Fabrication, Characterization, and In Vitro Digestion Behavior of Bigel Loaded with Notoginsenoside Rb1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Texture Properties
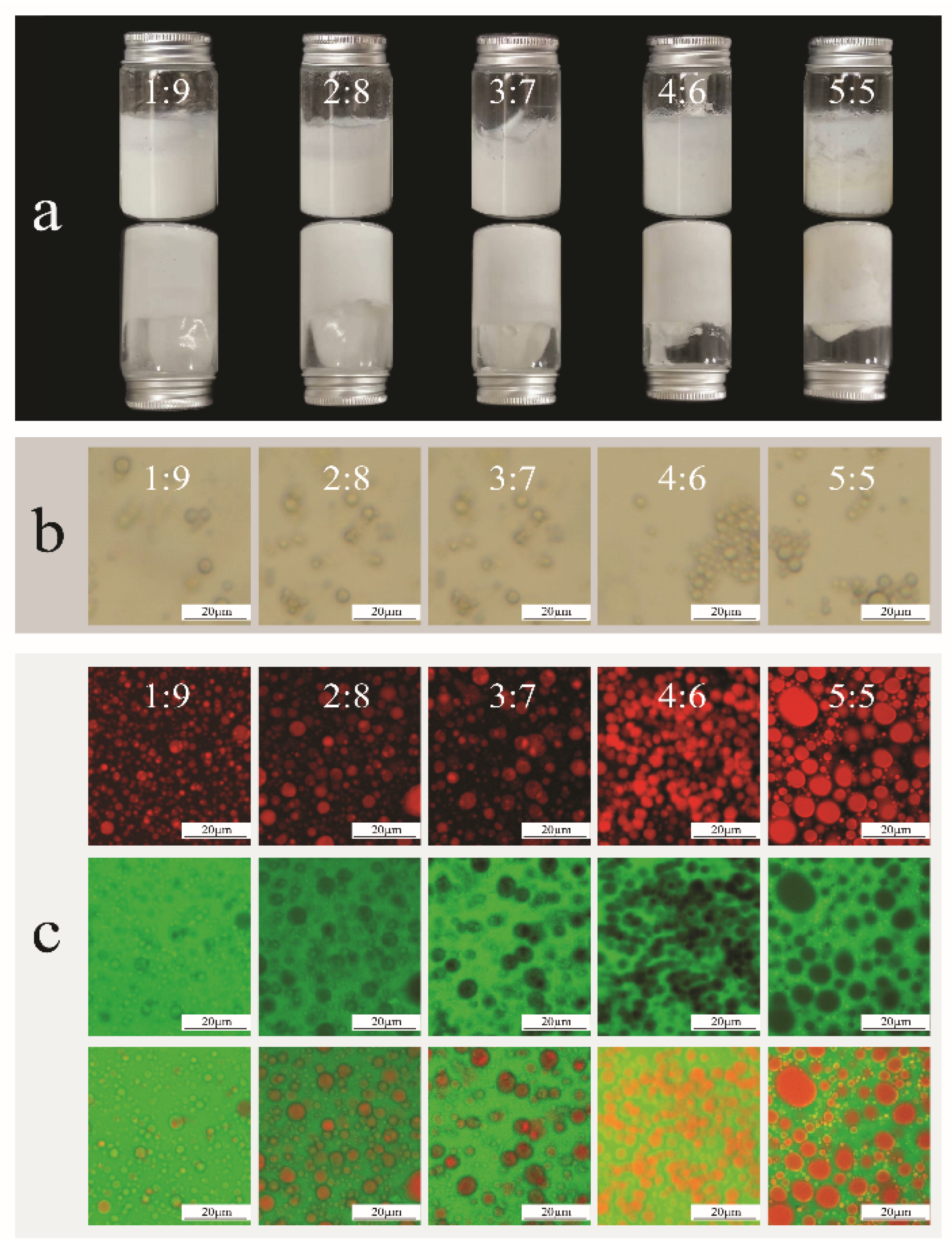
2.2. Microstructure Observation of Bigels
2.3. Bigel Stability Analysis of Bigels
2.4. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy Analysis of Bigels
2.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analysis of Bigels
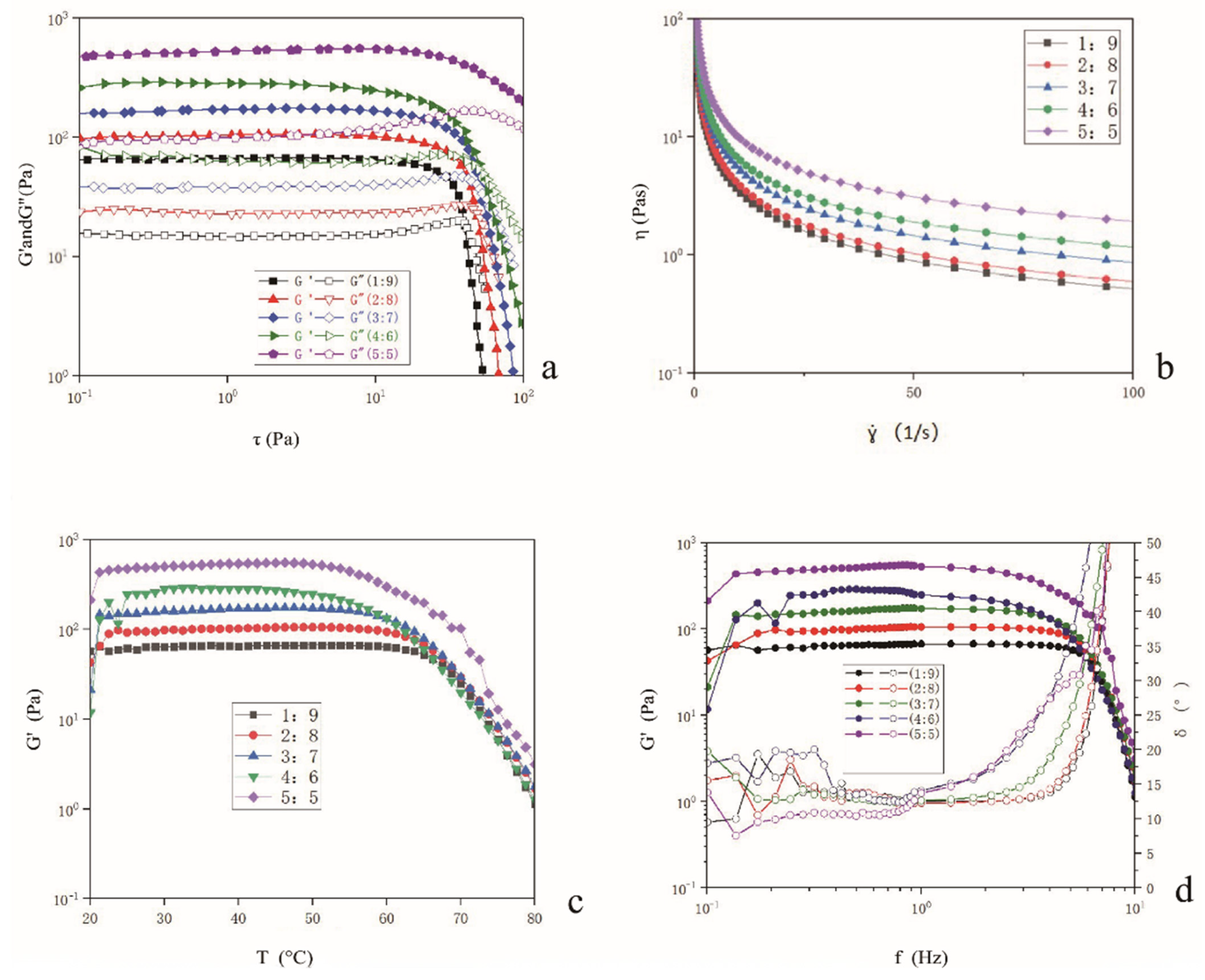
2.6. Determination of Rheological Properties of Bigels
2.7. Determination of the Rb1 Release Rate During Digestion
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Oleogels
4.3. Preparation of a Rb1-Loaded Hydrogel
4.4. Preparation of Rb1 Bigels
4.5. Texture Analysis
4.6. Microstructure Observation
4.7. Bigel Stability Analysis
4.8. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
4.9. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analysis
4.10. Determination of Rheological Properties
4.10.1. Stress Scanning
4.10.2. Flow Curve
4.10.3. Temperature Curve
4.10.4. Frequency Scanning
4.11. In Vitro Digestion Analysis
4.12. Data Processing and Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
| Rb1 | Notoginsenoside Rb1 |
| WHC | Water-holding capacity |
| OHC | Oil-holding capacity |
| EE | Encapsulation efficiency |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
References
- Zhang, H.Z.; Liu, D.H.; Zhang, D.K.; Wang, Y.H.; Li, G.; Yan, G.L.; Wang, J.B. Quality assessment of Panax notoginseng from different regions through the analysis of marker chemicals, biological potency and ecological factors. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.W.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, L.; Shang, J.; Yang, X.B. Antioxidant, antiproliferative, and pro-apoptotic activities of a saponin extract derived from the roots of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F.H. Chen. J. Med. Food 2012, 15, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.R.; Xiang, Z.J.; Ye, T.X.; Yuan, Y.J.; Guo, Z.X. Antioxidant activities of Salvia miltiorrhiza and Panax notoginseng. Food Chem. 2005, 99, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.T.; Yang, C.L.H.; Or, T.C.T.; Luo, D.; Li, J.C.B. Ginsenoside Rb1 from Panax notoginseng suppressed TNF-α-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 via the suppression of double-strand RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR)/NF-κB pathway. Molecules 2022, 27, 8050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.Q.; Chen, C.; Li, W. Ginsenoside Rb1 in cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases: A review of therapeutic potentials and molecular mechanisms. Chin. Herb. Med. 2024, 16, 489–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.W.; Guan, Y.H.; Lv, Z.; Yang, S.C.; Zhang, G.H.; Zhao, Y.H.; Zhao, M.; Chen, J.W. Optimization of saponin extraction from the leaves of Panax notoginseng and Panax quinquefolium and evaluation of their antioxidant, antihypertensive, hypoglycemic and anti-inflammatory activities. Food Chem. X 2024, 14, 101642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.J.; Sun, X.M.; Cheng, J.J.; Ban, Q.F.; Guo, M.R. Physicochemical, digestive, and sensory properties of Panax notoginseng saponins encapsulated by polymerized whey protein. Foods 2021, 10, 2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Zheng, H.; Zheng, T.; Jiang, J.N.; Yao, X.; Jia, F.; He, K.; Yang, Y. Quantitative changes and transformation mechanisms of saponin components in chinese herbal medicines during storage and processing: A review. Molecules 2024, 29, 4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.F.; Fang, X.L.; Chen, D.F. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of ginsenoside Rb1 and Rg1 from Panax notoginseng in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 84, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollom, M.A.; Clark, S.; Acevedo, N.C. Development and characterization of a novel soy lecithin-stearic acid and whey protein concentrate bigel system for potential edible applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupi, F.R.; Shakeel, A.; Greco, V.; Rossi, C.O.; Baldino, N.; Gabrielel, D. A rheological and microstructural characterisation of bigels for cosmetic and pharmaceutical uses. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 69, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, E.P.; Li, J.W.; Duan, Z.H.; Fan, L.P. Bigels as emerging biphasic systems: Properties, applications, and prospects in the food industry. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 154, 110089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Y.; Zheng, H.X.; Mo, Y.F.; Gao, Y.X.; Mao, L.K. Structural characterization of hydrogel-oleogel biphasic systems as affected by oleogelators. Food Res. Int. 2022, 158, 111536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.B.; Wang, Y.X.; Du, L.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Liu, Y.F.; Meng, Z. Catastrophic phase inversion of bigels characterized by fluorescence intensity-based 3D modeling and the formability for decorating and 3D printing. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 126, 107461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.X.; Chen, Z.J.; Meng, Z. Bigels constructed from hybrid gelator systems: Bulk phase-interface stability and 3D printing. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 5078–5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.M.; Gao, J.M.; Han, L.J.; Han, K.X.; Wei, W.; Wu, T.; Li, J.L.; Zhang, M. Development and characterization of novel bigels based on monoglyceride-beeswax oleogel and high acyl gellan gum hydrogel for lycopene delivery. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.X.; Mao, L.K.; Cui, M.N.; Liu, J.F.; Gao, Y.X. Development of food-grade bigels based on κ-carrageenan hydrogel and monoglyceride oleogels as carriers for β-carotene: Roles of oleogel fraction. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 105, 105855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Abdullah, T.W.; Chen, M.M.; Huang, Y.S.; Xiao, J. Oral sensation and gastrointestinal digestive profiles of bigels ttuned by the mass ratio of konjac glucomannan to gelatin in the binary hydrogel matrix. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 312, 120765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samui, T.; Goldenisy, D.; Rosen-Kligvasser, J.; Davidovich-Pinhas, M. The development and characterization of novel in-situ bigel formulation. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.J.; Liu, F.F.; Ma, Z.H.; Li, Y.; Zheng, H.Y. Effects of different gelation mechanisms on the structural properties of bigels: A comparative study. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 167, 111249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Alvi, T.; Biswas, A.; Shityakov, S.; Gusinskaia, T.; Lavrentev, F.; Radhakrishnan, M. Food gels: Principles, interaction mechanisms and its microstructure. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 63, 12530–12551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.l.; Yang, N.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Hou, J.W.; Gao, Y.D.; Tian, L.; Jin, Z.; Shen, Y.Y.; Guo, S.R. The gelling behavior of gellan in the presence of different sodium salts. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, K.; Qian, H.; Bhagyalakshmi, R.; Fatang, J. The Advances of characterization and evaluation methods for the compatibility and assembly structure stability of food soft matter. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.X.; Han, J.Z.; Xiao, Y.H.; Guo, R.H.; Liu, X.K.; Zhang, H.; Xu, X.B. Fabrication and characterization of novel food-grade bigels based on interfacial and bulk stabilization. Foods 2023, 12, 2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswajit, S.; Somali, D.; Deblu, S.; Preetam, S.; Biswaranjan, M.; Maciej, J.; Marek, W.; Haladhar, B.; Kunal, P. Variations in microstructural and physicochemical properties of soy wax/soybean oil-derived oleogels using soy Lecithin. Polymers 2022, 14, 3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.J.; Li, B.; Wu, A.; Li, J.W.; Tang, J.M.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Z.G. Gelatin-Wax-Based Bigel System: Innovative Research on a Low-Calorie Fat Substitute. LWT 2025, 224, 117836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, A.; Farooq, U.; Gabriele, D.; Marangoni, A.G.; Lupi, F.R. Bigels and multi-component organogels: An overview from rheological perspective. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.X.; Ge, Z.Z.; Zhang, L.H.; Wei, Z.; Wen, F. Dual stabilization, phase inversion and mechanical properties of a novel bigels system based on myofibrillar protein hydrogel and glycerol monostearate oleogel. J. Food Eng. 2025, 393, 112500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Qi, Q.; Yang, Y.H.; Chen, X.G.; Huang, Y.K.; Chen, P.F. Regulated release of anthocyanins via gelatin/pectin composite gels in simulated digestion. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 166, 111390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Sun, L.N.; Cao, H.; Zhong, Y.M.; Shao, Z.Z. Development of a dual-drug-loaded silk fibroin hydrogel and study on Its drugs release behaviors. Acta Chim. Sin. 2021, 79, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatiana, P.S.; Rosiane, L.C. Role of Process Variables on the formation and in vitro digestion of gellan gels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 192, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.N.; Yang, J.Y.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.X.; Mao, L.K. Modification of the interface of oleogel-hydrogel bigel beads for enhanced stability and prolonged release of bioactives. Food Chem. 2024, 468, 142448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.Q.; Zhang, X.X.; Niu, M.; Xia, C.X.; Dong, W.Y.; Li, C.M.; Li, K.K. Construction of a beeswax-based olive oil bigels system encapusulation of β-carotene by xanthan gum/gellan gum/inulin and evaluation of extrusion spreading performance using finite element abaqus simulations. Food Chem. 2025, 479, 143798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.Y.; Wang, Z.M.; Yu, D.; Yu, S.J.; Meng, H.C.; Zhang, T.; Li, L.L. Fabrication of ultrastable water-in-oil high internal phase emulsion as versatile delivery vehicle through synergetic stabilization. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 126, 107445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Tan, Y.X.; Xue, L.L.; Du, R.L.; Chen, J.J.; Li, C.; Li, T.T.; Bai, X.; Yang, S.J.; Xiong, L.L.; et al. Panax notoginseng saponin attenuates the hypoxic-ischemic injury in neonatal rats by regulating the expression of neurotrophin factors. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2021, 54, 6304–6321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.L.; Song, M.Y.; He, X.T.; Yang, F.Y.; Cao, Y.; Rogers, M.; Lan, Y.Q. Water-induced self-assembly of mixed gelator system (ceramide and lecithin) for edible oil structuring. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 3923–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.N.; Zhou, H.L.; Mundo, J.L.; Muriel, M.; Tan, Y.B.; Hung, P.; McClemengts, D.J. Fabrication and characterization of W/O/W cmulsions with crystalline lipid phase. J. Food Eng. 2020, 273, 109826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakouri, S.; Tehrani, M.M.; Koocheki, A.; Farhoosh, R.; Abdolshahi, A. The development and characterization of edible bigel a hydrogel/oleogel structure based on guar gum, walnut oil and rice bran wax for using as fat replacer. J. Polym. Environ. 2025, 33, 2058–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.Q.; Gong, T.; Hou, Y.J.; Yang, X.; Guo, Y.R. Alginate-stabilized thixotropic emulsion gels and their applications in fabrication of low-fat mayonnaise alternatives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 146, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, B.; Varidi, M.; Malekjani, N.; Jafari, S.M. Whey protein-based bigels for co-encapsulation of curcumin and gallic Acid: Characterization, stability and release kinetics. Future Foods 2024, 10, 100495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaimal, A.M.; Singhal, R.S. A bigel based formulation protects lutein better in the gastric environment with controlled release and antioxidant profile than other gel based systems. Food Chem. 2023, 423, 136304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Oleogel/Hydrogel (w/w) | Hardness (gf) | Cohesiveness | Chewiness (gf) | Springiness (mm) | Gumminess (gf) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:0 (−) | 928.62 ± 0.64 a | 0.27 ± 0.01 e | 64.10 ± 0.04 a | 0.26 ± 0.00 e | 247.03 ± 0.01 a |
| 1:9 (+) | 33.25 ± 0.38 f | 0.79 ± 0.01 ab | 20.53 ± 0.01 f | 0.78 ± 0.00 c | 26.44 ± 0.06 f |
| 2:8 (+) | 43.25 ± 0.33 e | 0.75 ± 0.01 cd | 25.56 ± 0.01 e | 0.77 ± 0.01 c | 32.97 ± 0.12 e |
| 3:7 (+) | 47.56 ± 0.38 d | 0.76 ± 0.01 bc | 28.98 ± 0.02 d | 0.80 ± 0.00 b | 36.38 ± 0.01 d |
| 4:6 (+) | 67.96 ± 0.48 c | 0.75 ± 0.01 cd | 40.44 ± 0.05 c | 0.79 ± 0.00 b | 51.32 ± 0.01 c |
| 5:5 (+) | 79.85 ± 0.38 b | 0.81 ± 0.02 a | 53.28 ± 0.10 b | 0.83 ± 0.00 a | 63.95 ± 0.01 b |
| 0:1 (+) | 31.74 ± 0.96 f | 0.72 ± 0.01 d | 17.27 ± 0.01 g | 0.76 ± 0.00 d | 22.73 ± 0.01 g |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Y.; Xiong, G.; Gong, X.; Xu, C.; Tian, Y.; Li, G. Fabrication, Characterization, and In Vitro Digestion Behavior of Bigel Loaded with Notoginsenoside Rb1. Gels 2025, 11, 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080624
Luo Y, Xiong G, Gong X, Xu C, Tian Y, Li G. Fabrication, Characterization, and In Vitro Digestion Behavior of Bigel Loaded with Notoginsenoside Rb1. Gels. 2025; 11(8):624. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080624
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Yang, Gao Xiong, Xiao Gong, Chunlei Xu, Yingqiu Tian, and Guanrong Li. 2025. "Fabrication, Characterization, and In Vitro Digestion Behavior of Bigel Loaded with Notoginsenoside Rb1" Gels 11, no. 8: 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080624
APA StyleLuo, Y., Xiong, G., Gong, X., Xu, C., Tian, Y., & Li, G. (2025). Fabrication, Characterization, and In Vitro Digestion Behavior of Bigel Loaded with Notoginsenoside Rb1. Gels, 11(8), 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080624





