramolecular Hydrogels. Langmuir 2017, 33, 2387–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draper, E.R.; Adams, D.J. How Should Multicomponent Supramolecular Gels Be Characterised? Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 3395–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, E.R.; Sproules, S.; Schweins, R.; Draper, E.R.; Adams, D.J. Controlled Tuning of the Properties in Optoelectronic Self-Sorted Gels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 8667–8670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, W.; Shigemitsu, H.; Fujisaku, T.; Kubota, R.; Minami, S.; Urayama, K.; Hamachi, I. Post-Assembly Fabrication of a Functional Multicomponent Supramolecular Hydrogel Based on a Self-Sorting Double Network. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4997–5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwell, D.J.; Smith, D.K. Photo-Patterned Multi-Domain Multi-Component Hybrid Hydrogels. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 7029–7032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilyev, G.; Koifman, N.; Shuster, M.; Gishvoliner, M.; Cohen, Y.; Zussman, E. Synergistic Effect of Two Organogelators for the Creation of Bio-Based, Shape-Stable Phase-Change Materials. Langmuir 2020, 36, 15572–15582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, D.; Srinivasan, S.; Rochas, C.; Ajayaghosh, A.; Guenet, J.M. Hybrid Thermoreversible Gels from Covalent Polymers and Organogels. Langmuir 2009, 25, 8593–8598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyrkova, I.; Moulin, E.; Armao, I.J.J.; Maaloum, M.; Heinrich, B.; Rawiso, M.; Niess, F.; Cid, J.-J.; Jouault, N.; Buhler, E.; et al. Supramolecular Self-Assembly and Radical Kinetics in Conducting Self-Replicating Nanowires. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 10111–10124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoukal, Z.; Elhasri, S.; Carvalho, A.; Schmutz, M.; Collin, D.; Vakayil, P.K.; Ajayaghosh, A.; Guenet, J.M. Hybrid Materials from Poly(Vinyl Chloride) and Organogels. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 1203–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebpour, P.; Heinrich, B.; Gavat, O.; Carvalho, A.; Moulin, E.; Giuseppone, N.; Guenet, J.M. Modulation of the Molecular Structure of Tri-Aryl Amine Fibrils in Hybrid Poly[Vinyl Chloride] Gel/Organogel Systems. Macromolecules 2021, 54, 8104–8111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawn, A.; Kumari, H. Low Molecular Weight Supramolecular Gels Under Shear: Rheology as the Tool for Elucidating Structure–Function Correlation. Chem.–A Eur. J. 2018, 24, 762–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, G.M.; Ross-Murphy, S.B. Rheological Characterisation of Polymer Gels. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1998, 23, 533–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelletto, V.; Hamley, I.W.; Adamcik, J.; Mezzenga, R.; Gummel, J. Modulating Self-Assembly of a Nanotape-Forming Peptide Amphiphile with an Oppositely Charged Surfactant. Soft Matter 2011, 8, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Solvent | C16H | C12H | C4H |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propylene carbonate | K*,1 | PG 4 | S |
| N,N-Dimethyl formamide | K 2 | S | S |
| Methanol | K | S | S |
| Ethanol | K | S | S |
| 1-Butanol | K | S | S |
| Dichloroethane | K | S | S |
| Tetrahydrofuran | S 3 | S | S |
| Ethyl acetate | K | S | S |
| Toluene | K | S | S |
| n-Octane | 2 | 6 | PG |
| Olive oil | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| Squalane | 1 | 2 | S |
| Mixed Molar Ratio | C16H/C12H | C16H/C4H | C12H/C4H | C16H/C12H/C4H |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5/1 | 3 | S 1 | S | |
| 2/1 | 2 | 2 | S | |
| 1/1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | |
| 1/2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| 1/5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| 5/1/1 | 3 | |||
| 1/5/1 | 2 | |||
| 1/1/5 | 1 | |||
| 2/1/1 | 3 | |||
| 1/2/1 | 3 | |||
| 1/1/2 | 1 | |||
| 1/1/1 | 2 |
| Samples 1 | Tgel to sol on Heating/°C (ΔH/mJ mg−1) | Tsol to gel on Cooling/°C (ΔH/mJ mg−1) |
|---|---|---|
| C16H | 69.5 (6.4) | 74.2 (6.4) |
| C12H | 65.1 (5.0) | 60.8 (5.0) |
| C16H/12H 1/1 | 47.1 (4.5) pt 2: 50.5, 59.7 | 45.6 (4.4) pt: 32.8, 41.7 |
| C16H/4H 1/1 | 58.2 (5.8) pt: 66.8, 81.5 | 51.5 (5.1) pt: 36.8, 47.7 |
| C12H/4H 1/1 | 56.9 (0.9) 73.7 (2.9) | 31.7 (2.0) |
| C16H/12H/4H 1/1/1 | 47.0 (2.3) | 30.5 (2.8) |
| C16H/12H/4H 2/1/1 | 44.2 (3.1) | 25.7 (3.2) |
| C16H/12H/4H 1/2/1 | 43.9 (2.6) | 33.4 (2.6) |
| C16H/12H/4H 1/1/2 | 45.3, 61.8 (3.6) | 39.4 (3.3) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ohsedo, Y. N-Alkylhydantoins as New Organogelators and Their Ability to Create Thixotropic Mixed Molecular Organogels. Gels 2022, 8, 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8100638
Ohsedo Y. N-Alkylhydantoins as New Organogelators and Their Ability to Create Thixotropic Mixed Molecular Organogels. Gels. 2022; 8(10):638. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8100638
Chicago/Turabian StyleOhsedo, Yutaka. 2022. "N-Alkylhydantoins as New Organogelators and Their Ability to Create Thixotropic Mixed Molecular Organogels" Gels 8, no. 10: 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8100638
APA StyleOhsedo, Y. (2022). N-Alkylhydantoins as New Organogelators and Their Ability to Create Thixotropic Mixed Molecular Organogels. Gels, 8(10), 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8100638






