Melanin as a Virulence Factor in Different Species of Genus Paracoccidioides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Strains
2.2. Growth Conditions
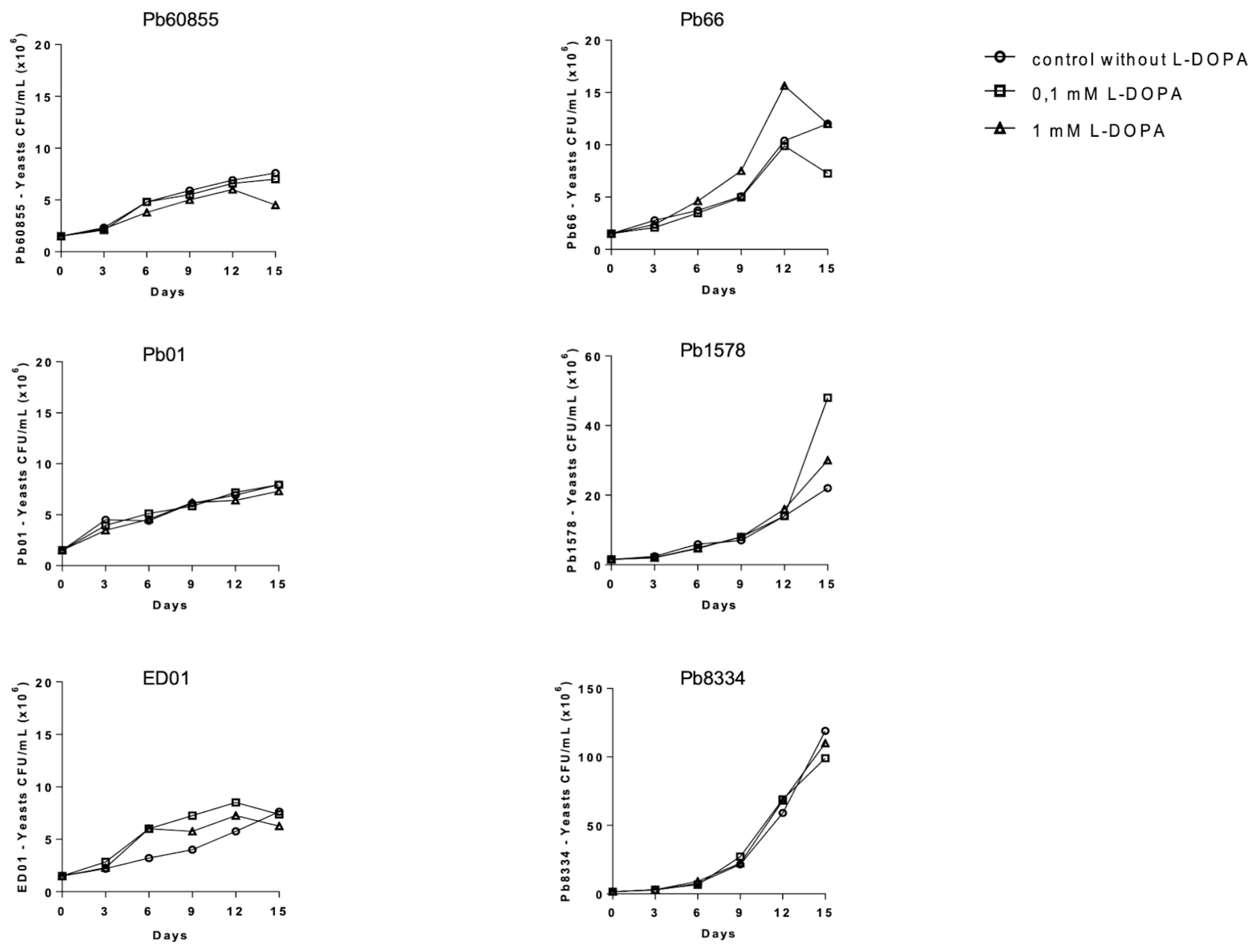
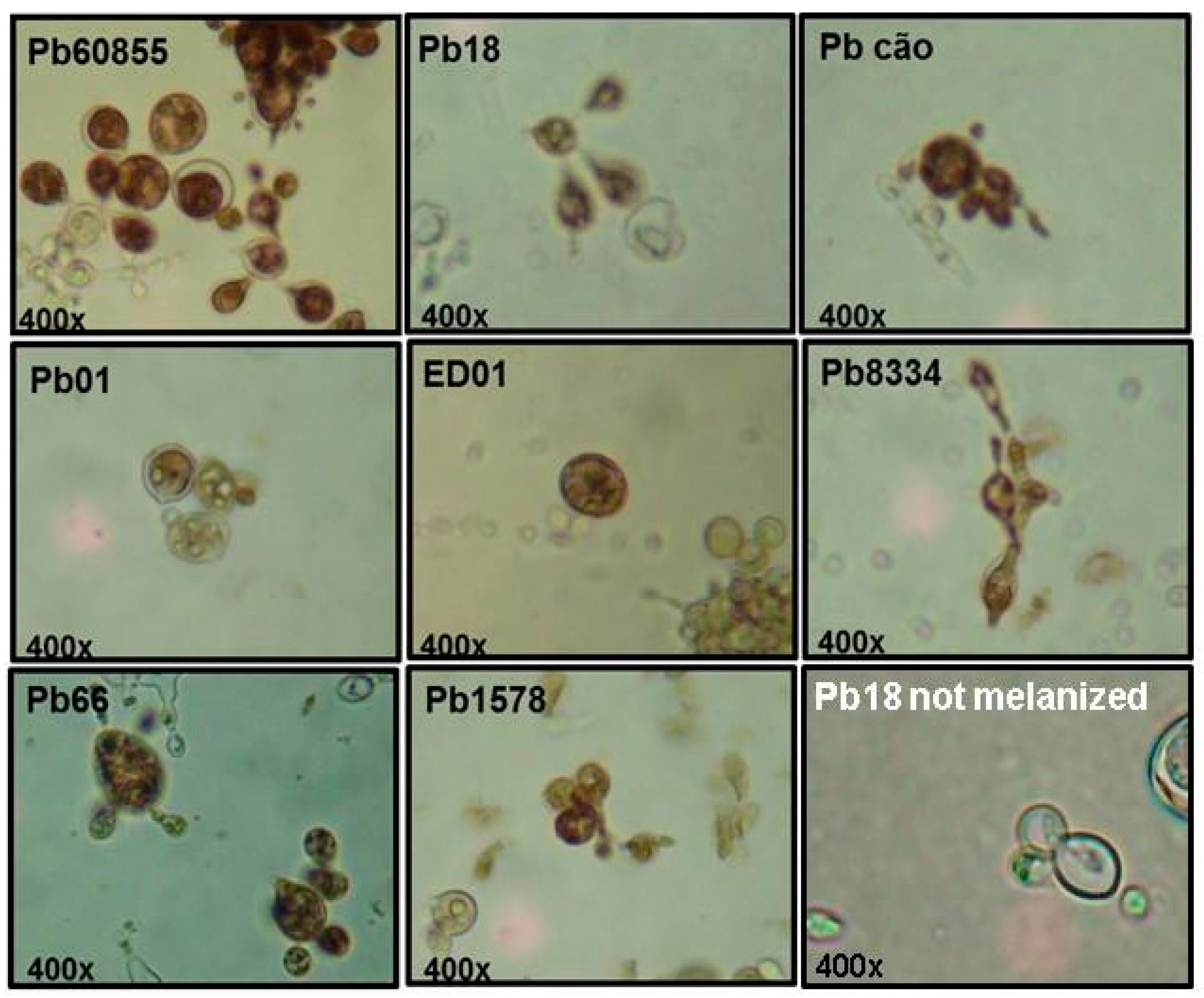
2.3. Growth Curves and Cell Melanization
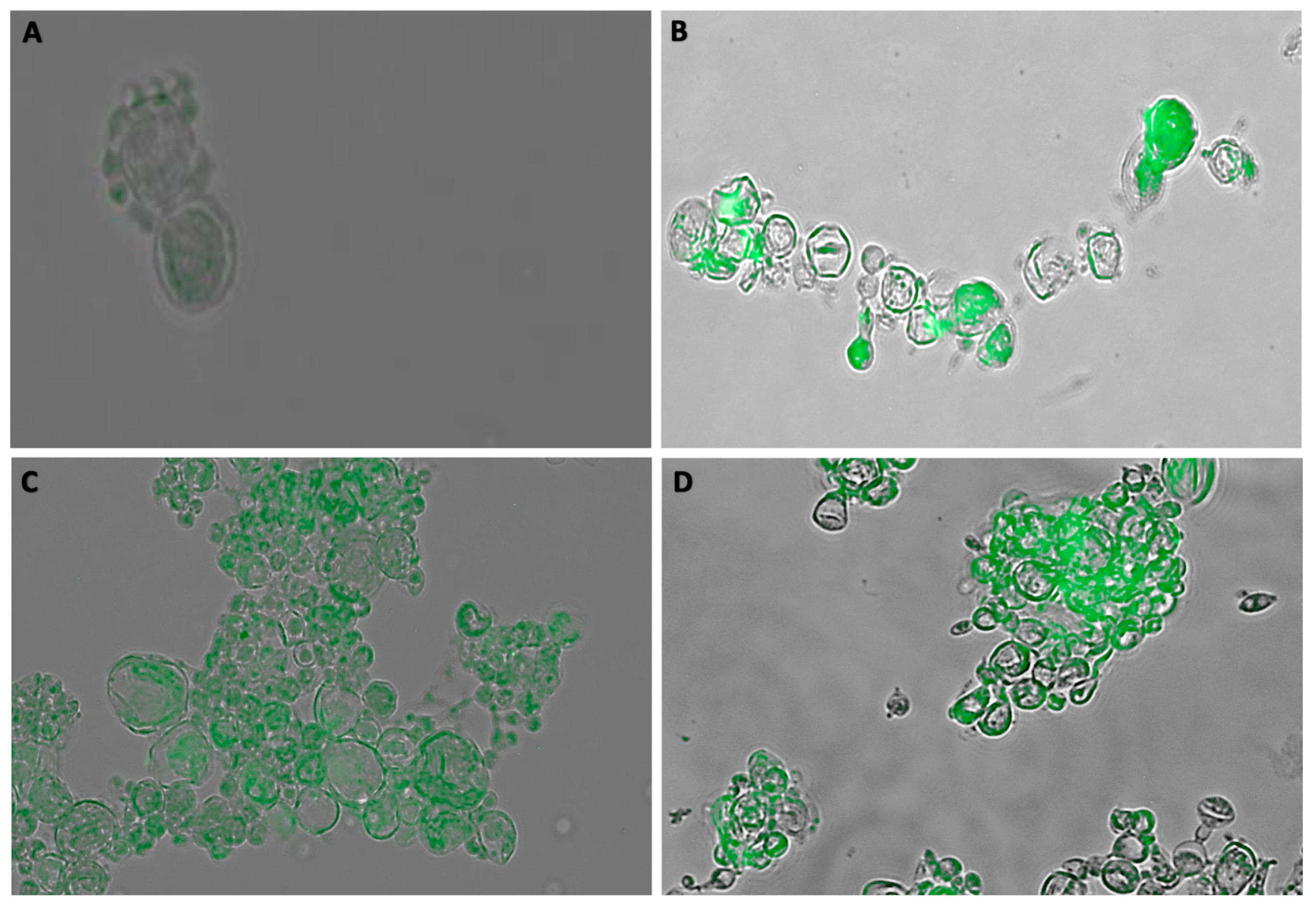
2.4. Immunofluorescence Assay
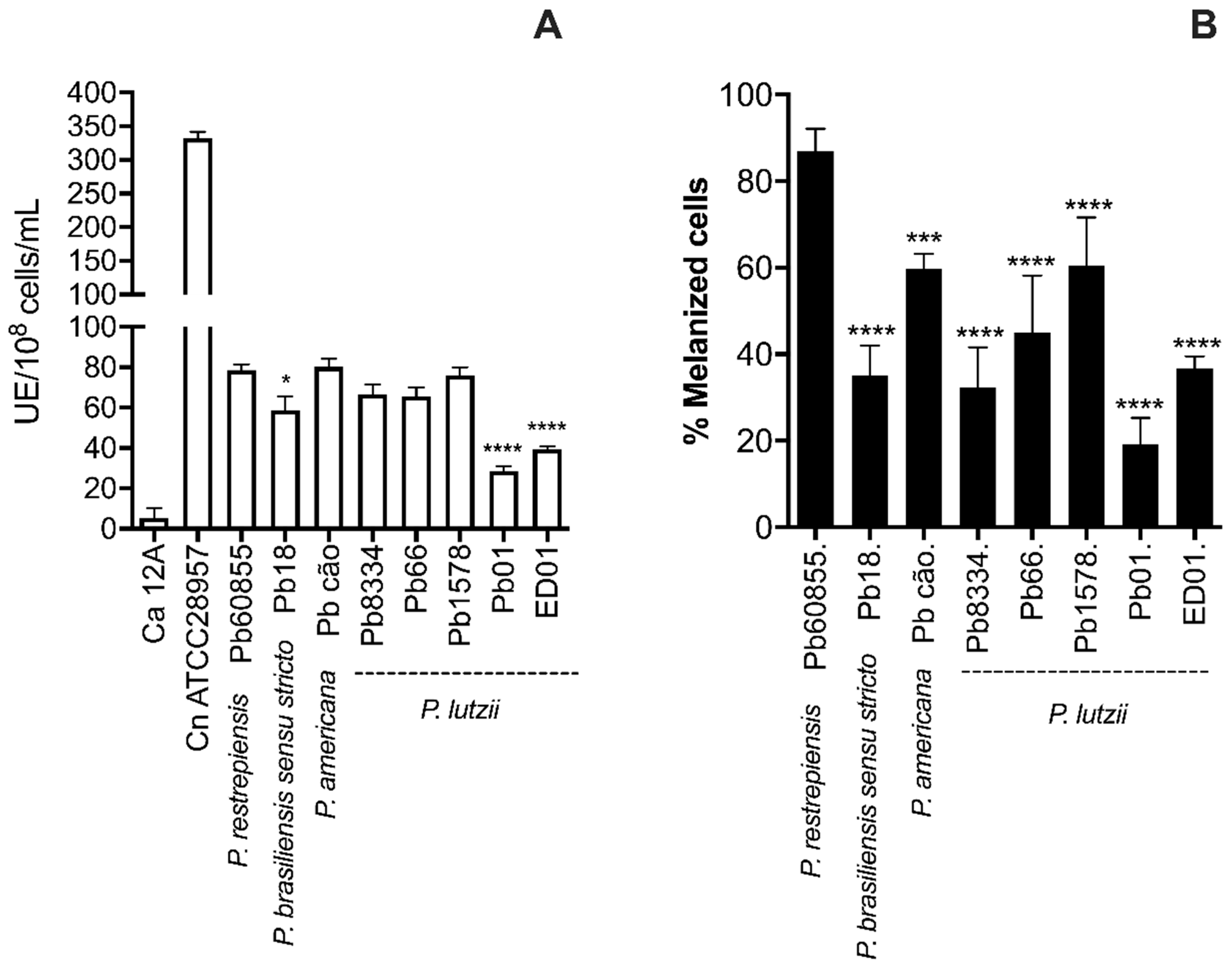
2.5. Laccase Activity
2.6. Phagocytosis Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Influence of L-DOPA on the Growth and Melanization of Yeasts in Liquid Medium among Paracoccidioides spp.
3.2. Analysis of Percentage of Melanization and Enzymatic Activities
3.3. Immunofluorescence Assay (IF)
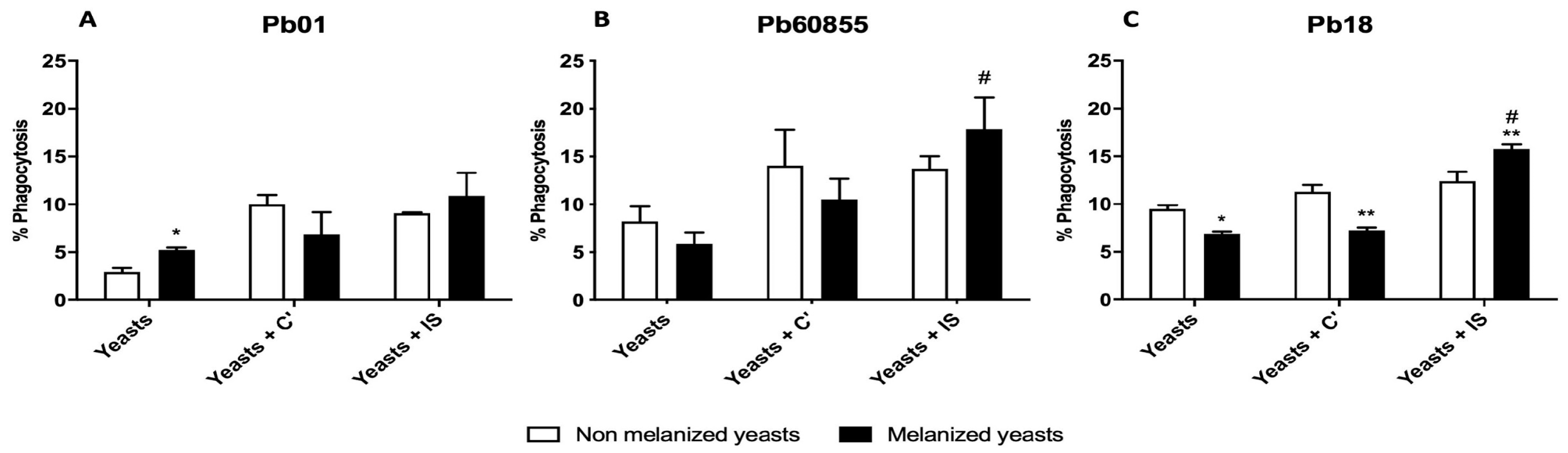
3.4. Phagocytosis Assay
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matute, D.R.; McEwen, J.G.; Puccia, R.; Montes, B.A.; San-Blas, G.; Bagagli, E.; Rauscher, J.T.; Restrepo, A.; Morais, F.; Nino-Vega, G.; et al. Cryptic speciation and recombination in the fungus Paracoccidioides brasiliensis as revealed by gene genealogies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brummer, E.; Castaneda, E.; Restrepo, A. Paracoccidioidomycosis: An update. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1993, 6, 89–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Camargo, Z.P.; de Franco, M.F. Current knowledge on pathogenesis and immunodiagnosis of paracoccidioidomycosis. Rev. Iberoam. Micol. 2000, 17, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bocca, A.L.; Amaral, A.C.; Teixeira, M.M.; Sato, P.K.; Shikanai-Yasuda, M.A.; Soares Felipe, M.S. Paracoccidioidomycosis: Eco-epidemiology, taxonomy and clinical and therapeutic issues. Future Microbiol. 2013, 8, 1177–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.E.; Dolin, R.; Blaser, M.J. Preface to the Eighth Edition. In Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, 8th ed.; Bennett, J.E., Dolin, R., Blaser, M.J., Eds.; W.B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shikanai-Yasuda, M.A.; Mendes, R.P.; Colombo, A.L.; Telles, F.Q.; Kono, A.; Paniago, A.M.M.; Nathan, A.; Valle, A.; Bagagli, E.; Benard, G.; et al. Brazilian guidelines for the clinical management of paracoccidioidomycosis. Epidemiol. Serv. Saude 2018, 27, e0500001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira Mde, M.; Theodoro, R.C.; Oliveira, F.F.; Machado, G.C.; Hahn, R.C.; Bagagli, E.; San-Blas, G.; Soares Felipe, M.S. Paracoccidioides lutzii sp. nov.: Biological and clinical implications. Med. Mycol. 2014, 52, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz-Telles, F.; Fahal, A.H.; Falci, D.R.; Caceres, D.H.; Chiller, T.; Pasqualotto, A.C. Neglected endemic mycoses. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, e367–e377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, C.M.; Madlun, E.E.; da Silva, S.P.; Pereira, M.; Felipe, M.S. Characterization of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis isolates by random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 505–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrero, L.L.; Nino-Vega, G.; Teixeira, M.M.; Carvalho, M.J.; Soares, C.M.; Pereira, M.; Jesuino, R.S.; McEwen, J.G.; Mendoza, L.; Taylor, J.W.; et al. New Paracoccidioides brasiliensis isolate reveals unexpected genomic variability in this human pathogen. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2008, 45, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.M.; Theodoro, R.C.; de Carvalho, M.J.; Fernandes, L.; Paes, H.C.; Hahn, R.C.; Mendoza, L.; Bagagli, E.; San-Blas, G.; Felipe, M.S. Phylogenetic analysis reveals a high level of speciation in the Paracoccidioides genus. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2009, 52, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arantes, T.D.; Theodoro, R.C.; Teixeira Mde, M.; Bosco Sde, M.; Bagagli, E. Environmental Mapping of Paracoccidioides spp. in Brazil Reveals New Clues into Genetic Diversity, Biogeography and Wild Host Association. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desjardins, C.A.; Champion, M.D.; Holder, J.W.; Muszewska, A.; Goldberg, J.; Bailao, A.M.; Brigido, M.M.; Ferreira, M.E.; Garcia, A.M.; Grynberg, M.; et al. Comparative genomic analysis of human fungal pathogens causing paracoccidioidomycosis. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pigosso, L.L.; Parente, A.F.; Coelho, A.S.; Silva, L.P.; Borges, C.L.; Bailao, A.M.; Soares, C.M. Comparative proteomics in the genus Paracoccidioides. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2013, 60, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turissini, D.A.; Gomez, O.M.; Teixeira, M.M.; McEwen, J.G.; Matute, D.R. Species boundaries in the human pathogen Paracoccidioides. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2017, 106, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urán, M.E.; Cano, L.E. Melanina: Implicaciones en la patogénesis de algunas enfermedades y su capacidad de evadir la respuesta inmune del hospedero. Infectio 2008, 12, 128–148. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman, H.C.; Casadevall, A. Synthesis and assembly of fungal melanin. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, M.B.; Marques, A.F.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Casadevall, A.; Travassos, L.R.; Taborda, C.P. Melanin in the dimorphic fungal pathogen Paracoccidioides brasiliensis: Effects on phagocytosis, intracellular resistance and drug susceptibility. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.B.; Thomaz, L.; Marques, A.F.; Svidzinski, A.E.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Casadevall, A.; Travassos, L.R.; Taborda, C.P. Resistance of melanized yeast cells of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis to antimicrobial oxidants and inhibition of phagocytosis using carbohydrates and monoclonal antibody to CD18. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2009, 104, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uran, M.E.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Restrepo, A.; Hamilton, A.J.; Gomez, B.L.; Cano, L.E. Detection of antibodies against Paracoccidioides brasiliensis melanin in in vitro and in vivo studies during infection. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 1680–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoro, R.C.; Teixeira Mde, M.; Felipe, M.S.; Paduan Kdos, S.; Ribolla, P.M.; San-Blas, G.; Bagagli, E. Genus paracoccidioides: Species recognition and biogeographic aspects. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, A.; Jimenez, B.E. Growth of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis yeast phase in a chemically defined culture medium. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1980, 12, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urán, M.E.; Castañeda, L.M.; Restrepo, Á.; Cano, L.E. Expresión de melanina en Paracoccidioides brasiliensis: Inducción química con L-DOPA y L-epinefrina. Med. UPB 2008, 27, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Youngchim, S.; Morris-Jones, R.; Hay, R.J.; Hamilton, A.J. Production of melanin by Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busetto, S.; Trevisan, E.; Patriarca, P.; Menegazzi, R. A single-step, sensitive flow cytofluorometric assay for the simultaneous assessment of membrane-bound and ingested Candida albicans in phagocytosing neutrophils. Cytometry A 2004, 58, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosas, A.L.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Feldmesser, M.; Cox, G.M.; McDade, H.C.; Casadevall, A. Synthesis of polymerized melanin by Cryptococcus neoformans in infected rodents. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 2845–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parise-fortes, M.; Miot, H.; Kurokawa, C.; Marques, M.; Alencar Marques, S. Immunology of paracoccidioidomycosis. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2011, 86, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, B.L.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Diez, S.; Youngchim, S.; Aisen, P.; Cano, L.E.; Restrepo, A.; Casadevall, A.; Hamilton, A.J. Detection of melanin-like pigments in the dimorphic fungal pathogen Paracoccidioides brasiliensis in vitro and during infection. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 5760–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas, A.L.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Casadevall, A. Passive immunization with melanin-binding monoclonal antibodies prolongs survival of mice with lethal Cryptococcus neoformans infection. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 3410–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, C.; Bocca, A.L.; Casadevall, A. The tools for virulence of Cryptococcus neoformans. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 87, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Gibbons, J.; Garcia-Rivera, J.; Casadevall, A.; Williamson, P.R. Laccase of Cryptococcus neoformans is a cell wall-associated virulence factor. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 5589–5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosanchuk, J.D.; Casadevall, A. The contribution of melanin to microbial pathogenesis. Cell. Microbiol. 2003, 5, 203–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, D.C.P.; Spadari, C.C.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Taborda, C.P.; Ishida, K. Miltefosine is fungicidal to Paracoccidioides spp. yeast cells but subinhibitory concentrations induce melanisation. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 49, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
C. P. Emidio, E.; E. Urán J., M.; B. R. Silva, L.; S. Dias, L.; Doprado, M.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Taborda, C.P. Melanin as a Virulence Factor in Different Species of Genus Paracoccidioides. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6040291
C. P. Emidio E, E. Urán J. M, B. R. Silva L, S. Dias L, Doprado M, Nosanchuk JD, Taborda CP. Melanin as a Virulence Factor in Different Species of Genus Paracoccidioides. Journal of Fungi. 2020; 6(4):291. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6040291
Chicago/Turabian StyleC. P. Emidio, Elúzia, Martha E. Urán J., Leandro B. R. Silva, Lucas S. Dias, Mariana Doprado, Joshua D. Nosanchuk, and Carlos Pelleschi Taborda. 2020. "Melanin as a Virulence Factor in Different Species of Genus Paracoccidioides" Journal of Fungi 6, no. 4: 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6040291
APA StyleC. P. Emidio, E., E. Urán J., M., B. R. Silva, L., S. Dias, L., Doprado, M., Nosanchuk, J. D., & Taborda, C. P. (2020). Melanin as a Virulence Factor in Different Species of Genus Paracoccidioides. Journal of Fungi, 6(4), 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6040291






