Ibuprofen-Loaded, Nanocellulose-Based Buccal Films: The Development and Evaluation of Promising Drug Delivery Systems for Special Populations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Development of Film Casting Formulations and IBU Incorporation
2.2. Rheology of Film Casting Hydrogels
2.3. DSC Analysis of IBU-Loaded Films
2.4. Thickness and IBU Loading Capacity of Films
2.5. Film Disintegration Behavior
2.6. Evaluation of IBU Release from Films
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Development of IBU-Loaded SMEDDS
4.2.1. Study of IBU Solubility
4.2.2. HPLC Analysis
4.2.3. Ternary Phase Diagram Construction
4.2.4. Microemulsion Loading with Ibuprofen
4.3. Development of Buccal Film Formulations
4.3.1. Rheological Study
4.3.2. DSC Analysis
4.3.3. Film Thickness Measurement
4.3.4. Total Content of IBU in Films
4.4. Determination of Disintegration Time
4.4.1. Basket Method
4.4.2. The Droplet Method
4.5. IBU Release from Films
4.5.1. USP I Method
4.5.2. Flow-Through Dissolution Method
4.5.3. Dissolution Results Analysis
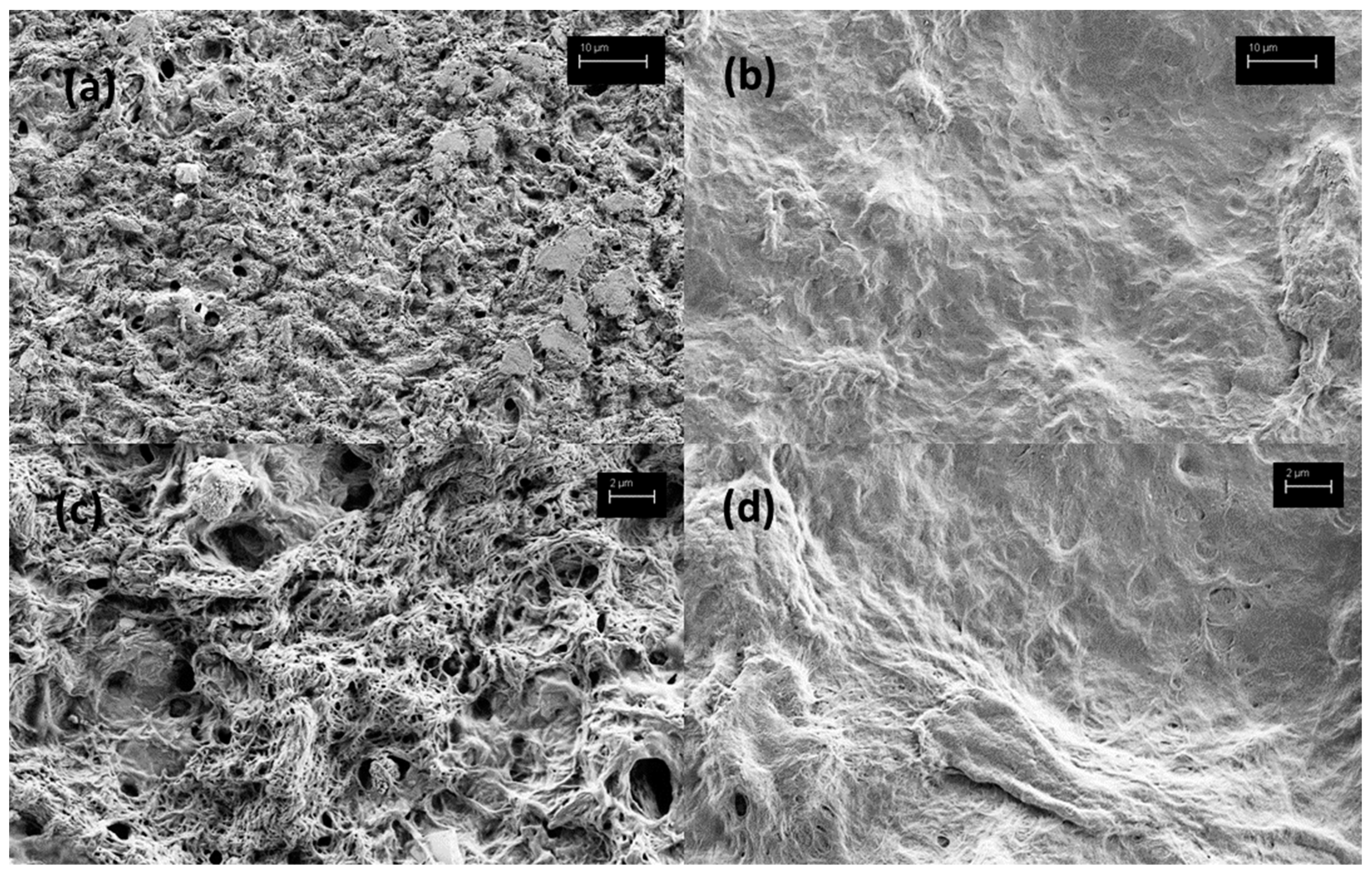
4.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacob, S.; Nair, A.B.; Boddu, S.H.S.; Gorain, B.; Sreeharsha, N.; Shah, J. An Updated Overview of the Emerging Role of Patch and Film-Based Buccal Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.S.; Kumar, T.P.; Gowda, D.V. Orodispersible Thin Film: A New Patient-Centered Innovation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Zhu, L.; Yang, N.; Li, H.; Yang, Q. Recent Advances of Oral Film as Platform for Drug Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 604, 120759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.O.; Brayden, D.J. Buccal Delivery of Small Molecules and Biologics: Of Mucoadhesive Polymers, Films, and Nanoparticles. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2017, 36, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montenegro-Nicolini, M.; Morales, J.O. Overview and Future Potential of Buccal Mucoadhesive Films as Drug Delivery Systems for Biologics. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shipp, L.; Liu, F.; Kerai-Varsani, L.; Okwuosa, T.C. Buccal Films: A Review of Therapeutic Opportunities, Formulations & Relevant Evaluation Approaches. J. Control Release 2022, 352, 1071–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, V.V.; Cabrera, P.; Ramírez-Lecaros, C.; Jara, M.O.; Brayden, D.J.; Morales, J.O. Buccal Delivery of Small Molecules and Biologics: Of Mucoadhesive Polymers, Films, and Nanoparticles—An Update. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 636, 122789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.L.; Fang, Y.; Han, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.Y.; Chow, S.F.; Lam, T.N.; Lee, W.Y.T. Orally-Dissolving Film for Sublingual and Buccal Delivery of Ropinirole. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 163, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, G.M.; Selmin, F.; Musazzi, U.M.; Gennari, C.G.M.; Minghetti, P.; Cilurzo, F. Trends in the Characterization Methods of Orodispersible Films. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaraju, T.; Gowthami, R.; Rajashekar, M.; Sandeep, S.; Mallesham, M.; Sathish, D.; Kumar, Y.S. Comprehensive Review on Oral Disintegrating Films. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yir-Erong, B.; Bayor, M.T.; Ayensu, I.; Gbedema, S.Y.; Boateng, J.S. Oral Thin Films as a Remedy for Noncompliance in Pediatric and Geriatric Patients. Ther. Deliv. 2019, 10, 443–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, J.O.; McConville, J.T. Manufacture and Characterization of Mucoadhesive Buccal Films. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 77, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.; Raj, M.C.; Joy, J.; Moores, A.; Drisko, G.L.; Sanchez, C. Nanocellulose, a Versatile Green Platform: From Biosources to Materials and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 11575–11625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimian, A.; Parsian, H.; Majidinia, M.; Rahimi, M.; Mir, S.M.; Samadi Kafil, H.; Shafiei-Irannejad, V.; Kheyrollah, M.; Ostadi, H.; Yousefi, B. Nanocrystalline Cellulose: Preparation, Physicochemical Properties, and Applications in Drug Delivery Systems. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, J.K.; Letchford, K.; Wasserman, B.Z.; Ye, L.; Hamad, W.Y.; Burt, H.M. The Use of Nanocrystalline Cellulose for the Binding and Controlled Release of Drugs. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huq, T.; Vu, K.D.; Riedl, B.; Bouchard, J.; Han, J.; Lacroix, M. Development of Probiotic Tablet Using Alginate, Pectin, and Cellulose Nanocrystals as Excipients. Cellulose 2016, 23, 1967–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolko Seljak, K.; Sterle Zorec, B.; Gosenca Matjaž, M. Nanocellulose-Based Film-Forming Hydrogels for Improved Outcomes in Atopic Skin. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poonguzhali, R.; Basha, S.K.; Kumari, V.S. Synthesis and Characterization of Chitosan-PVP-Nanocellulose Composites for in-Vitro Wound Dressing Application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, S.; Mandal, S.D.; Chuttani, K.; Sawant, K.K.; Subudhi, B.B. Design and Evaluation of Mucoadhesive Microemulsion for Neuroprotective Effect of Ibuprofen Following Intranasal Route in the MPTP Mice Model. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 42, 1340–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, Y.; Chen, S.; Hanawa, T. Solubility Enhancement of Ibuprofen by Adsorption onto Spherical Porous Calcium Silicate. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, J.; Luan, Y.; Li, F.; Cai, X.; Du, J.; Li, Z. Ibuprofen-Loaded Poly(Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid) Films for Controlled Drug Release. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, A.P.; Badshah, S.; Airoldi, C. Ibuprofen-Loaded Chitosan and Chemically Modified Chitosans—Release Features from Tablet and Film Forms. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 52, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Lin, J.; Jing, H.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Duan, Y. Recent Progress in Orodispersible Films-Mediated Therapeutic Applications: A Review. MedComm-Biomater. Appl. 2023, 2, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilc, B.; Planinšek, O. Evaluation of Monolayer and Bilayer Buccal Films Containing Metoclopramide. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Pharmacopoeia Online. Available online: https://pheur.edqm.eu/home (accessed on 29 November 2024).
- Bolko, K.; Zvonar, A.; Gašperlin, M. Mixed Lipid Phase SMEDDS as an Innovative Approach to Enhance Resveratrol Solubility. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2014, 40, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seljak, K.B.; Berginc, K.; Trontelj, J.; Zvonar, A.; Kristl, A.; Gašperlin, M. A Self-Microemulsifying Drug Delivery System to Overcome Intestinal Resveratrol Toxicity and Presystemic Metabolism. JPharmSci 2014, 103, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadhban, H.Y.; Ahmed, K.K. Nanosuspension-Based Repaglinide Fast-Dissolving Buccal Film for Dissolution Enhancement. AAPS PharmSciTech 2024, 25, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aranaz, I.; Alcántara, A.R.; Civera, M.C.; Arias, C.; Elorza, B.; Heras Caballero, A.; Acosta, N. Chitosan: An Overview of Its Properties and Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grilc, B.; Felicijan, T.; Parfant, T.P.; Planinšek, O. Formulation and Characterization of Buccal Films Containing Valsartan with Additional Support from Image Analysis. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.C.; Rocha, A.I.; Leal, P.; Estanqueiro, M.; Lobo, J.M.S. Development and Characterization of Mucoadhesive Buccal Gels Containing Lipid Nanoparticles of Ibuprofen. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 533, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilc, B.; Zdovc, J.; Planinšek, O. Advanced Flow Cell Design for in Vitro Release Testing of Mucoadhesive Buccal Films. Acta Pharm. 2020, 70, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, M.; Zhou, J.; Zou, A.; Li, W.; Yao, C.; Xie, S. DDSolver: An Add-In Program for Modeling and Comparison of Drug Dissolution Profiles. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



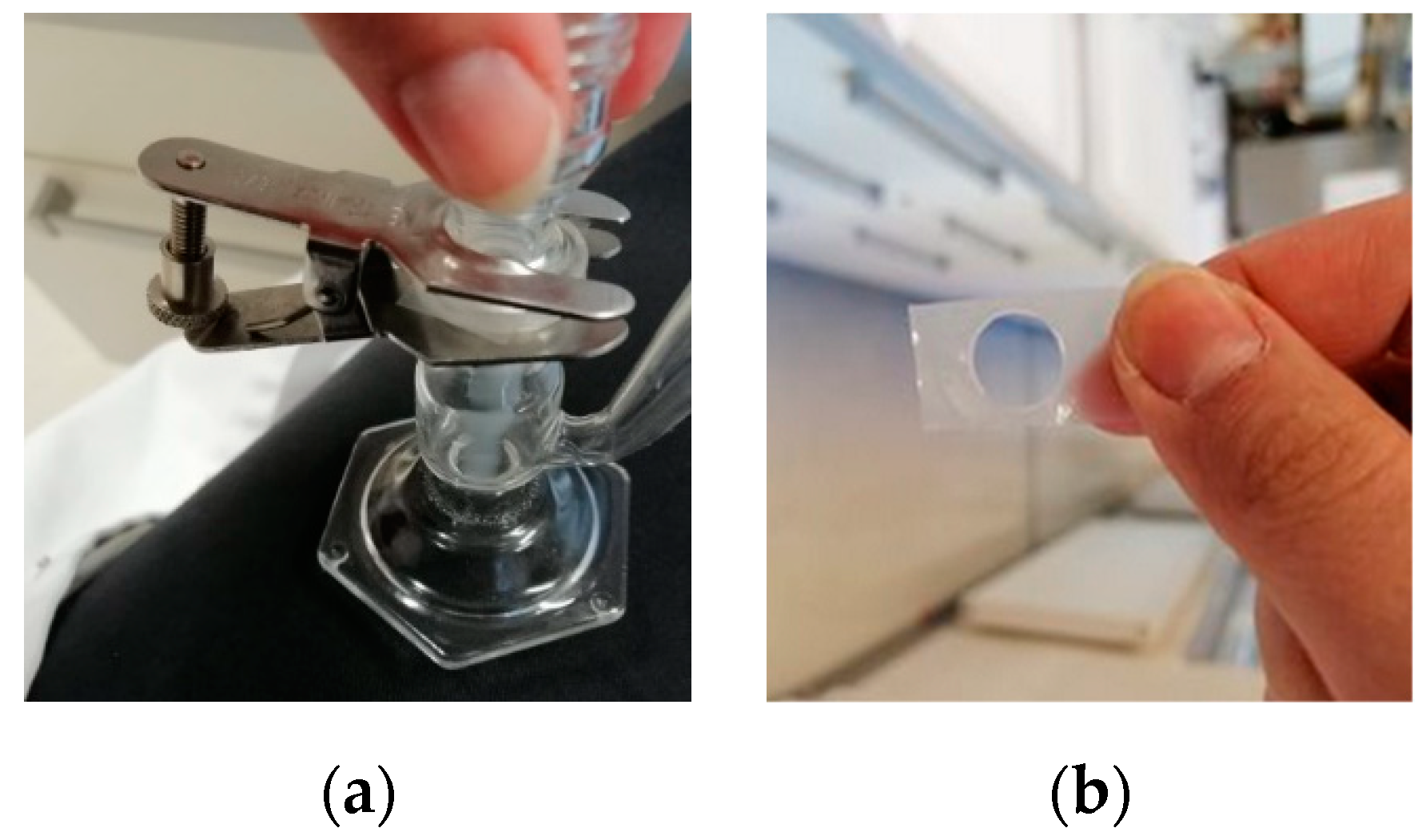

| Phase Type | Excipient | Saturated Solubility of IBU [mg/g] |
|---|---|---|
| Surfactant | Tween 20 | 272.16 |
| Kolliphor EL | 264.00 | |
| Labrasol | 258.50 | |
| Tween 80 | 254.66 | |
| Tween 85 | 225.40 | |
| Labrafil M2125 CS | 123.14 | |
| Oil | Capmul MCM | 196.58 |
| Oleic acid | 150.27 | |
| Castor oil | 139.64 |
| SAMPLE | gNCC/pNCC | ALG/PEC/CHI | Glycerol | Ibuprofen | SMEDDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gNCC–ALG | 1% | 2% | 3% | / | 3.4% |
| gNCC–ALG–IBU | 1% | 2% | 3% | 0.6% | 3.4% |
| pNCC–ALG | 1% | 2% | 3% | / | 3.4% |
| pNCC–ALG–IBU | 1% | 2% | 3% | 0.6% | 3.4% |
| gNCC–PEC | 0.6% | 1.2% | 3% | / | 3.4% |
| gNCC–PEC–IBU | 0.6% | 1.2% | 3% | 0.6% | 3.4% |
| pNCC–PEC | 0.57% | 1.15% | 3% | / | 3.4% |
| pNCC–PEC–IBU | 0.57% | 1.15% | 3% | 0.6% | 3.4% |
| gNCC–CHI | 0.5% | 1% | 3% | / | 3.4% |
| gNCC–CHI–IBU | 0.5% | 1% | 3% | 0.6% | 3.4% |
| pNCC–CHI | 0.5% | 1% | 3% | / | 3.4% |
| pNCC–CHI–IBU | 0.5% | 1% | 3% | 0.6% | 3.4% |
| Sample | Thickness [mm] | Total Weight [mg] | IBU Content [mg/per Film] | IBU/Film [%, m/m] | mg IBU/cm2 Film Surface |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gNCC–ALG–IBU | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 62.54 ± 3.61 | 3.71 ± 0.14 | 5.93 | 0.82 |
| pNCC–ALG–IBU | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 70.92 ± 3.68 | 3.60 ± 0.37 | 5.07 | 0.80 |
| gNCC–PEC–IBU | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 28.92 ± 1.29 | 1.76 ± 0.07 | 6.08 | 0.39 |
| pNCC–PEC–IBU | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 55.74 ± 4.08 | 2.43 ± 0.26 | 4.35 | 0.54 |
| gNCC–CHI–IBU | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 9.72 ± 1.09 | 1.86 ± 0.27 | 19.14 | 0.41 |
| pNCC–CHI–IBU | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 20.93 ± 1.64 | 0.91 ± 0.14 | 4.34 | 0.20 |
| Sample | Disintegration Time Basket Method [s] | Disintegration Time Droplet Method [s] |
|---|---|---|
| gNCC–ALG | 22.0 ± 3.5 | 112.8 ± 18.6 |
| gNCC–ALG–IBU | 26.0 ± 2.1 | 120.5 ± 6.0 |
| pNCC–ALG | 57.3 ± 5.6 | 451.0 ± 78.5 |
| pNCC–ALG–IBU | 56.0 ± 5.0 | 462.8 ± 74.6 |
| gNCC–PEC | 18.5 ± 1.0 | 31.5 ± 2.6 |
| gNCC–PEC–IBU | 17.3 ± 2.2 | 95.5 ± 12.7 |
| pNCC–PEC | 29.8 ± 2.1 | 220.5 ± 34.7 |
| pNCC–PEC–IBU | 29.5 ± 1.3 | 221.3 ± 25.5 |
| Lipid Phase | Surfactant | Lipid/Surfactant Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Capmul MCM | Tween 20 | 2/8 |
| 3/7 | ||
| 4/6 | ||
| Kolliphor EL | 2/8 | |
| 3/7 | ||
| 4/6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bolko Seljak, K.; Grilc, B.; Gašperlin, M.; Gosenca Matjaž, M. Ibuprofen-Loaded, Nanocellulose-Based Buccal Films: The Development and Evaluation of Promising Drug Delivery Systems for Special Populations. Gels 2025, 11, 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11030163
Bolko Seljak K, Grilc B, Gašperlin M, Gosenca Matjaž M. Ibuprofen-Loaded, Nanocellulose-Based Buccal Films: The Development and Evaluation of Promising Drug Delivery Systems for Special Populations. Gels. 2025; 11(3):163. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11030163
Chicago/Turabian StyleBolko Seljak, Katarina, Blaž Grilc, Mirjana Gašperlin, and Mirjam Gosenca Matjaž. 2025. "Ibuprofen-Loaded, Nanocellulose-Based Buccal Films: The Development and Evaluation of Promising Drug Delivery Systems for Special Populations" Gels 11, no. 3: 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11030163
APA StyleBolko Seljak, K., Grilc, B., Gašperlin, M., & Gosenca Matjaž, M. (2025). Ibuprofen-Loaded, Nanocellulose-Based Buccal Films: The Development and Evaluation of Promising Drug Delivery Systems for Special Populations. Gels, 11(3), 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11030163








