Development of a Novel Nanoclay-Doped Hydrogel Adsorbent for Efficient Removal of Heavy Metal Ions and Organic Dyes from Wastewater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
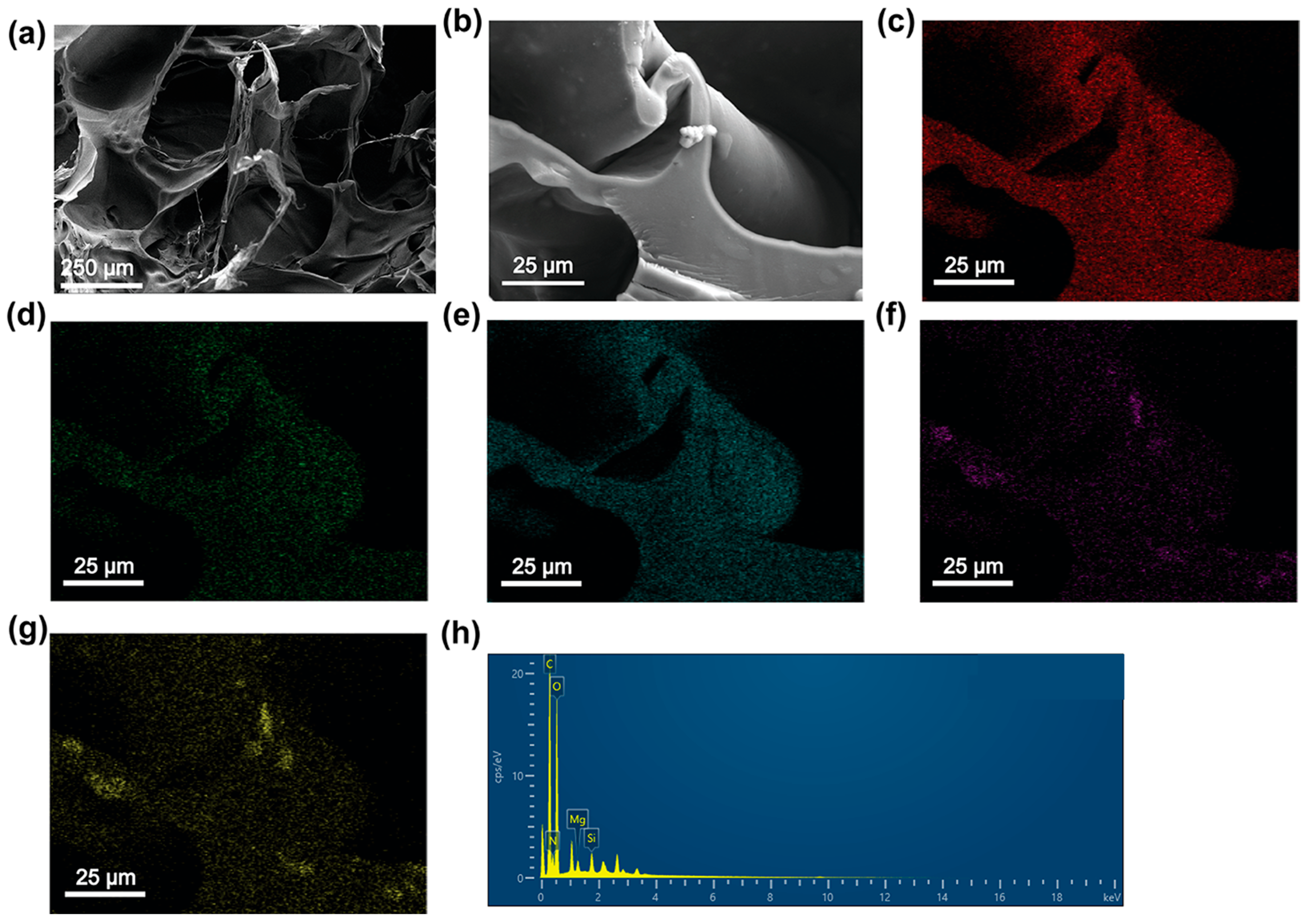
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of NxPP Hydrogels
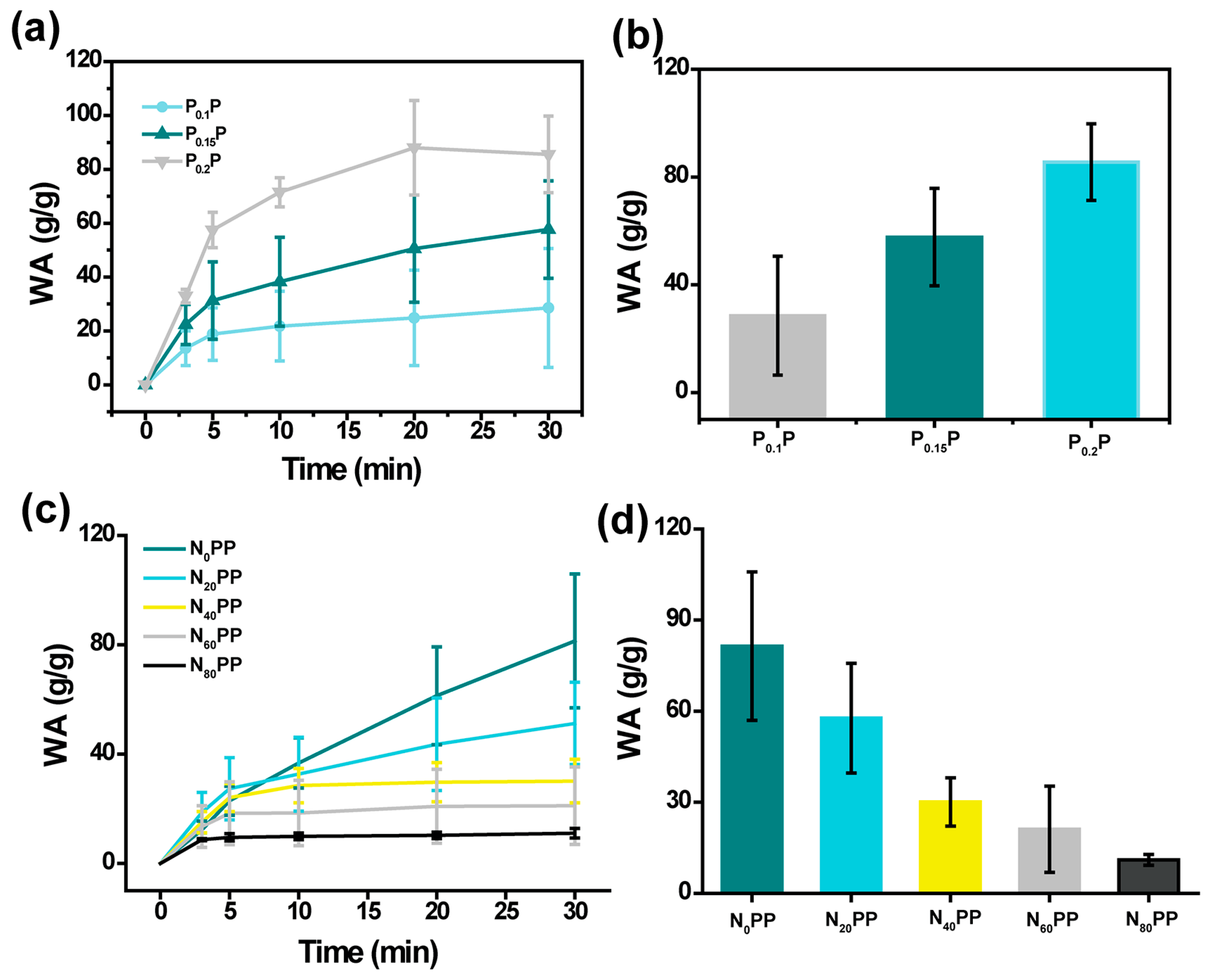
2.2. Swelling Properties of NxPP Hydrogels
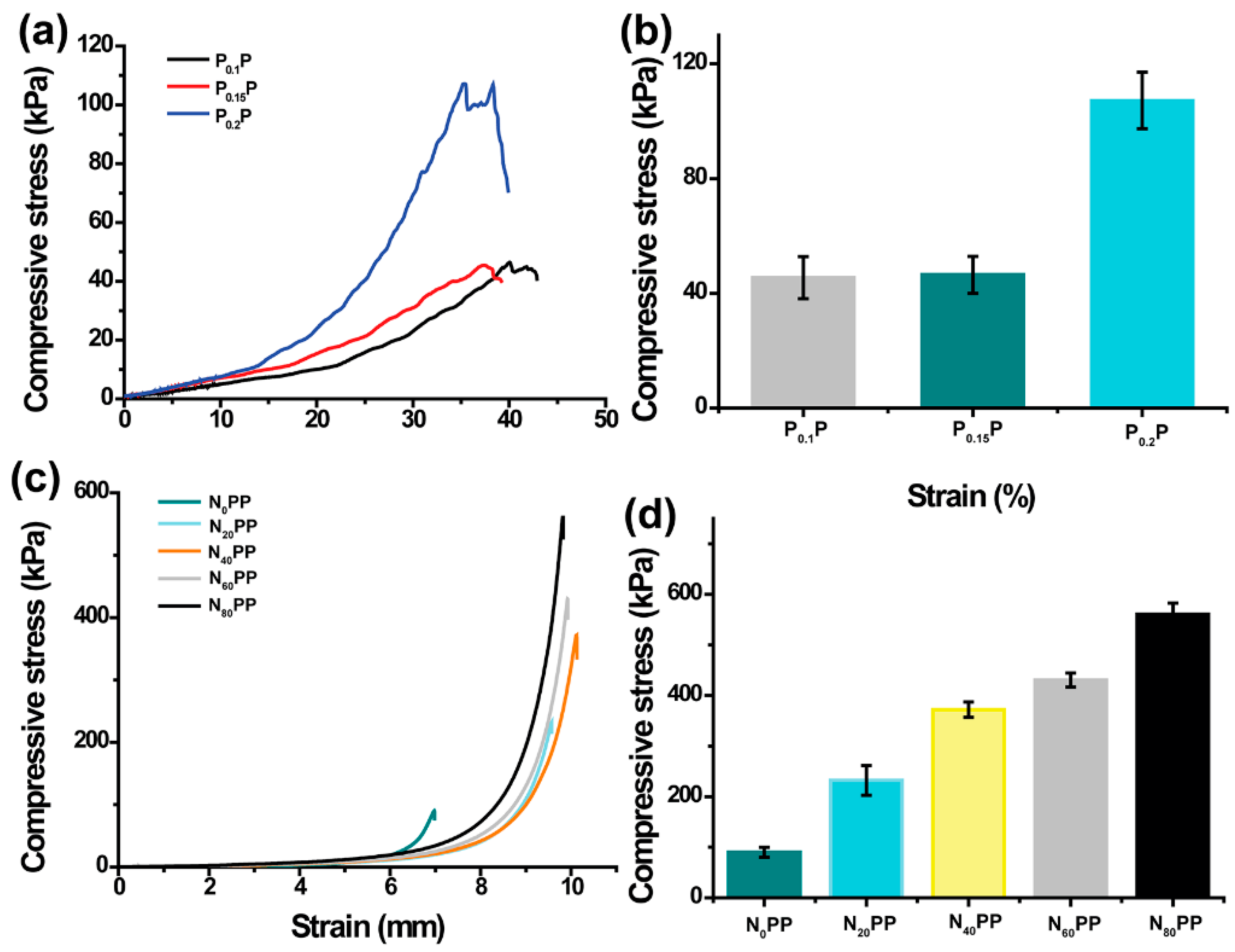
2.3. Mechanical Properties of NxPP Hydrogels
2.4. Cu2+ Adsorption Capacity of PxP Hydrogels and NxPP Hydrogels
2.5. Effect of pH and Temperature on NxPP Hydrogels’ Adsorption Capacity
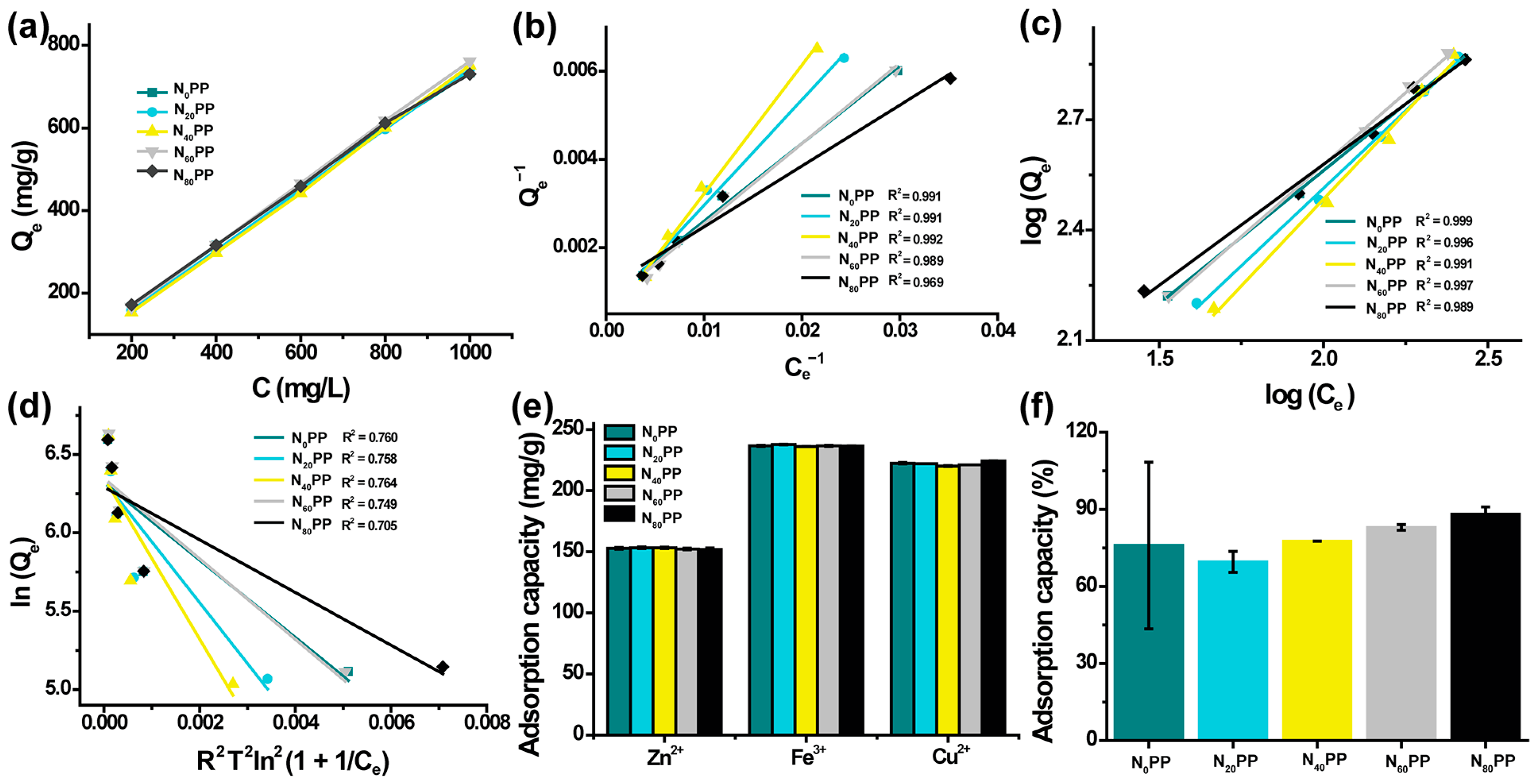
2.6. Adsorption Isotherms of NxPP Hydrogels
2.7. Adsorption Capacity of NxPP Hydrogels for Different Metal Ions
2.8. Adsorption Capacity of NxPP Hydrogels for (Methylene Blue) MB
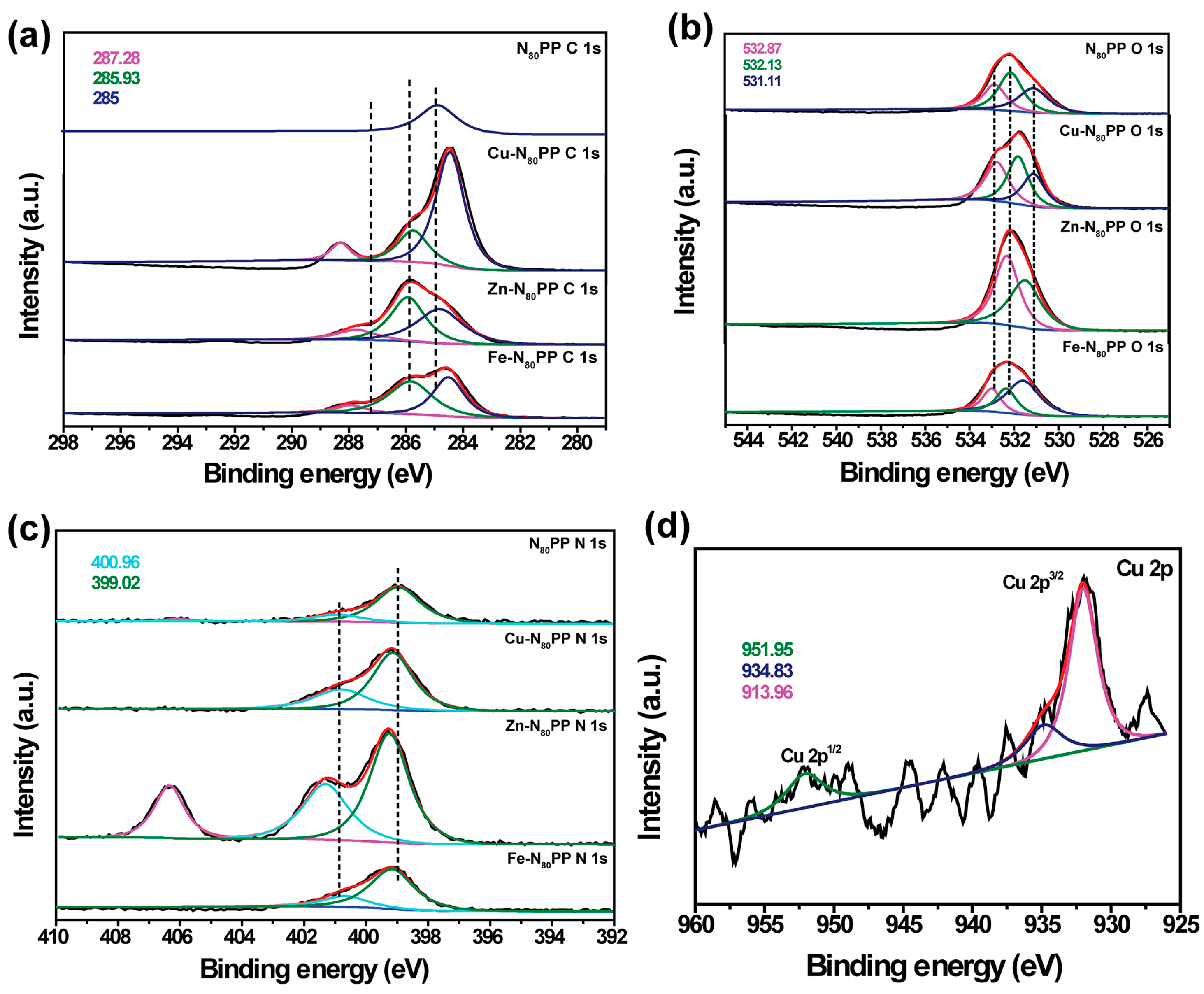
2.9. Adsorption Mechanism of NxPP Hydrogels
2.10. Reusability of NxPP Hydrogels
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Reagents
4.2. Preparation of γ-PGA/PEI (PxP) and NxPP Hydrogels
4.3. Characterizations
4.4. Swelling Performance of NxPP Hydrogels
4.5. Mechanical Study of NxPP Hydrogels
4.6. Adsorption Kinetics of PxP Hydrogels
4.7. Adsorption Kinetics of NxPP Hydrogels
4.8. Effect of pH on the Adsorption Capacity of NxPP Hydrogels
4.9. Effect of Temperature on the Adsorption Capacity of NxPP Hydrogels
4.10. Adsorption Study of NxPP Hydrogels for Different Metal Ions
4.11. Adsorption Capacity of NxPP Hydrogels for MB
4.12. Adsorption Mechanism Study of NxPP Hydrogels
4.13. Recovery and Reusability Study of NxPP Hydrogels
4.14. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karaouzas, I.; Kapetanaki, N.; Mentzafou, A.; Kanellopoulos, T.D.; Skoulikidis, N. Heavy metal contamination status in Greek surface waters: A review with application and evaluation of pollution indices. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Li, Y. Eco-friendly floatable foam hydrogel for the adsorption of heavy metal ions and use of the generated waste for the catalytic reduction of organic dyes. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 6914–6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, O.; Polat, T.G.; Diker, C.O.; Tunc, S. Agar/kappa-carrageenan composite hydrogel adsorbent for the removal of Methylene Blue from water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 160, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Hou, X.B.; Pan, Y.F.; Wang, L.D.; Xiao, H.N. Redox-responsive carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogel for adsorption and controlled release of dye. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 123, 109447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Do, J.Y.; Kim, J.; Kang, M. Fast and highly efficient removal of dye from aqueous solution using natural locust bean gum based hydrogels as adsorbent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 143, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabipour, M.; Pour, Z.S.; Sahraei, R.; Ghaemy, M.; Jazi, M.E.; Mlsna, T.E. pH-Sensitive Nanocomposite Hydrogels Based on Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Macromonomer and Graphene Oxide for Removal of Cationic Dyes from Aqueous Solutions. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 584–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, A.K.; Elkodous, M.A.; Ali, G.A.M. Recent advances in dye and metal ion removal using efficient adsorbents and novel nano-based materials: An overview. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 36528–36553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.C.; Zhu, W.K.; He, L.; Tan, F.R.; Zhu, N.M.; Zhou, Q.; He, M.X.; Hu, G.Q. Calcium-rich biochar from crab shell: An unexpected super adsorbent for dye removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 267, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolisetty, S.; Peydayesh, M.; Mezzenga, R. Sustainable technologies for water purification from heavy metals: Review and analysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 463–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehzad, H.; Ahmed, E.; Sharif, A.; Farooqi, Z.H.; Din, M.I.; Begum, R.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Ouyang, J.; Irfan, A.; et al. Modified alginate-chitosan-TiO(2) composites for adsorptive removal of Ni(II) ions from aqueous medium. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 194, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, G.Q.; Fan, S.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.S.; Hao, Z.P. Adsorption and membrane separation for removal and recovery of volatile organic compounds. J. Env. Environ. Sci. 2023, 123, 96–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.J.; Tong, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.; Bu, S.; Huang, H.G.; Huo, G.T.; Fang, J.M.; Ding, H.; Xu, W.G. Enhancing fine particle separation by hybrid-electrostatic-turbulence coagulation: An experimental and numerical investigation. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarpour, M.; Najjarizad-Peyvasti, S.; Khataee, A.; Karimi, A. Polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membranes incorporated with CeO2/GO nanocomposite for enhanced fouling resistance and dye separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poshina, D.N.; Raik, S.V.; Poshin, A.N.; Skorik, Y.A. Accessibility of chitin and chitosan in enzymatic hydrolysis: A review. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2018, 156, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhao, M.W.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, H.J.; Han, X.G.; Fan, Z.H.; Su, G.Y.; Pan, D.; Li, Z.Y. Research progress of adsorption and removal of heavy metals by chitosan and its derivatives: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, M.; Bhattacharjee, M.; Dhar, A.K.; Rahman, F.B.; Haque, S.; Rashid, T.U.; Kabir, S.M.F. Cellulose-Based Hydrogels for Wastewater Treatment: A Concise Review. Gels 2021, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Nazal, M.K.; Ihsanullah; Baig, N.; Osman, A.M. Removal of heavy metals and organic pollutants from water using dendritic polymers based adsorbents: A critical review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 191, 400–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bediako, J.K.; El Ouardi, Y.; Mouele, E.S.M.; Mensah, B.; Repo, E. Polyelectrolyte and polyelectrolyte complex-incorporated adsorbents in water and wastewater remediation—A review of recent advances. Chemosphere 2023, 325, 138418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Feng, C. How to Construct DNA Hydrogels for Environmental Applications: Advanced Water Treatment and Environmental Analysis. Small 2018, 14, e1703305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Wang, S. A Multifunctional γ-Polyglutamic Acid Hydrogel for Combined Tumor Photothermal and Chemotherapy. Gels 2025, 11, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; He, G.; Ning, X.; Wang, C.; Fan, L.; Yin, Y.; Cai, W. Hydroxypropyl chitosan-based dual self-healing hydrogel for adsorption of chromium ions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 174, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Rong, Z.; Zhu, K.; Wu, Y. Chitosan-based dual network composite hydrogel for efficient adsorption of methylene blue dye. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222 Pt A, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipa, C.; Cidade, M.T.; Borges, J.P.; Costa, L.C.; Silva, J.C.; Soares, P.I. Clay-based nanocomposite hydrogels for biomedical applications: A review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Fresneda, M.A.; González-Morales, E.; Gila-Vilchez, C.; Leon-Cecilla, A.; Merroun, M.L.; Medina-Castillo, A.L.; Lopez-Lopez, M.T. Clay–polymer hybrid hydrogels in the vanguard of technological innovations for bioremediation, metal biorecovery, and diverse applications. Mater. Horiz. 2024, 11, 5533–5549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, X.; Liu, X. Heavy Metal Removal from Wastewater Using Poly (Gamma-Glutamic Acid)-Based Hydrogel. Gels 2024, 10, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Xu, P.; Wang, H. Efficient and selective removal of heavy metals and dyes from aqueous solutions using Guipi residue-based hydrogel. Gels 2024, 10, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, F.; Zheng, Y.; Kang, J.; Qu, J.; Chen, J.P. Improvement of metal adsorption onto chitosan/Sargassum sp. composite sorbent by an innovative ion-imprint technology. Water Res. 2011, 45, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keirudin, A.A.; Zainuddin, N.; Yusof, N.A. Crosslinked carboxymethyl Sago starch/citric acid hydrogel for sorption of Pb2+, Cu2+, Ni2+ and Zn2+ from aqueous solution. Polymers 2020, 12, 2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Yang, J.; Lin, L.; Peng, K.; Chen, Y.; Jin, S.; Yao, W. Construction of physically crosslinked chitosan/sodium alginate/calcium ion double-network hydrogel and its application to heavy metal ions removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 393, 124728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagdat, S.; Tokay, F.; Demirci, S.; Yilmaz, S.; Sahiner, N. Removal of Cd(II), Co(II), Cr(III), Ni(II), Pb(II) and Zn(II) ions from wastewater using polyethyleneimine (PEI) cryogels. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 329, 117002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, N.; Li, L.; Hu, X. Recent trends in natural polymer-based hydrogels for biomedical applications. Biofunct. Mater. 2023, 2, 0004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Hydrogel | k1 (1/min) | Qe (mg/g) | R2 (Pseudo-First-Order) | k2 (g/mg·min) | Qe (mg/g) | R2 (Pseudo-Second-Order) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0PP | 0.12 | 65.4 | 0.970 | 0.0061 | 70.1 | 0.996 |
| N20PP | 0.14 | 70.3 | 0.975 | 0.0075 | 74.8 | 0.997 |
| N40PP | 0.16 | 75.6 | 0.981 | 0.0088 | 78.9 | 0.991 |
| N60PP | 0.18 | 78.7 | 0.984 | 0.0102 | 81.3 | 0.998 |
| N80PP | 0.19 | 79.8 | 0.980 | 0.0110 | 82.1 | 0.998 |
| Hydrogel | Qmax (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 (Langmuir) | KF | n | R2 (Freundlich) | β | E (KJ/mol) | R2 (Temkin) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0PP | 95.4 | 0.015 | 0.991 | 8.4 | 2.3 | 0.999 | 0.00465 | 10.37 | 0.760 |
| N20PP | 102.6 | 0.017 | 0.991 | 9.2 | 2.5 | 0.996 | 0.00405 | 11.11 | 0.758 |
| N40PP | 110.2 | 0.020 | 0.992 | 10.6 | 2.7 | 0.991 | 0.00355 | 11.87 | 0.764 |
| N60PP | 115.8 | 0.022 | 0.989 | 11.8 | 2.9 | 0.997 | 0.00312 | 12.66 | 0.749 |
| N80PP | 118.7 | 0.025 | 0.969 | 12.4 | 3.0 | 0.989 | 0.00282 | 13.32 | 0.705 |
| Cycle | N0PP (%) | N20PP (%) | N40PP (%) | N60PP (%) | N80PP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100.0 ± 1.3 | 100.0 ± 1.2 | 100.0 ± 1.1 | 100.0 ± 1.0 | 100.0 ± 0.9 |
| 2 | 97.3 ± 1.5 | 97.9 ± 1.4 | 98.1 ± 1.3 | 98.4 ± 1.1 | 98.6 ± 1.0 |
| 3 | 95.6 ± 1.6 | 96.4 ± 1.5 | 97.3 ± 1.3 | 97.7 ± 1.2 | 98.1 ± 1.0 |
| 4 | 93.8 ± 1.7 | 95.1 ± 1.6 | 96.2 ± 1.4 | 96.8 ± 1.2 | 97.5 ± 1.1 |
| 5 | 92.0 ± 1.8 | 94.2 ± 1.7 | 95.3 ± 1.5 | 96.1 ± 1.3 | 96.9 ± 1.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, H.; Xie, M.; He, S.; Lin, S.; Wang, S.; Liu, X. Development of a Novel Nanoclay-Doped Hydrogel Adsorbent for Efficient Removal of Heavy Metal Ions and Organic Dyes from Wastewater. Gels 2025, 11, 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040287
Zhao H, Xie M, He S, Lin S, Wang S, Liu X. Development of a Novel Nanoclay-Doped Hydrogel Adsorbent for Efficient Removal of Heavy Metal Ions and Organic Dyes from Wastewater. Gels. 2025; 11(4):287. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040287
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Hang, Mengmeng Xie, Siyu He, Saishi Lin, Shige Wang, and Xiuying Liu. 2025. "Development of a Novel Nanoclay-Doped Hydrogel Adsorbent for Efficient Removal of Heavy Metal Ions and Organic Dyes from Wastewater" Gels 11, no. 4: 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040287
APA StyleZhao, H., Xie, M., He, S., Lin, S., Wang, S., & Liu, X. (2025). Development of a Novel Nanoclay-Doped Hydrogel Adsorbent for Efficient Removal of Heavy Metal Ions and Organic Dyes from Wastewater. Gels, 11(4), 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040287







