One-Pot Synthesis of Gelatin/Gum Arabic Hydrogels Embedding Silver Nanoparticles as Antibacterial Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Oxidation of GA
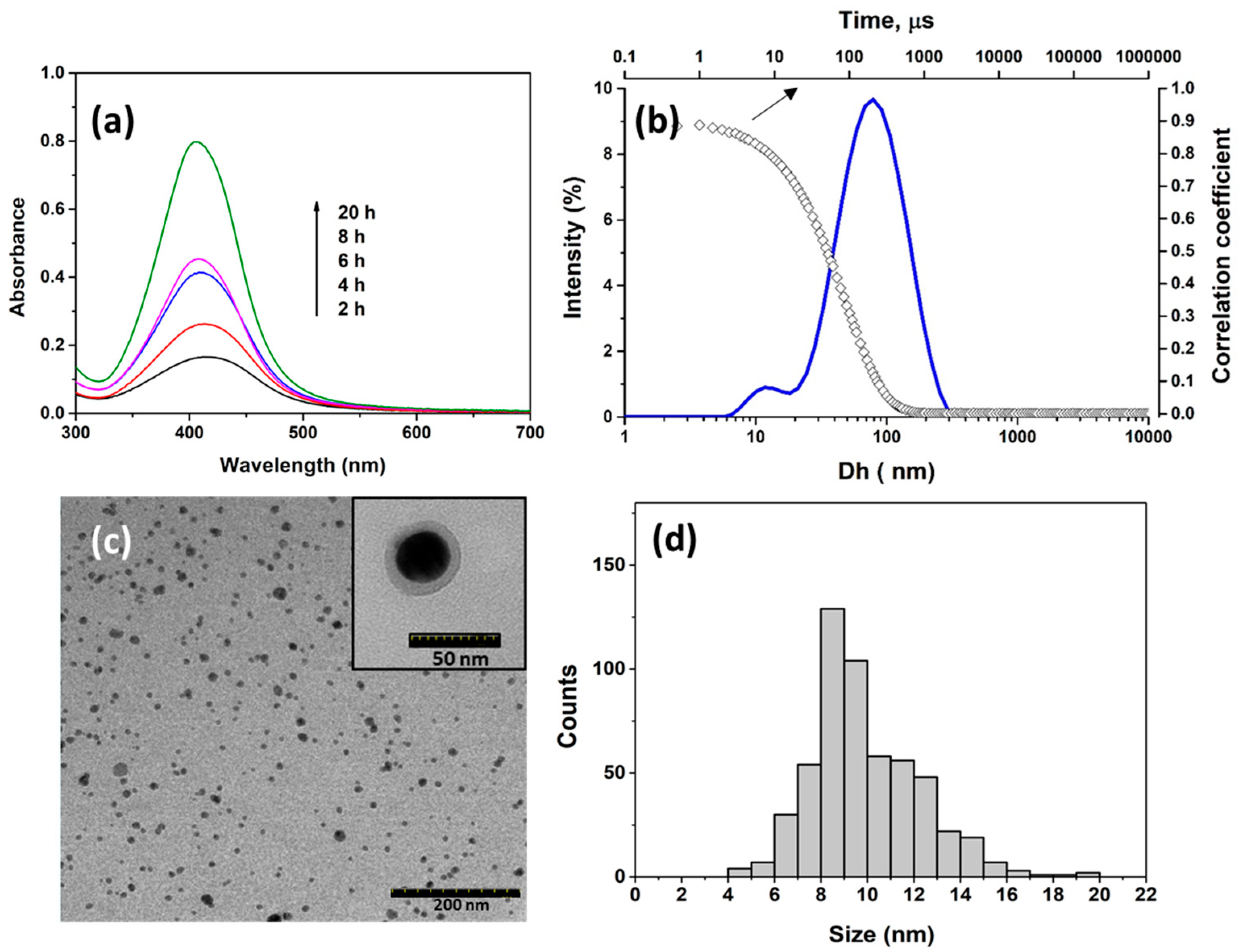
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of OGA-AgNPs
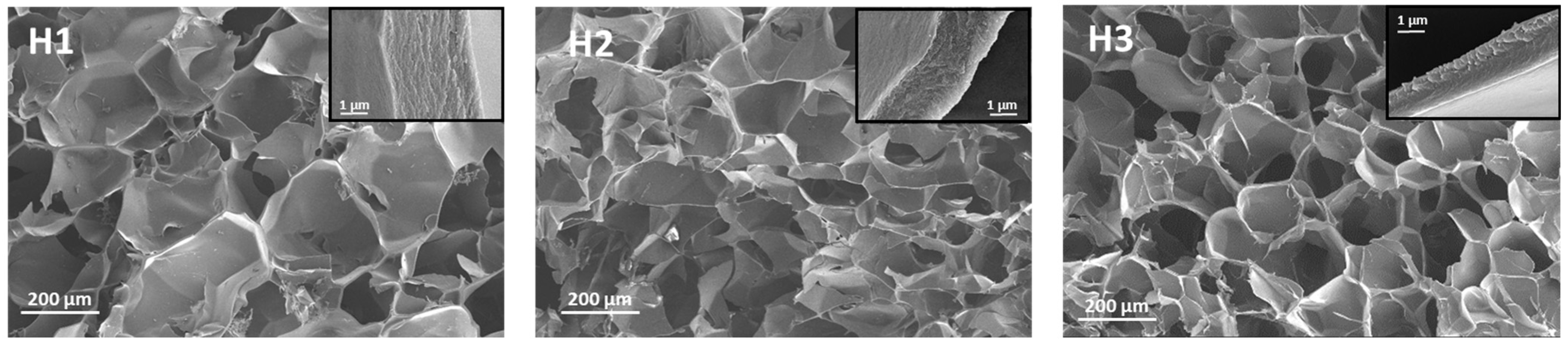
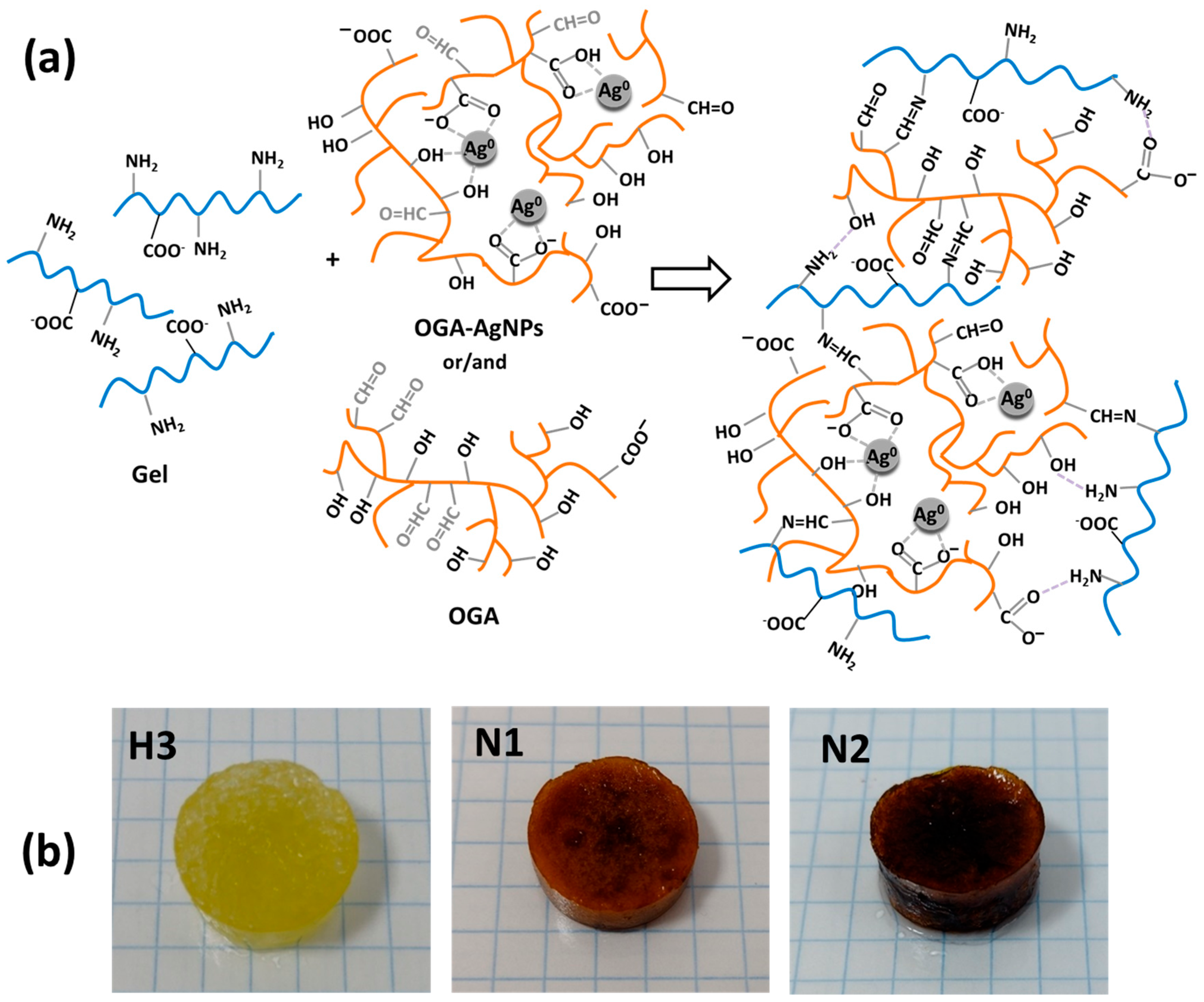
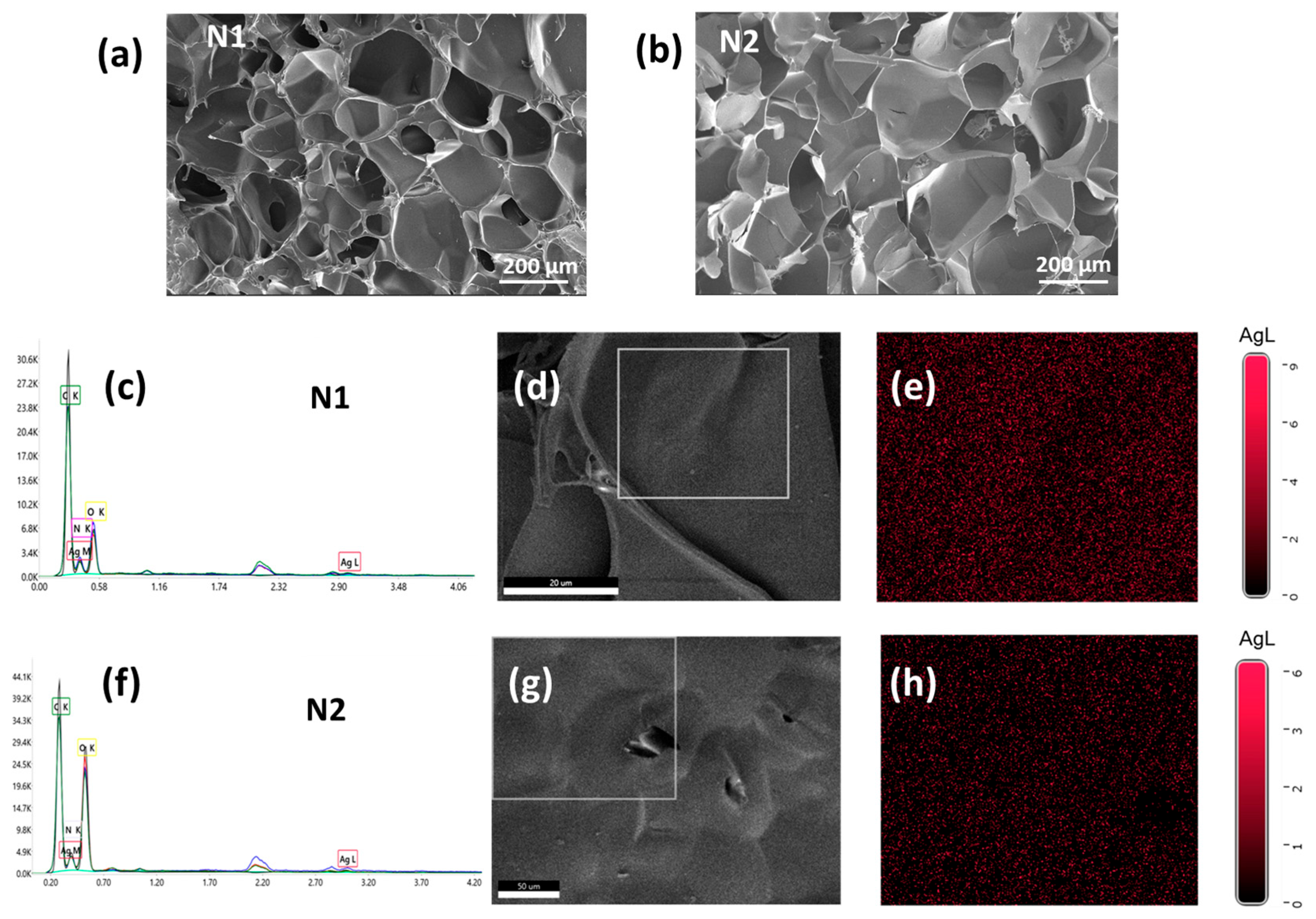
2.3. Preparation and Characterization of Hydrogels with and Without AgNPs
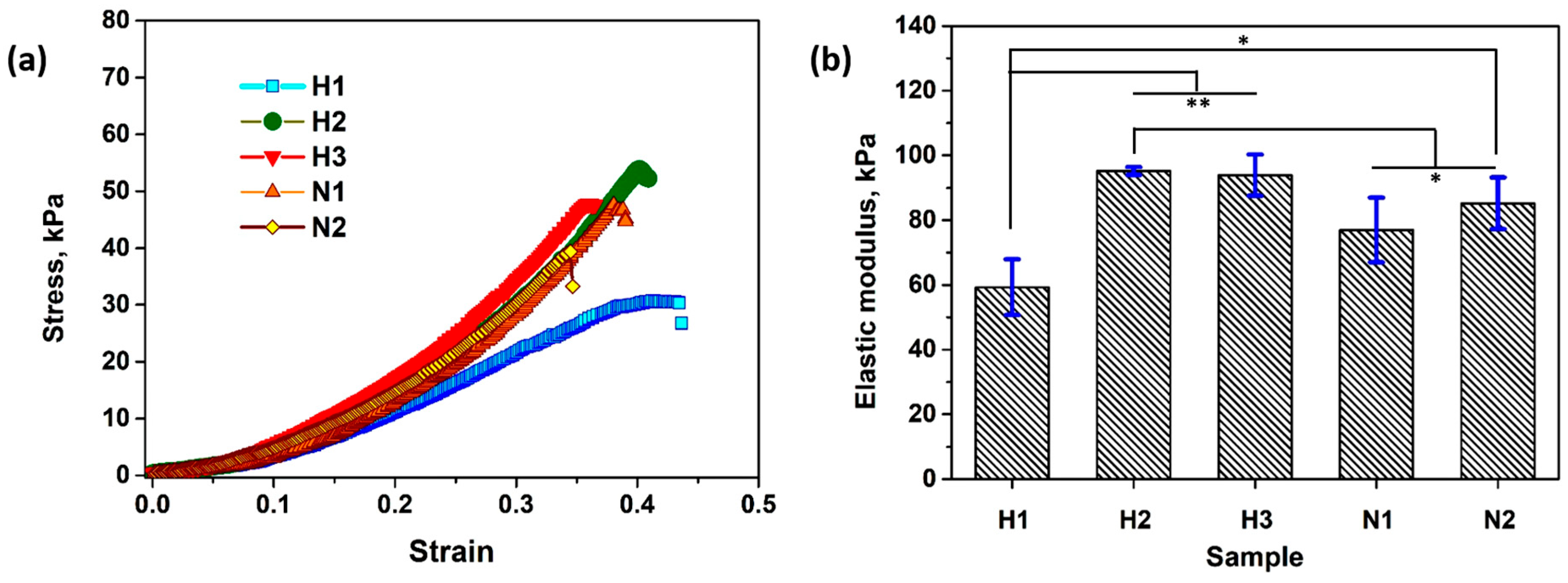
2.4. Compression Test
2.5. Hydrolytic Stability
2.6. Biological Activity of Composite Hydrogels
2.6.1. In Vitro Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity
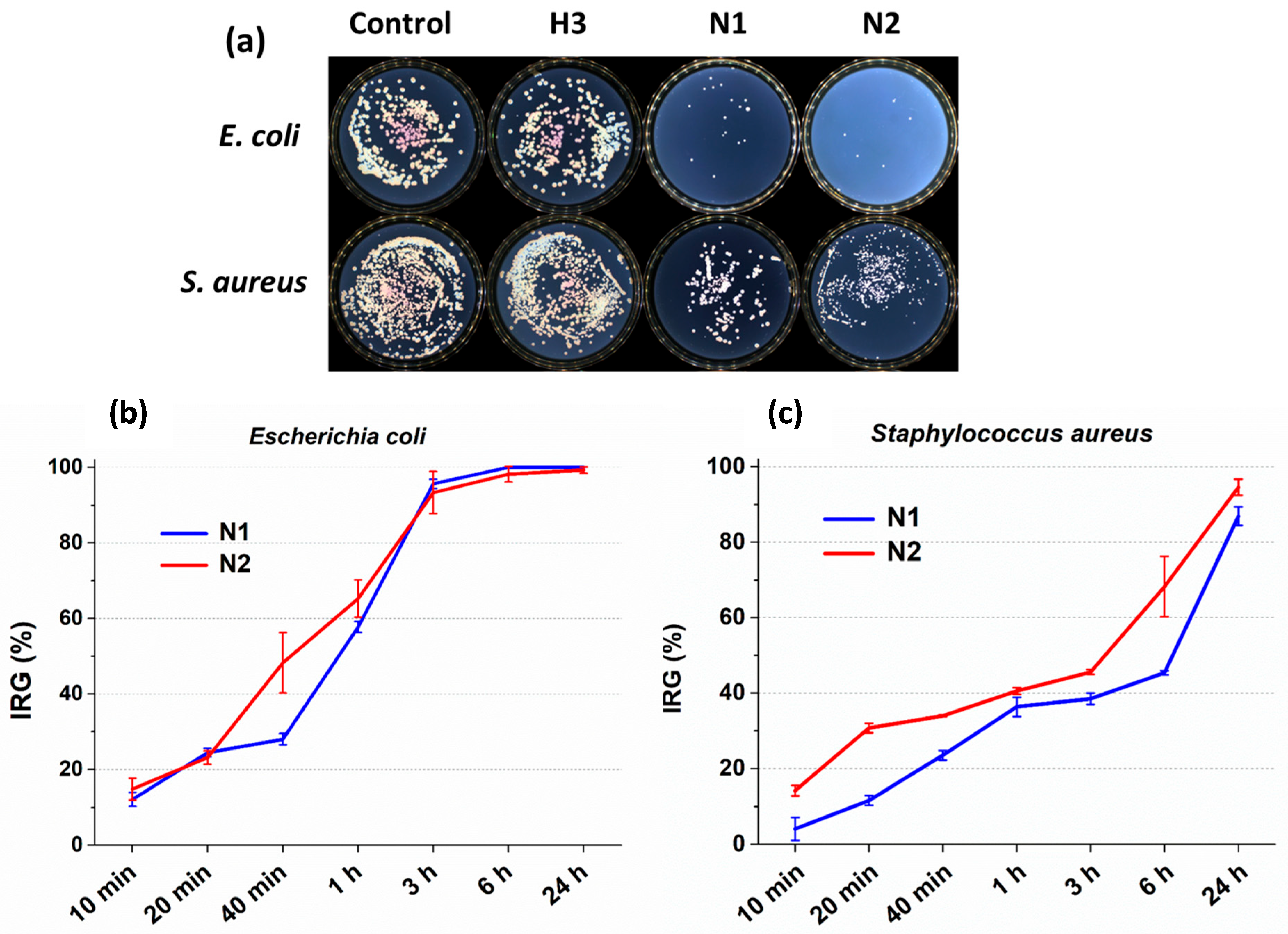
2.6.2. Antibacterial Studies
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Synthesis of Oxidized Gum Arabic (OGA)
4.3. Preparation of AgNPs Covered with OGA (OGA-AgNPs)
4.4. Preparation of Hydrogels
4.5. Characterization of OGA and OGA-AgNPs
4.6. Physicochemical Characterization of Hydrogels
4.7. Mechanical Properties
4.8. Hydrolytic Degradation
4.9. Antioxidant Activity
4.10. Antibacterial Activity
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mushtaq, F.; Raza, Z.A.; Batool, S.R.; Zahid, M.; Onder, O.C.; Rafique, A.; Nazeer, M.A. Preparation, properties, and applications of gelatin-based hydrogels (GHs) in the environmental, technological, and biomedical sectors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 218, 601–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanto, S.; Narayana, S.; Merai, K.P.; Kumar, J.A.; Bhunia, A.; Hani, U.; Al Fatease, A.; Gowda, B.H.J.; Nag, S.; Ahmed, M.G.; et al. Advancements in gelatin-based hydrogel systems for biomedical applications: A state-of-the-art review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndlovu, S.P.; Ngece, K.; Alven, S.; Aderibigbe, B.A. Gelatin-Based Hybrid Scaffolds: Promising Wound Dressings. Polymers 2021, 13, 2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gornall, J.L.; Terentjev, E.M. Helix-coil transition of gelatin: Helical morphology and stability. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Q.; Yates, K.; Vogt, C.; Qian, Z.; Frost, M.C.; Zhao, F. Increasing Mechanical Strength of Gelatin Hydrogels by Divalent Metal Ion Removal. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarika, P.R.; Cinthya, K.; Jayakrishnan, A.; Anilkumar, P.R.; James, N.R. Modified gum arabic cross-linked gelatin scaffold for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 43, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, X.; Tang, K. Pullulan dialdehyde crosslinked gelatin hydrogels with high strength for biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 216, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schacht, E.; Nobels, M.; Vansteenkiste, S.; Demeester, J.; Franssen, J.; Lemahieu, A. Some aspects of the crosslinking of gelatin by dextran dialdehyde. Polym. Gels Netw. 1993, 1, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yan, S.; Zhu, Y.; Ning, Y.; Chen, T.; Yang, Y.; Qi, B.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y. Crosslinking of gelatin Schiff base hydrogels with different structural dialdehyde polysaccharides as novel crosslinkers: Characterization and performance comparison. Food Chem. 2024, 456, 140090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiryaghoubi, N.; Fathi, M.; Safary, A.; Javadzadeh, Y.; Omidi, Y. In situ forming alginate/gelatin hydrogel scaffold through Schiff base reaction embedded with curcumin-loaded chitosan microspheres for bone tissue regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 256, 128335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Goyal, A. Applications of Natural Polymer Gum Arabic: A Review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2015, 18, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, A.R.; Osman, M.E.; Malik, A.A.; Baldwin, T.C. A comparison of the physicochemical and immunological properties of the plant gum exudates of Acacia senegal (gum arabic) and Acacia seyal (gum tahla). Food Addit. Contam. 1996, 13, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, M.A.; Fatima, W.; Imran, M.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Alshehri, S.; Shakeel, F. A Review on the Main Phytoconstituents, Traditional Uses, Inventions, and Patent Literature of Gum Arabic Emphasizing Acacia seyal. Molecules 2022, 27, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatnagar, M.; Parwania, L.; Sharmaa, V.; Gangulib, J.; Bhatnagar, A. Hemostatic, antibacterial biopolymers from Acacia arabica (Lam.) Willd. and Moringa oleifera (Lam.) as potential wound dressing materials. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 51, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mirghani, M.E.S.; Elnour, A.A.M.; Kabbashi, N.A.; Alam, M.Z.; Musa, K.H.; Abdullah, A. Determination of antioxidant activity of gum arabic: An exudation from two different locations. ScienceAsia 2018, 44, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Sharma, S.; Dhiman, A. Design of antibiotic containing hydrogel wound dressings: Biomedical properties and histological study of wound healing. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 457, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Sharma, S.; Dhiman, A. Acacia gum polysaccharide based hydrogel wound dressings: Synthesis, characterization, drug delivery and biomedical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 165, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Dhiman, A. Design of Acacia Gum–Carbopol–Cross-Linked-Polyvinylimidazole Hydrogel Wound Dressings for Antibiotic/Anesthetic Drug Delivery. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 9176–9188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elblbesy, M.A.; Hanafy, T.A.; Shawki, M.M. Polyvinyl alcohol/gum Arabic hydrogel preparation and cytotoxicity for wound healing improvement. e-Polymers 2022, 22, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Cheng, C.; Peng, X.; Zhang, K.; Yu, X. A self-healing and injectable oxidized quaternized guar gum/carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel with efficient hemostatic and antibacterial properties for wound dressing. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 209, 112207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, R.; Moghadas, H.; Moshkriz, A. Oxidized gum arabic cross-linked pectin/O-carboxymethyl chitosan: An antibiotic adsorbent hydrogel. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 39, 1350–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarika, P.R.; James, N.R. Preparation and characterisation of gelatin–gum arabic aldehyde nanogels via inverse miniemulsion technique. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 76, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekulapally, R.; Udayachandrika, K.; Hamlipur, S.; Nair, A.S.; Pal, B.; Singh, S. Tissue engineering of collagen scaffolds crosslinked with plant based polysaccharides. Prog. Biomater. 2021, 10, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghomi, E.R.; Khalili, S.; Khorasani, S.N.; Neisiany, R.E.; Ramakrishna, S. Wound dressings: Current advances and future directions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounden, V.; Singh, M. Hydrogels and Wound Healing: Current and Future Prospects. Gels 2024, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavassin, E.D.; de Figueiredo, L.F.P.; Otoch, J.P.; Seckler, M.M.; de Oliveira, R.A.; Franco, F.F.; Marangoni, V.S.; Zucolotto, V.; Levin, A.S.S.; Costa, S.F. Comparison of methods to detect the in vitro activity of silver nanoparticles (AgNP) against multidrug resistant bacteria. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.A.; Das, S.S.; Khatoon, A.; Ansari, M.T.; Afzal, M.; Hasnain, M.S.; Nayak, A.K. Bactericidal activity of silver nanoparticles: A mechanistic review. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2020, 3, 756–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari, K.; Mostafavi, E.; Afifi, A.M.; Izadiyan, Z.; Jahangirian, H.; Rafiee-Moghaddam, R.; Webster, T.J. Wound dressings functionalized with silver nanoparticles: Promises and pitfalls. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmy, A.; El-Shazly, M.; Seleem, A.; Abdelmohsen, U.; Salem, M.A.; Samir, A.; Rabeh, M.; Elshamy, A.; Singab, A.N.B. The synergistic effect of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles from a combined extract of parsley, corn silk, and gum arabic: In vivo antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial activities. Mater. Res. Express. 2020, 7, 025002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aabed, K.; Mohammed, A.E. Phytoproduct, Arabic gum and opophytum forsskalii seeds for bio-fabrication of silver nanoparticles: Antimicrobial and cytotoxic capabilities. Nanomater. 2021, 11, 2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tummalapalli, M.; Deopura, B.L.; Alam, M.S.; Gupta, B. Facile and green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using oxidized pectin. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 50, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Xiong, X.; Hu, F.; Li, J.; Li, P. Dialdehyde cellulose solution as reducing agent: Preparation of uniform silver nanoparticles and in situ synthesis of antibacterial composite films with high barrier properties. Molecules 2023, 28, 2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantin, M.; Spiridon, M.; Ichim, D.L.; Daraba, O.M.; Suflet, D.M.; Ignat, M.; Fundueanu, G. Synthesis, biological and catalytic activity of silver nanoparticles generated and covered by oxidized pullulan. Mater. Chem.Phys. 2023, 295, 127141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadaka, A.O.; Meyer, S.; Ahmed, O.; Geerts, G.; Madiehe, M.A.; Meyer, M.; Sibuyi, N.R.S. Broad Spectrum Anti-Bacterial Activity and Non-Selective Toxicity of Gum Arabic Silver Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Zhang, X.; Cai, H.; Cao, C. Facile and one-step synthesis of monodisperse silver nanoparticles using gum acacia in aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 196, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Yuan, Y.; Ding, L.; Li, J.; Jia, J.; Li, Z.; He, D.; Yu, Y. Multifunctional chitosan/gelatin@tannic acid cryogels decorated with in situ reduced silver nanoparticles for wound healing. Burn. Trauma. 2022, 10, tkac019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froelich, A.; Jakubowska, E.; Wojtyłko, M.; Jadach, B.; Gackowski, M.; Gadzinski, P.; Napierała, O.; Ravliv, Y.; Osmałek, T. Alginate-Based Materials Loaded with Nanoparticles in Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Galvez, J.; Martinez-Isasi, S.; Gomez-Salgado, J.; Rumbo-Prieto, J.M.; Sobrido-Prieto, M.; Sanchez-Hernandez, M.; Garcia-Martinez, M.; Fernandez-Garcia, D. Cytotoxicity and concentration of silver ions released from dressings in the treatment of infected wounds: A systematic review. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1331753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Ganie, S.A.; Mazumdar, N. A new study of iodine complexes of oxidized gum arabic: An interaction between iodine monochloride and aldehyde groups. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 180, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebe, H.S.; Sardjan, A.S.; Maßmann, S.C.; Flapper, J.; Van den Berg, K.J.; Eisink, N.N.H.M.; Kentgens, A.P.M.; Feringa, B.L.; Kumar, A.; Browne, W.R. Formation of substituted dioxanes in the oxidation of gum arabic with periodate. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domb, A.J.; Linden, G.; Polacheck, I.; Brenita, S. Nystatin-dextran conjugates: Synthesis and characterization. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1996, 34, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoub, R.M.A.; Elmubarak, A.H.; Misran, M.; Hassan, E.A.; Osman, M.E. Characterization and functional properties of some natural Acacia gums. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2018, 17, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.; Haripriya, S. Assessment of physical and structural characteristics of almond gum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, S.P.; Wang, C.; Cui, S.W.; Wang, Q.; Xie, M.Y.; Phillips, G.O. The core carbohydrate structure of Acacia seyal var. Seyal (gum arabic). Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramelle, D.; Sadovoy, A.; Gorelik, S.; Free, P.; Hobley, J.; Fernig, D.G. A rapid method to estimate the concentration of citrate capped silver nanoparticles from UV-visible light spectra. Analyst 2014, 139, 4855–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Wang, D.I.C.; Ting, Y.P. Silver nanoplates: From biological to biomimetic synthesis. ACS Nano 2007, 1, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantin, M.; Lupei, M.; Bucatariu, S.-M.; Pelin, I.M.; Doroftei, F.; Ichim, D.L.; Daraba, O.M.; Fundueanu, G. PVA/Chitosan Thin Films Containing Silver Nanoparticles and Ibuprofen for the Treatment of Periodontal Disease. Polymers 2022, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subasi, N.T. Overview of Schiff Bases. In Schiff Base in Organic, Inorganic and Physical Chemistry; Akitsu, T., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofner, C.M.; Bubnis, W.A. Chemical and swelling evaluations of amino group crosslinking in gelatin and modified gelatin matrices. Pharm. Res. 1996, 13, 1821–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percival, S.; Woods, E.J.; McCarty, S.; Hunt, J.A. The effects of pH on wound healing, biofilms, and antimicrobial efficacy. Wound Repair Regen. 2014, 22, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinstaff, M.W.; Butlin, J.; Carnahan, M.A.; D’alessio, K.R.; Hickey, T.P. Low-Swelling Hydrogel Sealants for Wound Repair. U.S. Patent WO2006US23639, 19 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cataliotti, R.S.; Aliotta, F.; Ponterio, R. Silver nanoparticles behave as hydrophobic solutes towards the liquid water structure in the interaction shell. A Raman study in the O–H stretching region. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 11258–11263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, I.; Constantin, M.; Pelin, I.M.; Suflet, D.M.; Ichim, D.L.; Daraba, O.M.; Fundueanu, G. Eco-Friendly Synthesized PVA/Chitosan/Oxalic Acid Nanocomposite Hydrogels Embedding Silver Nanoparticles as Antibacterial Materials. Gels 2022, 8, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Yan, D.; Cheng, X.; Kong, M.; Liu, Y.; Feng, C.; Chen, X. Biomaterials based on N,N,N-trimethyl chitosan fibers in wound dressing applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 89, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tong, L.; Zheng, Y.; Pang, S.; Sha, J.; Li, L.; Zhao, G. Hydrogels with self- healing ability, excellent mechanical properties and biocompatibility prepared from oxidized gum arabic. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 117, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baukum, J.; Pranjan, J.; Kaolaor, A.; Chuysinuan, P.; Suwantong, O.; Supaphol, P. The potential use of cross-linked alginate/gelatin hydrogels containing silver nanoparticles for wound dressing applications. Polym. Bull. 2020, 77, 2679–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suflet, D.M.; Popescu, I.; Pelin, I.M.; Ichim, D.L.; Daraba, O.M.; Constantin, M.; Fundueanu, G. Dual Cross-Linked Chitosan/PVA Hydrogels Containing Silver Nanoparticles with Antimicrobial Properties. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharia, M.-M.; Ghiorghita, C.-A.; Trofin, M.-A.; Doroftei, F.; Rosca, I.; Mihai, M. Multifunctional composites of zwitterionic resins and silver nanoparticles for point-of-demand antimicrobial applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 275, 125225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.-F.; Liu, N.-H.; Sun, H.; Xu, F. Preparation and Characterization of Electrospun PLCL/Poloxamer Nanofibers and Dextran/Gelatin Hydrogels for Skin Tissue Engineering. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschner, C.M.; Anseth, K.S. Hydrogels in healthcare: From static to dynamic material microenvironments. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 931–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, K.; Tao, L.; Jiang, S.; Yan, J.; Hu, S.; Yang, G.; Ma, C.; Cheng, S.; Wang, X.; Yin, J. Highly flexible hydrogel dressing with efficient antibacterial, antioxidative, and wound healing performances. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 1373–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeimaran, E.; Pourshahrestani, S.; Roder, J.; Detsch, R.; Boccaccini, A.R. 3 D Printing of Photocrosslinked Alginate Dialdehyde- Gelatin Hydrogels Reinforced with Cobalt- Containing Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles for Developing Skin Wound Dressings. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 2400913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, M.; Nazarpak, M.H.; Zamani, A.; Solouk, A. Evaluation of curcumin release from wound dressing based on gelatin and sturgeon- derived chondroitin sulfate. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 35, 106167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadem, E.; Kharaziha, M.; Salehi, S. Colorimetric pH- responsive and hemostatic hydrogel- based bioadhesives containing functionalized silver nanoparticles. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 20, 100650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quah, S.P.; Nykypanchuk, D.; Bhatia, S.R. Temperature- dependent structure and compressive mechanical behavior of alginate/polyethylene oxide–poly(propylene oxide)–poly(ethylene oxide) hydrogels. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2020, 108, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, J.H.; Wischke, C.; Lendlein, A. In vitro Degradation Analysis of 3D-architectured Gelatin-based Hydrogels. MRS Adv. 2020, 5, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, P.; Mishra, B.K.; Behera, G.B. Hydrolysis of Schiff Bases, 1: Kinetics and Mechanism of Spontaneous, Acid, and Base Hydrolysis of N-(2/4-hydroxybenzylidene)-2-aminobenzothiazoles. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 1991, 23, 639–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, O.; Song, S.J.; Lee, K.-J.; Park, M.H.; Lee, S.-H.; Hahn, S.K.; Kim, S.; Kim, B.-S. Mechanical properties and degradation behaviors of hyaluronic acid hydrogels cross-linked at various cross-linking densities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 70, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadilah, N.I.M.; Phang, S.J.; Kamaruzaman, N.; Salleh, A.; Zawani, M.; Sanyal, A.; Maarof, M.; Fauzi, M.B. Antioxidant Biomaterials in Cutaneous Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration: A Critical Review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, R.J.; Kellerby, S.S.; Decker, E.A. Antioxidant Activity of Proteins and Peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurilmala, M.; Hizbullah, H.H.; Karnia, E.; Kusumaningtyas, E.; Ochiai, Y. Characterization and Antioxidant Activity of Collagen, Gelatin, and the Derived Peptides from Yellowfin Tuna (Thunnus albacares) Skin. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedlovičová, Z.; Strapáč, I.; Baláž, M.; Salayová, A. A Brief Overview on Antioxidant Activity Determination of Silver Nanoparticles. Molecules 2020, 25, 3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajoka, M.S.R.; Mehwish, H.M.; Zhang, H.; Ashraf, M.; Fang, H.; Zeng, X.; Wu, Y.; Khurshid, M.; Zhao, L.; He, Z. Antibacterial and antioxidant activity of exopolysaccharide mediated silver nanoparticle synthesized by Lactobacillus brevis isolated from Chinese koumiss. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 186, 110734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugasundaram, T.; Radhakrishnan, M.; Gopikrishnan, V.; Pazhanimurugan, R.; Balagurunathan, R. A study of the bactericidal, anti-biofouling, cytotoxic and antioxidant properties of actinobacterially synthesised silver nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 111, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahlawat, G.; Shikha, S.; Chaddha, B.S.; Chaudhuri, S.R.; Mayilraj, S.; Choudhury, A.R. Microbial glycolipoprotein-capped silver nanoparticles as emerging antibacterial agents against cholera. Microb. Cell Fact. 2016, 15, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zvereva, M. The use of AgNP-containing nanocomposites based on galactomannan and κ-carrageenan for the creation of hydrogels with antiradical activity. Gels 2024, 10, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, K.; Witcomb, M.; Scurrell, M. Silver nanoparticle catalysed redox reaction: An electron relay effect. Mat. Chem. Phys. 2006, 97, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Cheng, W.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wu, L. Structural characterization, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of a novel polysaccharide from Zingiber officinalis and its application in synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Front. Nutr. Sec. Food Chem. 2022, 9, 917094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.; Rayhan, N.M.A.; Emon, S.H.; Islam, T.; Rathry, K.; Hasan, M.; Mansur, M.N.; Asraf, M.A. Antioxidant activity of Schiff base ligands using the DPPH scavenging assay: An updated review. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 33094–33123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Padmini, T.; Ponnuvel, K. Synthesis, characterization and antioxidant activities of Schiff bases are of cholesterol. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2017, 21 (Suppl. 1), S322–S328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, J.; Arora, S.; Rajwade, J.M.; Omray, P.; Khandelwal, S.; Paknikar, K.M. Silver Nanoparticles in Therapeutics: Development of an Antiimicrobial Gel Formulation for Topical Use. Mol. Pharm. 2009, 6, 1388–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayaz, A.M.; Balaji, K.; Girilal, M.; Yadav, R.; Kalaichelvan, P.T.; Venketesan, R. Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their synergistic effect with antibiotics: A study against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Nanomed. Nanotech. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lkhagvajav, N.; Yasa, I.; Celik, E.; Koizhaiganova, M.; Sari, O. Antimicrobial activity of colloidal silver nanoparticles prepared by sol-gel method. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostr. 2011, 6, 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, P.E.; Alves, R.B.T.; Pimentel-Filho, N.J.; de Sa, J.P.N.; Mantovani, H.C.; Pena, W.E.L.; de Andrade, N.J. Subinhibitory concentrations of silver nanoparticles and silver nitrate on the adaptative and cross-resistance to antibiotics on bovine mastitis pathogens. Ciênc. Rural 2021, 51, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, S.; Mukherji, S.; Mukherji, S. Immobilized silver nanoparticles enhance contact killing and show highest efficacy: Elucidation of the mechanism of bactericidal action of silver. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 7328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquina-Lemonche, L.; Burns, J.; Turner, R.D.; Kumar, S.; Tank, R.; Mullin, N.; Wilson, J.S.; Chakrabarti, B.; Bullough, P.A.; Foster, S.J.; et al. The Architecture of the Gram Positive Bacterial Cell Wall. Nature 2020, 582, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bapat, R.A.; Chaubal, T.V.; Joshi, C.P.; Bapat, P.R.; Choudhury, H.; Pandey, M.; Gorain, B.; Kesharwani, P. An overview of application of silver nanoparticles for biomaterials in dentistry. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 91, 881–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavi, M.; Rai, M. Recent advances in antibacterial applications of metal nanoparticles (MNPs) and metal nanocomposites (MNCs) against multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria. Expert Rev. Antiinfect. Ther. 2019, 17, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorrami, S.; Zarrabi, A.; Khaleghi, M.; Danaei, M.; Mozafari, M. Selective cytotoxicity of green synthesized silver nanoparticles against the MCF-7 tumor cell line and their enhanced antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 8013–8024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elebiary, D.M.; Mahdy, H.M.; Mansour, A.M.; Amer, W.H.; Abu-Elghait, M. Evaluation of Arabic gum antibacterial and wound healing activities against Staphylococcus aureus isolates obtained from skin infections. Microb. Biosyst. 2024, 9, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunnel, D.; Schacht, E. Chemical modification of pullulan: 1. Periodate oxidation. Polymer 1993, 34, 2628–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Heindel, N.D. Determination of degree of substitution of formyl groups in polyaldehyde dextran by the hydroxylamine hydrochloride method. Pharm. Res. 1991, 8, 400–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.W.; Rahman, S.; Studies on uronic acid materials. Part XX The viscosity –molecular weight relationship for Acacia Gums. Carbohyd. Res. 1967, 4, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solorio, L.; Zwolinski, C.; Lund, A.W.; Farrell, J.; Stegemann, J.P. Gelatin microspheres crosslinked with genipin for local delivery of growth factors. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2010, 4, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahoor, A.; Ahmadi, R.; Heydari, M.; Bagheri, M.; Behnamghader, A. Synthesis and evaluation of cross-linked gelatin nanoparticles for controlled release of an anti-diabetic drug: Gliclazide. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 154, 110856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshayedi, S.; Sarpoolaky, H.; Khavandi, A. Fabrication, swelling behavior, and water absorption kinetics of genipin-crosslinked gelatin–chitosan hydrogels. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2021, 61, 3094–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelin, I.M.; Silion, M.; Popescu, I.; Rîmbu, C.M.; Fundueanu, G.; Constantin, M. Pullulan/Poly(vinylalcohol) Hydrogels Loaded with Calendula officinalis Extract: Design and In Vitro Evaluation for Wound Healing Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample Code | Initial Mixture | Hydrogel Characteristics | Ag (wt.%) ** | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gel:OGA: OGA-AgNPs (%, wt:wt:wt) | CH=O: NH2 Molar Ratio | Ag (wt. %) | GF (%) | Cross-Linking of NH2 Groups (%) | Porosity (%) | SR * (g/g) | |||
| pH = 5.5 | pH = 7.4 | ||||||||
| H1 | 60:40:0 | 5.7:1 | - | 85.6 ± 0.4 | 55.9 ± 3.6 | 70.7 ± 0.2 | 7.2 ± 0.4 | 7.8 ± 0.2 | - |
| H2 | 50:50:0 | 8.6:1 | - | 86.6 ± 0.6 | 67.6 ± 1.1 | 76.2 ± 1.0 | 8.6 ± 0.3 | 8.6 ± 0.1 | - |
| H3 | 40:60:0 | 12.9:1 | - | 87.5 ± 0.1 | 70.0 ± 1.4 | 77.3 ± 0.3 | 9.1 ± 0.4 | 8.9 ± 0.3 | - |
| N1 | 40:30:30 | 10.8:1 | 0.9 | 87.3 ± 0.3 | 63.7 ± 2.8 | 72.4 ± 1.0 | 8.6 ± 0.3 | 8.4 ± 0.2 | 0.61 ± 0.02 |
| N2 | 40:0:60 | 8.7:1 | 1.8 | 87.4 ± 0.5 | 58.9 ± 1.1 | 64.6 ± 1.2 | 8.2 ± 0.2 | 8.0 ± 0.1 | 1.32 ± 0.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Popescu, I.; Pelin, I.M.; Rosca, I.; Constantin, M. One-Pot Synthesis of Gelatin/Gum Arabic Hydrogels Embedding Silver Nanoparticles as Antibacterial Materials. Gels 2025, 11, 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060429
Popescu I, Pelin IM, Rosca I, Constantin M. One-Pot Synthesis of Gelatin/Gum Arabic Hydrogels Embedding Silver Nanoparticles as Antibacterial Materials. Gels. 2025; 11(6):429. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060429
Chicago/Turabian StylePopescu, Irina, Irina Mihaela Pelin, Irina Rosca, and Marieta Constantin. 2025. "One-Pot Synthesis of Gelatin/Gum Arabic Hydrogels Embedding Silver Nanoparticles as Antibacterial Materials" Gels 11, no. 6: 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060429
APA StylePopescu, I., Pelin, I. M., Rosca, I., & Constantin, M. (2025). One-Pot Synthesis of Gelatin/Gum Arabic Hydrogels Embedding Silver Nanoparticles as Antibacterial Materials. Gels, 11(6), 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060429








