Novel Fat Replacers Based on Pork Lard and a Cold Gelling System in the Reformulation of Reduced-Fat Fresh Pork Sausages Containing Silicon from Diatomaceous Earth Powder
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
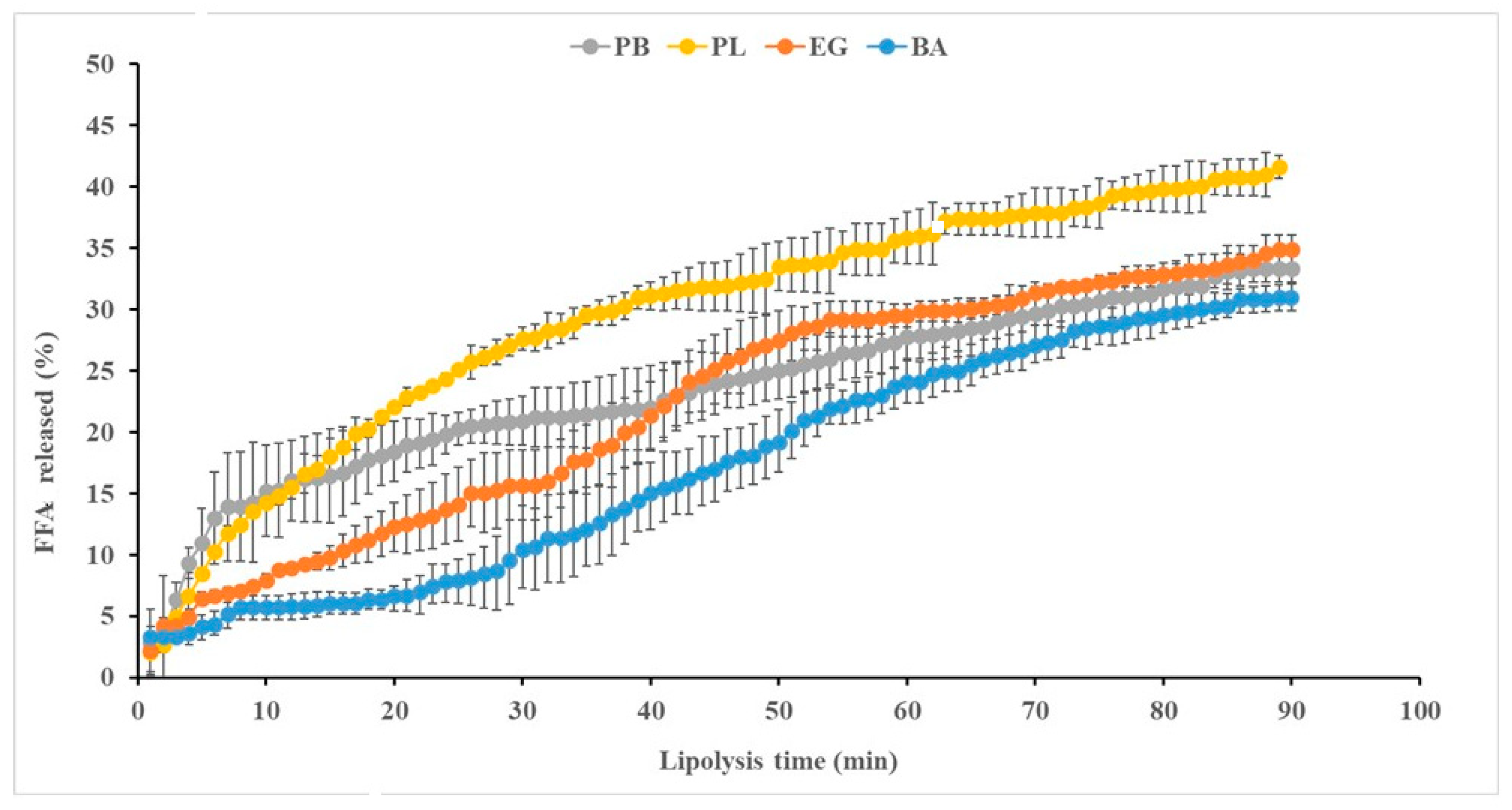
2.1. Visual Appearance, Physicochemical Characteristics, and Lipolysis During In Vitro GID of Pork Backfat, Pork Lard, and Fat Analogs
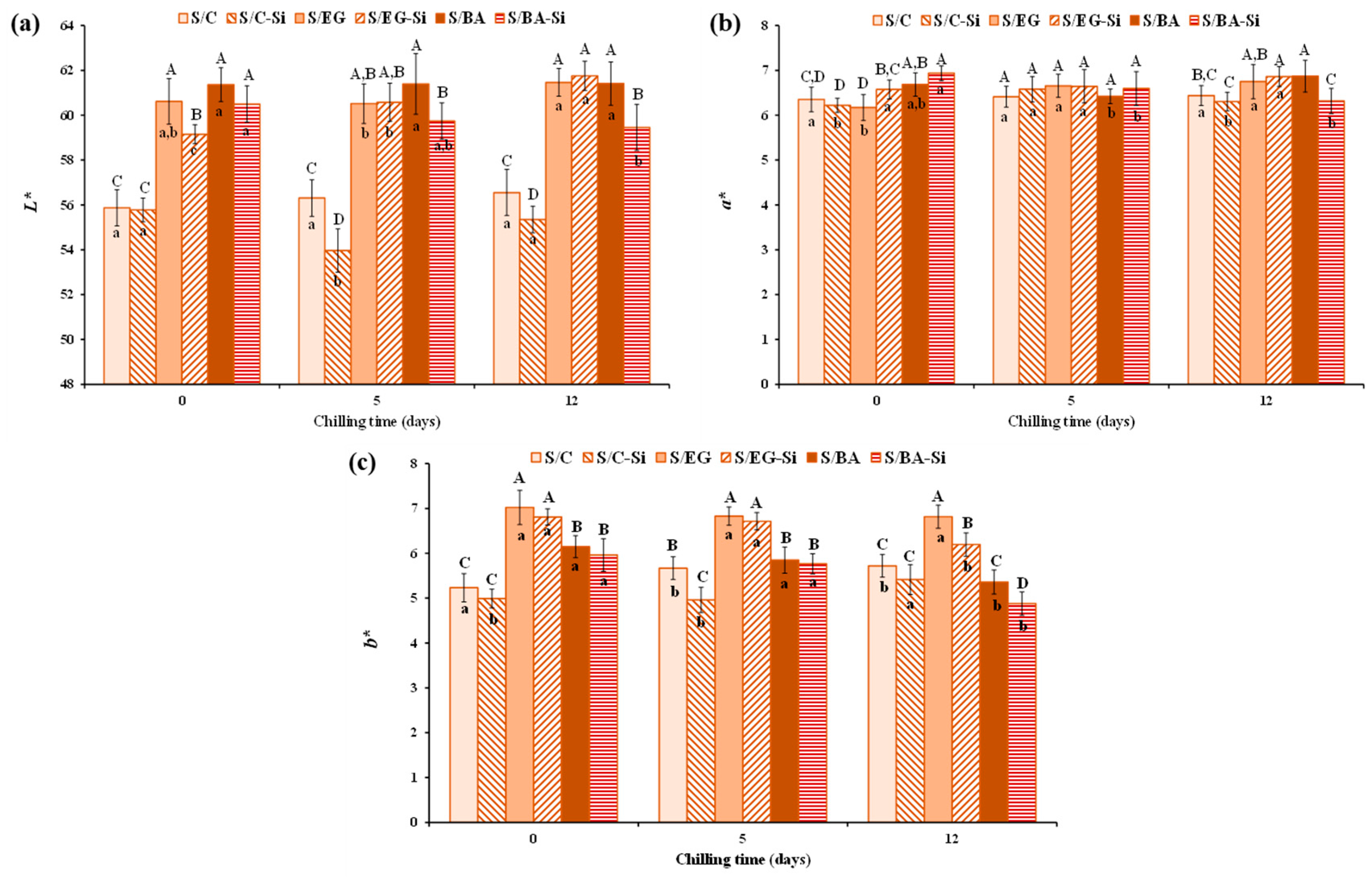
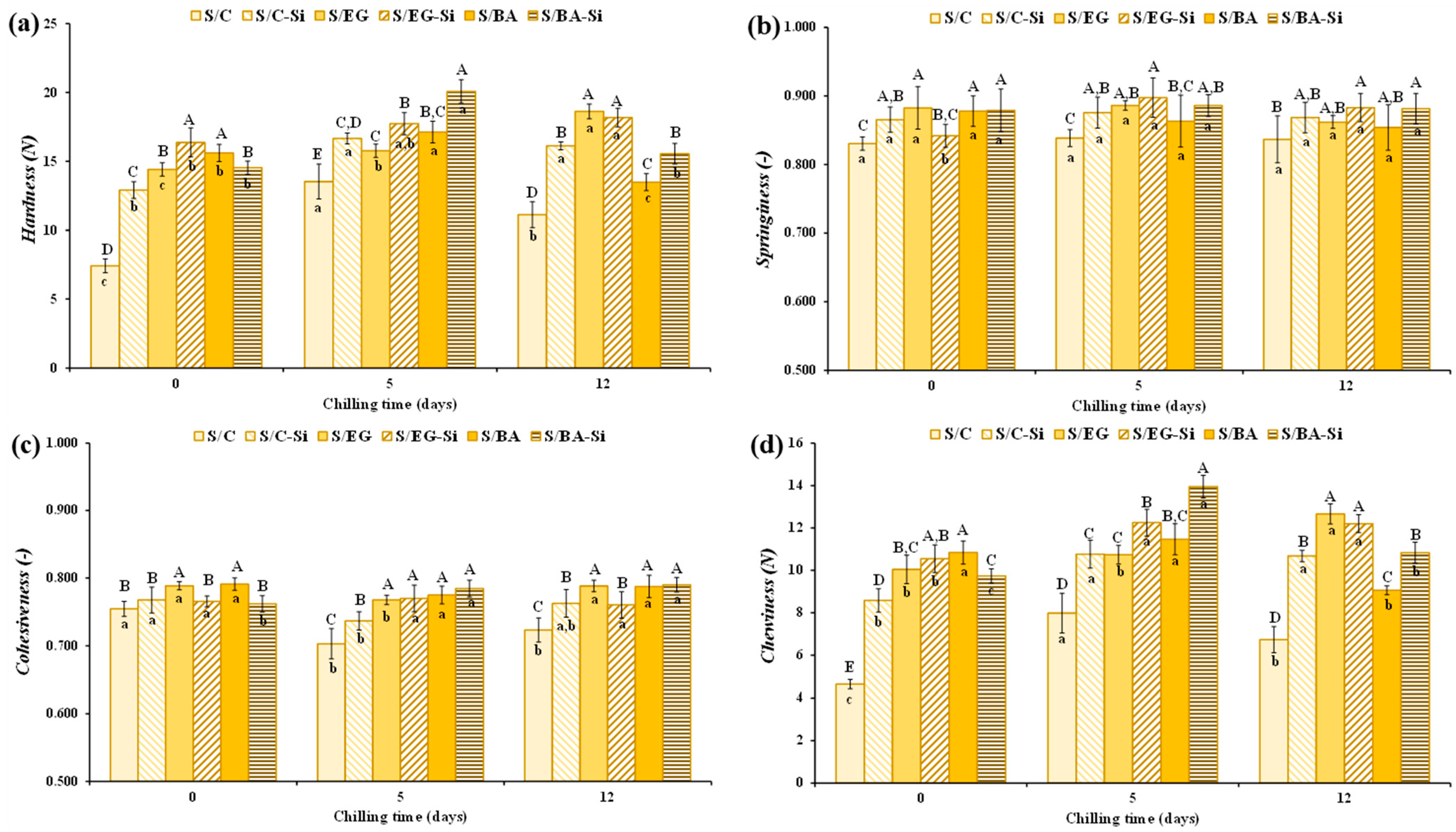
2.2. Characterization of Reformulated Fresh/Cooked Sausages
2.2.1. Proximate Composition and Energy Content
2.2.2. Physicochemical Properties
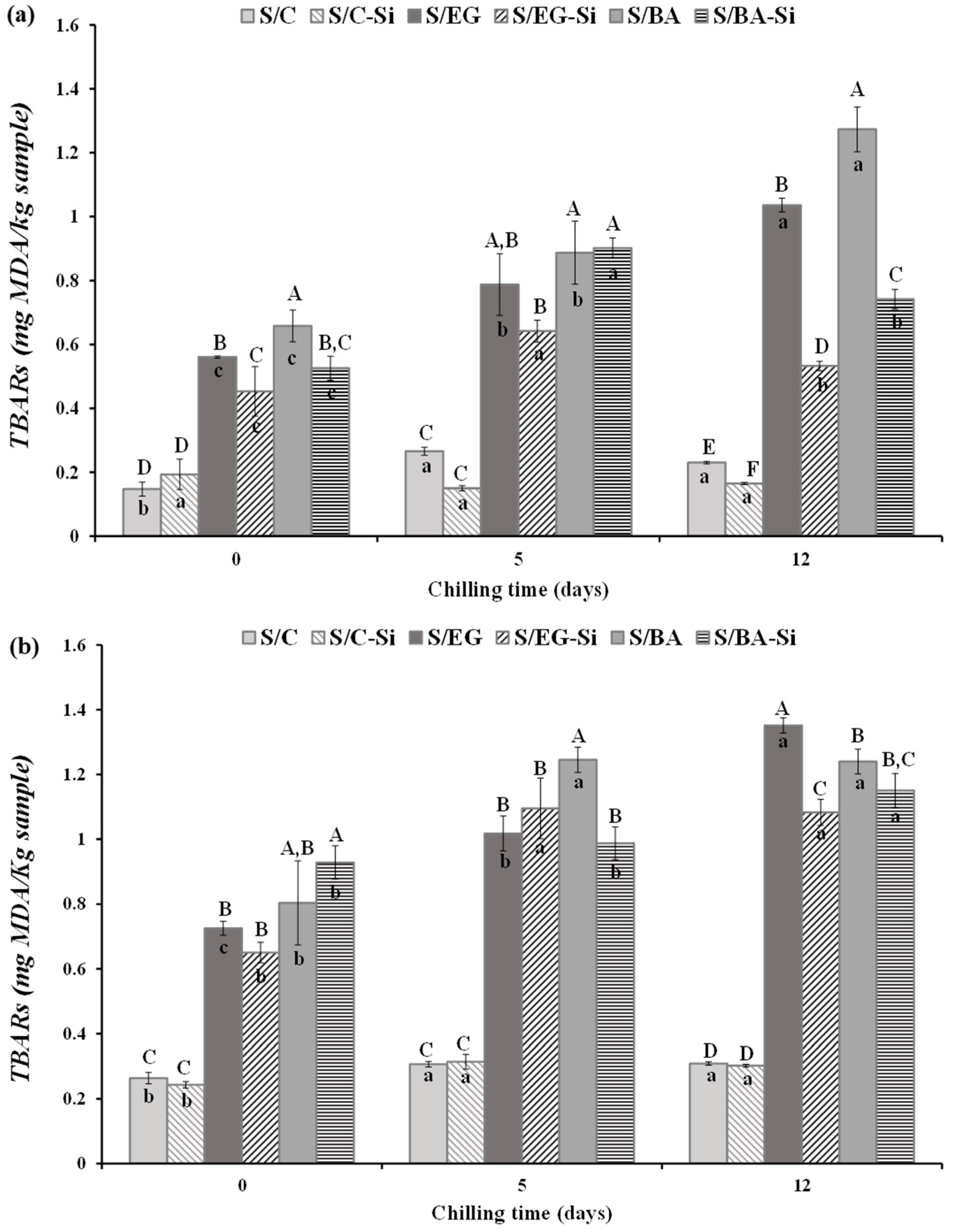
2.2.3. Lipid Oxidation
2.2.4. Sensory Analysis
2.2.5. Microbiological Analysis
2.3. Total FFA Released from Digested Cooked Sausages
2.4. FA Profile of Undigested and Digested Cooked Sausages
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Chemicals
4.2. Preparation of Fat Analogs (EG and BA)
4.3. Physicochemical Characteristics of PB, PL, and Fat Analogs (EG and BA)
4.4. Preparation of Fresh Sausage
4.5. Proximate Analysis and Energy Content of Cooked Sausages
4.6. Physicochemical Parameters of Fresh/Cooked Pork Sausages
4.6.1. Processing, Purge, and Cooking Losses
4.6.2. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA) and Color Measurements of Cooked Pork Sausages
4.7. Lipid Oxidation
4.8. Microbiological Analyses
4.9. Sensory Analysis
4.10. In Vitro GID of PB, PL, EG, BA, and Cooked Pork Sausages
4.11. Rate and Extent of Lipolysis of PB, PL, EG, and BA During In Vitro GID
4.12. Fatty Acid (FA) Profile of the Undigested and Digested Cooked Sausages and Bioaccessibility (BAC) of the Main FA After In Vitro GID
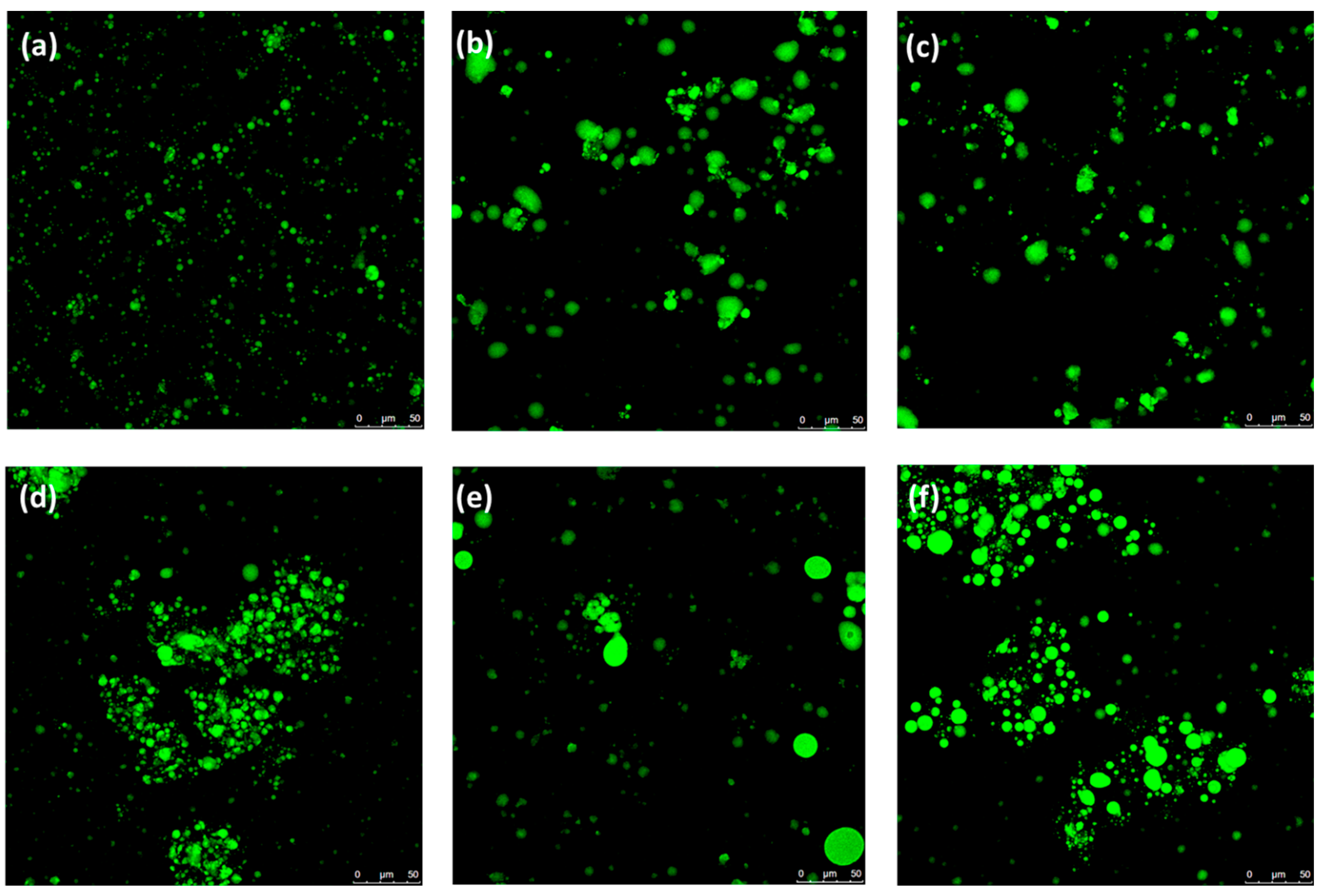
4.13. Microstructure Measurements
4.14. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jimenez-Colmenero, F.; Salcedo-Sandoval, L.; Bou, R.; Cofrades, S.; Herrero, A.M.; Ruiz-Capillas, C. Novel Applications of Oil Structuring Methods as a Strategy to Improve the Fat Content of Meat Products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 44, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, A.M.; Carmona, P.; Jiménez-Colmenero, F.; Ruíz-Capillas, C. Polysaccharide Gels as Oil Bulking Agents: Technological and Structural Properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 36, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, S.; Masoodi, F.A.; Rashid, R.; Naqash, F.; Ahmad, M. Oleogels for the Development of Healthy Meat Products: A Review. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhao, D.; Cao, J.; Liu, X. Application of Emulsion Gels as Fat Substitutes in Meat Products. Foods 2022, 11, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siri-Tarino, P.W.; Sun, Q.; Hu, F.B.; Krauss, R.M. Saturated Fatty Acids and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease: Modulation by Replacement Nutrients. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2010, 12, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cofrades, S.; Hernández-Martín, M.; Garcimartín, A.; Saiz, A.; López-Oliva, M.E.; Benedí, J.; Álvarez, M.D. Impact of Silicon Addition on the Development of Gelled Pork Lard Emulsions with Controlled Lipid Digestibility for Application as Fat Replacers. Gels 2023, 9, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyato, C.; Ansorena, D.; Berasategi, I.; Navarro-Blasco, I.; Astiasarán, I. Optimization of a Gelled Emulsion Intended To Supply ω-3 Fatty Acids into Meat Products by Means of Response Surface Methodology. Meat Sci. 2014, 98, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-López, J.A.; Garcimartín, A.; Merino, P.; López-Oliva, M.E.; Bastida, S.; Benedí, J.; Sánchez-Muniz, F.J.; Portero-Otin, M. Effects of Silicon vs. Hydroxytyrosol-Enriched Restructured Pork on Liver Oxidation Status of Aged Rats Fed High-Saturated/High-Cholesterol Diets. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cofrades, S.; Garcimartín, A.; Pérez-Mateos, M.; Saiz, A.; Redondo-Castillejo, R.; Bocanegra, A.; Benedí, J.; Álvarez, M.D. Stabilized Soy Protein Emulsion Enriched with Silicon and Containing or Not Methylcellulose as Novel Technological Alternatives to Reduce Animal Fat Digestion. Food Res. Int. 2023, 170, 112833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cofrades, S.; Saiz, A.; Álvarez, M.D. Biopolymeric Emulsions with Added Silicon as Pork Fat Substitutes in the Reformulation of Healthy Pâtés: Effect on Technological, Nutritional and Sensory Properties and on Lipid Digestibility after In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 210, 116865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R.; Dewettinck, K. Edible Oil Structuring: An Overview and Recent Updates. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, A.M.; Carmona, P.; Pintado, T.; Jiménez-Colmenero, F.; Ruíz-Capillas, C. Olive Oil-in-Water Emulsions Stabilized with Caseinate: Elucidation of Protein-Lipid Interactions by Infrared Spectroscopy. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallandre, S.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Improvement of Stability of Oil-in-Water Emulsions Containing Caseinate-Coated Droplets by Addition of Sodium Alginate. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, E518–E524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.-S.; Lee, J.-H. Melting, Crystallization, and In Vitro Digestion Properties of Fats Containing Stearoyl-Rich Triacylglycerols. Molecules 2022, 27, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, N.; Ye, A.; Wolber, F.M.; Singh, H. Effect of Gel Structure on the In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion Behaviour of Whey Protein Emulsion Gels and the Bioaccessibility of Capsaicinoids. Molecules 2021, 26, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellesi, F.A.; Pizones Ruiz-Henestrosa, V.M.; Pilosof, A.M.R. Lipolysis of Soy Protein and HPMC Mixed Emulsion as Modulated by Interfacial Competence of Emulsifiers. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 99, 105328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintado, T.; Herrero, A.M.; Jiménez-Colmenero, F.; Pasqualin Cavalheiro, C.; Ruiz-Capillas, C. Chia and Oat Emulsion Gels as New Animal Fat Replacers and Healthy Bioactive Sources in Fresh Sausage Formulation. Meat Sci. 2018, 135, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, Y.; Liu, H.; Liang, B.; He, H.; Fu, X.; Sun, C.; Li, X.; Ji, C. Preparation, Characterization of Curdlan-Based Emulsion Micro-Gel Particles and its Application in Low-Fat Pork Sausages. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 185, 115160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boles, J.A.; Shand, P.J. Effects of Raw Binder System, Meat Cut and Prior Freezing on Restructured Beef. Meat Sci. 1999, 53, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, G.; Jin, S.; Choi, J. Effects of Physicochemical Characteristics and Storage Stability of Porcine Albumin Protein Hydrolysates in Pork Sausage. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. 2022, 10, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paglarini, C.S.; Furtado, G.F.; Honório, A.R.; Mokarzel, L.; Vidal, V.A.S.; Ribeiro, A.P.B.; Cunha, R.L.; Pollonio, M.A.R. Functional Emulsion Gels as Pork Back Fat Replacers in Bologna Sausage. Food Struct. 2019, 20, 100105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Colmenero, F.; Herrero, A.; Pintado, T.; Solas, M.T.; Ruiz-Capillas, C. Influence of Emulsified Olive Oil Stabilizing System Used for Pork Backfat Replacement in Frankfurters. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 2068–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintado, T.; Cofrades, S. Quality Characteristics of Healthy Dry Fermented Sausages Formulated with a Mixture of Olive and Chia Oil Structured in Oleogel or Emulsion Gel as Animal Fat Replacer. Foods 2020, 9, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.E.; Stepanyan, V.; Allen, P.; O’Grady, M.N.; Kerry, J.P. Evaluation of the Effects of Selected Plant-Derived Nutraceuticals on the Quality and Shelf-Life Stability of Raw and Cooked Pork Sausages. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alirezalu, K.; Hesari, J.; Yaghoubi, M.; Khaneghah, A.M.; Alirezalu, A.; Pateiro, M.; Lorenzo, J.M. Combined Effects of ε-Polylysine and ε-Polylysine Nanoparticles with Plant Extracts on the Shelf Life and Quality Characteristics of Nitrite-Free Frankfurter-Type Sausages. Meat Sci. 2021, 172, 108318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Holman, B.W.; Ponnampalam, E.N.; Kerr, M.G.; Bailes, K.L.; Kilgannon, A.K.; Collins, D.; Hopkins, D.L. Understanding Beef Flavour and Overall Liking Traits Using Two Different Methods for Determination of Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substance (TBARS). Meat Sci. 2019, 149, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyato, C.; Astiasaran, I.; Barriuso, B.; Ansorena, D. A New Polyunsaturated Gelled Emulsion as Replacer of Pork Back-Fat in Burger Patties: Effect on Lipid Composition, Oxidative Stability and Sensory Acceptability. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizzi, L.; Cofrades, S.; Bou, R.; Pintado, T.; López-Caballero, M.E.; Zaide, F.; Jiménez-Colmenero, F. Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Effects of Combined High Pressure Processing and Sage in Beef Burgers during Prolonged Chilled Storage. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 51, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathenjwa, S.A.; Hugo, C.J.; Bothma, C.; Hugo, A. Effect of Alternative Preservatives on the Microbial Quality, Lipid Stability and Sensory Evaluation of Boerewors. Meat Sci. 2012, 91, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Capillas, C.; Cofrades, S.; Serrano, A.; Jiménez-Colmenero, F. Biogenic amines in restructured beef steaks as affected by added walnuts and cold storage. J. Food Protect. 2004, 67, 607–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio-Grao, A.; Calvo-Lerma, J.; Heredia, A.; Andrés, A. Fat Digestibility in Meat Products: Influence of Food Structure and Gastrointestinal Conditions. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 70, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; McClements, D.J. Modulating Lipid Droplet Intestinal Lipolysis by Electrostatic Complexation with Anionic Polysaccharides: Influence of Cosurfactants. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, X.; Ke, W.; Li, S.; Mao, X.; Shan, K.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, D.; Li, C. Effect of Wheat Aleurone on Lard Emulsions during In Vitro Digestion. Food Chem. 2024, 435, 137530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Pando, G.; Cofrades, S.; Rodríguez-Salas, L.; Jiménez-Colmenero, F. A Healthier Oil Combination and Konjac Gel as Functional Ingredients in Low-Fat Pork Liver Pâté. Meat Sci. 2011, 88, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas-González, R.; Pérez-Álvarez, J.A.; Viuda-Martos, M.; Fernández-López, J. Pork Liver Pâté Enriched with Persimmon Coproducts: Effect of In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion on its Fatty Acid and Polyphenol Profile Stability. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lairon, D. Designing Functional Foods. In Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition; McClements, D.J., Decker, E.A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 68–93. [Google Scholar]
- Solomando, J.C.; Antequera, T.; Perez-Palacios, T. Lipid Digestion Products in Meat Derivatives Enriched with Fish Oil Microcapsules. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 68, 103916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International; Association of Officiating Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A Rapid Method of Total Lipid Extraction and Purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Union (EU). Regulation (EU) No. 1169/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the provision of food information to consumers. Off. J. Eur. Union Eur. Comm. 2011, 304, 18–63. [Google Scholar]
- Wee, M.S.M.; Goh, A.T.; Stieger, M.; Forde, C.G. Correlation of Instrumental Texture Properties from Textural Profile Analysis (TPA) with Eating Behaviours and Macronutrient Composition for a Wide Range of Solid Foods. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 5301–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodkorb, A.; Egger, L.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Assunção, R.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Boutrou, R.; Carrière, F.; et al. INFOGEST Static In Vitro Simulation of Gastrointestinal Food Digestion. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 991–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Ye, A.; Singh, H. On the Role of Bile Salts in the Digestion of Emulsified Lipids. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 60, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.R.F.; Tweed, J.K.S.; Kim, E.J.; Scollan, N.D. Beef, Chicken and Lamb Fatty Acid Analysis-a Simplified Direct Bimethylation Procedure Using Freeze-Dried Material. Meat Sci. 2012, 92, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
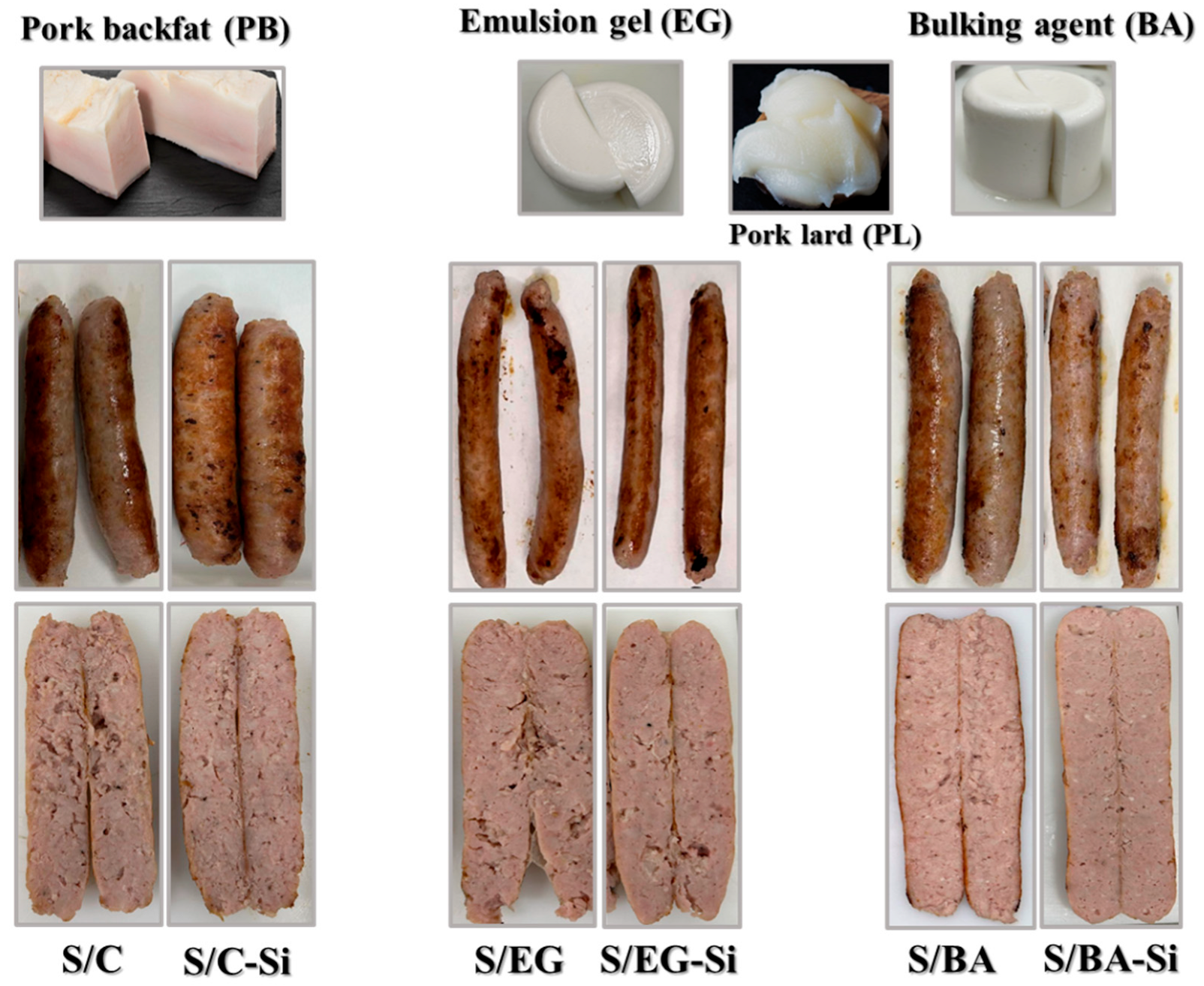

| PB | PL | EG | BA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Texture | ||||
| Force at 10 mm (N) | 2.83 ± 0.23 | 0.011 ± 0.00 | 0.274 ± 0.071 B | 0.735 ± 0.09 A |
| Total work (mJ) | 12.0 ± 0.29 | 0.081 ± 0.01 | 2.59 ± 0.33 B | 5.90 ± 0.43 A |
| Breaking force (N) | - | - | 0.429 ± 0.033 B | 1.03 ± 0.06 A |
| Breaking work (mJ) | - | - | 1.05 ± 0.14 B | 2.21 ± 0.16 A |
| Color | ||||
| L* | 75.05 ± 1.27 D | 82.17 ± 0.94 C | 90.41 ± 1.51 A | 85.25 ± 0.98 B |
| a* | 2.57 ± 0.06 A | −1.92 ± 0.08 C | −1.19 ± 0.68 B | −1.18 ± 0.14 B |
| b* | 3.11 ± 0.07 C | 0.992 ± 0.06 D | 4.74 ± 0.29 A | 4.43 ± 0.28 B |
| S/C | S/C-Si | S/EG | S/EG-Si | S/BA | S/BA-Si | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | 63.38 ± 0.19 A | 62.78 ± 0.17 B | 62.37 ± 0.15 B | 59.88 ± 0.11 C | 63.65 ± 0.46 A | 59.97 ± 0.55 C |
| Protein | 18.70 ± 0.56 A | 18.13 ± 0.63 A | 16.44 ± 0.12 B | 16.02 ± 0.28 B | 16.14 ± 0.12 B | 16.66 ± 0.24 B |
| Fat | 13.11 ± 0.53 B | 13.41 ± 0.41 B | 15.48 ± 0.51 A | 15.30 ± 0.48 A | 15.33 ± 0.43 A | 15.87 ± 0.28 A |
| Ash | 3.39 ± 0.06 B | 5.45 ± 0.11 A | 3.42 ± 0.37 B | 5.45 ± 0.37 A | 3.36 ± 0.02 B | 5.71 ± 0.03 A |
| Energy content | 192.79 | 204.65 | 205.08 | 201.78 | 198.53 | 209.47 |
| Sample | Appearance | Color | Odor | Flavor | Texture | Overall Acceptability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC | 7.77 ± 1.3 A | 7.85 ± 1.3 A | 7.27 ± 1.5 A | 6.67 ± 2.2 A,B | 5.83 ± 2.3 A | 6.34 ± 2.1 A,B |
| SC-Si | 7.61 ± 1.3 A | 7.61 ± 1.4 A | 7.91 ± 1.4 A | 7.57 ± 1.7 A | 7.57 ± 1.7 A | 7.16 ± 2.0 A |
| S/EG | 6.65 ± 1.8 A | 6.60 ± 2.0 A | 7.14 ± 1.8 A | 6.87 ± 2.2 A,B | 6.88 ± 2.1 A | 6.88 ± 2.1 A,B |
| S/EG-Si | 7.21 ± 1.9 A | 7.27 ± 1.9 A | 7.43 ± 1.6 A | 6.64 ± 2.4 A,B | 6.02 ± 2.6 A | 6.46 ± 2.3 A,B |
| S/BA | 6.47 ± 2.2 A | 6.60 ± 2.1 A | 6.86 ± 1.9 A | 5.75 ± 2.5 B | 5.69 ± 2.5 A | 5.57 ± 2.5 B |
| S/BA-Si | 7.18 ± 2.3 A | 7.25 ± 1.9 A | 7.05 ± 2.1 A | 6.13 ± 2.3 A,B | 6.38 ± 2.2 A | 6.26 ± 2.0 A,B |
| Sample | Storage Time (Days) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 12 | ||
| Total viable count | S/C | 5.95 ± 0.01 Eb | 6.29 ± 0.03 Ca | 6.27 ± 0.04 Da |
| S/C-Si | 6.31 ± 0.03 Db | 6.62 ± 0.15 Ba | 6.48 ± 0.04 Ba,b | |
| S/EG | 7.71 ± 0.03 Aa,b | 7.84 ± 0.003 Aa | 7.58 ± 0.11 Ab | |
| S/EG-Si | 7.56 ± 0.07 Bc | 7.93 ± 0.03 Aa | 7.71 ± 0.03 Ab | |
| S/BA | 6.66 ± 0.57 Ca | 6.67 ± 0.03 Ba | 6.44 ± 0.01 B,Cb | |
| S/BA-Si | 6.58 ± 0.02 Ca | 6.56 ± 0.01 Ba | 6.32 ± 0.04 C,Db | |
| Lactic acid bacteria | S/C | 3.95 ± 0.0 Cc | 4.26 ± 0.01 B,Ca | 4.11 ± 0.07 Cb |
| S/C-Si | 3.86 ± 0.0 Dc | 4.85 ± 0.01 Aa | 4.70 ± 0.01 Ab | |
| S/EG | 4.27 ± 0.01 Ba | 4.15 ± 0.21 Ca | 4.16 ± 0.05 Ca | |
| S/EG-Si | 4.28 ± 0.02 Ba | 4.28 ± 0.08 B,Ca | 4.19 ± 0.07 Ca | |
| S/BA | 4.34 ± 0.02 A,Bb | 4.42 ± 0.01 Bb | 4.59 ± 0.10 A,Ba | |
| S/BA-Si | 4.39 ± 0.04 Aa | 4.42 ± 0.04 Ba | 4.46 ± 0.01 Ba | |
| Enterobacteriaceae | S/C | 2.75 ± 0.03 Db | 3.06 ± 0.02 Ca | 2.76 ± 0.06 Cb |
| S/C-Si | 2.63 ± 0.01 Da,b | 2.76 ± 0.03 Ca | 2.50 ± 0.15 Db | |
| S/EG | 4.46 ± 0.08 Aa | 4.11 ± 0. 18 Ab | 4.04 ± 0.01 Ab | |
| S/EG-Si | 3.99 ± 0.09 Ba | 3.59 ± 0.19 Bb | 3.25 ± 0.02 Bc | |
| S/BA | 3.98 ± 0.14 Aa | 3.97 ± 0.18 A,Ba | 3.83 ± 0.10 Aa | |
| S/BA-Si | 3.57 ± 0.22 Ca | 3.76 ± 0.10 A,Ba | 3.85 ± 0.05 Aa | |
| S/C | S/C-Si | S/EG | S/EG-Si | S/BA | S/BA-Si | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total FFA | - | 554.02 ± 2.09 A | 518.47 ± 5.72 B | 512.80 ± 4.20 B | 454.82 ± 3.56 D | 518.31 ± 1.53 B | 500.71 ± 5.06 C |
| FA profile | Before in vitro GID * | After in vitro GID | |||||
| SFA | |||||||
| Palmitic C16:0 | 178.83 ± 7.45 | 71.15 ± 0.98 B | 82.58 ± 0.78 A | 64.48 ± 0.48 D | 53.63 ± 0.61 F | 67.07 ± 0.20 C | 60.29 ± 1.52 E |
| Stearic C18:0 | 98.00 ± 4.58 | 82.89 ± 0.19 A | 76.83 ± 0.86 C | 71.93 ± 0.50 E | 65.54 ± 0.46 F | 79.23 ± 0.25 B | 73.04 ± 0.79 D |
| Other SFA | 31.92 ± 1.69 | 7.74 ± 0.06 | 8.65 ± 0.09 | 6.74 ± 0.02 | 5.81 ± 0.03 | 6.90 ± 0.21 | 7.27 ± 0.01 |
| ∑SFA | 308.75 ± 13.72 | 161.78 ± 1.24 | 168.05 ± 1.73 | 143.15 ± 0.96 | 124.98 ± 1.10 | 140.23 ± 2.52 | 153.57 ± 0.44 |
| MUFA | |||||||
| Vaccenic C18:1n-7 | 26.11 ± 1.13 | 21.61 ± 0.06 A | 19.19 ± 0.26 D | 21.21 ± 0.20 B | 18.31 ± 0.10 E | 19.98 ± 0.09 C | 20.08 ± 0.11 C |
| Oleic C18:1n-9 | 338.8 ± 18.12 | 281.2 ± 0.74 A | 242.0 ± 2.80 E | 266.5 ± 2.26 C | 237.6 ± 1.81 F | 270.6 ± 0.88 B | 259.0 ± 1.81 D |
| Other MUFA | 2.36 ± 0.20 | 23.33 ± 0.04 | 20.52 ± 0.23 | 21.00 ± 0.22 | 17.18 ± 0.13 | 21.18 ± 0.18 | 21.38 ± 0.11 |
| ∑MUFA | 367.27 ± 19.45 | 326.09 ± 0.83 | 281.67 ± 3.29 | 308.75 ± 2.68 | 273.12 ± 2.04 | 300.29 ± 2.10 | 311.96 ± 1.09 |
| PUFA | |||||||
| Linoleic C18:2n-6 | 62.40 ± 2.18 | 53.60 ± 0.09 B | 54.65 ± 0.59 A | 49.89 ± 0.48 C | 46.86 ± 0.38 E | 43.40 ± 0.06 F | 48.67 ± 0.34 D |
| Other PUFA | 24.30 ± 0.85 | 12.55 ± 0.08 | 14.11 ± 0.11 | 11.02 ± 0.09 | 9.86 ± 0.05 | 11.52 ± 0.13 | 9.39 ± 0.06 |
| ∑PUFA | 86.70 ± 3.03 | 66.15 ± 0.01 | 68.75 ± 0.70 | 60.91 ± 0.57 | 56.73 ± 0.43 | 60.19 ± 0.46 | 52.79 ± 0.00 |
| After In Vitro GID | S/C | S/C-Si | S/EG | S/EG-Si | S/BA | S/BA-Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main FA | ||||||
| SFA | ||||||
| Palmitic C16:0 | 39.79 ± 0.39 B | 46.18 ± 0.31 A | 36.05 ± 0.19 D | 29.99 ± 0.24 F | 37.51 ± 0.08 C | 33.71 ± 0.60 E |
| Stearic C18:0 | 84.58 ± 0.14 A | 78.39 ± 0.62 C | 73.40 ± 0.36 E | 66.88 ± 0.33 F | 80.84 ± 0.18 B | 74.53 ± 0.57 D |
| MUFA | ||||||
| Vaccenic C18:1n-7 | 82.74 ± 0.15 A | 73.47 ± 0.69 D | 81.21 ± 0.54 B | 70.11 ± 0.26 E | 76.50 ± 0.25 C | 76.88 ± 0.30 C |
| Oleic C18:1n-9 | 82.99 ± 0.15 A | 71.43 ± 0.58 E | 78.66 ± 0.47 C | 70.13 ± 0.38 F | 79.87 ± 0.18 B | 76.45 ± 0.38 D |
| PUFA | ||||||
| Linoleic C18:2n-6 | 85.90 ± 0.10 B | 87.58 ± 0.67 A | 79.95 ± 0.55 C | 75.10 ± 0.43 E | 69.55 ± 0.07 F | 77.99 ± 0.38 D |
| Fat Analog | Sodium Caseinate | Texturizing Mixture | Sodium Alginate | CaSO4 | Pyrophosphate | Water | Pork lard (PL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EG | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0.15 | 0.1 | 53.75 | 40 |
| BA | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0.15 | 0.1 | 56.75 | 40 |
| Fresh Sausages | Meat | Pork Backfat (PB) | EG | BA | DP | Water | Seasoning |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S/C | 60.00 | 13.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 23.00 | 4.00 |
| S/C-Si | 60.00 | 13.00 | 0 | 0 | 1.50 | 21.50 | 4.00 |
| S/EG | 60.00 | 3.25 | 21.45 | 0 | 0 | 11.30 | 4.00 |
| S/EG-Si | 60.00 | 3.25 | 21.45 | 0 | 1.50 | 9.80 | 4.00 |
| S/BA | 60.00 | 3.25 | 0 | 21.45 | 0 | 11.30 | 4.00 |
| S/BA-Si | 60.00 | 3.25 | 0 | 21.45 | 1.50 | 9.80 | 4.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Álvarez, M.D.; Saiz, A.; Cofrades, S. Novel Fat Replacers Based on Pork Lard and a Cold Gelling System in the Reformulation of Reduced-Fat Fresh Pork Sausages Containing Silicon from Diatomaceous Earth Powder. Gels 2025, 11, 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080618
Álvarez MD, Saiz A, Cofrades S. Novel Fat Replacers Based on Pork Lard and a Cold Gelling System in the Reformulation of Reduced-Fat Fresh Pork Sausages Containing Silicon from Diatomaceous Earth Powder. Gels. 2025; 11(8):618. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080618
Chicago/Turabian StyleÁlvarez, María Dolores, Arancha Saiz, and Susana Cofrades. 2025. "Novel Fat Replacers Based on Pork Lard and a Cold Gelling System in the Reformulation of Reduced-Fat Fresh Pork Sausages Containing Silicon from Diatomaceous Earth Powder" Gels 11, no. 8: 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080618
APA StyleÁlvarez, M. D., Saiz, A., & Cofrades, S. (2025). Novel Fat Replacers Based on Pork Lard and a Cold Gelling System in the Reformulation of Reduced-Fat Fresh Pork Sausages Containing Silicon from Diatomaceous Earth Powder. Gels, 11(8), 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080618







