Designing Gel-Inspired Food-Grade O/W Pickering Emulsions with Bacterial Nanocellulose–Chitosan Complexes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Evaluation of Parent O/W Emulsions
2.2. Characterization of CH/BNC Complexes
2.3. Characterization of Pickering O/W Complex Emulsions
2.4. Effect of Environmental Stressors on Emulsions Stability
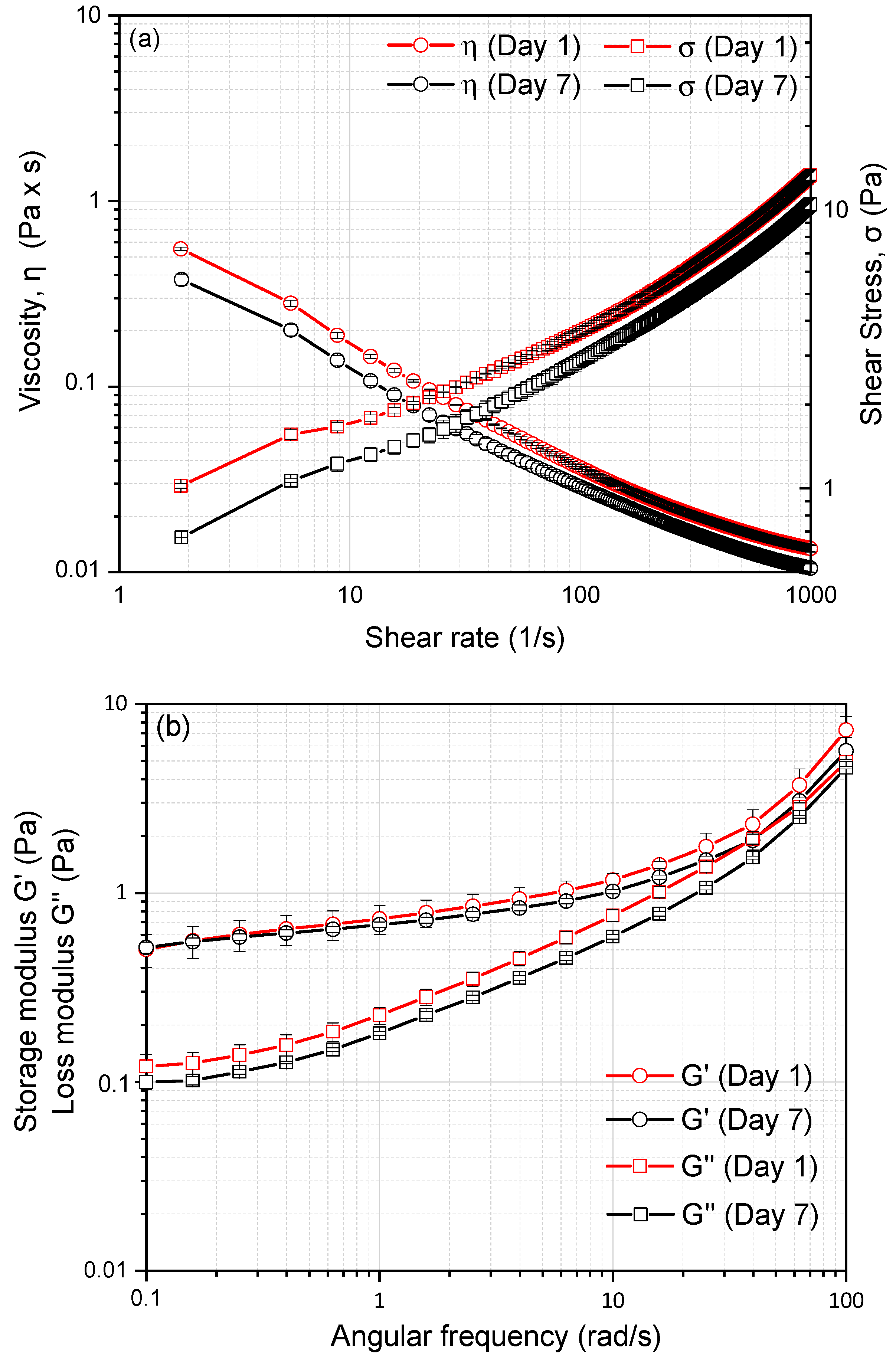
2.5. Dynamic Shear Rheology of CH/BNC1(25:75)-Based Emulsions
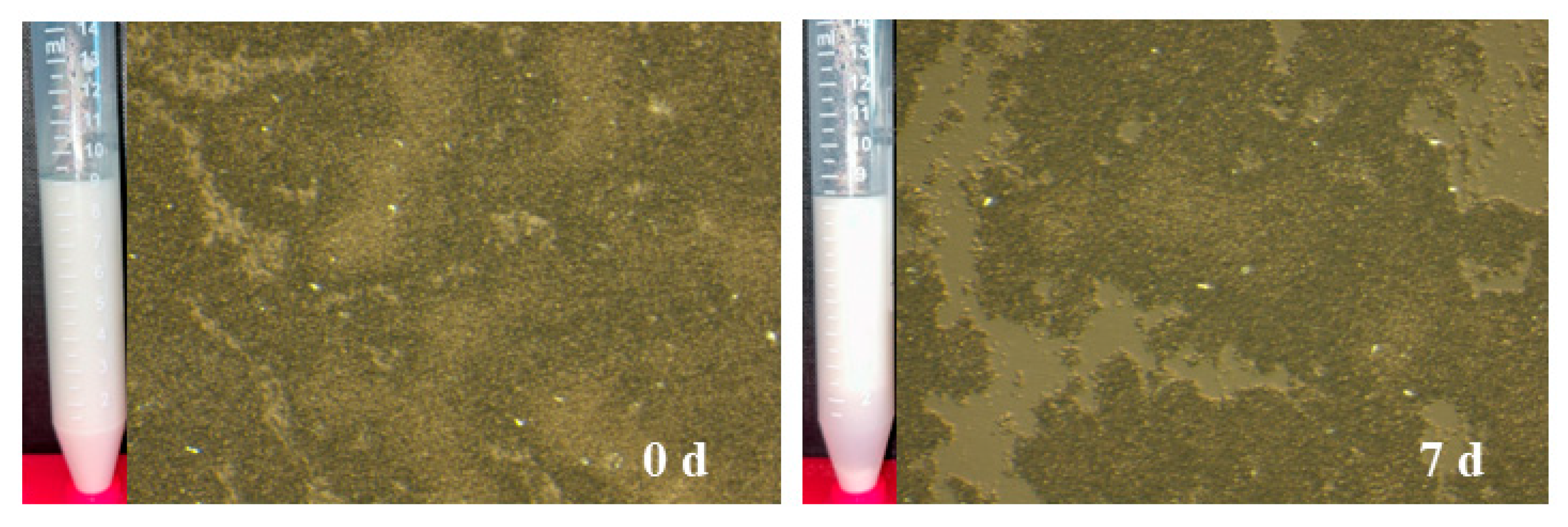
2.6. Evaluation of CH/BNC1 (25:75) Emulsifiers as Carriers for Renewable Proteins
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Production of Simple-Emulsifier (Parent) O/W Pickering Emulsions
4.3. Preparation of CH/BC-Based Complexes
4.4. Production of Complex-Emulsifier O/W Pickering Emulsions
4.5. Stability Evaluation of Complex-Emulsifier O/W Pickering Emulsions Under Different Values of pH and Ionic Strength
4.6. Complexation Studies of O/W Emulsions with Protein
4.7. Characterization of O/W Emulsions and Complexes
4.7.1. Emulsion Stability Index (ESI)
4.7.2. Particle Size and ζ-Potential Measurements
4.7.3. Viscosity Measurements
4.7.4. Dynamic Shear Rheological Measurements
4.7.5. Microstructural Morphology
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panagopoulou, E.; Tsouko, E.; Kopsahelis, N.; Koutinas, A.; Mandala, I.; Evageliou, V. Olive Oil Emulsions Formed by Catastrophic Phase Inversion Using Bacterial Cellulose and Whey Protein Isolate. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 486, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos-Díaz, C.; Garrido-Miranda, K.A.; Palacio, D.A.; Chacón-Fuentes, M.; Opazo-Navarrete, M.; Bustamante, M. Food-Grade Oil-in-Water (O/W) Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by Agri-Food Byproduct Particles. Colloids Interfaces 2023, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, C.; Savoire, R.; Harscoat-Schiavo, C.; Pintori, D.; Monteil, J.; Faure, C.; Leal-Calderon, F. Redispersible Dry Emulsions Stabilized by Plant Material: Rapeseed Press-Cake or Cocoa Powder. LWT 2019, 113, 108311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassaing, B.; Koren, O.; Goodrich, J.K.; Poole, A.C.; Srinivasan, S.; Ley, R.E.; Gewirtz, A.T. Dietary Emulsifiers Impact the Mouse Gut Microbiota Promoting Colitis and Metabolic Syndrome. Nature 2015, 519, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwangi, W.W.; Ho, K.-W.; Tey, B.-T.; Chan, E.-S. Effects of Environmental Factors on the Physical Stability of Pickering-Emulsions Stabilized by Chitosan Particles. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 60, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyer, E.; Mekhloufi, G.; Rosilio, V.; Grossiord, J.-L.; Agnely, F. Proteins, Polysaccharides, and Their Complexes Used as Stabilizers for Emulsions: Alternatives to Synthetic Surfactants in the Pharmaceutical Field? Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 436, 359–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClements, D.J.; Gumus, C.E. Natural Emulsifiers—Biosurfactants, Phospholipids, Biopolymers, and Colloidal Particles: Molecular and Physicochemical Basis of Functional Performance. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 234, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Carvalho-Guimarães, F.B.; Correa, K.L.; de Souza, T.P.; Rodríguez Amado, J.R.; Ribeiro-Costa, R.M.; Silva-Júnior, J.O. A Review of Pickering Emulsions: Perspectives and Applications. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, A.; Dickinson, E. Sustainable Food-Grade Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by Plant-Based Particles. Emuls. Microemulsions 2020, 49, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velandia, S.F.; Marchal, P.; Sadtler, V.; Arnoux, P.; Bonn, D.; Roques-Carmes, T. Globular Proteins as Pickering Emulsion Stabilizers: Particles or Surfactants? Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 704, 135469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Ma, C.; Cui, F.; McClements, D.J.; Liu, X.; Liu, F. Protein-Stabilized Pickering Emulsions: Formation, Stability, Properties, and Applications in Foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthymiou, M.-N.; Tsouko, E.; Vlassi, E.; Papagiannopoulos, A.; Koutinas, A.; Pispas, S. Bio-Based and Nanostructured Hybrids for Green and Active Food Packaging. In Bio- and Nano-Sensing Technologies for Food Processing and Packaging; Shukla, A.K., Ed.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2022; pp. 81–128. ISBN 978-1-83916-432-3. [Google Scholar]
- Selianitis, D.; Efthymiou, M.-N.; Tsouko, E.; Papagiannopoulos, A.; Koutinas, A.; Pispas, S. Nanocellulose Production from Different Sources and Their Self-Assembly in Composite Materials. In Handbook of Nanocelluloses; Barhoum, A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–32. ISBN 978-3-030-62976-2. [Google Scholar]
- Natsia, A.; Tsouko, E.; Pateraki, C.; Efthymiou, M.-N.; Papagiannopoulos, A.; Selianitis, D.; Pispas, S.; Bethanis, K.; Koutinas, A. Valorization of Wheat Milling By-Products into Bacterial Nanocellulose via Ex-Situ Modification Following Circular Economy Principles. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 29, 100832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.C.; Lin, D.H.; Liu, D.J.; Yang, X.B. Emulsions Stabilized by Nanofibers from Bacterial Cellulose: New Potential Food-Grade Pickering Emulsions. Food Res. Int. 2018, 103, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibi, Y.; Lucia, L.A.; Rojas, O.J. Cellulose Nanocrystals: Chemistry, Self-Assembly, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3479–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paximada, P.; Tsouko, E.; Kopsahelis, N.; Koutinas, A.A.; Mandala, I. Bacterial Cellulose as Stabilizer of o/w Emulsions. Funct. Hydrocoll. Key Hum. Health 2016, 53, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahariah, P.; Másson, M. Antimicrobial Chitosan and Chitosan Derivatives: A Review of the Structure–Activity Relationship. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 3846–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Fan, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Recent Advances on Formation Mechanism and Functionality of Chitosan-Based Conjugates and Their Application in o/w Emulsion Systems: A Review. Food Chem. 2022, 380, 131838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janmohammadi, M.; Nazemi, Z.; Salehi, A.O.M.; Seyfoori, A.; John, J.V.; Nourbakhsh, M.S.; Akbari, M. Cellulose-Based Composite Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering and Localized Drug Delivery. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 20, 137–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, R.; Wang, M.; Qi, Z.; Hira, N.U.A.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, H.; Iqbal, S.; Wang, J.; Stuart, M.A.C.; Guo, X. Pickering Emulsions Based on the pH-Responsive Assembly of Food-Grade Chitosan. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 17915–17922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcclements, D.J. Critical Review of Techniques and Methodologies for Characterization of Emulsion Stability. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 47, 611–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, A.; Staroszczyk, H. Bacterial Cellulose vs. Bacterial Cellulose Nanocrystals as Stabilizer Agents for O/W Pickering Emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 145, 109080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalashnikova, I.; Bizot, H.; Cathala, B.; Capron, I. Modulation of Cellulose Nanocrystals Amphiphilic Properties to Stabilize Oil/Water Interface. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, N.O.F.; Bourbon, A.I.; Martins, D.; Pereira, A.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Pastrana, L.; Gama, M.; Azeredo, H.M.C.; Rosa, M.F.; Gonçalves, C. Bacterial Cellulose Nanocrystals or Nanofibrils as Pickering Stabilizers in Low-Oil Emulsions: A Comparative Study. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 157, 110427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez Saelices, C.; Capron, I. Design of Pickering Micro- and Nanoemulsions Based on the Structural Characteristics of Nanocelluloses. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Zheng, M.; Xu, Q.; Zhong, C. Rheological Behaviors of Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by TEMPO-Oxidized Bacterial Cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 215, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-Y.; Heuzey, M.-C. Chitosan-Based Conventional and Pickering Emulsions with Long-Term Stability. Langmuir 2016, 32, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karppinen, A.; Saarinen, T.; Salmela, J.; Laukkanen, A.; Nuopponen, M.; Seppälä, J. Flocculation of Microfibrillated Cellulose in Shear Flow. Cellulose 2012, 19, 1807–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indriyati; Dara, F.; Primadona, I.; Srikandace, Y.; Karina, M. Development of Bacterial Cellulose/Chitosan Films: Structural, Physicochemical and Antimicrobial Properties. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, H.M.; Pei, Y.; Luo, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, S. Novel Stable Pickering Emulsion Based Solid Foams Efficiently Stabilized by Microcrystalline Cellulose/Chitosan Complex Particles. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 106044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Tang, H.; Wan, S.; Qin, W.; Zeng, Q.; Huang, J.; Yu, G.; Feng, Y.; Li, J. Depletion Stabilization of Emulsions Based on Bacterial Cellulose/Carboxymethyl Chitosan Complexes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 297, 119904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Liu, T.-X.; Li, X.-T.; Tang, C.-H. Novel Nanoparticles from Insoluble Soybean Polysaccharides of Okara as Unique Pickering Stabilizers for Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, M.S.; Golmohammadi, A.; Nematollahzadeh, A.; Fiori, F.; Rovera, C.; Farris, S. Preparation of Cinnamon Essential Oil Emulsion by Bacterial Cellulose Nanocrystals and Fish Gelatin. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 109, 106111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffarionpour, S. Nanocellulose for Stabilization of Pickering Emulsions and Delivery of Nutraceuticals and Its Interfacial Adsorption Mechanism. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2020, 13, 1292–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, D.; Estevinho, B.; Rocha, F.; Dourado, F.; Gama, M. A Dry and Fully Dispersible Bacterial Cellulose Formulation as a Stabilizer for Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 230, 115657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jourdain, L.S.; Schmitt, C.; Leser, M.E.; Murray, B.S.; Dickinson, E. Mixed Layers of Sodium Caseinate + Dextran Sulfate: Influence of Order of Addition to Oil−Water Interface. Langmuir 2009, 25, 10026–10037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, R.; Yang, X.; Lin, D. PH Sensitive Double-Layered Emulsions Stabilized by Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibers/Soy Protein Isolate/Chitosan Complex Enhanced the Bioaccessibility of Curcumin: In Vitro Study. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuppolini, S.; Salama, A.; Cruz-Maya, I.; Guarino, V.; Borriello, A. Cellulose Amphiphilic Materials: Chemistry, Process and Applications. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, M.; Huang, M.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, T.; Huang, M. Effect of Ultrasound Assisted Emulsification in the Production of Pickering Emulsion Formulated with Chitosan Self-Assembled Particles: Stability, Macro, and Micro Rheological Properties. LWT 2022, 154, 112595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, D.; Shen, R.; Yang, X. Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibers Improved the Emulsifying Capacity of Soy Protein Isolate as a Stabilizer for Pickering High Internal-Phase Emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Yin, S.-W.; Tang, C.-H.; Wu, L.-Y.; Yang, X.-Q. Development of Antioxidant Pickering High Internal Phase Emulsions (HIPEs) Stabilized by Protein/Polysaccharide Hybrid Particles as Potential Alternative for PHOs. Food Chem. 2017, 231, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Wei, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Xue, C.; Huang, Q. Oleogel-Based Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by Ovotransferrin–Carboxymethyl Chitosan Nanoparticles for Delivery of Curcumin. LWT 2022, 157, 113121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Gaur, T.; Mandal, A. Characterization of SPN Pickering Emulsions for Application in Enhanced Oil Recovery. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 54, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, H.; Sui, X.; Jiang, L. Deciphering the Structural Network That Confers Stability to High Internal Phase Pickering Emulsions by Cross-Linked Soy Protein Microgels and Their In Vitro Digestion Profiles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 9796–9803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Liang, G.; Li, X.; He, Z.; Zeng, M.; Gao, D.; Qin, F.; Goff, H.D.; Chen, J. Impact of Soy Proteins, Hydrolysates and Monoglycerides at the Oil/Water Interface in Emulsions on Interfacial Properties and Emulsion Stability. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 177, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Cui, S.; Gong, J.; Miller, S.S.; Wang, Q.; Hua, Y. Stability of Citral in Oil-in-Water Emulsions Protected by a Soy Protein–Polysaccharide Maillard Reaction Product. Food Res. Int. 2015, 69, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, L. Protein–Polysaccharide Interactions and Aggregates in Food Formulations. Formul. Cosmet. 2020, 48, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardaxi, A.; Papagiannopoulos, A.; Gerogianni, I.; Pispas, S.; Mousdis, G.; Tsouko, E. Structural and Colloidal Attributes of Protein Matrices Extracted from Renewable Resources and Evaluation of Their Film-Forming Capacity for Sustainable Food Packaging. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2024, 18, 995–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-L.; Chen, Q.-H.; Li, X.-Y.; Su, J.; He, S.; Liu, J.; Yuan, Y. Formation and Characterisation of Food Protein–Polysaccharide Thermal Complex Particles: Effects of pH, Temperature and Polysaccharide Type. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 1368–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelu, M. Hydrogels with Essential Oils: Recent Advances in Designs and Applications. Gels 2024, 10, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efthymiou, M.-N.; Tsouko, E.; Pateraki, C.; Papagiannopoulos, A.; Tzamalis, P.; Pispas, S.; Bethanis, K.; Mantala, I.; Koutinas, A. Property Evaluation of Bacterial Cellulose Nanostructures Produced from Confectionery Wastes. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 186, 108575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardaxi, A.; Pispas, S. Random Cationic Copolymers as Nanocarriers for Ovalbumin. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 80, 104177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannopoulos, A.; Sotiropoulos, K.; Pispas, S. Particle Tracking Microrheology of the Power-Law Viscoelasticity of Xanthan Solutions. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
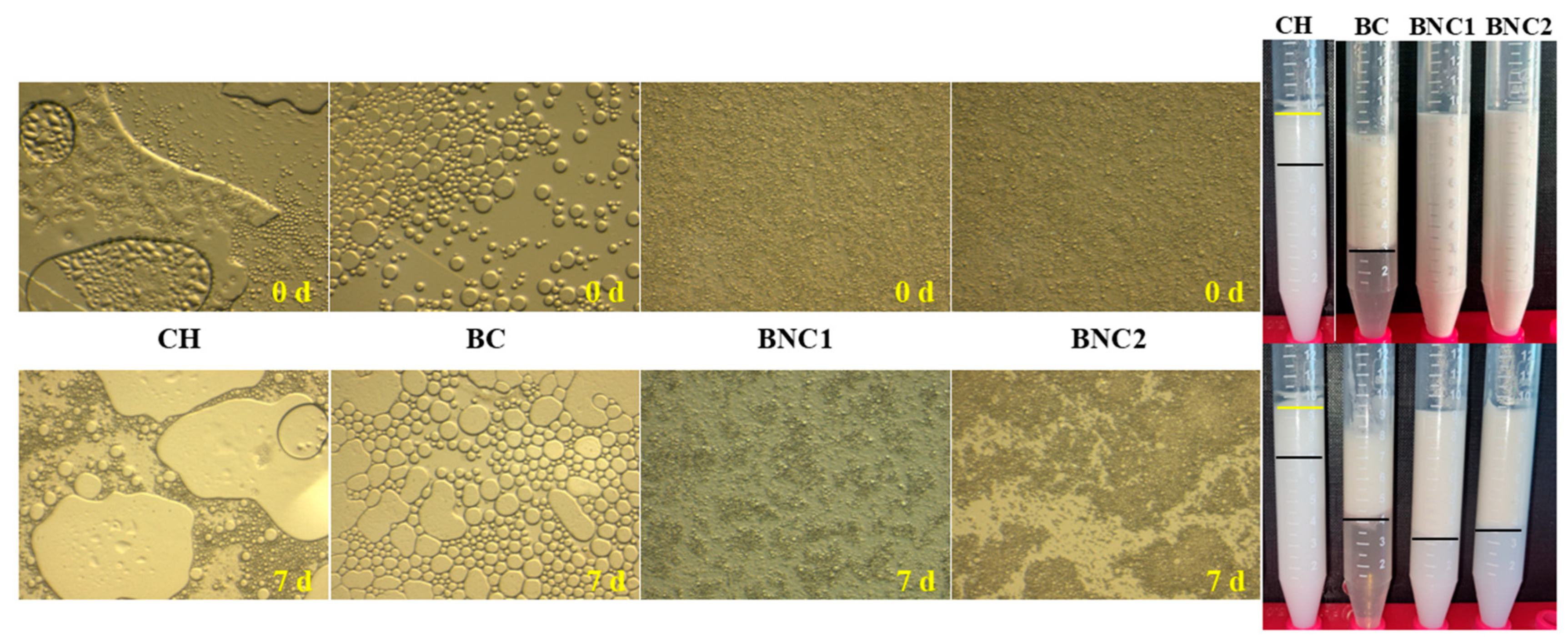
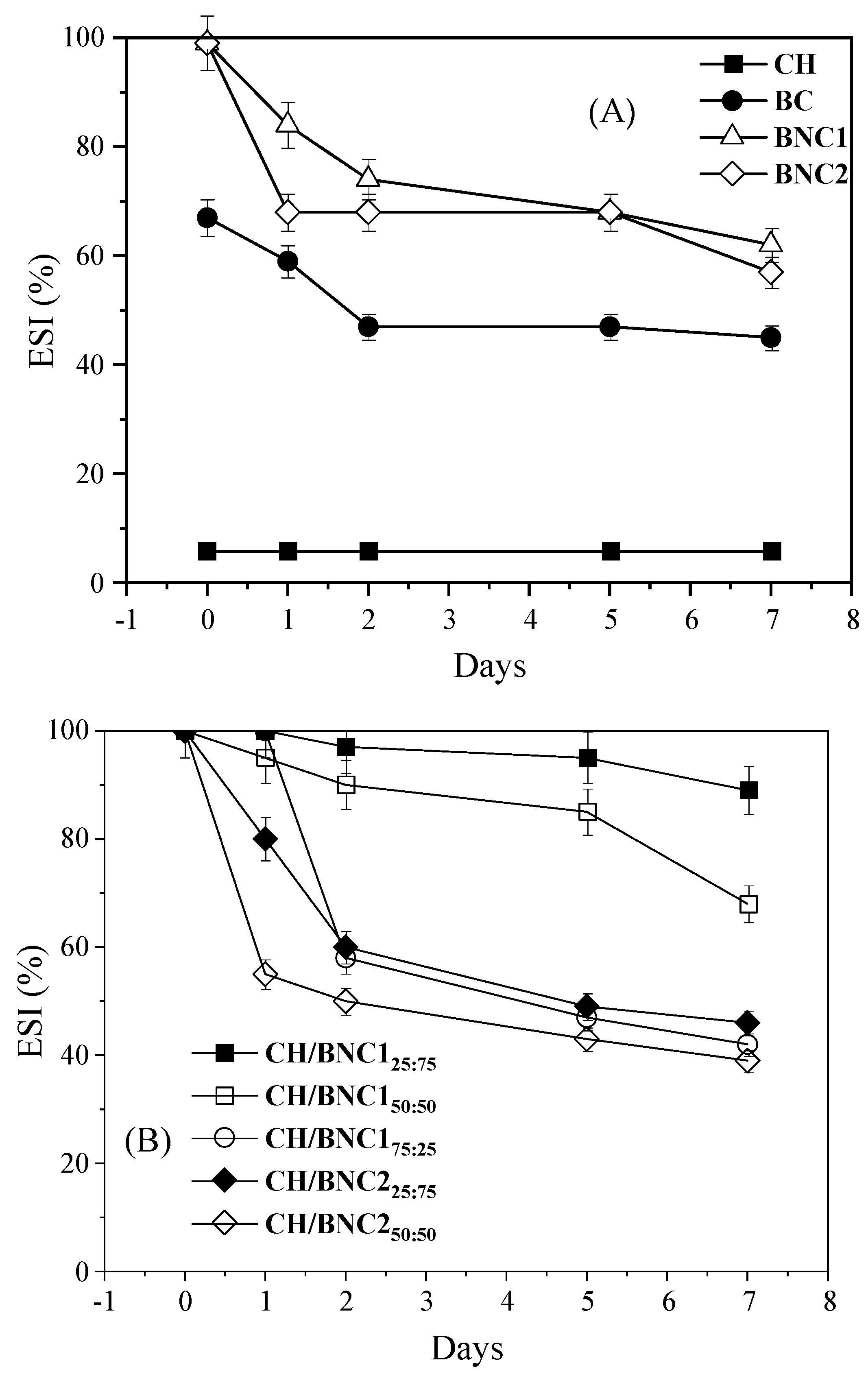
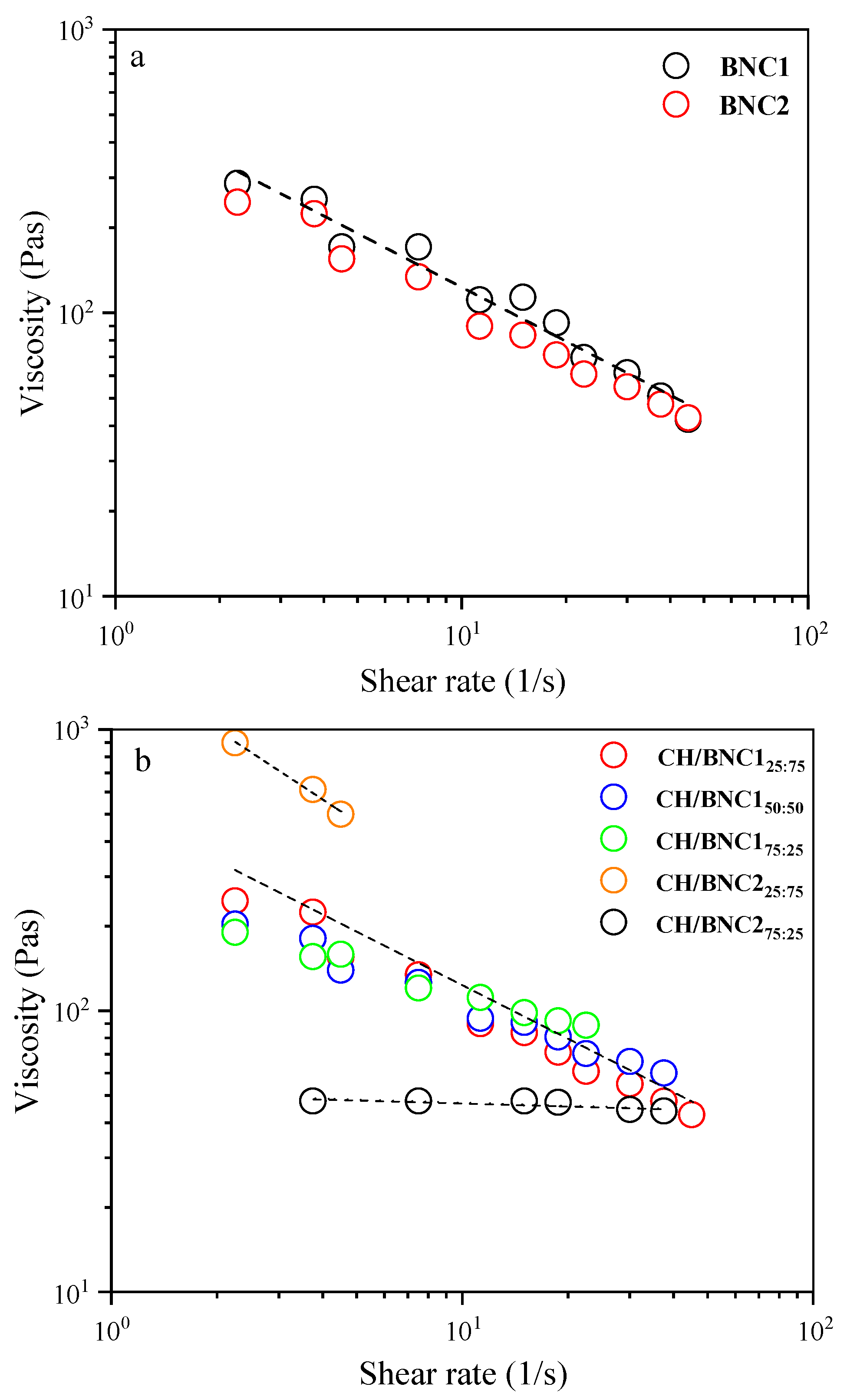
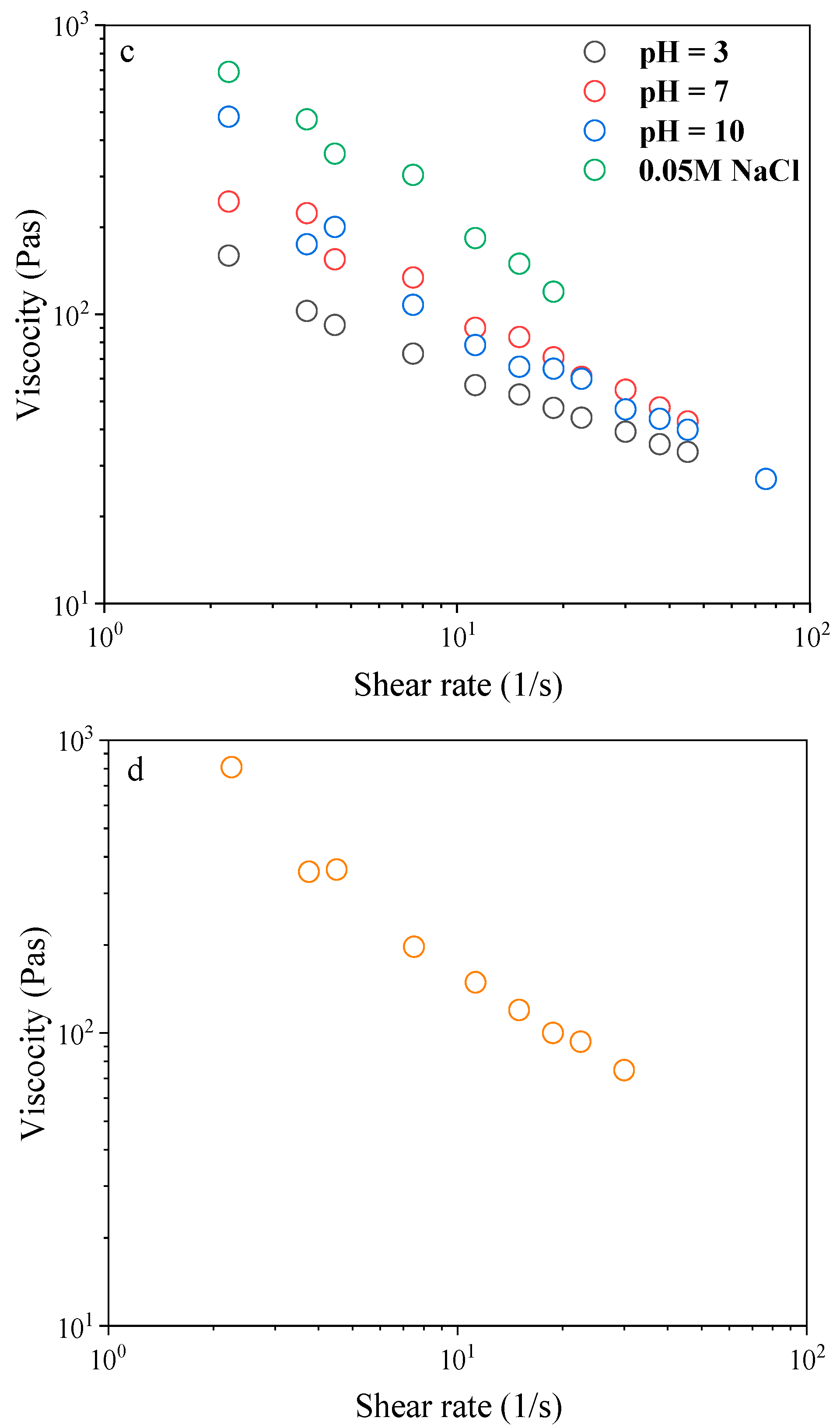
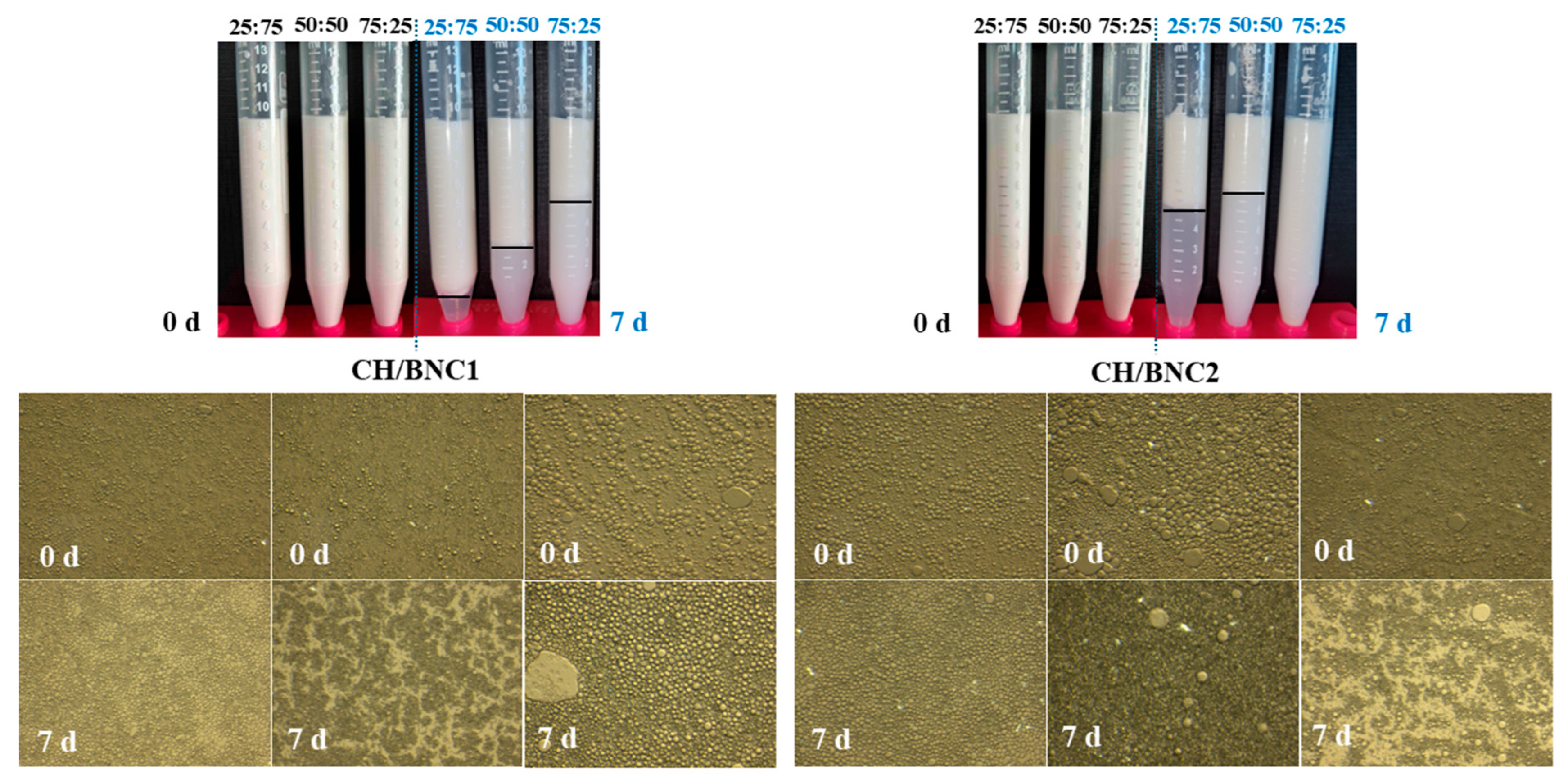
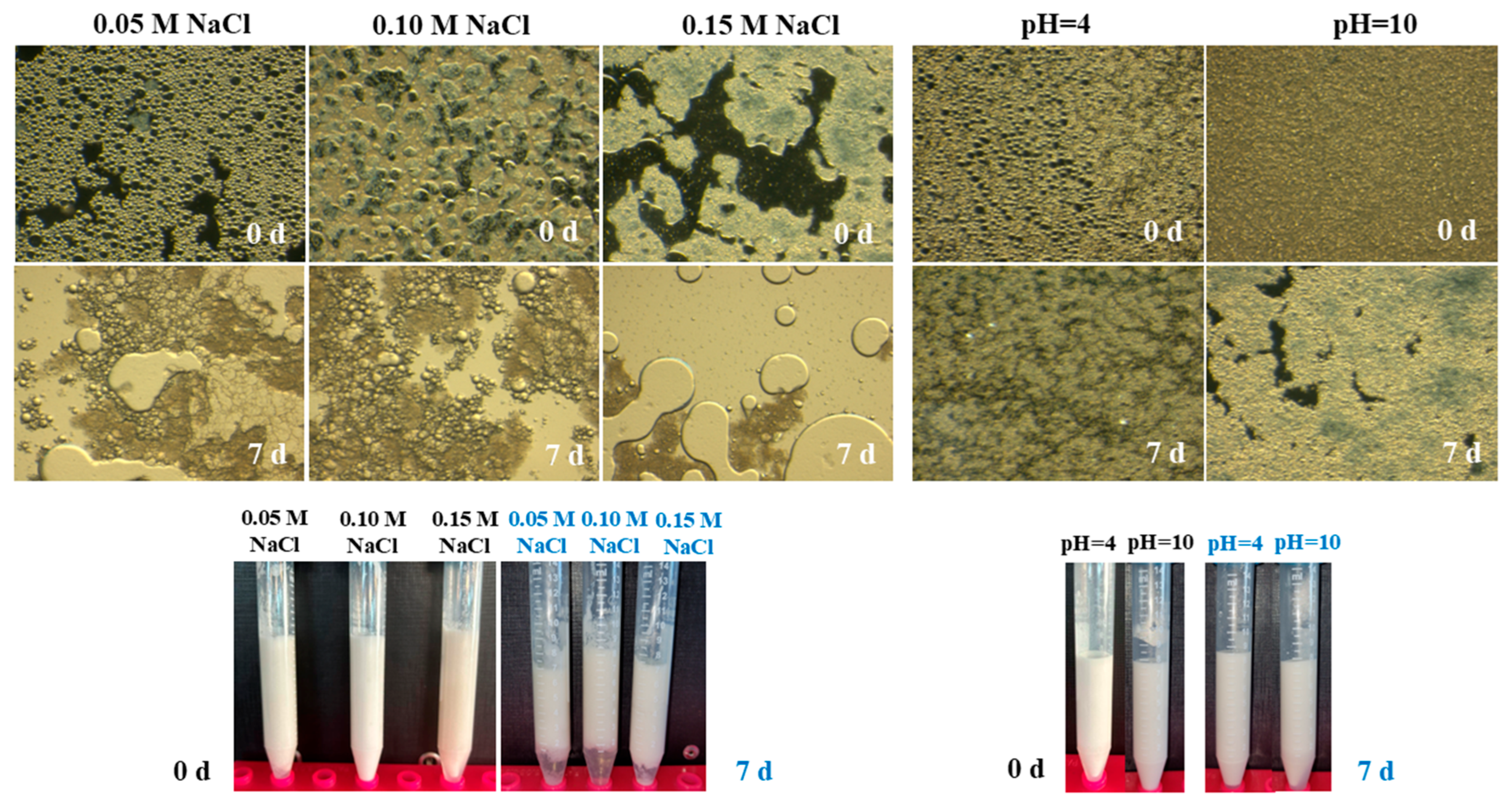
| Compounds | Storage (d) | ζ-Potential (mV) | Rh (nm) | PDI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biopolymers | ||||
| CH | - | 54.1 ± 4.8 | 84 nm/859 nm/6.8 μm | 0.52 |
| BC | - | −16.6 ± 6.5 | 69 nm/584 nm/637 nm | 0.50 |
| BNC1 | - | −34.7 ± 4.1 | 74 nm/471 nm | 0.49 |
| BNC2 | - | −27.5 ± 3.8 | 60 nm/387 nm/3 μm | 0.49 |
| CH/BNC complexes | ||||
| CH/BNC125:75 | - | 5.7 ± 2.3 | 228 nm/7.8 μm | 0.46 |
| CH/BNC150:50 | - | 10.5 ± 3.9 | 1.6 μm/8.5 μm | 0.29 |
| CH/BNC175:25 | - | 22.5 ± 2.9 | 1 μm/8.6 μm | 0.43 |
| CH/BNC225:75 | - | 5.3 ± 1.3 | 1.2 μm/8.1 μm | 0.39 |
| CH/BNC250:50 | - | 11.6 ± 5.2 | 1.9 μm/8.6 μm | 0.36 |
| CH/BNC225:75 | - | 22.1 ± 3.5 | 56 nm/1.41 μm/8 μm | 0.33 |
| Parent o/w emulsions | ||||
| CH | 0 | 4.9 ± 1.3 | 134 nm/7.5 μm | 0.48 |
| 7 | 10.7 ± 2.8 | 211 nm/8.1 μm | 0.47 | |
| BC | 0 | −8.60 ± 3.2 | 147 nm/7.8 μm | 0.42 |
| 7 | −29.1 ± 5.7 | 260 nm/7.6 μm | 0.37 | |
| BNC1 | 0 | −12.4 ± 3.1 | 81 nm/192 nm/8 μm | 0.43 |
| 7 | −27.2 ± 3.9 | 120 nm/1.1 μm/8.1 μm | 0.36 | |
| BNC2 | 0 | −21.8 ± 2.7 | 89 nm/156 nm/8 μm | 0.33 |
| 7 | −27.3 ± 2.5 | 2.3 μm/8.5 μm | 0.34 | |
| Complex o/w Pickering emulsions | ||||
| CH/BNC125:75 | 0 | 5.9 ± 1.3 | 75 nm/8.4 μm | 0.38 |
| 7 | 5.7 ± 1.3 | 228 nm/7.8 μm | 0.46 | |
| CH/BNC150:50 | 0 | 11.7 ± 4.0 | 164 nm/1.4 μm/8.5 μm | 0.30 |
| 7 | 10.5 ± 3.9 | 1.6 μm/8.5 μm | 0.29 | |
| CH/BNC175:25 | 0 | 21.4 ± 3.4 | 1.9 μm/8.3 μm | 0.30 |
| 7 | 22.5 ± 2.9 | 1 μm/8.6 μm | 0.43 | |
| CH/BNC225:75 | 0 | 5.2 ± 3.6 | 1.9 μm/8.3 μm | 0.31 |
| 7 | 5.3 ± 2.3 | 1.2 μm/8.1 μm | 0.39 | |
| CH/BNC250:50 | 0 | −1.3 ± 0.1 | 32 nm/354 nm/1.8 μm | 0.46 |
| 7 | 11.6 ± 4.2 | 1.9 μm/8.6 μm | 0.36 | |
| CH/BNC275:25 | 0 | 13.5 ± 3.6 | 90 nm/1 μm/8.3 μm | 0.52 |
| 7 | 22.1 ± 3.5 | 56 nm/1.4 μm/8 μm | 0.33 | |
| Effect of pH and ionic strength on CH/BNC125:75 based emulsions | ||||
| CH/BNC125:75—pH = 4 | 0 | 5.4 ± 2.3 | 1.4 μm/8.3 μm | 0.43 |
| 7 | 11.6 ± 3.4 | 1.6 μm/19.4 μm | 0.37 | |
| CH/BNC125:75—pH = 10 | 0 | −56.4 ± 6.7 | 116 nm/598 nm | 0.51 |
| 7 | −24.7 ± 3.1 | 140 nm/534 nm | 0.49 | |
| CH/BNC125:75—0.05 M NaCl | 0 | −15.5 ± 5.9 | 497 nm/7.8 μm | 0.32 |
| 7 | −16.1 ± 3.4 | 406 nm | 0.48 | |
| CH/BNC125:75—0.1 M NaCl | 0 | −35.2 ± 8.7 | 357 nm/7.9 μm | 0.32 |
| 7 | −13.4 ± 4.7 | 429 nm/7.5 μm | 0.49 | |
| CH/BNC125:75—0.15 M NaCl | 0 | −30.7 ± 4.1 | 313 nm/7.8 μm | 0.36 |
| 7 | −4.1 ± 2.1 | 348 nm/8.2 μm | 0.41 | |
| o/w emulsions stabilized with CH/BNC125:75 and SFS PI | ||||
| CH/BNC125:75—SFS | 0 | 9.7 ± 3.7 | 90 nm/1.4 μm | 0.49 |
| 7 | 32.8 ± 8.5 | 258 nm | 0.48 | |
| Sample | N | m |
|---|---|---|
| BNC2 | 525 | 0.63 |
| CH/BNC125:75 | 427 | 0.61 |
| CH/BNC150:50 | 295 | 0.45 |
| CH/BNC175:25 | 240 | 0.34 |
| CH/BNC225:75 | 1778 | 0.82 |
| CH/BNC225:75 | 51 | 0.035 |
| Storage (Days) | k | n | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.211 | 0.597 | 0.993 |
| 7 | 0.052 | 0.586 | 0.995 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vardaxi, A.; Apostolidis, E.; Mandala, I.G.; Pispas, S.; Papagiannopoulos, A.; Tsouko, E. Designing Gel-Inspired Food-Grade O/W Pickering Emulsions with Bacterial Nanocellulose–Chitosan Complexes. Gels 2025, 11, 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080577
Vardaxi A, Apostolidis E, Mandala IG, Pispas S, Papagiannopoulos A, Tsouko E. Designing Gel-Inspired Food-Grade O/W Pickering Emulsions with Bacterial Nanocellulose–Chitosan Complexes. Gels. 2025; 11(8):577. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080577
Chicago/Turabian StyleVardaxi, Antiopi, Eftychios Apostolidis, Ioanna G. Mandala, Stergios Pispas, Aristeidis Papagiannopoulos, and Erminta Tsouko. 2025. "Designing Gel-Inspired Food-Grade O/W Pickering Emulsions with Bacterial Nanocellulose–Chitosan Complexes" Gels 11, no. 8: 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080577
APA StyleVardaxi, A., Apostolidis, E., Mandala, I. G., Pispas, S., Papagiannopoulos, A., & Tsouko, E. (2025). Designing Gel-Inspired Food-Grade O/W Pickering Emulsions with Bacterial Nanocellulose–Chitosan Complexes. Gels, 11(8), 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11080577








