Mechanical Properties and Structures of Clay-Polyelectrolyte Blend Hydrogels
Abstract
1. Introduction
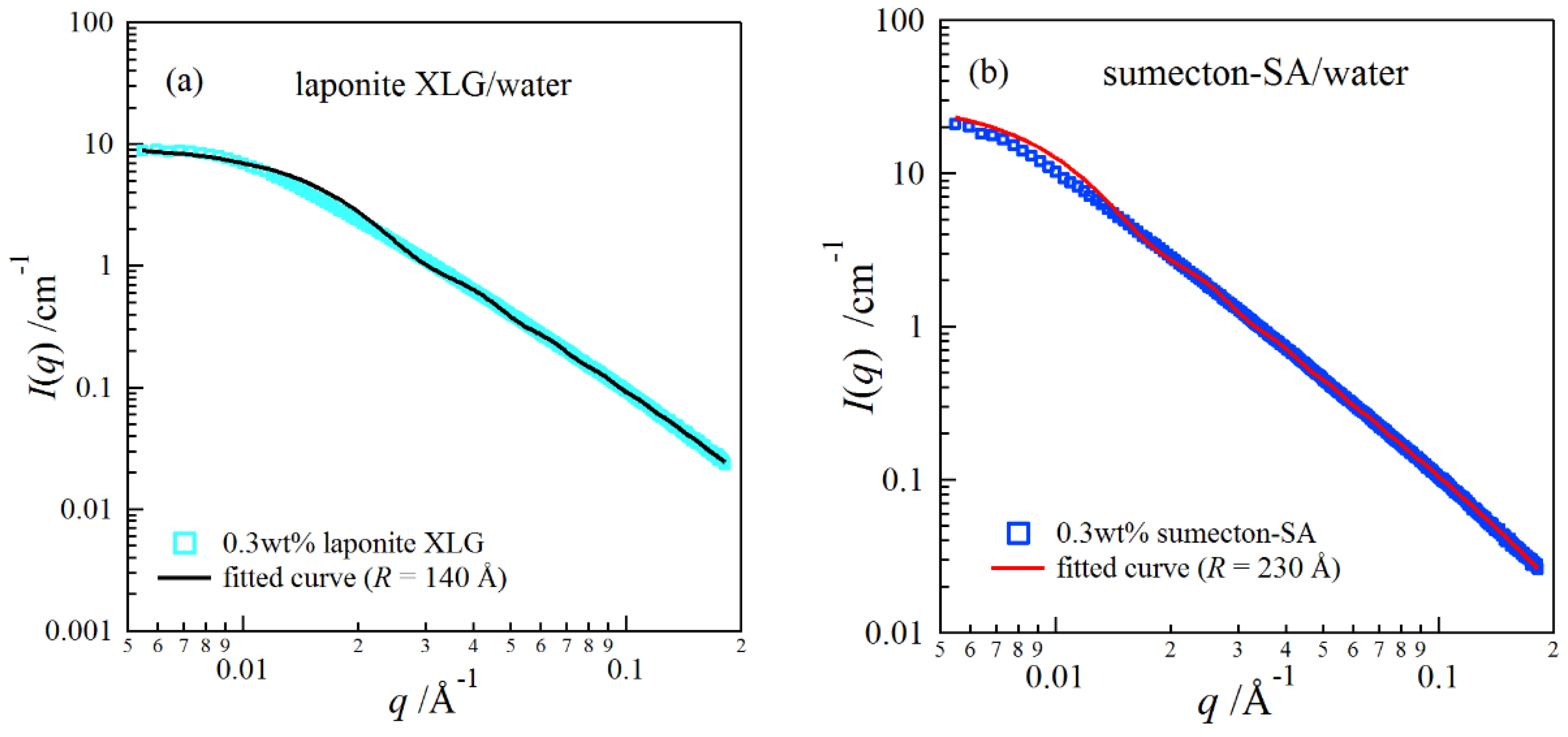
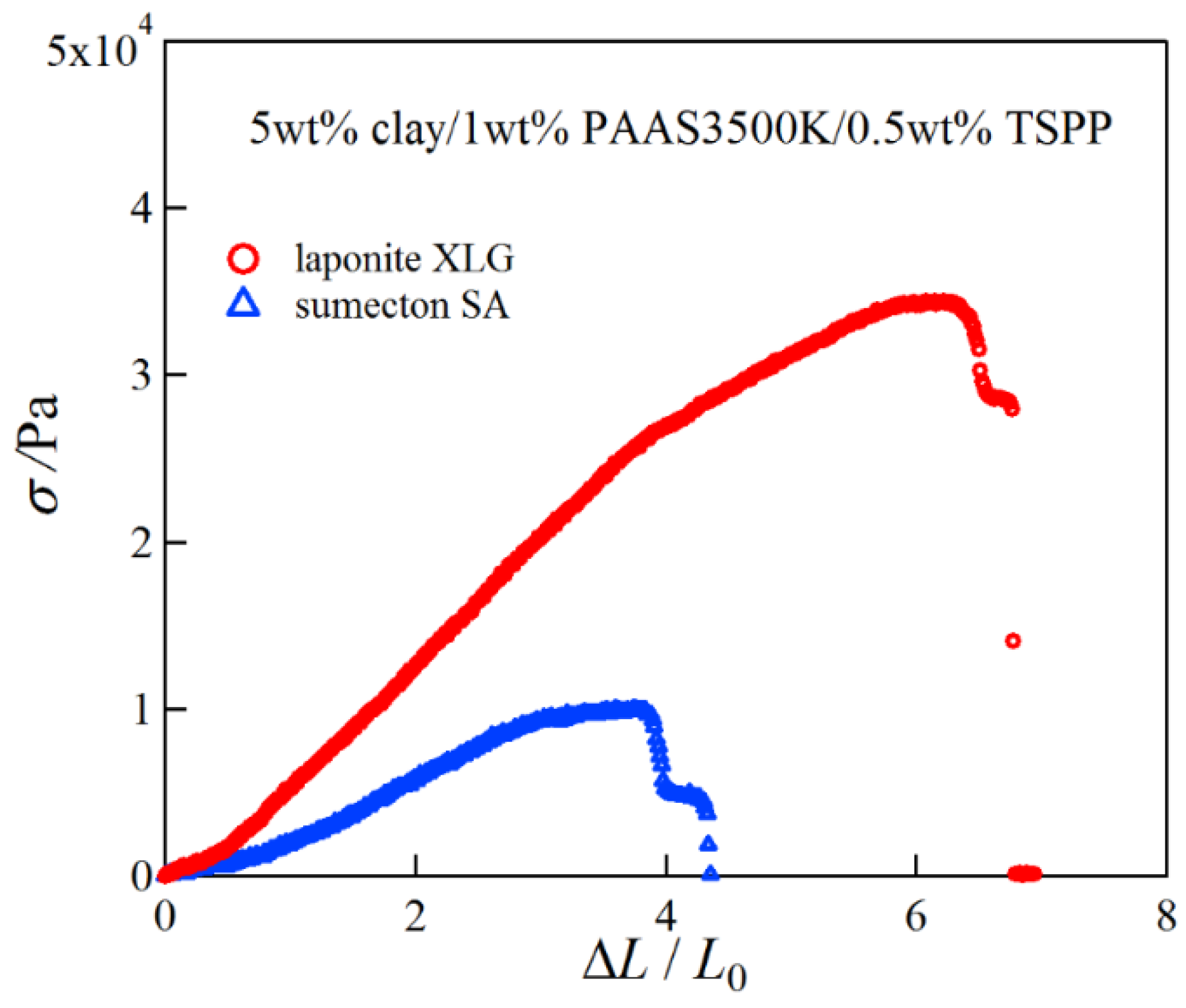
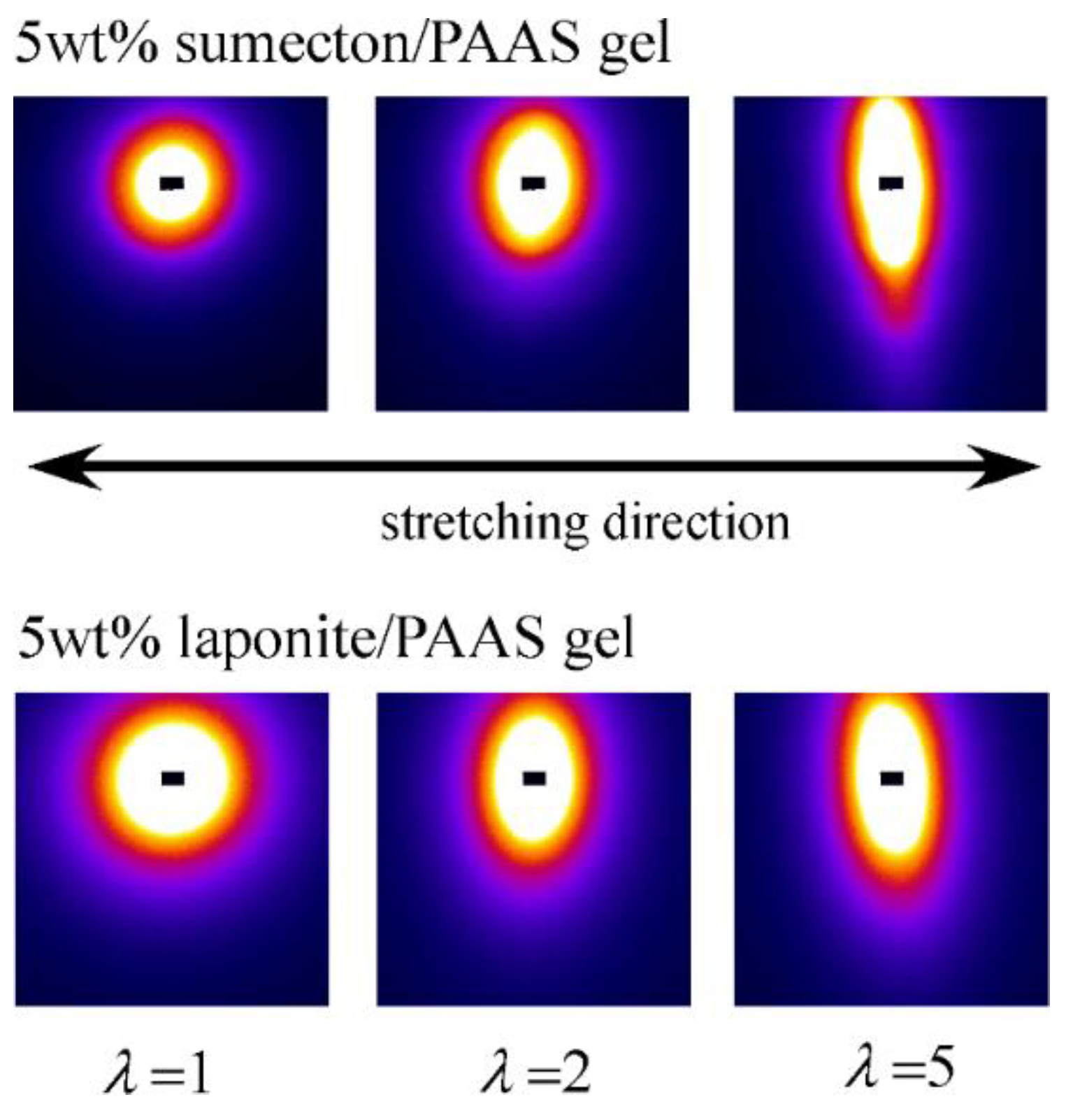
2. Results and Discussion
3. Conclusions
4. Experiments
4.1. Sample and Sample Preparation
4.2. Transmittance and pH Measurements
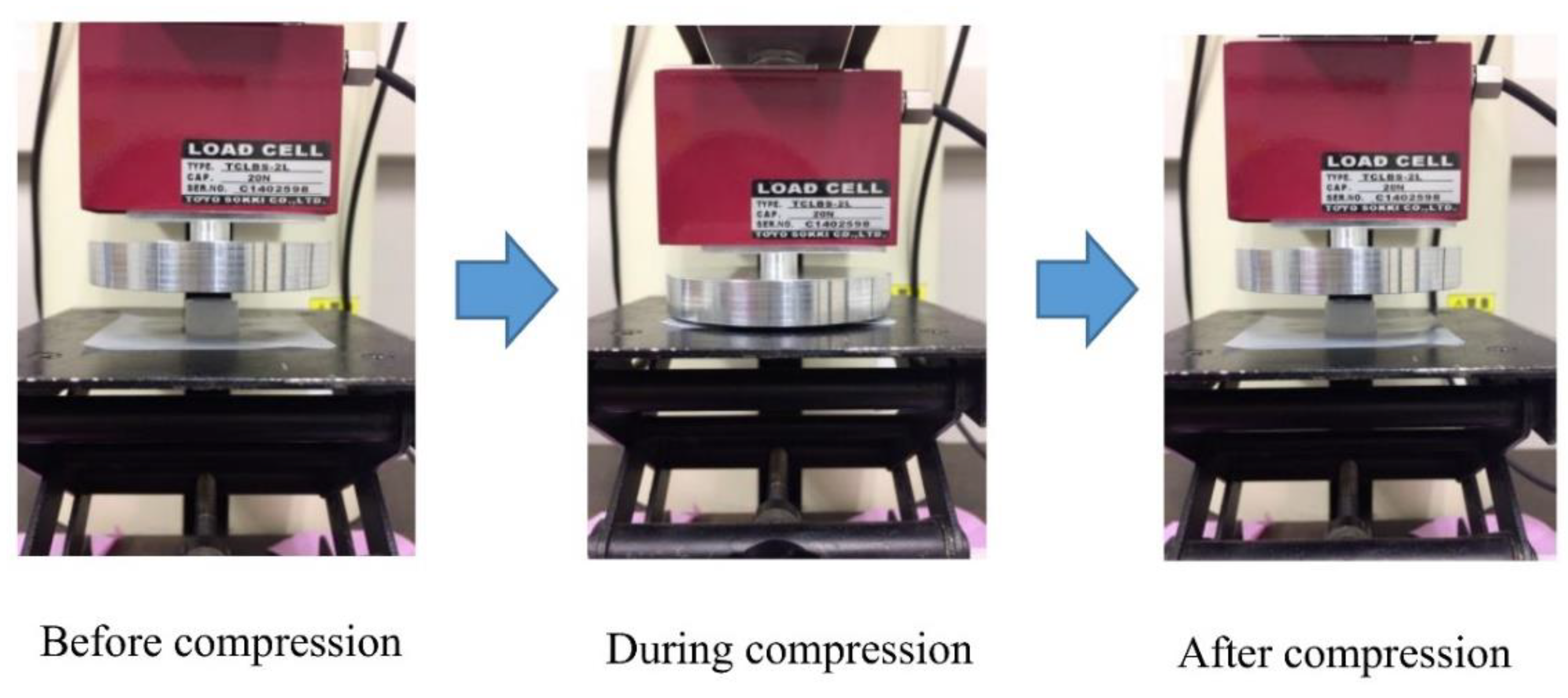
4.3. Compression and Tensile Measurements
4.4. Synchrotron Small-Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS)
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haraguchi, K. Synthesis and properties of soft nanocomposite materials with novel organic/inorganic network structures. Polym. J. 2011, 43, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Mynar, J.L.; Yoshida, M.; Lee, E.; Lee, M.; Okuro, K.; Kinbara, K.; Aida, T. High-water-content mouldable hydrogels by mixing clay and a dendritic molecular binder. Nature 2010, 463, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Sun, W.; Tong, Z. Programmable and bidirectional bending of soft actuators based on janus structure with sticky tough PAA-clay hydrogel. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 11866–11873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haraguchi, K.; Li, H.J.; Matsuda, K.; Takehisa, T.; Elliott, E. Mechanism of Forming Organic/Inorganic Network Structures during In-situ Free-Radical Polymerization in PNIPA-Clay Nanocomposite Hydrogels. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 3482–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Mu, C.; Lin, W.; Ngai, T. Gelatin Effects on the Physicochemical and Hemocompatible Properties of Gelatin/PAAm/Laponite Nanocomposite Hydrogels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 18732–18741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyaci, T.; Orakdogen, N. Poly (N,N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate-co-2-acrylamido-2-methyl-propanosulfonic acid)/Laponite nanocomposite hydrogels and cryogels with improved mechanical strength and rapid dynamic properties. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 121–122, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Xu, S.; Wu, R.; Wang, J.; Gu, R.; Du, J. A transparent Laponite polymer nanocomposite hydrogel synthesis via in-situ copolymerization of two ionic monomers. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 72, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, K.; Takehisa, T. Nanocomposite hydrogels: A unique organic–inorganic network structure with extraordinary mechanical, optical, and swelling/de-swelling properties. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1120–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, K.; Takada, T. Synthesis and characteristics of nanocomposite gels prepared by in situ photopolymerization in an aqueous system. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 4294–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.X.; Xia, M.G.; Cunningham, A.; Chen, W.; Sun, B.; Zhu, M.F. Mechanical properties of biocompatible clay/P(MEO2MA-co-OEGMA) nanocomposite hydrogels. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. 2017, 72, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haraguchi, K. Nanocomposite Gels-Fundamental Significance and New Functions. Kobunshi Ronbunshu 2008, 65, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeno, H.; Nakamura, W. Structural and mechanical properties of composite hydrogels composed of clay and a polyelectrolyte prepared by mixing. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2013, 291, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeno, H.; Kimura, Y. Molecularweight effects on tensile properties of blend hydrogels composed of clay and polymers. Polymer 2016, 85, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeno, H.; Sato, C. Effects of molecular mass of polymer and composition on the compressive properties of hydrogels composed of Laponite and sodium polyacrylate. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 123, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeno, H.; Kimura, Y.; Nakamura, W. Mechanical, swelling, and structural properties of mechanically tough clay-sodium polyacrylate blend hydrogels. Gels 2017, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glatter, O.; Kratky, O. Small Angle X-ray Scattering; Academic Press: London, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Takeno, H. X-ray and Neutron Techniques for Nanomaterials Characterization; Kumar, C.S.S.R., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 717–760. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Kim, J.H.; Chung, I.J. Effect of the clay size on the dispersion morphology and emulsion stability of ABS/layered silicate nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 119, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, R.J. Methods of X-ray and Neutron Scattering in Polymer Science; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Ilavsky, J.; Long, G.G.; Quintana, J.P.G.; Allen, A.J.; Jemian, P.R. Glassy carbon as an absolute intensity calibration standard for small-angle scattering. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2010, 41, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


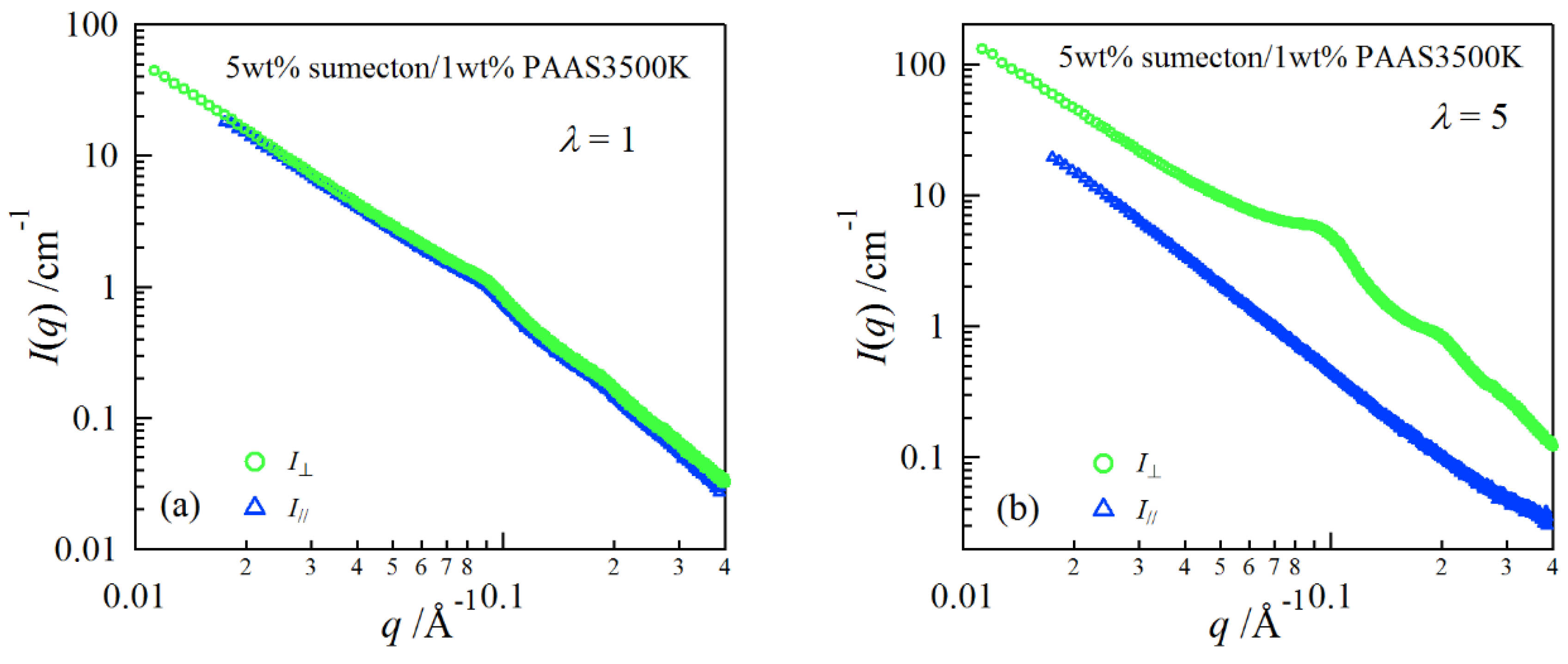
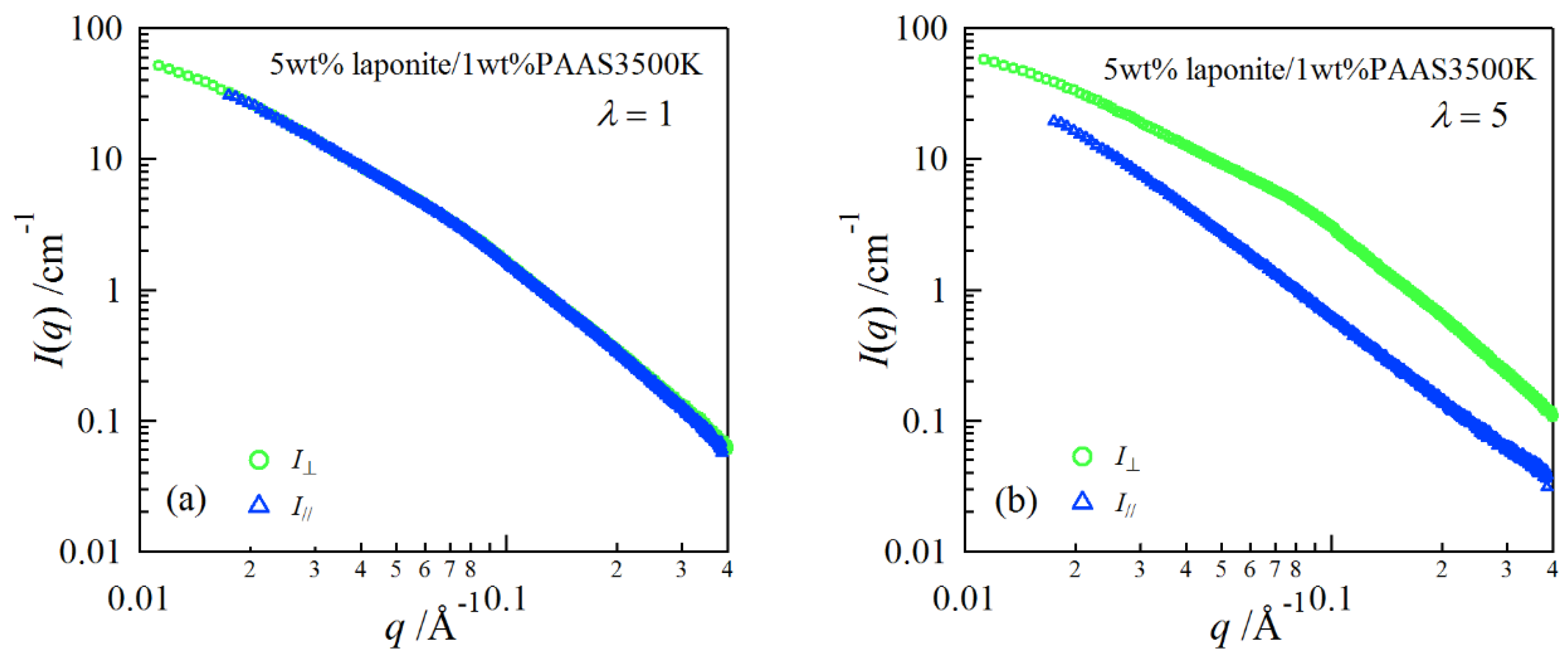
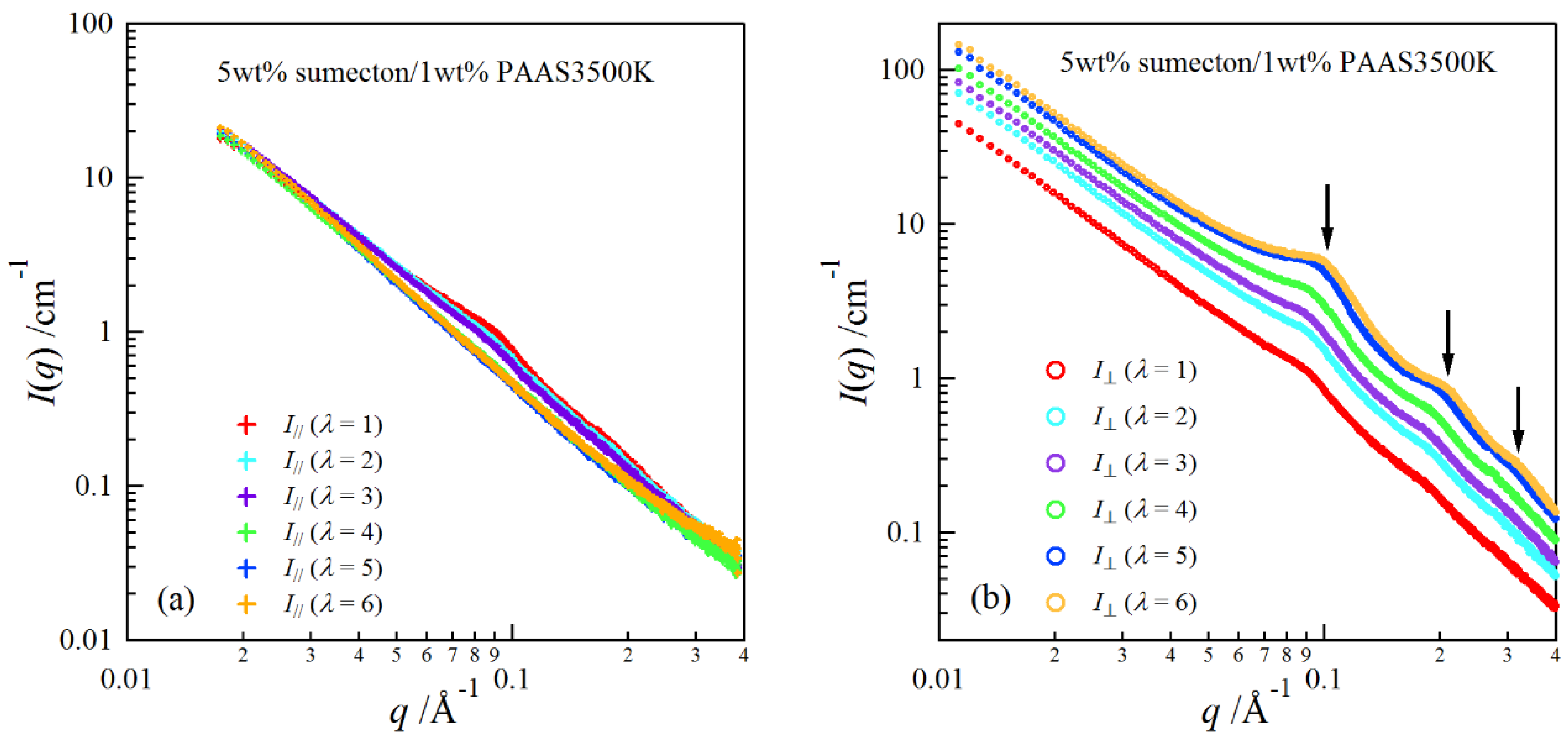
| Clay | pH | E/× 103 Pa | Transmittance/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sumecton (x = 5) | 9.95 | 2.4 ± 0.2 | 9.96 |
| Laponite (x = 5) | 9.90 | 3.7 ± 0.1 | 84.7 |
| Sumecton (x = 10) | 9.92 | 4.7 ± 0.3 | 1.10 |
| Laponite (x = 10) | 9.86 | 26 ± 7.3 | 60.7 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takeno, H.; Nagai, S. Mechanical Properties and Structures of Clay-Polyelectrolyte Blend Hydrogels. Gels 2018, 4, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels4030071
Takeno H, Nagai S. Mechanical Properties and Structures of Clay-Polyelectrolyte Blend Hydrogels. Gels. 2018; 4(3):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels4030071
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakeno, Hiroyuki, and Shiori Nagai. 2018. "Mechanical Properties and Structures of Clay-Polyelectrolyte Blend Hydrogels" Gels 4, no. 3: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels4030071
APA StyleTakeno, H., & Nagai, S. (2018). Mechanical Properties and Structures of Clay-Polyelectrolyte Blend Hydrogels. Gels, 4(3), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels4030071






