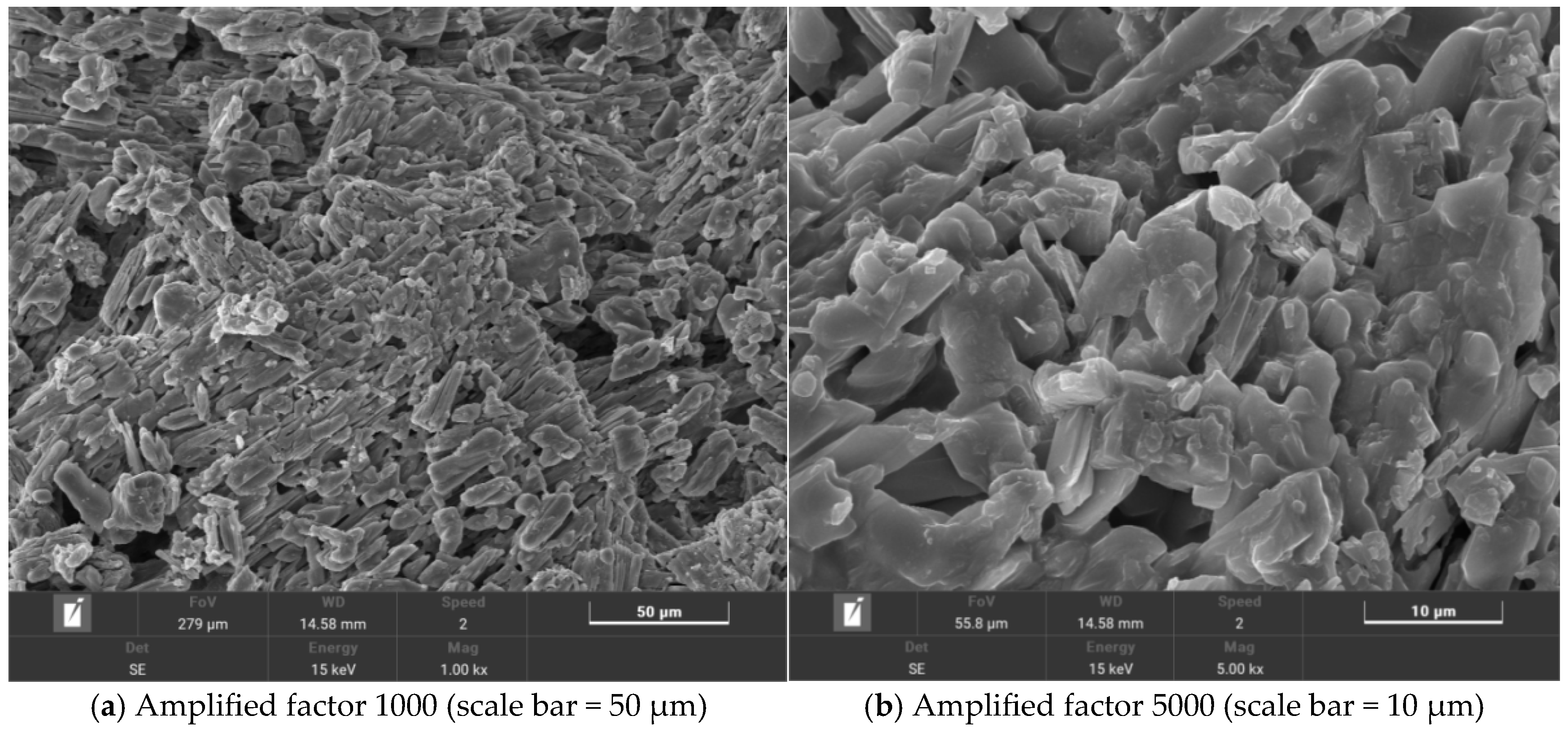
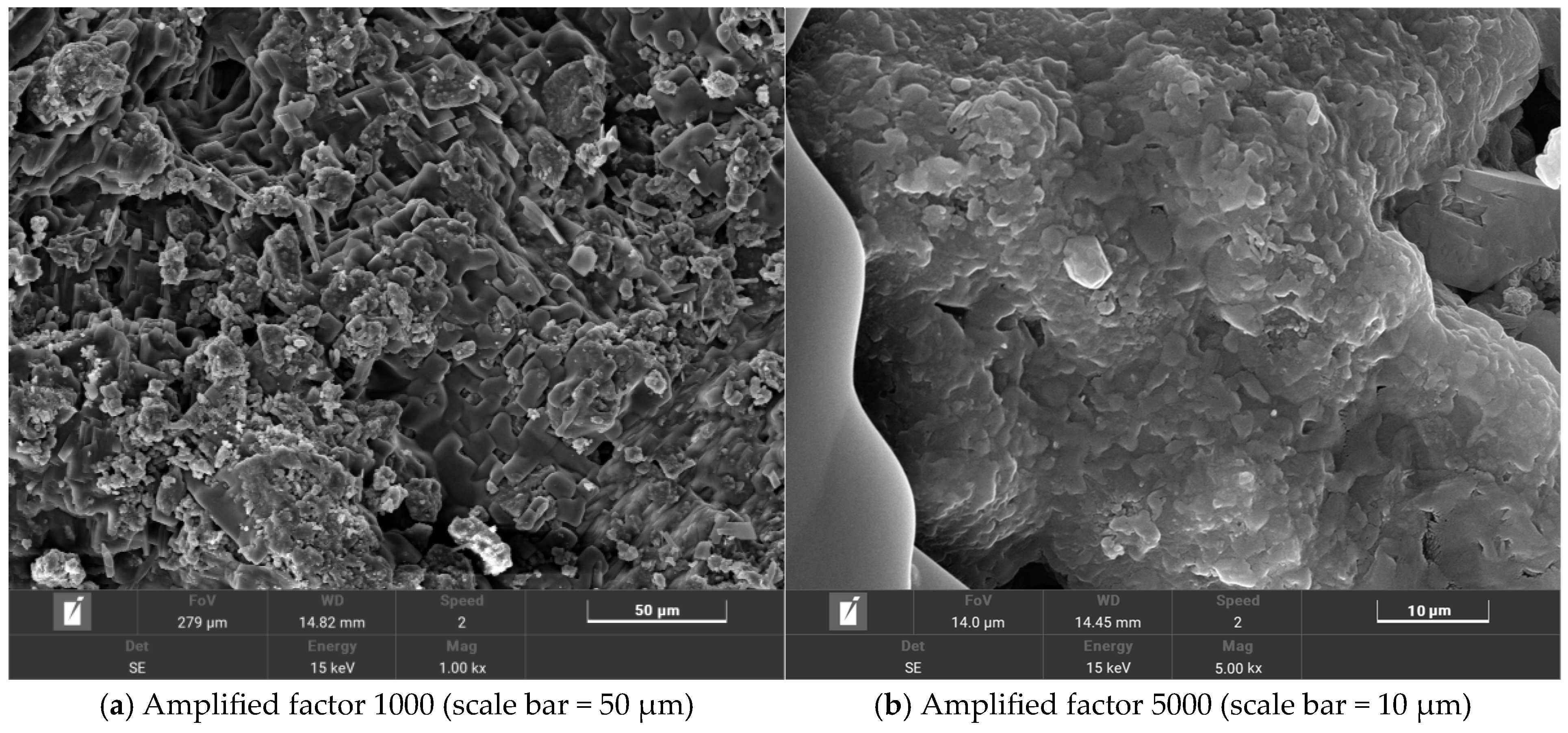
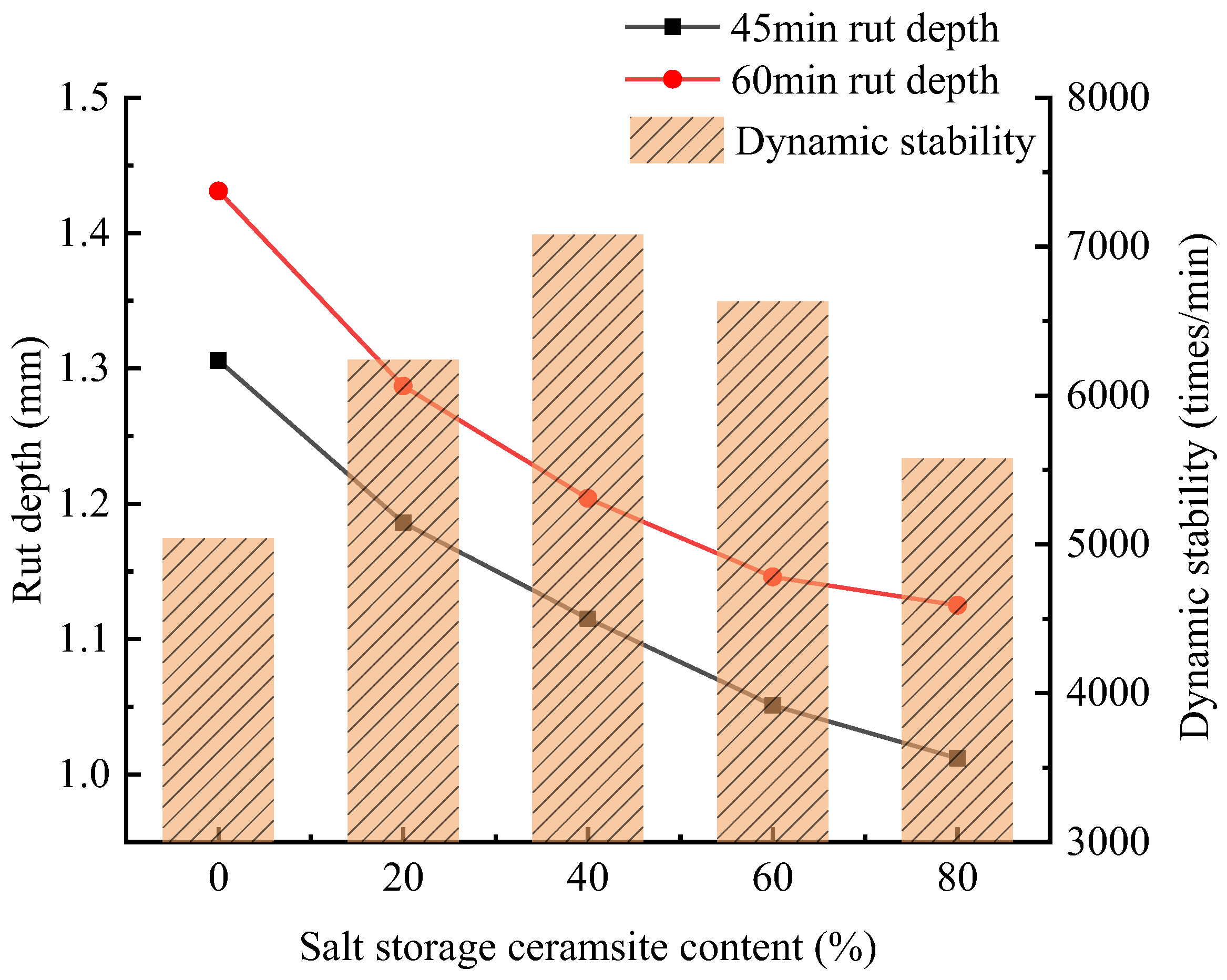
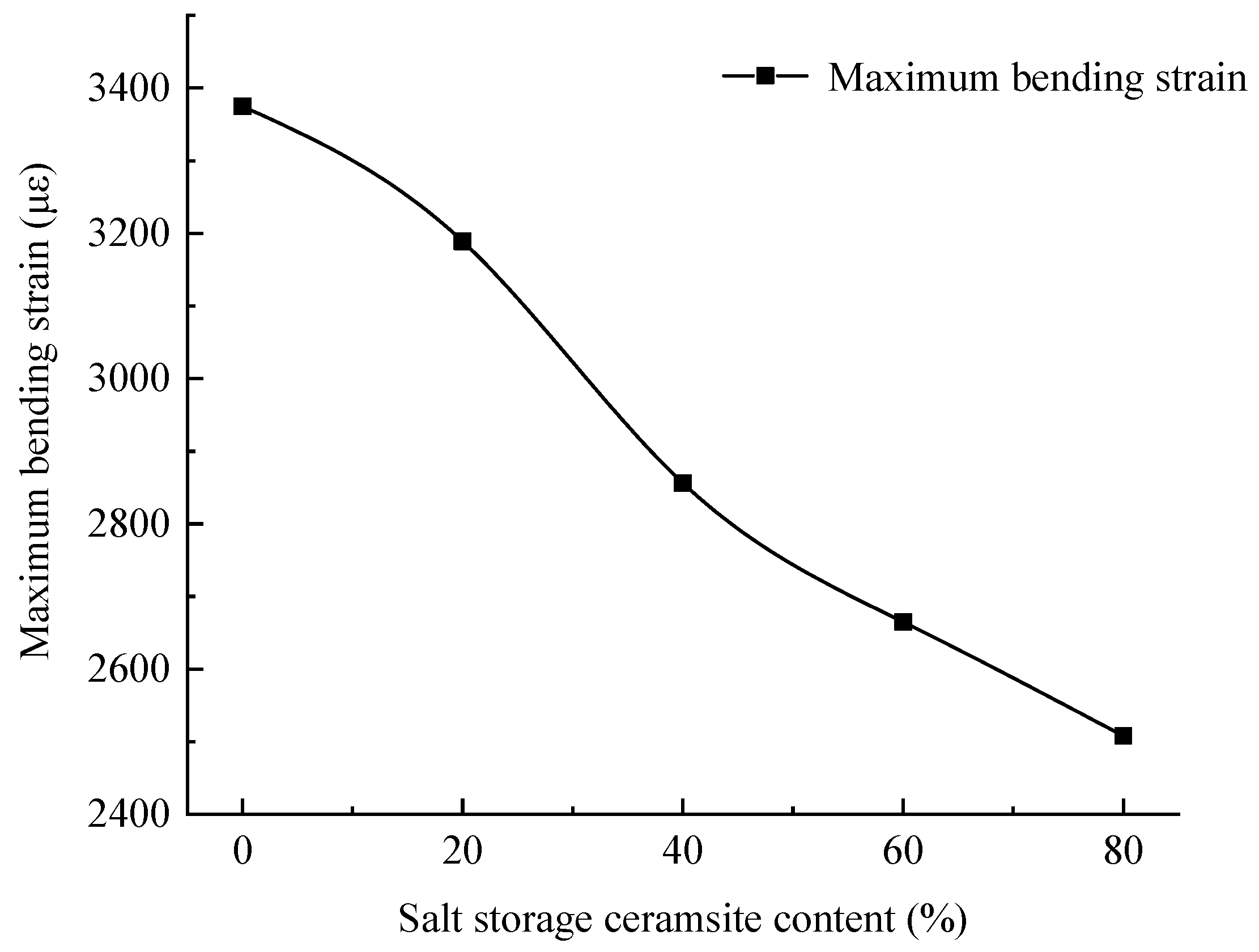
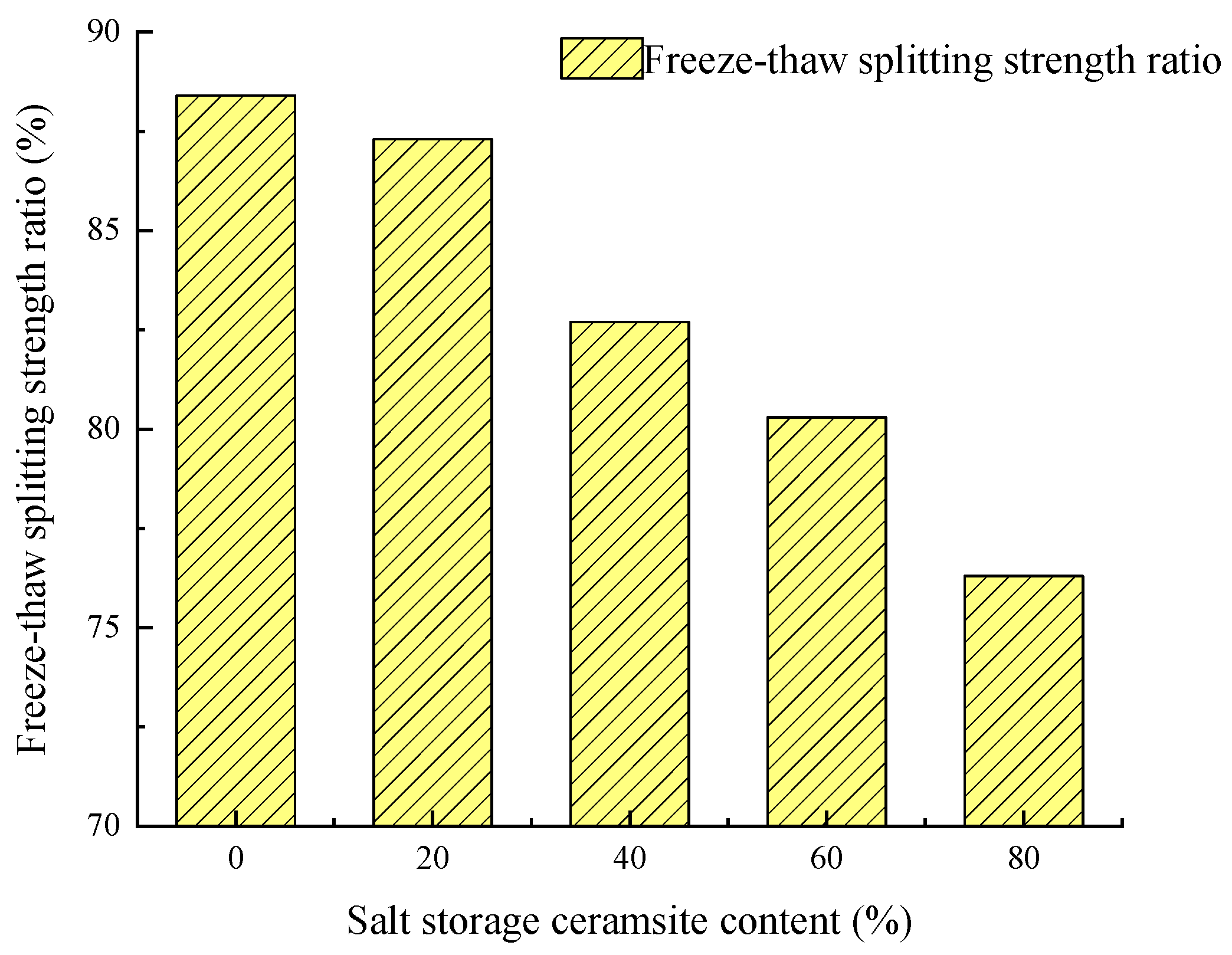
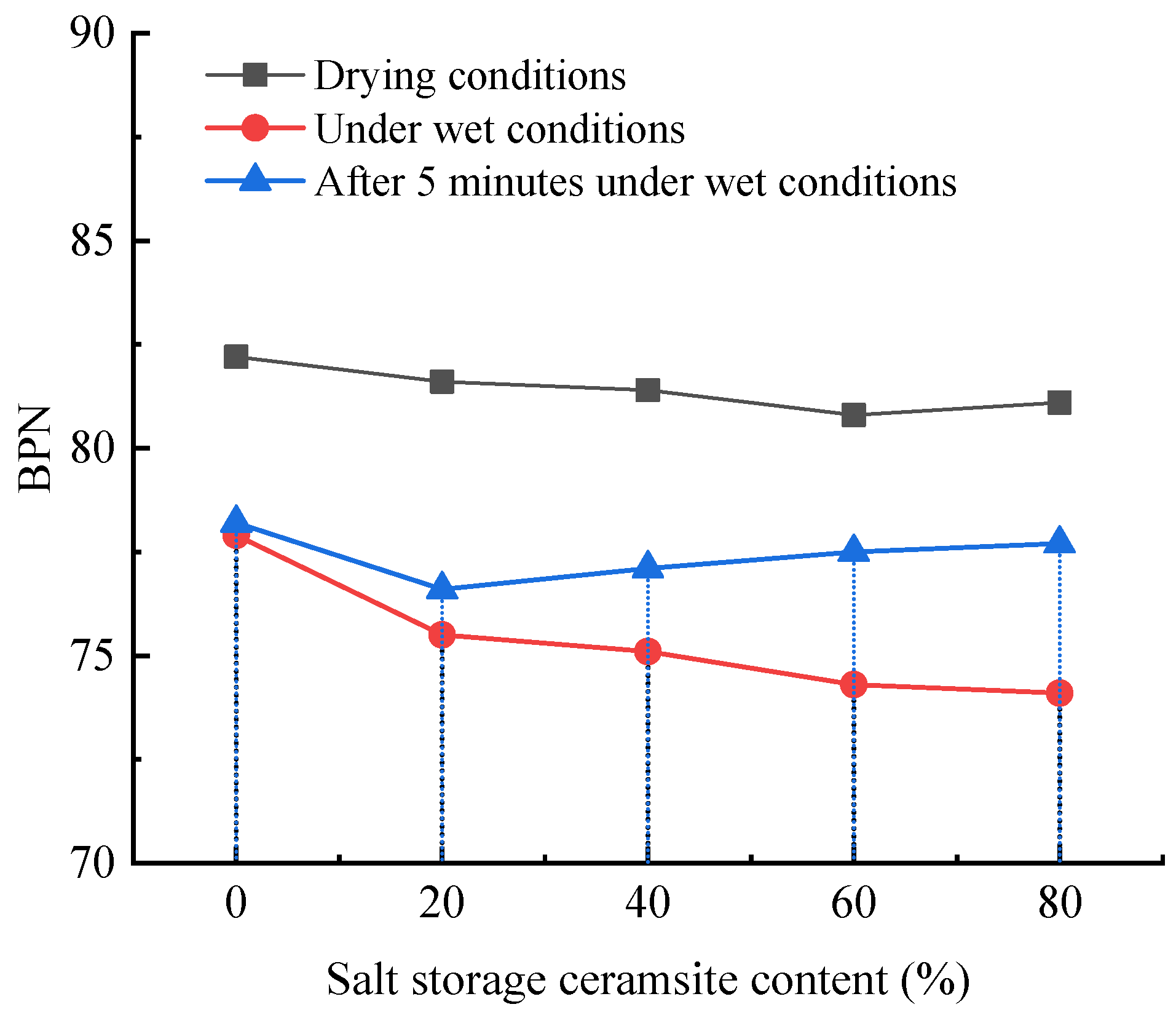
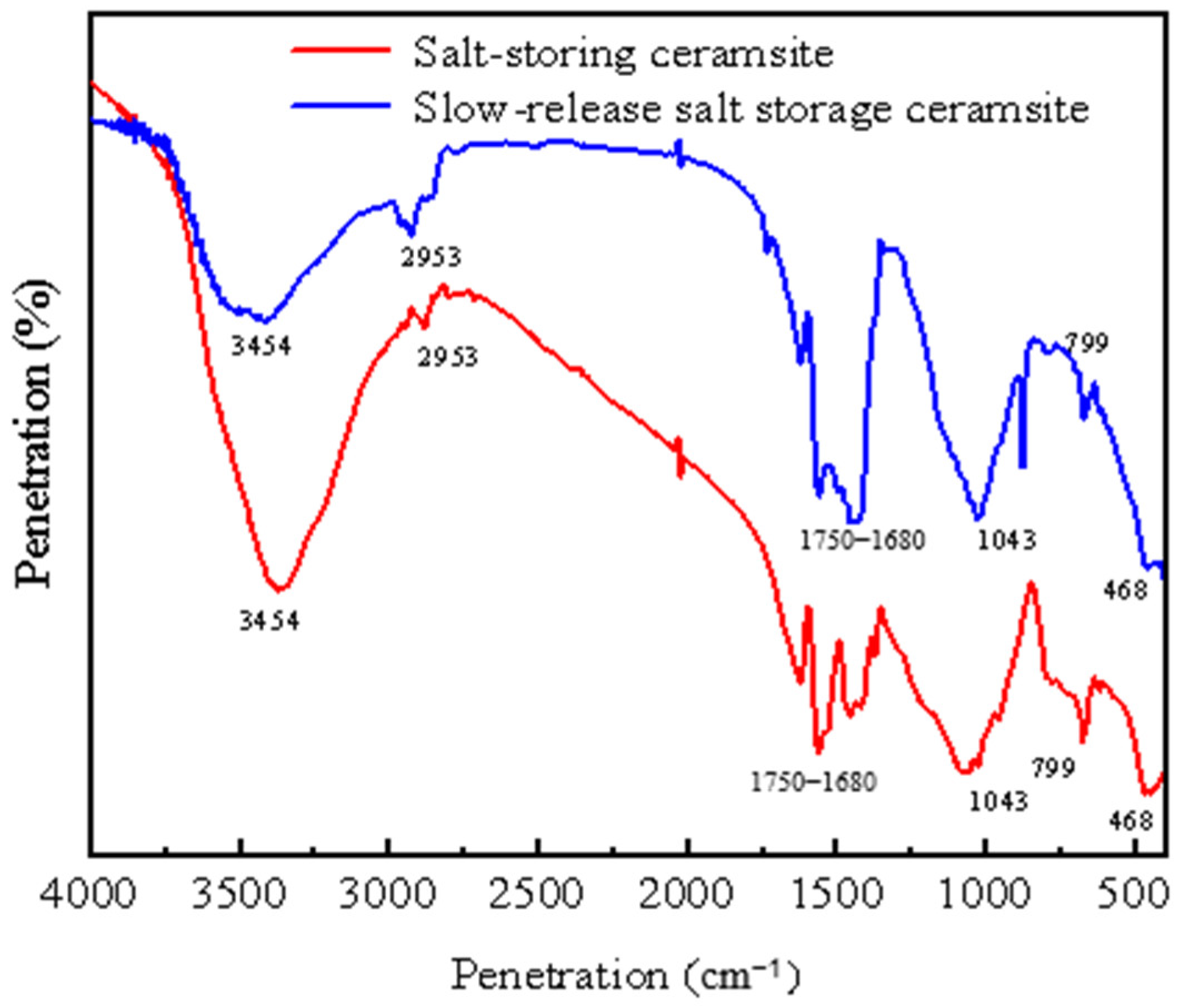
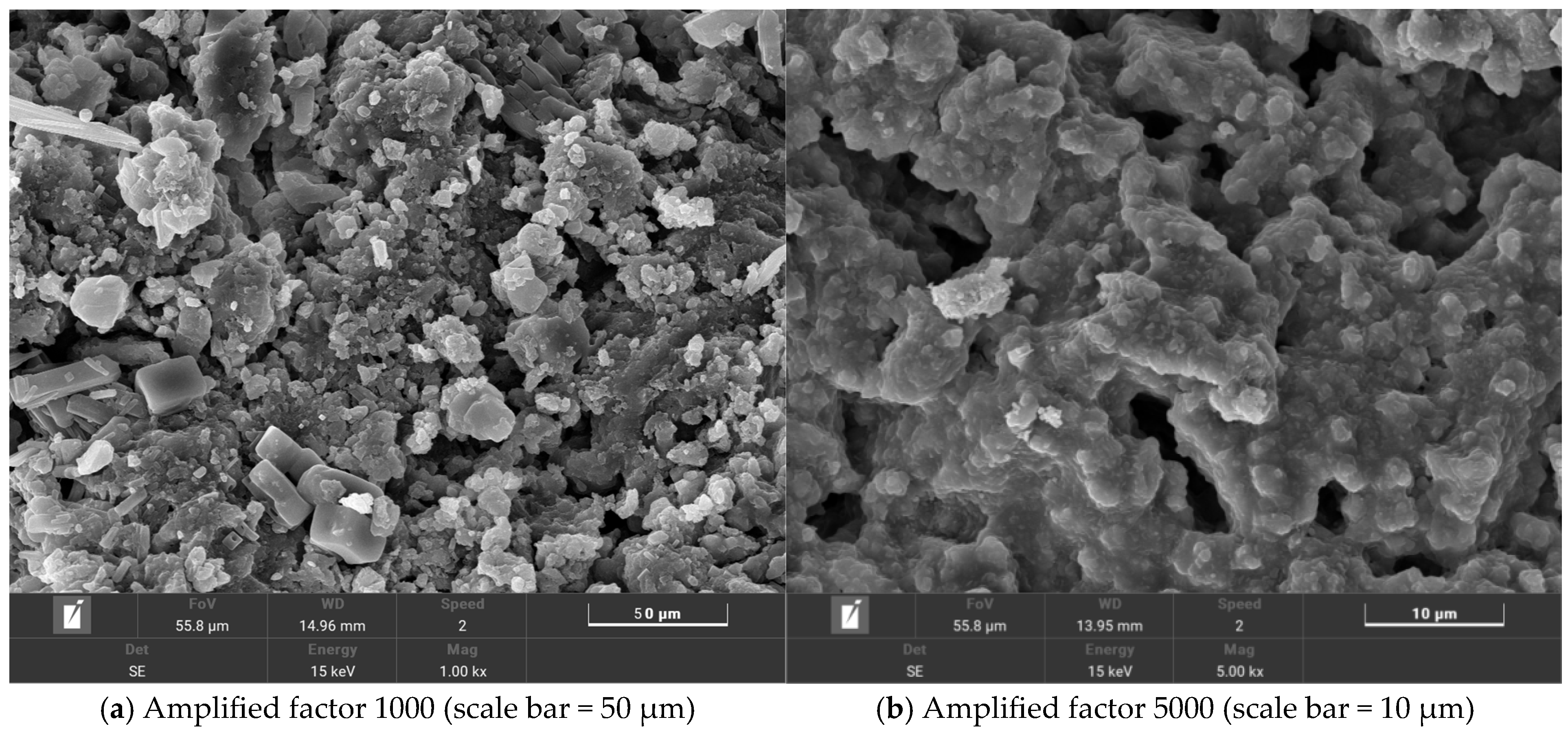
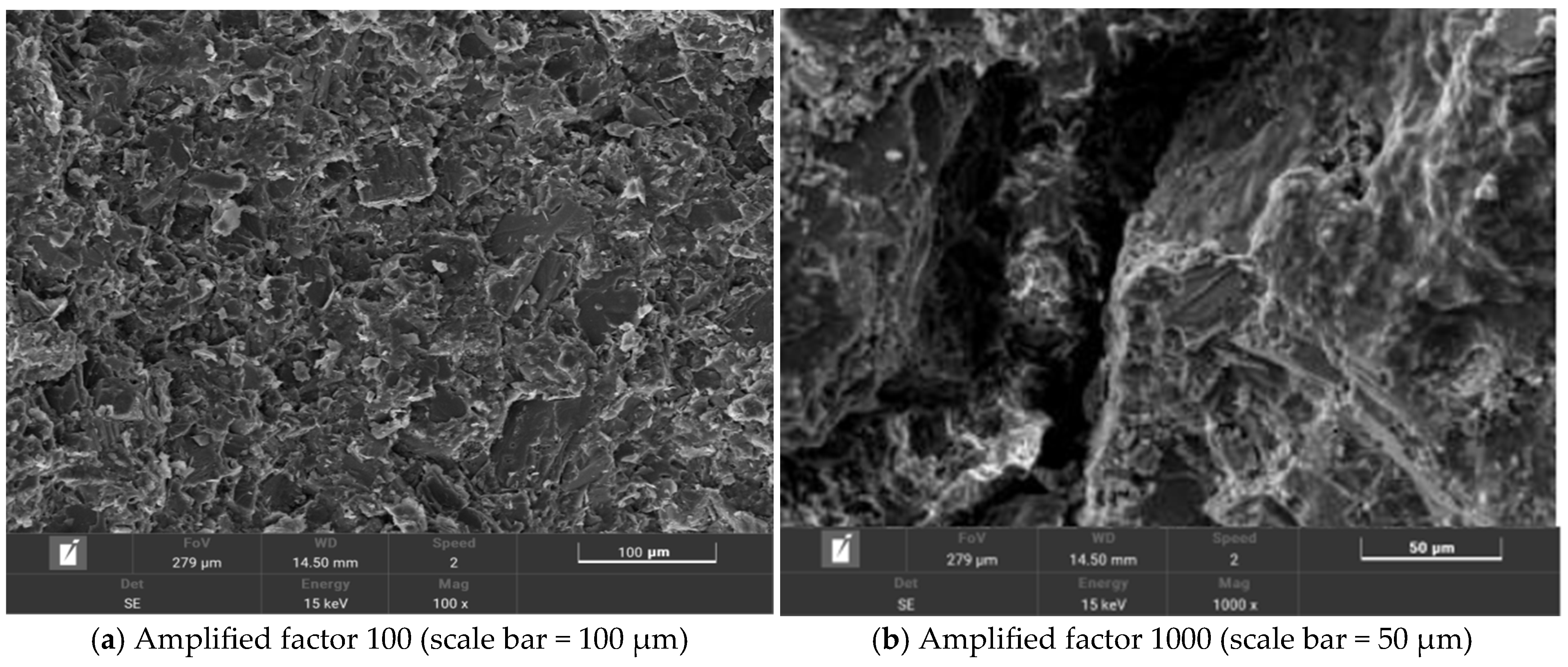
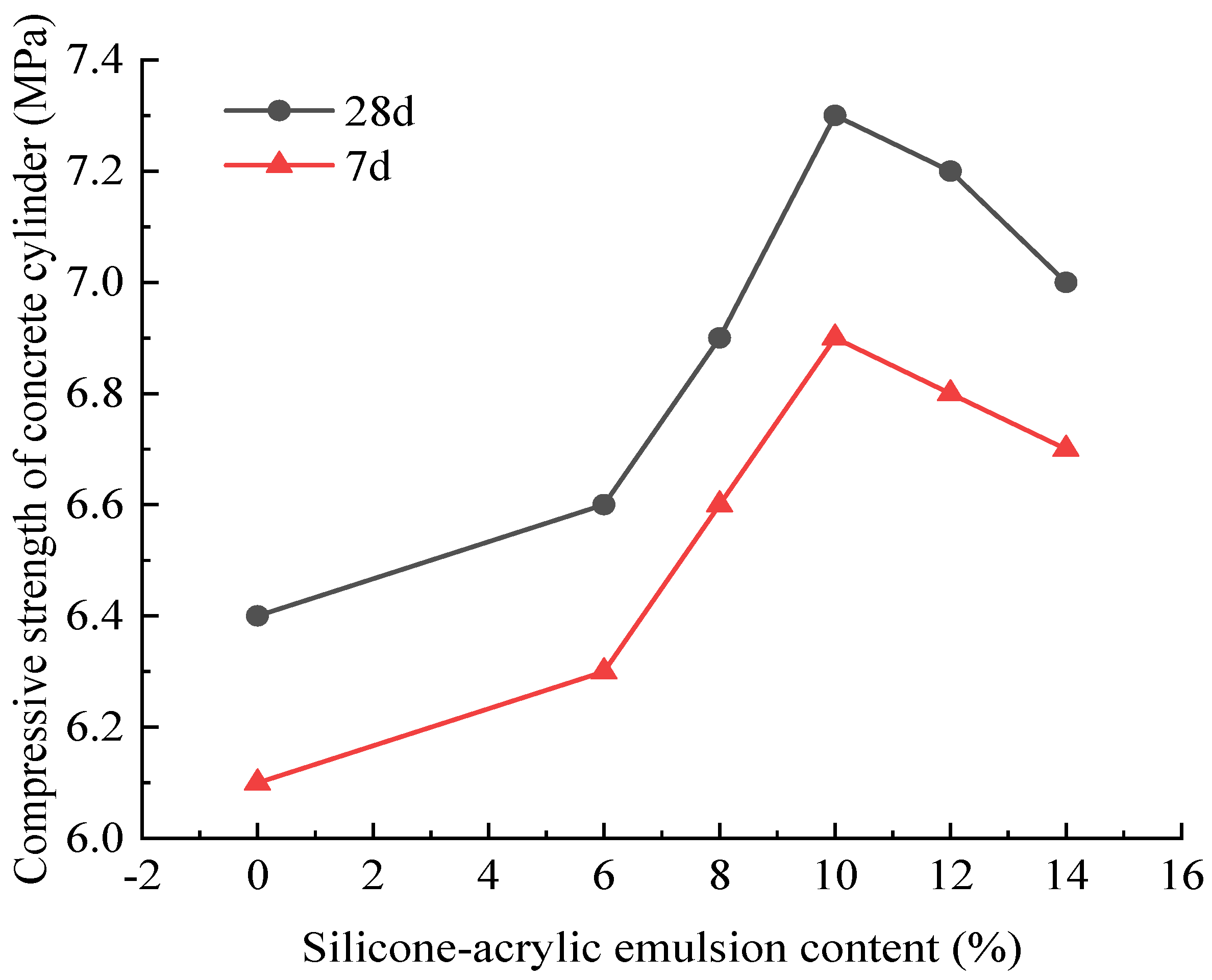
With an increasing amount of road traffic, road surfacees will exhibit the phenomenon of tectonic depth attenuation and flatness reduction [
1]. At present, the treatment methods of China’s highway maintenance include washing and planing the original road surface to lay a new asphalt surface layer, micro-surface or thin slurry sealing layer, and paving anti-skid wear layer [
2]. When an anti-skid wear layer is applied to a road surface, damage to the structural layer of the road surface is reduced, improving the performance of the surface and extending its service life [
3]. When the paving thickness is small, usually in the range of 15~25 mm, it can reduce the consumption of materials and energy, reduce initial costs and maintenance costs, and is an environmentally friendly road paving technology, in-line with the concept of global environmental protection.
At present, in most of the northern regions of China in winter, snow and ice phenomena appear on road surfaces in rainy and snowy weather, resulting in a reduced friction coefficient of automobile tires, resulting in vehicle slippage and braking difficulties, which can easily lead to loss of control of vehicles and, therefore, traffic accidents. An active slow-release type of snow- and ice-melting material combined with asphalt pavement pre-conservation technology, salt-storing pavement de-icing, and snow-removal technology are needed, based on an innovative anti-slip wear layer with excellent anti-skid and wear-resistant performance [
4], in order to prepare asphalt pavement for active pre-maintenance and achieve the effect of actively melting ice and snow on road surfaces. This can not only serve a winter pavement snow-melting and de-icing function, but also can effectively reduce the adverse effects of salt-storing snowmelt on asphalt pavements. Therefore, it is of great significance to develop pavement materials with snow-melting and ice-melting effects and maintenance functions.
Ice- and snow-melting salt material is coated on the salt-storing carrier using a modification process based on slow-release gel technology, prepared as a powder or granular composite materials [
5], that can replace the aggregate and mineral powder in the asphalt mixture [
6]. In recent years, experts have introduced wear layer technology into ice- and snow-melting pavements, and the results have proved that the developed materials have certain ice- and snow-melting effects. Therefore, in this paper, through the development of a slow-release composite snow-melting agent, attached to the pores of a porous aggregate, combined with anti-skid wear layer maintenance technology and salt-storing aggregate-replacing parts of aggregates of the same particle size, we study the ice- and snow-melting performance of a road treated with an active slow-release snow-melting anti-skid wear layer so as to achieve an active and lasting snow- and ice-melting function from the pavement. This is of positive significance for the coordinated and sustainable development of our society, economy, and environment, as well as for the promotion of the high-quality development of transportation engineering. Anti-skid wearing layer technology research first began in France, and scholars worldwide have proposed a thin asphalt concrete surface layer, ultra-thin asphalt concrete (UTAC), a Novachip anti-skid wearing layer based on synchronized paving technology, a Novachip ultra-thin wearing layer, and an open-graded anti-skid wearing layer (OGFC). On the basis of previous research, American scholars successively launched SUP-5 and SMA-5, two more advanced fine-grained ultra-thin wearing layer technologies. In recent years, domestic and foreign ultra-thin wearing course technology has developed rapidly, with different types and functions of thin-layer technology emerging frequently, such as high-toughness ultra-thin asphalt wearing course [
7,
8,
9], SMC warm-mixed thin layer [
10], ECA easy-to-consolidate ultra-thin wearing course [
11], temperature-controlled ultra-thin wearing course [
12], as well as active-melting snow and ice ultra-thin wearing course, etc. At present, active-melting snow and ice anti-skid layer is the most advanced thin-layer technology. At present, the active ice- and snow-melting anti-skid wear layer is divided into salt-storing ice- and snow-melting anti-skid wear layer and energy-conversion anti-skid wear layer according to the principle of melting ice and snow. Energy-transforming anti-skid wear layer melting ice and snow consumes a lot of energy, and the energy and heat inevitably affect the pavement structure [
13,
14], which can be avoided using a salt-storage melting ice and snow anti-skid wear layer. Ice- and snow-melting materials are combined in some form (filler or aggregate) with ultra-thin wear layer materials, thus introducing three new influencing factors, i.e., changes in the oil/gravel ratio due to differences in filler properties [
15,
16], changes in the mix structure due to particle interferences [
17,
18], and changes in the voids caused by the salt that is removed [
19,
20]. Based on the above problems, researchers have carried out related research work. For example, Sun Dahang [
21] proposed a new evaluation index and design method for an ice-suppressing anti-skid wear layer; Liu Yang [
22] investigated the impact of slow-release ice-melting and snow-melting material doping on the road performance of ultra-thin wear layer by using single-factor analysis and constructed an optimal custom model to optimize the composition of the material based on the Response Surface Analysis method; Chen Shuanfa [
23] obtained the basic composition and key design parameters of the material from three aspects, namely, the composition of the mineral grades, asphalt paste characteristics, and road performance of TSSAM, and verified the basic material composition and long-lasting snow-melting performance and road performance of TSSAM under different conditions. Chen Shuanfa [
23], regarding the TSSAM mineral gradation composition, asphalt slurry characteristics, and road performance, researched the basic composition of the material and the key design parameters, and verified snow-melting performance and snow-melting long-lasting performance under different conditions; Chen Xiao [
24] used SMA-5 gradation as an ultra-thin snow melting cover, and, through the study of road performance and snow-melting and ice suppression function, concluded that, when the mixing amount of the snow-melting agent is 33%, the ultra-thin snow-melting covers with various road performance and snow-melting performance all meet the requirements. The road performance and snow- and ice-melting performance of the ultra-thin snow-melting cover meet the requirements.
Comprehensive research has shown that an active slow-release ice-melting snow anti-skid wear layer, compared to other salt-storing pavement de-icing and snow-removal technology [
25], can improve asphalt pavement skid resistance and abrasion resistance, can be considered to extend the service life of the pavement, and represents a new technology for snow-melting and de-icing, offering better road performance. However, due to the lack of actual engineering experience, design specifications, and evaluation standards, active slow-release ice-melting and snow-melting anti-skid wear layer pre-maintenance technology is still in its infancy. How to prepare slow-release composite snow-melting agents, combined with anti-skid wear layer maintenance technology, salt-storing aggregates [
26,
27,
28,
29] as a partial replacement for aggregates of the same particle size, the study of active slow-release ice-melting and snow-melting [
30,
31,
32,
33], and the performance of the snow-melting wear layer, as well as snow- and ice-melting performance, in order to achieve active and durable road melting and snow-melting functions, is an important issue to be solved at present [
34,
35,
36]. Function is an important problem to be solved at present. Many scholars have performed research on the anti-slip performance of the anti-skid wear layer, surface functional layer performance, and snow-melting on pavements, mainly including the anti-skid performance of wear layers, surface functional layer performance, and a series of research and development work on snow-melting technology on pavements; however, in the current literature, few studies have addressed snow-melting performance and the mechanisms of active slow-release anti-ice wear layers. This paper, therefore, investigates the performance and underlying mechanisms of gel-modified salt-storing ceramsite in anti-skid wearing layers, addressing this identified gap in knowledge. Compared to traditional de-icing methods (e.g., bulk salt application or heated pavements), our gel-modified salt-storing ceramsite approach has comparable initial costs, but significantly lower long-term maintenance requirements, and its slow-release functionality extends the economic service life of pavements. This paper explores the advantages of anti-skid wear layers with environmentally friendly slow-release snow- and ice-melting functions.