In Vitro Digestibility of Starch Gel in Cooked Rice Prepared with Thermo-Reversible Short-Chain Glucan Aggregates (SCGAs)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Thermo-Reversibility of SCGAs
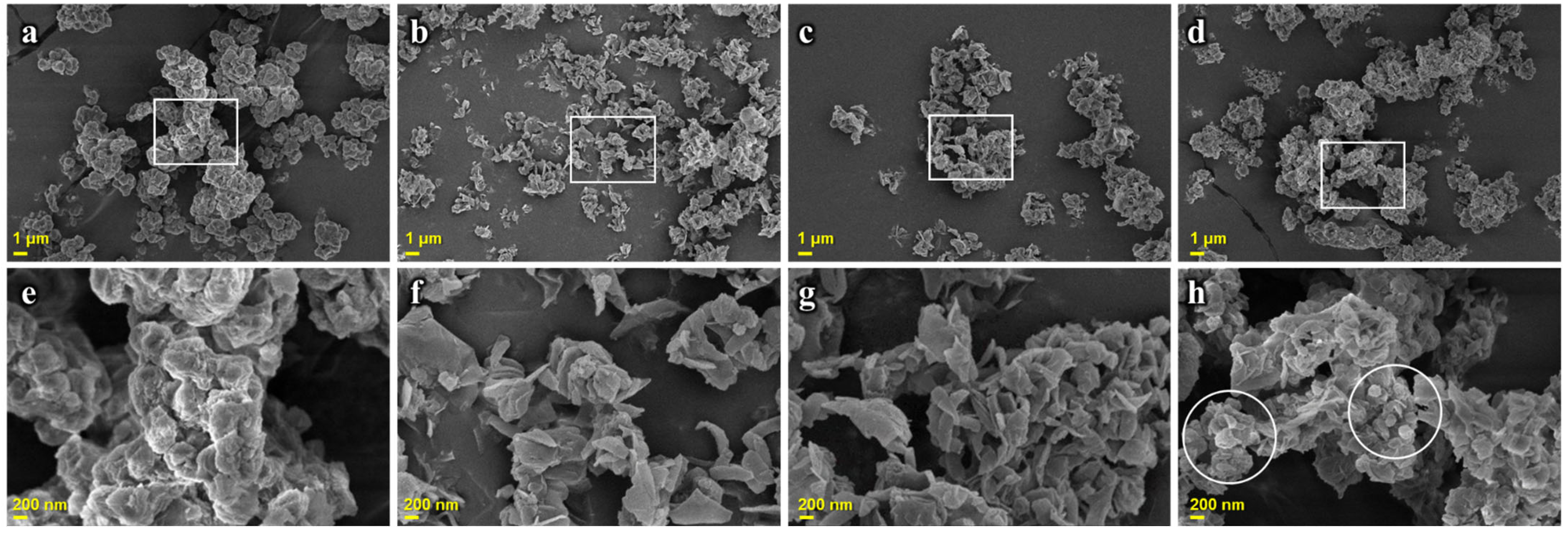
2.1.1. Morphology
2.1.2. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Patterns
2.1.3. Thermal Properties
2.1.4. In Vitro Digestibility
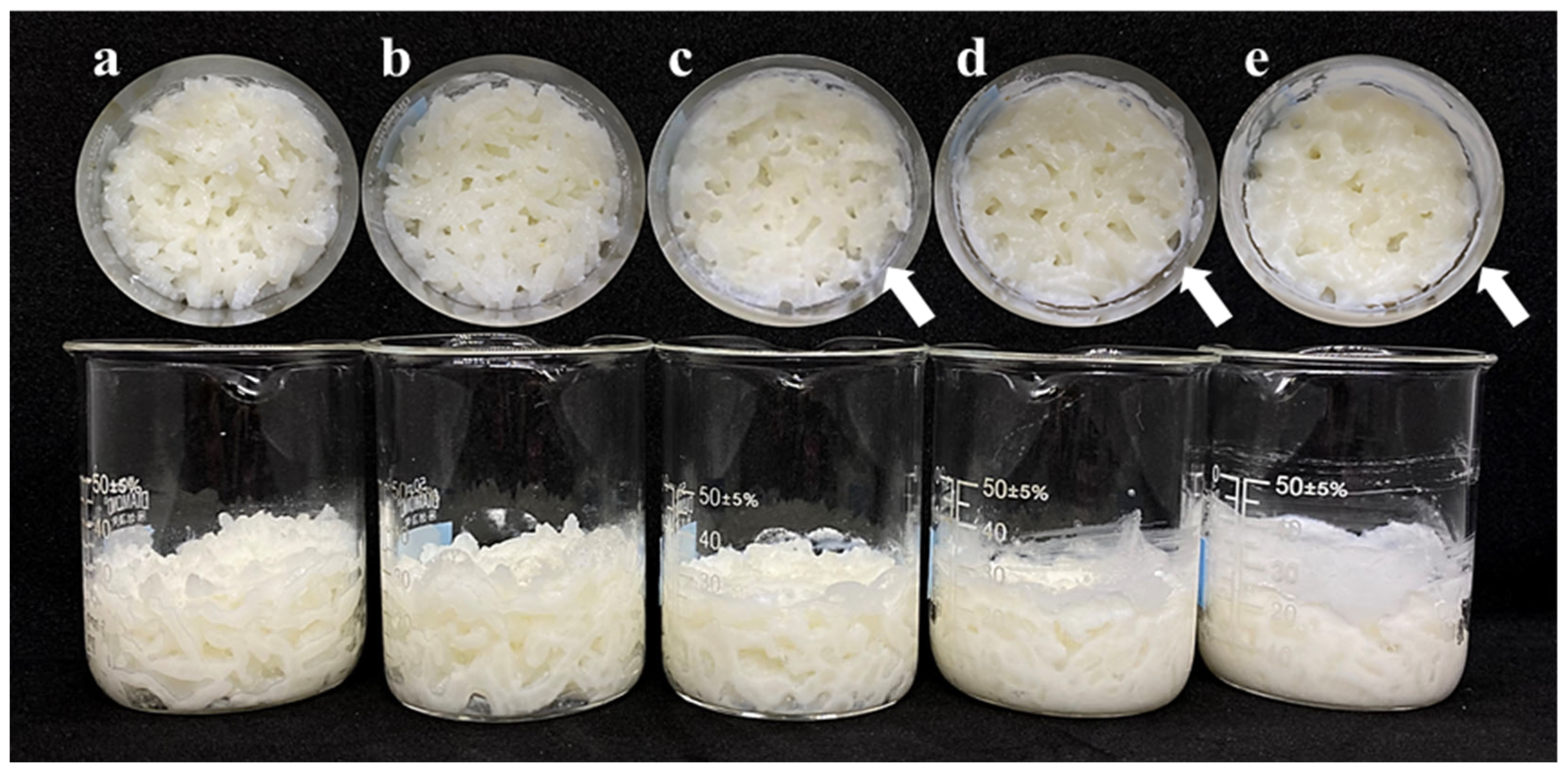
2.2. Application of SCGAs in Cooked Rice
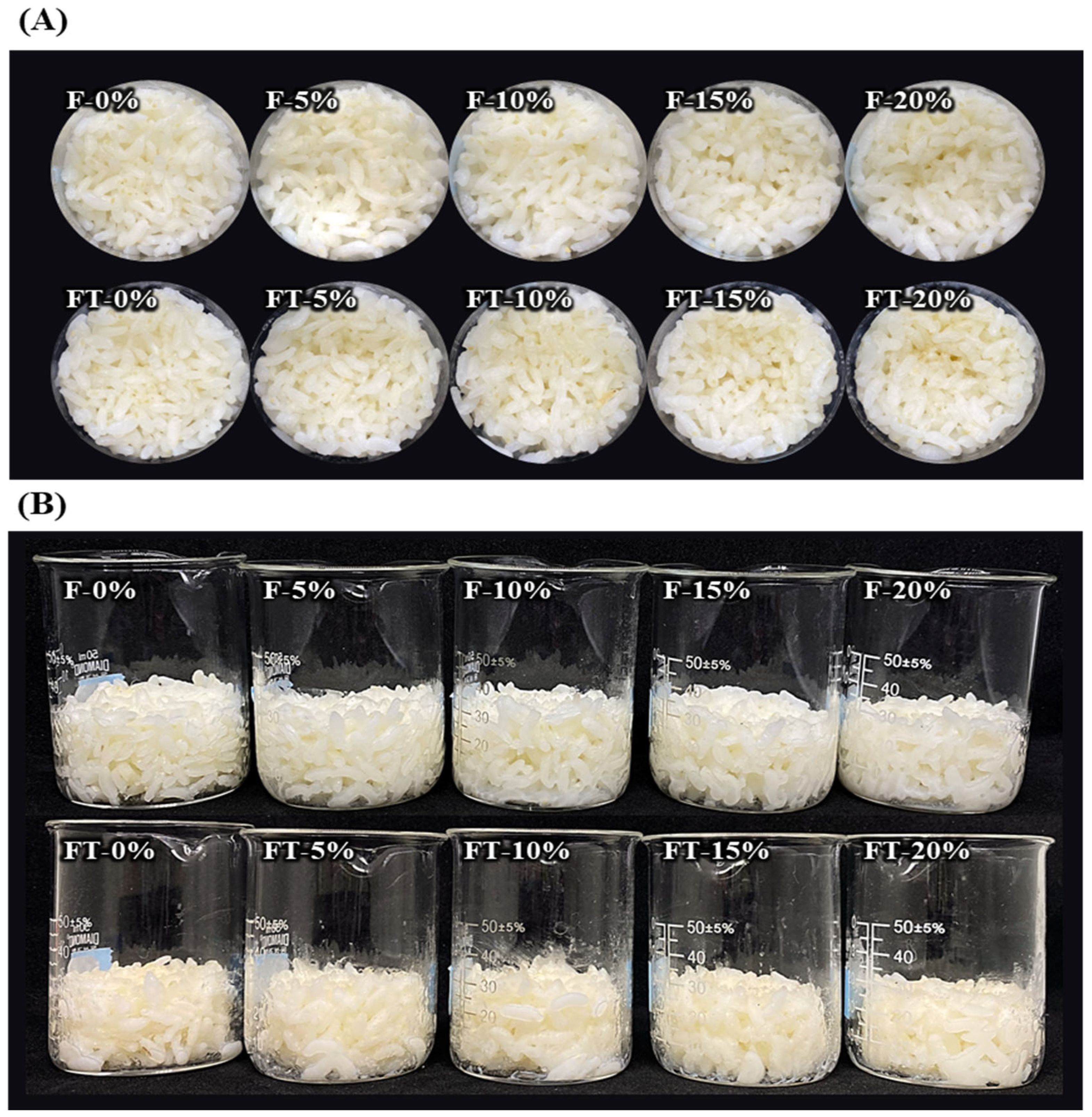
2.2.1. Appearance of Cooked Rice
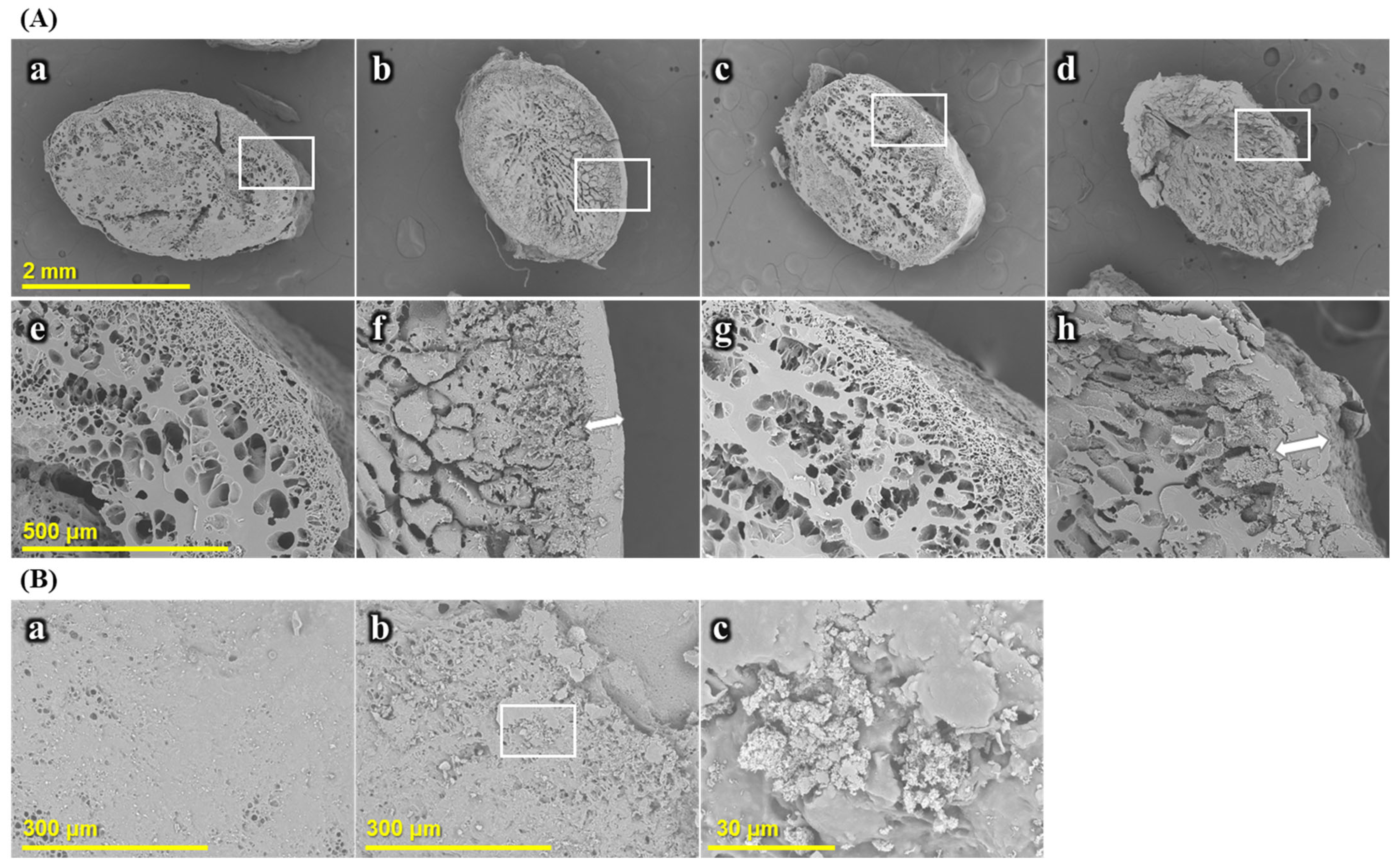
2.2.2. Morphology of Cooked Rice
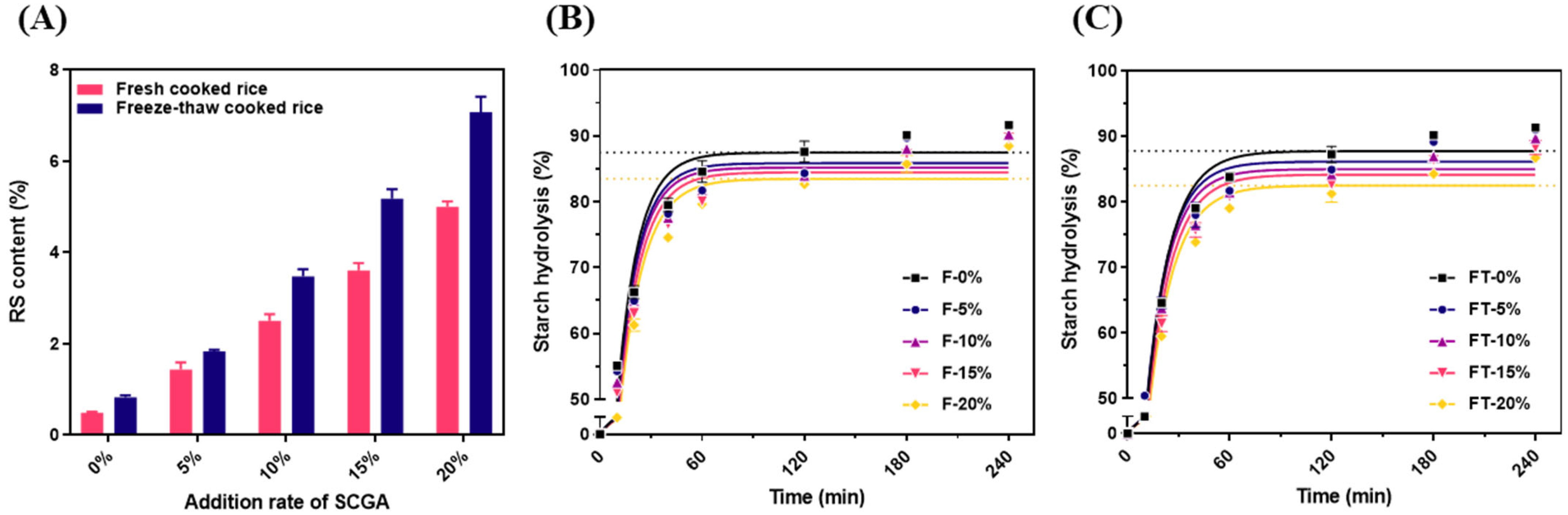
2.2.3. In Vitro Digestibility of Starch Gels and Estimated Glycemic Index (eGI) of Cooked Rice
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Short-Chain Glucan Aggregates (SCGAs)
4.3. Thermo-Reversibility of SCGA
4.3.1. Preparation of Cooked SCGA
4.3.2. Morphology
4.3.3. X-Ray Diffraction Patterns
4.3.4. Thermal Properties
4.3.5. In Vitro Digestibility
4.4. Application to Cooked Rice
4.4.1. Preparation of Cooked Rice with or Without SCGA
4.4.2. Morphology
4.4.3. In-Vitro Digestibility of Starch Gels and Estimated Glycemic Index (eGI)
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. Retrogradation properties of high amylose rice flour and rice starch by physical modification. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.S.; Wang, P.; Wang, N.; Yang, L.; Xiao, Z. Brown rice versus white rice: Nutritional quality, potential health benefits, development of food products, and preservation technologies. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1070–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliano, B.O. Structure, chemistry, and function of the rice grain and its fractions. Cereal Foods World 1992, 37, 772–779. [Google Scholar]
- Brand-Miller, J.C. Glycemic load and chronic disease. Nutr. Rev. 2003, 61, S49–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.W.; Venn, B.; Lu, J.; Monro, J.; Rush, E. Effect of cold storage and reheating of parboiled rice on postprandial glycaemic response, satiety, palatability and chewed particle size distribution. Nutrients 2017, 9, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Panda, P.A.; Lal, M.K.; Ngangkham, U.; Sahu, C.; Soren, K.R.; Subudhi, H.N.; Samantaray, S.; Sharma, S. Addition of pulses, cooking oils, and vegetables enhances resistant starch and lowers the glycemic index of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Starch-Stärke 2020, 72, 1900081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englyst, H.N.; Kingman, S.; Cummings, J. Classification and measurement of nutritionally important starch fractions. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 46, S33–S50. [Google Scholar]
- Goñi, I.; Garcia-Alonso, A.; Saura-Calixto, F. A starch hydrolysis procedure to estimate glycemic index. Nutr. Res. 1997, 17, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, U.; Robin, F. Slowly digestible starch–its structure and health implications: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 18, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topping, D.L.; Clifton, P.M. Short-chain fatty acids and human colonic function: Roles of resistant starch and nonstarch polysaccharides. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 1031–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Yadav, B.S.; Ritika. Resistant starch: Physiological roles and food applications. Food Rev. Int. 2008, 24, 193–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Zaragoza, E.; Sánchez-Zapata, E.; Sendra, E.; Sayas, E.; Navarro, C.; Fernández-López, J.; Pérez-Alvarez, J.A. Resistant starch as prebiotic: A review. Starch-Stärke 2011, 63, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Hu, X.; Boye, J.I. Research advances on the formation mechanism of resistant starch type III: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 276–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.-M.; Park, C.-S.; Kim, Y.-R.; Baik, M.-Y. Preparation and characterization of self-assembled short-chain glucan aggregates (SCGAs) derived from various starches. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 114, 106517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-Y.; Oh, S.-M.; Shin, J.-S.; Bae, J.-E.; Ye, S.-J.; Choi, H.-W.; Baik, M.-Y. Effect of debranching enzymes on self-assembly kinetics and physicochemical characteristics of short-chain glucan aggregates (SCGAs). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 9157–9164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-E.; Oh, S.-M.; Shin, J.-S.; Bae, J.-E.; Ye, S.-J.; Baik, M.-Y. Effect of insoluble glucan on self-assembly kinetics and physicochemical properties of starch microparticle (SMP). Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Oh, S.M.; Kim, H.Y.; Choi, J.H.; Shin, J.S.; Bae, J.E.; Ye, S.J.; Baik, M.-Y. Self-assembly kinetics of short chain glucan aggregates (SCGA). Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-G.; Ye, S.-J.; Oh, S.-M.; Shin, J.-S.; Bae, J.-E.; Choi, H.-W.; Baik, M.-Y. Quality Characteristics and In Vitro Digestibility of Starch Gel in White Noodles Prepared with Short-Chain Glucan Aggregates (SCGA). Gels 2025, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Qin, Y.; Xu, X.; Jin, Z. Novel approach with controlled nucleation and growth for green synthesis of size-controlled cyclodextrin-based metal–organic frameworks based on short-chain starch nanoparticles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9785–9793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Shi, Y.-C. Preparation, structure, and digestibility of crystalline A-and B-type aggregates from debranched waxy starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 105, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-M.; Kim, Y.-R.; Park, C.-S.; Seo, D.-H.; Baik, M.-Y. Thermo-reversibility of short-chain glucan aggregates (SCGA) derived from various starches. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 146, 109256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q. Physicochemical properties of starch nanocomposite films enhanced by self-assembled potato starch nanoparticles. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 69, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Qin, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, Q.; Xiong, L.; Liu, Z. Preparation and characterization of starch nanoparticles via self-assembly at moderate temperature. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 84, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Shi, Y.-C. Structure and digestibility of crystalline short-chain amylose from debranched waxy wheat, waxy maize, and waxy potato starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 79, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Xiong, L.; Li, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Sun, Q. Fractionation of debranched starch with different molecular weights via edible alcohol precipitation. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 83, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Li, X.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q. Retrogradation property of starch nanoparticles prepared by pullulanase and recrystallization. Starch-Stärke 2016, 68, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, M.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, T. Effect of pullulanase debranching and recrystallization on structure and digestibility of waxy maize starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 76, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiatponglarp, W.; Tongta, S.; Rolland-Sabaté, A.; Buléon, A. Crystallization and chain reorganization of debranched rice starches in relation to resistant starch formation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 122, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Yang, J.; Ge, S.; Chang, R.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q. Preparation and characterization of size-controlled starch nanoparticles based on short linear chains from debranched waxy corn starch. Lwt 2016, 74, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.-T.; Chang, E.-H.; Chung, H.-J. Thermal transition characteristics of heat–moisture treated corn and potato starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 2001, 46, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanthan, T. Physicochemical properties of small-and large-granule starches of waxy, regular, and high-amylose barleys. Cereal Chem. 1996, 73, 199–207. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Sweedman, M.C.; Shi, Y.-C. Structure, birefringence and digestibility of spherulites produced from debranched waxy maize starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 1486–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Medina, R.; del Mar Munio, M.; Guadix, E.M.; Guadix, A. Production of resistant starch by enzymatic debranching in legume flours. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 1176–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.J.; Kim, Y.; Choi, S.J.; Moon, T.W. Slowly digestible starch from heat-moisture treated waxy potato starch: Preparation, structural characteristics, and glucose response in mice. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 1222–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, K.S.; Choi, S.J.; Moon, T.W. Structure and digestibility of debranched and hydrothermally treated water yam starch. Starch-Stärke 2013, 65, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhan, J.; Zhao, J.; Xie, Z.; Xu, X.; Jin, Z. Preparation of products rich in slowly digestible starch (SDS) from rice starch by a dual-retrogradation treatment. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Chen, F.; Kong, F.; Gao, Q.; Aadil, R.M.; Yu, S. Structure and digestibility of debranched and repeatedly crystallized waxy rice starch. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, L.R.; Cai, L.; Shi, Y.-C. Mechanism and enzymatic contribution to in vitro test method of digestion for maize starches differing in amylose content. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 4379–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Qian, H.; Qi, X.; Wu, G. Research on migration path and structuring role of water in rice grain during soaking. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 92, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Hu, X.; Zhang, F.; Fang, C.; Liu, C.; Luo, S. Freeze-thaw stability of rice starch modified by improved extrusion cooking technology. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, M.; Jeong, H.-Y.; Lim, S.-T.; Chung, H.-J. The cooking method features controlling eating quality of cooked rice: An explanation from the view of starch structure in leachate and morphological characteristics. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 111980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Ma, Y.; Sun, D.-W. Effects of freezing rates on starch retrogradation and textural properties of cooked rice during storage. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 1138–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunyanart, T.; Charoenrein, S. Effect of sucrose on the freeze–thaw stability of rice starch gels: Correlation with microstructure and freezable water. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 74, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.-j.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.C. Retrogradation of heat-gelatinized rice grain in sealed packaging: Investigation of moisture relocation. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 37, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funami, T.; Kataoka, Y.; Omoto, T.; Goto, Y.; Asai, I.; Nishinari, K. Food hydrocolloids control the gelatinization and retrogradation behavior of starch. 2a. Functions of guar gums with different molecular weights on the gelatinization behavior of corn starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2005, 19, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, L.W.; Kasapis, S.; Lim, K.M.; Foo, C.W. Structural enhancement leading to retardation of in vitro digestion of rice dough in the presence of alginate. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1458–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayimbila, F.; Keawsompong, S. In vitro starch digestion and colonic fermentation of Thai jasmine rice. Starch-Stärke 2018, 70, 1800049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, M.S.; Henry, C.J. Reducing the glycemic impact of carbohydrates on foods and meals: Strategies for the food industry and consumers with special focus on Asia. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 670–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonia, S.; Witjaksono, F.; Ridwan, R. Effect of cooling of cooked white rice on resistant starch content and glycemic response. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 24, 620–625. [Google Scholar]
- Patindol, J.A.; Guraya, H.S.; Champagne, E.T.; McClung, A.M. Nutritionally important starch fractions of rice cultivars grown in Southern United States. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, H137–H144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yglesias, R.; Jackson, D.S. Evaluation of liquid nitrogen freeze drying and ethanol dehydration as methods to preserve partially cooked starch and masa systems. Cereal Chem. 2005, 82, 702–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCleary, B.V.; McLoughlin, C.; Charmier, L.M.; McGeough, P. Measurement of available carbohydrates, digestible, and resistant starch in food ingredients and products. Cereal Chem. 2020, 97, 114–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


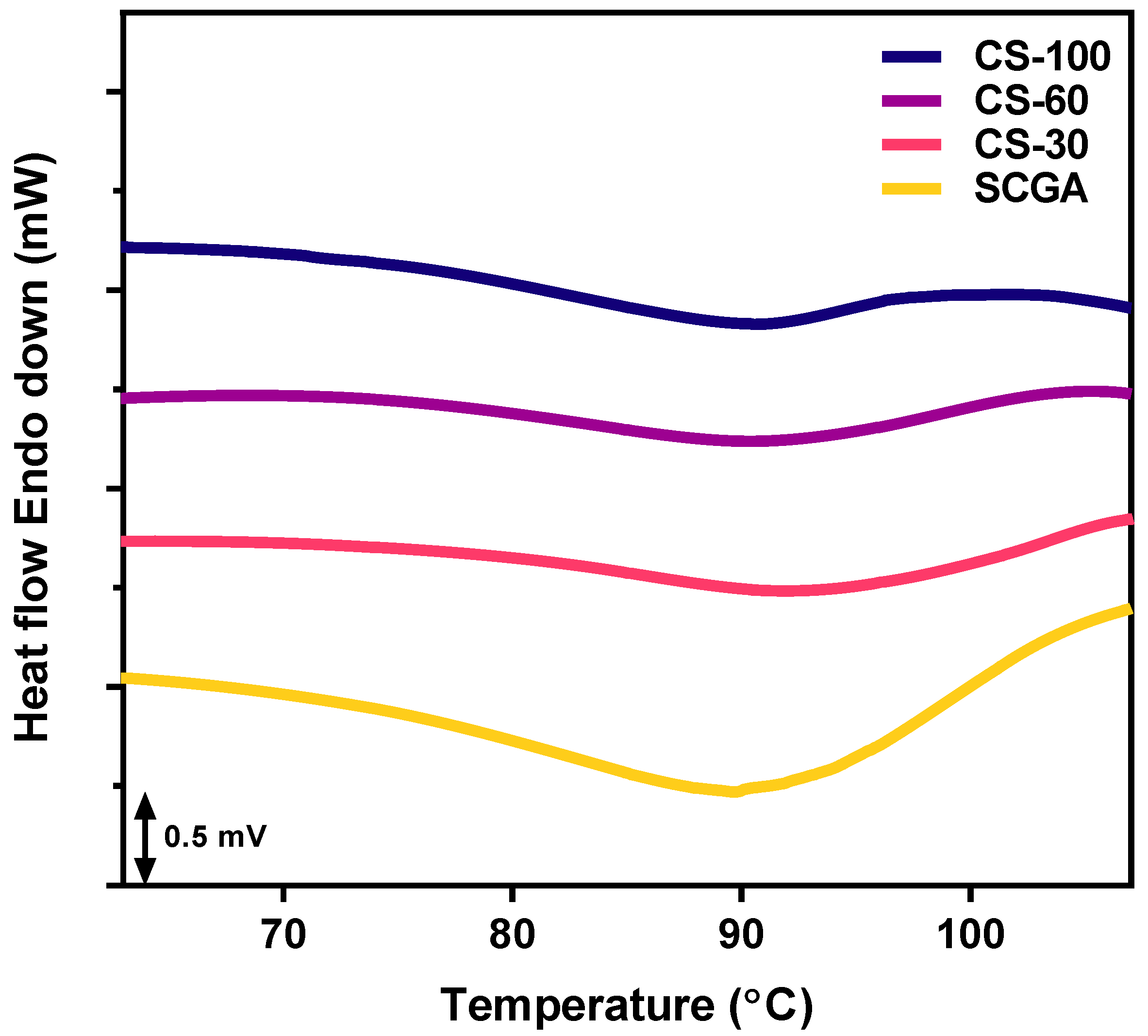

| Sample | To (°C) | Tp (°C) | Tc (°C) | Tc − To (°C) | ∆H (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCGA | 69.6 ± 2.2 b* | 91.2 ± 1.3 b | 105.3 ± 0.9 a | 35.7 ± 2.9 a | 27.8 ± 1.3 a |
| CS-100 | 76.0 ± 0.7 a | 91.6 ± 1.1 ab | 100.2 ± 1.8 b | 24.2 ± 2.5 b | 6.9 ± 0.6 c |
| CS-60 | 74.8 ± 0.4 a | 91.4 ± 1.0 b | 103.1 ± 0.6 ab | 28.3 ± 1.0 b | 7.7 ± 0.5 c |
| CS-30 | 75.8 ± 0.5 a | 94.7 ± 1.3 a | 105.4 ± 1.3 a | 29.6 ± 1.5 b | 9.1 ± 0.6 b |
| Sample | RDS (%) | SDS (%) | RS (%) | SDS + RS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCGA | 30.9 ± 1.2 a* | 26.6 ± 1.5 c | 42.5 ± 2.2 a | 73.3 ± 1.2 c |
| CS-100 | 24.9 ± 0.7 b | 43.7 ± 2.9 a | 31.4 ± 2.5 b | 75.1 ± 0.7 b |
| CS-60 | 22.6 ± 1.9 bc | 41.2 ± 0.7 a | 36.1 ± 1.4 b | 77.3 ± 1.9 ab |
| CS-30 | 19.9 ± 2.7 c | 32.6 ± 2.1 b | 47.5 ± 2.6 a | 80.1 ± 2.7 a |
| Addition Rate (%) | Starch Fractions | Hydrolysis Kinetics | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RDS (%) | SDS (%) | RS (%) | C∞ (%) * | k (min−1) * | HI * | eGI * | |
| Fresh cooked rice | |||||||
| 0 | 97.63 ± 0.20 a** | 1.87 ± 0.21 d | 0.49 ± 0.02 f | 87.5 ± 0.7 a | 0.082 ± 0.003 a | 88.8 ± 0.6 a | 88.4 ± 0.3 a |
| 5 | 96.12 ± 0.23 bc | 2.44 ± 0.27 cd | 1.44 ± 0.16 e | 85.9 ± 0.3 bc | 0.082 ± 0.001 a | 87.0 ± 0.1 bc | 87.4 ± 0.1 bc |
| 10 | 94.33 ± 0.24 de | 3.16 ± 0.35 bc | 2.51 ± 0.14 d | 85.2 ± 0.3 bcd | 0.081 ± 0.001 ab | 86.2 ± 0.5 cd | 87.0 0.2 cd |
| 15 | 92.48 ± 0.45 f | 3.95 ± 0.27 ab | 3.57 ± 0.20 c | 84.5 ± 0.2 d | 0.077 ± 0.001 bc | 85.2 ± 0.2 de | 86.4 ± 0.1 de |
| 20 | 90.59 ± 0.14 g | 4.41 ± 0.27 a | 5.00 ± 0.12 b | 83.3 ± 0.3 ef | 0.073 ± 0.001 cde | 84.0 ± 0.2 f | 85.7 ± 0.1 f |
| Freeze–thaw cooked rice | |||||||
| 0 | 96.73 ± 0.19 ab | 2.44 ± 0.23 cd | 0.83 ± 0.05 f | 87.8 ± 0.6 a | 0.071 ± 0.002 de | 88.1 ± 0.6 ab | 88.0 ± 0.3 ab |
| 5 | 95.25 ± 0.30 cd | 2.91 ± 0.31 c | 1.84 ± 0.03 e | 86.2 ± 0.4 b | 0.075 ± 0.001 cd | 86.8 0.5 c | 87.2 0.3 c |
| 10 | 93.46 ± 0.27 ef | 3.06 ± 0.32 bc | 3.48 ± 0.16 c | 85.0 ± 0.1 cd | 0.074 ± 0.001 cd | 85.6 ± 0.1 d | 86.6 ± 0.0 d |
| 15 | 90.94 ± 0.47 g | 3.88 ± 0.48 ab | 5.18 ± 0.21 b | 84.2 ± 0.3 de | 0.070 ± 0.001 de | 84.4 ± 0.5 ef | 85.9 ± 0.3 ef |
| 20 | 88.46 ± 0.60 h | 4.46 ± 0.43 a | 7.10 ± 0.33 a | 82.5 ± 0.4 f | 0.069 ± 0.000 e | 82.5 ± 0.2 g | 84.9 ± 0.1 g |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoon, S.-E.; Ye, S.-J.; Kim, M.-S.; Oh, S.-M.; Shin, J.-S.; Bae, J.-E.; Choi, H.-W.; Baik, M.Y. In Vitro Digestibility of Starch Gel in Cooked Rice Prepared with Thermo-Reversible Short-Chain Glucan Aggregates (SCGAs). Gels 2025, 11, 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090701
Yoon S-E, Ye S-J, Kim M-S, Oh S-M, Shin J-S, Bae J-E, Choi H-W, Baik MY. In Vitro Digestibility of Starch Gel in Cooked Rice Prepared with Thermo-Reversible Short-Chain Glucan Aggregates (SCGAs). Gels. 2025; 11(9):701. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090701
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoon, So-Eun, Sang-Jin Ye, Min-Seok Kim, Seon-Min Oh, Jae-Sung Shin, Ji-Eun Bae, Hyun-Wook Choi, and Moo Yeol Baik. 2025. "In Vitro Digestibility of Starch Gel in Cooked Rice Prepared with Thermo-Reversible Short-Chain Glucan Aggregates (SCGAs)" Gels 11, no. 9: 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090701
APA StyleYoon, S.-E., Ye, S.-J., Kim, M.-S., Oh, S.-M., Shin, J.-S., Bae, J.-E., Choi, H.-W., & Baik, M. Y. (2025). In Vitro Digestibility of Starch Gel in Cooked Rice Prepared with Thermo-Reversible Short-Chain Glucan Aggregates (SCGAs). Gels, 11(9), 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090701









