A Robust Natural Rubber–Polyzwitterion Composite Hydrogel for Highly Enhanced Marine Anti-Biofouling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
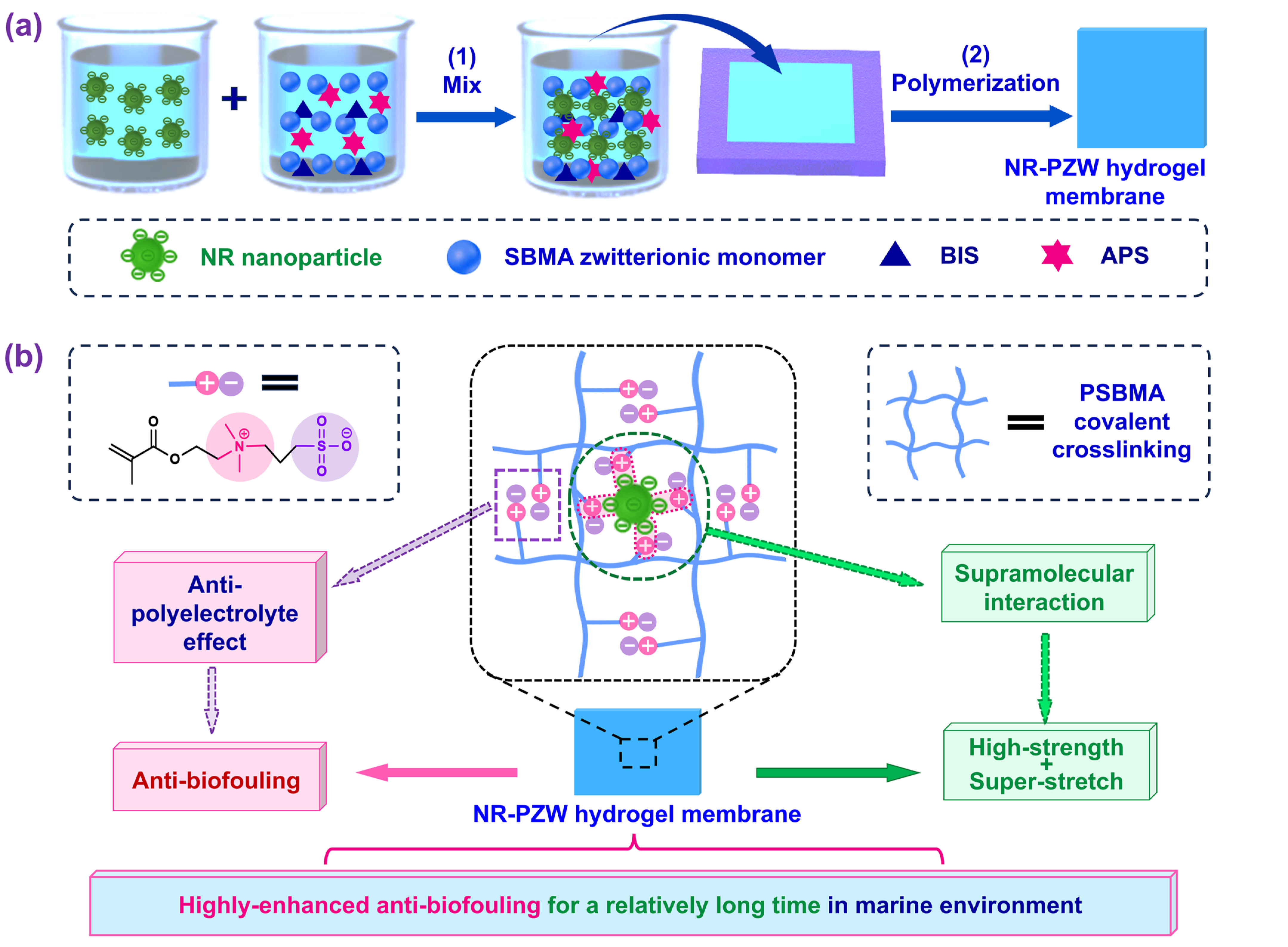
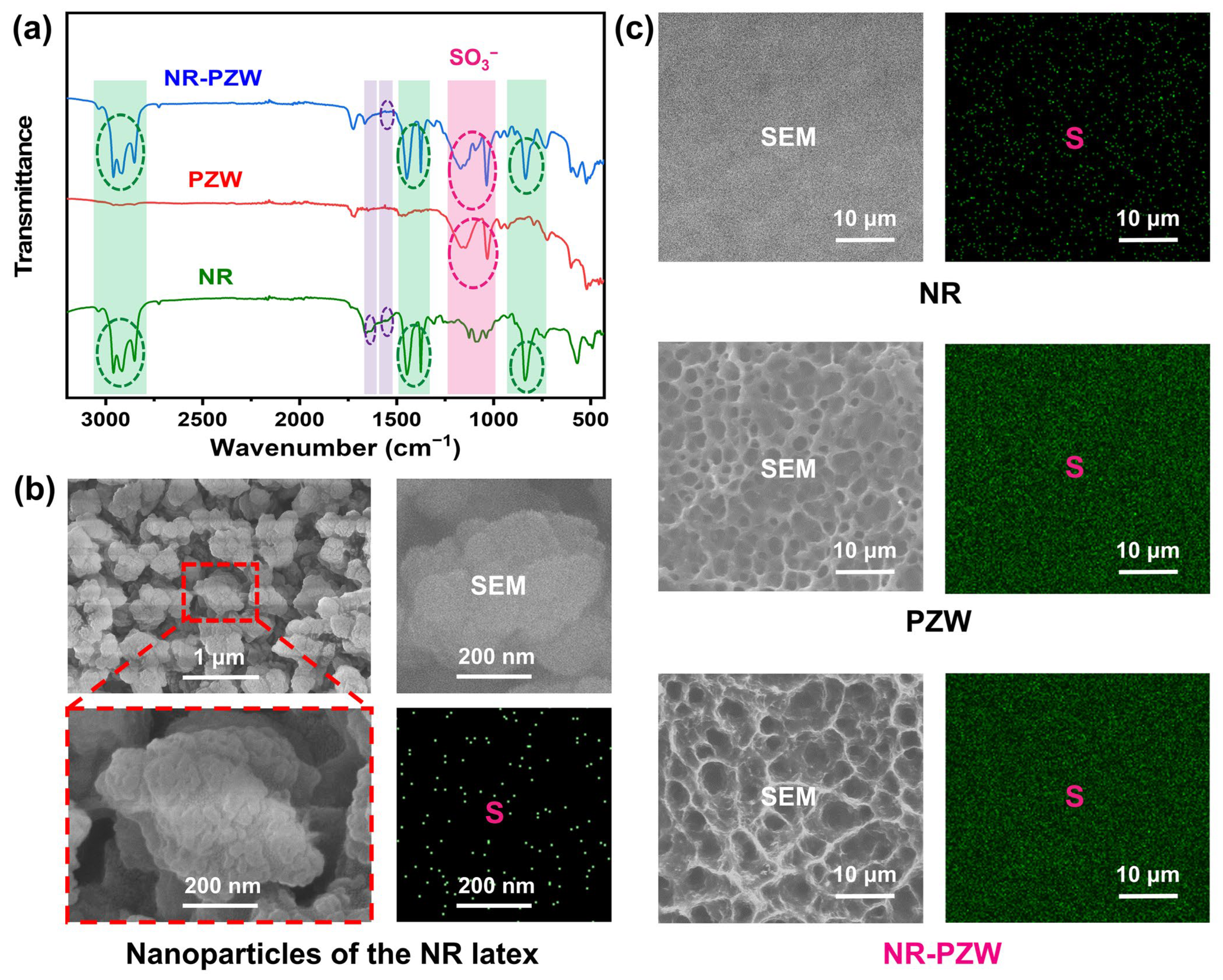
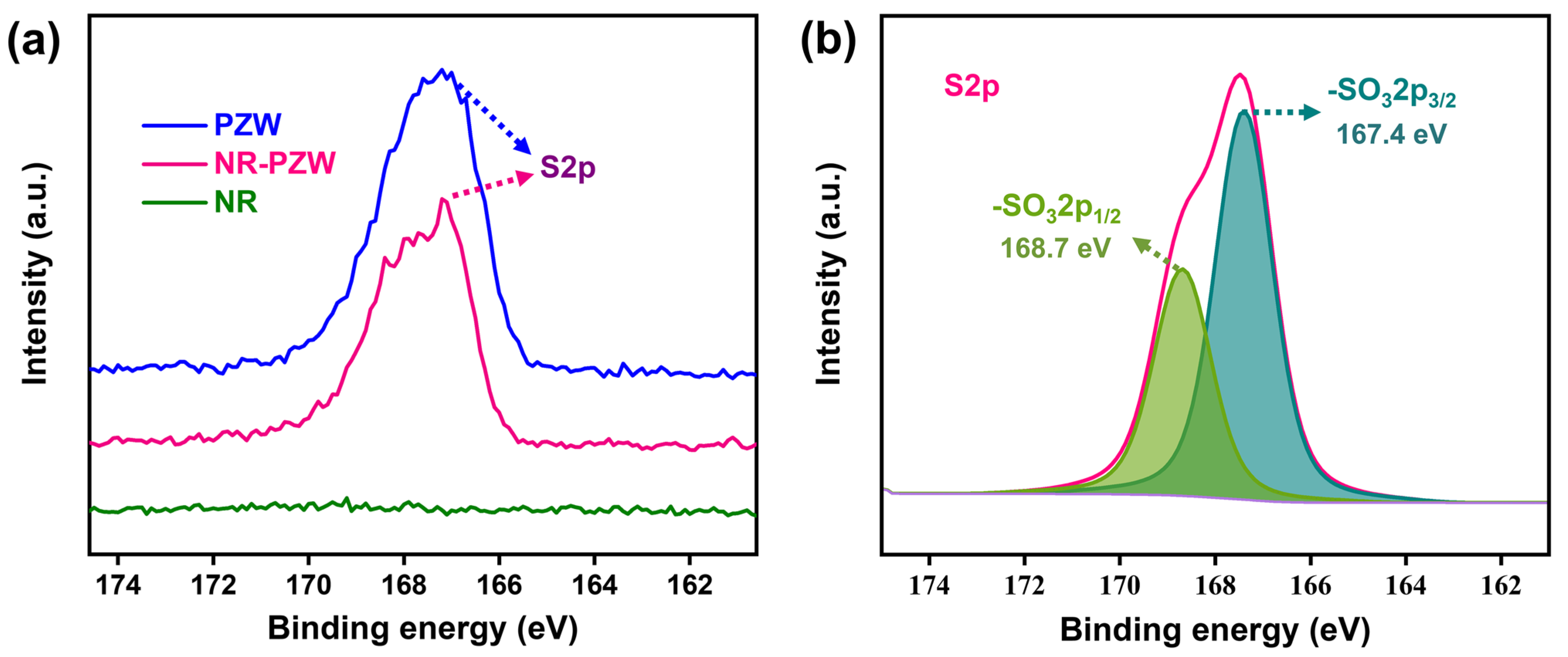
2.1. Basic Characterizations of the NR-PZW Hydrogel Membrane
2.2. Mechanical Properties of NR-PZW Hydrogel
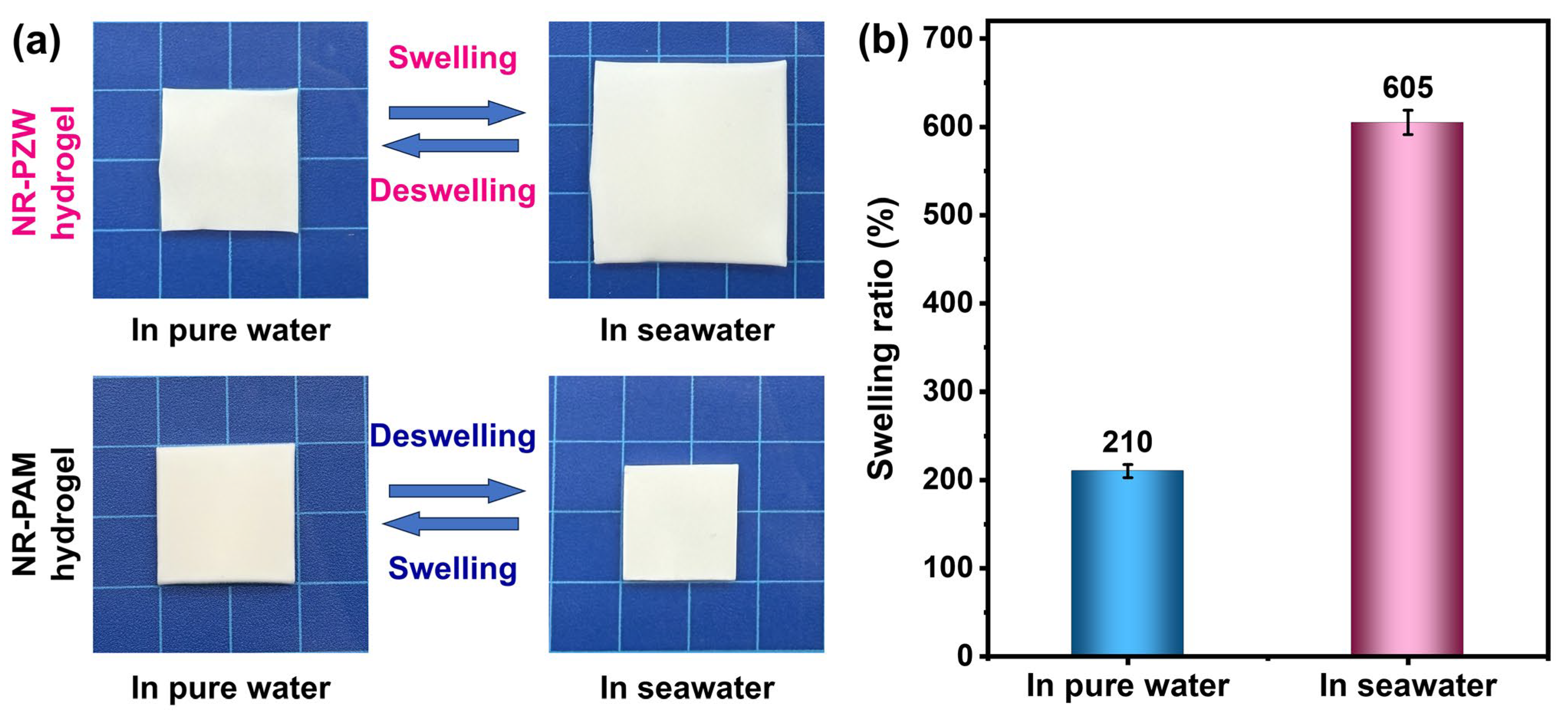
2.3. Swelling–Deswelling Performance of NR-PZW Hydrogel
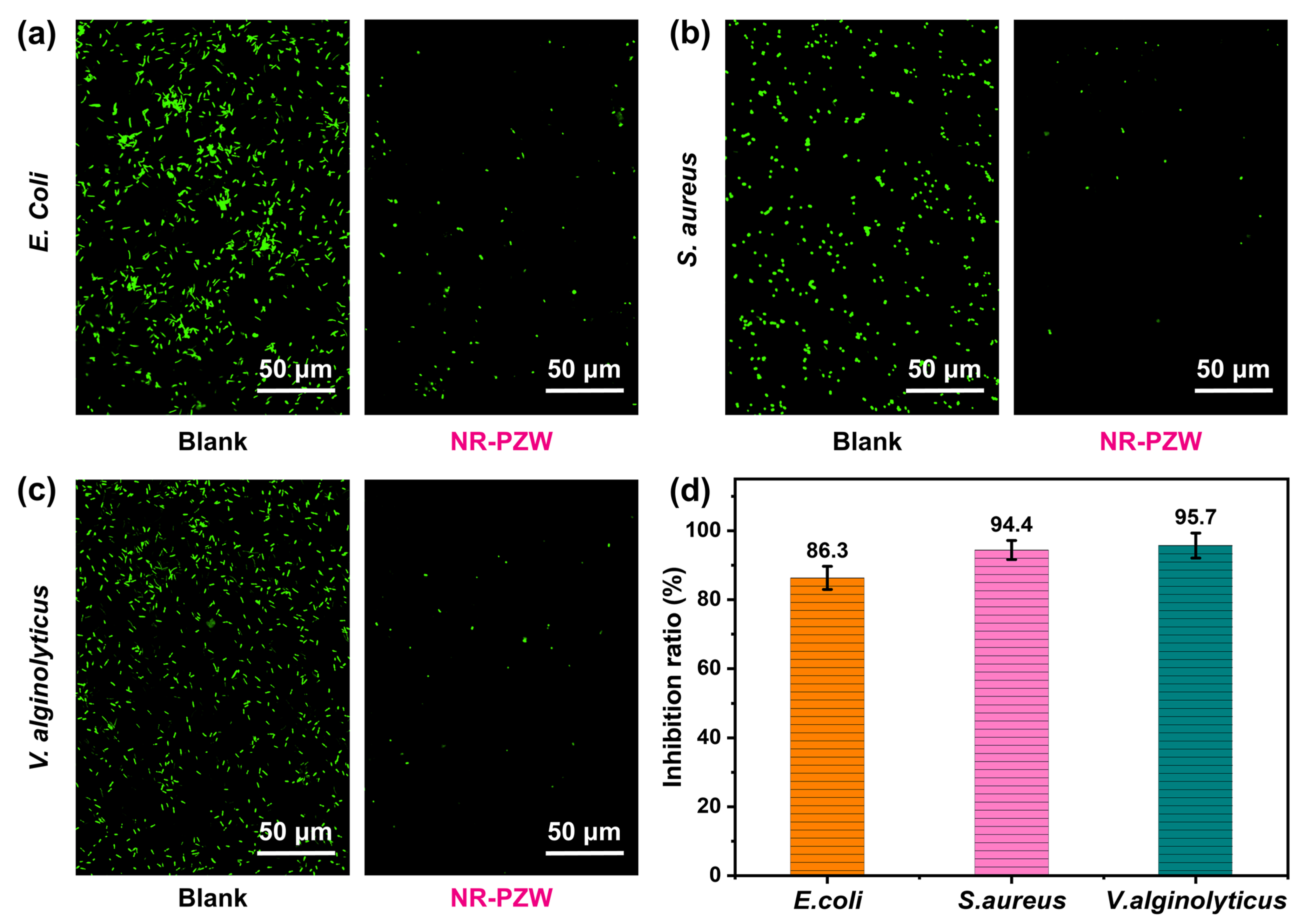
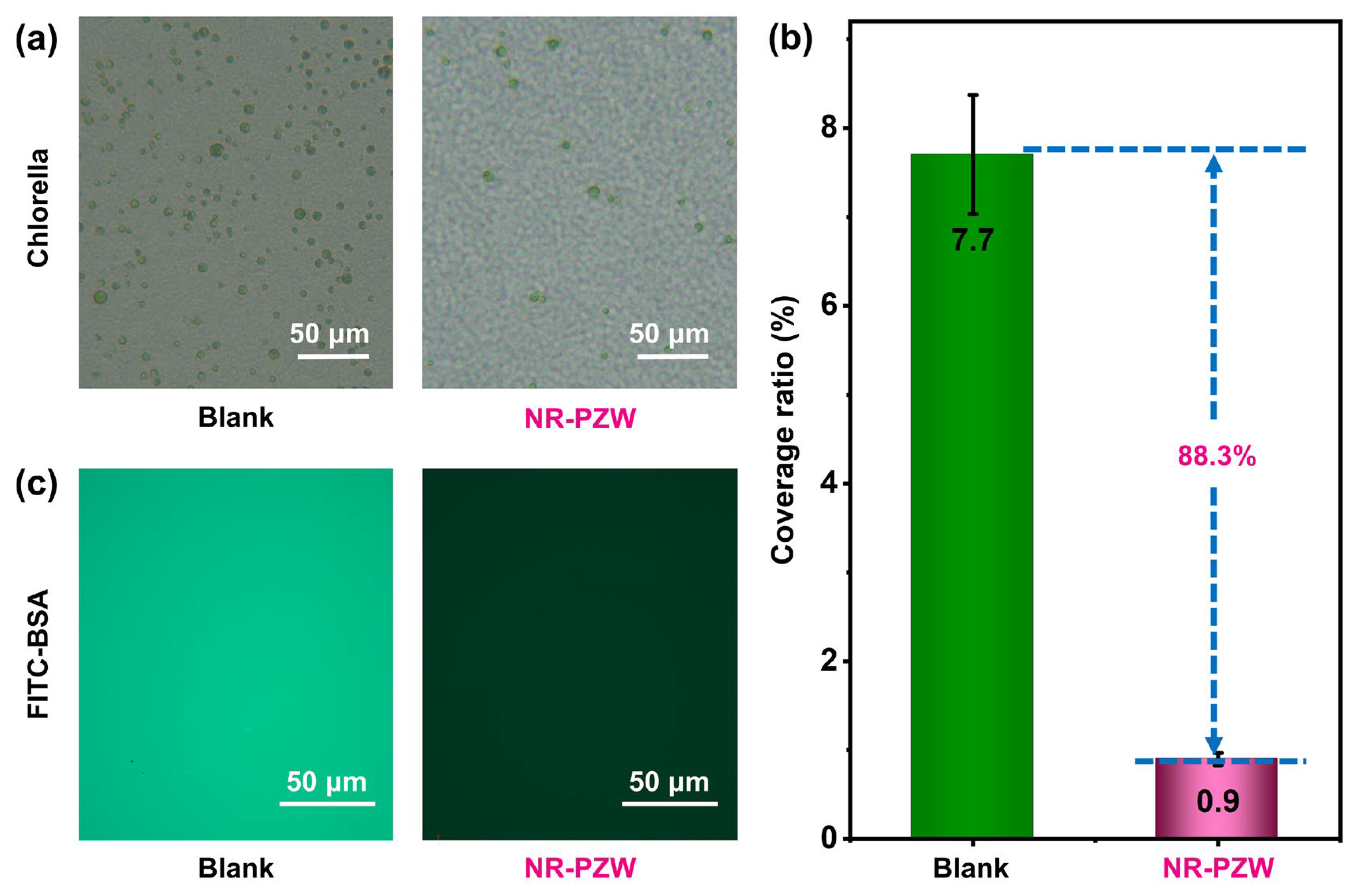
2.4. Anti-Biofouling Properties of NR-PZW Hydrogel
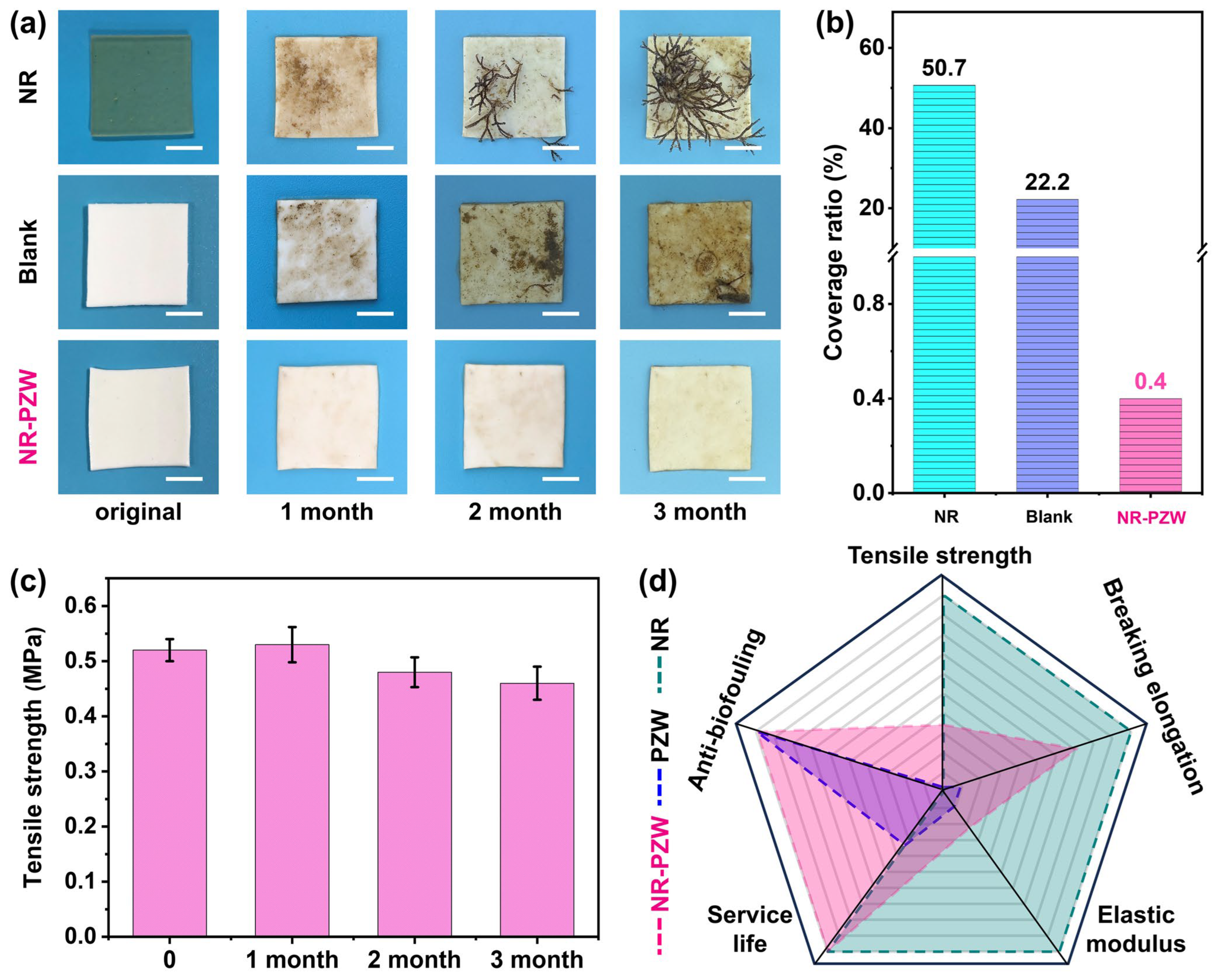
2.5. Anti-Biofouling Properties of NR-PZW Hydrogel in Real Marine Environment
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Characterization
4.3. Experimental Methods
4.3.1. Preparation of NR-PZW Composite Hydrogel
4.3.2. Swelling Performance Test of NR-PZW Composite Hydrogel
4.3.3. Antibacterial Adhesion Test of NR-PZW Composite Hydrogel
4.3.4. Anti-Algae Adhesion Test of NR-PZW Composite Hydrogel
4.3.5. Anti-Protein Adhesion Test of NR-PZW Composite Hydrogel
4.3.6. Real Marine Anti-Biofouling Test of NR-PZW Composite Hydrogel
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, L.; Yin, Y.; Jin, H.; Bing, W.; Jin, E.; Zhao, J.; Ren, L. Novel marine antifouling coatings inspired by corals. Mater. Today Chem. 2020, 17, 100294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Mishra, V.; Negi, S.; Kar, S. A systematic review on polymer-based superhydrophobic coating for preventing biofouling menace. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2023, 20, 1499–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.W.; Duan, J.Z.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.D.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Zhai, X.F.; Zhang, Y.M.; Wang, W.C.; Yang, Z.X.; Hou, B.R. Transparent and mechanically durable silicone/ZrO2 sol hybrid coating with enhanced antifouling properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 490, 151516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maan, A.M.C.; Hofman, A.H.; de Vos, W.M.; Kamperman, M. Recent developments and practical feasibility of polymer-based antifouling coatings. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.W.; Wang, T.T.; Liu, J.Q. Recent development of polydopamine anti-bacterial nanomaterials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 23, 7278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielo, I.; Giacobello, F.; Castellano, A.; Sfameni, S.; Rando, G.; Plutino, M.R. Development of antibacterial and antifouling innovative and eco-sustainable sol-gel based materials: From marine areas protection to healthcare applications. Gels 2022, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzullo, P.; Gruttadauria, M.; D’Anna, F. Quaternary ammonium salts-based materials: A review on environmental toxicity, anti-fouling mechanisms and applications in marine and water treatment industries. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Yu, Q.; Chen, H. Responsive and synergistic antibacterial coatings: Fighting against bacteria in a smart and effective way. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1801381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Yu, Q.; Chen, H. Dual-Function antibacterial surfaces to resist and kill bacteria: Printing a picture with two brushes simultaneously. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 70, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.Q.; Sun, J.W.; Wang, Q.F.; Duan, J.Z.; Liu, X.D.; Guo, D.; Hou, B.R. Eco-friendly covalently connected silicone hydrogel with negatively charged surface for marine anti-biofouling. Prog. Org. Coat. 2024, 197, 108833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V’edie, E.; Brisset, H.; Briand, J.F.; Bressy, C. Bioinspiration and microtopography as nontoxic strategies for marine bioadhesion control. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2100094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawignon, F.J.; Liu, J.B.; Qin, L.G.; Kouediatouka, A.N.; Ma, Z.Y.; Lv, B.H.; Dong, G.N. The optimization of biomimetic sharkskin riblet for the adaptation of drag reduction. Ocean Eng. 2023, 275, 114135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satasiya, G.; Kumar, M.A.; Ray, S. Biofouling dynamics and antifouling innovations: Transitioning from traditional biocides to nanotechnological interventions. Environ. Res. 2025, 269, 120943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, E.R.; Ferreira, O.; Ramalho, P.A.; Azevedo, N.F.; Bay’on, R.; Igartua, A.; Calhorda, M.J. Eco-friendly non-biocide-release coatings for marine biofouling prevention. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2499–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guazzelli, E.; Perondi, F.; Criscitiello, F.; Pretti, C.; Oliva, M.; Casu, V.; Martinelli, E. New amphiphilic copolymers for PDMS-based nanocomposite films with longterm marine antifouling performance. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 9764–9776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerström, M.; Wrange, A.L.; Oliveira, D.R.; Granhag, L.; Larsson, A.I.; Ytreberg, E. Are silicone foul-release coatings a viable and environmentally sustainable alternative to biocidal antifouling coatings in the Baltic Sea region? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 184, 114102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, J.C.; Domingues, J.M.; Miranda, C.S.; Felgueiras, H.P. Bioactivity of Chitosan-Based Particles Loaded with Plant-Derived Extracts for Biomedical Applications: Emphasis on Antimicrobial Fiber-Based Systems. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.M.; Gou, J.L.; Feng, H.M.; Sun, X.; Qin, X.D.; Wang, W.; Li, W.; Chen, S.G. Improved antifouling ability for double-network hydrogel coatings with excellent elastic and toughness under marine tidal environment. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 25, 2201801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivero-Lopez, M.; Muras, A.; Silva, D.; Serro, A.P.; Otero, A.; Concheiro, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C. Resveratrol-loaded hydrogel contact lenses with antioxidant and antibiofilm performance. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandel, D.R.; Kwak, D.; Lee, S.M.; Lim, Y.J.; Subedi, S.; Lee, J.W. Harnessing natural antifouling agents for enhancing water and wastewater treatment membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 359, 130254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, H.; Bernstein, R. Zwitterionic hydrogel modified reduced graphene oxide/ZnO nanocomposite blended membrane with high antifouling and antibiofouling performances. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 613, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.K.; Fang, Z.Q.; Hu, D.X.; Jiang, H.; Huang, L.; Mao, Q.T.; Wang, G.Q.; Li, J.P.; Liu, Z.Z.; Ma, C.X. Nano-CeO2-loaded polyzwitterionic double-network high-strength hydrogel for highly enhanced synergistic marine antifouling. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 38795–38807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Sun, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.W.; Chen, L.; Feng, X.L.; Wang, J.G.; Wang, N.; Zhang, D.; Ma, C.X. Anti-biofouling polyzwitterion-poly(amidoxime) composite hydrogel for highly enhanced uranium extraction from seawater. Gels 2024, 10, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Song, Y.; Park, S.; Kim, Y.; Mun, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, K.G.; Im, S.G. Synthesis of a stretchable polyampholyte hydrophilic film with compositional gradient for long-term stable, substrate-independent fouling-resistant coating. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2113253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.C.; Hu, Z.K.; Huang, Z.S.; Wu, S.W.; Yan, J.H.; Cen, K.F.; Bo, Z.; Xiong, G.P.; Ostrikov, K. Three-dimensional zwitterionic hydrogel-based evaporators with simultaneous ultrahigh evaporation rates and anti-fouling performance. Nano Energy 2024, 127, 109784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.S.; Wen, C.Y.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.C.; Zhu, Y.N.; Zheng, J.; Cheng, G.; Bai, J.; Xu, T.; Ji, J.; et al. Zwitterionic biomaterials. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 17073–17154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.P.; Katsuyama, Y.; Kurokawa, T.; Osada, Y. Double-network hydrogels with extremely high mechanical strength. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1155–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, R.; Shimano, K.; Okazaki, H.; Kurokawa, T.; Nakajima, T.; Nonoyama, T.; King, D.R.; Gong, J.P. Tough particle-based double network hydrogels for functional solid surface coatings. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 5, 1801018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.J.; Du, M.; Wu, Z.L.; Song, Y.H.; Zheng, Q. Strategy to construct polyzwitterionic hydrogel coating with antifouling, drag reducing and weak swelling performance. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 2081–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruseva, K.; Todorova, K.; Zhivkova, T.; Milcheva, R.; Ivanov, D.; Dimitrov, P.; Alexandrova, R.; Vassileva, E. Novel triple stimuli responsive interpenetrating poly(carboxybetaine methacrylate)/poly(sulfobetaine methacrylate) network. Gels 2023, 9, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, R.R.; Wen, S.X.; Wang, J.W.; Chen, L.; Yan, B.J.; Peng, S.Y.; Ma, C.; Cao, X.Y.; Ma, C.X. Antibiofouling ultrathin poly(amidoxime) membrane for enhanced U(VI) recovery from wastewater and seawater. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 21272–21285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.S.; Liu, J.Y.; Chen, R.R.; Yu, J.; Li, R.M.; Liu, P.L.; Wang, J. Mussel-inspired anti-biofouling and robust hybrid nanocomposite hydrogel for uranium extraction from seawater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 381, 120984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, S.; Ahmed, R.; Rehman, A.U.; García-Peñas, A.; Zahoor, A.; Khan, F.; Vatankhah-Varnosfaderani, M.; Alshahrani, T.; Stadler, F.J. Study of the synergistic influence of zwitterionic interactions and graphene oxide on water diffusion mechanism and mechanical properties in hybrid hydrogel network. Chemosphere 2023, 314, 137710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sällström, N.; Capel, A.; Lewis, M.P.; Engstrom, D.S.; Martin, S. 3D-printable zwitterionic nano-composite hydrogel system for biomedical applications. J. Tissue Eng. 2020, 11, 2041731420967294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H.; Li, Z.W.; Zhou, S.H.; Zhang, J.M.; Zong, L. Biomimetic multiscale oriented PVA/NRL hydrogel enabled multistimulus responsive and smart shape memory actuator. Small 2024, 20, 2311240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, L.X.; Hao, J.C. Emulsion-based organohydrogels with switchable wettability and underwater adhesion toward durable and ecofriendly marine antifouling coatings. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 3060–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; He, G.L.; Li, Y.L.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, W.Y.; Dong, L.; Yu, L.M.; Wang, L. Preparation and properties of composite amphiphilic hydrogel anti-fouling materials. Prog. Org. Coat. 2023, 179, 107527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.Q.; Li, X.Y.; Li, X.H.; Zheng, B.R.; Li, D.Z.; Xu, D.K.; Wang, F.H. Nacre-inspired metal-organic framework coatings reinforced by multiscale hierarchical cross-linking for integrated antifouling and anti-microbial corrosion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2305995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawit, H.; Mehmood, S.; Hussain, Z.; Islam, S.R.; Wang, Z.L.; Cao, Y.; Liu, X.Z.; Wang, Z.X.; Pei, R.J. Fabrication of nanoparticle-reinforced composite hydrogel for improved durability, antifouling, and thrombosis-resistance in arteriovenous grafts. Colloids Surf. B 2024, 247, 114420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ru, R.T.; Ge, C.J.; Zhang, L.L.; Sun, H.F. Construction of highly hydrated and mechanically strong anti-fouling coatings for deep-sea probes based on poly(vinyl alcohol) tannic acid zwitterion coatings. New J. Chem. 2024, 48, 11729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.M.; Qi, Y.H.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Q.; Gu, C.J.; Zhang, Z.P. Highly efficient antifouling and toughening hydrogel for ship coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 662, 160102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ref | Hydrogels | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Breaking Elongation (%) | Anti-Bacterial | Anti-Algae | Anti-Protein | Marine Test (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This work | NR-PZW | 0.52 | 738 | √ | √ | √ | 90 |
| [29] | PSBMA/PAA | 0.4 | 251 | √ | √ | ||
| [36] | COHG | 0.1 | 310 | √ | |||
| [37] | amphiphilic | 0.1 | 23 | √ | √ | 30 | |
| [38] | MOF/SA | 0.4 | 580 | √ | √ | √ | |
| [22] | PSBMA/PVA | 2.4 | 420 | √ | √ | √ | 180 |
| [39] | SBMA/PVA/SA | 0.1 | 42 | √ | √ | ||
| [23] | ZW/PAO | 0.1 | 63 | √ | 25 | ||
| [40] | TA/PVA | 0.4 | 228 | √ | √ | 90 | |
| [41] | PEG | 0.4 | 1600 | √ | √ | 120 | |
| [10] | Gel/TA/Si | 1.0 | 197 | √ | √ | 180 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; John, D.; Yan, Y.; Feng, X.; Wei, Q.; Ma, C.; Liu, Z.; Mao, H.; Wong, T.-W.; Chen, Y. A Robust Natural Rubber–Polyzwitterion Composite Hydrogel for Highly Enhanced Marine Anti-Biofouling. Gels 2025, 11, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11030203
Sun Y, John D, Yan Y, Feng X, Wei Q, Ma C, Liu Z, Mao H, Wong T-W, Chen Y. A Robust Natural Rubber–Polyzwitterion Composite Hydrogel for Highly Enhanced Marine Anti-Biofouling. Gels. 2025; 11(3):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11030203
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Ye, Dominic John, Yuxin Yan, Xueliang Feng, Qingrong Wei, Chunxin Ma, Zhenzhong Liu, Haimei Mao, Tuck-Whye Wong, and Yun Chen. 2025. "A Robust Natural Rubber–Polyzwitterion Composite Hydrogel for Highly Enhanced Marine Anti-Biofouling" Gels 11, no. 3: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11030203
APA StyleSun, Y., John, D., Yan, Y., Feng, X., Wei, Q., Ma, C., Liu, Z., Mao, H., Wong, T.-W., & Chen, Y. (2025). A Robust Natural Rubber–Polyzwitterion Composite Hydrogel for Highly Enhanced Marine Anti-Biofouling. Gels, 11(3), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11030203








