Physicochemical, Sensorial and Calcium Bioavailability of Jelly Prepared Using Fish Gelatin in Combination with Furcellaran and Calcium L-Threonate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Textural Properties of Formulated Jellies
2.1.1. Gel Strength
2.1.2. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA)
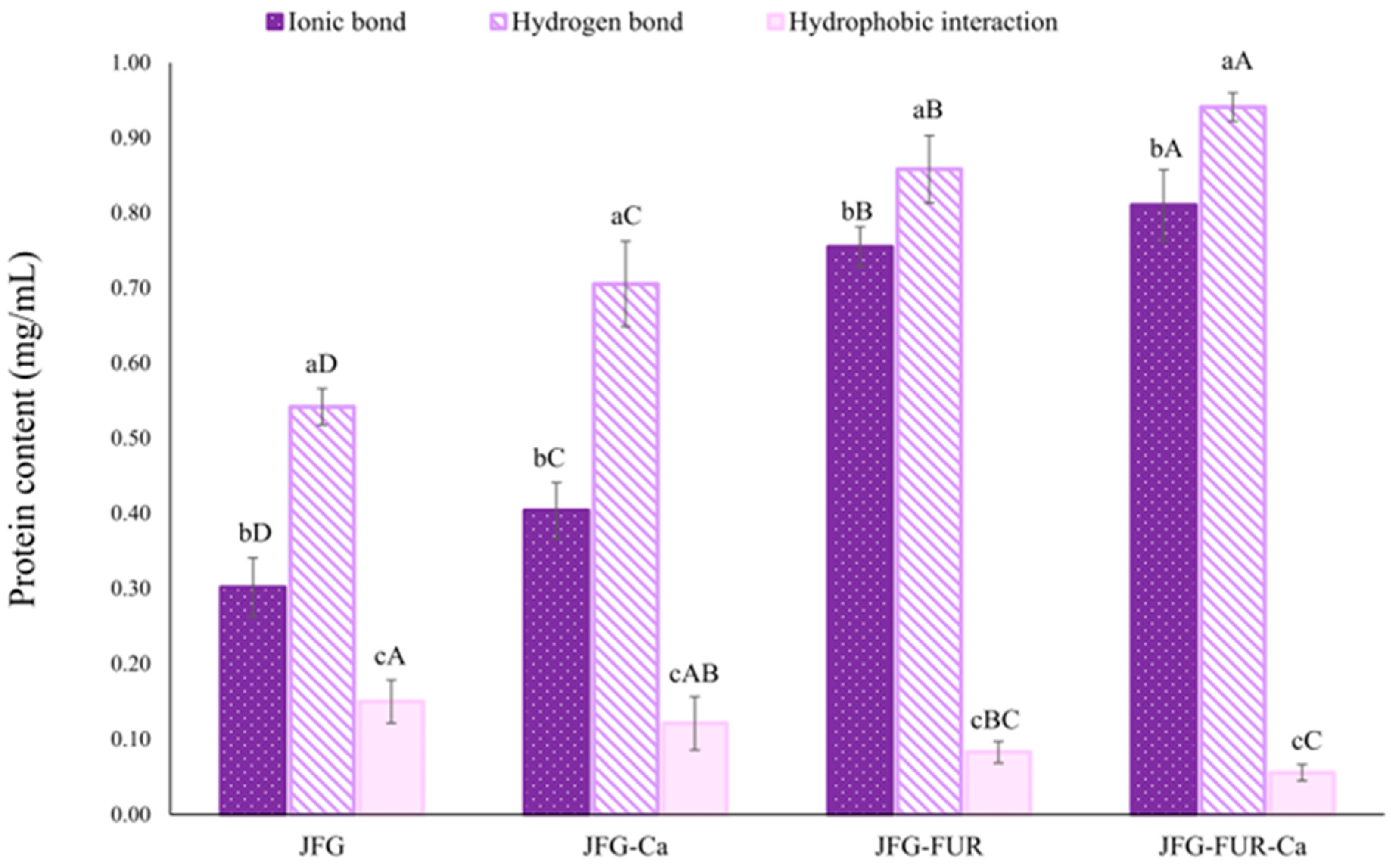
2.2. Intermolecular Force of Jelly Samples
2.3. Syneresis of Jelly Samples
2.4. Changes in the Appearance of Jelly Samples
2.5. Rheological Behaviors of Jelly Samples
2.5.1. Temperature Sweep
2.5.2. Frequency Sweep
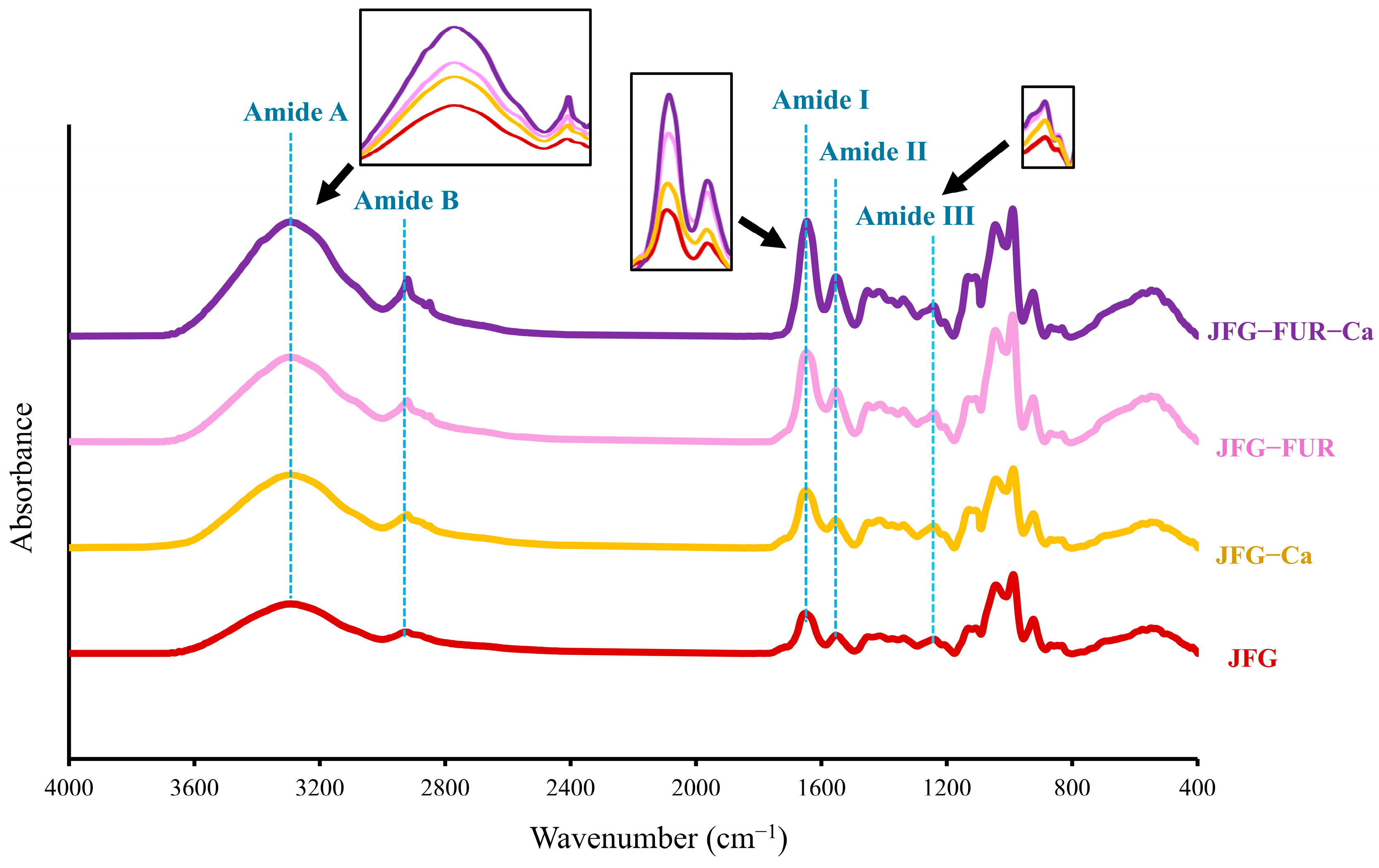
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectra of Jelly Samples
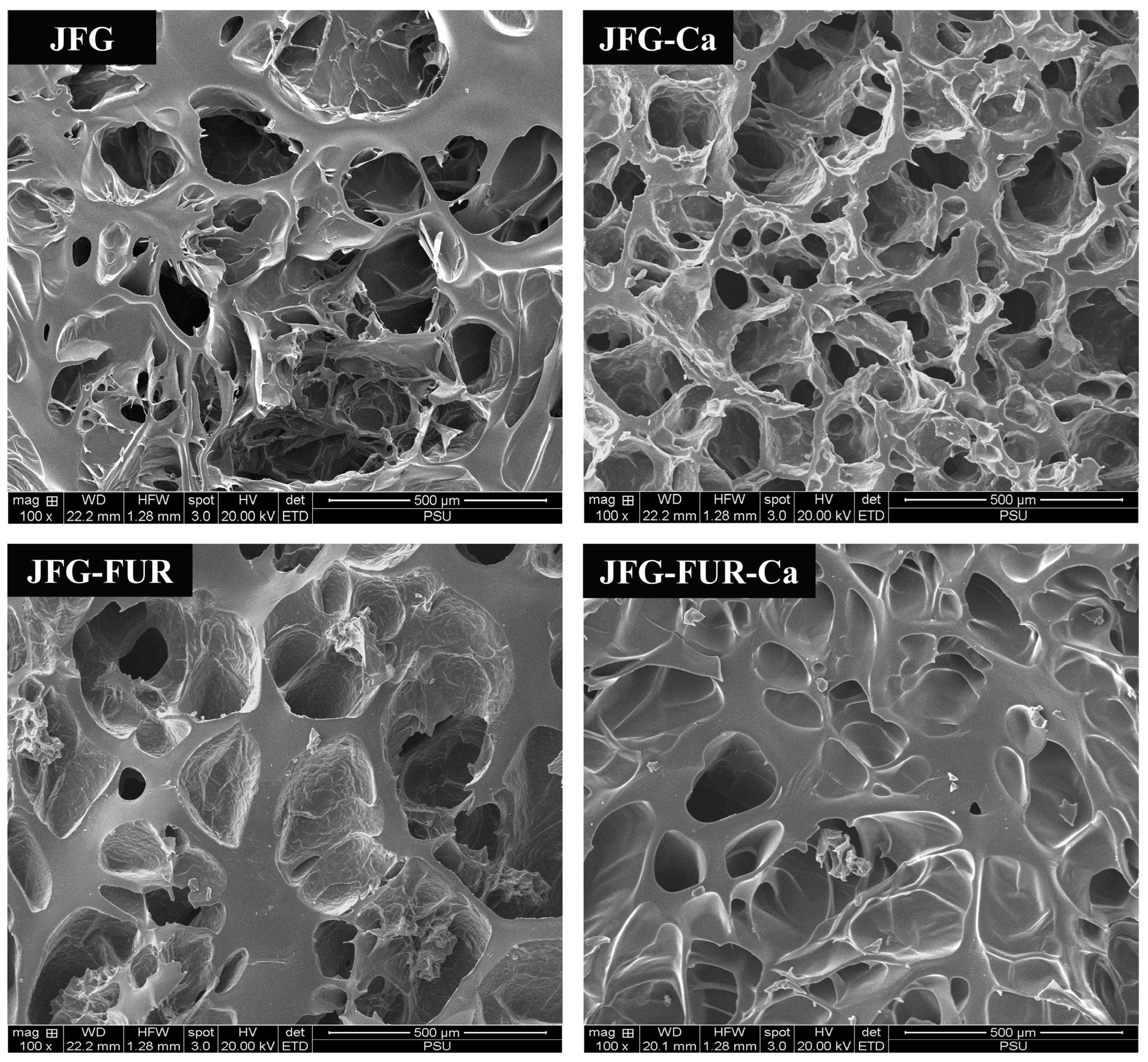
2.7. Microstructure of Jelly Samples
2.8. Sensory Evaluation of Jelly Samples
2.9. Calcium Bioavailability of Jelly Samples After Digestion Through Gastrointestinal Tract Model System
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of the Jelly Samples
4.3. Analyses
4.3.1. Texture Measurement
4.3.2. Evaluation of Intermolecular Forces
4.3.3. Rheological Analysis
4.3.4. Determination of Color
4.3.5. Measurement of Syneresis
4.3.6. FTIR Spectroscopy
4.3.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.3.8. Sensory Evaluation
4.3.9. Influence of Gastrointestinal Tract Model System on the Calcium Bioavailability of Jelly Products
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mia, M.E.; Sagor, S.R.; Misti, M.R.; Sultana, Z.; Nurain, N. Physicochemical properties and consumer preferences of Java apple (Syzygium samarangense) fruit jelly. Eur. J. Nutr. Food Saf. 2025, 17, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Song, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, P.; Ma, J.; Zhao, B.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wen, P. The impacts of different modification techniques on the gel properties and structural characteristics of fish gelatin. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 158, 110536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Sun, W.; Yang, Y.; Jia, R.; Zhan, S.; Ou, C.; Huang, T. Phosphorylated Fish Gelatin and the Quality of Jelly Gels: Gelling and Microbiomics Analysis. Foods 2023, 12, 3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallego, M.; Arnal, M.; Talens, P.; Toldrá, F.; Mora, L. Effect of Gelatin Coating Enriched with Antioxidant Tomato By-Products on the Quality of Pork Meat. Polymers 2020, 12, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedis Kaynarca, G.; Gümüş, T.; Damla Altan Kamer, D. Rheological properties of fish (Sparus aurata) skin gelatin modified by agricultural wastes extracts. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Regenstein, J.M.; Lv, S.; Lu, J.; Jiang, S. An overview of gelatin derived from aquatic animals: Properties and modification. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 68, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcharat, T.; Benjakul, S. Property of fish gelatin gel as affected by the incorporation of gellan and calcium chloride. Food Biophys. 2017, 12, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Tang, J.; Wang, R.; Liu, W.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Q.; Niu, L.; Zhang, C. Gellan gum improves the gel properties and thermal stability of tilapia (Oreochromis spp.) skin gelatin sterilized at 121 °C. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e17131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, S.R.; Voron’ko, N.G.; Kuchina, Y.A.; Kolotova, D.S. Modified Fish Gelatin as an Alternative to Mammalian Gelatin in Modern Food Technologies. Polymers 2020, 12, 3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.-N.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Zhou, Z.-Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.-F.; Chen, J.-P.; Zhao, Q.-L.; Leong, C.K.; Xia, Q.-Y.; Zhong, S.-Y.; et al. Co-assembly of ι-, κ-, and λ-carrageenan with fish gelatin: Modulating physicochemical and gelling properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 331, 148523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, I.J.; Draget, K.I.; Smidsrød, O. Physical behaviour of fish gelatin-κ-carrageenan mixtures. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 56, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermakova, E.; Skvortsova, P.; Zuev, Y. Molecular structure and interactions in carrageenan-gelatin complexes: A combined computational and experimental study. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1351, 144185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chailom, P.; Pattarakankul, T.; Palaga, T.; Hoven, V.P. Fish Gelatin-Hyaluronic Acid Scaffold for Construction of an Artificial Three-Dimensional Skin Model. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 8172–8181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Tu, Z.-c.; Wang, H.; Shangguan, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, N.-h.; Bansal, N. Pectin and enzyme complex modified fish scales gelatin: Rheological behavior, gel properties and nanostructure. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 156, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.H.; Lim, B.L.; Chow, K.H.; Chong, S.M.; Chang, Y.C. Using fish gelatin and pectin to make a low-fat spread. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 1637–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzak, M.A.; Kim, M.; Chung, D. Elucidation of aqueous interactions between fish gelatin and sodium alginate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 148, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcharat, T.; Benjakul, S.; Hemar, Y. Improvement of gel properties of fish gelatin using gellan. Int. J. Food Eng. 2017, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.-D.; Huang, J.-J.; Wu, J.-L.; Cai, X.-X.; Tian, Y.-Q.; Rao, P.-F.; Huang, J.-L.; Wang, S.-Y. Fabrication, interaction mechanism, functional properties, and applications of fish gelatin-polysaccharide composites: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 122, 107106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štěpánková, K.; Ozaltin, K.; Gorejová, R.; Doudová, H.; Bergerová, E.D.; Maskalová, I.; Stupavská, M.; Sťahel, P.; Trunec, D.; Pelková, J.; et al. Sulfation of furcellaran and its effect on hemocompatibility in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 258, 128840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, E.; Żak, J.; Janik, M.; Cholewa-Wójcik, A.; Juszczak, L.; Szuwarzyński, M.; Mazur, T.; Konieczna-Molenda, A.; Jamróz, E. Double-Layer Films Based on Furcellaran/Chitosan Complex—Structural and Functional Characteristics of Packaging Materials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcharat, T.; Chaijan, M.; Indriani, S.; Pongsetkul, J.; Karnjanapratum, S.; Nalinanon, S. Modulating fish gelatin gelling properties through furcellaran addition: A structural and physicochemical analysis. Gels 2025, 11, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robal, M.; Brenner, T.; Matsukawa, S.; Ogawa, H.; Truus, K.; Rudolph, B.; Tuvikene, R. Monocationic salts of carrageenans: Preparation and physico-chemical properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Wei, L.; Sun, L.; Xu, Q.; Cao, J.; Li, H.; Pang, Z.; Liu, X. Fabrication of food polysaccharide, protein, and polysaccharide-protein composite gels via calcium ion inducement: Gelation mechanisms, conditional factors, and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawless, H.T.; Rapacki, F.; Horne, J.; Hayes, A.; Wang, G. The taste of calcium chloride in mixtures with NaCl, sucrose and citric acid. Food Qual. Prefer. 2004, 15, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety. Opinion on calcium L-threonate for use as a source of calcium in food supplements-scientific panel on food additives and nutrient sources added to food (ANS). EFSA J. 2008, 6, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, P.; Jiang, J. Pharmacokinetics and safety of calcium L-threonate in healthy volunteers after single and multiple oral administrations. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2011, 32, 1555–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaney, R.P. Calcium, dairy products and osteoporosis. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2000, 19, 83S–99S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Xiao, J.; Zhu, M.; Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y. Study of Physicochemical and Gelation Properties of Fish Gelatin from Different Sources. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Yang, X.; Li, D.; Wang, G.; Wang, S.; Guo, Y.; Yang, X. Incorporation of Nicandra physalodes (Linn.) Gaertn. pectin as a way to improve the textural properties of fish gelatin gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudie, K.J.; McCreath, S.J.; Parkinson, J.A.; Davidson, C.M.; Liggat, J.J. Investigation of the influence of pH on the properties and morphology of gelatin hydrogels. J. Polym. Sci. 2023, 61, 2316–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piculell, L. Gelling Carrageenans; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; Volume 239. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Tu, Z.-c.; Sha, X.-m.; Wang, H.; Hu, Y.-m.; Hu, Z.-z. Gelling properties and interaction analysis of fish gelatin–low-methoxyl pectin system with different concentrations of Ca2+. LWT 2020, 132, 109826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, M.; Lyu, J.; Wang, F.; Xie, J.; Bai, L.; Bi, J. Analysis of gelation properties of peach-κ-carrageenan gels: Effect of erythritol. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2023, 30, 100385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanprasert, S.; Kumnerdsiri, P.; Seubsai, A.; Lueangjaroenkit, P.; Pongsetkul, J.; Petcharat, T.; Kaewprachu, P.; Sai-ut, S.; Rawdkuen, S.; Teerapattarakan, N.; et al. Techno-functional gelling mechanism and rheological properties of gelatin capsule-waste gel modified with kappa-carrageenan for future functional food applications. Future Foods 2025, 12, 100723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnjanapratum, S.; Surya, R.; Senphan, T.; Yarnpakdee, S.; Pongsetkul, J.; Petsong, K. Development of a novel protein and calcium fortified plant-based yogurt by addition of pea protein isolate and bio-calcium from Nile tilapia bones. Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2025, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stępień, A.; Juszczak, L.; Synkiewicz-Musialska, B.; Zachariasz, P.; Jamróz, E. Influence of furcellaran and safflower oil concentration on the properties of model emulgel systems. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 134751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardani, M.; Kilicli, M.; Toker, O.S.; Yeganehzad, S.; Niazmand, R.; Palabiyik, I.; Konar, N. Investigation of process parameters and albumin concentration as foaming agent on quality of marshmallow dough: Production simulation with rheometer. Rheol. Acta 2022, 61, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, M.V.; Shamasundar, B.A. Texture profile analysis and functional properties of gelatin from the skin of three species of fresh water fish. Int. J. Food Prop. 2015, 18, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, C.; Wang, C.; Zheng, Y.; Ye, K.; Li, C.; Zhou, G. Effects of gellan gum and inulin on mixed-gel properties and molecular structure of gelatin. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 1336–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, F.-J.; Lai, K.-M.; Hsu, K.-C. A comparative study on physical properties and chemical interactions of gels from tilapia meat pastes induced by heat and pressure. J. Texture Stud. 2010, 41, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.A.; Bhat, R. Fish gelatin: Properties, challenges, and prospects as an alternative to mammalian gelatins. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Sun, W.; Zhan, S.; Jia, R.; Lou, Q.; Huang, T. Glycosylation with different saccharides on the gelling, rheological and structural properties of fish gelatin. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 150, 109699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sow, L.C.; Peh, Y.R.; Pekerti, B.N.; Fu, C.; Bansal, N.; Yang, H. Nanostructural analysis and textural modification of tilapia fish gelatin affected by gellan and calcium chloride addition. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 85, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Bhattacharya, S. Compressive textural attributes, opacity and syneresis of gels prepared from gellan, agar and their mixtures. J. Food Eng. 2011, 102, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, C.J.F.; Garcia-Rojas, E.E. Interpolymeric complexing between egg white proteins and xanthan gum: Effect of salt and protein/polysaccharide ratio. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 66, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamróz, E.; Kopel, P.; Juszczak, L.; Kawecka, A.; Bytesnikova, Z.; Milosavljević, V.; Kucharek, M.; Makarewicz, M.; Adam, V. Development and characterisation of furcellaran-gelatin films containing SeNPs and AgNPs that have antimicrobial activity. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 83, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesch, R.; Ramon, O.; Ladyzhinski, I.; Cohen, Y.; Mizrahi, S. Water sorption isotherm of solution containing hydrogels at high water activity. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1999, 34, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenova, M.G.; Antipova, A.S.; Belyakova, L.E. Food protein interactions in sugar solutions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 7, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Shim, J.; Bae, I.Y.; Cha, J.; Park, C.S.; Lee, H.G. Characterization of gellan/gelatin mixed solutions and gels. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2003, 36, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinthusamran, S.; Benjakul, S.; Swedlund, P.J.; Hemar, Y. Physical and rheological properties of fish gelatin gel as influenced by κ-carrageenan. Food Biosci. 2017, 20, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashayar, G.; Bain, P.A.; Salari, S.; Dozic, A.; Kleverlaan, C.J.; Feilzer, A.J. Perceptibility and acceptability thresholds for colour differences in dentistry. J. Dent. 2014, 42, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, L.; Singh, J.; Singh, H.; McCarthy, O.J. Starch–cassia gum interactions: A microstructure—Rheology study. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahali, K.; Ben Messaoud, G.; Kahn, C.J.F.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, L.; Kaci, M.; Cleymand, F.; Fleutot, S.; Linder, M.; Desobry, S.; Arab-Tehrany, E. Synthesis and Characterization of Nanofunctionalized Gelatin Methacrylate Hydrogels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, P.N.; Macwan, P.M.; Kamaliya, B.; Kumar, A. Rheological investigations and swelling behavior of gum ghatti-cl-poly(acrylic acid) hydrogel reinforced with graphene oxide. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Eng. 2025, 20, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, A. Infrared spectroscopy of proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA—Bioenerg. 2007, 1767, 1073–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szanto, L.G.; Marc, R.A.; Mureşan, A.E.; Mureșan, C.C.; Puşcaş, A.; Ranga, F.; Fetea, F.; Moraru, P.I.; Filip, M.; Muste, S. Improving Jelly Nutrient Profile with Bioactive Compounds from Pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) Extracts. Forests 2025, 16, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, S.R.; Voron’ko, N.G.; Kuchina, Y.A. Intermolecular interactions in the formation of polysaccharide-gelatin complexes: A spectroscopic study. Polymers 2022, 14, 2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, S.R.; Ilyin, S.O.; Maklakova, A.A.; Kulichikhin, V.G.; Malkin, A.Y. The rheology of gelatin hydrogels modified by κ-carrageenan. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janik, M.; Jamróz, E.; Tkaczewska, J.; Juszczak, L.; Kulawik, P.; Szuwarzyński, M.; Khachatryan, K.; Kopel, P. Utilisation of carp skin post-production waste in binary films based on furcellaran and chitosan to obtain packaging materials for storing blueberries. Materials 2021, 14, 7848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Regenstein, J.M.; Rahman, H.U.U.; Sahar, A.; Aadil, R.M.; Tariq, A.; Fatima, I.; Bilal, A.; He, L. Physicochemical and functional properties of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) skin gelatin in comparison to commercial bovine gelatin. Food Chem. Adv. 2025, 8, 101088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjakul, S.; Oungbho, K.; Visessanguan, W.; Thiansilakul, Y.; Roytrakul, S. Characteristics of gelatin from the skins of bigeye snapper, Priacanthus tayenus and Priacanthus macracanthus. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhao, S.; Lu, W.; Chen, N.; Zhu, D.; Li, Y. Preparation and characterization of enzymatically cross-linked gelatin/cellulose nanocrystal composite hydrogels. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 10794–10803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcharat, T.; Chaijan, M.; Karnjanapratum, S. Effect of furcellaran incorporation on gel properties of sardine surimi. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 5957–5967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.S.; Regenstein, J.M. Physicochemical and Sensory Characteristics of Fish Gelatin. J. Food Sci. 2000, 65, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayarri, S.; Izquierdo, L.; Costell, E. Sweetening power of aspartame in hydrocolloids gels: Influence of texture. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoi, F.C.; Ningtyas, D.W.; Geoffroy, Z.; Prakash, S. Protein-based hydrocolloids: Effect on the particle size distribution, tribo-rheological behaviour and mouthfeel characteristics of low-fat chocolate flavoured milk. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 115, 106628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, A.D.T.; Fonseca, G.G.; Balbinot, E.; Machado, A.; Prentice, C. Physical and chemical properties of wami tilapia skin gelatin. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 33, 592–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuvikene, R.; Truus, K.; Robal, M.; Volobujeva, O.; Mellikov, E.; Pehk, T.; Kollist, A.; Kailas, T.; Vaher, M. The extraction, structure, and gelling properties of hybrid galactan from the red alga Furcellaria lumbricalis (Baltic Sea, Estonia). J. Appl. Phycol. 2010, 22, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai Ministry of Public Health. Notification of the Ministry of Public Health (No. 182) B.E. 2541 (1998) Re: Nutrition Labelling. Available online: https://www.ecolex.org/details/legislation/notification-of-the-ministry-of-public-health-no-182-be-2541-1998-re-nutrition-labelling-lex-faoc160326/?q=Notification+of+the+Ministry+of+Public+Health+%28No.+182%29+B.E.+2541+%281998%29+Re%3A+Nutrition+Labelling (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Wang, J.; Aalaei, K.; Skibsted, L.H.; Ahrné, L.M. Calcium bioaccessibility increased during gastrointestinal digestion of α-lactalbumin and β-lactoglobulin. Food Res. Int. 2023, 164, 112415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petsong, K.; Yarnpakdee, S.; Senphan, T.; Sriket, C.; Kingwascharapong, P.; Moula Ali, A.M.; Surya, R.; Karnjanapratum, S. Impact of Bio-calcium from Nile Tilapia Bone as a Supporting Material on the Stability Enhancement of Immobilized Probiotics. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2025, 18, 6442–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugara, B.; Ambarwati, K.; Damayanthi, E. Mineral bioavailability in jelly drink made of green okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) and strawberry (Fragaria ananassa) extract. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 196, 012007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Han, L.; Yu, W.; Zhao, W.; Pan, J.; Prakash, S.; Dong, X. Carrageenan addition improves the melting temperature and 3D printing performance of the gelatin system. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 144, 108918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, N.; Yan, B.; Gao, W.; Huang, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Fan, D. Effects of preheating-induced denaturation treatments on the printability and instant curing property of soy protein during microwave 3D printing. Food Chem. 2022, 397, 133682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawdkuen, S.; Faseha, A.; Benjakul, S.; Kaewprachu, P. Application of anthocyanin as a color indicator in gelatin films. Food Biosci. 2020, 36, 100603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanprasert, S.; Kumnerdsiri, P.; Seubsai, A.; Lueangjaroenkit, P.; Pongsetkul, J.; Indriani, S.; Petcharat, T.; Sai-ut, S.; Hunsakul, K.; Issara, U.; et al. Techno-functional, rheological, and physico-chemical properties of gelatin capsule by-product for future functional food ingredients. Foods 2025, 14, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indriani, S.; Benjakul, S.; Quan, T.H.; Sitanggang, A.B.; Chaijan, M.; Kaewthong, P.; Petcharat, T.; Karnjanapratum, S. Effect of different ultrasound-assisted process modes on extraction yield and molecular characteristics of pepsin-soluble collagen from Asian bullfrog skin. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2023, 16, 3019–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcharat, T.; Sae-leaw, T.; Benjakul, S.; Quan, T.H.; Indriani, S.; Phimolsiripol, Y.; Karnjanapratum, S. Extraction of Kratom (Mitragyna speciosa) leaf compounds by enzymatic hydrolysis-assisted process: Yield, characteristics and its in vitro cytotoxicity in cell lines. Process Biochem. 2024, 142, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somjid, P.; Panpipat, W.; Petcharat, T.; Chaijan, M. Biochemical property and gel-forming ability of mackerel (Auxis thazard) surimi prepared by ultrasonic assisted washing. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 36199–36207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meilgaard, M.C.; Carr, B.T.; Civille, G.V. Sensory Evaluation Techniques; CRC press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Benjakul, S.; Mad-Ali, S.; Senphan, T.; Sookchoo, P. Biocalcium powder from precooked skipjack tuna bone: Production and its characteristics. J. Food Biochem. 2017, 41, e12412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Samples | Hardness (N) | Springiness | Cohesiveness | Gumminess (N) | Chewiness (N × mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JFG | 26.21 ± 0.70 d | 0.93 ± 0.02 a | 0.87 ± 0.04 a | 22.81 ± 1.46 d | 21.29 ± 1.55 d |
| JFG-Ca | 30.55 ± 0.68 c | 0.93 ± 0.01 a | 0.86 ± 0.03 a | 26.12 ± 0.90 c | 24.19 ± 0.86 c |
| JFG-FUR | 66.41 ± 1.31 b | 0.89 ± 0.01 b | 0.77 ± 0.01 b | 51.33 ± 0.84 b | 45.59 ± 1.16 b |
| JFG-FUR-Ca | 78.14 ± 1.76 a | 0.86 ± 0.01 c | 0.71 ± 0.01 c | 55.55 ± 2.19 a | 47.89 ± 2.51 a |
| Samples | Syneresis (%) | Gelling Temperature (°C) | Melting Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| JFG | 0.04 ± 0.00 a | 19.69 ± 0.29 c | 26.28 ± 0.28 c |
| JFG-Ca | 0.04 ± 0.01 a | 20.03 ± 0.38 c | 27.06 ± 0.60 c |
| JFG-FUR | 0.04 ± 0.00 a | 41.27 ± 0.57 b | 44.68 ± 0.51 b |
| JFG-FUR-Ca | 0.04 ± 0.00 a | 44.94 ± 0.58 a | 50.23 ± 0.39 a |
| Samples | L* | a* | b* | ∆E* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JFG | 63.85 ± 0.47 a | 14.49 ± 0.34 a | 9.49 ± 0.23 a | 34.68 ± 0.54 c |
| JFG-Ca | 63.28 ± 0.94 a | 13.97 ± 0.36 a | 9.22 ± 0.42 a | 35.39 ± 0.64 c |
| JFG-FUR | 49.50 ± 0.19 b | 3.29 ± 0.08 b | 2.86 ± 0.12 b | 44.65 ± 0.15 b |
| JFG-FUR-Ca | 43.88 ± 0.72 c | 2.57 ± 0.13 c | 1.07 ± 0.03 c | 50.20 ± 0.70 a |
| Sample | Appearance | Color | Odor | Firmness | Springiness | Taste | Mouth Feel | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JFG | 8.12 ± 0.85 a | 8.22 ± 1.30 a | 6.52 ± 1.82 b | 8.26 ± 1.60 a | 8.00 ± 1.48 a | 7.30 ± 1.45 a | 7.86 ± 1.83 a | 8.42 ± 1.23 a |
| JFG-Ca | 8.26 ± 0.92 a | 8.28 ± 1.28 a | 6.60 ± 1.53 b | 8.04 ±1.46 a | 8.02 ± 1.24 a | 7.02 ± 2.32 ab | 7.54 ± 1.40 a | 8.28 ± 1.18 a |
| JFG-FUR | 7.60 ± 1.14 b | 7.68 ± 1.04 b | 7.76 ± 1.29 a | 7.34 ±1.22 b | 7.18 ± 1.04 b | 6.42 ± 1.67 b | 5.76 ± 2.02 b | 7.66 ± 1.02 b |
| JFG-FUR-Ca | 7.70 ± 1.16 b | 7.82 ± 1.22 b | 7.36 ± 1.59 a | 7.28 ± 1.08 c | 6.62 ± 0.75 c | 6.46 ± 1.42 b | 6.52 ± 1.61 c | 7.52 ± 1.09 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Petcharat, T.; Chaijan, M.; Indriani, S.; Karnjanapratum, S.; Nirmal, N.; Singh, J.; Nairfana, I.; Nalinanon, S. Physicochemical, Sensorial and Calcium Bioavailability of Jelly Prepared Using Fish Gelatin in Combination with Furcellaran and Calcium L-Threonate. Gels 2026, 12, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels12010026
Petcharat T, Chaijan M, Indriani S, Karnjanapratum S, Nirmal N, Singh J, Nairfana I, Nalinanon S. Physicochemical, Sensorial and Calcium Bioavailability of Jelly Prepared Using Fish Gelatin in Combination with Furcellaran and Calcium L-Threonate. Gels. 2026; 12(1):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels12010026
Chicago/Turabian StylePetcharat, Tanyamon, Manat Chaijan, Sylvia Indriani, Supatra Karnjanapratum, Nilesh Nirmal, Jaspreet Singh, Ihlana Nairfana, and Sitthipong Nalinanon. 2026. "Physicochemical, Sensorial and Calcium Bioavailability of Jelly Prepared Using Fish Gelatin in Combination with Furcellaran and Calcium L-Threonate" Gels 12, no. 1: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels12010026
APA StylePetcharat, T., Chaijan, M., Indriani, S., Karnjanapratum, S., Nirmal, N., Singh, J., Nairfana, I., & Nalinanon, S. (2026). Physicochemical, Sensorial and Calcium Bioavailability of Jelly Prepared Using Fish Gelatin in Combination with Furcellaran and Calcium L-Threonate. Gels, 12(1), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels12010026











