Vaccine-Mediated Protection of Mice Against African and Asian Clinical Strains of Cryptococcus neoformans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
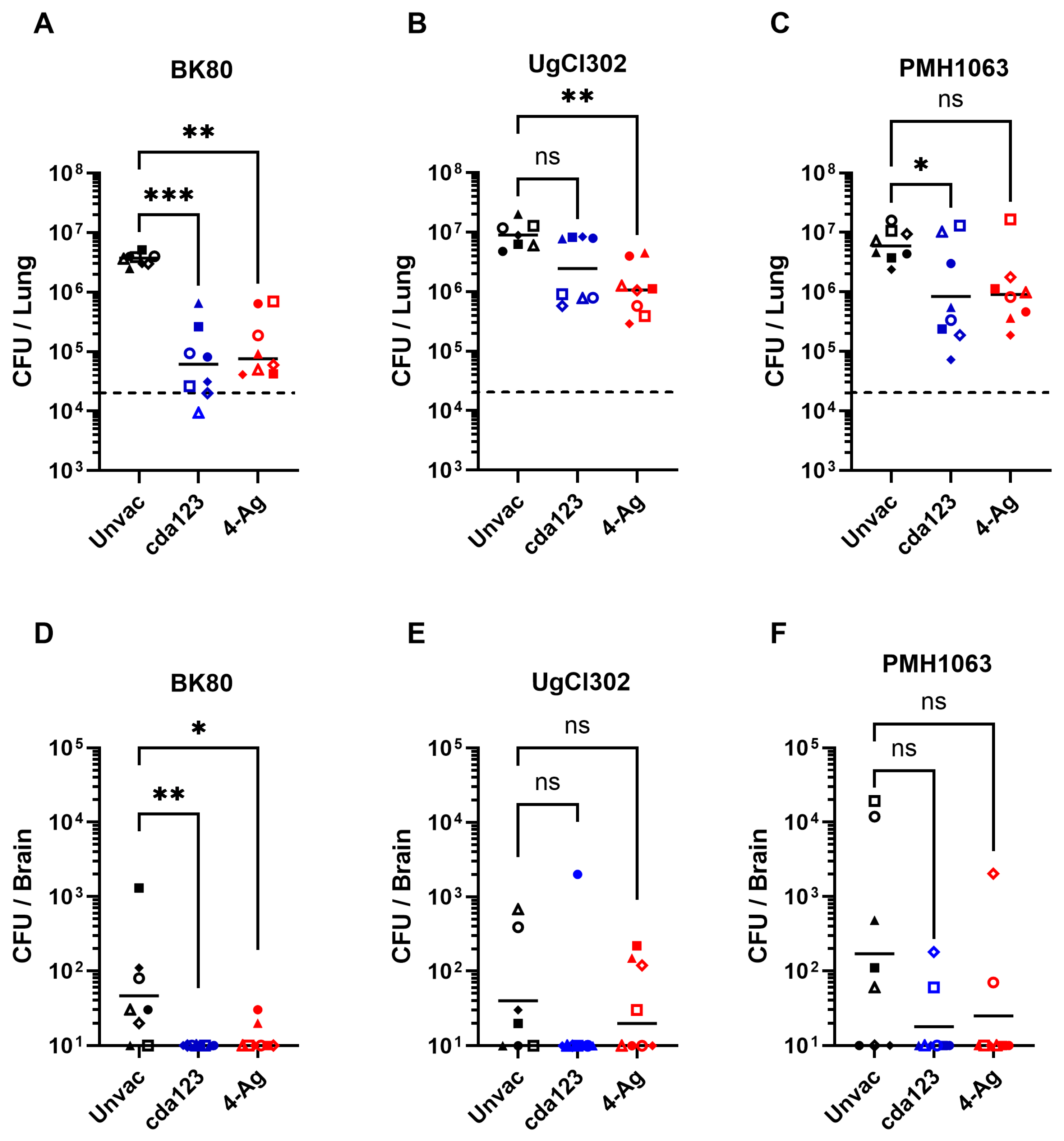
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Cda | Chitin deacetylase |
| cda123 | cda1Δ2Δ3Δ avirulent cryptococcus strain |
| CAF01 | Cationic adjuvant formulation 01 |
| 4-Ag | Four-antigen vaccine |
| Cpd1Δ | Carboxypeptidase 1 trimmed of its region of human homology |
| Blp4 | Barwin-like domain protein 4 |
| YPD | Yeast-peptone-dextrose |
| Ova DPI | Ovalbumin Days post infection |
References
- Meya, D.B.; Williamson, P.R. Cryptococcal Disease in Diverse Hosts. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 1597–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasingham, R.; Govender, N.P.; Jordan, A.; Loyse, A.; Shroufi, A.; Denning, D.W.; Meya, D.B.; Chiller, T.M.; Boulware, D.R. The global burden of HIV-associated cryptococcal infection in adults in 2020: A modelling analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 1748–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagen, F.; Khayhan, K.; Theelen, B.; Kolecka, A.; Polacheck, I.; Sionov, E.; Falk, R.; Parnmen, S.; Lumbsch, H.T.; Boekhout, T. Recognition of seven species in the Cryptococcus gattii/Cryptococcus neoformans species complex. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2015, 78, 16–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon-Chung, K.J.; Bennett, J.E.; Wickes, B.L.; Meyer, W.; Cuomo, C.A.; Wollenburg, K.R.; Bicanic, T.A.; Castaneda, E.; Chang, Y.C.; Chen, J.; et al. The Case for Adopting the “Species Complex” Nomenclature for the Etiologic Agents of Cryptococcosis. mSphere 2017, 2, e00357-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desjardins, C.A.; Giamberardino, C.; Sykes, S.M.; Yu, C.H.; Tenor, J.L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, T.; Jones, A.M.; Sun, S.; Haverkamp, M.R.; et al. Population genomics and the evolution of virulence in the fungal pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 1207–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litvintseva, A.P.; Thakur, R.; Vilgalys, R.; Mitchell, T.G. Multilocus Sequence Typing Reveals Three Genetic Subpopulations of Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii (Serotype A), Including a Unique Population in Botswana. Genetics 2006, 172, 2223–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, K.M.; Kono, T.J.Y.; Betancourt, J.J.; Wang, Y.; Kabbale, K.D.; Ding, M.; Kezh, P.; Ha, G.; Yoder, J.M.; Fulton, S.R.; et al. Single nucleotide polymorphisms are associated with strain-specific virulence differences among clinical isolates of Cryptococcus neoformans. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassaza, K.; Wasswa, F.; Nielsen, K.; Bazira, J. Cryptococcus neoformans Genotypic Diversity and Disease Outcome Among HIV Patients in Africa. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.V.N.; Wang, R.; Specht, C.A.; Levitz, S.M. Vaccines for human fungal diseases: Close but still a long way to go. npj Vaccines 2021, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, C.A.; Wang, R.; Oliveira, L.V.N.; Hester, M.M.; Gomez, C.; Mou, Z.; Carlson, D.; Lee, C.K.; Hole, C.R.; Lam, W.C.; et al. Immunological correlates of protection mediated by a whole organism, Cryptococcus neoformans, vaccine deficient in chitosan. mBio 2024, 15, e0174624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhya, R.; Lam, W.C.; Maybruck, B.; Specht, C.A.; Levitz, S.M.; Lodge, J.K. Induction of Protective Immunity to Cryptococcal Infection in Mice by a Heat-Killed, Chitosan-Deficient Strain of Cryptococcus neoformans. mBio 2016, 7, e0054700516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Oliveira, L.V.N.; Hester, M.M.; Carlson, D.; Christensen, D.; Specht, C.A.; Levitz, S.M. Protection against experimental cryptococcosis elicited by Cationic Adjuvant Formulation 01-adjuvanted subunit vaccines. PLOS Pathog. 2024, 20, e1012220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hester, M.M.; Lee, C.K.; Abraham, A.; Khoshkenar, P.; Ostroff, G.R.; Levitz, S.M.; Specht, C.A. Protection of mice against experimental cryptococcosis using glucan particle-based vaccines containing novel recombinant antigens. Vaccine 2020, 38, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, C.A.; Lee, C.K.; Huang, H.; Hester, M.M.; Liu, J.; Luckie, B.A.; Torres Santana, M.A.; Mirza, Z.; Khoshkenar, P.; Abraham, A.; et al. Vaccination with Recombinant Cryptococcus Proteins in Glucan Particles Protects Mice against Cryptococcosis in a Manner Dependent upon Mouse Strain and Cryptococcal Species. mBio 2017, 8, e01872-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, G.K.; Andersen, P.; Christensen, D. Immunocorrelates of CAF family adjuvants. Semin. Immunol. 2018, 39, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, K.; Cox, G.M.; Wang, P.; Toffaletti, D.L.; Perfect, J.R.; Heitman, J. Sexual cycle of Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii and virulence of congenic a and alpha isolates. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 4831–4841. [Google Scholar]
- Janbon, G.; Ormerod, K.L.; Paulet, D.; Byrnes, E.J., 3rd; Yadav, V.; Chatterjee, G.; Mullapudi, N.; Hon, C.C.; Billmyre, R.B.; Brunel, F.; et al. Analysis of the genome and transcriptome of Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii reveals complex RNA expression and microevolution leading to virulence attenuation. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvintseva, A.P.; Mitchell, T.G. Most environmental isolates of Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii (serotype A) are not lethal for mice. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 3188–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukaremera, L.; McDonald, T.R.; Nielsen, J.N.; Molenaar, C.J.; Akampurira, A.; Schutz, C.; Taseera, K.; Muzoora, C.; Meintjes, G.; Meya, D.B.; et al. The Mouse Inhalation Model of Cryptococcus neoformans Infection Recapitulates Strain Virulence in Humans and Shows that Closely Related Strains Can Possess Differential Virulence. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, e00046-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanh, L.T.; Toffaletti, D.L.; Tenor, J.L.; Giamberardino, C.; Sempowski, G.D.; Asfaw, Y.; Phan, H.T.; Van Duong, A.; Trinh, N.M.; Thwaites, G.E.; et al. Assessing the virulence of Cryptococcus neoformans causing meningitis in HIV infected and uninfected patients in Vietnam. Med. Mycol. 2020, 58, 1149–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiesner, D.L.; Moskalenko, O.; Corcoran, J.M.; McDonald, T.; Rolfes, M.A.; Meya, D.B.; Kajumbula, H.; Kambugu, A.; Bohjanen, P.R.; Knight, J.F.; et al. Cryptococcal genotype influences immunologic response and human clinical outcome after meningitis. mBio 2012, 3, e00196-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, P.M.; Thanh, L.T.; Trieu, P.H.; Van Anh, D.; Trinh, N.M.; Beardsley, J.; Kibengo, F.; Chierakul, W.; Dance, D.A.B.; Rattanavong, S.; et al. Three phylogenetic groups have driven the recent population expansion of Cryptococcus neoformans. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulware, D.R.; von Hohenberg, M.; Rolfes, M.A.; Bahr, N.C.; Rhein, J.; Akampurira, A.; Williams, D.A.; Taseera, K.; Schutz, C.; McDonald, T.; et al. Human Immune Response Varies by the Degree of Relative Cryptococcal Antigen Shedding. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2015, 3, ofv194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, K.; Marra, R.E.; Hagen, F.; Boekhout, T.; Mitchell, T.G.; Cox, G.M.; Heitman, J. Interaction between genetic background and the mating-type locus in Cryptococcus neoformans virulence potential. Genetics 2005, 171, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.-H.; Sephton-Clark, P.; Tenor, J.L.; Toffaletti, D.L.; Giamberardino, C.; Haverkamp, M.; Cuomo, C.A.; Perfect, J.R. Gene Expression of Diverse Cryptococcus Isolates during Infection of the Human Central Nervous System. mBio 2021, 12, e02313-02321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.V.N.; Hargarten, J.C.; Wang, R.; Carlson, D.; Park, Y.-D.; Specht, C.A.; Williamson, P.R.; Levitz, S.M. Peripheral blood CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses to Cryptococcus candidate vaccine antigens in human subjects with and without cryptococcosis. J. Infect. 2025, 91, 106521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Oliveira, L.V.N.; Lourenco, D.; Gomez, C.L.; Lee, C.K.; Hester, M.M.; Mou, Z.; Ostroff, G.R.; Specht, C.A.; Levitz, S.M. Immunological correlates of protection following vaccination with glucan particles containing Cryptococcus neoformans chitin deacetylases. npj Vaccines 2023, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Litvintseva, A.P.; Frazzitta, A.E.; Haverkamp, M.R.; Wang, L.; Fang, C.; Muthoga, C.; Mitchell, T.G.; Perfect, J.R. Comparative analyses of clinical and environmental populations of Cryptococcus neoformans in Botswana. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 3559–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, M.A.; David-Palma, M.; Aylward, J.; Pham, N.Q.; Visagie, C.M.; Fuchs, T.; Yilmaz, N.; Roets, F.; Sun, S.; Taylor, J.W.; et al. Decoding Cryptococcus: From African biodiversity to worldwide prevalence. PLOS Pathog. 2025, 21, e1012876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira-Paim, K.; Andrade-Silva, L.; Fonseca, F.M.; Ferreira, T.B.; Mora, D.J.; Andrade-Silva, J.; Khan, A.; Dao, A.; Reis, E.C.; Almeida, M.T.G.; et al. MLST-Based Population Genetic Analysis in a Global Context Reveals Clonality amongst Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii VNI Isolates from HIV Patients in Southeastern Brazil. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.N.; Qihui, S.; Thanh, L.T.; Trieu, P.H.; Van, A.D.; Thu, N.H.; Chau, T.T.H.; Lan, N.P.H.; Chau, N.V.V.; Ashton, P.M.; et al. Comparative genomics of Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii associated with meningitis in HIV infected and uninfected patients in Vietnam. PLOS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyke, M.C.C.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Hardison, S.E.; Leopold Wager, C.M.; Castro-Lopez, N.; Hole, C.R.; Wozniak, K.L.; Wormley, F.L. Induction of Broad-Spectrum Protective Immunity against Disparate Cryptococcus Serotypes. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yauch, L.E.; Lam, J.S.; Levitz, S.M. Direct inhibition of T-cell responses by the Cryptococcus capsular polysaccharide glucuronoxylomannan. PLoS Pathog. 2006, 2, e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, R.M.; Chen, J.; Yauch, L.E.; Rottman, J.B.; Levitz, S.M. Opsonic requirements for dendritic cell-mediated responses to Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wormley, F.L., Jr.; Perfect, J.R.; Steele, C.; Cox, G.M. Protection against cryptococcosis by using a murine gamma interferonproducing Cryptococcus neoformans strain. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 1453–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, J.N.; Meintjes, G.; Rebe, K.; Williams, G.N.; Bicanic, T.; Williams, A.; Schutz, C.; Bekker, L.G.; Wood, R.; Harrison, T.S. Adjunctive interferon-gamma immunotherapy for the treatment of HIV-associated cryptococcal meningitis: A randomized controlled trial. AIDS 2012, 26, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, P.G.; Bustamante, B.; Ticona, E.; Hamill, R.J.; Johnson, P.C.; Reboli, A.; Aberg, J.; Hasbun, R.; Hsu, H.H. Recombinant interferon- gamma 1b as adjunctive therapy for AIDS-related acute cryptococcal meningitis. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, 2185–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitz, S.M.; Golenbock, D.T. Beyond empiricism: Informing vaccine development through innate immunity research. Cell 2012, 148, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ambati, S.; Meagher, R.B.; Lin, X. Developing mRNA lipid nanoparticle vaccine effective for cryptococcosis in a 510 murine model. npj Vaccines 2025, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Strain | Country | Lineage |
|---|---|---|
| KN99 (Control) | USA | VNIb |
| BK80 | Vietnam | VNIa ST4 |
| BMD1338 | Vietnam | VNIa ST5 |
| UgCl302 | Uganda | VNIa ST93 |
| UgCl395 | Uganda | VNIa ST93 |
| PMH1063 | Botswana | VNBII |
| PMH1065 | Botswana | VNI |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carlson, D.; Wang, R.; Hastings, Z.; Oliveira, L.V.N.; Hester, M.M.; Rodriguez, N.; Pedersen, G.K.; Tenor, J.L.; Perfect, J.R.; Specht, C.A.; et al. Vaccine-Mediated Protection of Mice Against African and Asian Clinical Strains of Cryptococcus neoformans. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 886. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11120886
Carlson D, Wang R, Hastings Z, Oliveira LVN, Hester MM, Rodriguez N, Pedersen GK, Tenor JL, Perfect JR, Specht CA, et al. Vaccine-Mediated Protection of Mice Against African and Asian Clinical Strains of Cryptococcus neoformans. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(12):886. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11120886
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarlson, Diana, Ruiying Wang, Zachary Hastings, Lorena V. N. Oliveira, Maureen M. Hester, Nicolle Rodriguez, Gabriel Kristian Pedersen, Jennifer L. Tenor, John R. Perfect, Charles A. Specht, and et al. 2025. "Vaccine-Mediated Protection of Mice Against African and Asian Clinical Strains of Cryptococcus neoformans" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 12: 886. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11120886
APA StyleCarlson, D., Wang, R., Hastings, Z., Oliveira, L. V. N., Hester, M. M., Rodriguez, N., Pedersen, G. K., Tenor, J. L., Perfect, J. R., Specht, C. A., & Levitz, S. M. (2025). Vaccine-Mediated Protection of Mice Against African and Asian Clinical Strains of Cryptococcus neoformans. Journal of Fungi, 11(12), 886. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11120886







