Nitrogen, Iron, and Zinc Acquisition: Key Nutrients to Aspergillus fumigatus Virulence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
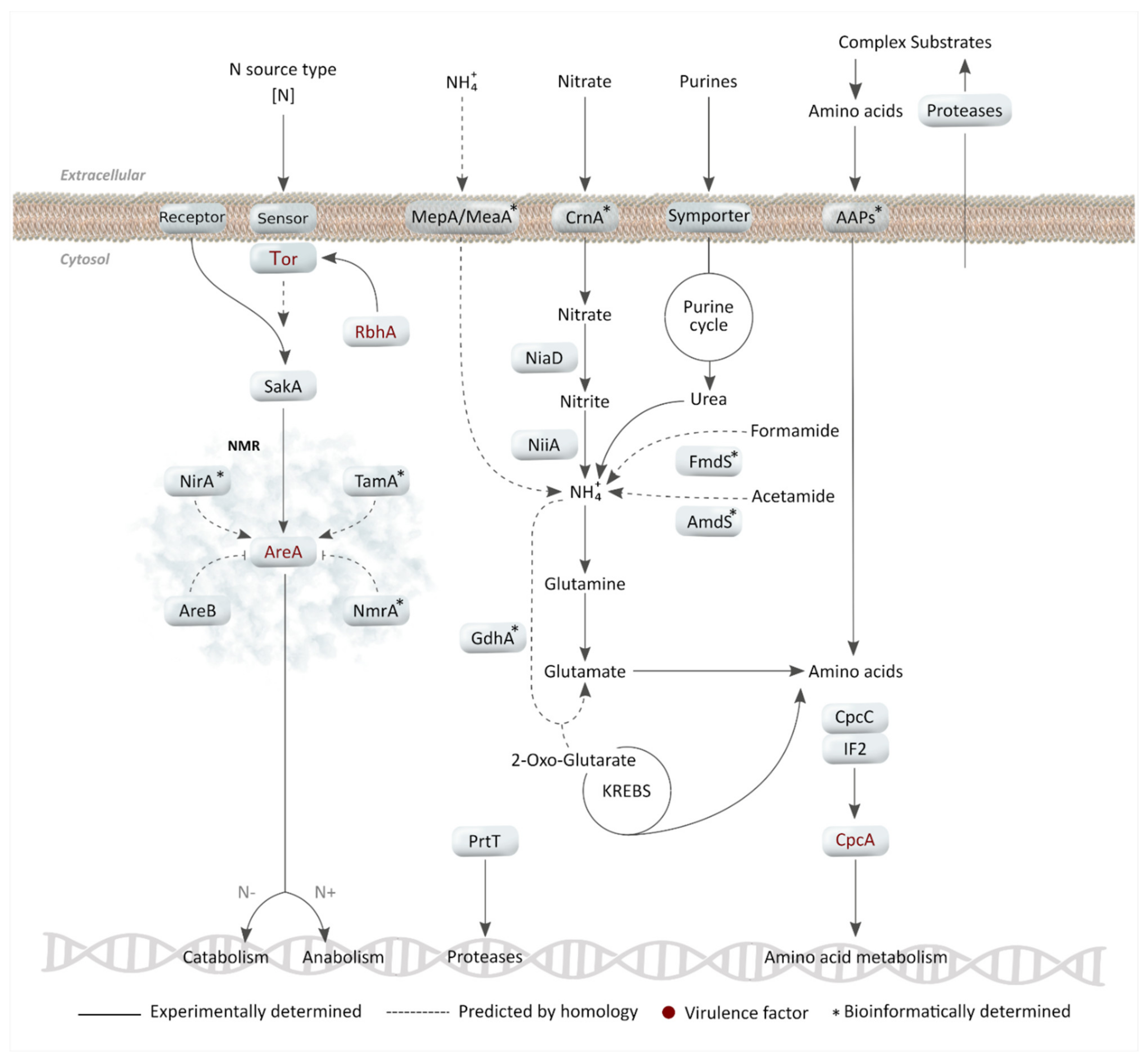
2. Nitrogen Metabolism
2.1. Primary Nitrogen Sources: Ammonium and Glutamine Assimilation
2.2. Nitrate and Other Secondary Nitrogen Sources
2.3. Nitrogen Metabolite Repression (NMR) as a Regulatory Mechanism
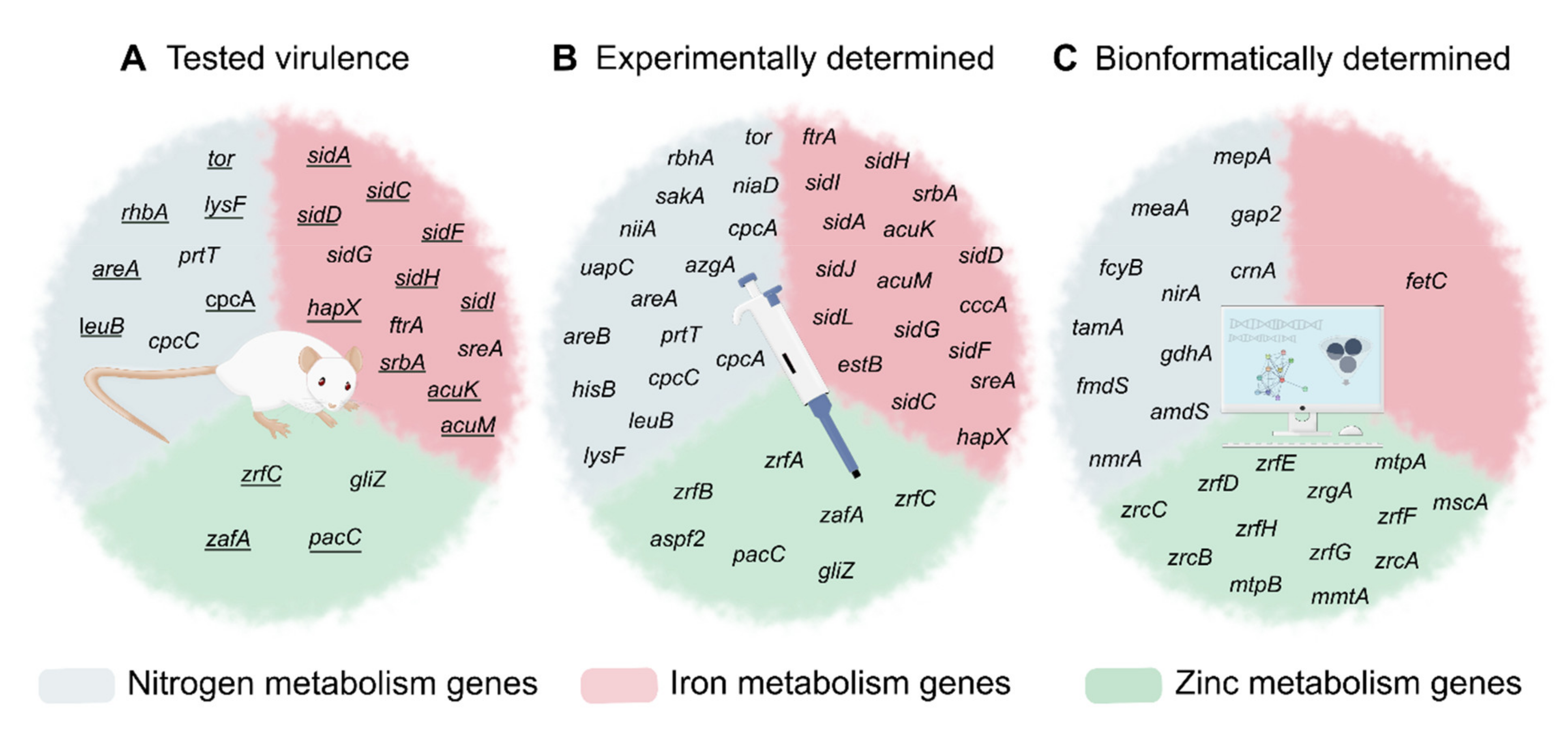
2.4. Importance of Nitrogen Acquisition for A. fumigatus Virulence
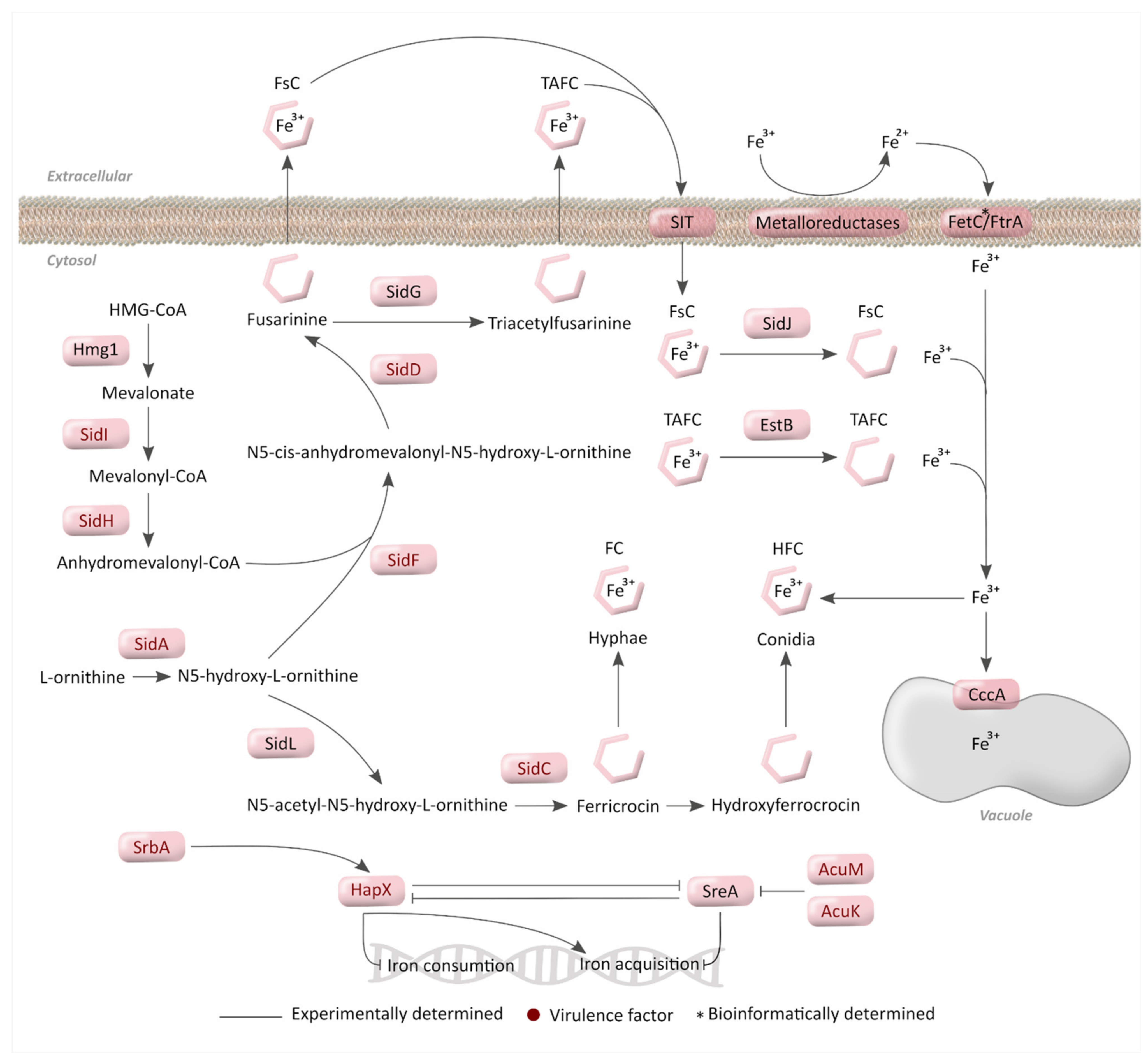
3. Iron Metabolism
3.1. Mechanisms for Iron Acquisition and Storage in A. fumigatus
3.2. Regulatory Mechanisms for Iron Homeostasis
3.3. Importance of Iron Metabolism for A. fumigatus Virulence
4. Zinc Metabolism
4.1. Zinc Acquisition and Homeostasis
4.2. Regulatory Mechanisms
4.3. Importance of Zn Acquisition for A. fumigatus Virulence
5. Interaction between Metabolic Pathways
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Latgé, J.P. The pathobiology of Aspergillus fumigatus. Trends Microbiol. 2001, 9, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulussen, C.; Hallsworth, J.E.; Álvarez-Pérez, S.; Nierman, W.C.; Hamill, P.G.; Blain, D.; Rediers, H.; Lievens, B. Ecology of aspergillosis: Insights into the pathogenic potency of Aspergillus fumigatus and some other Aspergillus species. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 296–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Latgé, J. Aspergillus fumigatus and Aspergillosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 310–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maschmeyer, G.; Haas, A.; Cornely, O.A. Invasive aspergillosis: Epidemiology, diagnosis and management in immunocompromised patients. Drugs 2007, 67, 1567–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balloy, V.; Chignard, M. The innate immune response to Aspergillus fumigatus. Microbes Infect. 2009, 11, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mccormick, A.; Loeffler, J.; Ebel, F. Aspergillus fumigatus: Contours of an opportunistic human pathogen. Cell. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 1535–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, A.; Fernandez-Molina, J.V.; Bikandi, J.; Ramırez, A.; Margareto, J.; Sendino, J.; Hernando, F.L.; Ponton, J.; Garaizar, J.; Rementeria, A. What makes Aspergillus fumigatus a successful pathogen? Genes and molecules involved in invasive aspergillosis. Rev. Iberoam. Micol. 2010, 27, 155–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Cuesta, U.; Aparicio-Fernandez, L.; Guruceaga, X.; Martin-Souto, L.; Abad-Diaz-de-Cerio, A.; Antoran, A.; Buldain, I.; Hernando, F.L.; Ramirez-Garcia, A.; Rementeria, A. Melanin and pyomelanin in Aspergillus fumigatus: From its genetics to host interaction. Int. Microbiol. 2020, 23, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravelat, F.N.; Beauvais, A.; Liu, H.; Lee, M.J.; Snarr, B.D.; Chen, D.; Xu, W.; Kravtsov, I.; Hoareau, C.M.Q.; Vanier, G.; et al. Aspergillus Galactosaminogalactan Mediates Adherence to Host Constituents and Conceals Hyphal β-Glucan from the Immune System. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambou, K.; Lamarre, C.; Beau, R.; Dufour, N.; Latge, J.P. Functional analysis of the superoxide dismutase family in Aspergillus fumigatus. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 75, 910–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlam, D.; Canton, J.; Carreño, M.; Kopinski, H.; Freeman, S.A.; Grinstein, S.; Fairn, G.D. Gliotoxin Suppresses Macrophage Immune Function by Subverting Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-Trisphosphate Homeostasis. MBio 2016, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guruceaga, X.; Ezpeleta, G.; Mayayo, E.; Sueiro-Olivares, M.; Abad-Diaz-de-Cerio, A.; Aguirre, J.M. A possible role for fumagillin in cellular damage during host infection by Aspergillus fumigatus. Virulence 2018, 9, 1548–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guruceaga, X.; Perez-Cuesta, U.; Abad-Diaz de Cerio, A.; Gonzalez, O.; Alonso, R.M.; Hernando, F.L.; Ramirez-Garcia, A.; Rementeria, A. Fumagillin, a Mycotoxin of Aspergillus fumigatus: Biosynthesis, Biological Activities, Detection, and Applications. Toxins 2020, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Latgé, J.-P.; Chamilos, G. Aspergillus fumigatus and Aspergillosis in 2019. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, 1–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, E.D. Nutritional Immunity: Host’s Attempt to Withhold Iron From Microbial Invaders. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1975, 231, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clohessy, P.; Goldn, B. Calprotectin-Mediated Zinc Chelation as a Biostatic Mechanism in Host Defence. Scand. J. Immunol. 1995, 42, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerwien, F.; Skrahina, V.; Kasper, L.; Hube, B.; Brunke, S. Metals in fungal virulence. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, I.R.; Morrow, C.A.; Fraser, J.A. Nitrogen regulation of virulence in clinically prevalent fungal pathogens. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2013, 345, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krappmann, S.; Braus, G.H. Nitrogen metabolism of Aspergillus and its role in pathogenicity. Med. Mycol. 2005, 43, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, K.H.; Hynes, M.J.; Davis, M.A. Recent advances in nitrogen regulation: A comparison between Saccharomyces cerevisiae and filamentous fungi. Eukaryot. Cell 2008, 7, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amaar, Y.G.; Moore, M.M. Mapping of the nitrate-assimilation gene cluster (crnA-niiA-niaD) and characterization of the nitrite reductase gene (niiA) in the opportunistic fungal pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. Curr. Genet. 1998, 33, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroll, K.; Pähtz, V.; Hillmann, F.; Vaknin, Y.; Schmidt-Heck, W.; Roth, M.; Jacobsen, I.D.; Osherov, N.; Brakhage, A.A.; Kniemeyer, O. Identification of hypoxia-inducible target genes of Aspergillus fumigatus by transcriptome analysis reveals cellular respiration as an important contributor to hypoxic survival. Eukaryot. Cell 2014, 13, 1241–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goudela, S.; Reichard, U.; Amillis, S.; Diallinas, G. Characterization and kinetics of the major purine transporters in Aspergillus fumigatus. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2008, 45, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensel, M.; Arst, H.N.; Aufauvre-Brown, A.; Holden, D.W. The role of the Aspergillus fumigatus areA gene in invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1998, 258, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldin, C.; Valiante, V.; Krüger, T.; Schafferer, L.; Haas, H.; Kniemeyer, O.; Brakhage, A.A. Comparative proteomics of a tor inducible Aspergillus fumigatus mutant reveals involvement of the Tor kinase in iron regulation. Proteomics 2015, 15, 2230–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panepinto, J.C.; Oliver, B.G.; Fortwendel, J.R.; Smith, D.L.H.; Askew, D.S.; Rhodes, J.C. Deletion of the Aspergillus fumigatus gene encoding the Ras-related protein rhbA reduces virulence in a model of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 2819–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, T.; Nguyen, C.K.; Romans, A.; May, G.S. A mitogen-activated protein kinase that senses nitrogen regulates conidial germination and growth in Aspergillus fumigatus. Eukaryot. Cell 2004, 3, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergmann, A.; Hartmann, T.; Cairns, T.; Bignell, E.M.; Krappmann, S. A regulator of Aspergillus fumigatus extracellular proteolytic activity is dispensable for virulence. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 4041–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasse, C.; Bignell, E.M.; Hasenberg, M.; Haynes, K.; Gunzer, M.; Braus, G.H.; Krappmann, S. Basal expression of the Aspergillus fumigatus transcriptional activator CpcA is sufficient to support pulmonary aspergillosis. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2008, 45, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krappmann, S.; Bignell, E.M.; Reichard, U.; Rogers, T.; Haynes, K.; Braus, G.H. The Aspergillus fumigatus transcriptional activator CpcA contributes significantly to the virulence of this fungal pathogen. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 52, 785–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietl, A.M.; Amich, J.; Leal, S.; Beckmann, N.; Binder, U.; Beilhack, A.; Pearlman, E.; Haas, H. Histidine biosynthesis plays a crucial role in metal homeostasis and virulence of Aspergillus fumigatus. Virulence 2016, 7, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liebmann, B.; Mühleisen, T.W.; Müller, M.; Hecht, M.; Weidner, G.; Braun, A.; Brock, M.; Brakhage, A.A. Deletion of the Aspergillus fumigatus lysine biosynthesis gene lysF encoding homoaconitase leads to attenuated virulence in a low-dose mouse infection model of invasive aspergillosis. Arch. Microbiol. 2004, 181, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polotnianka, R.; Monahan, B.; Hynes, M.J. TamA interacts with LeuB, the homologue of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Leu3p, to regulate gdhA expression in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2004, 272, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ries, L.N.A.; Beattie, S.; Cramer, R.A.; Goldman, G.H. Overview of carbon and nitrogen catabolite metabolism in the virulence of human pathogenic fungi. Mol. Microbiol. 2018, 107, 277–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morozov, I.Y.; Galbis-Martinez, M.; Jones, M.G.; Caddick, M.X. Characterization of nitrogen metabolite signalling in Aspergillus via the regulated degradation of areA mRNA. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 42, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brega, E.; Zufferey, R.; Mamoun, C. Ben Candida albicans Csy1p Is a Nutrient Sensor Important for Activation of Amino Acid Uptake and Hyphal Morphogenesis. Eukaryot. Cell 2004, 3, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kraidlova, L.; van Zeebroeck, G.; van Dijck, P.; Sychrová, H. The Candida albicans GAP gene family encodes permeases involved in general and specific amino acid uptake and sensing. Eukaryot. Cell 2011, 10, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fraser, J.A.; Davis, M.A.; Hynes, M.J. The formamidase gene of Aspergillus nidulans: Regulation by nitrogen metabolite repression and transcriptional interference by an overlapping upstream gene. Genetics 2001, 157, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.A.; Cobbett, C.S.; Hynes, M.J. An amdS-lacZ fusion for studying gene regulation in Aspergillus. Gene 1988, 63, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnell, E.; Rousseau, K.; Thornton, D.J.; Bowyer, P.; Herrick, S.E. Expression and secretion of Aspergillus fumigatus proteases are regulated in response to different protein substrates. Fungal Biol. 2012, 116, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, D.J.; Davis, M.A.; Wong, K.H.; Kreutzberger, S.D.; Hynes, M.J.; Todd, R.B. Dual DNA binding and coactivator functions of Aspergillus nidulans TamA, a Zn ( II ) 2Cys6 transcription factor. Mol. Microbiol. 2014, 92, 1198–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glatigny, A.; Scazzocchio, C. Cloning and molecular characterization of hxA, the gene coding for the xanthine dehydrogenase (purine hydroxylase I) of Aspergillus nidulans. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 3534–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oestreicher, N.; Scazzocchio, C. Sequence, regulation, and mutational analysis of the gene encoding urate oxidase in Aspergillus nidulans. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 23382–23389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arst, H.N.; Cove, D.J. Nitrogen metabolite repression in Aspergillus nidulans. MGG Mol. Gen. Genet. 1973, 126, 111–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrianopoulos, A.; Kourambas, S.; Sharp, J.A.; Davis, M.A.; Hynes, M.J. Characterization of the Aspergillus nidulans nmrA gene involved in nitrogen metabolite repression. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 1973–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, M.A.; Small, A.J.; Kourambas, S.; Hynes, M.J. The tamA gene of Aspergillus nidulans contains a putative zinc cluster motif which is not required for gene function. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 3406–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hynes, M.J. Studies on the role of the area gene in the regulation of nitrogen catabolism in Aspergillus nidulans. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 1975, 28, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beck, T.; Hall, M.N. The TOR signalling pathway controls nuclear localization of nutrient- regulated transcription factors. Nature 1999, 402, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.H.; Hynes, M.J.; Todd, R.B.; Davis, M.A. Deletion and overexpression of the Aspergillus nidulans GATA factor AreB reveals unexpected pleiotropy. Microbiology 2009, 155, 3868–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Macios, M.; Caddick, M.X.; Weglenski, P.; Scazzocchio, C.; Dzikowska, A. The GATA factors AREA and AREB together with the co-repressor NMRA, negatively regulate arginine catabolism in Aspergillus nidulans in response to nitrogen and carbon source. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2012, 49, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, A.; Fedorova, N.D.; Crabtree, J.; Yu, Y.; Kim, S.; Chen, D.; Loss, O.; Cairns, T.; Goldman, G.; Armstrong-James, D.; et al. Sub-telomere directed gene expression during initiation of invasive aspergillosis. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarre, C.; Sokol, S.; Debeaupuis, J.P.; Henry, C.; Lacroix, C.; Glaser, P.; Coppée, J.Y.; François, J.M.; Latgé, J.P. Transcriptomic analysis of the exit from dormancy of Aspergillus fumigatus conidia. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Leeuwen, M.R.; Krijgsheld, P.; Bleichrodt, R.; Menke, H.; Stam, H.; Stark, J.; Wösten, H.A.B.; Dijksterhuis, J. Germination of conidia of Aspergillus niger is accompanied by major changes in RNA profiles. Stud. Mycol. 2012, 74, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, H. Iron—A key nexus in the virulence of Aspergillus fumigatus. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andreini, C.; Bertini, I.; Cavallaro, G.; Holliday, G.L.; Thornton, J.M. Metal ions in biological catalysis: From enzyme databases to general principles. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 13, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallner, A.; Blatzer, M.; Schrettl, M.; Sarg, B.; Lindner, H.; Haas, H. Ferricrocin, a siderophore involved in intra- and transcellular iron distribution in Aspergillus fumigatus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 4194–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matthaiou, E.I.; Sass, G.; Stevens, D.A.; Hsu, J.L. Iron: An essential nutrient for Aspergillus fumigatus and a fulcrum for pathogenesis. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 31, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrettl, M.; Bignell, E.; Kragl, C.; Joechl, C.; Rogers, T.; Arst, H.N.; Haynes, K.; Haas, H. Siderophore biosynthesis but not reductive iron assimilation is essential for Aspergillus fumigatus virulence. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schrettl, M.; Bignell, E.; Kragl, C.; Sabiha, Y.; Loss, O.; Eisendle, M.; Wallner, A.; Arst, H.N.; Haynes, K.; Haas, H. Distinct roles for intra- and extracellular siderophores during Aspergillus fumigatus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, 1195–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmin, S.; Alcazar-Fuoli, L.; Gründlinger, M.; Puempel, T.; Cairns, T.; Blatzer, M.; Lopez, J.F.; Grimalt, J.O.; Bignell, E.; Haas, H. Mevalonate governs interdependency of ergosterol and siderophore biosyntheses in the fungal pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gründlinger, M.; Gsaller, F.; Schrettl, M.; Lindner, H.; Haasa, H. Aspergillus fumigatus SidJ mediates intracellular siderophore hydrolysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 7534–7536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blatzer, M.; Schrettl, M.; Sarg, B.; Lindner, H.H.; Pfaller, K.; Haas, H. SidL, an Aspergillus fumigatus transacetylase involved in biosynthesis of the siderophores ferricrocin and hydroxyferricrocin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 4959–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kragl, C.; Schrettl, M.; Abt, B.; Sarg, B.; Lindner, H.H.; Haas, H. EstB-mediated hydrolysis of the siderophore triacetylfusarinine C optimizes iron uptake of Aspergillus fumigatus. Eukaryot. Cell 2007, 6, 1278–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gsaller, F.; Eisendle, M.; Lechner, B.E.; Schrettl, M.; Lindner, H.; Geley, S.; Haas, H. The interplay between vacuolar and siderophore-mediated iron storage in Aspergillus fumigatus. Metallomics 2012, 4, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schrettl, M.; Kim, H.S.; Eisendle, M.; Kragl, C.; Nierman, W.C.; Heinekamp, T.; Werner, E.R.; Jacobsen, I.; Illmer, P.; Yi, H.; et al. SreA-mediated iron regulation in Aspergillus fumigatus. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 70, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schrettl, M.; Beckmann, N.; Varga, J.; Heinekamp, T.; Jacobsen, I.D.; Jöchl, C.; Moussa, T.A.; Wang, S.; Gsaller, F.; Blatzer, M.; et al. HapX-Mediated adaption to iron starvation is crucial for virulence of Aspergillus fumigatus. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Gravelat, F.N.; Chiantg, L.Y.; Chen, D.; Vanier, G.; Ejzykowicz, D.E.; Inrahim, A.S.; Nierman, W.C.; Sheppard, D.C.; Filler, S.G. Aspergillus fumigatus AcuM regulates both iron acquisition and gluconeogenesis. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 78, 1038–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pongpom, M.; Liu, H.; Xu, W.; Snarr, B.D.; Sheppard, D.C.; Mitchell, A.P.; Filler, S.G. Divergent targets of Aspergillus fumigatus AcuK and AcuM transcription factors during growth in vitro versus invasive disease. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaplan, C.D.; Kaplan, J. Iron acquisition and transcriptional regulation. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4536–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckmann, N.; Schafferer, L.; Schrettl, M.; Binder, U.; Talasz, H.; Lindner, H.; Haas, H. Characterization of the Link between Ornithine, Arginine, Polyamine and Siderophore Metabolism in Aspergillus fumigatus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, H. Fungal siderophore metabolism with a focus on Aspergillus fumigatus. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 1266–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haas, H. Molecular genetics of fungal siderophore biosynthesis and uptake: The role of siderophores in iron uptake and storage. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 62, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heymann, P.; Gerads, M.; Schaller, M.; Dromer, F.; Winkelmann, G.; Ernst, J.F. The siderophore iron transporter of Candida albicans (Sit1p/Arn1p) mediates uptake of ferrichrome-type siderophores and is required for epithelial invasion. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 5246–5255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tangen, K.L.; Jung, W.H.; Sham, A.P.; Lian, T.; Kronstad, J.W. The iron- and cAMP-regulated gene SIT1 influences ferrioxamine B utilization, melanization and cell wall structure in Cryptococcus neoformans. Microbiology 2007, 153, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haas, H.; Eisendle, M.; Turgeon, B.G. Siderophores in Fungal Physiology and Virulence. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2008, 46, 149–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberegger, H.; Schoeser, M.; Zadra, I.; Abt, B.; Haas, H. SREA is involved in regulation of siderophore biosynthesis, utilization and uptake in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 41, 1077–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gsaller, F.; Hortschansky, P.; Beattie, S.R.; Klammer, V.; Tuppatsch, K.; Lechner, B.E.; Rietzschel, N.; Werner, E.R.; Vogan, A.A.; Chung, D.; et al. The Janus transcription factor Hap X controls fungal adaptation to both iron starvation and iron excess. EMBO J. 2014, 33, 2261–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hortschansky, P.; Eisendle, M.; Al-Abdallah, Q.; Schmidt, A.D.; Bergmann, S.; Thön, M.; Kniemeyer, O.; Abt, B.; Seeber, B.; Werner, E.R.; et al. Interaction of HapX with the CCAAT-binding complex—A novel mechanism of gene regulation by iron. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 3157–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vödisch, M.; Albrecht, D.; Leßing, F.; Schmidt, A.D.; Winkler, R.; Guthke, R.; Brakhage, A.A.; Kniemeyer, O. Two-dimensional proteome reference maps for the human pathogenic filamentous fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Proteomics 2009, 9, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blatzer, M.; Barker, B.M.; Willger, S.D.; Beckmann, N.; Blosser, S.J.; Cornish, E.J.; Mazurie, A.; Grahl, N.; Haas, H.; Cramer, R.A. SREBP coordinates iron and ergosterol homeostasis to mediate triazole drug and hypoxia responses in the human fungal pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bignell, E.; Negrete-Urtasun, S.; Calcagno, A.M.; Haynes, K.; Arst, H.M.; Rogers, T. The Aspergillus pH-responsive transcription factor PacC regulates virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 1072–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganz Tomas Iron in Innate Immunity: Starve the Invaders Tomas. Clin. Lymphoma 2010, 9, 19–22. [CrossRef]
- Cassat, J.E.; Skaar, E.P. Iron in infection and immunity. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 13, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsu, J.L.; Manouvakhova, O.V.; Clemons, K.V.; Inayathullah, M.; Tu, A.B.; Sobel, R.A.; Tian, A.; Nazik, H.; Pothineni, V.R.; Pasupneti, S.; et al. Microhemorrhage-associated tissue iron enhances the risk for Aspergillus fumigatus invasion in a mouse model of airway transplantation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexander, J.; Limaye, A.P.; Ko, C.W.; Bronner, M.P.; Kowdley, K.V. Association of Hepatic Iron Overload With Invasive Fungal Infection in Liver Transplant Recipients. Liver Transplant. 2006, 12, 1799–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozyilmaz, E.; Aydogdu, M.; Sucak, G.; Aki, S.Z.; Ozkurt, Z.N.; Yegin, Z.A.; Kokturk, N. Risk factors for fungal pulmonary infections in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients: The role of iron overload. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2010, 45, 1528–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iglesias-Osma, C.; Gonzalez-Villaron, L.; San Miguel, J.F.; Caballero, M.D.; Vazquez, L.; De Castro, S. Iron metabolism and fungal infections in patients with haematological malignancies. J. Clin. Pathol. 1995, 48, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leal, S.M.J.; Roy, S.; Vareechon, C.; de Jesus Carrion, S.; Clark, H.; Lopez-Berges, M.S.; DiPietro, A.; Schrettl, M.; Beckmann, N.; Redl, B.; et al. Targeting Iron Acquisition Blocks Infection with the Fungal Pathogens Aspergillus fumigatus and Fusarium oxysporum. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrettl, M.; Ibrahim-Granet, O.; Droin, S.; Huerre, M.; Latgé, J.P.; Haas, H. The crucial role of the Aspergillus fumigatus siderophore system in interaction with alveolar macrophages. Microbes Infect. 2010, 12, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, M.; Nairz, M.; Schroll, A.; Schrettl, M.; Haas, H.; Weiss, G. Effects of the Aspergillus fumigatus siderophore systems on the regulation of macrophage immune effector pathways and iron homeostasis. Immunobiology 2008, 213, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keown, K.; Reid, A.; Moore, J.E.; Taggart, C.C.; Downey, D.G. Coinfection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Aspergillus fumigatus in cystic fibrosis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2020, 29, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreini, C.; Banci, L.; Bertini, I.; Rosato, A. Counting the zinc-proteins encoded in the human genome. J. Proteome Res. 2006, 5, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outten, C.E.; O’Halloran, T.V. Femtomolar sensitivity of metalloregulatory proteins controlling zinc homeostasis. Science 2001, 292, 2488–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vicentefranqueira, R.; Moreno, M.Á.; Leal, F.; Calera, J.A. The zrfA and zrfB Genes of Aspergillus fumigatus Encode the Zinc Transporter Proteins of a Zinc Uptake System Induced in an Acid, Zinc-Depleted Environment. Eukaryot. Cell 2005, 4, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amich, J.; Vicentefranqueira, R.; Leal, F.; Calera, J.A. Aspergillus fumigatus survival in alkaline and extreme zinc-limiting environments relies on the induction of a zinc homeostasis system encoded by the zrfc and aspf2 genes. Eukaryot. Cell 2010, 9, 424–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno, M.Á.; Ibrahim-Granet, O.; Vicentefranqueira, R.; Amich, J.; Ave, P.; Leal, F.; Latgé, J.P.; Calera, J.A. The regulation of zinc homeostasis by the ZafA transcriptional activator is essential for Aspergillus fumigatus virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 64, 1182–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amich, J.; Leal, F.; Calera, J.A. Repression of the acid ZrfA/ZrfB zinc-uptake system of Aspergillus fumigatus mediated by PacC under neutral, zinc-limiting conditions. Int. Microbiol. 2009, 12, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, H.; Kang, S.; Park, Y.S.; Yun, C.W. The role of zinc in gliotoxin biosynthesis of Aspergillus fumigatus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martínez, C.E.; Motto, H.L. Solubility of lead, zinc and copper added to mineral soils. Environ. Pollut. 2000, 107, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danchin, A. Zinc, an unexpected integrator of metabolism? Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 895–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amich, J.; Calera, J.A. Zinc acquisition: A key aspect in Aspergillus fumigatus virulence. Mycopathologia 2014, 178, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foote, J.W.; Delves, H.T. Albumin bound and α2-macroglobulin bound zinc concentrations in the sera of healthy adults. J. Clin. Pathol. 1984, 37, 1050–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amich, J.; Vicentefranqueira, R.; Mellado, E.; Ruiz-Carmuega, A.; Leal, F.; Calera, J.A. The ZrfC alkaline zinc transporter is required for Aspergillus fumigatus virulence and its growth in the presence of the Zn/Mn-chelating protein calprotectin. Cell. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 548–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briard, B.; Mislin, G.L.A.; Latge, J.; Beauvais, A. Interactions between Aspergillus fumigatus and Pulmonary Bacteria: Current State of the Field, New Data, and Future Perspective. J. Fungi 2019, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baltussen, T.J.H.; Zoll, J.; Verweij, P.E.; Melchers, W.J.G. Molecular Mechanisms of Conidial Germination in Aspergillus ssp. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2020, 84, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortwendel, J.R.; Panepinto, J.C.; Seitz, A.E.; Askew, D.S.; Rhodes, J.C. Aspergillus fumigatus rasA and rasB regulate the timing and morphology of asexual development. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2004, 41, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, N.; Orasch, T.; Zhang, S.; Gao, L.; Xu, X.; Hortschansky, P.; Ye, J.; Zhang, F.; Xu, K.; Gsaller, F.; et al. The Zn2Cys6-type transcription factor LeuB cross-links regulation of leucine biosynthesis and iron acquisition in Aspergillus fumigatus. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hagag, S.; Kubitschek-Barreira, P.; Neves, G.W.P.; Amar, D.; Nierman, W.; Shalit, I.; Shamir, R.; Lopes-Bezerra, L.; Osherov, N. Transcriptional and proteomic analysis of the Aspergillus fumigatus ΔprtT protease-deficient mutant. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasmin, S.; Abt, B.; Schrettl, M.; Moussa, T.A.A.; Werner, E.R.; Haas, H. The interplay between iron and zinc metabolism in Aspergillus fumigatus. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2009, 46, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, H.L.; Jhingran, A.; Sun, Y.; Vareechon, C.; de Jesus Carrion, S.; Chazin, W.J.; Calera, J.A.; Hohl, T.M.; Pearlman, E. Zinc and Manganese Chelation by Neutrophil S100A8/A9 (Calprotectin) Limits Extracellular Aspergillus fumigatus Hyphal Growth and Corneal Infection. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertuzzi, M.; Schrettl, M.; Alcazar-Fuoli, L.; Cairns, T.C.; Muñoz, A.; Walker, L.A.; Herbst, S.; Safari, M.; Cheverton, A.M.; Chen, D.; et al. The pH-Responsive PacC Transcription Factor of Aspergillus fumigatus Governs Epithelial Entry and Tissue Invasion during Pulmonary Aspergillosis. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fasoyin, O.E.; Yang, K.; Qiu, M.; Wang, B.; Wang, S.; Wang, S. Regulation of morphology, aflatoxin production, and virulence of Aspergillus flavus by the major nitrogen regulatory gene areA. Toxins 2019, 11, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teichert, S.; Wottawa, M.; Schönig, B.; Tudzynski, B. Role of the Fusarium fujikuroi TOR kinase in nitrogen regulation and secondary metabolism. Eukaryot. Cell 2006, 5, 1807–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hillmann, F.; Novohradská, S.; Mattern, D.J.; Forberger, T.; Heinekamp, T.; Westermann, M.; Winckler, T.; Brakhage, A.A. Virulence determinants of the human pathogenic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus protect against soil amoeba predation. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 2858–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Function | Systematic Name | Standard Name | Phenotype | Virulence | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Putative ammonium transporter | Afu1g10930 | mepA | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Putative ammonium transporter | Afu2g05880 | meaA | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Putative amino acid permease | Afu7g04290 | gap2p | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Putative nitrate transporter | Afu1g12850 | crnA | Unknown | Unknown | [21] |
| Putative nitrate reductase | Afu1g12830 | niaD | Viable | Unknown | [22] |
| Putative nitrite reductase | Afu1g12840 | niiA | Viable | Unknown | [21] |
| High-affinity purine transporter | Afu7g05910 | uapC | Viable | Unknown | [23] |
| High-affinity purine transporter | Afu5g09750 | azgA | Viable | Unknown | [23] |
| Putative purine-cytosine permease | Afu2g09860 | fcyB | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Putative formamidase | Afu2g02020 | fmdS | Unknown | Unknown | |
| General amidase | Afu6g08000 | amdS | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Putative glutamate dehydrogenase | Afu4g06620 | gdhA | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Nitrogen GATA-like transcription factor | Afu6g01970 | areA | Decreased utilization of nitrogen sources | Decreased | [24] |
| Putative nitrogen metabolite repression regulator | Afu5g02920 | nmrA | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Putative co-activator of areA | Afu3g08050 | tamA | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Putative nitrogen GATA-like transcription factor | Afu2g13380 | areB | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Putative regulator of nitrate assimilation | Afu5g12020 | nirA | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Tor Kinase | Afu2g10270 | tor | Inviable | Absent | [25] |
| Ras-like signaling protein | Afu5g05480 | rbhA | Viable | Decreased | [26] |
| Mitogen-activated protein kinase | Afu1g12940 | sakA | Decreased growth and germination | Unknown | [27] |
| Transcriptional regulator of extracellular proteases | Afu4g10120 | prtT | Decreased nitrogen utilization and proteases secretion | Normal | [28] |
| Putative protein kinase for IF2 | Afu5g06750 | cpcC | Decreased resistance to starvation | Normal | [29] |
| Transcriptional activator of the CPC system | Afu4g12470 | cpcA | Decreased competitive fitness | Decreased | [30] |
| Imidazol-glycerol-phosphate dehydratase | Afu6g04700 | hisB | Histidine auxotrophy | Decreased | [31] |
| Homoaconitase | Afu5g08890 | lysF | Lysine auxotrophy | Decreased | [32] |
| Leucine transcriptional activator | Afu2g03460 | leuB | Decreased growth without leucine or iron | Decreased | [33] |
| Function | Systematic Name | Standard Name | Phenotype | Virulence | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Putative ferroxidase | Afu5g03790 | fetC | Unknown | Unknown | |
| High-affinity iron permease | Afu5g03800 | ftrA | Viable | Normal | [58] |
| L-ornithine N5-oxygenase | Afu2g07680 | sidA | Decreased iron utilization and conidiation | Decreased | [58] |
| Ferricrocin non-ribosomal peptide synthetase | Afu1g17200 | sidC | Intracellular siderophores non-productive | Decreased | [59] |
| Fusarinine C non-ribosomal peptide synthetase | Afu3g03420 | sidD | Extracellular siderophores non-productive | Decreased | [59] |
| Hydroxyornithine transacylase | Afu3g03400 | sidF | Extracellular siderophores non-productive | Decreased | [59] |
| Acetyltransferase | Afu3g03650 | sidG | Triacylfusarinine non-productive | Normal | [59] |
| Mevalonyl-CoA hydratase | Afu3g03410 | sidH | Extracellular siderophores non-productive | Decreased | [60] |
| Mevalonyl-CoA ligase | Afu1g17190 | sidI | Extracellular siderophores non-productive | Decreased | [60] |
| Fusarinine C esterase | Afu3g03390 | sidJ | Viable | Unknown | [61] |
| GNAT-type acetyltransferase | Afu1g04450 | sidL | Intracellular siderophores non-productive | Unknown | [62] |
| Triacetylfusarinine C esterase | Afu3g03660 | estB | Viable | Unknown | [63] |
| Iron vacuolar transporter | Afu4g12530 | cccA | Decreased iron resistance | Unknown | [64] |
| Iron GATA transcription factor | Afu5g11260 | sreA | Decreased iron and oxidative stress resistance | Normal | [65] |
| Iron bZIP transcription factor | Afu5g03920 | hapX | Decreased conidiation and siderophore production | Decreased | [66] |
| Sterol regulatory element-binding protein | Afu2g01260 | srbA | Inviable in anaerobic conditions | Decreased | [62] |
| Regulator of genes involved in gluconeogenesis | Afu2g12330 | acuM | Decreased iron and carbon utilization | Decreased | [67] |
| Regulator of genes involved in gluconeogenesis | Afu2g05830 | acuK | Decreased iron and carbon utilization | Decreased | [68] |
| Function | Systematic Name | Standard Name | Phenotype | Virulence | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma membrane zinc transporter | Afu1g01550 | zrfA | Decreased growth in Zn-limitation acid conditions | Unknown | [9] |
| Plasma membrane zinc transporter | Afu2g03860 | zrfB | Decreased growth in Zn-limitation acid conditions | Unknown | [94] |
| Plasma membrane zinc transporter | Afu4g09560 | zrfC | Decreased growth in Zn-limitation neutral/alkaline conditions | Decreased | [95] |
| Zinc C2H2 transcription factor | Afu1g10080 | zafA | Decreased growth and germination in Zn-limitation | Decreased | [96] |
| pH-responsive C2H2 transcription factor | Afu3g11970 | pacC | Decreased alkaline pH resistance | Decreased | [97] |
| Allergen | Afu4g09580 | aspf2 | Expressed in alkaline zinc-limiting conditions | Unknown | [95] |
| Zn2Cys6 binuclear transcription factor of Gliotoxin biosynthetic cluster | Afu6g09630 | gliZ | Absence of gliotoxin production | Normal | [98] |
| Putative zinc importer | Afu6g00470 | zrfD | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Putative zinc importer | Afu8g04010 | zrfE | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Putative zinc importer | Afu2g08740 | zrfF | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Putative zinc importer | Afu2g01460 | zrfG | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Putative zinc importer | Afu2g12050 | zrfH | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Putative zinc exporter | Afu1g12090 | zrgA | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Putative zinc exporter | Afu6g14170 | mscA | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Putative zinc exporter | Afu1g14440 | mtpA | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Putative zinc exporter | Afu6g00440 | mtpB | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Putative zinc exporter | Afu7g06570 | zrcA | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Putative zinc exporter | Afu4g04150 | zrcB | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Putative zinc exporter | Afu2g14570 | zrcC | Unknown | Unknown | |
| Putative zinc exporter | Afu5g09830 | mmtA | Unknown | Unknown |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perez-Cuesta, U.; Guruceaga, X.; Cendon-Sanchez, S.; Pelegri-Martinez, E.; Hernando, F.L.; Ramirez-Garcia, A.; Abad-Diaz-de-Cerio, A.; Rementeria, A. Nitrogen, Iron, and Zinc Acquisition: Key Nutrients to Aspergillus fumigatus Virulence. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7070518
Perez-Cuesta U, Guruceaga X, Cendon-Sanchez S, Pelegri-Martinez E, Hernando FL, Ramirez-Garcia A, Abad-Diaz-de-Cerio A, Rementeria A. Nitrogen, Iron, and Zinc Acquisition: Key Nutrients to Aspergillus fumigatus Virulence. Journal of Fungi. 2021; 7(7):518. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7070518
Chicago/Turabian StylePerez-Cuesta, Uxue, Xabier Guruceaga, Saioa Cendon-Sanchez, Eduardo Pelegri-Martinez, Fernando L. Hernando, Andoni Ramirez-Garcia, Ana Abad-Diaz-de-Cerio, and Aitor Rementeria. 2021. "Nitrogen, Iron, and Zinc Acquisition: Key Nutrients to Aspergillus fumigatus Virulence" Journal of Fungi 7, no. 7: 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7070518
APA StylePerez-Cuesta, U., Guruceaga, X., Cendon-Sanchez, S., Pelegri-Martinez, E., Hernando, F. L., Ramirez-Garcia, A., Abad-Diaz-de-Cerio, A., & Rementeria, A. (2021). Nitrogen, Iron, and Zinc Acquisition: Key Nutrients to Aspergillus fumigatus Virulence. Journal of Fungi, 7(7), 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7070518







