Porous and Tough Polyacrylamide/Carboxymethyl Cellulose Gels Chemically Crosslinked via Cryo-UV Polymerization for Sustained Drug Release
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
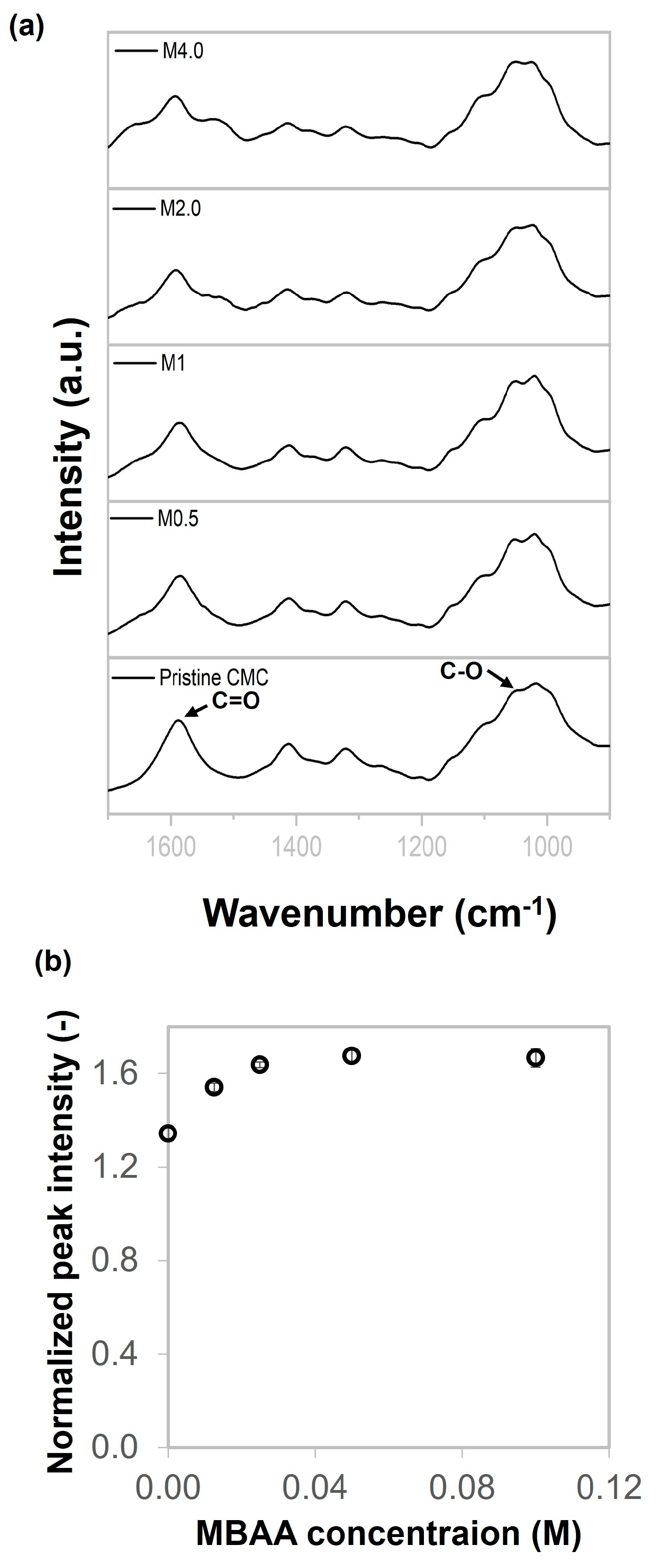
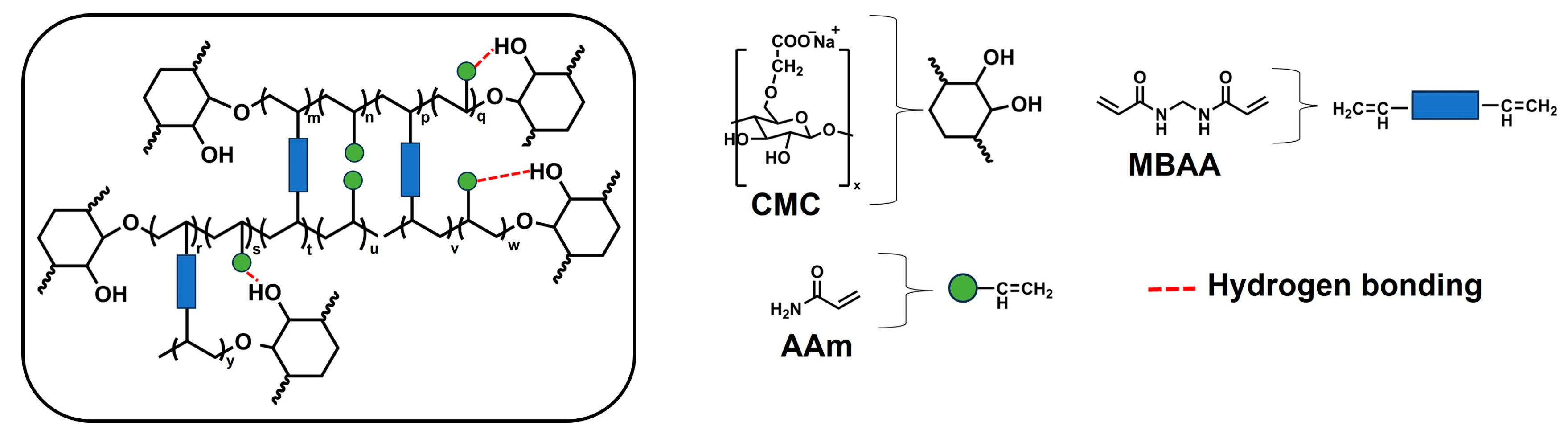
2.1. Chemical Characterizations
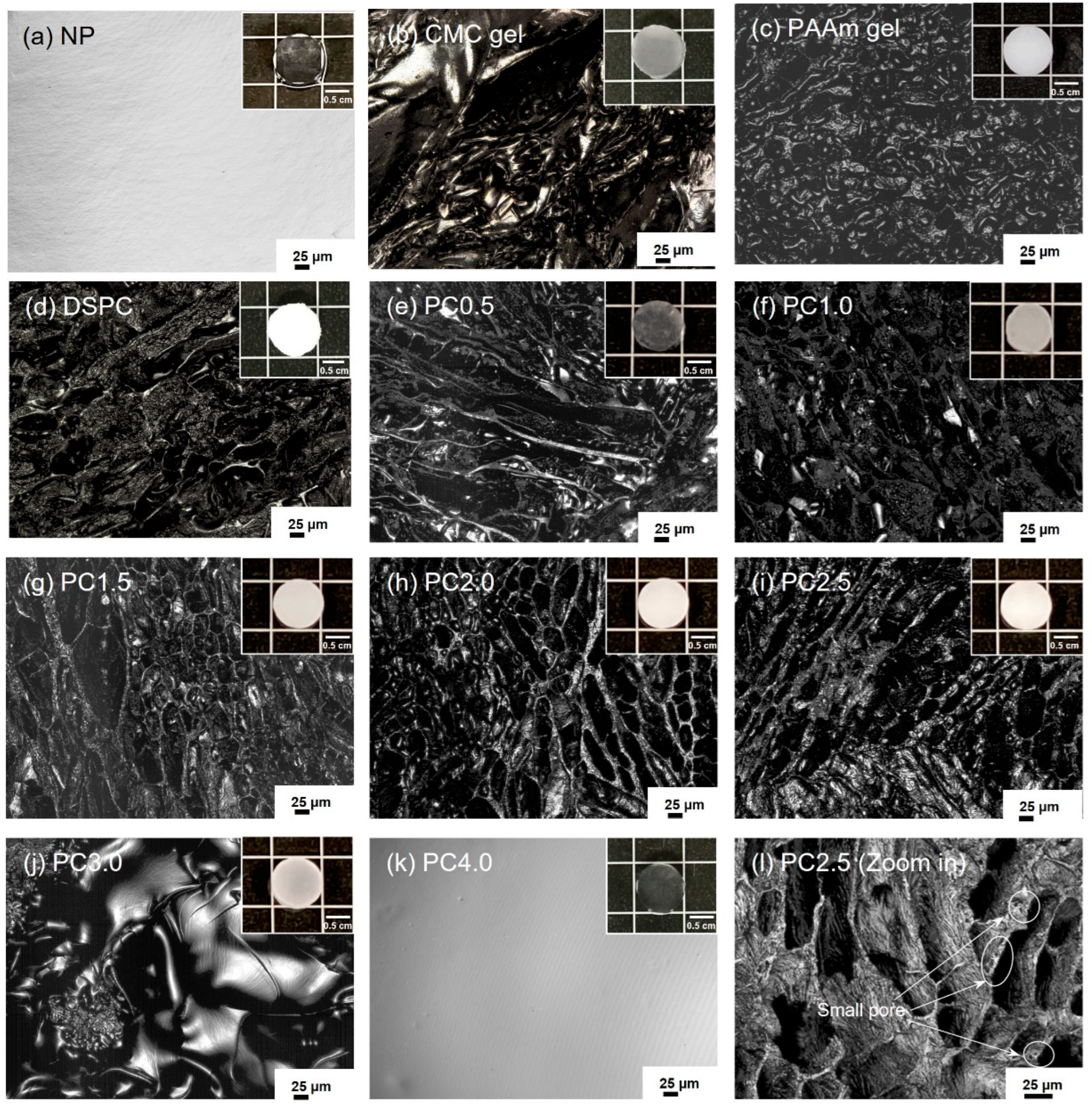
2.2. Morphologies of CMC Gel, NP, PAAm Gel, DSPC, and PC Gels
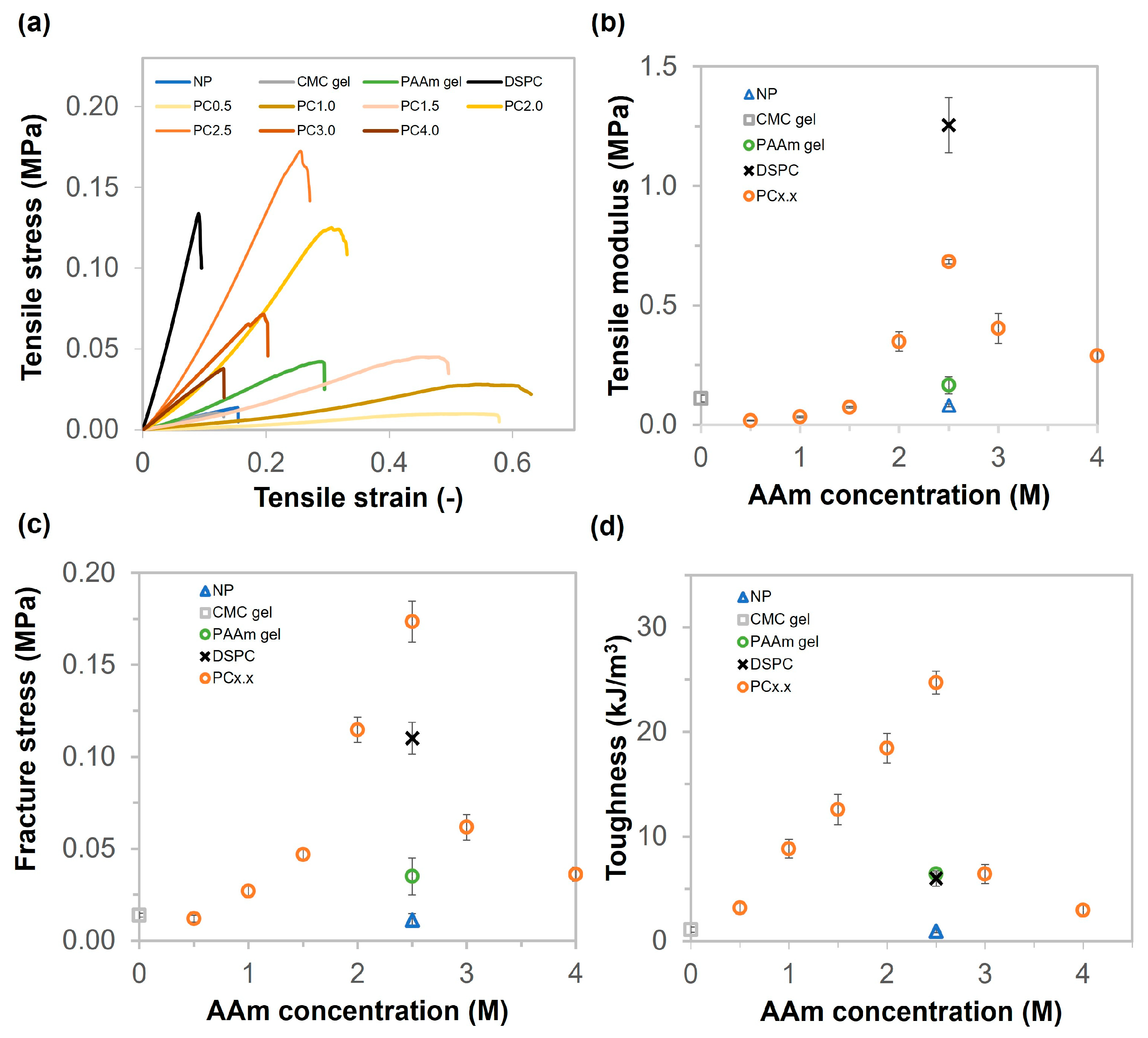
2.3. Mechanical Properties of CMC Gel, PAAm Gel, NP, DSPC, and PC Gels
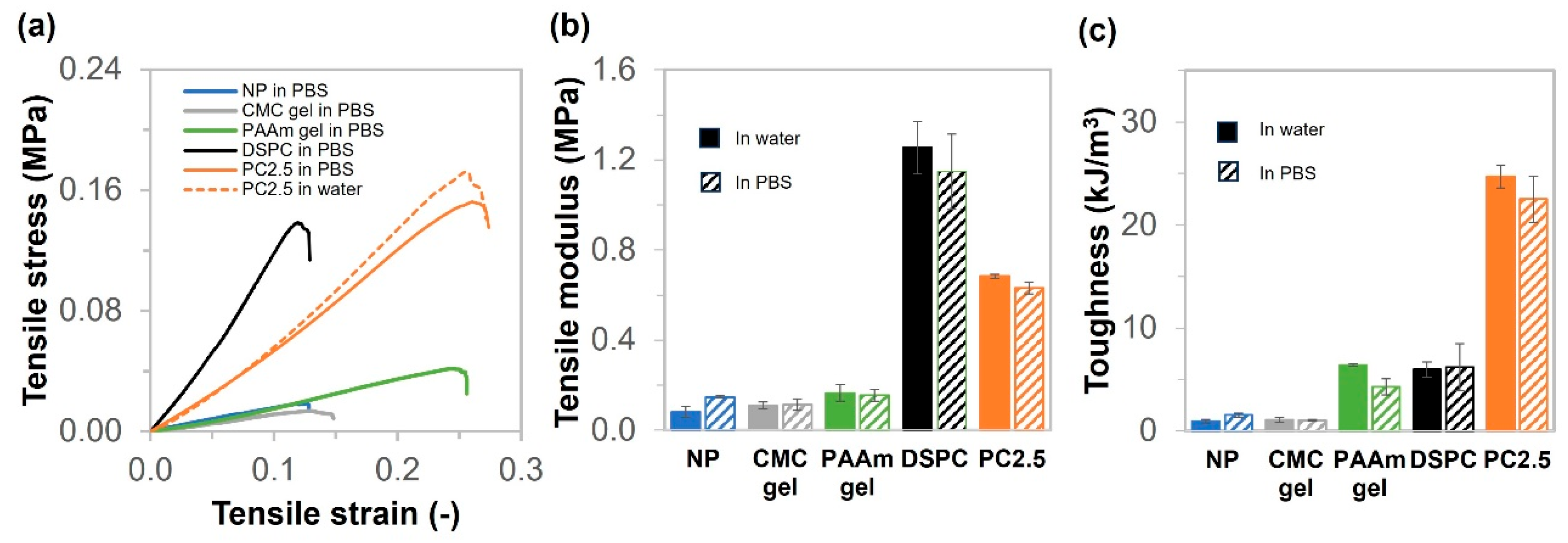
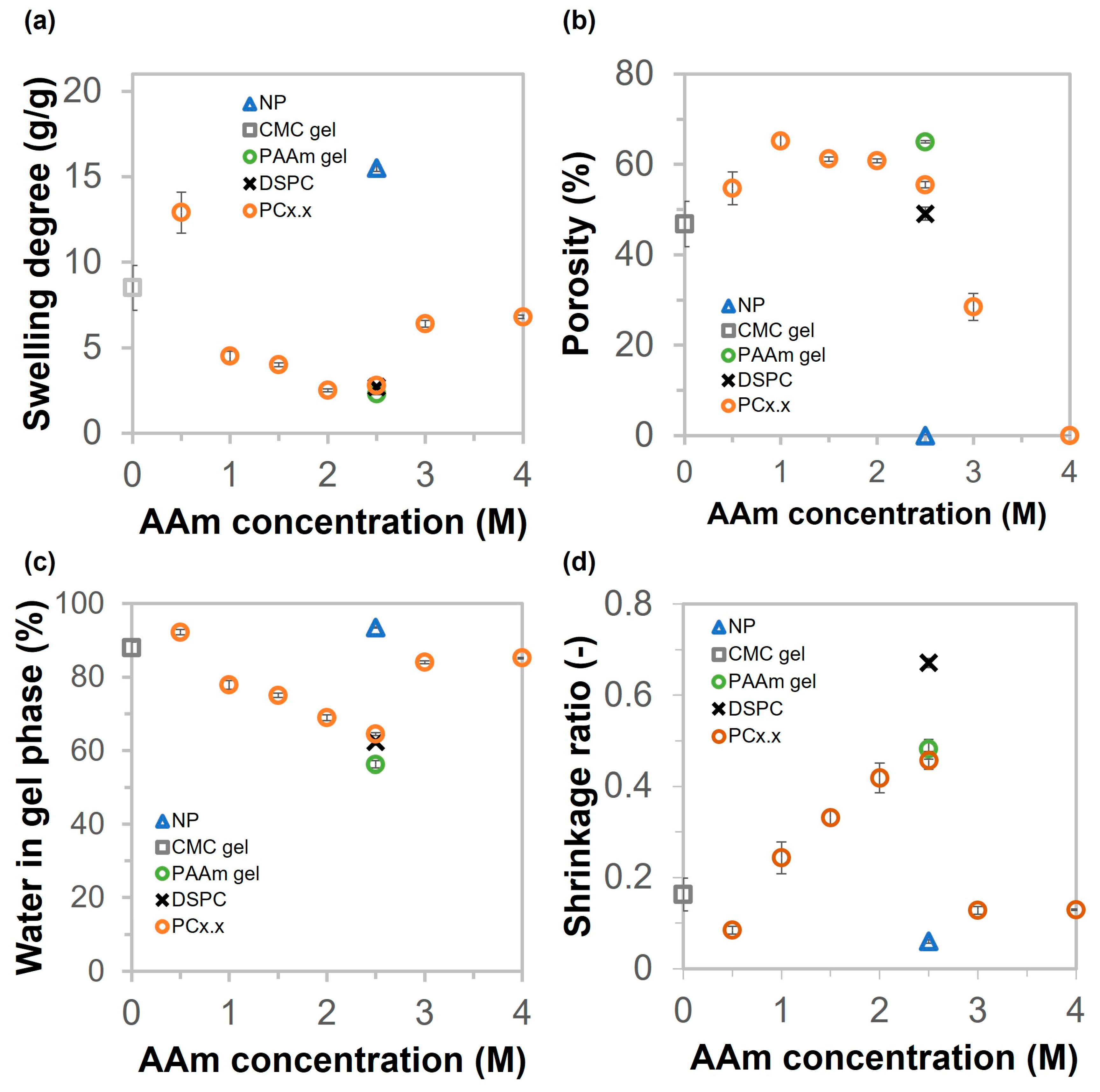
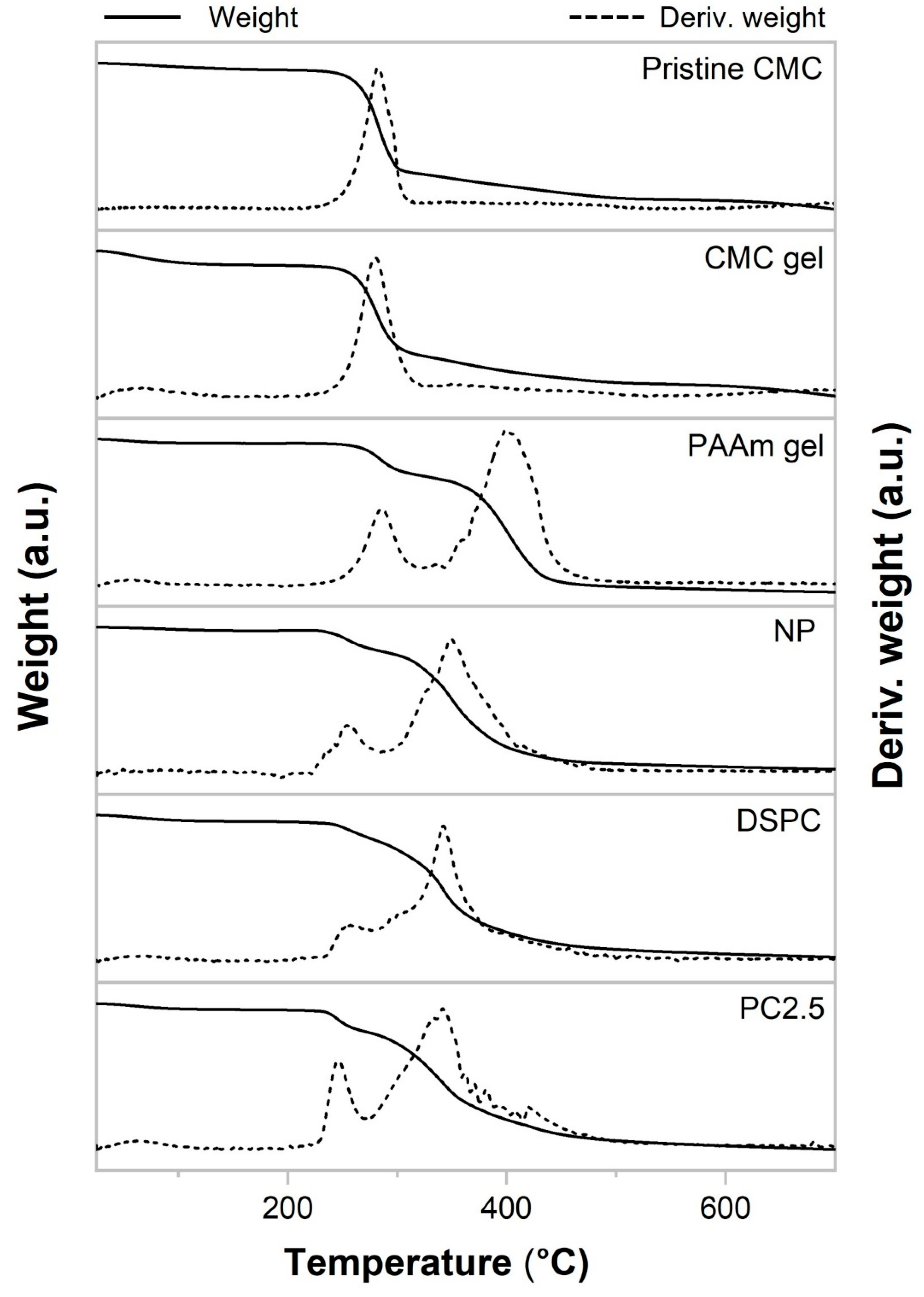
2.4. Physical Properties and Thermal Stability of NP, CMC Gel, PAAm Gel, DSPC, and PC Gels
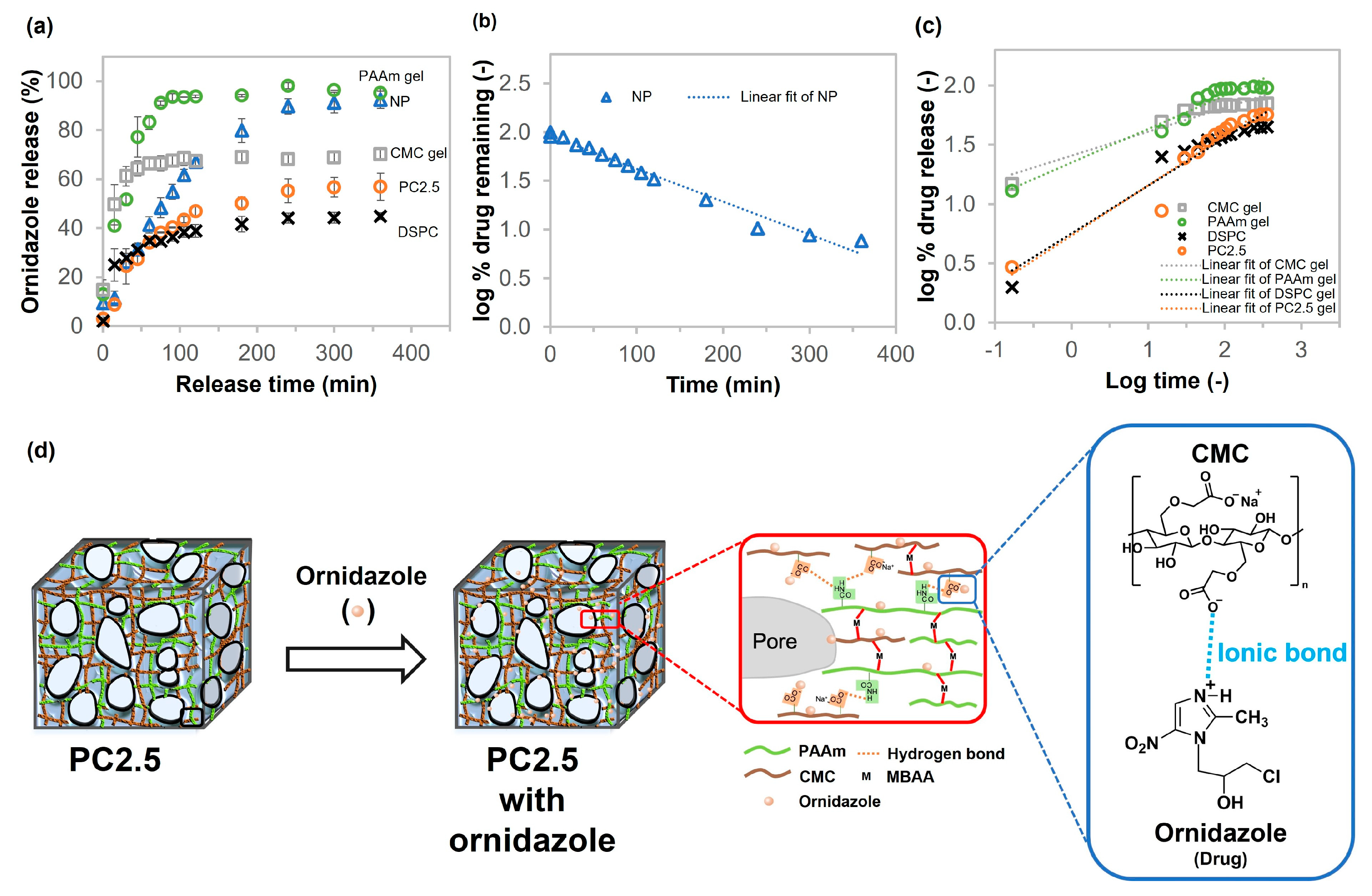
2.5. Drug Release Profiles of CMC Gel, PAAm Gel, NP, DSPC, and PC Gel
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of PAAm/CMC Porous Gels
4.3. Characterization
4.4. Mechanical Tests
4.5. Swelling Behavior, Porosity, and Water in the Gel Phase
4.5.1. Swelling Degree
4.5.2. Porosity
4.5.3. Water Content in the Gel Phase
4.5.4. Drug Release Test
4.6. Cytotoxicity Test
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAm | Acrylamide |
| PAAm | Polyacrylamide |
| CMC | Carboxymethyl cellulose |
| MBAA | N, N’-methylenebisacrylamide |
| α-keto | 2-oxoglutaric acid |
| NP | PAAm/CMC non-cryo gel |
| PC | PAAm/CMC porous gel |
| DSPC | Dual-step synthesis porous gel |
| CMC gel | CMC porous gel |
| PAAm gel | PAAm porous gel |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared |
References
- Kunjalukkal Padmanabhan, S.; Lamanna, L.; Friuli, M.; Sannino, A.; Demitri, C.; Licciulli, A. Carboxymethylcellulose-Based Hydrogel Obtained from Bacterial Cellulose. Molecules 2023, 28, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, H.; Shao, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, H. Multifunctional Carboxymethyl Cellulose Sodium Encapsulated Phosphorus-Enriched Biochar Composites: Multistage Adsorption of Heavy Metals and Controllable Release of Soil Fertilization. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 453, 139809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Xuan, Y.; Zhang, S. Synthesis and Applications of Carboxymethyl Cellulose Hydrogels. Gels 2022, 8, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, K.; Iida, M.; Yano, K.; Nishida, T. Metal Ion Absorption of Carboxymethylcellulose Gel Formed by γ-Ray Irradiation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2004, 38, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanafi, N.M.; Rahman, N.A.; Rosdi, N.H. Citric Acid Cross-Linking of Highly Porous Carboxymethyl Cellulose/Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Composite Hydrogel Films for Controlled Release Applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 7, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Chen, G.; Chen, W.; Huang, J.; Tian, J.; Wan, X.; He, M.; Zhang, H. Multivalent Cations-Triggered Rapid Shape Memory Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose/Polyacrylamide Hydrogels with Tunable Mechanical Strength. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 178, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, Y.; Sohail Khan, M.; Bansal, M.; Kumar Singh, M.; Pragatheesh, K.; Thakur, A. A Review of Carboxymethyl Cellulose Composite-Based Hydrogels in Drug Delivery Applications. Results Chem. 2024, 10, 101695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Bang, S.; Kim, S.; Jo, S.Y.; Kim, B.-C.; Hwang, Y.; Noh, I. Synthesis and In Vitro Characterizations of Porous Carboxymethyl Cellulose-Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Hydrogel Film. Biomater. Res. 2024, 19, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, D.; Kim, C.; Kim, Y.; Jung, S. Dual Crosslinked Carboxymethyl Cellulose/Polyacrylamide Interpenetrating Hydrogels with Highly Enhanced Mechanical Strength and Superabsorbent Properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 127, 109586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinu, M.V.; Ozmen, M.M.; Dragan, E.S.; Okay, O. Freezing as a Path to Build Macroporous Structures: Superfast Responsive Polyacrylamide Hydrogels. Polymer 2007, 48, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Liu, C.; Gong, K.; Li, H.; Song, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, D.; Liu, J.; Guo, J.; Fang, L. Mussel-Inspired Quaternary Composite Hydrogels with High Strength and High Tissue Adhesion for Transdermal Drug Delivery: Synergistic Hydrogen Bonding and Drug Release Mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 465, 142942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Ren, X.; Gao, G.; Duan, L. High Strength, Anti-Freezing and Strain Sensing Carboxymethyl Cellulose-Based Organohydrogel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 223, 115051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemvichian, K.; Chanthawong, A.; Suwanmala, P. Synthesis and Characterization of Superabsorbent Polymer Prepared by Radiation-Induced Graft Copolymerization of Acrylamide onto Carboxymethyl Cellulose for Controlled Release of Agrochemicals. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2014, 103, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godiya, C.B.; Cheng, X.; Li, D.; Chen, Z.; Lu, X. Carboxymethyl Cellulose/Polyacrylamide Composite Hydrogel for Cascaded Treatment/Reuse of Heavy Metal Ions in Wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohy Eldin, M.S.; Omer, A.M.; Soliman, E.A.; Hassan, E.A. Superabsorbent Polyacrylamide Grafted Carboxymethyl Cellulose PH Sensitive Hydrogel: I. Preparation and Characterization. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 3196–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, A.M.; Tamer, T.M.; Hassan, M.E.; Khalifa, R.E.; Abd El-Monaem, E.M.; Eltaweil, A.S.; Mohy Eldin, M.S. Fabrication of Grafted Carboxymethyl Cellulose Superabsorbent Hydrogel for Water Retention and Sustained Release of Ethephon in Sandy Soil. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 48, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriero, V.C.; Di Muzio, L.; Petralito, S.; Casadei, M.A.; Paolicelli, P. Cryogel Scaffolds for Tissue-Engineering: Advances and Challenges for Effective Bone and Cartilage Regeneration. Gels 2023, 9, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wei, X.; You, J.; Feng, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Cryogels with Controllable Physico-Chemical Properties as Advanced Delivery Systems for Biomedical Applications. Mater. Today Bio 2025, 32, 101815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, P.D.; Tsvetanov, C.B. Cryogels via UV Irradiation. In Polymeric Cryogels; Okay, O., Ed.; Advances in Polymer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 199–222. [Google Scholar]
- Okay, O. Cryogelation Reactions and Cryogels: Principles and Challenges. Turk. J. Chem. 2023, 47, 910–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozinsky, V.I. A Brief History of Polymeric Cryogels. In Polymeric Cryogels; Okay, O., Ed.; Advances in Polymer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Petrov, P.; Petrova, E.; Stamenova, R.; Tsvetanov, C.B.; Riess, G. Cryogels of Cellulose Derivatives Prepared via UV Irradiation of Moderately Frozen Systems. Polymer 2006, 47, 6481–6484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, P.; Petrova, E.; Tchorbanov, B.; Tsvetanov, C.B. Synthesis of Biodegradable Hydroxyethylcellulose Cryogels by UV Irradiation. Polymer 2007, 48, 4943–4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, T.; Borsa, J.; Takács, E.; Wojnárovits, L. Synthesis of Cellulose-Based Superabsorbent Hydrogels by High-Energy Irradiation in the Presence of Crosslinking Agent. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2016, 118, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.-Y.; Dai, Z.; Di, B.; Xu, L.-L. Advances in Cryochemistry: Mechanisms, Reactions and Applications. Molecules 2021, 26, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wach, R.A.; Rokita, B.; Bartoszek, N.; Katsumura, Y.; Ulanski, P.; Rosiak, J.M. Hydroxyl Radical-Induced Crosslinking and Radiation-Initiated Hydrogel Formation in Dilute Aqueous Solutions of Carboxymethylcellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 112, 412–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, B.; Wach, R.A.; Mitomo, H.; Yoshii, F.; Kume, T. Hydrogel of Biodegradable Cellulose Derivatives. I. Radiation-Induced Crosslinking of CMC. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 78, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, M.; Abdel-Latif, D.A.; Ji, H.F. Synthesis and Application of Photo-Active Carboxymethyl Cellulose Derivatives. React. Funct. Polym. 2016, 102, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McOscar, T.V.C.; Gramlich, W.M. Hydrogels from Norbornene-Functionalized Carboxymethyl Cellulose Using a UV-Initiated Thiol-Ene Click Reaction. Cellulose 2018, 25, 6531–6545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melilli, G.; Carmagnola, I.; Tonda-Turo, C.; Pirri, F.; Ciardelli, G.; Sangermano, M.; Hakkarainen, M.; Chiappone, A. DLP 3D Printing Meets Lignocellulosic Biopolymers: Carboxymethyl Cellulose Inks for 3D Biocompatible Hydrogels. Polymers 2020, 12, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Meng, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhong, S.; Gao, Y.; He, W.; Cui, X. Photocrosslinked Carboxymethylcellulose-Based Hydrogels: Synthesis, Characterization for Curcumin Delivery and Wound Healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 275, 133558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wan, J.; Deng, J.; Qin, W.; Zhao, N.; Luo, X.; He, M.; Chen, X. Preparation of Acrylamide and Carboxymethyl Cellulose Graft Copolymers and the Effect of Molecular Weight on the Flocculation Properties in Simulated Dyeing Wastewater under Different PH Conditions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 1142–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Li, G.; He, Y.-G.; Ren, F.-X.; Wang, G. Synthesis, Characterization, and Applied Properties of Carboxymethyl Cellulose and Polyacrylamide Graft Copolymer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 78, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, K.M.; Zakaria, S.; Sajab, M.S.; Gan, S.; Kaco, H. Superabsorbent Hydrogel from Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunch Cellulose and Sodium Carboxymethylcellulose. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foudazi, R.; Zowada, R.; Manas-Zloczower, I.; Feke, D.L. Porous Hydrogels: Present Challenges and Future Opportunities. Langmuir 2023, 39, 2092–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, K.; Shen, S.; Yun, J.; Wang, L.; He, X.; Yu, X. Preparation of Polyacrylamide-Based Supermacroporous Monolithic Cryogel Beds under Freezing-Temperature Variation Conditions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 6701–6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlačík, T.; Nonoyama, T.; Guo, H.; Kiyama, R.; Nakajima, T.; Takeda, Y.; Kurokawa, T.; Gong, J.P. Preparation of Tough Double- and Triple-Network Supermacroporous Hydrogels through Repeated Cryogelation. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 8576–8586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zheng, H.; Poh, P.; Machens, H.-G.; Schilling, A. Hydrogels for Engineering of Perfusable Vascular Networks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 15997–16016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okay, O.; Lozinsky, V.I. Synthesis and Structure–Property Relationships of Cryogels. In Polymeric Cryogels; Okay, O., Ed.; Advances in Polymer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 103–157. [Google Scholar]
- Isobe, N.; Kimura, S.; Wada, M.; Deguchi, S. Poroelasticity of Cellulose Hydrogel. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 92, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettignano, A.; Charlot, A.; Fleury, E. Solvent-Free Synthesis of Amidated Carboxymethyl Cellulose Derivatives: Effect on the Thermal Properties. Polymers 2019, 11, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyke, J.D.; Kasperski, K.L. Thermogravimetric Study of Polyacrylamide with Evolved Gas Analysis. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1993, 31, 1807–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusty, K.; Swain, S.K. Nano Silver Decorated Polyacrylamide/Dextran Nanohydrogels Hybrid Composites for Drug Delivery Applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 85, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Das, D.; Ghosh, P.; Ghosh, A.; Dhara, S.; Panda, A.B.; Pal, S. Novel PH-Responsive Graft Copolymer Based on HPMC and Poly(Acrylamide) Synthesised by Microwave Irradiation: Application in Controlled Release of Ornidazole. Cellulose 2015, 22, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeuba, A.I.; Faithpraise, F.O.; Nwokolo, K.I.; Umo, F.E.; Echem, O.C.; Ibrahim, A.T.; Edet, H.O.; Ita, B.I.; Okafor, P.C.; Asogwa, F.C.; et al. A Combined Electrochemical and DFT Investigation of Ornidazole as a Benign Anti-Corrosion Agent for Carbon Steel Materials in Acidizing Environments. Results Mater. 2024, 21, 100542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafezi Moghaddam, R.; Dadfarnia, S.; Shabani, A.M.H.; Moghaddam, Z.H.; Tavakol, M. Electron Beam Irradiation Synthesis of Porous and Non-Porous Pectin Based Hydrogels for a Tetracycline Drug Delivery System. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 102, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viboonratanasri, D.; Thongdee, P.; Prajuabsuk, M.; Pungpo, P.; Vayachuta, L.; Prompinit, P. Precisely Controlled Delivery of Plant Hormone Using Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Zeolite A Hydrofilm Composite. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2021, 61, 2172–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsmeyer, R.W.; Gurny, R.; Doelker, E.; Buri, P.; Peppas, N.A. Mechanisms of Solute Release from Porous Hydrophilic Polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 1983, 15, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Okeil, A.; Taha, G.M. Investigation and Kinetics of Hydrogel Scaffold with Sustained Release Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 17393–17411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mito, K.; Haque, M.A.; Nakajima, T.; Uchiumi, M.; Kurokawa, T.; Nonoyama, T.; Gong, J.P. Supramolecular Hydrogels with Multi-Cylindrical Lamellar Bilayers: Swelling-Induced Contraction and Anisotropic Molecular Diffusion. Polymer 2017, 128, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Energy Type and Source | CMC Concentration (W/V) % | Requirement | Solvent | Yield * (%) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ionizing radiation | 0.5 |
|
| 70 | [26] |
| Gamma ray | 30 |
|
| 82 | [27] |
| Gamma ray | 15 |
|
| ~60 | [24] |
| UV lamp | 5 |
|
| 75 | [28] |
| UV lamp (10 mW/cm2) | 1 |
|
| No data | [29] |
| Light-emitting diode light (30 mW/cm2) A medium-pressure mercury lamp with UV lamp (12 mW/cm2) (post-curing) | 2 |
|
| 87 | [30] |
| UV lamp | 1 |
|
| ~95 | [31] |
| UV lamp (1.0 mW/cm2) | 6 |
|
| ~99 | This work |
| Sample Name | Kinetic Model | Remark | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero Order | First Order | Higuchi | Korsmeyer–Peppas | ||
| R2 | R2 | R2 | R2 | n | |
| NP | 0.8399 | 0.9763 | 0.9623 | 0.8018 | 0.34 |
| CMC gel | 0.2949 | 0.3621 | 0.5817 | 0.9003 | 0.20 |
| PAAm gel | 0.4379 | 0.6478 | 0.7316 | 0.9379 | 0.28 |
| DSPC | 0.5302 | 0.6090 | 0.8094 | 0.9318 | 0.40 |
| PC2.5 | 0.7168 | 0.8093 | 0.9266 | 0.9369 | 0.42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Viboonratanasri, D.; King, D.R.; Okumura, T.; Terkawi, M.A.; Katsuyama, Y.; Lama, M.; Yasui, T.; Kurokawa, T. Porous and Tough Polyacrylamide/Carboxymethyl Cellulose Gels Chemically Crosslinked via Cryo-UV Polymerization for Sustained Drug Release. Gels 2025, 11, 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060453
Viboonratanasri D, King DR, Okumura T, Terkawi MA, Katsuyama Y, Lama M, Yasui T, Kurokawa T. Porous and Tough Polyacrylamide/Carboxymethyl Cellulose Gels Chemically Crosslinked via Cryo-UV Polymerization for Sustained Drug Release. Gels. 2025; 11(6):453. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060453
Chicago/Turabian StyleViboonratanasri, Duangkamon, Daniel Rudolf King, Tsuyoshi Okumura, Mohamad Alaa Terkawi, Yoshinori Katsuyama, Milena Lama, Tomoki Yasui, and Takayuki Kurokawa. 2025. "Porous and Tough Polyacrylamide/Carboxymethyl Cellulose Gels Chemically Crosslinked via Cryo-UV Polymerization for Sustained Drug Release" Gels 11, no. 6: 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060453
APA StyleViboonratanasri, D., King, D. R., Okumura, T., Terkawi, M. A., Katsuyama, Y., Lama, M., Yasui, T., & Kurokawa, T. (2025). Porous and Tough Polyacrylamide/Carboxymethyl Cellulose Gels Chemically Crosslinked via Cryo-UV Polymerization for Sustained Drug Release. Gels, 11(6), 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060453







