Root Colonization by Fungal Entomopathogen Systemically Primes Belowground Plant Defense against Cabbage Root Fly
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study System
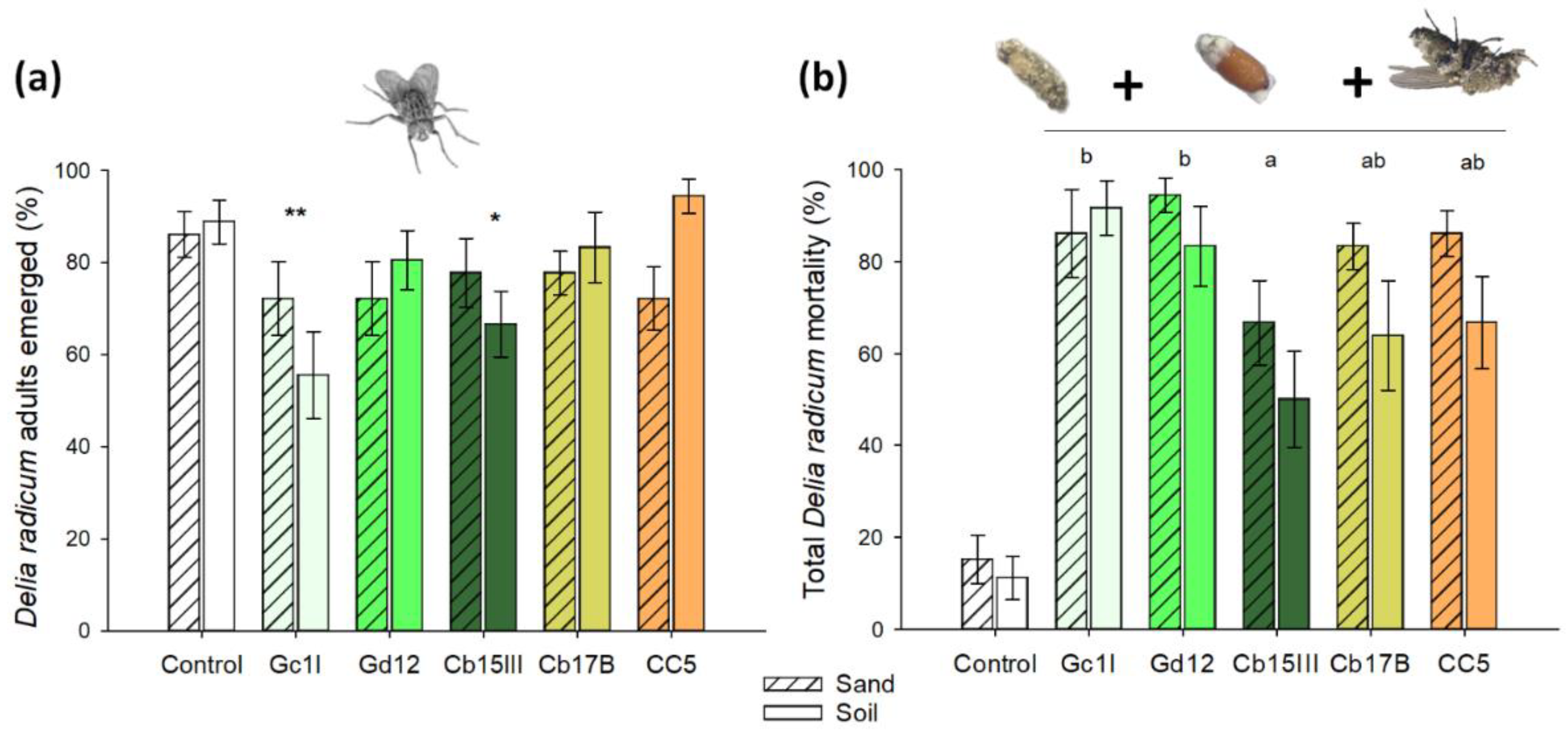
2.2. Susceptibility of CRF to Different M. brunneum Isolates in Substrate without the Plant
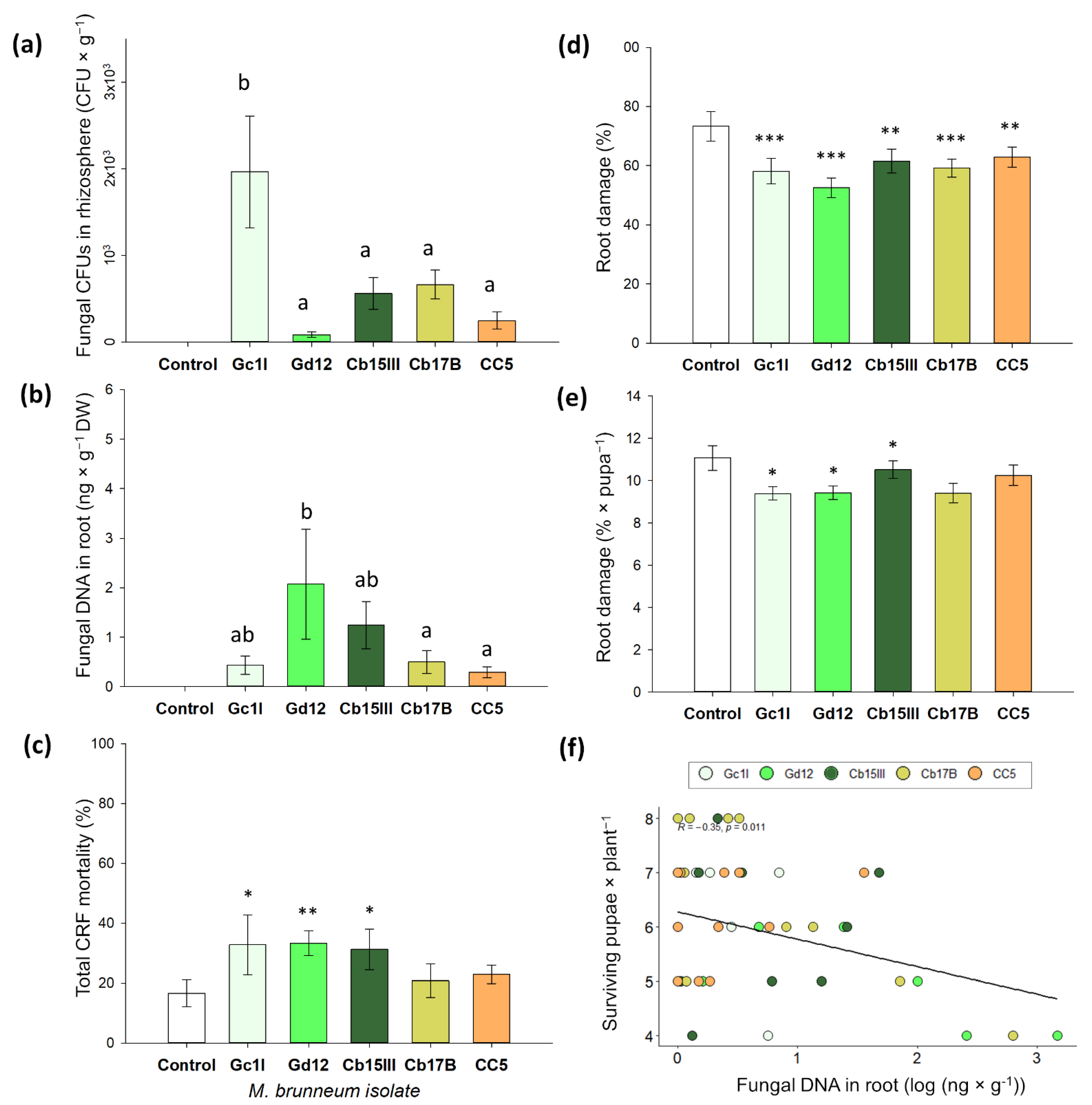
2.3. Rhizosphere Competence, Endophytism, and Plant Protection of M. brunneum Isolates
2.4. Quantification of Rhizospheric and Endophytic Metarhizium Brunneum
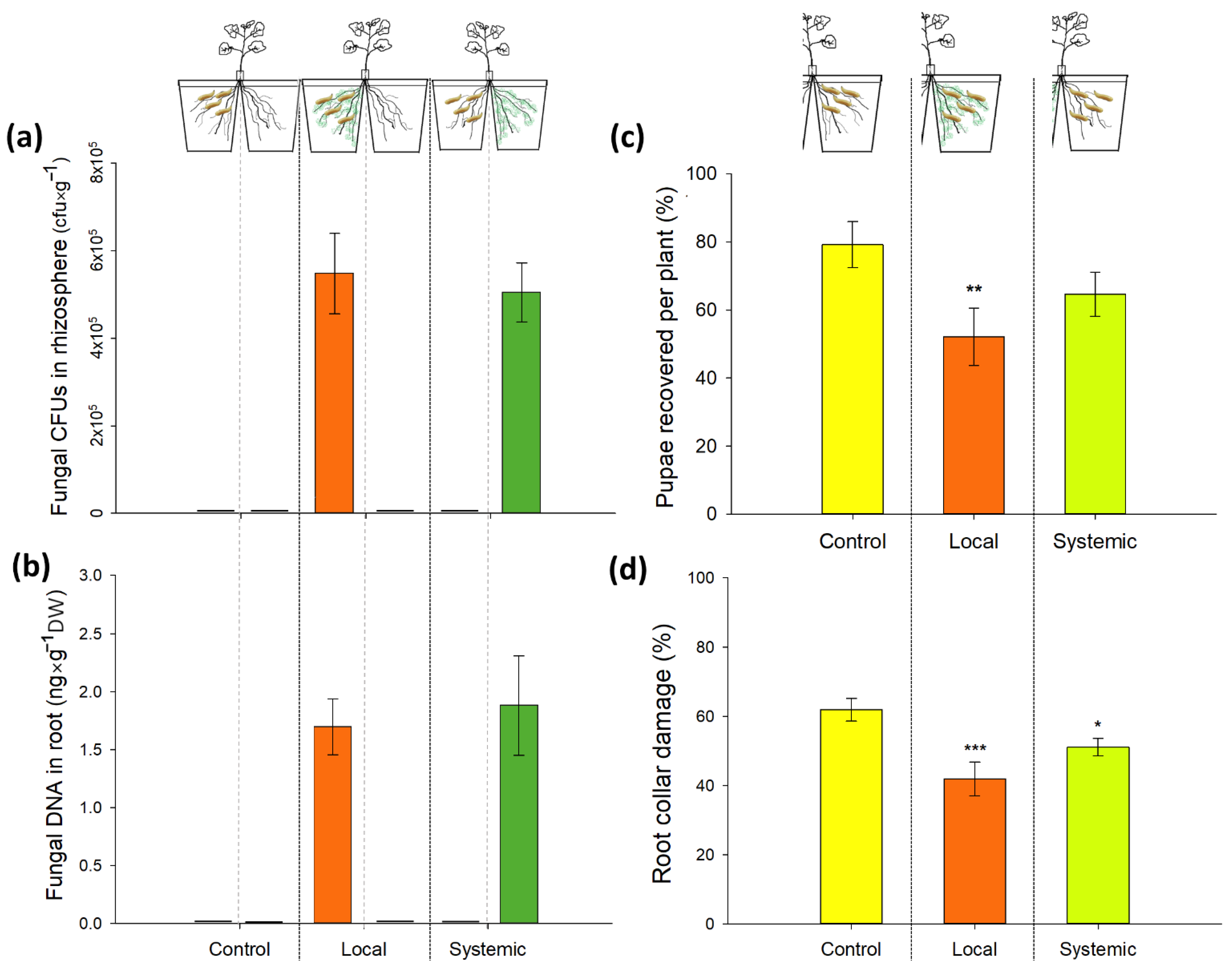
2.5. Direct and Systemic Effects of M. brunneum Isolate Gd12 on CRF Survival and Root Damage: Split-Root Setup and Bioassay
- (1)
- Control—one compartment mock-inoculated with 0.1% Tween 80;
- (2)
- Fungus—compartment A: M. brunneum (Mb-L), B: 0.1% Tween 80 (Mb-S);
- (3)
- Herbivore—compartment A: CRF (Dr-L), B: 0.1% Tween 80 (Dr-S);
- (4)
- Fungus/herbivore (local)—compartment A: M. brunneum + CRF (Mb-L/Dr-L), B: 0.1% Tween 80 (Mb-S/Dr-S);
- (5)
- Fungus/herbivore (systemic)—compartment A: CRF (Dr-L/Mb-S), B: M. brunneum (Mb-L/Dr-S).
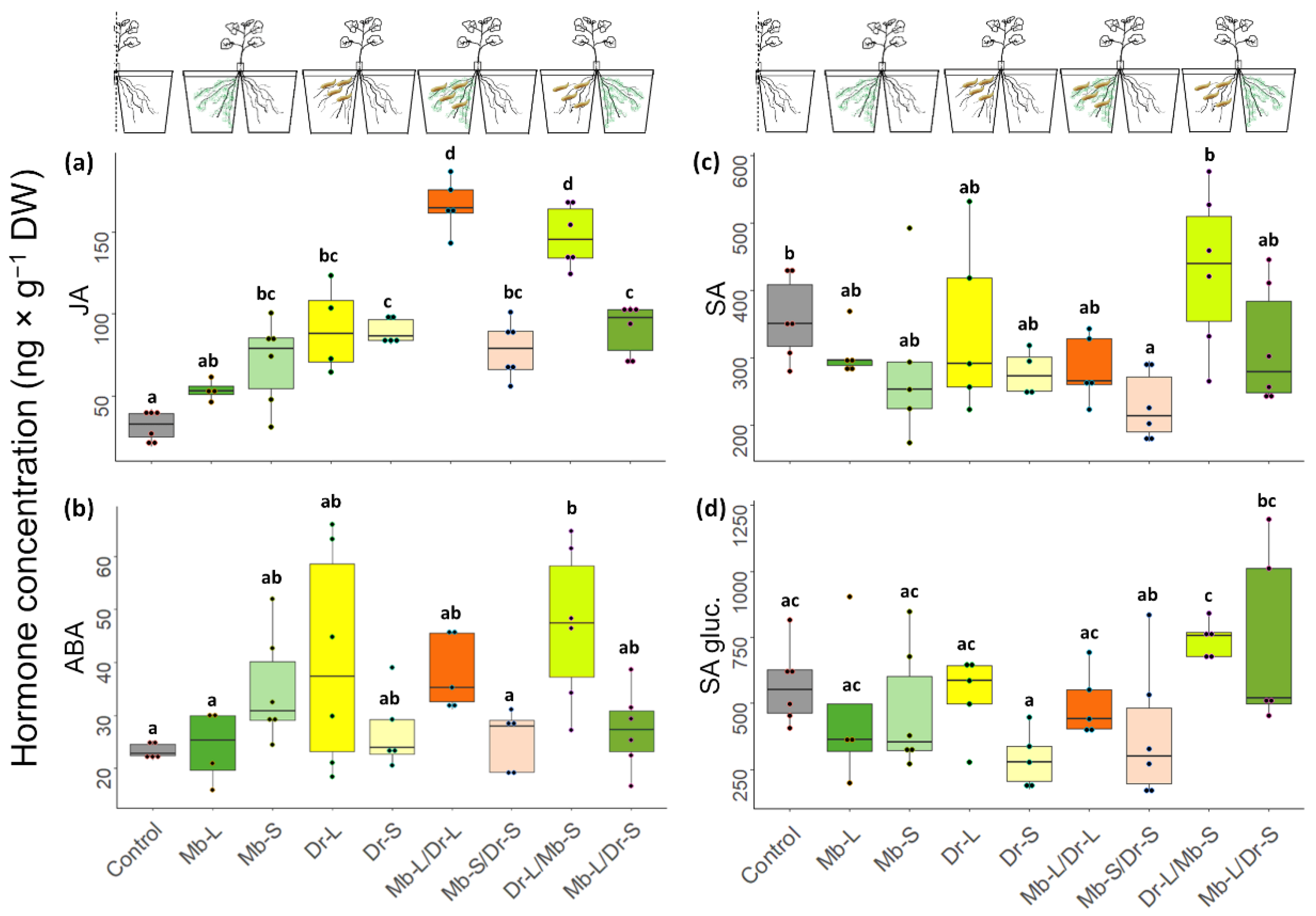
2.6. Direct and Systemic Plant Responses to Fungus and Herbivore: Gene Expression
2.7. Direct and Systemic Plant Responses to Fungus and Herbivore: Phytohormone Analysis
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Susceptibility of CRF to Different M. brunneum Isolates in Substrate
3.2. Rhizosphere Competence, Endophytism, and Plant Protection of M. brunneum Isolates
3.3. Direct and Systemic Effects of M. brunneum Isolate Gd12 on CRF Survival and Root Damage: Bioassay
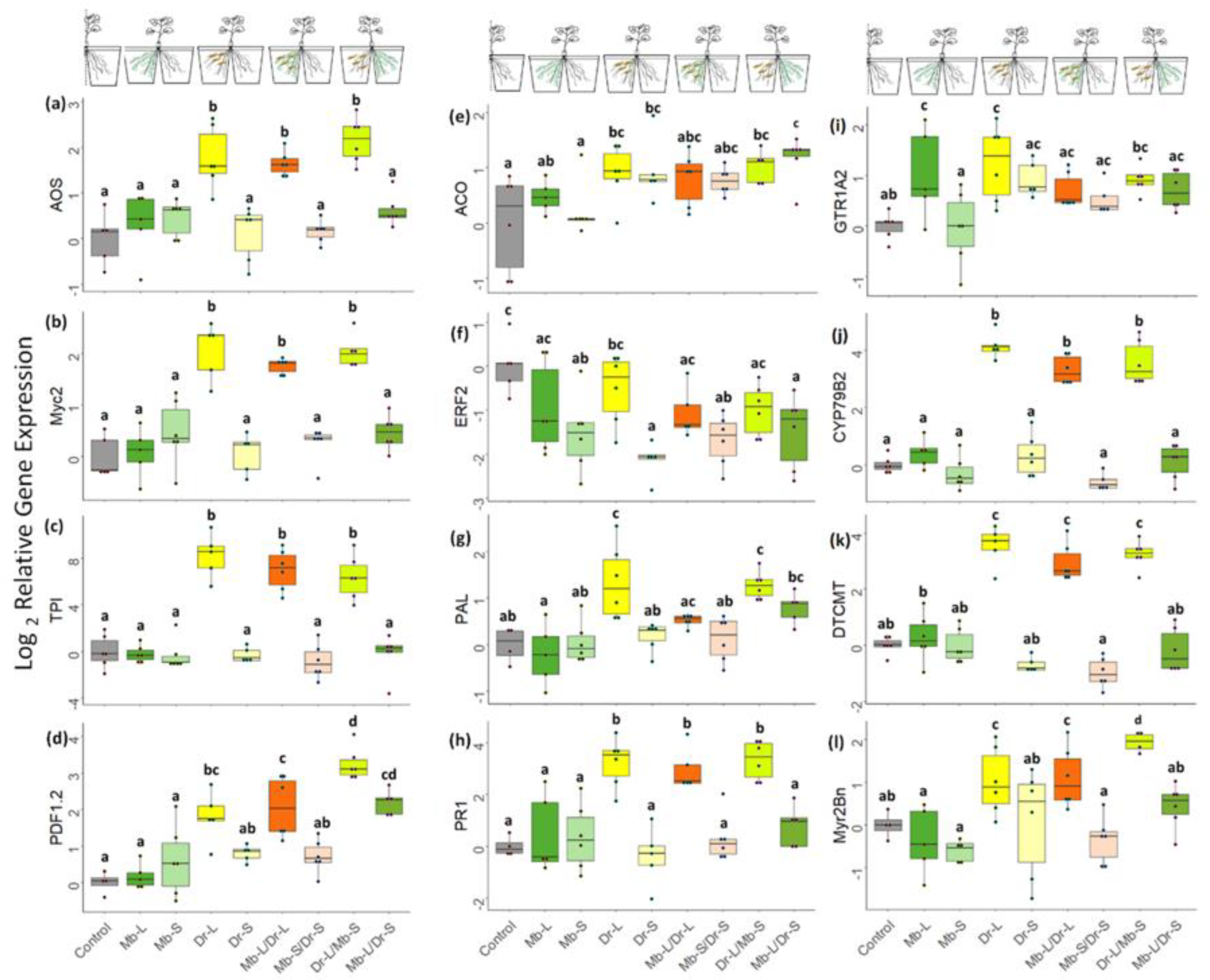
3.4. Direct and Systemic Plant Responses to CRF and M. brunneum: Gene Expression and Phytohormone Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, G.; Leger, R. Field studies using a recombinant mycoinsecticide (Metarhizium anisopliae) reveal that it is rhizosphere competent. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 6383–6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasan, R.K.; Bidochka, M.J. The insect-pathogenic fungus Metarhizium robertsii (Clavicipitaceae) is also an endophyte that stimulates plant root development. Am. J. Bot. 2012, 99, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruck, D.J. Ecology of Metarhizium anisopliae in soilless potting media and the rhizosphere: Implications for pest management. Biol. Control 2005, 32, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St. Leger, R.J. Studies on adaptations of Metarhizium anisopliae to life in the soil. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2008, 98, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gange, A.C.; Koricheva, J.; Currie, A.F.; Jaber, L.R.; Vidal, S. Meta-analysis of the role of entomopathogenic and unspecialized fungal endophytes as plant bodyguards. New Phytol. 2019, 223, 2002–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega, F.E. The use of fungal entomopathogens as endophytes in biological control: A review. Mycologia 2018, 110, 4–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-Franco, F.; Hampton, J.G.; Narciso, J.; Rostás, M.; Wessman, P.; Saville, D.J.; Jackson, T.A.; Glare, T.R. Effects of a maize root pest and fungal pathogen on entomopathogenic fungal rhizosphere colonization, endophytism and induction of plant hormones. Biol. Control 2020, 150, 104347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachapa, J.C.; Meyling, N.V.; Burow, M.; Hauser, T.P. Induction and priming of plant defense by root-associated insect-pathogenic fungi. J. Chem. Ecol. 2020, 47, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wees, S.C.; de Swart, E.; van Pelt, J.A.; van Loon, L.C.; Pieterse, C.M. Enhancement of induced disease resistance by simultaneous activation of salicylate- and jasmonate-dependent defense pathways in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8711–8716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Ravindran, P.; Kumar, P.P. Plant hormone-mediated regulation of stress responses. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda, A.; Zheng, S.J.; van Loon, J.J.A.; Pieterse, C.M.J.; Dicke, M. Helping plants to deal with insects: The role of beneficial soil-borne microbes. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieterse, C.M.J.; Zamioudis, C.; Berendsen, R.L.; Weller, D.M.; Van Wees, S.C.M.; Bakker, P.A.H.M. Induced systemic resistance by beneficial microbes. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2014, 52, 347–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raad, M.; Glare, T.R.; Brochero, H.L.; Müller, C.; Rostás, M. Transcriptional reprogramming of Arabidopsis thaliana defence pathways by the entomopathogen Beauveria bassiana correlates with resistance against a fungal pathogen but not against insects. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Zhao, X.; Huang, S.; Deng, J.; Li, X.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, Y. Pest management via endophytic colonization of tobacco seedlings by the insect fungal pathogen Beauveria bassiana. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 2007–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasool, S.; Vidkjær, N.H.; Hooshmand, K.; Jensen, B.; Fomsgaard, I.S.; Meyling, N.V. Seed inoculations with entomopathogenic fungi affect aphid populations coinciding with modulation of plant secondary metabolite profiles across plant families. New Phytol. 2021, 229, 1715–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Medina, A.; Fernandez, I.; Lok, G.B.; Pozo, M.J.; Pieterse, C.M.J.; Van Wees, S.C.M. Shifting from priming of salicylic acid- to jasmonic acid-regulated defences by Trichoderma protects tomato against the root knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 1363–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Medina, A.; Fernandez, I.; Sánchez-Guzmán, M.; Jung, S.; Pascual, J.; Pozo, M. Deciphering the hormonal signalling network behind the systemic resistance induced by Trichoderma harzianum in tomato. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrath, U.; Beckers, G.J.M.; Flors, V.; García-Agustín, P.; Jakab, G.; Mauch, F.; Newman, M.-A.; Pieterse, C.M.J.; Poinssot, B.; Pozo, M.J.; et al. Priming: Getting ready for battle. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2006, 19, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, V.; Thulke, O.; Conrath, U. A benzothiadiazole primes parsley cells for augmented elicitation of defense responses. Plant Physiol. 1998, 117, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikano, I.; Rosa, C.; Tan, C.-W.; Felton, G.W. Tritrophic interactions: Microbe-mediated plant effects on insect herbivores. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2017, 55, 313–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.; Hauschild, R.; Sikora, R.A. Fusarium oxysporum endophytes induced systemic resistance against Radopholus similis on banana. Nematology 2006, 8, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahremani, Z.; Escudero, N.; Saus, E.; Gabaldón, T.; Sorribas, F.J. Pochonia chlamydosporia induces plant-dependent systemic resistance to Meloidogyne incognita. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Z.; Fayolle, L.; Van Tuinen, D.; Chatagnier, O.; Li, X.; Gianinazzi, S.; Gianinazzi-Pearson, V. Local and systemic mycorrhiza-induced protection against the ectoparasitic nematode Xiphinema index involves priming of defence gene responses in grapevine. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 3657–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinuz, A.; Zewdu, G.; Ludwig, N.; Grundler, F.; Sikora, R.A.; Schouten, A. The application of Arabidopsis thaliana in studying tripartite interactions among plants, beneficial fungal endophytes and biotrophic plant-parasitic nematodes. Planta 2015, 241, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, A.; Le Tron, S.; Dugravot, S.; Cortesero, A.M. Field evaluation of the combined deterrent and attractive effects of dimethyl disulfide on Delia radicum and its natural enemies. Biol. Control 2009, 49, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, R.S.; Sears, M.K. Assessment of larval feeding damage of the cabbage maggot (Diptera: Anthomyiidae) in relation to oviposition preference on canola. J. Econ. Entomol. 1992, 85, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keunecke, H. Einfluss von Kohlfliegenbefall auf die Infektion und Schadwirkung von Verticillium longisporum und Phoma lingam an Raps; Georg-August-Universität: Göttingen, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Soroka, J.J.; Weiss, R.M.; Grenkow, L.F.; Olfert, O.O. Relationships among root maggot (Delia spp., Diptera: Anthomyiidae) infestation, root injury, and seed yields of canola Brassica napus L. and Brassica rapa L. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2020, 100, 575–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vänninen, I.; Hokkanen, H.; Tyni-Juslin, J. Screening of field performance of entomopathogenic fungi and nematodes against cabbage root flies (Delia radicum L. and D. floralis (Fall.); Diptera, Anthomyiidae). Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Soil Plant Sci. 1999, 49, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razinger, J.; Lutz, M.; Schroers, H.-J.; Urek, G.; Grunder, J. Evaluation of insect associated and plant growth promoting fungi in the control of cabbage root flies. J. Econ. Entomol. 2014, 107, 1348–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrand, V.; Buffet, J.P.; Guertin, C. Susceptibility of cabbage maggot larvae (Diptera: Anthomyiidae) to Hypocreales entomopathogenic fungi. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vänninen, I.; Hokkanen, H.; Tyni-Juslin, J. Attempts to control cabbage root flies Delia radicum L. and Delia floralis (Fall,) (Dipt., Anthomyiidae) with entomopathogenic fungi: Laboratory and greenhouse tests. J. Appl. Entomol. 1999, 123, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruck, D.J.; Snelling, J.E.; Dreves, A.J.; Jaronski, S.T. Laboratory bioassays of entomopathogenic fungi for control of Delia radicum (L.) larvae. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2005, 89, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razinger, J.; Lutz, M.; Grunder, J.; Urek, G. Laboratory investigation of cauliflower-fungus-insect interactions for cabbage maggot control. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 2578–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pava-Ripoll, M.; Angelini, C.; Fang, W.; Wang, S.; Posada, F.J.; St Leger, R. The rhizosphere-competent entomopathogen Metarhizium anisopliae expresses a specific subset of genes in plant root exudates. Microbiology 2011, 157, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelone, S.; Piña-Torres, I.H.; Padilla-Guerrero, I.E.; Bidochka, M.J. “Sleepers” and “creepers”: A theoretical study of colony polymorphisms in the fungus Metarhizium related to insect pathogenicity and plant rhizosphere colonization. Insects 2018, 9, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabanás, C.G.L.; Sesmero, R.; Valverde-Corredor, A.; Javier López-Escudero, F.; Mercado-Blanco, J. A split-root system to assess biocontrol effectiveness and defense-related genetic responses in above-ground tissues during the tripartite interaction Verticillium dahliae-olive-Pseudomonas fluorescens PICF7 in roots. Plant Soil 2017, 417, 433–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, M.B.; de Medeiros, H.A.; Morán-Diez, M.E.; Castillo, P.; Hermosa, R.; Monte, E. A split-root method to study systemic and heritable traits induced by Trichoderma in tomato plants. In Methods in Rhizosphere Biology Research. Rhizosphere Biology; Reinhardt, D., Sharma, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 151–166. ISBN 9789811357671. [Google Scholar]
- Kafle, A.; Frank, H.E.R.; Rose, B.D.; Garcia, K. Split down the middle: Studying arbuscular mycorrhizal and ectomycorrhizal symbioses using split-root assays. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 1288–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, W.S. A method for computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J. Econ. Entomol. 1925, 18, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, H.; Forer, A.; Schinner, F. Development of media for the selective isolation and maintenance of virulence of Beauveria brongniartii. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Microbial Control of Soil Dwelling Pests, Lincoln, New Zealand, 21–23 February 1996; Jackson, T.A., Glare, T.R., Eds.; AgResearch: Lincoln, New Zealand, 1996; pp. 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Satomura, T. Extraction of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus spores from clayey soil. Tropics 2007, 16, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brandfass, C.; Karlovsky, P. Simultaneous detection of Fusarium culmorum and F. graminearum in plant material by duplex pcr with melting curve analysis. BMC Microbiol. 2006, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Rehner, S.A.; Widmer, F.; Enkerli, J. A PCR-based tool for cultivation-independent detection and quantification of Metarhizium Clade 1. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2011, 108, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koressaar, T.; Lepamets, M.; Kaplinski, L.; Raime, K.; Andreson, R.; Remm, M. Primer3_masker: Integrating masking of template sequence with primer design software. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1937–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, M.; Munné-Bosch, S. Rapid and sensitive hormonal profiling of complex plant samples by liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Plant Methods 2011, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzl, T.; Haedrich, J.; Schaechtele, A.; Robouch, P.; Stroka, J. Guidance Document on the Estimation of LOD and LOQ for Measurements in the Field of Contaminants in Feed and Food; EUR 28099; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2016; ISBN 9789279617683. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017.
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B. Modern Applied Statistics with S, 4th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002; ISBN 0387954570. [Google Scholar]
- Cribari-Neto, F.; Zeileis, A. Beta regression in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 34, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hothorn, T.; Bretz, F.; Westfall, P. Simultaneous inference in general parametric models. Biom. J. 2008, 50, 346–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsa, S.; Ortiz, V.; Gómez-Jiménez, M.I.; Kramer, M.; Vega, F.E. Root environment is a key determinant of fungal entomopathogen endophytism following seed treatment in the common bean, Phaseolus vulgaris. Biol. Control 2018, 116, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.M.; Stimac, J.L.; Alves, S.B. Soil antagonism affecting the dose—Response of workers of the red imported fire ant, Solenopsis invicta, to Beauveria bassiana conidia. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1993, 61, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingg, A.J.; Donaldson, M.D. Biotic and abiotic factors affecting stability of Beauveria bassiana conidia in soil. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1981, 38, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meadow, R.; Vandenberg, J.D.; Shelton, A.M. Exchange of inoculum of Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) Vuill. (Hyphomycetes) between adult flies of the cabbage maggot Delia radicum L. (Diptera: Anthomyiidae). Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2000, 10, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razinger, J.; Schroers, H.J.; Urek, G. Virulence of Metarhizium brunneum to field collected Agriotes spp. wireworms. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2018, 20, 309–320. [Google Scholar]
- Moonjely, S.; Bidochka, M.J. Generalist and specialist Metarhizium insect pathogens retain ancestral ability to colonize plant roots. Fungal Ecol. 2019, 41, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razinger, J.; Lutz, M.; Schroers, H.J.; Palmisano, M.; Wohler, C.; Urek, G.; Grunder, J. Direct plantlet inoculation with soil or insect-associated fungi may control cabbage root fly maggots. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2014, 120, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkooranee, J.T.; Aledan, T.R.; Ali, A.K.; Lu, G.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Fu, C.; Li, M. Detecting the hormonal pathways in oilseed rape behind induced systemic resistance by Trichoderma harzianum TH12 to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karssemeijer, P.N.; Reichelt, M.; Gershenzon, J.; van Loon, J.; Dicke, M. Foliar herbivory by caterpillars and aphids differentially affects phytohormonal signalling in roots and plant defence to a root herbivore. Plant Cell Environ. 2020, 43, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieterse, C.M.J.; Van Der Does, D.; Zamioudis, C.; Leon-Reyes, A.; Van Wees, S.C.M. Hormonal modulation of plant immunity. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 28, 489–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Timko, M.P. Jasmonic acid signaling and molecular crosstalk with other phytohormones. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazebnik, J.; Frago, E.; Dicke, M.; van Loon, J.J.A. Phytohormone mediation of interactions between herbivores and plant pathogens. J. Chem. Ecol. 2014, 40, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Poecke, R.M.P.; Dicke, M. Indirect defence of plants against herbivores: Using Arabidopsis thaliana as a model plant. Plant Biol. 2004, 6, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dicke, M.; Kroes, A.; Liu, W.; Gols, R. Interactive effects of cabbage aphid and caterpillar herbivory on transcription of plant genes associated with phytohormonal signalling in wild cabbage. J. Chem. Ecol. 2016, 42, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefevere, H.; Bauters, L.; Gheysen, G. Salicylic acid biosynthesis in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dam, N.M.; Wondafrash, M.; Mathur, V.; Tytgat, T.O.G. Differences in hormonal signaling triggered by two root-feeding nematode species result in contrasting effects on aphid population growth. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 6, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalikova, Z.; Kubes, J.; Skalicky, M.; Kuchtickova, N.; Maskova, L.; Tuma, J.; Vachova, P.; Hejnak, V. Changes in content of polyphenols and ascorbic acid in leaves of white cabbage after pest infestation. Molecules 2019, 24, 2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onkokesung, N.; Reichelt, M.; Van Doorn, A.; Schuurink, R.C.; Van Loon, J.J.A.; Dicke, M. Modulation of flavonoid metabolites in Arabidopsis thaliana through overexpression of the MYB75 transcription factor: Role of kaempferol-3,7- dirhamnoside in resistance to the specialist insect herbivore Pieris brassicae. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 2203–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.W.H.; Malchev, I.T.; Rajcan, I.; Kott, L.S. Identification of putative quantitative trait loci associated with a flavonoid related to resistance to cabbage seedpod weevil (Ceutorhynchus obstrictus) in canola derived from an intergeneric cross, Sinapis alba × Brassica napus. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, P.S.; Dugravot, S.; Cortesero, A.M.; Poinsot, D.; Raaijmakers, C.E.; Hassan, H.M.; Van Dam, N.M. Broccoli and turnip plants display contrasting responses to belowground induction by Delia radicum infestation and phytohormone applications. Phytochemistry 2012, 73, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Geem, M.; Gols, R.; Raaijmakers, C.E.; Harvey, J.A. Effects of population-related variation in plant primary and secondary metabolites on aboveground and belowground multitrophic interactions. Chemoecology 2016, 26, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennies, H. Evaluation of Resistance Mechanisms against Delia radicum L. and Psylliodes chrysocephala L. in Brassicaceous Accessions. Ph.D. Thesis, Georg-August-Universität, Göttingen, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Touw, A.J.; Verdecia Mogena, A.; Maedicke, A.; Sontowski, R.; van Dam, N.M.; Tsunoda, T. Both biosynthesis and transport are involved in glucosinolate accumulation during root-herbivory in Brassica rapa. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 10, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sontowski, R.; Gorringe, N.J.; Pencs, S.; Schedl, A.; Touw, A.J.; van Dam, N.M. Same difference? low and high glucosinolate Brassica rapa varieties show similar responses upon feeding by two specialist root herbivores. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedras, M.S.C.; Yaya, E.E. Phytoalexins from Brassicaceae: News from the front. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björkman, M.; Ahuja, I.; Schjøll, A.F.; Van Dam, N.M.; Bones, A.M.; Meadow, R. Feeding of turnip root fly (Delia floralis) and cabbage root fly (Delia radicum) larvae on Brassica napus L. transgenic MINELESS plants-effects on insect development. In Integrated Protection in Field Vegetables; IOBC-WPRS Bulletin; NTNU: Trondheim, Norway, 2014; Volume 107, pp. 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Tsunoda, T.; Grosser, K.; van Dam, N.M. Locally and systemically induced glucosinolates follow optimal defence allocation theory upon root herbivory. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 2127–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Posada-Vergara, C.; Lohaus, K.; Alhussein, M.; Vidal, S.; Rostás, M. Root Colonization by Fungal Entomopathogen Systemically Primes Belowground Plant Defense against Cabbage Root Fly. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 969. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8090969
Posada-Vergara C, Lohaus K, Alhussein M, Vidal S, Rostás M. Root Colonization by Fungal Entomopathogen Systemically Primes Belowground Plant Defense against Cabbage Root Fly. Journal of Fungi. 2022; 8(9):969. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8090969
Chicago/Turabian StylePosada-Vergara, Catalina, Katharina Lohaus, Mohammad Alhussein, Stefan Vidal, and Michael Rostás. 2022. "Root Colonization by Fungal Entomopathogen Systemically Primes Belowground Plant Defense against Cabbage Root Fly" Journal of Fungi 8, no. 9: 969. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8090969
APA StylePosada-Vergara, C., Lohaus, K., Alhussein, M., Vidal, S., & Rostás, M. (2022). Root Colonization by Fungal Entomopathogen Systemically Primes Belowground Plant Defense against Cabbage Root Fly. Journal of Fungi, 8(9), 969. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8090969






