Study on Gel–Resin Composite for Losting Circulation Control to Improve Plugging Effect in Fracture Formation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation and Characterization
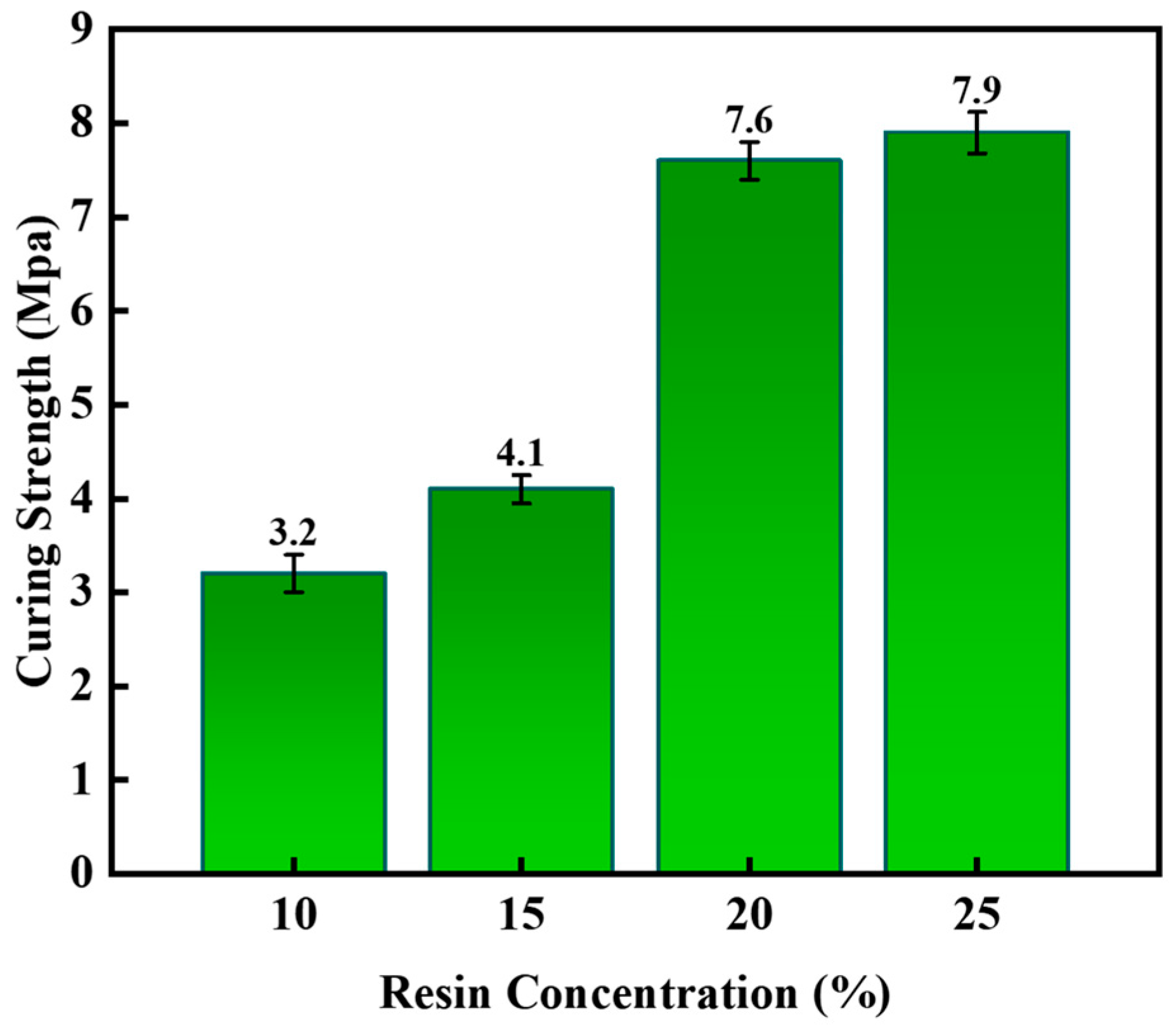
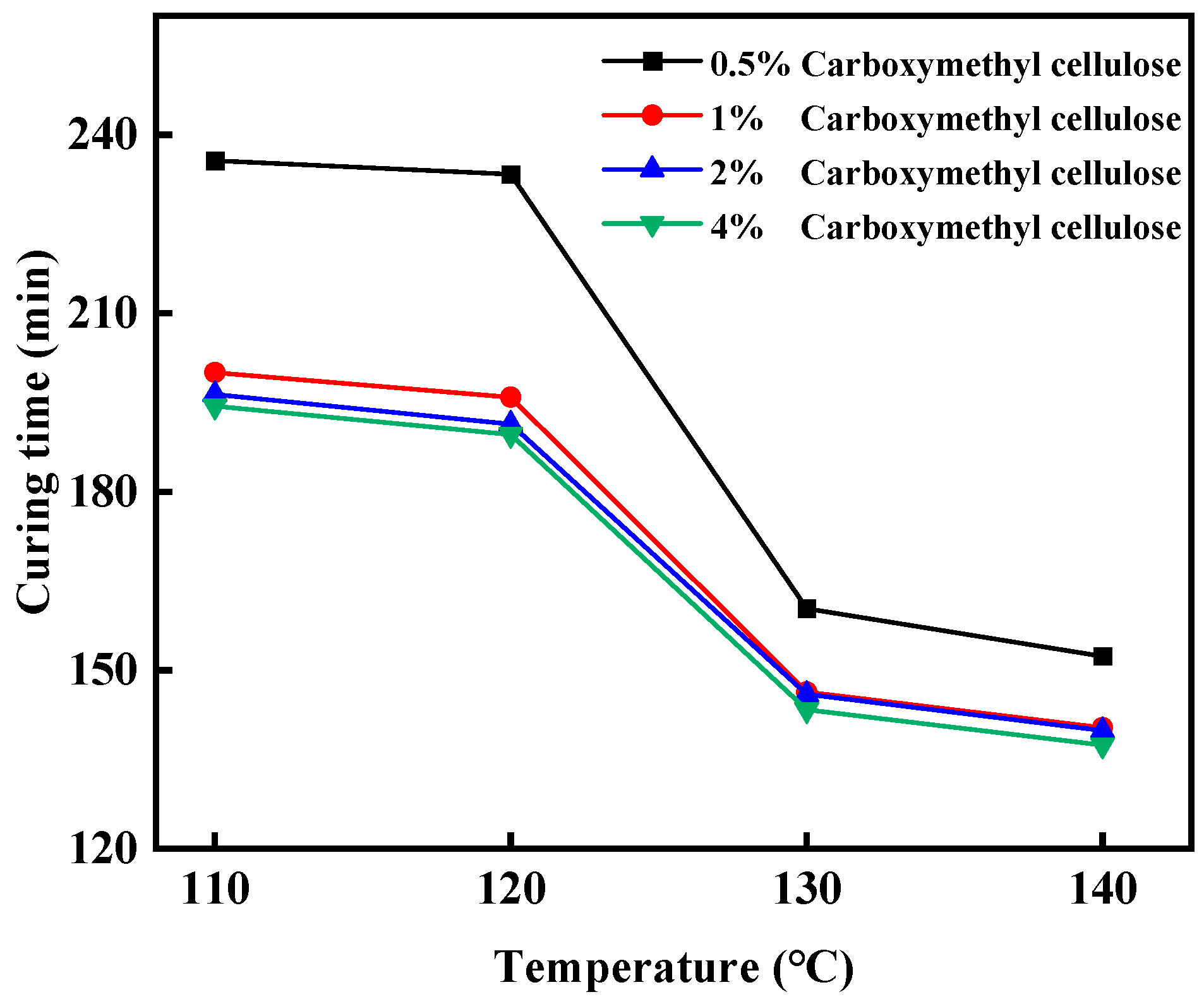
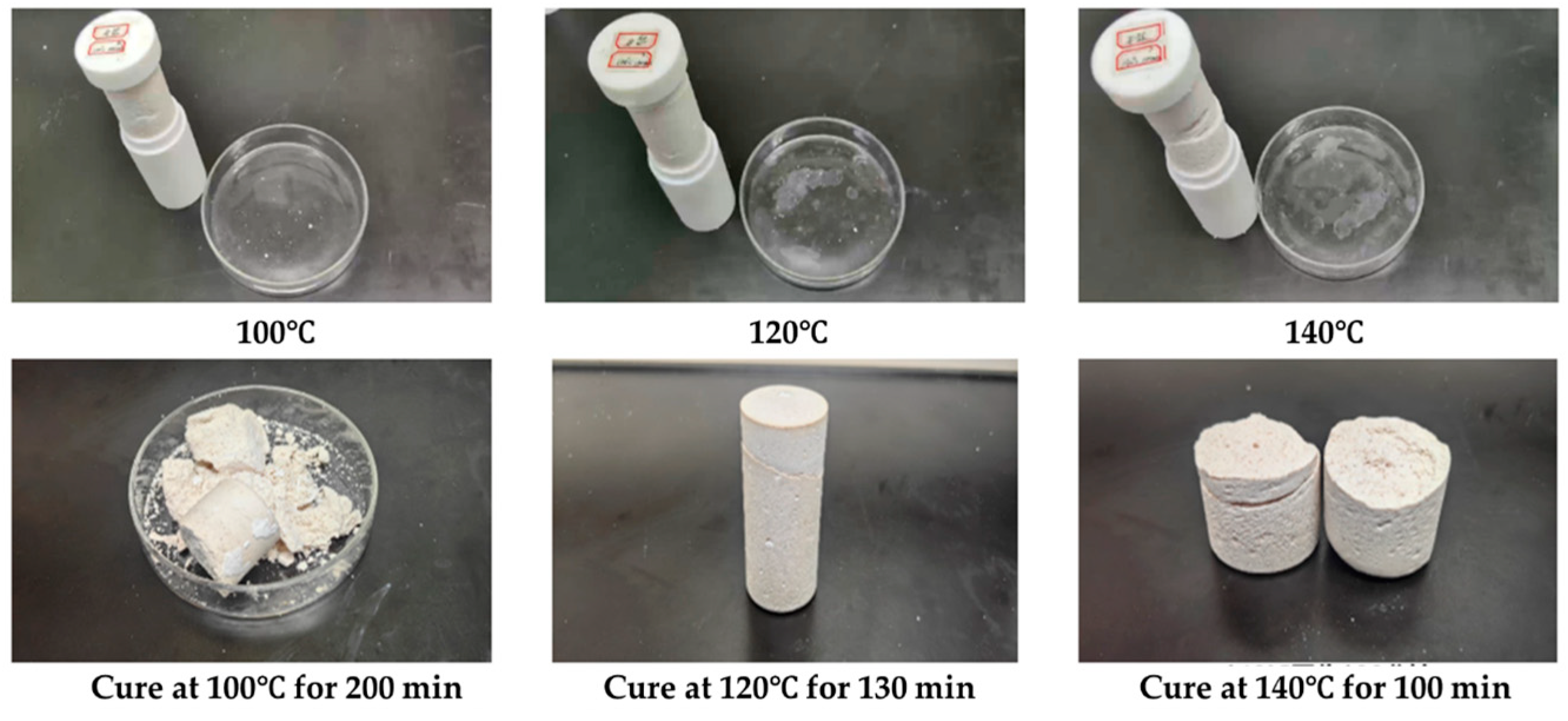
2.1.1. The Optimization of the Formulation of the Gel–Resin Composite
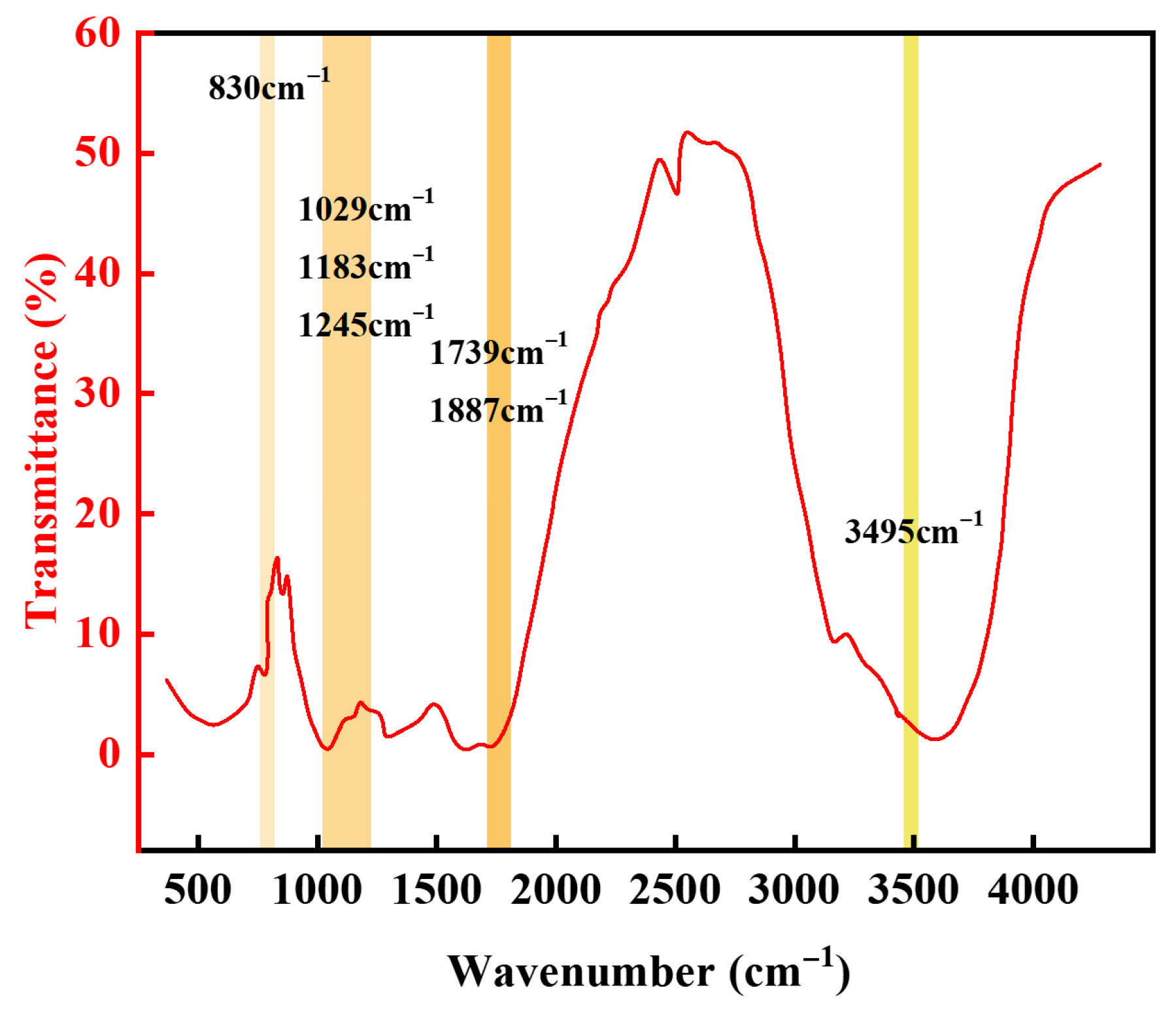
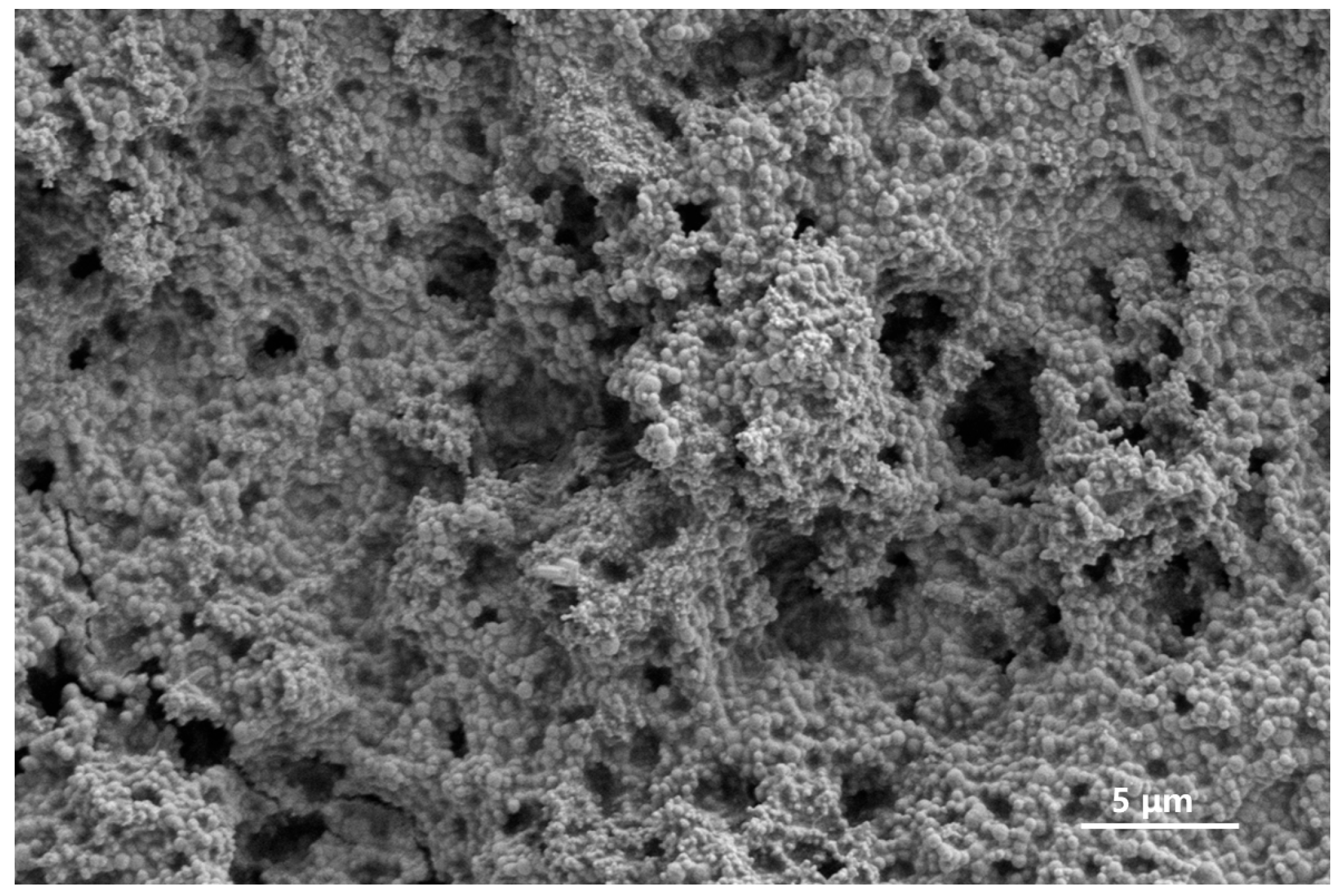
2.1.2. Characterization of the Gel–Resin Composite
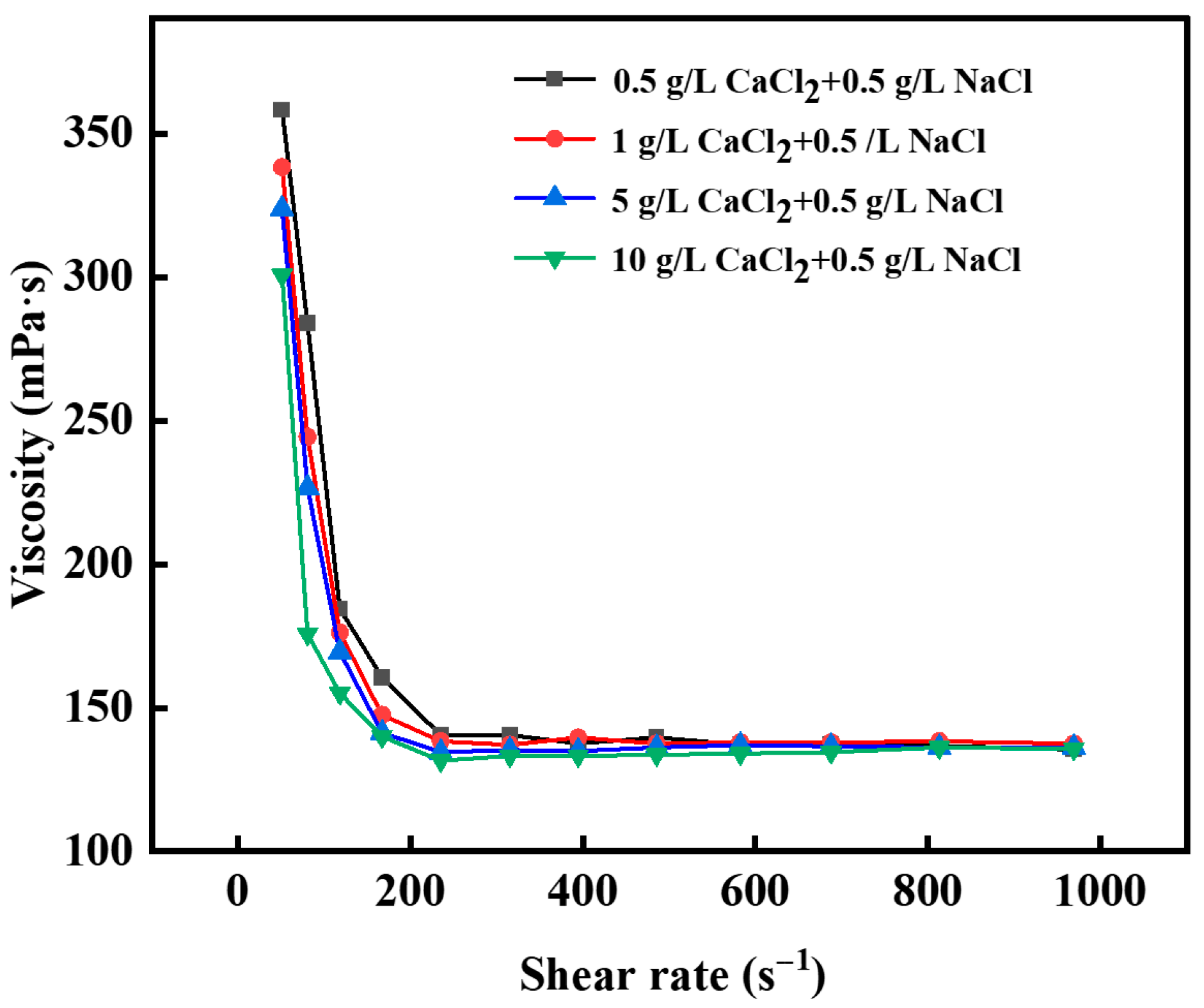
2.2. The Rheological Properties of the Gel–Resin Composite Coagulation System
2.3. Factors Affecting Coagulation Performance of Gel–Resin Composite System
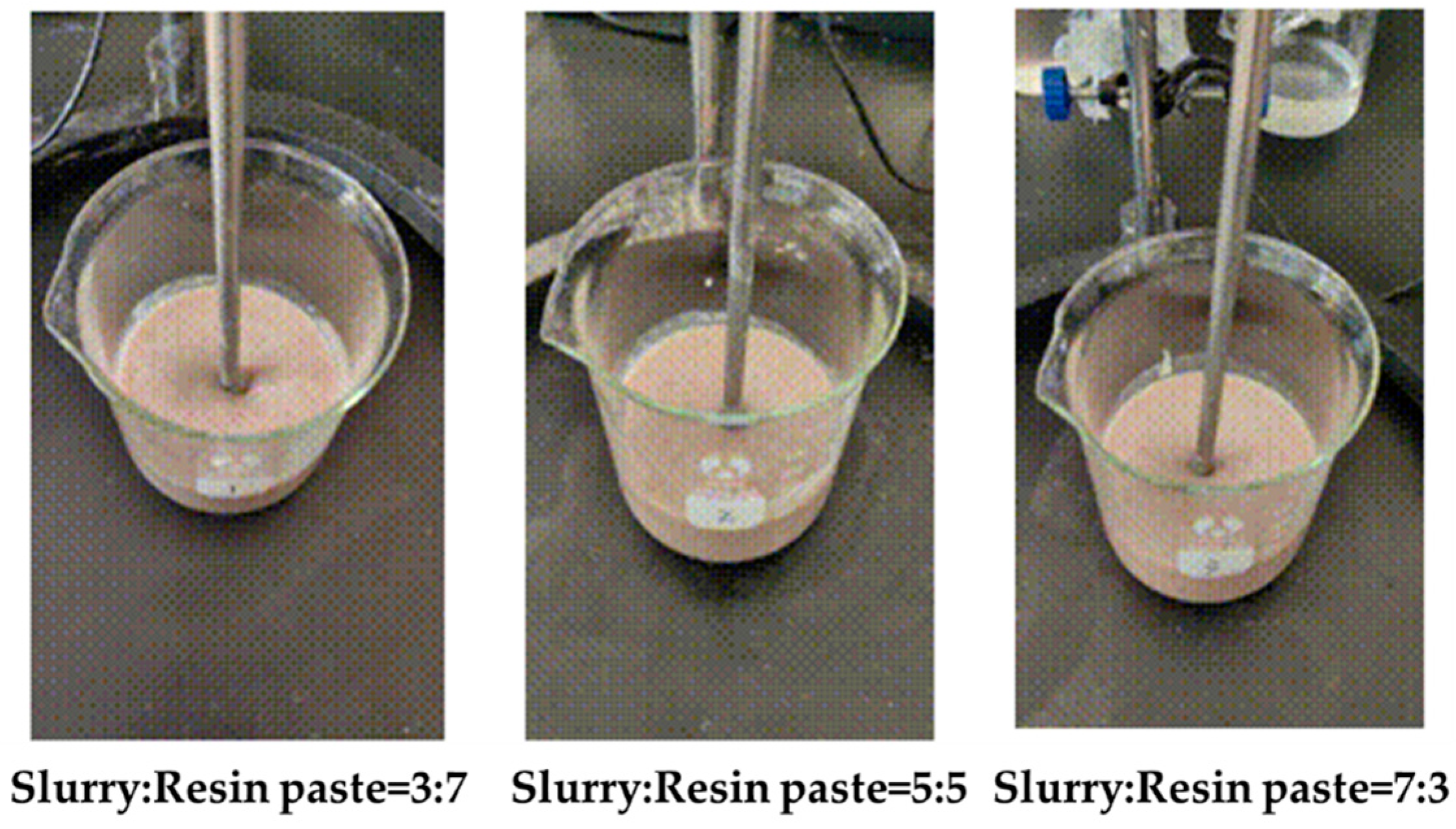
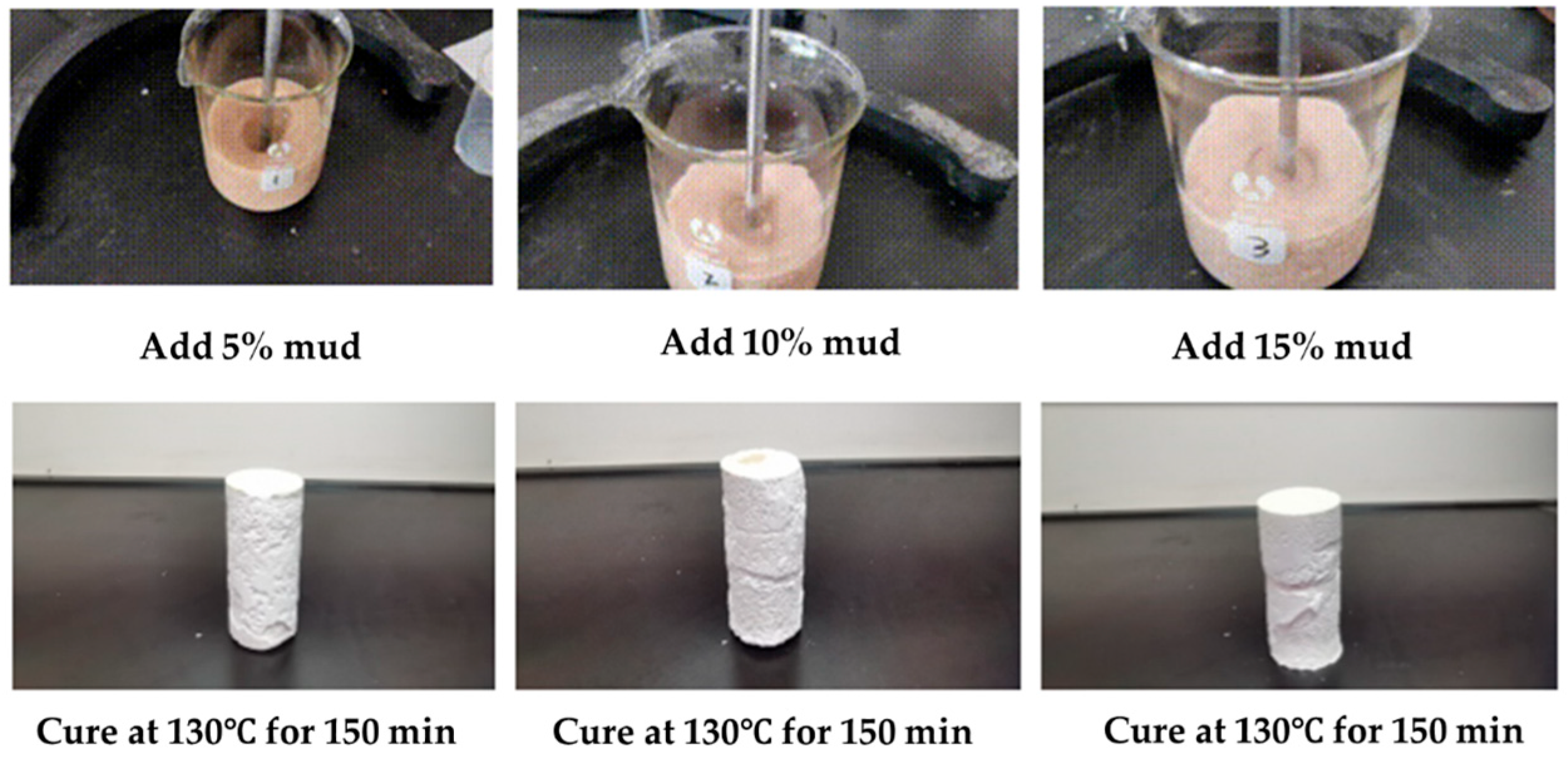
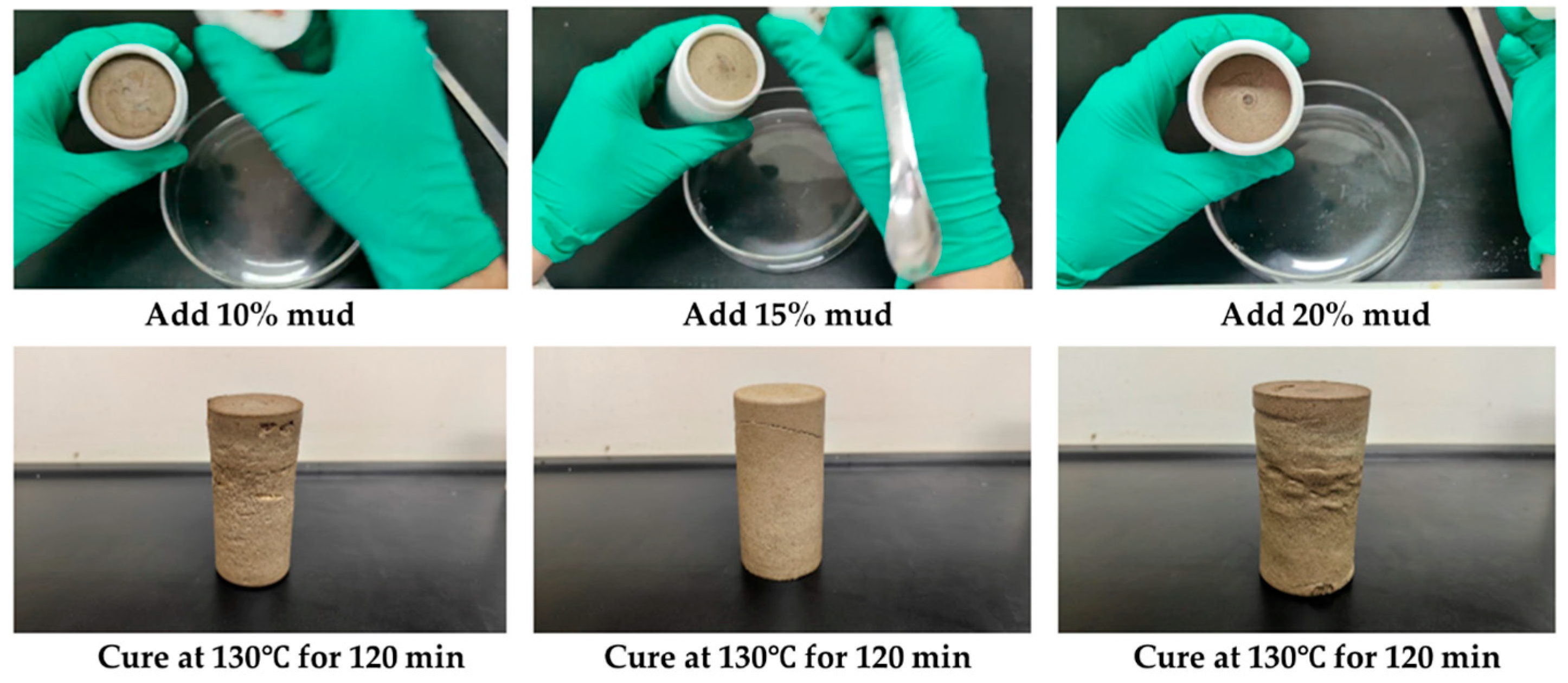
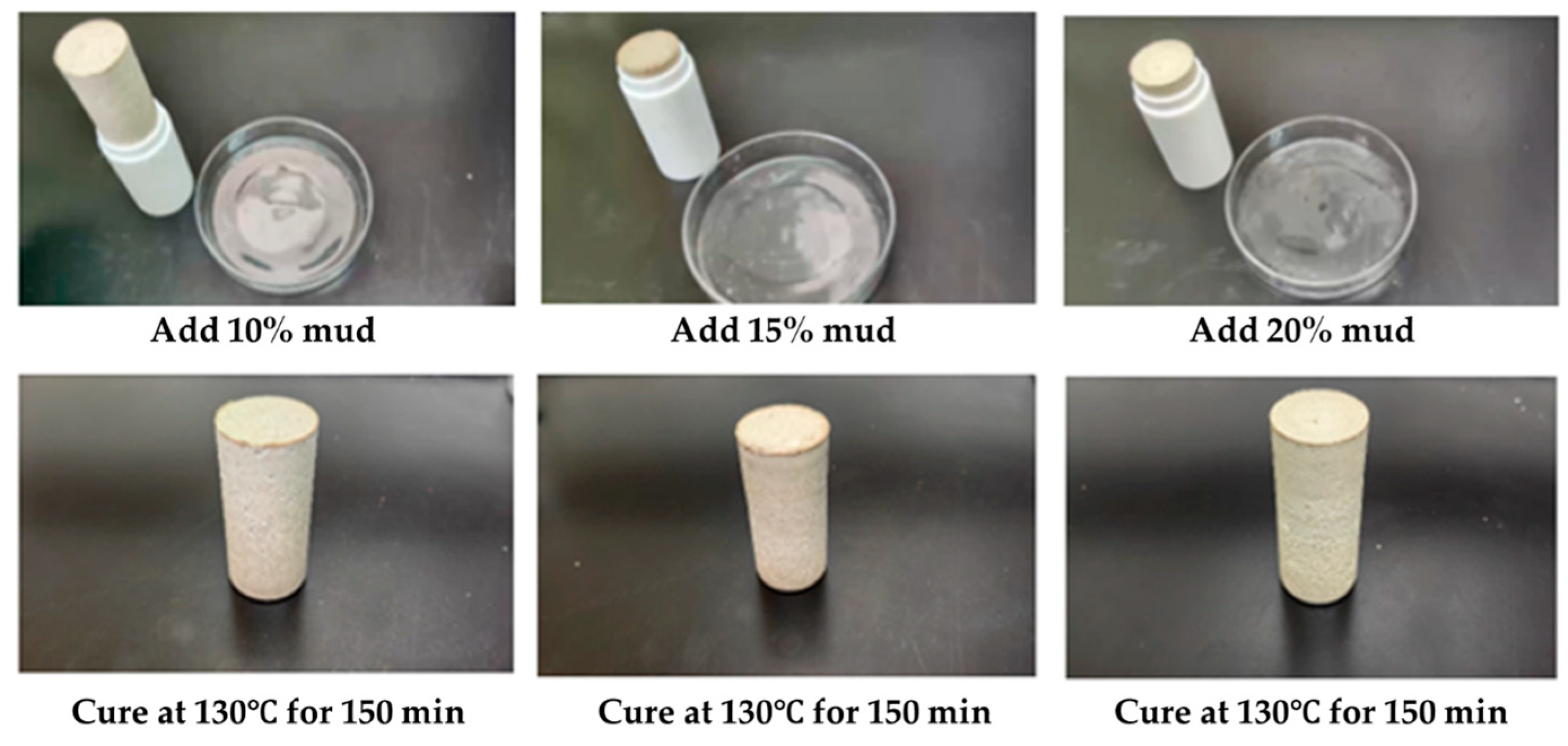
2.3.1. Effect of Drilling Fluid Mix on Coagulation System of Gel–Resin Complex
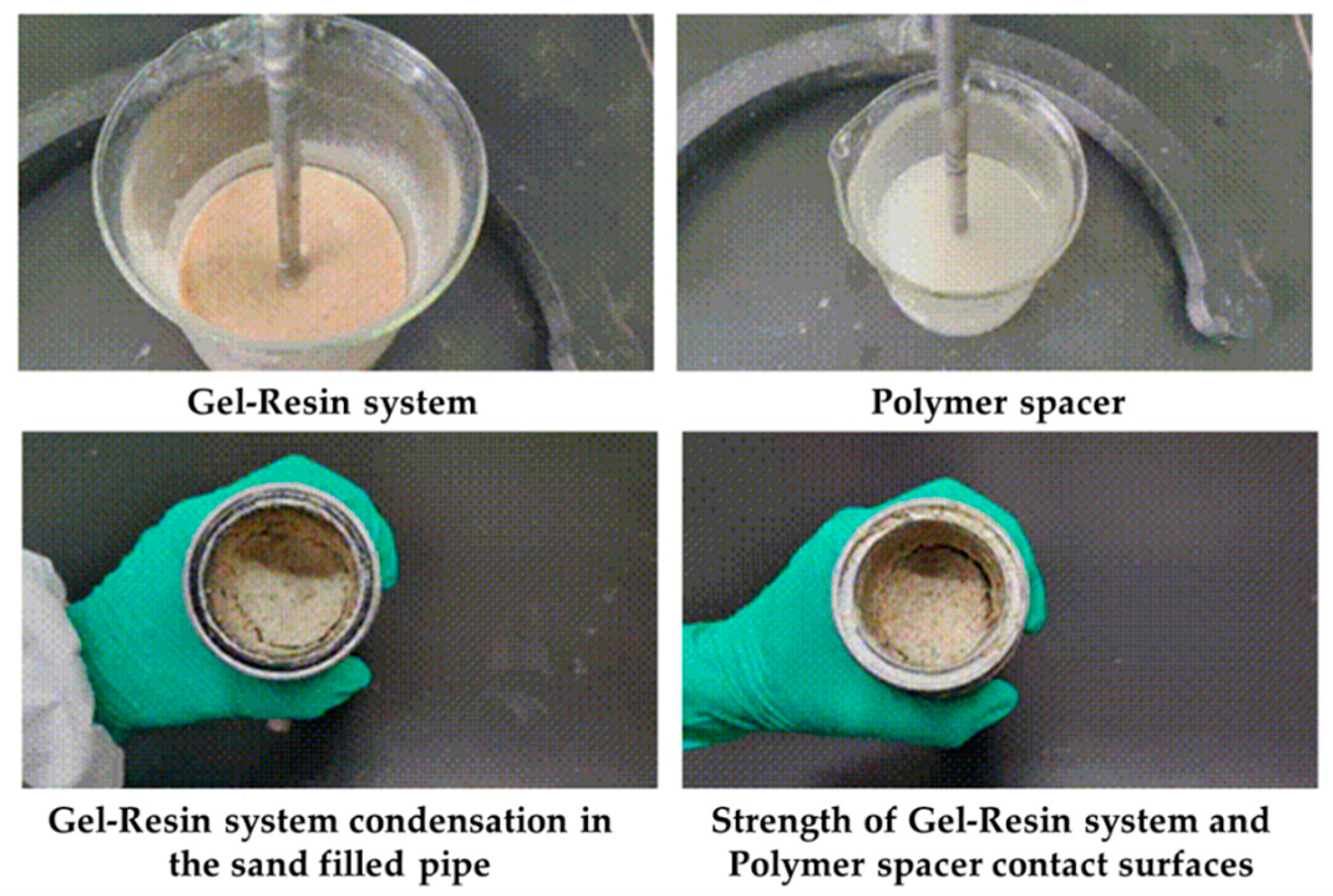
2.3.2. The Influence of Drilling Fluid Pollution on the Gel–Resin Composite System
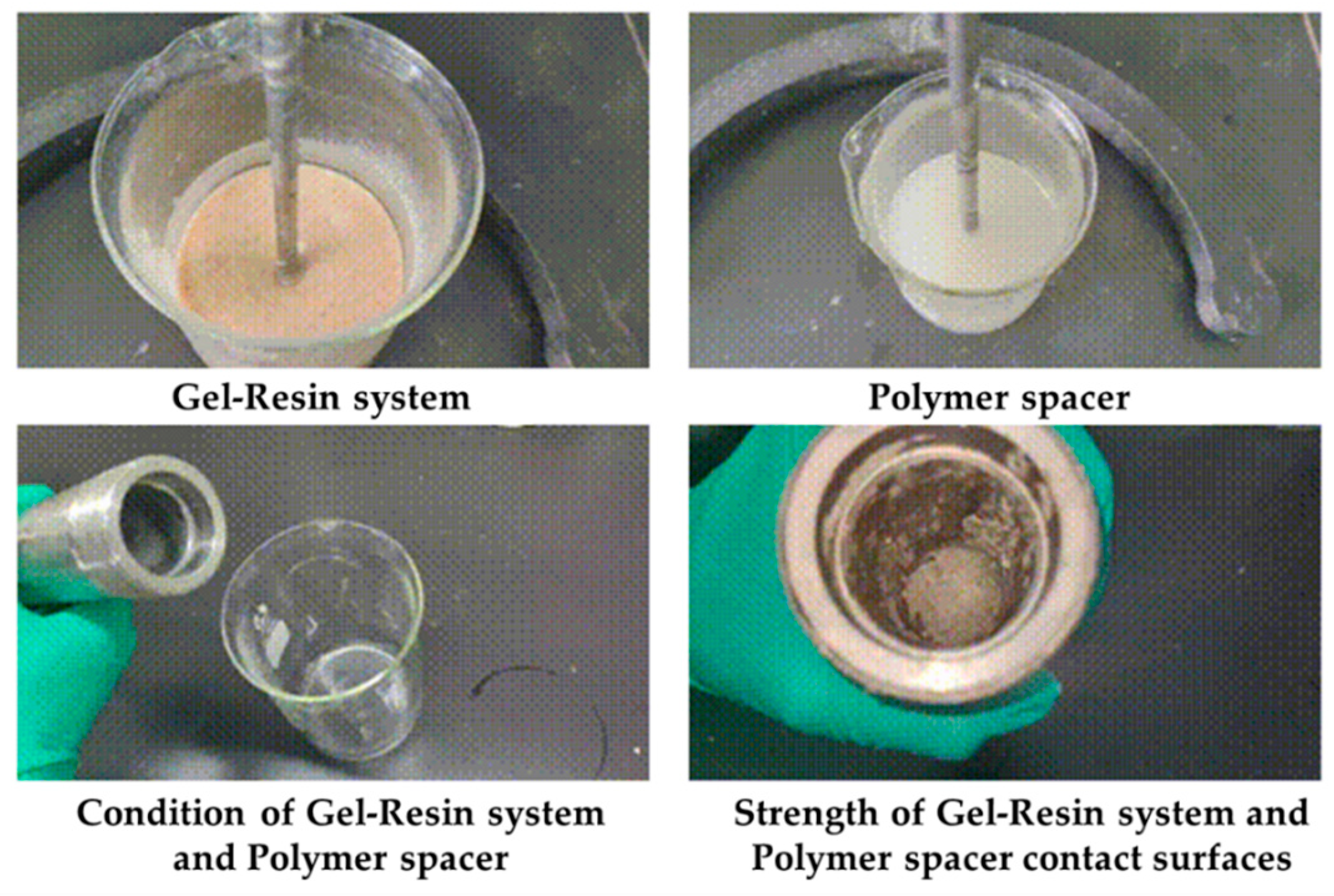
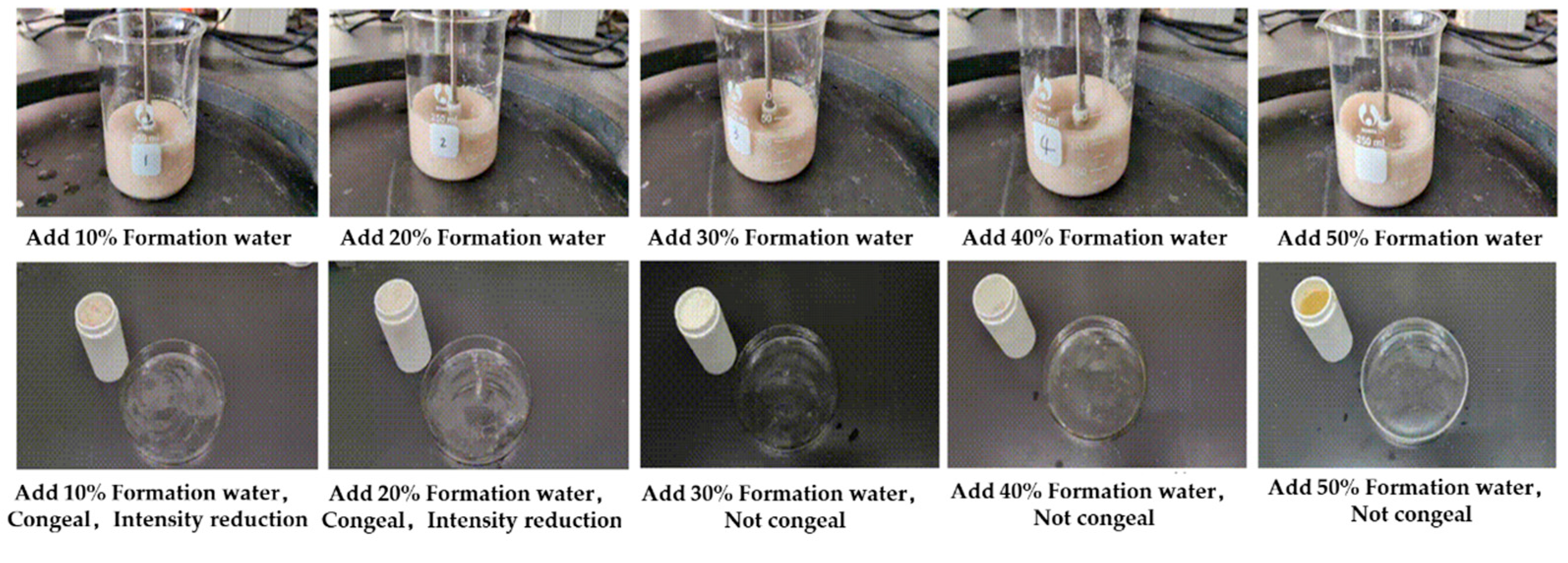
2.3.3. The Influence of Formation Water on the Gel–Resin Coagulation System
2.3.4. The Influence of Polymer Gel Isolation Fluid on the Gel–Resin Composite System
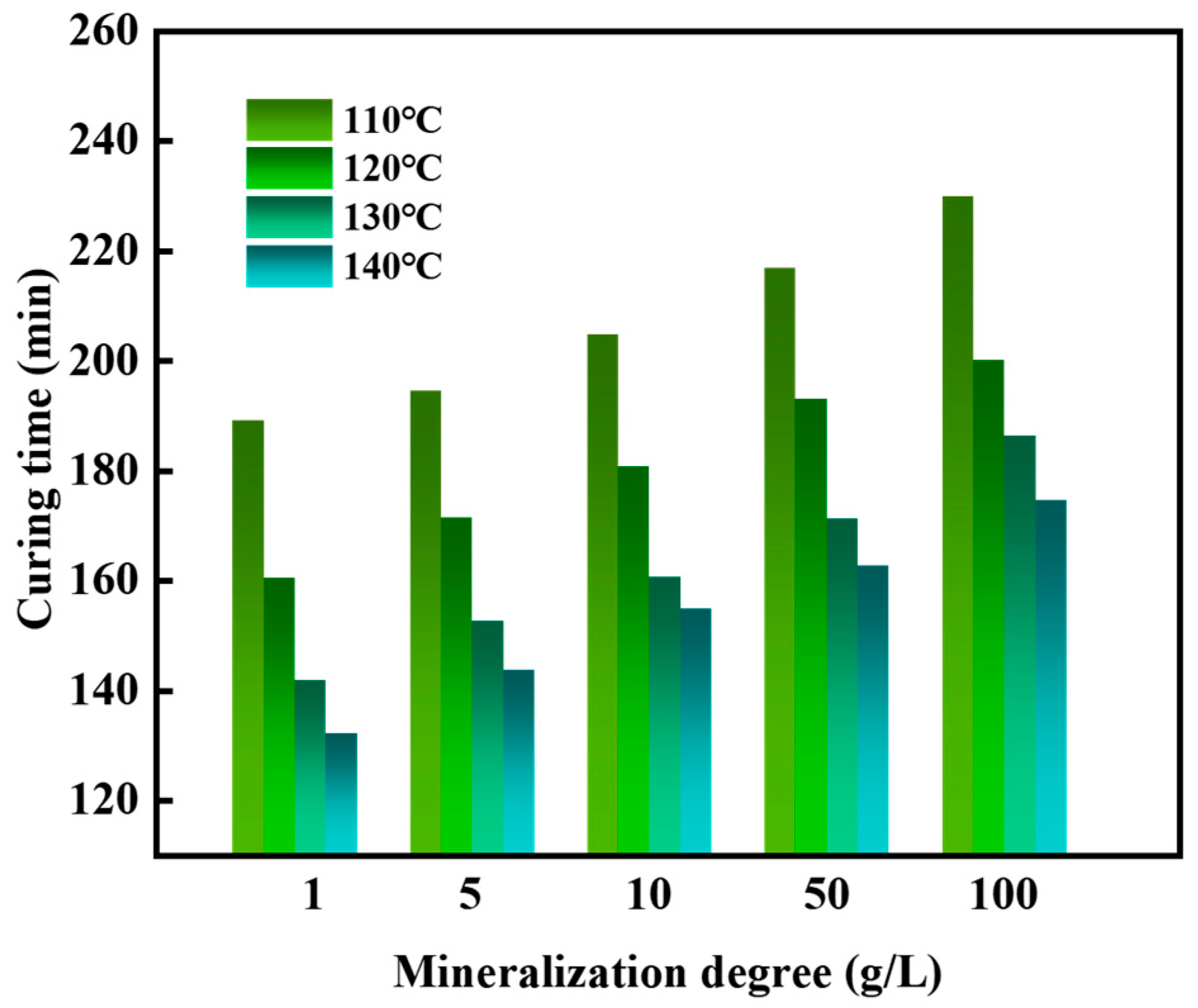
2.3.5. The Influence of Mineralization on the Coagulation Effect of the Gel–Resin System
2.4. The Working Performance of the Gel–Resin Coagulation Composite System
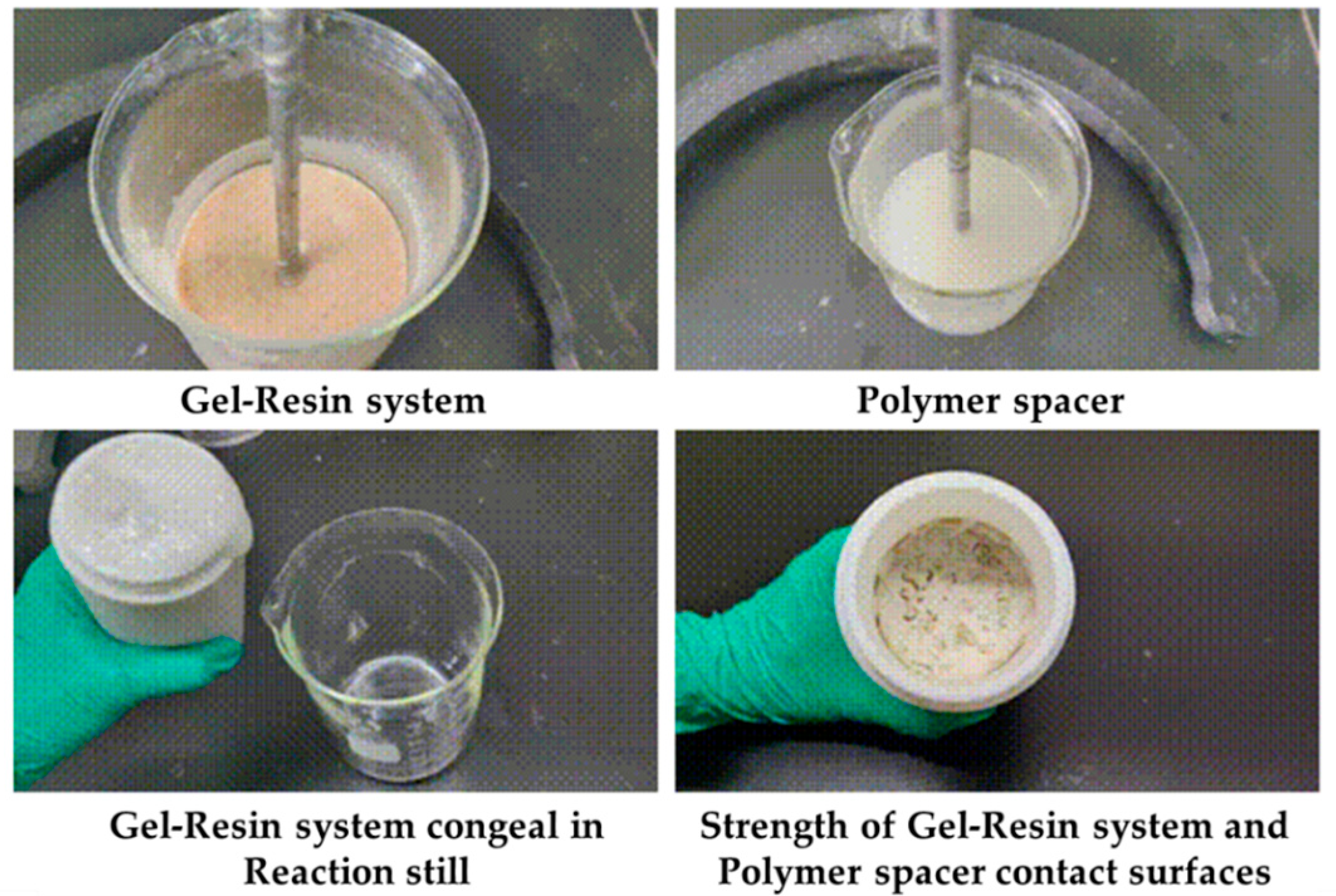
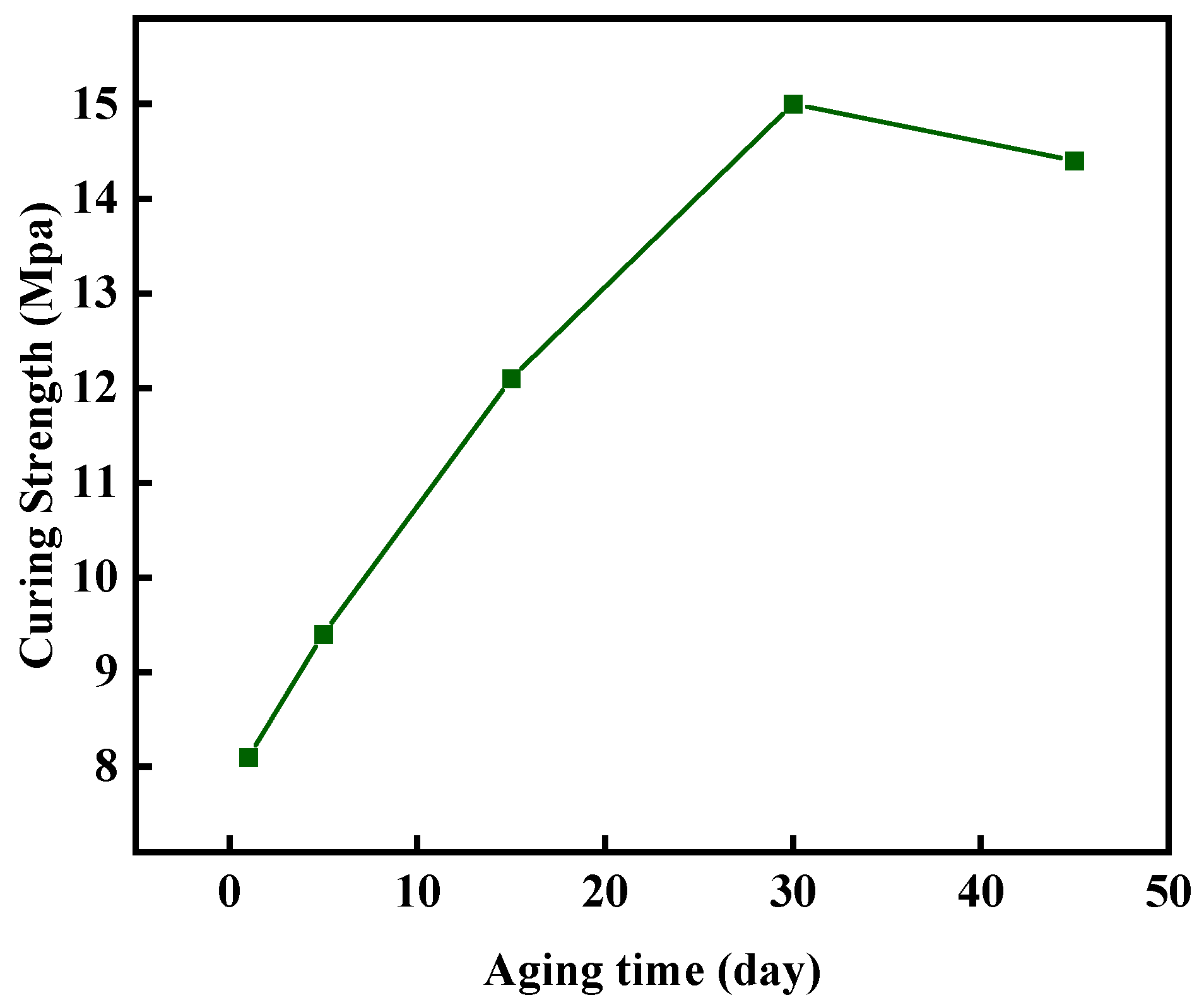
2.4.1. Long-Term Stability of Gel–Resin Composite System at High Temperature
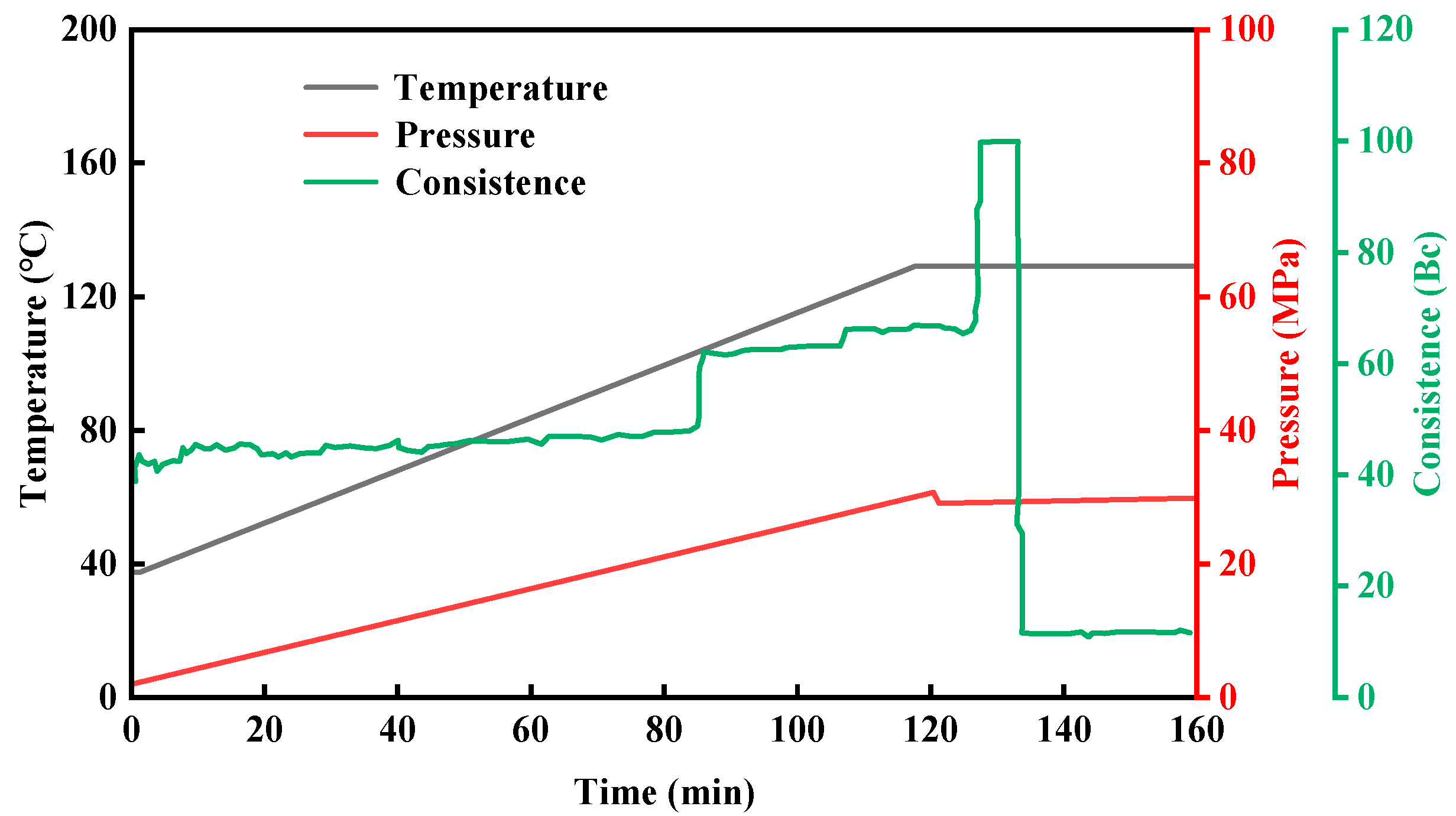
2.4.2. Evaluation of the Thickening Performance of the Gel–Resin Composite Coagulation System
2.5. Mechanism and Effect Evaluation of Gel–Resin Composite Coagulation System for Pressure-Bearing Leakage Plugging
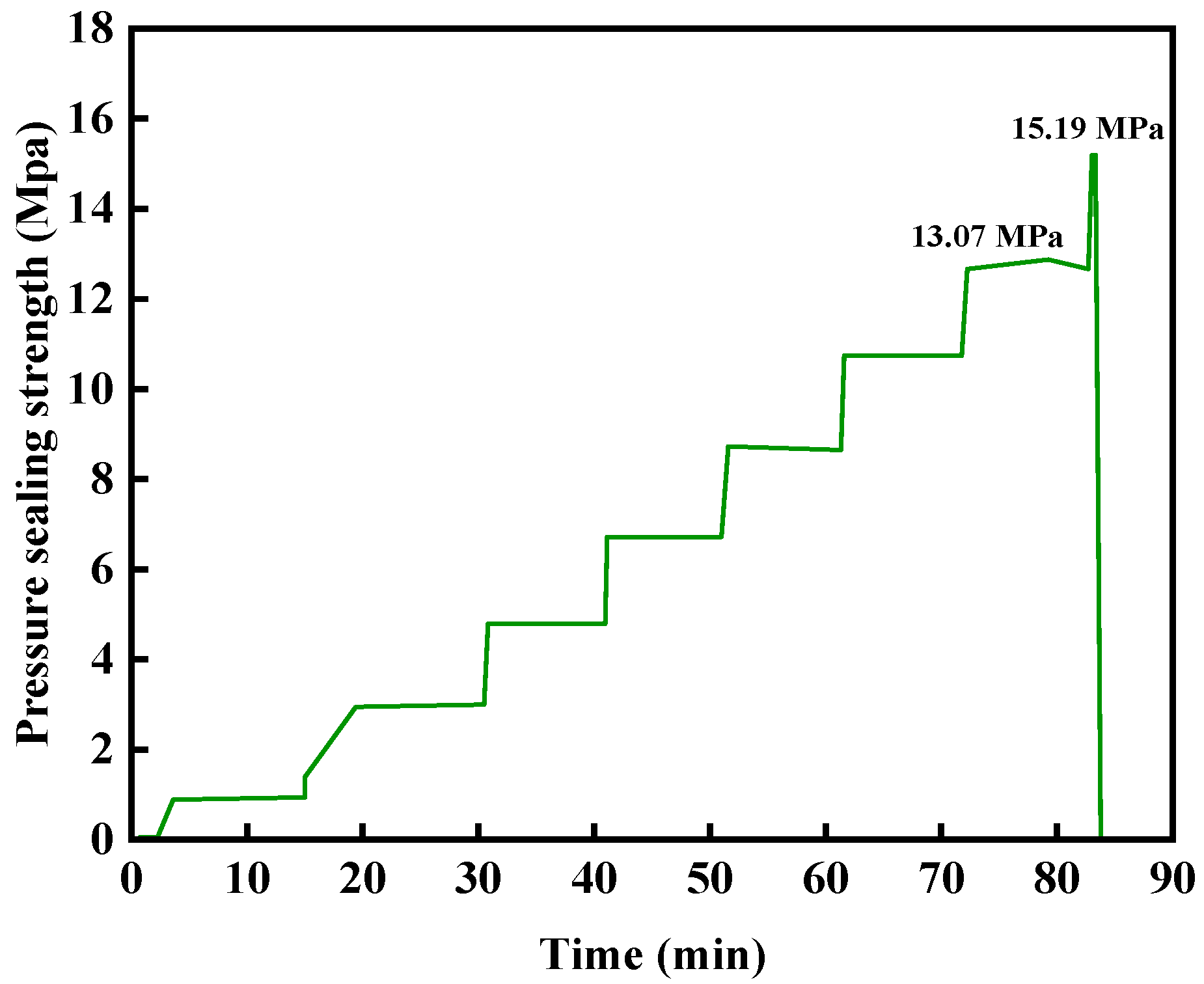
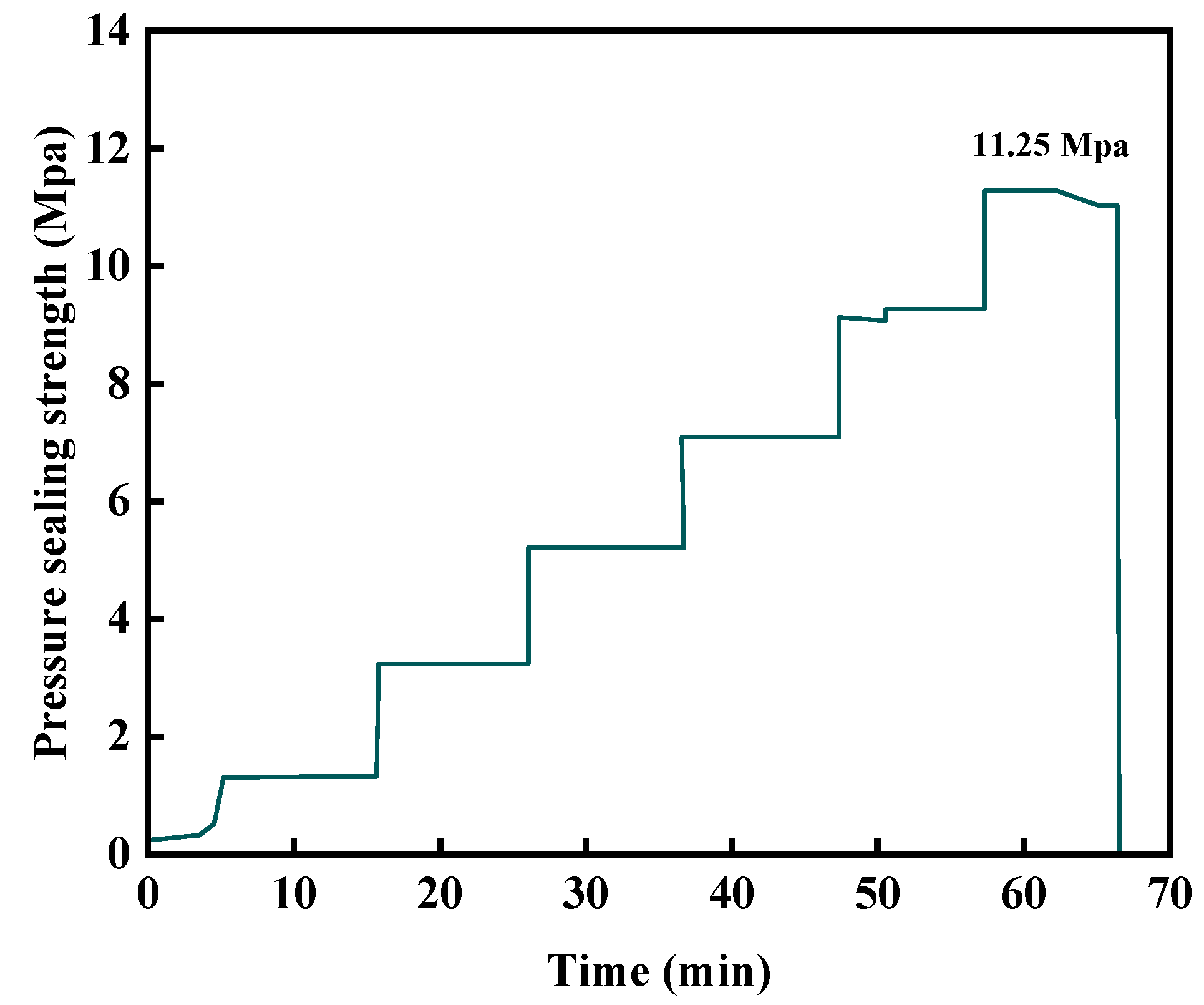
2.5.1. The Pressure-Bearing Plugging Ability of the Gel–Resin Composite Coagulation System in the Wedge-Shaped Crack
2.5.2. The Pressure-Bearing Leakage-Stopping Ability of the Resin Leakage-Stopping Agent After Stepwise Pressure Testing in Cracks and Sand-Filled Tubes
2.6. The Unblocking Performance of the Gel–Resin Composite System
3. Conclusions
- (1)
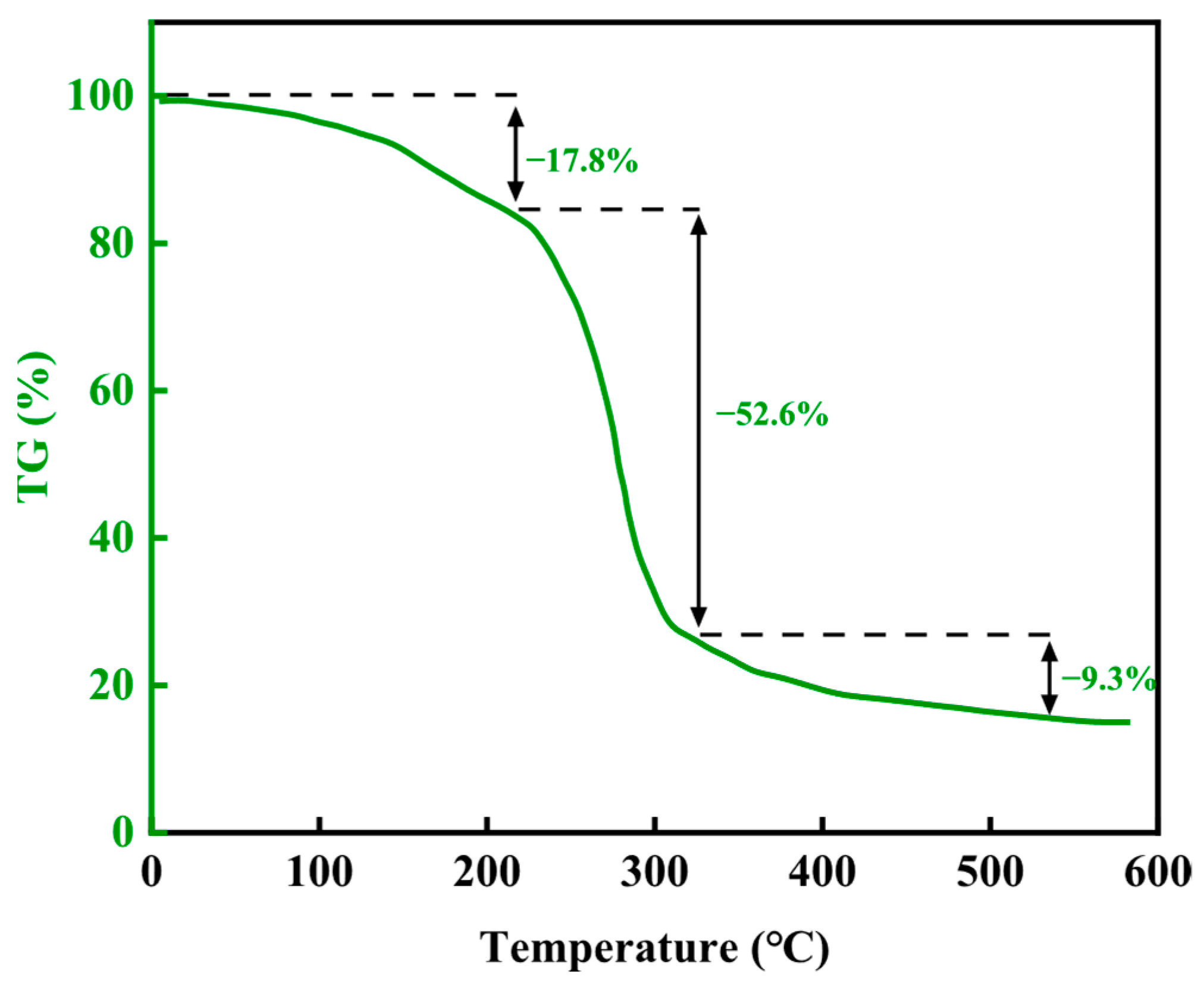
- By optimizing the formulations of bisphenol, A epoxy resin (20%), hexamethylenetetramine (3%), and hydroxyethyl cellulose (1%) and adding nano-silica and walnut shell particle fillers, a leak-stopping system with both a controllable curing property and high strength was constructed. After aging at 140 °C for 45 days, this system still maintains a compressive strength of 14.4 MPa, with an initial decomposition temperature of 220 °C, demonstrating excellent thermal stability.
- (2)
- When faced with contamination by foreign drilling fluids and high-salinity conditions, the resin plugging system demonstrated good anti-contamination and salt tolerance. After contamination with 20% Tarim drilling fluid, the compressive strength of the cured resin remained at 5.04 MPa. At a salinity of 100 g/L, the setting time ranged from 133 to 230 min, and the compressive strength after setting ranged from 7.7 to 11.3 MPa.
- (3)
- The resin plugging system demonstrated an excellent performance in key aspects: (a) after aging for 45 days at 140 °C, the compressive strength of the cured resin plug reached 14.4 MPa; (b) the cured resin exhibited minimal adhesion to the drill rod; and (c) the uncured resin system showed a strong viscosity (or shear) recovery capability.
- (4)
- The cured gel–resin plug exhibited an effective pressure sealing capability at 140 °C in a sand-packed tube test. Specifically, the plugging system was breached after 7 min under a constant differential pressure of 11.25 MPa applied across a sand-packed tube equipped with a 6 mm outlet orifice. This demonstrates its capability to effectively seal fractures and holes.
- (5)
- Degradation tests showed that cured resin material (140 °C) mixed with 15% hydrochloric acid at a volume ratio of 1:2 (resin:acid) achieved a degradation rate of 97.69% after 24 h, indicating that the resin leakage plugging material has an excellent degradation performance.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Rheology
4.3. Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
4.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis
4.5. Sealing Performance
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Hu, H.; Wang, J. Interpretable Lost Circulation Analysis: Labeled, Identified, and Analyzed Lost Circulation in Drilling Operations. SPE J. 2024, 29, 1692–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomassi, A.; Falegnami, A.; Romano, E. Unveiling simplexity: A new paradigm for understanding complex adaptive systems and driving technological innovation. Innovation 2025, 100954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Kang, Y.; Xu, C.; Shang, X.; You, Z.; Zhang, J. Fracture Plugging Zone for Lost Circulation Control in Fractured Reservoirs: Multiscale Structure and Structure Characterization Methods. Powder Technol. 2020, 370, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Pu, H.; Peng, G.; Wang, J. Borehole Temperature Distribution When Drilling Fluid Loss Occurs in the Two-Dimensional Area at the Bottom-Hole during Drilling. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 83, 103523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-B.; Jiang, H.-Z.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Liu, H.-N.; Ma, X.; Zhu, J.-J.; Zhang, X.-F.; Kang, W.-L. Development and evaluation of organic/metal ion double crosslinking polymer gel for anti-CO2 gas channeling in high temperature and low permeability reservoirs. Pet. Sci. 2025, 22, 724–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkatatny, S.; Ahmed, A.; Abughaban, M.; Patil, S. Deep Illustration for Loss of Circulation While Drilling. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 45, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Yang, H.; Ning, C.; Peng, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Shi, H.; Wang, R.; Sarsenbekuly, B.; Kang, W. Amphiphilic polymer with ultra-high salt resistance and emulsification for enhanced oil recovery in heavy oil cold recovery production. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2025, 252, 213920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Jiang, H.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Peng, L.; Wang, R.; Li, H.; Kang, W.; Sarsenbekuly, B. Viscoelastic displacement mechanism of fluorescent polymer microspheres based on macroscopic and microscopic displacement experiments. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 042022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Lou, Y.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, X. Study on the Model and Law for Radial Leakage of Drilling Fluid in Fractured Formations. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 39840–39847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yan, X.; Kang, Y.; You, L.; Zhang, J. Structural Failure Mechanism and Strengthening Method of Fracture Plugging Zone for Lost Circulation Control in Deep Naturally Fractured Reservoirs. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2020, 47, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Gao, S.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhai, R.; Dong, A.; Zhang, J. A Review in Polymers for Fluid Loss Control in Drilling Operations. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2024, 225, 2300390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabbasi, S.M.; Ameri, M.J.; Alsaba, M.; Karami, M.; Zargarbashi, A. The Evolution of Lost Circulation Prevention and Mitigation Based on Wellbore Strengthening Theory: A Review on Experimental Issues. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 211, 110149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, R.S.; Salih, N.M.; Kamal, I.; Préat, A. X-ray Computed Tomography (CT) to Scan the Structure and Characterize the Mud Cake Incorporated with Various Magnetic NPs Concentration: An Application to Evaluate the Wellbore Stability and Formation Damage. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Gray, K.E. Review of Fundamental Studies on Lost Circulation and Wellbore Strengthening. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 152, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Chen, M.; Hou, B.; Sun, Z.; Jin, Y. Drilling Fluid Loss Model and Loss Dynamic Behavior in Fractured Formations. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2014, 41, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Jiang, G.; Ni, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Luo, X. Styrene Butadiene Resin/Nano-SiO2 Composite as a Water-and-Oil-Dispersible Plugging Agent for Oil-Based Drilling Fluid. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 606, 125245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Yu, B.; Zou, M.; Mei, M. Fractal Analysis of Invasion Depth of Extraneous Fluids in Porous Media. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 5178–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Kang, Y.; Lin, C.; Xu, C.; Zhang, L.; You, L. A Novel Experimental Study on Plugging Performance of Lost Circulation Materials for Pressure-Sensitive Fracture. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 242, 213214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmousalami, H.; Sakr, I. Artificial Intelligence for Drilling Lost Circulation: A Systematic Literature Review. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 239, 212837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amish, M.; Khodja, M. Review of Detection, Prediction and Treatment of Fluid Loss Events. Arab. J. Geosci. 2024, 18, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yu, B.; Ma, C. Synthesis and Evaluation of High-Temperature Resistant Polymer Plugging Agent for Water-Based Drilling Fluids. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 44616–44623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, L.; Yan, Y.; Shang, Q.; Huang, M.; Pu, K.; Bai, X. Preparation and Performance Evaluation of Intelligent Plugging Agent for Thermo-Sensitive Water-Based Drilling Fluid. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, e55732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.H. Drilling Fluids for Shale Fields: Case Studies and Lessons Learnt. Unconv. Resour. 2024, 4, 100070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zeng, J.; Song, H.; Li, F. Research on Ultrasonic Excitation for the Removal of Drilling Fluid Plug, Paraffin Deposition Plug, Polymer Plug and Inorganic Scale Plug for near-Well Ultrasonic Processing Technology. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 36, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xie, C.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, G.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Dong, T.; Guo, C. Performance of Self-Healing Microgel Incorporating Nano-Silica as Plugging Material for Drilling Fluid. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 386, 122392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, B.; Xu, P.; Xu, M.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S. Synthesis and Plugging Effect of Inverse Emulsion Polymerization Microspheres (OPME) for Oil-Based Drilling Fluids. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 104577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Wang, C.; Huang, W.; Zhang, S.; Chen, H.; Wu, B. Composite of Carboxylized Graphene Oxide with Nanosilica for Shale Plugging. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2025, 200, 112574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashkari, R.; Tabatabaei-Nezhad, S.A.; Husein, M.M. Shape Memory Polyurethane as a Drilling Fluid Lost Circulation Material. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2021, 306, 2100354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Bai, Y.; Sun, J.; Lv, K.; Lang, Y. Recent Advances of Thermosetting Resin and Its Application Prospect in Oil and Gas Drilling and Production Engineering. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 230, 212222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muylaert, I.; Verberckmoes, A.; De Decker, J.; Van Der Voort, P. Ordered Mesoporous Phenolic Resins: Highly Versatile and Ultra Stable Support Materials. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 175, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanqari, K.; Wagle, V.; Al-Yami, A.; Mohammed, A. A Novel Epoxy Resin Composition as a Lost Circulation Material: Formulation, Lab Testing and Field Execution. In Proceedings of the SPE International Conference on Oilfield Chemistry, Woodlands, TX, USA, 6–7 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, P.; Qiu, Z.; Zang, X.; Zhong, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, T. Epoxy Resin Microencapsulated by Complex Coacervation as Physical-Chemical Synergetic Lost Circulation Control Material. Energy 2024, 293, 130630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, K. A Novel Self-Healing and Degradable Plugging Material for High Temperature Gas Well. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 376, 121473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Sun, J.; Wang, R.; Liu, F.; Cheng, R.; Qu, Y.; Hao, H.; Bai, Y.; Li, Y.; Geng, Y. Shape Memory Resin with High Temperature Resistance for Plugging Fracture Formations Drilled with Oil-Based Drilling Fluid. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 243, 213355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Lou, E.; Zhang, S.; Lu, H.; Wang, Z. Preparation and Performance of Resin-Gel–Rubber Expandable Lost Circulation Material Blend. Gels 2023, 9, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, S. An Effective Method for Preparation of Liquid Phosphoric Anhydride and Its Application in Flame Retardant Epoxy Resin. Materials 2021, 14, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilyin, S.O. Structural Rheology in the Development and Study of Complex Polymer Materials. Polymers 2024, 16, 2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 10426-2:2003; Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries Cements and Materials for Well Cementing Part 2: Testing of Well Cements. MOD, Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
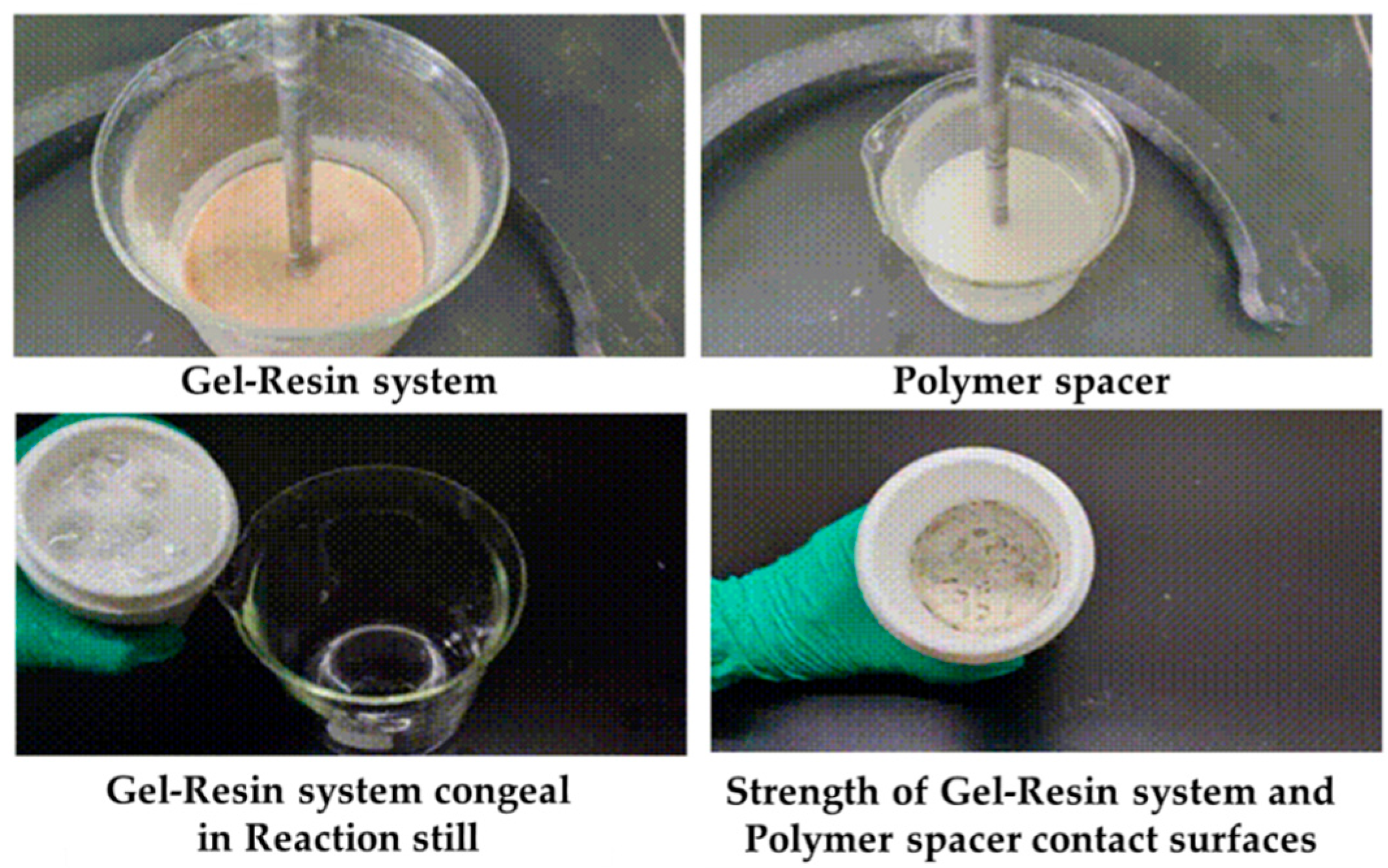

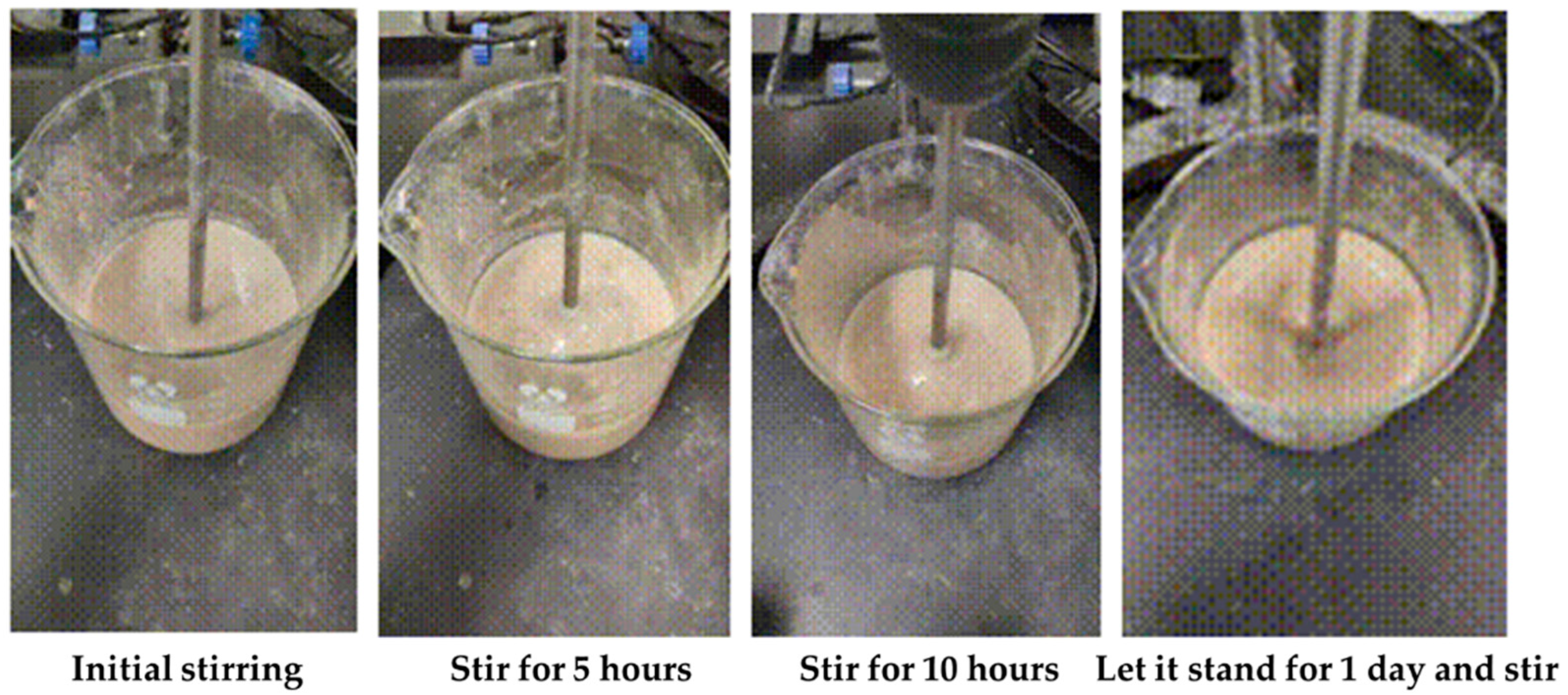

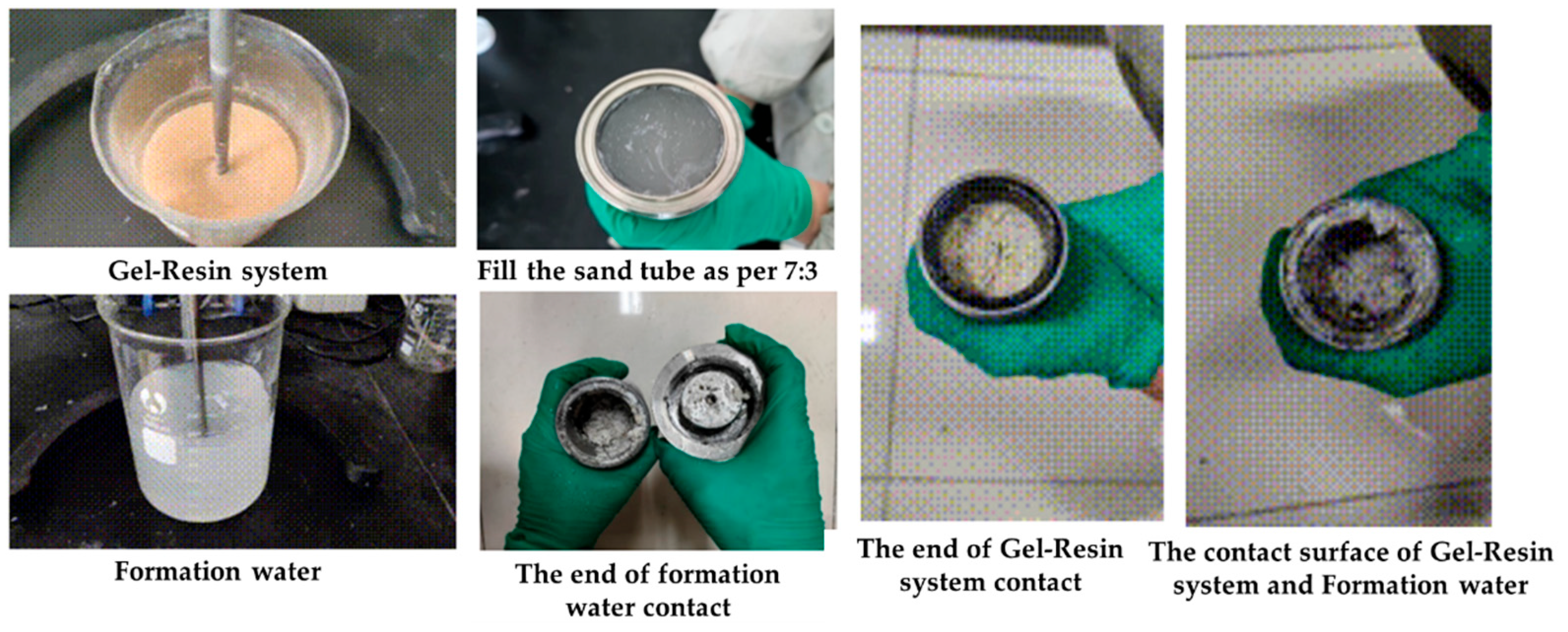







| Rheology | φ600 | φ300 | φ200 | φ100 | φ6 | φ3 | Initial/Final Shear Force | Apparent Viscosity | Plastic Viscosity | Dynamic Shear |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original state | 93 | 61 | 39 | 24 | 13 | 8 | 3.5/8 | 46.5 | 32 | 13.9 |
| Stirring for 5 h | 99 | 71 | 41 | 25 | 16 | 12 | 9.5/9 | 49.6 | 28 | 20.6 |
| Stirring for 10 h | 102 | 88 | 44 | 26 | 22 | 16 | 5.5/8.8 | 51 | 14 | 35.4 |
| Standing for 1 d | 151 | 89 | 72 | 33 | 30 | 19 | 8/9 | 75.5 | 62 | 12.9 |
| Rheology | φ600 | φ300 | φ200 | φ100 | φ6 | φ3 | Initial/Final Shear Force | Apparent Viscosity | Plastic Viscosity | Dynamic Shear |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Well slurry | 18 | 12 | 10 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 6/7 | 9 | 6 | 2.9 |
| Gel–resin slurry | 180 | 123 | 92 | 59 | 13 | 9 | 5.5/9.5 | 90 | 57 | 31.6 |
| Gel–resin paste: Well slurry 3:7 | 185 | 161 | 119 | 77 | 20 | 10 | 6/8 | 92.5 | 24 | 65.6 |
| Gel–resin paste: Well slurry 5:5 | 205 | 153 | 112 | 67 | 16 | 13 | 8/11 | 102.5 | 52 | 48.4 |
| Gel–resin paste: Well slurry 7:3 | 207 | 184 | 134 | 70 | 24 | 22 | 10/12 | 103.5 | 23 | 77.1 |
| Sample | Conditions for Condensation | Sample Diameter/mm | Maximum Force Value/N | Compressive Strength/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Add 10% polymeric sulfonate drilling fluid | 130 °C 150 min | 36.57 | 6199 | 6.36 |
| Add 15% polymeric sulfonate drilling fluid | 130 °C 150 min | 37.35 | 5463 | 5.75 |
| Add 20% polymeric sulfonate drilling fluid | 130 °C 150 min | 35.53 | 4386 | 4.29 |
| Recipe Name | Material Name | Use Ratio/% |
|---|---|---|
| Tarim drilling fluid system | Bentonite | 4.0 |
| Caustic soda | 0.2 | |
| Sodium carbonate | 0.1 | |
| Potassium salt of polyacrylamide | 0.1 | |
| Polymer filtration reducer | 0.2 | |
| Cationic cellulose | 0.3 | |
| Hydrolyzed polyacrylamide ammonium salt | 0.5 | |
| Sulfonated phenolic resin (dry powder) | 1.0 | |
| Lignite resin | 1.0 | |
| Potassium chloride | 3.0 | |
| Silanol inhibitor | 1.0 | |
| Asphalt anti-collapse agent | 2.0 | |
| Ultrafine calcium carbonate | 1.0 |
| Sample | Conditions for Condensation | Sample Diameter/mm | Maximum Force Value/N | Compressive Strength/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Add 10% drilling fluid | 130 °C 150 min | 37.56 | 8186 | 7.39 |
| Add 15% drilling fluid | 130 °C 150 min | 36.83 | 7107 | 6.14 |
| Add 20% drilling fluid | 130 °C 150 min | 37.12 | 5872 | 5.04 |
| Acid Solubility Conditions | 140 °C, 24 h | 80 °C, 72 h | 80 °C, 72 h |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mass before acid dissolution (g) | 80.09 | 89.34 | 101.42 |
| Filling material quality (g) | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Quality after acid dissolution (g) | 9.66 | 10.82 | 10.59 |
| Acid solubility degradation rate (%) | 97.69 | 96.53 | 97.23 |
| Reagent | Parameter | Purity | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bisphenol A-type epoxy resin | Epoxy value (0.43) | 99.0% | Saen Chemical Technology (Shanghai, China) Co., Ltd. |
| Hexamethylene tetramine | \ | 98.0% | Saen Chemical Technology (Shanghai, Shina) Co., Ltd. |
| Hydroxyethyl cellulose | Molecular weight (736.7) | 98.0% | Sinopharm Chemical Reagents Co., Ltd (Beijing, China). |
| Diethylene triamine | \ | 97.0% | Aladdin Biochemical Technology (Shanghai, China) Co., Ltd. |
| Nano-silica dioxide | Average particle (330 nm) | \ | Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) |
| Quartz sand | Average particle (60 mesh) | \ | Shandong Xiya Chemical Co., Ltd. (Binzhou, China) |
| Walnut shell | Average particle (3 mm) | \ | Shandong Xiya Chemical Co., Ltd. (Binzhou, China) |
| Barite | \ | \ | Shandong Xiya Chemical Co., Ltd. (Binzhou, China) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Wang, T.; Zhang, S.; Bai, Y.; Qin, G.; Yang, J. Study on Gel–Resin Composite for Losting Circulation Control to Improve Plugging Effect in Fracture Formation. Gels 2025, 11, 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080617
Zhu J, Wang T, Zhang S, Bai Y, Qin G, Yang J. Study on Gel–Resin Composite for Losting Circulation Control to Improve Plugging Effect in Fracture Formation. Gels. 2025; 11(8):617. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080617
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Jinzhi, Tao Wang, Shaojun Zhang, Yingrui Bai, Guochuan Qin, and Jingbin Yang. 2025. "Study on Gel–Resin Composite for Losting Circulation Control to Improve Plugging Effect in Fracture Formation" Gels 11, no. 8: 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080617
APA StyleZhu, J., Wang, T., Zhang, S., Bai, Y., Qin, G., & Yang, J. (2025). Study on Gel–Resin Composite for Losting Circulation Control to Improve Plugging Effect in Fracture Formation. Gels, 11(8), 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080617







